Automated Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss in Two-Dimensional (2D) Radiographs Using Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results
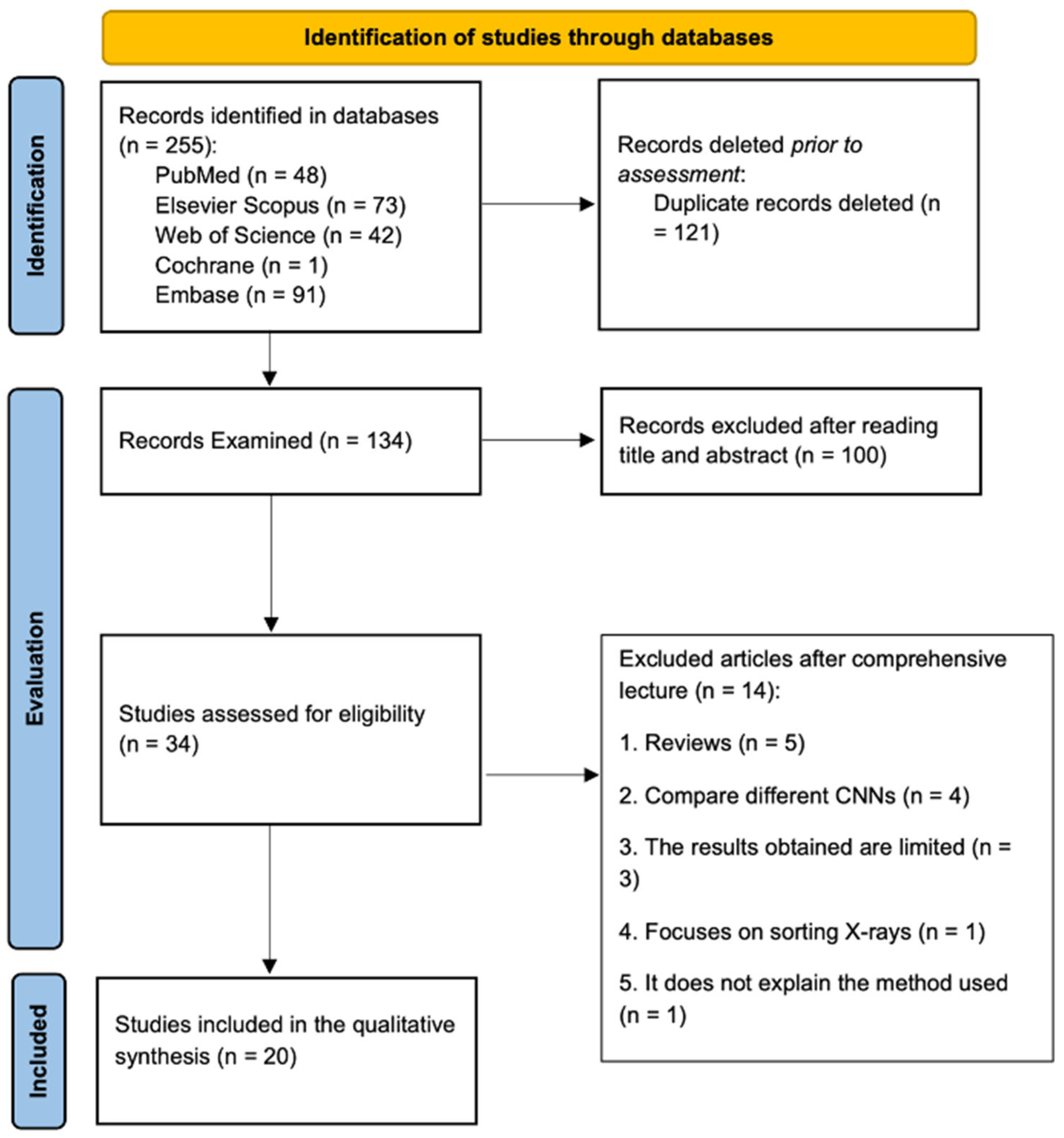
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Study Focus
3.4. Radiographs Employed
3.5. Patient Sample
3.6. AI Technique Employed
3.7. Reference Standard
3.8. Index Used
3.9. Accuracy of the Studies
3.10. Risk of Bias Assessment Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Radiographic Techniques
4.2. AI Architectures/Models Used
4.3. Comparison with Traditional Methods
4.4. Advantages of AI-Based Methods
4.5. Limitations of AI Methods
4.6. Impact of AI on Clinical Practice
4.7. Perspective of Future Work
4.8. Limitations of the Present Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nair, P.N.R. On the causes of persistent apical periodontitis: A review. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 249–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, S.; Menezes, R. MicroRNAs: Emerging players in apical periodontitis. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2021, 29, e20201058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun Saylan, B.C.; Baydar, O.; Yeşilova, E.; Kurt Bayrakdar, S.; Bilgir, E.; Bayrakdar, İ.Ş.; Çelik, Ö.; Orhan, K. Assessing the Effectiveness of Artificial Intelligence Models for Detecting Alveolar Bone Loss in Periodontal Disease: A Panoramic Radiograph Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, T.; Lamster, I.B.; Levin, L. Current Concepts in the Management of Periodontitis. Int. Dent. J. 2021, 71, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinane, D.F.; Stathopoulou, P.G.; Papapanou, P.N. Periodontal diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer. 2017, 3, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łasica, A.; Golec, P.; Laskus, A.; Zalewska, M.; Gędaj, M.; Popowska, M. Periodontitis: Etiology, conventional treatments, and emerging bacteriophage and predatory bacteria therapies. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1469414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasner, N.S.; Schure, R.S. Periodontal Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, S.; Mealey, B.L.; Mariotti, A.; Chapple, I.L.C. Dental plaque-induced gingival conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Könönen, E.; Gursoy, M.; Gursoy, U.K. Periodontitis: A Multifaceted Disease of Tooth-Supporting Tissues. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.R. Periodontitis: An Oral Disease with Severe Consequences. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, L.; Ye, S.; Ye, Z.; Yang, L.; Xu, X. Oral microbiota-host interaction: The chief culprit of alveolar bone resorption. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1254516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASALE RAE. Diccionario de la Lengua Española—Edición del Tricentenario; Real Academia Española: Madrid, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Noorbakhsh-Sabet, N.; Zand, R.; Zhang, Y.; Abedi, V. Artificial Intelligence Transforms the Future of Health Care. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A Survey of Convolutional Neural Networks: Analysis, Applications, and Prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 6999–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwono, P.; Ma’arif, A.; Rahmaniarm, W.; Fathurrahmanm, H.I.K.; Friskym, A.Z.K.; ul Haq, Q.M. Understanding of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): A Review. Int. J. Robot. Control Syst. 2022, 2, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Chen, L.; Sun, Q. Deep learning method to automatically diagnose periodontal bone loss and periodontitis stage in dental panoramic radiograph. J. Dent. 2024, 150, 105373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt-Bayrakdar, S.; Bayrakdar, İ.Ş.; Yavuz, M.B.; Sali, N.; Çelik, Ö.; Köse, O.; Uzun Saylan, B.C.; Kuleli, B.; Jagtap, R.; Orhan, K. Detection of periodontal bone loss patterns and furcation defects from panoramic radiographs using deep learning algorithm: A retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stera, G.; Giusti, M.; Magnini, A.; Calistri, L.; Izzetti, R.; Nardi, C. Diagnostic accuracy of periapical radiography and panoramic radiography in the detection of apical periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiol. Med. 2024, 129, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Bois, A.H.; Kardachi, B.; Bartold, P.M. Is there a role for the use of volumetric cone beam computed tomography in periodontics? Aust. Dent. J. 2012, 57 (Suppl. S1), 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberghe, B.; Jacobs, R.; Yang, J. Diagnostic validity (or acuity) of 2D CCD versus 3D TCHC-images for assessing periodontal breakdown. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2007, 104, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boztuna, M.; Firincioglulari, M.; Akkaya, N.; Orhan, K. Segmentation of periapical lesions with automatic deep learning on panoramic radiographs: An artificial intelligence study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. Declaración PRISMA 2020: Una guía actualizada para la publicación de revisiones sistemáticas. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2021, 74, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.M.; Klugar, M.; Ding, S.; Carmody, D.P.; Hakonsen, S.J.; Jadotte, Y.T.; White, S.; Munn, Z. Diagnostic test accuracy: Methods for systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.H.; Huang, D.; Weng, H.; Zeng, X.T. Methodological quality (risk of bias) assessment tools for primary and secondary medical studies: What are they and which is better? Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Chae, S.G.; Bae, S.J.; Hwang, K.G. Unsupervised few shot learning architecture for diagnosis of periodontal disease in dental panoramic radiographs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Shao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Pan, K.; Jin, C.; Ji, H.; Du, Y.; Yu, X. Periapical lesion detection in periapical radiographs using the latest convolutional neural network ConvNeXt and its integrated models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagareddy, B.; Vadlamani, R.; Venkannagari, N.R.; Jain, S.; Basheer, S.N.; Murugesan, S. Comparison of the Artificial Intelligence Versus Traditional Radiographic Interpretation in Detecting Periapical Periodontitis: A Diagnostic Accuracy Study. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16 (Suppl. S4), 3676–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Ouyang, H.; Cao, Y.; Huang, T.; Ahn, E.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H. Automated periodontitis bone loss diagnosis in panoramic radiographs using a bespoke two-stage detector. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Wu, Y.F.; Aung, L.M.; Lin, J.C.Y.; Ngo, S.T.; Su, J.N.; Lin, Y.M.; Chang, W.J. Automatic recognition of teeth and periodontal bone loss measurement in digital radiographs using deep-learning artificial intelligence. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icoz, D.; Terzioglu, H.; Ozel, M.A.; Karakurt, R. Evaluation of an artificial intelligence system for the diagnosis of apical periodontitis on digital panoramic images. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2023, 26, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyildiz, B.G.; Karakis, R.; Terzioglu, B.; Ozdemir, D. Comparison of deep learning methods for the radiographic detection of patients with different periodontitis stages. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2024, 53, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.H.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, M.K.; Chen, T.E.; Lan, T.H.; Chang, C.M.; Tseng, T.Y.; Wang, T.; Du, J.K. Convolutional-neural-network-based radiographs evaluation assisting in early diagnosis of the periodontal bone loss via periapical radiograph. J. Dent. Sci. 2024, 19, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Liao, W.; Ying, S.; Zhao, Z. Artificial intelligence for caries and periapical periodontitis detection. J. Dent. 2022, 122, 104107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, G.; Awawdeh, M.; Farook, F.F.; Aljohani, M.; Aldhafiri, R.M.; Aldhoayan, M. Artificial intelligence (AI) diagnostic tools: Utilizing a convolutional neural network (CNN) to assess periodontal bone level radiographically-a retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, V.P.; Yansane, A.I.M.; Brandon, R.G.; Vaderhobli, R.; Lin, G.H.; Hekmatian, H.; Deng, W.; Joshi, N.; Bhandari, H.; Sadat, A.S.; et al. A generative adversarial inpainting network to enhance prediction of periodontal clinical attachment level. J. Dent. 2022, 123, 104211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadrożny, Ł.; Regulski, P.; Brus-Sawczuk, K.; Czajkowska, M.; Parkanyi, L.; Ganz, S.; Mijiritsky, E. Artificial Intelligence Application in Assessment of Panoramic Radiographs. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danks, R.P.; Bano, S.; Orishko, A.; Tan, H.J.; Moreno Sancho, F.; D’Aiuto, F.; Stoyanov, D. Automating Periodontal bone loss measurement via dental landmark localisation. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, S.; Çelik, Ö.; Bayrakdar, İ.Ş.; Orhan, K.; Bilgir, E.; Odabas, A.; Aslan, A. Success of Artificial Intelligence System in Determining Alveolar Bone Loss from Dental Panoramic Radiography Images. Cumhur. Dent. J. 2020, 23, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Puri, S.; Prabhu, S.; Smriti, K. Anomaly Detection in Panoramic Dental X-Rays Using a Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Osaka, Japan, 16–19 November 2020; pp. 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.S.; Song, I.S.; Jung, K.H. DeNTNet: Deep Neural Transfer Network for the detection of periodontal bone loss using panoramic dental radiographs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoromokos, N.; Parinussa, S.; Claessen, F.; Moin, D.A.; Loos, B.G. Estimation of Alveolar Bone Loss in Periodontitis Using Machine Learning. Int. Dent. J. 2022, 72, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.F.; Ai, Q.Y.H.; Leung, Y.Y.; Yeung, A.W.K. Potential and impact of artificial intelligence algorithms in dento-maxillofacial radiology. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 5535–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jundaeng, J.; Chamchong, R.; Nithikathkul, C. Artificial intelligence-powered innovations in periodontal diagnosis: A new era in dental healthcare. Front. Med. Technol. 2024, 6, 1469852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Tay, F.R.; Gu, L. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, M.S.; Kim, J.E.; Hwang, J.J.; Han, S.S.; Kim, J.S.; Yi, W.J.; Park, I.W. Artificial intelligence in oral and maxillofacial radiology: What is currently possible? Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2021, 50, 20200375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbiero, P.; Squillero, G.; Tonda, A. Modeling Generalization in Machine Learning: A Methodological and Computational Study. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.15680v1. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, K.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Tanaka, R.; Bornstein, M.M. Current Applications, Opportunities, and Limitations of AI for 3D Imaging in Dental Research and Practice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, H.R.; Lu, L.; Liu, J.; Yao, J.; Seff, A.; Cherry, K.; Kim, L.; Summers, R.M. Improving Computer-Aided Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Random View Aggregation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.; Song, K.D.; Chung, J.W. Basics of Deep Learning: A Radiologist’s Guide to Understanding Published Radiology Articles on Deep Learning. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendicke, F.; Golla, T.; Dreher, M.; Krois, J. Convolutional neural networks for dental image diagnostics: A scoping review. J. Dent. 2019, 91, 103226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrabi, F.; Ammenwerth, E.; McNair, J.B.; De Keizer, N.F.; Hyppönen, H.; Nykänen, P.; Rigby, M.; Scott, P.J.; Vehko, T.; Wong, Z.S.Y.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Decision Support: Challenges for Evaluating AI and Practical Implications. Yearb. Med. Inform. 2019, 28, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassija, V.; Chamola, V.; Mahapatra, A.; Singal, A.; Goel, D.; Huang, K.; Scardapane, S.; Spinelli, I.; Mahmud, M.; Hussain, A. Interpreting Black-Box Models: A Review on Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Cogn. Comput. 2024, 16, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendicke, F.; Samek, W.; Krois, J. Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry: Chances and Challenges. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norori, N.; Hu, Q.; Aellen, F.M.; Faraci, F.D.; Tzovara, A. Addressing bias in big data and AI for health care: A call for open science. Patterns 2021, 2, 100347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, R.H.; Doi, C.; Yoda, N.; Astuti, E.R.; Sasaki, K. Current applications and development of artificial intelligence for digital dental radiography. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2022, 51, 20210197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-León, M.; Gómez-Polo, M.; Barmak, A.B.; Inam, W.; Kan, J.Y.; Kois, J.C.; Akal, O. Artificial intelligence models for diagnosing gingivitis and periodontal disease: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 130, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram Mohan, K.; Mathew Fenn, S. Artificial Intelligence and Its Theranostic Applications in Dentistry. Cureus 2023, 15, e38711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, W.N.; Gerke, S.; Cohen, I.G. Potential liability for physicians using artificial intelligence. JAMA 2019, 322, 1765–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pubmed | ((“Periodontal Diseases”[Mesh]) Or (“Alveolar Bone Loss”[Mesh]) Or (“Periapical Periodontitis”[Mesh]) Or (“Periodontal Bone Loss”) Or (“Alveolar Bone Resorption”)) And ((“Periapical Radiographs”) Or (“Dental Radiographs”) Or (“Dental Imaging”) Or (“Panoramic Radiography”) Or (“Orthopantomography”)) And ((“Deep Learning”) Or (“Convolutional Neural Networks”) Or (“Vision Transformer Networks”) Or (“Artificial Intelligence”) Or (“Automated Detection”) Or (“Machine Learning”)) |
| Web of Science | ((“Periodontal Diseases”) OR (“Alveolar Bone Loss”) OR (“Periapical Periodontitis”) OR (“periodontal bone loss”) OR (“alveolar bone resorption”)) AND ((“periapical radiographs”) OR (“dental radiographs”) OR (“dental imaging”) OR (“panoramic radiography”) OR (“orthopantomography”)) AND ((“Deep Learning”) OR (“Convolutional Neural Networks”) OR (“Vision Transformer Networks”) OR (“artificial intelligence”) OR (“automated detection”) OR (“machine learning”)) |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Periodontal Diseases” OR “Alveolar Bone Loss” OR “Periapical Periodontitis” OR “periodontal bone loss” OR “alveolar bone resorption”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“periapical radiographs” OR “dental radiographs” OR “dental imaging” OR “panoramic radiography” OR “orthopantomography”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Deep Learning” OR “Convolutional Neural Networks” OR “Vision Transformer Networks” OR “artificial intelligence” OR “automated detection” OR “machine learning”) |
| Cochrane | (“Periodontal Diseases” OR “Alveolar Bone Loss” OR “Periapical Periodontitis” OR “periodontal bone loss” OR “alveolar bone resorption”) AND (“periapical radiographs” OR “dental radiographs” OR “dental imaging” OR “panoramic radiography” OR “orthopantomography”) AND (“Deep Learning” OR “Convolutional Neural Networks” OR “Vision Transformer Networks” OR “artificial intelligence” OR “automated detection” OR “machine learning”) |
| Embase | (‘periodontal diseases’/exp OR ‘periodontal diseases’ OR ‘alveolar bone loss’/exp OR ‘alveolar bone loss’ OR ‘periapical periodontitis’/exp OR ‘periapical periodontitis’ OR ‘periodontal bone loss’/exp OR ‘periodontal bone loss’ OR ‘alveolar bone resorption’/exp OR ‘alveolar bone resorption’) AND (‘periapical radiographs’ OR ‘dental radiographs’ OR ‘dental imaging’ OR ‘panoramic radiography’/exp OR ‘panoramic radiography’ OR ‘orthopantomography’/exp OR ‘orthopantomography’) AND (‘deep learning’/exp OR ‘deep learning’ OR ‘convolutional neural networks’/exp OR ‘convolutional neural networks’ OR ‘vision transformer networks’ OR ‘artificial intelligence’/exp OR ‘artificial intelligence’ OR ‘automated detection’ OR ‘machine learning’/exp OR ‘machine learning’) |
| Author and Year | Type of Study | Object of Study | Type of X-Ray | Sample Studied (Number of X-Rays) | Training, Testing, and Validation Data | Number of Patients | AI Technique Used | Reference Standard For Comparison | Index(es) Used for Model Quantification | Index Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim et al. (2024) [28] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Classification of Periodontal Disease | OPG | 100 | N/S | N/S | UNet-CVAE | Overseen by study investigators | Accuracy | 0.827 |
| Precision | 0.696 | |||||||||
| Sensitivity | 0.794 | |||||||||
| Specificity | 0.842 | |||||||||
| Xue et al. (2024) [18] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | OPG | 320 | (288, 32, N/S) | 320 | RNC | Dental care | F1 Score | Stage 1 91.78% |
| Stage 2 82.90% | ||||||||||
| Stage 3 92.71% | ||||||||||
| Precision | 89.45% | |||||||||
| Boztuna et al. (2024) [23] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Bone loss in apical periodontitis | OPG | 400 | (340, 20, 40) | N/S | U2-Net (RNC) | Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Resident and Dental Radiologist | DICE | 0.788 |
| Intersection upon union | 0.715 | |||||||||
| Precision | 0.776 | |||||||||
| Recovery | 0.854 | |||||||||
| F1 Score | 0.81 | |||||||||
| Liu et al. (2024) [29] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Bone loss in apical periodontitis | Periapical | 1305 | (3132, 200, 261) | N/S | YoCNET (Yolov5 + ConvNeXt) RNC | Dental Radiologists (3) | Accuracy | 90.93% |
| Precision | 98.88% | |||||||||
| Sensitivity | 0.8530 | |||||||||
| F1 Score | 0.9159 | |||||||||
| Nagareddy et al. (2024) [30] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Bone loss in apical periodontitis | Periapical | 30 | N/S | N/S | Diagnocat | Dental Radiologists (2) | Accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, confidence interval, and correlation of the two radiologists with AI | Sensitivity R1 93.8%/R2 83.3%/AI 86.5% Specificity R1 96.7%/R2 80%/IA 88.1% R1 (84.8 ± 8.76)/R2 (84.2 ± 7.74)/AI (86.5 ± 9.18) confidence interval Correlation with AI: R1 0.383 and R2 0.347 |
| Kong et al. (2023) [31] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | OPG | 1747 | Random Split | N/S | Two-stage RNC-based Periodontitis Detection Network (PDRNC) | Dental care | F1 Score | No injuries 0.929 |
| Mild 0.051 | ||||||||||
| Severe 0.020 | ||||||||||
| Precision | Accuracy: 0.762 | |||||||||
| Chen et al. (2023) [32] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | Periapical and bite fins | 8000 | N/S | 270 | RNC with VGG-16 and U-Net architecture | Experienced dentists specializing in periodontics and radiology | Precision | 97.0% |
| Icoz et al. (2023) [33] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Bone loss in apical periodontitis | OPG | 306 | N/S | N/S | YOLO-based computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) (RNC) | Dentists, maxillofacials and radiologists | Accuracy (PPV) | Clearly visible apical periodontitis (0.93 sensitivity, 0.96 F) |
| Recovery (sensitivity) | Clearly visible apical periodontitis in the mandible (0.93 sensitivity, 0.96 F) | |||||||||
| Ayyildiz et al. (2023) [34] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | OPG | 2533 | (2026, 506, N/S) | N/S | RNC-based autonomous transfer (TL) learning methods | Experienced dentists | Accuracy | 0.907 |
| AUROC | 0.888 | |||||||||
| Specificity | 0.944 | |||||||||
| Precision | 0.88 | |||||||||
| Sensitivity | 0.883 | |||||||||
| F1 Score | 0.856 | |||||||||
| Chen et al. (2024) [35] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal Bone Loss and Classification of Periodontal Disease | Periapical | 336 | (82, 336, 20) | N/S | Mask-RRNC and U-Net (RNC) | Three periodontists | Diagnostic accuracy | 72.80% |
| AUROC | 0.946 | |||||||||
| F1 Score | 0.891 | |||||||||
| Sensitivity | 0.88 | |||||||||
| Specificity | 0.906 | |||||||||
| Saylan et al. (2023) [5] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | OPG | 685 | (549, 68, 68) | N/S | YOLO-v5 (RNC) | Oral and maxillofacial radiologist and periodontist | Sensitivity | 0.75 |
| Precision | 0.76 | |||||||||
| F1 Score | 0.76 | |||||||||
| Li et al. (2022) [36] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Caries and periodontitis | Periapical | 4129 | N/S | 4525 | Modified ResNet backbone | Experienced dentists, junior, and a computer scientist | F1 Score | F1: 0.8283 |
| Sensitivity | SEN: 0.8200 | |||||||||
| Specificity | SPEC: 0.8400 | |||||||||
| VPP | PPV: 0.8367 | |||||||||
| VPN | NPV: 0.8235 | |||||||||
| Tsoromokos et al. (2022) [44] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | Periapical | 446 | (327, 70, 49) | 54 | CNN | Dental care | Sensitivity | 0.96 |
| Specificity | 0.41 | |||||||||
| Accuracy | 0.80 | |||||||||
| Alotaibi et al. (2022) [37] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | Periapical | 1724 | (1206, 173, 345) | 1610 | RNC | Experienced dentists and a periodontist | Precision | Accuracy, recovery score F1 binary rating >70% |
| F1 Score | F1 45–70% | |||||||||
| Bone Loss Prediction 0.75 | ||||||||||
| Mild bone loss 0.45 | ||||||||||
| Normal bone levels 0.70 | ||||||||||
| Sensitivity | 0.73 | |||||||||
| Specificity | 0.79 | |||||||||
| Kearney et al. (2022) [38] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | Periapical and bite fins | 103,914 | (80,326, N/S, 12,901) | 10,489 | Generative Partial Convolution Adversarial Restoration (RNC) Network | A periodontist and two general dentists | Absolute Mean Error | 1.5 mm |
| Zadrożny et al. (2022) [39] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Missing teeth, caries, fillings, prosthetic restorations, root canals, residual roots, periapical lesions, and periodontal bone loss | OPG | 30 | N/S | 30 | Diagnocat (RNC) | Three dentists | Sensitivity, specificity | Periapical lesions: AI sensitivity (0.390), IA specificity (0.981) |
| Periodontal bone loss: Sensitivity IA 0.801; AI specificity 0.847; | ||||||||||
| Danks et al. (2021) [40] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | Periapical | 340 | N/S | 63 | Deep neural network with hourglass architecture (RNC) | Two periodontists in postgraduate studies | Percentage of correct Keypoints (PCK), error level, and accuracy level | PCK: 88.9% (one root), 73.9% (two roots), 74.4% (three roots), 83.3% (all three root types together) |
| Periodontists’ assessment error: 10.69% ± 9.15 | ||||||||||
| Periodontist accuracy level: 58% | ||||||||||
| Bayrakdar et al. (2020) [41] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | OPG | 2276 | (1856, 210, 210) | N/S | RNC Google Net Inception v3 | Oral and maxillofacial radiologist and periodontist | Sensitivity | 0.9429 |
| Specificity | 0.8857 | |||||||||
| Accuracy | 0.8919 | |||||||||
| Precision | 0.9143 | |||||||||
| F1 Score | 0.9167 | |||||||||
| Verma et al. (2020) [42] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Cavities, periapical lesions, alteration of alveolar bone height, and impactions of the third molar | OPG | 366 (increased to 1098) | (878, 220, 87) | N/S | RNC and SVM (Support Vector Machine) | Dentist, Dental Radiologist | Precision | 0.9869 |
| Specificity | 0.9857 | |||||||||
| Sensitivity | 0.9795 | |||||||||
| Kim et al. (2019) [43] | Diagnostic accuracy study | Periodontal bone loss | OPG | 12,179 | (11,189, 800, 190) | N/S | DeNTNet | Dental care | F1 Score | 0.71 |
| Sensitivity | 0.87 | |||||||||
| AUROC | 0.95 | |||||||||
| Specificity | 0.96 | |||||||||
| VPP | 0.6 | |||||||||
| VPN | 0.97 |
| Risk of Bias | Applicability Concerns | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUADAS-2 Category | Patient Selection | Index calculated | Reference Standard | Flow and timing | Patient Selection | Reference Standard |
| Cohen’s Kappa (κ) | 0.8864 | 0.8276 | 0.7727 | 0.7727 | 0.7727 | 0.6429 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iacob, A.M.; Castrillón Fernández, M.; Fernández Robledo, L.; Barbeito Castro, E.; Escobedo Martínez, M.F. Automated Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss in Two-Dimensional (2D) Radiographs Using Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090413
Iacob AM, Castrillón Fernández M, Fernández Robledo L, Barbeito Castro E, Escobedo Martínez MF. Automated Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss in Two-Dimensional (2D) Radiographs Using Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(9):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090413
Chicago/Turabian StyleIacob, Alin M., Marta Castrillón Fernández, Laura Fernández Robledo, Enrique Barbeito Castro, and Matías Ferrán Escobedo Martínez. 2025. "Automated Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss in Two-Dimensional (2D) Radiographs Using Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 9: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090413
APA StyleIacob, A. M., Castrillón Fernández, M., Fernández Robledo, L., Barbeito Castro, E., & Escobedo Martínez, M. F. (2025). Automated Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss in Two-Dimensional (2D) Radiographs Using Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review. Dentistry Journal, 13(9), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090413






