Relationship Between the Salivary Microbiome and Oral Malodor Metabolites in Older Thai Individuals with Periodontitis and the Cytotoxic Effects of Malodor Compounds on Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma (HSC-4) Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects and Clinical Examination
2.2. Organoleptic Measurement
2.3. Saliva Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, and Amplification of 16s rDNA
2.4. Metagenomics and Data Processing
2.5. UHPLC-MS Analysis
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Treatment and Cell Viability Assay
2.8. Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics and Periodontal Parameters
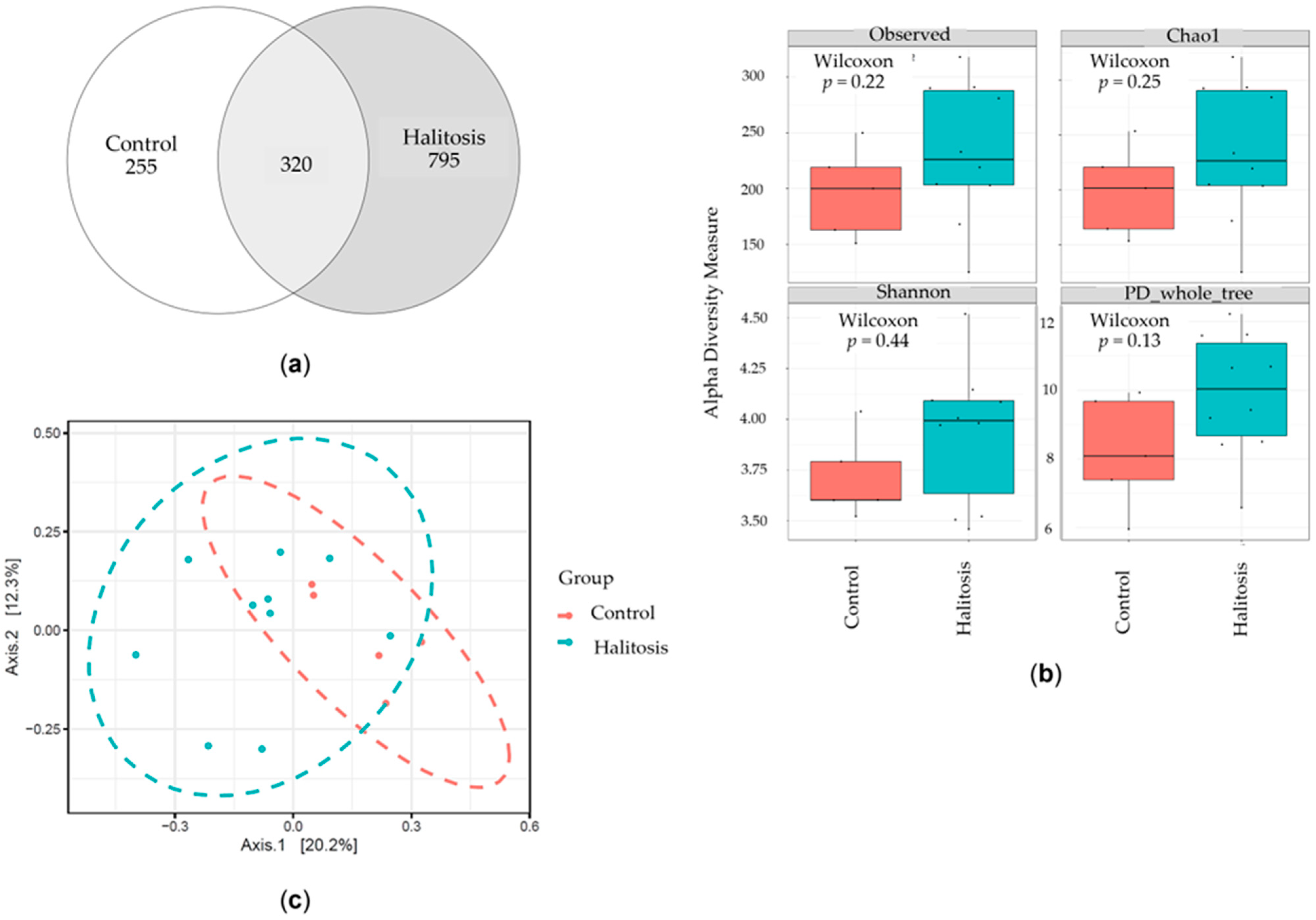
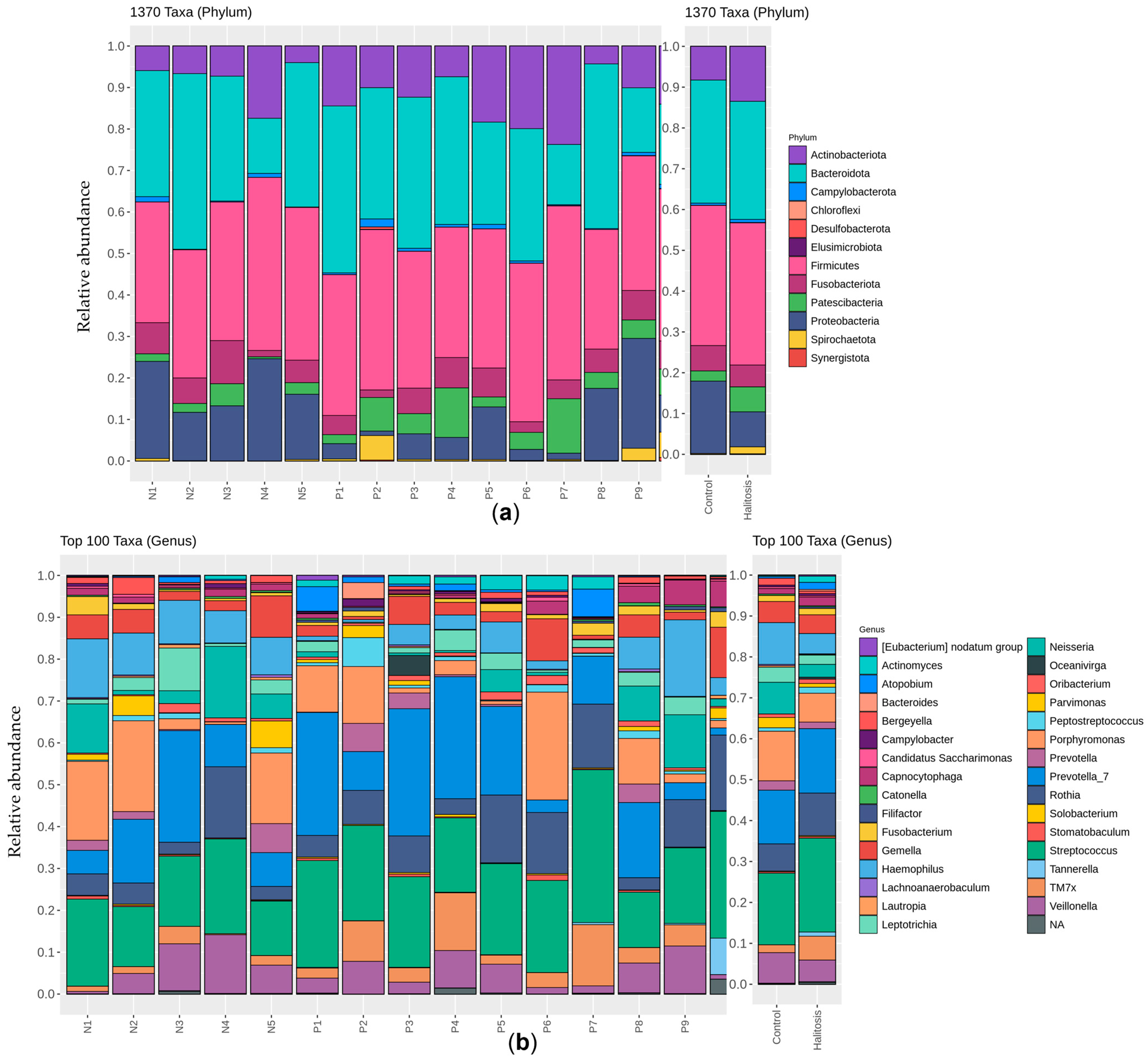
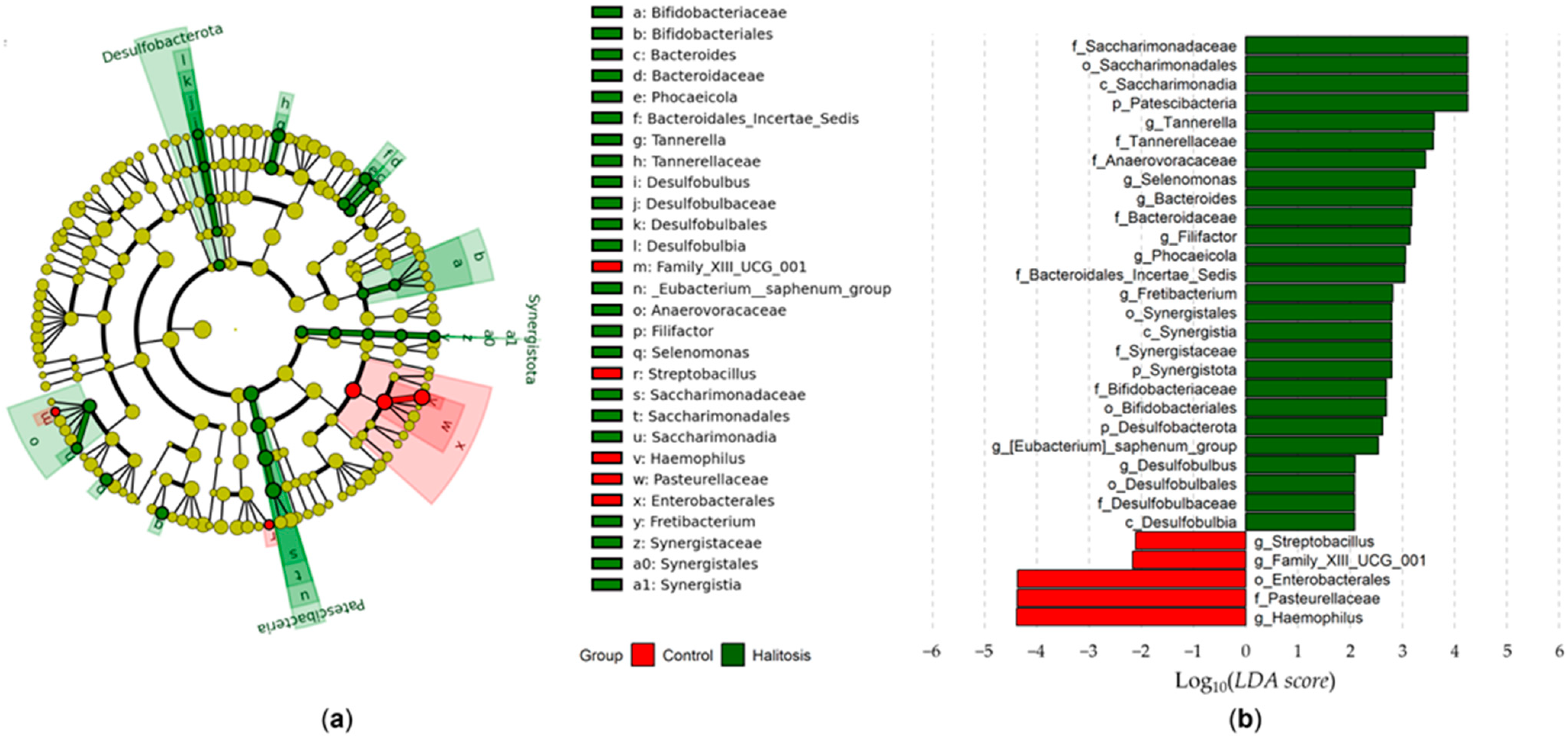
3.2. Salivary Microbiome
3.3. Metabolite Profiling
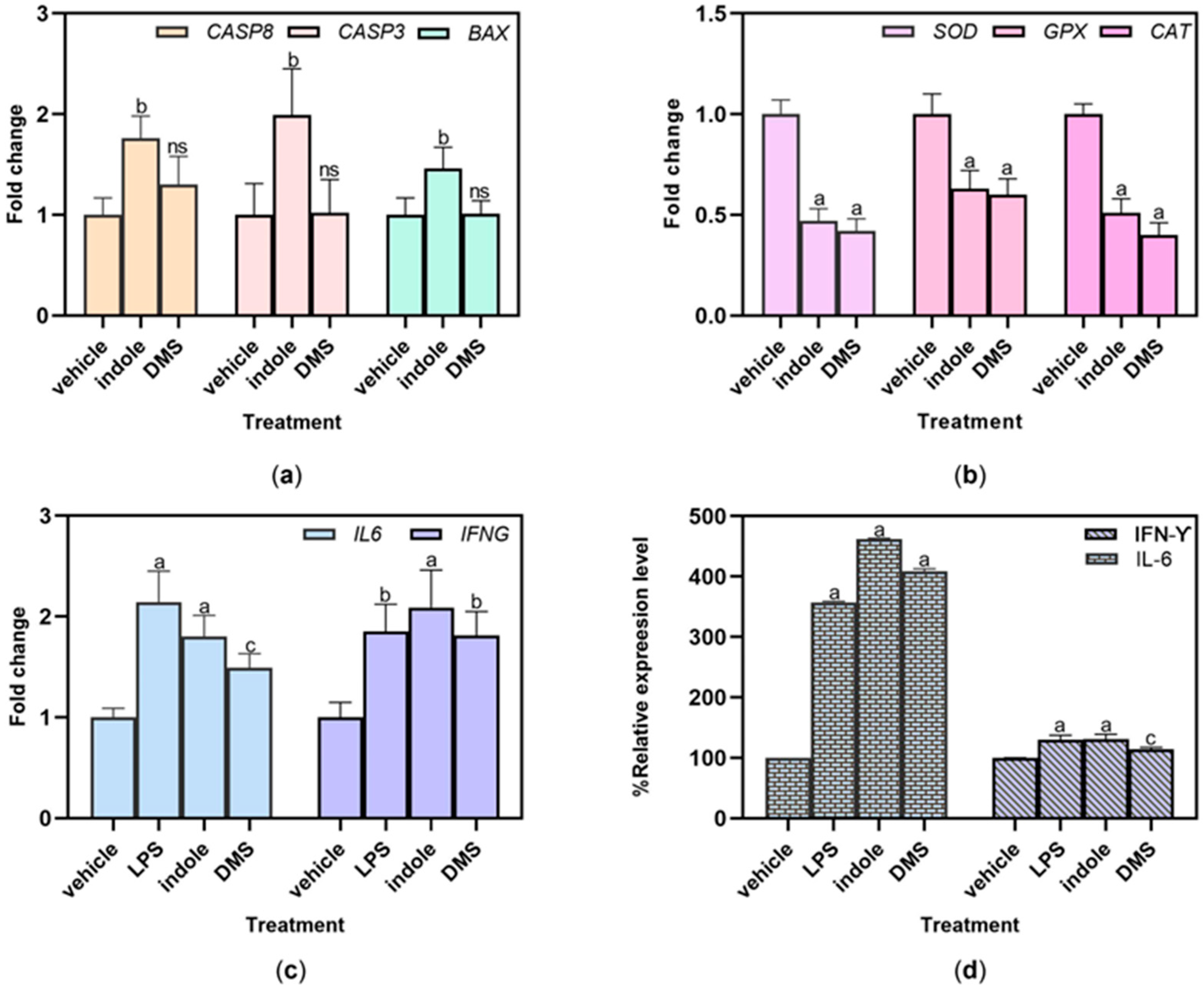
3.4. Effect of Malodor Substances on HSC-4 Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seerangaiyan, K.; Jüch, F.; Winkel, E.G. Tongue coating: Its characteristics and role in intra-oral halitosis and general health—A review. J. Breath Res. 2018, 12, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, U.; Sharma, G.; Juneja, M.; Nagpal, A. Halitosis: Current concepts on etiology, diagnosis and management. Eur. J. Dent. 2016, 10, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampelska, K.; Jaworska, M.M.; Babalska, Z.; Karpiński, T.M. The Role of Oral Microbiota in Intra-Oral Halitosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylıkcı, B.U.; Colak, H. Halitosis: From diagnosis to management. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2013, 4, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izidoro, C.; Botelho, J.; Machado, V.; Reis, A.M.; Proença, L.; Alves, R.C.; Mendes, J.J. Revisiting Standard and Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Halitosis: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, C.; Greenman, J. Halitology (breath odour: Aetiopathogenesis and management). Oral Dis. 2012, 18, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amou, T.; Hinode, D.; Yoshioka, M.; Grenier, D. Relationship between halitosis and periodontal disease—Associated oral bacteria in tongue coatings. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2014, 12, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanowski, M.; Monedeiro, F.; Złoch, M.; Ratiu, I.A.; Pomastowski, P.; Ligor, T.; De Martinis, B.S.; Buszewski, B. Profiling of VOCs released from different salivary bacteria treated with non-lethal concentrations of silver nitrate. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 578, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslund, K.; Lehto, M.; Pussinen, P.; Hartonen, K.; Groop, P.H.; Halonen, L.; Metsälä, M. Identifying volatile in vitro biomarkers for oral bacteria with proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslund, K.; Lehto, M.; Pussinen, P.; Metsälä, M. Volatile composition of the morning breath. J. Breath Res. 2022, 16, 046010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awano, S.; Gohara, K.; Kurihara, E.; Ansai, T.; Takehara, T. The relationship between the presence of periodontopathogenic bacteria in saliva and halitosis. Int. Dent. J. 2002, 52 (Suppl. 3), 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangerman, A. Halitosis in medicine: A review. Int. Dent. J. 2002, 52 (Suppl. 3), 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Koga, T. Methyl mercaptan production by periodontal bacteria. Int. Dent. J. 2002, 52 (Suppl. 3), 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Kho, H.S.; Chung, S.C.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, Y.K. The relationship between volatile sulfur compounds and major halitosis-inducing factors. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codipilly, D.; Kleinberg, I. Generation of indole/skatole during malodor formation in the salivary sediment model system and initial examination of the oral bacteria involved. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 017017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, S.; Kozlovsky, A.; Gordon, D.; Gelernter, I.; Sintov, A.; Rosenberg, M. Cadaverine as a putative component of oral malodor. J. Dent. Res. 1994, 73, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L.; Nascimento, M.; Burne, R.A. Progress toward understanding the contribution of alkali generation in dental biofilms to inhibition of dental caries. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2012, 4, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Shin, S.-I.; Hong, J.-Y. Investigation of volatile sulfur compound level and halitosis in patients with gingivitis and periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, D.P.; Miranda, P.C.; Almeida, T.F.G.; Scalco, M.; Fregni, F.; Amorim, R.F.B. Assessment of the accuracy of portable monitors for halitosis evaluation in subjects without malodor complaint. Are they reliable for clinical practice? J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2017, 25, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenman, J.; Lenton, P.; Seemann, R.; Nachnani, S. Organoleptic assessment of halitosis for dental professionals--general recommendations. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 017102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkar, A.; Wilson, E.; Harrrison, T.; Shaw, D.; Creaser, C. Untargeted metabolic profiling of saliva by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for the identification of potential diagnostic biomarkers of asthma. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5407–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, V.M.; Ciancio, S.G.; Shibly, O.; Xu, T.; Devizio, W.; Trivedi, H.M.; Guo, L.; Jönsson, T.J. Metabolomics Reveals Elevated Macromolecular Degradation in Periodontal Disease. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesan, J.T.; Morelli, T.; Moss, K.; Barros, S.P.; Ward, M.; Jenkins, W.; Aspiras, M.B.; Offenbacher, S. Association of Synergistetes and Cyclodipeptides with Periodontitis. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregy, L.; Müggler, A.R.; Martinez-Lozano Sinues, P.; García-Gómez, D.; Suter, Y.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Kohler, M.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Zenobi, R. Differentiation of oral bacteria in in vitro cultures and human saliva by secondary electrospray ionization—Mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Sathirapongsasuti, J.F.; Izard, J.; Segata, N.; Gevers, D.; Raes, J.; Huttenhower, C. Microbial co-occurrence relationships in the human microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rôças, I.N.; Paiva, S.S.; Magalhães, K.M.; Guimarães-Pinto, T. Cultivable bacteria in infected root canals as identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 22, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.K.; Seo, S.H.; Park, S.E.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, E.J.; Na, C.S.; Cho, K.M.; Kwon, S.J.; Moon, Y.H.; Son, H.S. Identification of Salivary Microorganisms and Metabolites Associated with Halitosis. Metabolites 2021, 11, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Xun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, C.; et al. Tongue Coating and the Salivary Microbial Communities Vary in Children with Halitosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, M.; Zhu, C.; Feng, X.P. Relationship of tongue coating microbiome on volatile sulfur compounds in healthy and halitosis adults. J. Breath Res. 2019, 14, 016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Porsch, M.; Grosse, I.; Hoffmann, K.; Schaller, H.G.; Reichert, S. Comparison of the oral microbiome of patients with generalized aggressive periodontitis and periodontitis-free subjects. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 99, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, R.; Liu, J.; Wen, X.; Zhang, L. Halitosis: Etiology, prevention, and the role of microbiota. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 6383–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lo, K.L.; Liman, A.N.; Feng, X.P.; Ye, W. Tongue-Coating Microbial and Metabolic Characteristics in Halitosis. J. Dent. Res. 2024, 103, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanowski, M.; Pomastowski, P.; Ligor, T.; Buszewski, B. Saliva—Volatile Biomarkers and Profiles. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Saliva Metabolomics Opens Door to Biomarker Discovery, Disease Diagnosis, and Treatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, I.J.; Jung, T.Y.; Son, Y.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.H. Detection of volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) in exhaled breath as a potential diagnostic method for oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, J.; Shen, X.; Lyu, J.; Yan, C.; Tang, B.; Ma, W.; Xie, H.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, L.; et al. Oral Microbiota from Periodontitis Promote Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Development via γδ T Cell Activation. mSystems 2022, 7, e0046922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentel, S.; Gallo, K.; Wagendorf, O.; Preissner, R.; Nahles, S.; Heiland, M.; Preissner, S. Prediction of oral squamous cell carcinoma based on machine learning of breath samples: A prospective controlled study. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouza, M.; Gonzalez-Soto, J.; Pereiro, R.; de Vicente, J.C.; Sanz-Medel, A. Exhaled breath and oral cavity VOCs as potential biomarkers in oral cancer patients. J. Breath Res. 2017, 11, 016015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, M.K.; Mahmoodi, M.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Darehkordi, A.; Hajizadeh, M.R.; Khorramdelazad, H.; Sayadi, A.R.; Falahati-Pour, S.K.; Hassanshahi, G. Indole itself and its novel derivative affect PML cells proliferation via controlling the expression of cell cycle genes. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.S.; Dias, F.R.F.; Cunha, A.C.; Fernandes, P.D. Benzo[f]indole-4,9-dione Derivatives Effectively Inhibit the Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Molecules 2021, 26, 4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, H.; Zhu, B.; Shimoishi, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Murata, Y. Effect of dimethyl sulfides on the induction of apoptosis in human leukemia Jurkat cells and HL-60 cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 2966–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löe, H. The Gingival Index, the Plaque Index and the Retention Index Systems. J. Periodontol. 1967, 38, S610–S616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Sanz, M. Implementation of the new classification of periodontal diseases: Decision-making algorithms for clinical practice and education. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregy, L.; Hirsiger, C.; Gartenmann, S.; Bruderer, T.; Zenobi, R.; Schmidlin, P.R. Metabolic changes during periodontitis therapy assessed by real-time ambient mass spectrometry. Clin. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 14 Pt A, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srila, W.; Baumann, M.; Riedl, M.; Rangnoi, K.; Borth, N.; Yamabhai, M. Glutamine synthetase (GS) knockout (KO) using CRISPR/Cpf1 diversely enhances selection efficiency of CHO cells expressing therapeutic antibodies. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G. Immunomicrobial pathogenesis of periodontitis: Keystones, pathobionts, and host response. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelino, M.; Eyre, S.; Moat, J.; Fox, G.; Martin, P.; Ho, P.; Upton, M.; Barton, A. Optimisation of methods for bacterial skin microbiome investigation: Primer selection and comparison of the 454 versus MiSeq platform. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Hemme, C.; Beleno, J.; Shi, Z.J.; Ning, D.; Qin, Y.; Tu, Q.; Jorgensen, M.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; et al. Oral microbiota of periodontal health and disease and their changes after nonsurgical periodontal therapy. Isme J. 2018, 12, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ileri Keceli, T.; Gulmez, D.; Dolgun, A.; Tekcicek, M. The relationship between tongue brushing and halitosis in children: A randomized controlled trial. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, L.F.; Fermiano, D.; Feres, M.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Teles, F.R.; Mayer, M.P.; Faveri, M. Levels of Selenomonas species in generalized aggressive periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2012, 47, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socransky, S.S.; Haffajee, A.D.; Cugini, M.A.; Smith, C.; Kent, R.L., Jr. Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1998, 25, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.; Badran, Z.; Boghossian, A.; Alharbi, A.M.; Alfahemi, H.; Khan, N.A. The increasing importance of the oral microbiome in periodontal health and disease. Future Sci. OA 2023, 9, Fso856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogilnicka, I.; Bogucki, P.; Ufnal, M. Microbiota and Malodor-Etiology and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, N. Studies on the experimental allergic rhinitis induced by Japanese cedar pollen--role of cysteinyl leukotrienes in nasal allergic symptoms. Yakugaku Zasshi 2003, 123, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barnes, V.M.; Teles, R.; Trivedi, H.M.; Devizio, W.; Xu, T.; Mitchell, M.W.; Milburn, M.V.; Guo, L. Acceleration of Purine Degradation by Periodontal Diseases. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.M.; Park, S.-H.; Nam, M.J. Induction of apoptosis in indole-3-carbinol-treated lung cancer H1299 cells via ROS level elevation. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.L.; Pugine, S.M.P.; Ferreira, M.S.L.; Lins, P.G.; Costa, E.J.X.; de Melo, M.P. Influence of indole acetic acid on antioxidant levels and enzyme activities of glucose metabolism in rat liver. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2007, 25, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.L.; Wu, P.F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.J.; Shen, Z.C.; Luo, H.; Chen, H.; Long, L.H.; Chen, J.G.; Wang, F. Dimethyl sulfide protects against oxidative stress and extends lifespan via a methionine sulfoxide reductase A-dependent catalytic mechanism. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liao, A.; Wu, J. The role of indole derivative in the growth of plants: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1120613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Periodontally Healthy Controls (n = 10) | Periodontitis Patients (n = 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 22.34 ± 3.51 | 58.34 ± 4.17 a |
| PSI baseline | <2 | 3.94 |
| O’Leary PSI (%) | 87.90 ± 9.33 | 88.82 ± 9.20 ns |
| BOP (%) | 55.67 ± 8.55 | 73.98 ± 8.14 a |
| PPD (mm) | 2.33 ± 0.59 | 4.56 ± 1.86 (min 2, max 10) b |
| Clinical attachment loss (mm) | No loss | 4.89 ± 2.09 (min 2, max 10) a |
| Organoleptic score (0–4) | 0 (No malodor) | 3.29 ± 0.73 (2–4) a |
| No. | Retention Time (min) | Regulation | m/z | Proposed Elemental Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.3 | Up | 116.0714 | C5H9NO2 |
| 2 | 5.5 | Down | 600.3079 | Unidentified * |
| 3 | 6.5 | Up | 203.1010 | C8H14N2O4 |
| 4 | 7.4 | H | 517.2246 | C32H28N4O3 |
| 5 | 7.8 | C | 139.0489 | C6H6N2O2 |
| 6 | 9.2 | Down | 527.2835 | C28H38N4O6 |
| 7 | 9.6 | Down | 600.2726 | C29H37N5O9 |
| 8 | 11.9 | Up | 182.0798 | C9H11NO3 |
| 9 | 12.2 | H | 132.1006 | C6H13NO2 |
| 10 | 15.6 | H | 711.3402 | C38H50N2O11 |
| 11 | 19.1 | Down | 367.1968 | C16H30O9 |
| 12 | 20.3 | Up | 120.0821 | C8H9N |
| 13 | 21.4 | Up | 720.4030 | Unidentified * |
| 14 | 22.5 | Up | 216.0962 | Unidentified * |
| 15 | 22.7 | C | 155.0821 | C7H11N2O2 |
| 16 | 24.5 | Up | 279.1317 | C14H18N2O4 |
| 17 | 24.8 | Up | 458.2525 | C23H39NO6S |
| 18 | 27.9 | Down | 588.5022 | C37H65NO4 |
| 19 | 28.4 | H | 188.0683 | C6H10ClN5 |
| 20 | 29.9 | Up | 561.3016 | Unidentified * |
| 21 | 33.6 | H | 739.2892 | Unidentified * |
| 22 | 36.5 | H | 819.2567 | Unidentified * |
| 23 | 41.0 | C | 437.2343 | C28H28N4O |
| 24 | 41.9 | Up | 716.3843 | C25H50N17O6S |
| 25 | 42.8 | C | 525.2880 | C24H44O12 |
| 26 | 45.3 | Up | 742.4410 | Unidentified * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srila, W.; Sripilai, K.; Binlateh, T.; Thammanichanon, P.; Tiskratok, W.; Noisa, P.; Jitprasertwong, P. Relationship Between the Salivary Microbiome and Oral Malodor Metabolites in Older Thai Individuals with Periodontitis and the Cytotoxic Effects of Malodor Compounds on Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma (HSC-4) Cells. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13010036
Srila W, Sripilai K, Binlateh T, Thammanichanon P, Tiskratok W, Noisa P, Jitprasertwong P. Relationship Between the Salivary Microbiome and Oral Malodor Metabolites in Older Thai Individuals with Periodontitis and the Cytotoxic Effects of Malodor Compounds on Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma (HSC-4) Cells. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrila, Witsanu, Kritsana Sripilai, Thunwa Binlateh, Peungchaleoy Thammanichanon, Watcharaphol Tiskratok, Parinya Noisa, and Paiboon Jitprasertwong. 2025. "Relationship Between the Salivary Microbiome and Oral Malodor Metabolites in Older Thai Individuals with Periodontitis and the Cytotoxic Effects of Malodor Compounds on Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma (HSC-4) Cells" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13010036
APA StyleSrila, W., Sripilai, K., Binlateh, T., Thammanichanon, P., Tiskratok, W., Noisa, P., & Jitprasertwong, P. (2025). Relationship Between the Salivary Microbiome and Oral Malodor Metabolites in Older Thai Individuals with Periodontitis and the Cytotoxic Effects of Malodor Compounds on Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma (HSC-4) Cells. Dentistry Journal, 13(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13010036







