Intra- and Interobserver Reliability of Bone Volume Estimation Using OsiriX Software in Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
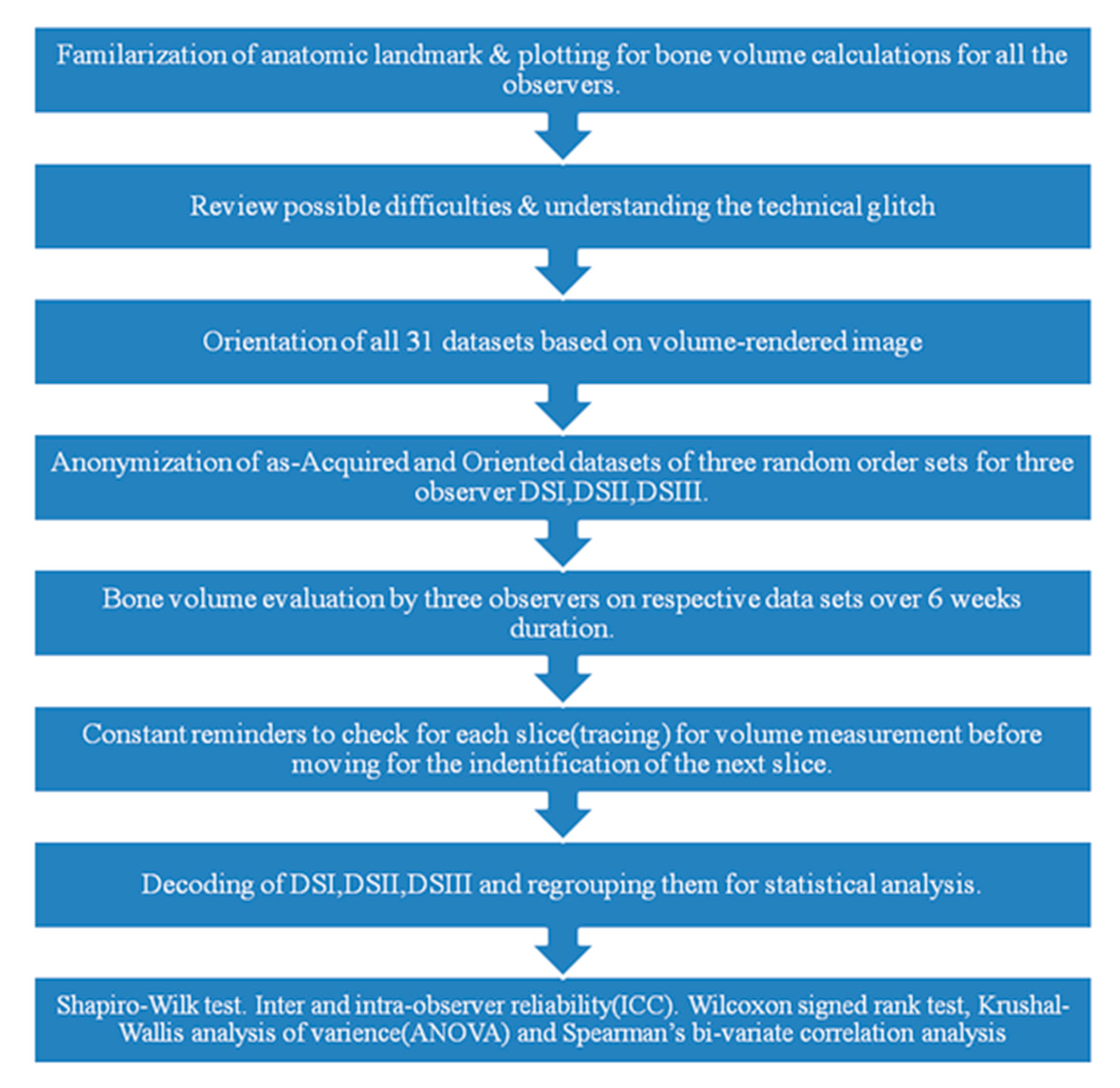
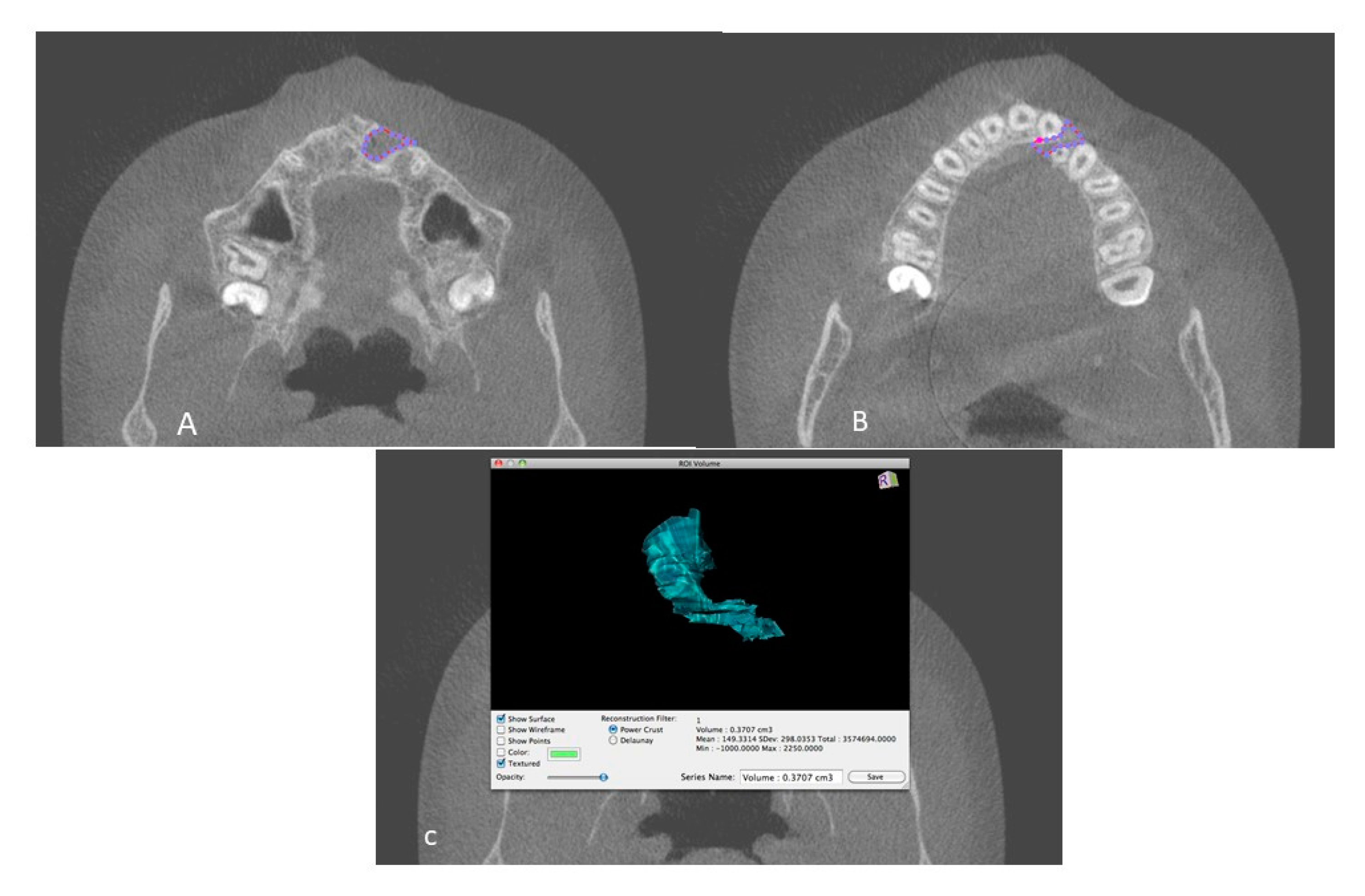
2.2. Measurements and Data Acquisition
2.3. Blinding
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
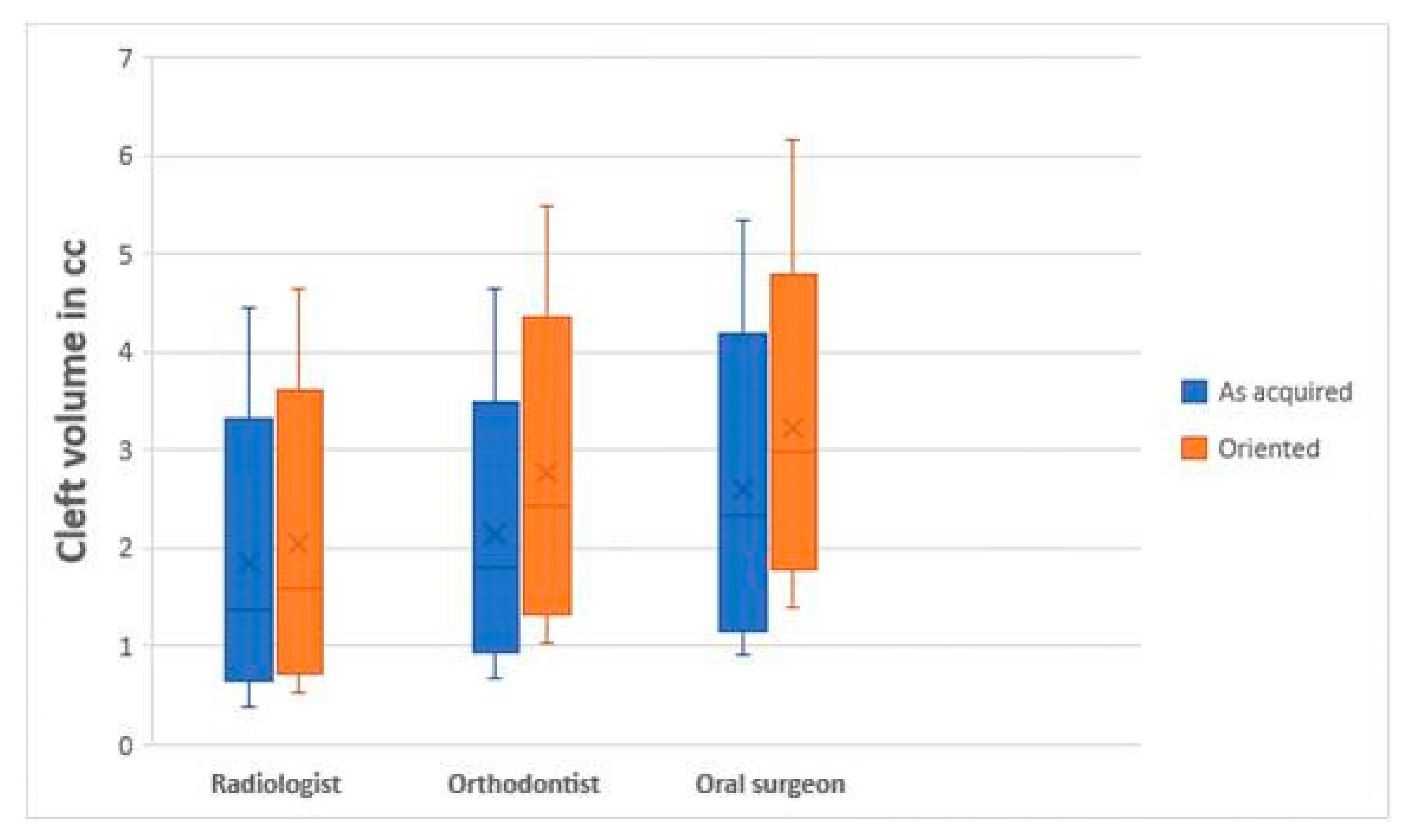
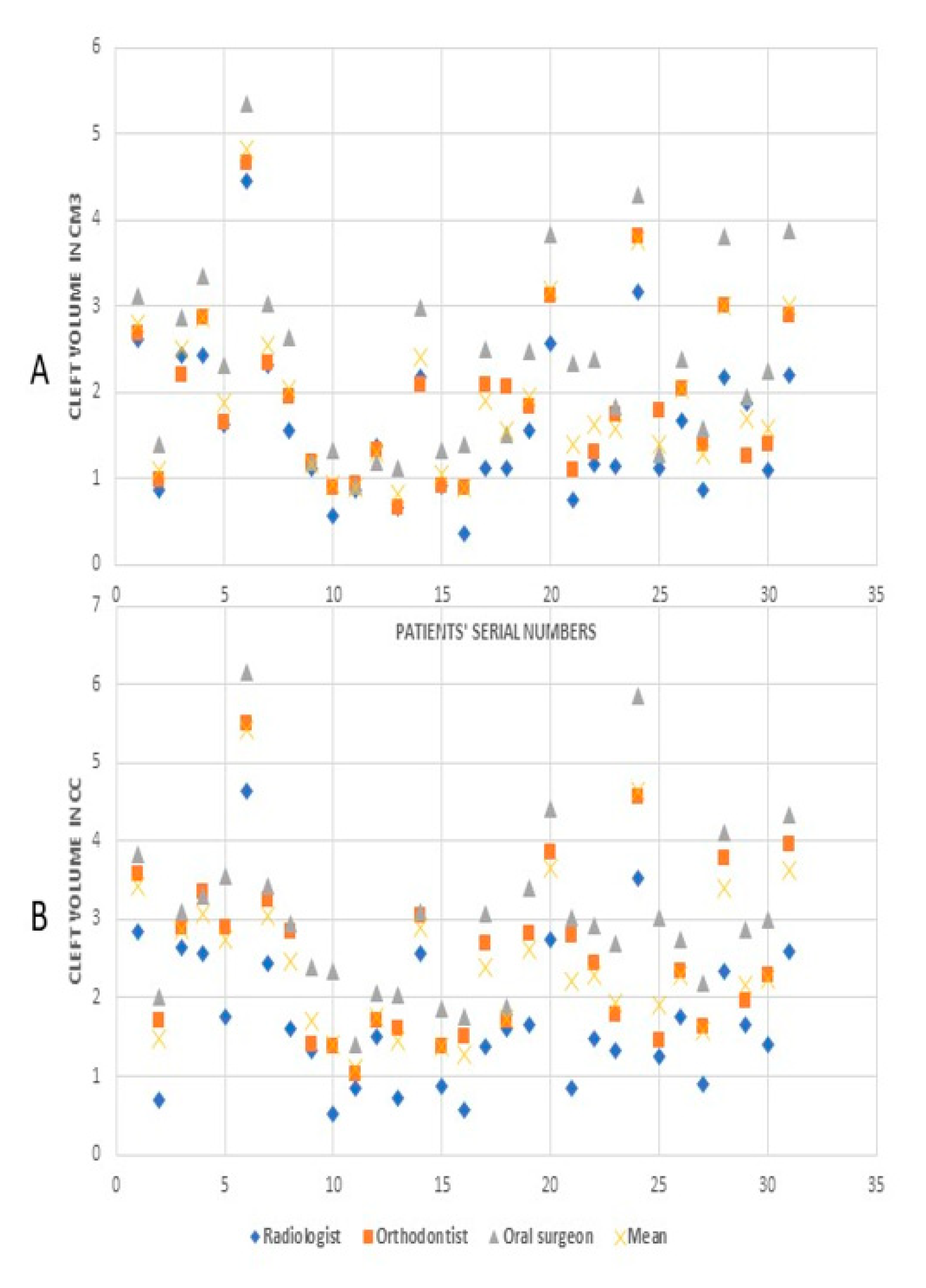
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
- Although there was clinical difference in bone volume measurement by the three observers, it was insignificant statistically.
- Clefts on the left side in the patients had significantly more bone required than the right side, whereas age and gender had no relation with bone needed to fill the defect.
- OsiriX software provided good reliability in measurements of bone volume, proving to be a promising tool for valuable clinical information according to treatment protocol.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alonso, N.; Tanikawa, D.Y.S.; Freitas, R.D.S.; Canan, L.; Ozawa, T.O.; Rocha, D.L. Evaluation of Maxillary Alveolar Reconstruction Using a Resorbable Collagen Sponge with Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 in Cleft Lip and Palate Patients. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2010, 16, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.C.; Sun, M.; Yin, N.B.; Li, H.D. A Novel Method to Calculate the Volume of Alveolar Cleft Defect Before Surgery. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2018, 29, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khojasteh, A.; Kheiri, L.; Motamedian, S.R.; Nadjmi, N. Regenerative medicine in the treatment of alveolar cleft defect: Asystematic review of the literature. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitt, D.E.; Agir, H.; David, D.J. From Birth to Maturity: A Group of Patients Who Have Completed Their Protocol Management. Part I. Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 113, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seike, T.; Hashimoto, I.; Matsumoto, K.; Tanaka, E.; Nakanishi, H. Early postoperative evaluation of secondary bone grafting into the alveolar cleft and its effects on subsequent orthodontic treatment. J. Med Investig. 2012, 59, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Ishii, T.; Kishi, K. Assessment of Bioabsorbable Hydroxyapatite for Secondary Bone Grafting in Unilateral Alveolar Clefts. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 2019, 57, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Shin, D.H.; Jo, D.I.; Kim, C.K.; Uhm, K.I. Influence of the alveolar cleft type on preoperative estimation using 3D CTassessment for alveolar cleft. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2012, 39, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mulder, D.; Cadenas de Llano-Pérula, M.; Jacobs, R.; Verdonck, A.; Willems, G. Three-dimensional radiological evaluation of secondary alveolar bone grafting in cleft lip and palate patients: A systematic review. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2018, 48, 20180047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochhar, A.S.; Sidhu, M.S.; Prabhakar, M.; Bhasin, R.; Kochhar, G.K.; Dadlani, H.; Spagnuolo, G. Frontal and Axial Evaluation of Craniofacial Morphology in Repaired Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients Utilizing Cone Beam Computed Tomography; An Observational Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P.-Y.; Denadai, R.; Hallac, R.R.; Dumrongwongsiri, S.; Hsieh, W.-C.; Pai, B.C.; Lo, L.-J. Comparative Volume Analysis of Alveolar Defects by 3D Simulation. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergland, O.; Semb, G.; Abyholm, F.E. Elimination of the residual alveolar cleft by secondary bone grafting and subsequent orthodontic treatment. Cleft Palate J. 1986, 23, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Helms, J.A.; Speidel, T.M.; Denis, K.L. Effect of timing on long-term clinical success of alveolar cleft bone grafts. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1987, 92, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Yin, N.; Wang, Y. In-Depth Volumetric Analysis of Alveolar Cleft Defects Using Three-Dimensionally Printed Models. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.B.B.; De Menezes, L.M.; Azeredo, F.; Filho, L.S.L. Volumetric assessment of alveolar clefts: A literature review. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Jiang, M.; Xu, X.; Li, J. A new method of volumetric assessment of alveolar bone grafting for cleft patients using cone beam computed tomography. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2017, 124, e171–e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-N.; Xu, Y.-B.; Jiang, H.; Wan, L.; Du, Y.-F. Accurate Evaluation of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography to Volumetrically Assess Bone Grafting in Alveolar Cleft Patients. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2015, 26, e535–e539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevidanes, L.H.S.; De Oliveira, A.E.F.; Motta, A.; Phillips, C.; Burke, B.; Tyndall, N. Head Orientation in CBCT-generated Cephalograms. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, B.; Van Der Stelt, P.F.; Sanderink, G. Accuracy of three-dimensional measurements obtained from cone beam computed tomography surface-rendered images for cephalometric analysis: Influence of patient scanning position. Eur. J. Orthod. 2009, 31, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kharbanda, O.P.; Balachandran, R.; Sardana, V.; Kalra, S.; Chaurasia, S.; Sardana, H.K. Precision of manual landmark identification between as-received and ori-ented volume-rendered cone-beam computed tomography images. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 151, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderup, B.W.; Küseler, A.; Jensen, J.; Cattaneo, P.M. A novel semi automatic technique for volumetric assessment of the alveo-lar bone defect using cone beam computed tomography. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2015, 52, e47–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, A.; Spadola, L.; Ratib, O. OsiriX: An Open-Source Software for Navigating in Multidimensional DICOM Images. J. Digit. Imaging 2004, 17, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberoi, S.; Chigurupati, R.; Gill, P.; Hoffman, W.Y.; Vargervik, K. Volumetric Assessment of Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 2009, 46, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandersluis, Y.R.; Fisher, D.M.; Stevens, K.; Tompson, B.D.; Lou, W.; Suri, S. Comparison of dental outcomes in patients with non-syndromic complete unilateral cleft lip and palate who receive secondary alveolar bone grafting before or after emergence of the permanent maxillary canine. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 157, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monga, N.; Kharbanda, O.P.; Balachandran, R.; Neelapu, B.C. Palatal volume estimation in operated unilateral and bilateral cleft lip and palate subjects using digital study models. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2020, 23, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quereshy, F.A.; Barnum, G.; Demko, C.; Horan, M.; Palomo, J.M.; Baur, D.A.; Jannuzzi, J. Use of Cone Beam Computed Tomography to Volumetrically Assess Alveolar Cleft Defects—Preliminary Results. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaven, C.P.; McIntyre, G.T.; Mossey, P.A. Accuracy of both virtual and printed 3-dimensional models for volumetric meas-urement of alveolar clefts before grafting with alveolar bone compared with a validated algorithm: A preliminary investi-gation. Br. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 55, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Yin, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Assessment of Bone Formation After Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting With and Without Platelet-Rich Plasma Using Computer-Aided Engineering Techniques. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2020, 31, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.W.; Fallis, D.W.; Packer, M.D. Three-dimensional reproducibility of natural head position. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 143, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, Ö.S.; Kayıpmaz, S.; Sahin, B. The Effect of Slice Thickness on the Assessment of Bone Defect Volumes by the Cavalieri Principle Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. J. Digit. Imaging 2012, 26, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Molen, A.D. Considerations in the use of cone-beam computed tomography for buccal bone measurements. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137 (Suppl. 4), S130–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feichtinger, M.; Zemann, W.; Mossböck, R.; Kärcher, H. Three-dimensional evaluation of secondary alveolar bone grafting using a 3D-navigation system based on computed tomography: A two-year follow-up. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 46, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feichtinger, M.; Mossböck, R.; Kärcher, H. Evaluation of bone volume following bone grafting in patients with unilateral clefts of lip, alveolus and palate using a CT-guided three-dimensional navigation system. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 34, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakajima, T.; Hayasi, T. Computed tomographic evaluation of bone formation after secondary bone grafting of alveolar clefts. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 57, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, G.L.; Emodi, O.; Pretti, H.; van Aalst, J.A.; de Almeida, S.M.; Tyndall, D.A.; Pimenta, L.A. GAND classification and volumetric assessment of unilateral cleft lip and palate mal-formations using cone beam computed tomography. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirlak, B.; Tang, C.J.; Becker, D.; Palomo, J.M.; Gosain, A.K. Volumetric Analysis of Simulated Alveolar Cleft Defects and Bone Grafts Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 131, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradrick, J.P.; Smith, A.S.; Ohman, J.C.; Indresano, A.T. Estimation of Maxillary Alveolar Cleft Volume by Three-Dimensional CT. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1990, 14, 994–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botel, U.; Fleiner, B.; Steckeler, S. Harvesting iliac crest bone spans in 172 maxillary cleft repairs: A retrospective study. Fortschr. Kiefer Gesichts-Chir. 1993, 38, 123–125. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Boyne, P.J.; Christiansen, E.L.; Thompson, J.R. Advanced imaging of osseous maxillary clefts. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 1993, 31, 195–207. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, L.; Chan, Y.M.; Jayaratne, Y.S.; Lo, J. Three-dimensional cephalometric norms of Chinese adults in Hong Kong with balanced facial profile. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2011, 112, e56–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; McNamaraJr, J.A.; Sigler, L.M.; Baccetti, T. Comparison of craniofacial characteristics of typical Chinese and Caucasian young adults. Eur. J. Orthod. 2011, 33, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirota, T.; Kurabayashi, H.; Ogura, H.; Seki, K.; Maki, K.; Shintani, S. Analysis of bone volume using computer simulation system for secondary bone graft in alveolar cleft. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable(s) | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 9 | 6 | 19.4 |
| 10 | 11 | 35.4 | |
| 11 | 7 | 22.6 | |
| ≥12 | 7 | 22.6 | |
| Gender | Girls | 14 | 45.2 |
| Boys | 17 | 54.8 | |
| Type (side)of cleft | Unilateral left | 13 | 41.9 |
| Unilateral right | 18 | 58.1 | |
| As-Acquired | Oriented | Gender | Age | Type (Side) of Cleft | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-acquired | - | 0.97 * | −0.20 | 0.18 | 0.20 * |
| Oriented | - | −0.16 | 0.23 | 0.17 * | |
| Gender | - | −0.88 | 0.01 | ||
| Age | - | −0.14 | |||
| Type of cleft | - |
| Unilateral Cleft on Left Side (n = 13) | ||||||||
| As-Acquired | Oriented | |||||||
| Radiologist | Orthodontist | Oral Maxillofacial Surgeon | Collective Mean | Radiologist | Orthodontist | Oral Maxillofacial Surgeon | Collective Mean | |
| Mean | 1.93 | 2.18 | 2.66 | 2.26 | 2.12 | 2.79 | 3.29 | 2.73 |
| Median | 1.87 | 2.07 | 2.46 | 1.95 | 1.66 | 2.81 | 3.10 | 2.62 |
| SD | 1.09 | 1.15 | 1.31 | 1.16 | 1.11 | 1.31 | 1.44 | 1.27 |
| Unilateral Cleft on Right Side (n =18) | ||||||||
| As-Acquired | Oriented | |||||||
| Radiologist | Orthodontist | Oral Maxillofacial Surgeon | Collective Mean | Radiologist | Orthodontist | Oral Maxillofacial Surgeon | Collective Mean | |
| Mean | 1.37 | 1.70 | 2.18 | 1.75 | 1.49 | 2.37 | 2.88 | 2.25 |
| Median | 1.14 | 1.70 | 2.27 | 1.58 | 1.39 | 2.31 | 2.96 | 2.22 |
| SD | 0.62 | 0.69 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.84 | 0.73 | 0.72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kochhar, A.S.; Sidhu, M.S.; Prabhakar, M.; Bhasin, R.; Kochhar, G.K.; Dadlani, H.; Spagnuolo, G.; Mehta, V.V. Intra- and Interobserver Reliability of Bone Volume Estimation Using OsiriX Software in Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9020014
Kochhar AS, Sidhu MS, Prabhakar M, Bhasin R, Kochhar GK, Dadlani H, Spagnuolo G, Mehta VV. Intra- and Interobserver Reliability of Bone Volume Estimation Using OsiriX Software in Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Dentistry Journal. 2021; 9(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleKochhar, Anuraj Singh, Maninder Singh Sidhu, Mona Prabhakar, Ritasha Bhasin, Gulsheen Kaur Kochhar, Himanshu Dadlani, Gianrico Spagnuolo, and Viral Vijay Mehta. 2021. "Intra- and Interobserver Reliability of Bone Volume Estimation Using OsiriX Software in Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography" Dentistry Journal 9, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9020014
APA StyleKochhar, A. S., Sidhu, M. S., Prabhakar, M., Bhasin, R., Kochhar, G. K., Dadlani, H., Spagnuolo, G., & Mehta, V. V. (2021). Intra- and Interobserver Reliability of Bone Volume Estimation Using OsiriX Software in Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Dentistry Journal, 9(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9020014









