Green-Synthesized Nano-Silver Fluoride for Remineralization of Enamel Lesions in Primary Teeth: A Comparative In Vitro Study with SDF and SDF/KI
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulation and Characterization of Green-Synthesized NSF, Structural and Morphological Analysis
2.2. Teeth Sample Preparation
2.3. Induction of Artificial Initial Carious Lesions
2.4. Experimental Grouping and Treatment Protocol
- Gr-SDF—Single application of 38% SDF (Riva Star Step 1, SDI Dental Limited, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia).
- Gr-RS—Single application with a two-step Riva Star capsule system (Riva Star Step 1 and Step 2, SDI Dental Limited, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia).
- Gr-NSFs—Single application of laboratory-synthesized NSF using a green method with green tea extract.
- Gr-NSFd—Double application of laboratory synthesized NSF using a green method with green tea extract at one-week interval.
- Gr-C—Control group with no treatment.
2.5. Surface Microhardness Evaluation
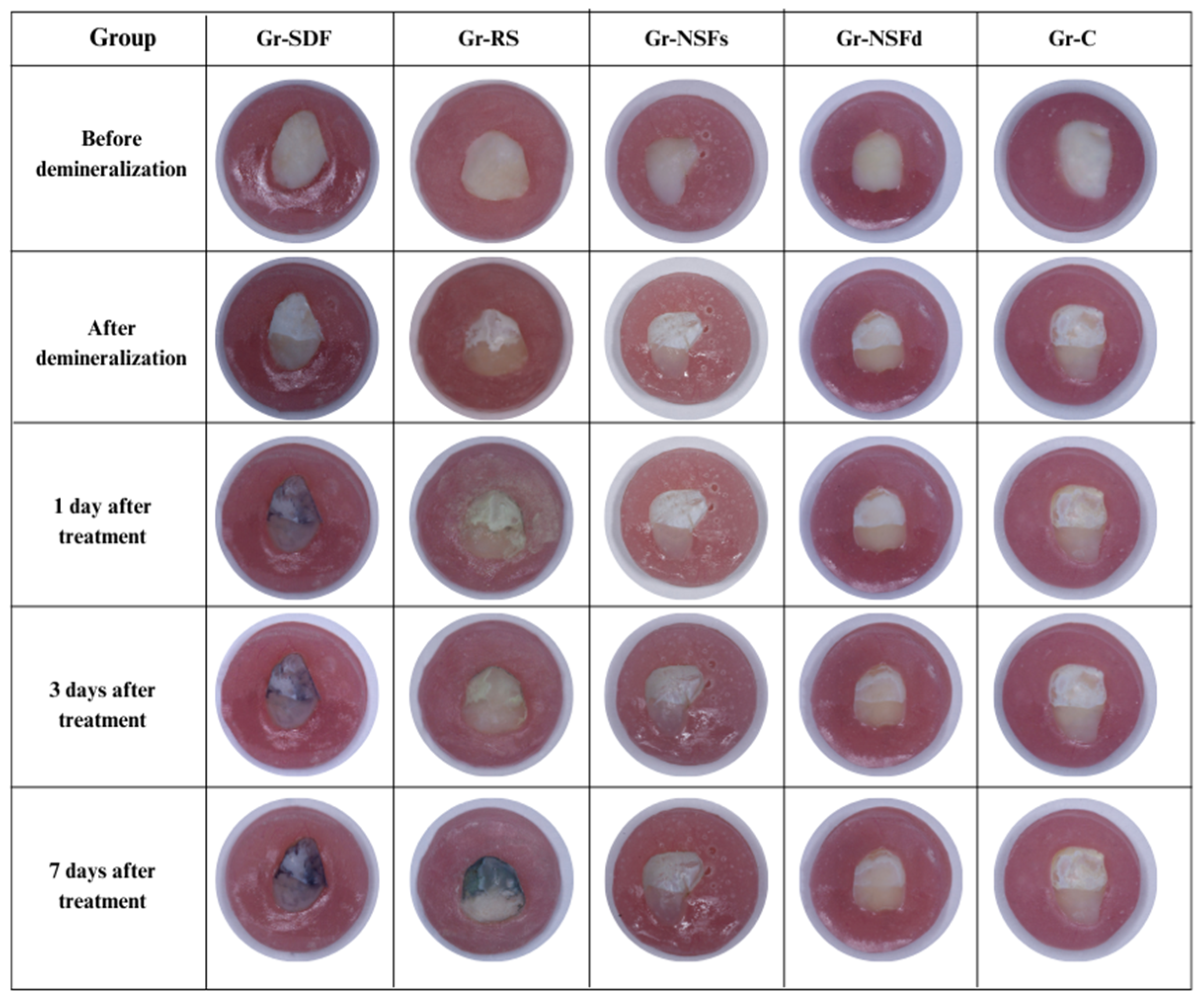
2.6. Photographic Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
- VHN-1: Difference between VHN after demineralization and baseline (VHN-C minus VHN-S), representing mineral loss.
- VHN-2: Difference between post-treatment and post-demineralization values (VHN-T minus VHN-C), representing remineralization.
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Green-Synthesized NSF, Structural and Morphological Analysis
3.2. Surface Microhardness Assessment
3.3. Photographic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECC | early childhood caries |
| SDF | silver diamine fluoride |
| KI | potassium iodide |
| NSF | nano-silver fluoride |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| EDX | energy-dispersive X-ray |
| VHN | Vicker’s hardness number |
| IQR | interquartile ranges |
| NaF | sodium fluoride |
References
- Zou, J.; Du, Q.; Ge, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Song, G.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X.; Jiang, B.; et al. Expert consensus on early childhood caries management. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Bernabé, E.; Dahiya, M.; Bhandari, B.; Murray, C.J.; Marcenes, W. Global burden of untreated caries: A systematic review and metaregression. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, L.J. Contemporary technologies for remineralisation therapies: A review. Int. Dent. SA 2009, 11, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croll, T.P.; Berg, J.H. Delivery Methods of Silver Diammine Fluoride to Contacting Proximal Tooth Surfaces and History of Silver in Dentistry. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2020, 41, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.Y.; Botelho, M.G.; Matinlinna, J.P. Silver compounds used in dentistry for caries management: A review. J. Dent. 2012, 40, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwall-Cohen, J.; Greenwall, L.; Barry, S. Silver diamine fluoride—An overview of the literature and current clinical techniques. Br. Dent. J. 2020, 228, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, M.; Yoshida, S.; Sobue, S.; Kato, J.; Nishida, M. Effect of topically applied ammoniacal silver fluoride on dental caries in children. J. Osaka Univ. Dent. Sch. 1969, 9, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hihara, T.; Nishino, M.; Yasutomi, Y.; Tominaga, T.; Mori, Y.; Arita, K. Effects of diamine silver fluoride on arrestment and prevention of caries in primary tooth. Dent. Jpn. 1994, 31, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yee, R.; Holmgren, C.; Mulder, J.; Lama, D.; Walker, D.; van Palenstein Helderman, W. Efficacy of Silver Diamine Fluoride for Ar-resting Caries Treatment. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 644–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llodra, J.C.; Rodriguez, A.; Ferrer, B.; Menardia, V.; Ramos, T.; Morato, M. Efficacy of silver diamine fluoride for caries reduction in primary teeth and first permanent molars of schoolchildren: 36-month clinical trial. J. Dent. Res. 2005, 84, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, E.C.M.; Chu, C.H.; Lin, H.C. A Community-based Caries Control Program for Pre-school Children Using Topical Fluorides: 18-month Results. J. Dent. Res. 2001, 80, 2071–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabangkhru, S.; Duangthip, D.; Chu, C.H.; Phonghanyudh, A.; Jirarattanasopha, V. A randomized clinical trial to arrest dentin caries in young children using silver diamine fluoride. J. Dent. 2020, 99, 103375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, O.Y.; Mei, M.L.; Zhao, I.S.; Li, Q.L.; Lo, E.C.M.; Chu, C.H. Remineralisation of enamel with silver diamine fluoride and sodium fluoride. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, e344–e352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romão, D.A.; Fernández, C.E.; Santos Lde, M. Commercial Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) Products on Caries Lesion Progression in Primary Enamel: An In Vitro Study. Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2020, 18, b871057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.E.; Erdenebulgan, M.; Kang, C.M.; Jung, H.I.; Song, J.S. Effect of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Potassium Iodide Solution on Enamel Remineralization and Discoloration in Artificial Caries. Materials 2022, 15, 4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.; Neill, C.; Felsenfeld, J.; Primus, C. Potassium Iodide. The Solution to Silver Diamine Fluoride Discoloration? Health 2017, 5, 555655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, A.N.; Chimata, V.K.; Katge, F.A.; Nanavati, K.K.; Shetty, S.K. Comparative Evaluation of Effect of Potassium Iodide and Glutathione on Tooth Discoloration after Application of 38% Silver Diamine Fluoride in Primary Molars: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2021, 14, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, J.O.; Vaghela, P.M. Silver diamine fluoride: A successful anticarious solution with limits. Adv. Dent. Res. 2018, 29, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Turton, B.; Cherian, S.; Anthonappa, R. Silver diamine fluoride staining with potassium iodide: A prospective cohort study. Int. Dent. J. 2024, 74, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeevanandam, J.; Barhoum, A.; Chan, Y.S.; Dufresne, A.; Danquah, M.K. Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: History, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1050–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The Antibacterial Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application in Dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khubchandani, M.; Thosar, N.R.; Dangore-Khasbage, S.; Srivastava, R. Applications of silver nanoparticles in pediatric dentistry: An overview. Cureus 2022, 14, e26956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targino, A.G.; Flores, M.A.; dos Santos Junior, V.E.; de Godoy Bené Bezerra, F.; de Luna Freire, H.; Galembeck, A.; Rosenblatt, A. An innovative approach to treating dental decay in children. A new anti-caries agent. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozari, A.; Ajami, S.; Rafiei, A.; Niazi, E. Impact of Nano Hydroxyapatite, Nano Silver Fluoride and Sodium Fluoride Varnish on Primary Teeth Enamel Remineralization: An In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, ZC97–ZC100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Lo, E.C.M.; Tang, J.; Li, Q.; So, L.Y.; Chu, C.H. Synthesis and Characterization of Fluoridated Silver Nanoparticles and Their Potential as a Non-Staining Anti-Caries Agent. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Munir, S.; Zeb, N.; Ullah, A.; Khan, B.; Ali, J.; Bilal, M.; Omer, M.; Alamzeb, M.; Salman, S.M.; et al. Green nanotechnology: A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles—An ecofriendly approach. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5087–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, N.A.N.; Arham, N.A.; Jai, J.; Hadi, A. Plant Extract as Reducing Agent in Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles: A Review. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 832, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moezizadeh, M. Anticariogenic effect of tea: A review of literature. J. Dent. Oral Hyg. 2013, 5, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Rolim, W.R.; Pelegrino, M.T.; de Araújo Lima, B.; Ferraz, L.S.; Costa, F.N.; Bernardes, J.S.; Rodigues, T.; Brocchi, M.; Seabra, A.B. Green tea extract mediated biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Characterization, cytotoxicity evaluation and antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, P.; Eswara, U.; Maheshwar Reddy, K.R. Effect of different types of tea on Streptococcus mutans: An in vitro study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2012, 23, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nerabieah, Z.; Arrag, E.A.; Comisi, J.C.; Rajab, A. Effectiveness of a novel nano-silver fluoride with green tea extract compared with silver diamine fluoride: A randomized, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Int. J. Dent. Oral Sci. 2020, 7, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.B.; Gao, S.S.; Yu, H.Y. Effect of nano-hydroxyapatite concentration on remineralization of initial enamel lesion in vitro. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 034104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y. Statistical notes for clinical researchers: Sample size calculation 3. Comparison of several means using one-way ANOVA. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2016, 41, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaechi, B.T.; Porteous, N.; Ramalingam, K.; Mensinkai, P.K.; Ccahuana Vasquez, R.A.; Sadeghpour, A.; Nakamoto, T. Remineralization of artificial enamel lesions by theobromine. Caries Res. 2013, 47, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathishkumar, M.; Sneha, K.; Yun, Y.S. Immobilization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Curcuma longa tuber powder and extract on cotton cloth for bactericidal activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7958–7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengke, M.F.; Fleet, M.E.; Southam, G. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by filamentous cyanobacteria from a silver (I) nitrate complex. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2694–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Sun, Y.; Mahmud, S.; Liu, H. Biological and Environmental Applications of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using the Aqueous Extract of Ginkgo biloba Leaf. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2020, 30, 1653–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.P.; Lahtinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Tansy fruit mediated greener synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Cate, J.M.; Duijsters, P.P. Alternating demineralization and remineralization of artificial enamel lesions. Caries Res. 1982, 16, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damato, F.A.; Strang, R.; Stephen, K.W. Effect of fluoride concentration on remineralization of carious enamel an in vitro pH-cycling study. Caries Res. 1990, 24, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, P.D. Microbiologic aspects of dental plaque and dental caries. Dent. Clin. North Am. 1999, 43, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzalaf, M.A.; Hannas, A.R.; Magalhães, A.C.; Rios, D.; Honório, H.M.; Delbem, A.C. pH-cycling models for in vitro evaluation of the efficacy of fluoridated dentifrices for caries control: Strengths and limitations. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2010, 18, 316–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlSheikh, R.N. The use of silver diamine fluoride to prevent/treat enamel carious lesions: A narrative review. Peer J. 2024, 12, e17897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcorn, A.A.; Al Dehailan, L.; Cook, N.B.; Tang, Q.; Lippert, F. Longitudinal in vitro effects of silver diamine fluoride on early enamel caries lesions. Oper. Dent. 2022, 47, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punhagui, M.F.; Jussiani, E.I.; Andrello, A.C.; Favaro, J.C.; Guiraldo, R.D.; Lopes, M.B.; Berger, S.B. Effect of application time and concentration of silver diamine fluoride on the enamel remineralization. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2021, 13, e653–e658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira Costa e Silva, A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mota, C.C.B.O.; Clayton Cabral Correia Lins, E.; Correia de Melo Júnior, P.; de Souza Lima, M.G.; Arnaud, M.; Galembeck, A.; Targino Gadelha, A.; Pereira, J.R.D.; et al. In Vitro morphological, optical and microbiological evaluation of nanosilver fluoride in the remineralization of deciduous teeth enamel. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2018, 7, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahoth, A.S.; Jeon, M.J.; Park, J.W. Synergistic effect of nanosilver fluoride with L-arginine on remineralization of early carious lesions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quritum, M.; Abdella, A.; Amer, H.; El Desouky, L.M.; El Tantawi, M. Effectiveness of nanosilver fluoride and silver diamine fluoride in arresting early childhood caries: A randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atteya, S.M.; Amer, H.A.; Saleh, S.M.; Safwat, Y. Self-assembling peptide and nano-silver fluoride in remineralizing early enamel carious lesions: Randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokce, A.N.; Kelesoglu, E.; Sagır, K.; Kargul, B. Remineralization potential of a novel varnish: An in vitro comparative evaluation. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2024, 48, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butera, A.; Maiorani, C.; Gallo, S.; Pascadopoli, M.; Quintini, M.; Lelli, M.; Tarterini, F.; Foltran, I.; Scribante, A. Biomimetic action of zinc hydroxyapatite on remineralization of enamel and dentin: A review. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Group | Material | Composition | Application Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gr-SDF | 38% SDF (Riva Star Step 1, SDI Dental Limited, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia) | Silver (Ag), fluoride (F), ammonia (NH3) | One drop of Step 1 capsule is applied with a microbrush for 60 s. Excess material is removed using sterile gauze. |
| Gr-RS | 38% SDF + KI (Riva Star Step 1 + Step 2, SDI Dental Limited, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia) | Step 1: Silver (Ag), fluoride (F), ammonia (NH3) Step 2: potassium iodide (KI) | One drop of Step 1 capsule is applied with a microbrush for 60 s. Afterwards, two drops of Step 2 capsule are applied, resulting in a milky-white precipitate. Application continues until the precipitation becomes transparent. Excess material is removed using sterile gauze. |
| Gr-NSFs | Green-synthesized NSF (laboratory prepared) | AgNO3, K2CO3, NaF, aqueous extract of Camellia sinensis | The solution is applied with a microbrush for 60 s. Excess material is removed with sterile gauze. |
| Gr-NSFd | Green-synthesized NSF (laboratory prepared) | AgNO3, K2CO3, NaF, aqueous extract of Camellia sinensis; | Same protocol as for Gr-NSFs, repeated twice at a one-week interval. |
| Gr-C | Control (no treatment) | - | No treatment applied. Underwent pH cycling only. |
| Solution Type | Composition | pH |
|---|---|---|
| Demineralizing | CaCl2, NaH2PO4, CH3COOH, KOH | 4.4 |
| Remineralizing | NaCl, C3H6O3, NaOH | 7.4 ± 0.1 |
| Gr-SDF (1) | Gr-RS (2) | Gr-NSFs (3) | Gr-NSFd (4) | Gr-C (5) | p-Value M–W U Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | |
| VHN-1 | −99.85 (43.88) | −37.00 (29.75) | −81.95 (62.30) | −79.15 (67.85) | −37.65 (62.83) | 2↔3: p < 0.001 |
| VHN-2 | 23.10 (24.88) | 27.60 (50.83) | 10.65 (15.50) | 29.15 (14.78) | 2.85 (7.80) | 1↔5: p < 0.001 2↔5: p < 0.001 4↔5: p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palankalieva, A.; Katsarov, P.; Belcheva, A. Green-Synthesized Nano-Silver Fluoride for Remineralization of Enamel Lesions in Primary Teeth: A Comparative In Vitro Study with SDF and SDF/KI. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13070331
Palankalieva A, Katsarov P, Belcheva A. Green-Synthesized Nano-Silver Fluoride for Remineralization of Enamel Lesions in Primary Teeth: A Comparative In Vitro Study with SDF and SDF/KI. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(7):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13070331
Chicago/Turabian StylePalankalieva, Antonia, Plamen Katsarov, and Ani Belcheva. 2025. "Green-Synthesized Nano-Silver Fluoride for Remineralization of Enamel Lesions in Primary Teeth: A Comparative In Vitro Study with SDF and SDF/KI" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 7: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13070331
APA StylePalankalieva, A., Katsarov, P., & Belcheva, A. (2025). Green-Synthesized Nano-Silver Fluoride for Remineralization of Enamel Lesions in Primary Teeth: A Comparative In Vitro Study with SDF and SDF/KI. Dentistry Journal, 13(7), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13070331









