Current Controversies on the Pathogenesis of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Abstract
:1. Introduction
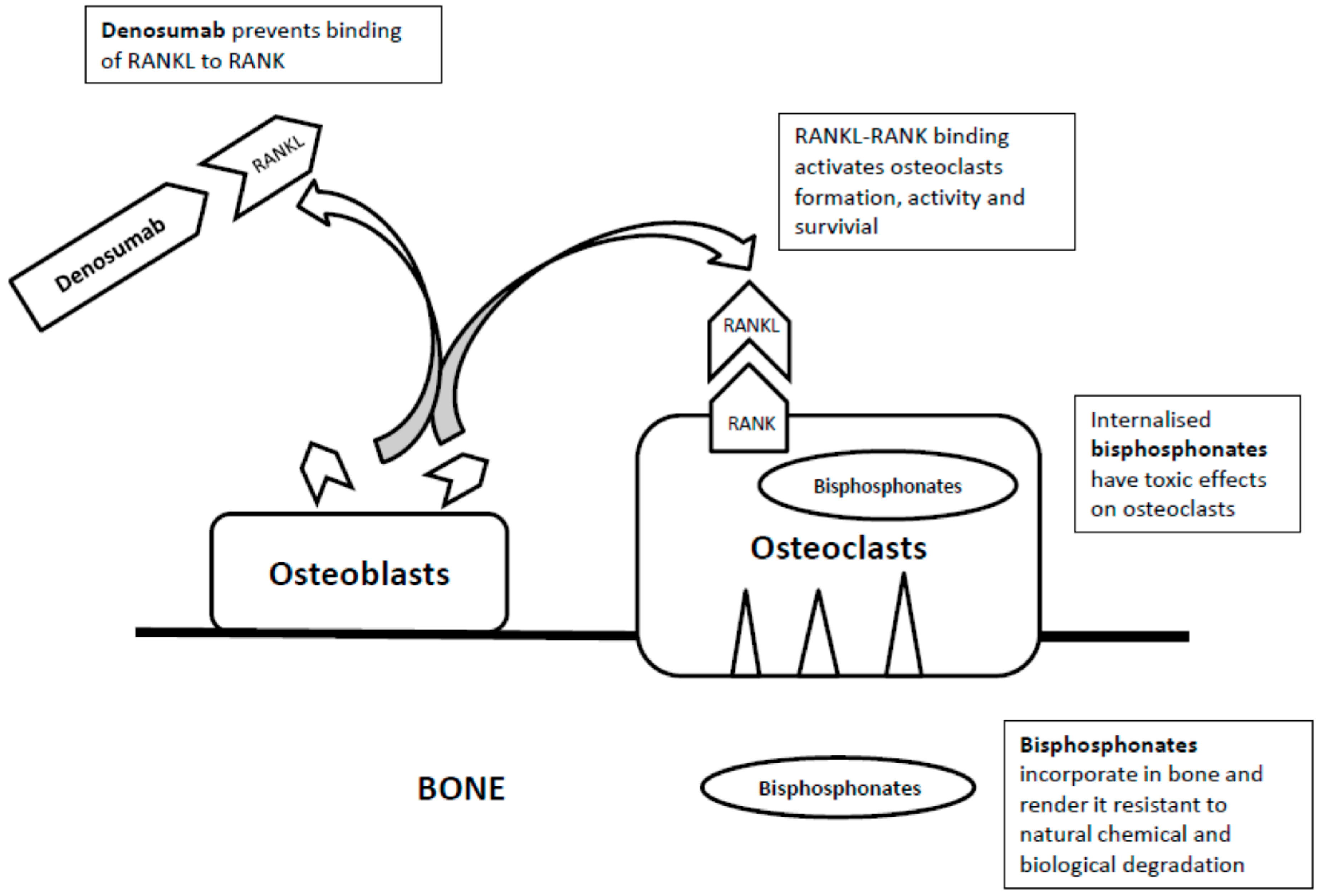
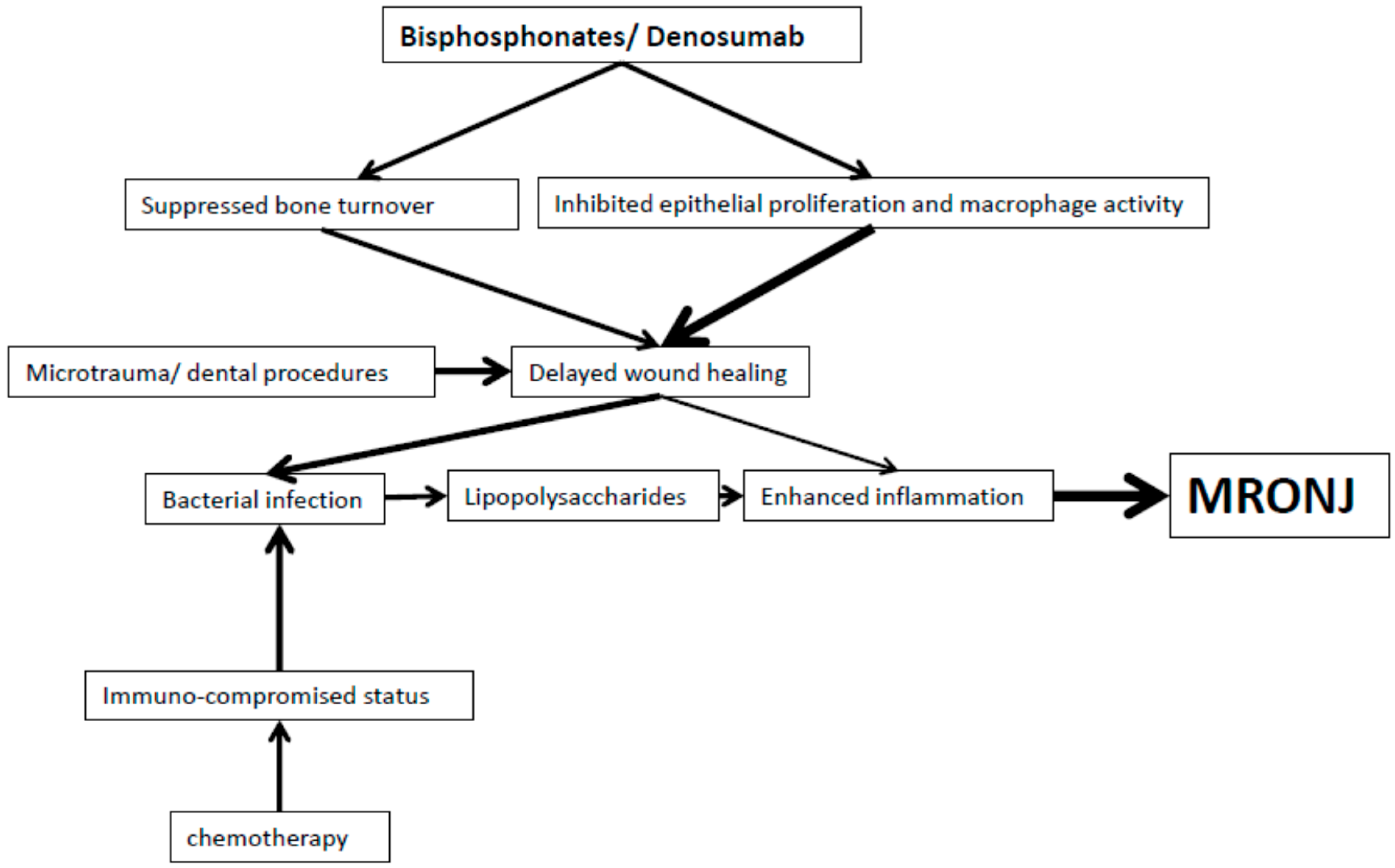
2. Bisphosphonates
3. Denosumab
4. Anti-Angiogenic Drugs
5. Summary
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marx, R.E. Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: A growing epidemic. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Fantasia, J.; Goodday, R.; Aghaloo, T.; Mehrotra, B.; O’Ryan, F. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw—2014 update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1938–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, C.; Al-Nawas, B.; Frickhofen, N.; Gamm, H.; Beck, J.; Reinsch, L.; Blum, C.; Grötz, K.A.; Wagner, W. Prevalence of bisphosphonate associated osteonecrosis of the jaws in multiple myeloma patients. Head Face Med. 2010, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Assael, L.A.; Landesberg, R.; Marx, R.E.; Mehrotra, B. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. American association of oral and maxillofacial surgeons position paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw—2009 update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67 (Suppl. 5), 2–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- NSW Health. Prevention of Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ) in Patients on Bisphosphonate Therapies; GL 2010_010; NSW Health: Sydney, Austrilia, 2010.
- Lam, D.K.; Sandor, G.K.B.; Holmes, H.I.; Evans, A.W.; Clokie, C.M. A review on bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaws and its management. JCDA 2007, 73, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andriani, A.; Petrucci, M.T.; Caravita, T.; Montanaro, M.; Villivà, N.; Levi, A.; Siniscalchi, A.; Bongarzoni, V.; Pisani, F.; De Muro, M.; et al. Evolution of bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients with multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia: A retrospective multicentric study. Blood Cancer J. 2012, 2, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E.; Sawatari, Y.; Fortin, M.; Broumand, V. Bisphosphonate induced exposed bone (osteonecrosis/osteopetrosis) of the jaws: Risk factors, recognition, prevention, and treatment. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badros, A.; Weikel, D.; Salama, A.; Goloubeva, O.; Schneider, A.; Rapoport, A.; Fenton, R.; Gahres, N.; Sausville, E.; Ord, R.; et al. Ostonecrosis of the jaw in multiple myeloma patients: Clinical features and risk factors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durie, B.G.; Katz, M.; Crowley, J. Osteonecrosis of the jaw and bisphosphonates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mcleod, N.M.H.; Brennan, P.A.; Ruggiero, S.L. Bisphosphonate osteonecrosis of the jaw: A historical and contemporary review. Surgeon 2012, 10, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Mehrotra, B.; Rosenberg, T.J.; Engroff, S.L. Osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with the use of bisphosphonates: A review of 63 cases. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Fantasia, J.; Carlson, E. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Background and guidelines for diagnosis, staging and management. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 102, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahtsevanos, K.; Kyrgidis, A.; Verrou, E.; Katodritou, E.; Triaridis, S.; Andreadis, C.G.; Boukovinas, I.; Koloutsos, G.E.; Teleioudis, Z.; Kitikidou, K.; et al. Longitudinal cohort study of risk factors in cancer patients of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5356–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, F.; Brown, J.E.; Van Poznak, C.; Stemmer, S.M.; Stopeck, A.T.; Diel, I.J.; Takahashi, S.; Shore, N.; Henry, D.H.; Barrios, C.H.; et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of osteonecrosis of the jaw: Integrated analysis from three blinded active-controlled phase III trials in cancer patients with bone metastases. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 23, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehm, T.; Beck, V.; Banys, M.; Lipp, H.P.; Hairass, M.; Reinert, S.; Solomayer, E.F.; Wallwiener, D.; Krimmel, M. Bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ): Incidence and risk factors in patients with breast cancer and gynecological malignancies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 112, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrgidis, A.; Vahtsevanos, K.; Koloutsos, G.; Andreadis, C.; Boukovinas, I.; Teleioudis, Z.; Patrikidou, A.; Triaridis, S. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: A case-control study of risk factors in breast cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4634–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Halloran, M.; Boyd, N.M.; Smith, A. Denosumab and osteonecrosis of the jaws—The pharmacology, pathogenesis and a report of two cases. Aust. Dent. J. 2014, 59, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treister, N.S.; Sook-Bin, W. Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaws. In Primer on the Metabolic Bone Diseases and Disorders of Mineral Metabolism, 7th ed.; Rosen, C.J., Compston, J.E., Lian, J.B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Chapter 107; pp. 505–509. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.R.; Burr, D.B. Mandible matrix necrosis in beagle dogs after 3 years of daily oral bisphosphonate treatment. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, R.P.; Fung, E. Resolution of bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the mandible: Possible application for intermittent low-dose parathyroid hormone [rhPTH(1–34)]. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.; Seeman, E. Teriparatide therapy for alendronate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2473–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.N.; Adachi, J.D. Resolution of osteonecrosis of the jaw after teriparatide [recombinant human PTH-(1–34)] therapy. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1835–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, K.S.; Kocar, M. Imaging findings in bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaws. Radiol. Oncol. 2010, 44, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisdas, S.; Chambron, P.N.; Smolarz, A.; Sader, R.; Vogl, T.J.; Mack, M.G. Biphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaws: CT and MRI spectrum of findings in 32 patients. Clin. Radiol. 2008, 63, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malden, N.; Lopes, V. An epidemiological study of alendronate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. A case series from the south-east of Scotland with attention given to case definition and prevalence. J. Bone Miner Metab. 2012, 30, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodson, T.B.; Raje, N.S.; Caruso, P.A.; Rosenberg, A.E. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 9-2008. A 65-year-old woman with a nonhealing ulcer of the jaw. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.; Arslanoglu, A.; Yildirm, N.; Silbergleit, R.; Aygun, N. Imaging findings of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw with emphasis on early magnetic resonance imaging findings. J. Comput. Assist Tomogr. 2009, 33, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.E.; Barrios, C.H.; Diel, I.J.; Facon, T.; Fizazi, K.; Ibrahim, T.; Saad, F.; Senecal, F.; Stemmer, S.M.; Stopeck, A.; et al. Incidence and outcomes of Osteonecrosis of the Jaw from an Integrated Analysis of Three Pivotal Randomized Double-Blind, Double-Dummy Phase 3 Trials Comparing Denosumab and Zoledronic Acid for Treatment of Bone Metastases in Advanced Cancer Patients or Myeloma. Bone 2011, 48, S18–S19. [Google Scholar]
- Kyrgidis, A.; Toulis, K.A. Denosumab-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. Osteoporos Int. 2011, 22, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.X.; Tang, L.N.; He, A.N.; Yao, Y.; Shen, Z. Risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer patients receiving denosumab: A meta-analysis of seven randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 19, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reszka, A.A.; Halasy-Nagy, J.; Rodan, G.A. Nitrogen-bisphosphonates block retinoblastoma phosphorylation and cell growth by inhibiting the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway in a keratinocyte model for esophageal irritation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landesberg, R.; Cozin, M.; Cremers, S.; Woo, V.; Kousteni, S.; Sinha, S.; Garrett-Sinha, L.; Raghavan, S. Inhibition of oral mucosal cell wound healing by bisphosphonates. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, J.; Bava, U.; Callon, K.E.; Bai, J.; Naot, D.; Reid, I.R. Bone-bound bisphosphonate inhibits growth of adjacent non-bone cells. Bone 2011, 49, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.; Bonjean, K.; Ruetz, S.; Bellahcène, A.; Devy, L.; Foidart, J.M.; Castronovo, V.; Green, J.R. Novel antiangiogenic effects of the bisphosphonate compound zoledronic acid. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, P.; Boissier, S.; Filleur, S.; Guglielmi, J.; Cabon, F.; Colombel, M.; Clézardin, P. Bisphosphonates inhibit angiogenesis in vitro and testosterone-stimulated vascular regrowth in the ventral prostate in castrated rats. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6538–6544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.; Kunkel, M.; Weber, A.; James Kirkpatrick, C. Osteonecrosis of the jaws in patients treated with bisphosphonates—histomorphologic analysis in comparison with infected osteoradionecrosis. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2006, 35, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellstein, J.W.; Marek, C.L. Bisphosphonate osteochemonecrosis (bis-phossy jaw): Is this phossy jaw of the 21st century? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, D.; Cornell, S.A.; Gustafson, S.K.; Needle, S.J.; Ullrich, J.W.; Bilder, G.E.; Perrone, M.H. Bisphosphonates used for the treatment of bone disorders inhibit Squalene synthase and cholesterol biosynthesis. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rogers, M.J.; Chilton, K.M.; Coxon, F.P.; Lawry, J.; Smith, M.O.; Suri, S.; Russell, R.G. Bisphosphonates induce apoptosis in mouse macrophage-like cells in vitro by a nitric oxide-independent mechanism. J. Bone Miner Res. 1996, 11, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, K.; Rogers, M.J.; Coxon, F.P.; Crockett, J.C. Cytosolic entry of bisphosphonate drugs requires acidification of vesicles after fluid-phase endocytosis. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebara, S.N.; Moubayed, H. Risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer patients taking bisphosphonates. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2009, 66, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.P.; Meghji, S.; Wilson, M.; Reddi, K.; White, P.; Henderson, B. Bacterially induced bone destruction: Mechanisms and misconceptions. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meghji, S.; Crean, S.J.; Hill, P.A.; Sheikh, M.; Nair, S.P.; Heron, K.; Henderson, B.; Mawer, E.B.; Harris, M. Surface-associated protein from Staphylococcus aureus stimulates osteoclastogenesis: Possible role in S. aureus-induced bone pathology. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 37, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Bostanci, N.; Hashim, A.; Johansson, A.; Aduse-Opoku, J.; Curtis, M.A.; Hughes, F.J. Regulation of RANKL and OPG gene expression in human gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells by Porphyromonas gingivalis: A putative role of the Arg-gingipains. Microb. Pathog. 2007, 43, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Meier, A.; Guggenheim, B.; Bostanci, N. Oral biofilm challenge regulates the RANKL–OPG system in periodontal ligament and dental pulp cells. Microb. Pathog. 2011, 50, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Lin, X.; Seliger, A.R.; Eastcott, J.; Kawai, T.; Taubman, M.A. Expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand by B cells in response to oral bacteria. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 24, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vij, R.; Horvath, N.; Spencer, A.; Taylor, K.; Vadhan-Raj, S.; Vescio, R.; Smith, J.; Qian, Y.; Yeh, H.; Jun, S. An open-label, phase 2 trial of denosumab in the treatment of relapsed or plateau-phase multiple myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2009, 84, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizazi, K.; Bosserman, L.; Gao, G.; Skacel, T.; Markus, R. Denosumab treatment of prostate cancer with bone metastases and increased urine N-telopeptide levels after therapy with intravenous bisphosphonates: Results of a randomized phase II trial. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacey, D.L.; Timms, E.; Tan, H.L.; Kelley, M.J.; Dunstan, C.R.; Burgess, T.; Elliott, R.; Colombero, A.; Elliott, G.; Scully, S.; et al. Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 1998, 93, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, T.L.; Qian, Y.; Kaufman, S.; Ring, B.D.; Van, G.; Capparelli, C.; Kelley, M.; Hsu, H.; Boyle, W.J.; Dunstan, C.R.; et al. The ligand for osteoprotegerin (OPGL) directly activates mature osteoclasts. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 145, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacey, D.L.; Tan, H.L.; Lu, J.; Kaufman, S.; Van, G.; Qiu, W.; Rattan, A.; Scully, S.; Fletcher, F.; Juan, T.; et al. Osteoprotegerin ligand modulates murine osteoclast survival in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazianas, M. Osteonecrosis of the jaw and the role of macrophages. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari-Lacraz, S.; Ferrari, S. Do RANKL inhibitors (denosumab) affect inflammation and immunity? Osteoporos Int. 2011, 22, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loser, K.; Mehling, A.; Loeser, S.; Apelt, J.; Kuhn, A.; Grabbe, S.; Schwarz, T.; Penninger, J.M.; Beissert, S. Epidermal RANKL controls regulatory T-cell numbers via activation of dendritic cells. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 2011, 473, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite de Oliveira, R.; Hamm, A.; Mazzone, M. Growing tumour vessels: More than one way to skin a cat—Implications for angiogenesis targeted cancer therapies. Mol. Aspects Med. 2011, 32, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, L.M.; Hicklin, D.J. VEGF-targeted therapy: Mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cher, M.L.; Towler, D.A.; Rafii, S.; Rowley, D.; Donahue, H.J.; Keller, E.; Herlyn, M.; Cho, E.A.; Chung, L.W. Cancer interaction with the bone microenvironment. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Kaneda, T.; Arakawa, T.; Morita, S.; Sato, T.; Yomada, T.; Hanada, K.; Kumegawa, M.; Hakeda, Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) directly enhances osteoclastic bone resorption and survival of mature osteoclasts. FEBS Lett. 2000, 473, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, S.E.; Lennard, T.W.; Williams, J.R.; Birch, M.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in osteoclast differentiation and function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarneri, V.; Miles, D.; Robert, N.; Morita, S.; Sato, T.; Yomada, T.; Hanada, K.; Kumegawa, M.; Hakeda, Y. Bevacizumab and osteonecrosis of the jaw: Incidence and association with bisphosphonate therapy in three large prospective trials in advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 122, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescaille, G.; Coudert, A.E.; Baaroun, V.; Ostertag, A.; Charpentier, E.; Javelot, M.J.; Tolédo, R.; Goudot, P.; Azérad, J.; Berdal, A.; et al. Clinical study evaluating the effect of bevacizumab on the severity of zoledronic acid-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer patients. Bone 2014, 58, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozas, G.; Allgar, V.; Greenwood, G.; Maraveyas, A. Osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients treated with sunitinib and zoledronic acid. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, e15116. [Google Scholar]
- Beuselinck, B.; Wolter, P.; Karadimou, A.; Elaidi, R.; Dumez, H.; Rogiers, A.; Van Cann, T.; Willems, L.; Body, J.J.; Berkers, J.; et al. Concomitant oral tyrosine kinase inhibitors and bisphosphonates in advanced renal cell carcinoma with bone metastases. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, C.D.; De Boer, R.H. Profile of cabozantinib and its potential in the treatment of advanced medullary thyroid cancer. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2013, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Elisei, R.; Schlumberger, M.J.; Muller, S.P.; Schöffski, P.; Brose, M.S.; Shah, M.H.; Licitra, L.; Jarzab, B.; Medvedev, V.; Kreissl, M.C.; et al. Cabozantinib in progressive medullary thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3639–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutcheson, A.; Cheng, A.; Kunchar, R.; Stein, B.; Sambrook, P.; Goss, A. A C-terminal crosslinking telopeptide test-based protocol for patients on oral bisphosphonates requiring extraction: A prospective single centre controlled study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, R.A.; Fuleihan, G.E.H.; Bauer, D.C.; Camacho, P.M.; Clarke, B.L.; Clines, G.A.; Compston, J.E.; Drake, M.T.; Edwards, B.J.; Favus, M.J.; et al. Managing osteoporosis in patients on long-term bisphosphonate treatment: Report of a task force of the American Society of Bone and Mineral Research. J. Bone Miner Res. 2016, 31, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wat, W.Z.M. Current Controversies on the Pathogenesis of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Dent. J. 2016, 4, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj4040038
Wat WZM. Current Controversies on the Pathogenesis of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Dentistry Journal. 2016; 4(4):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj4040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleWat, Winnie Zee Man. 2016. "Current Controversies on the Pathogenesis of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw" Dentistry Journal 4, no. 4: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj4040038
APA StyleWat, W. Z. M. (2016). Current Controversies on the Pathogenesis of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Dentistry Journal, 4(4), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj4040038




