Role of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Alveolar Bone Remodeling during Orthodontic Retention Phase in Rat Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
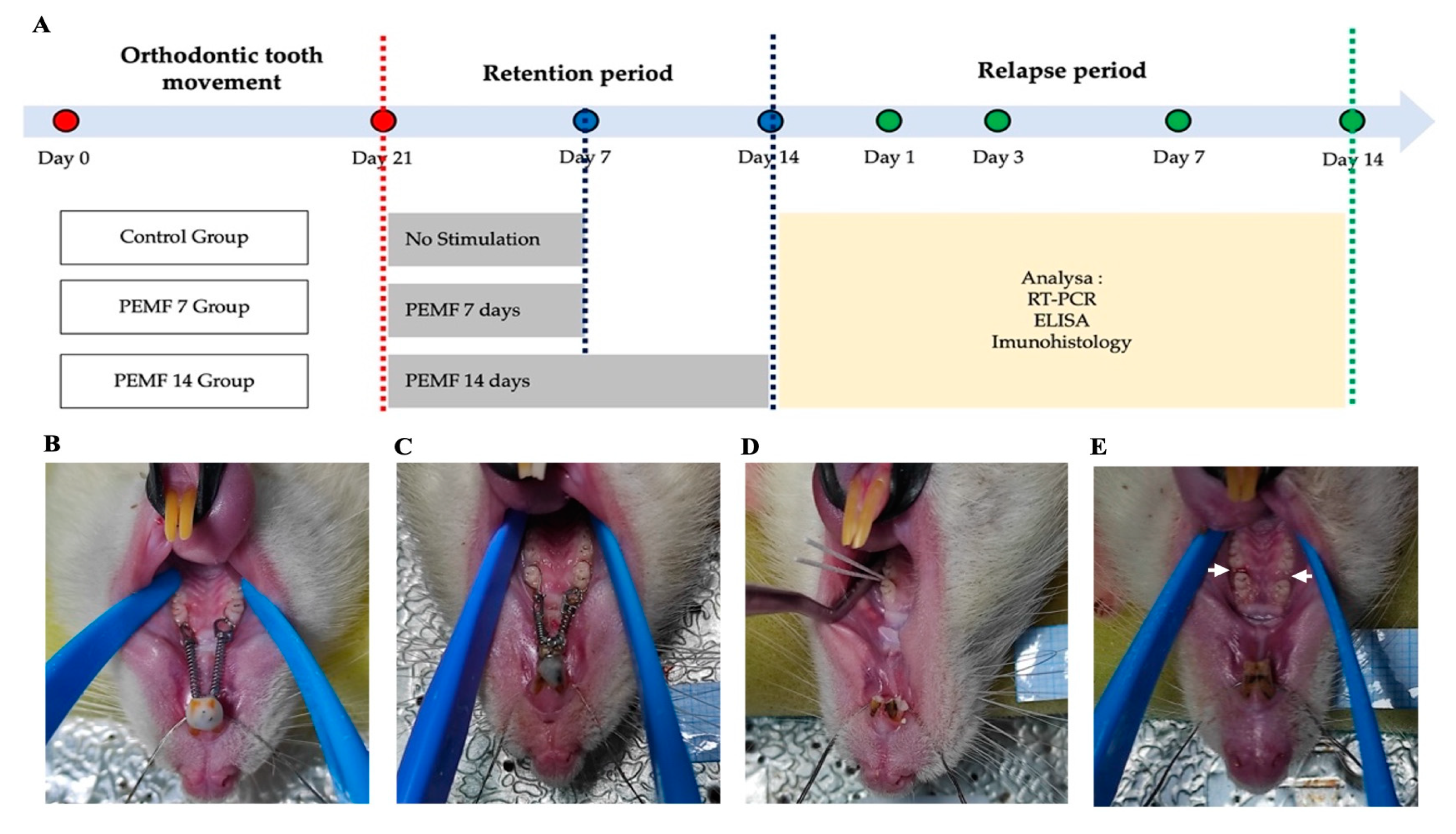
2.1. Experimental Animal Models
2.2. Orthodontic Tooth Movement in Rat Models
2.3. Retention Phase
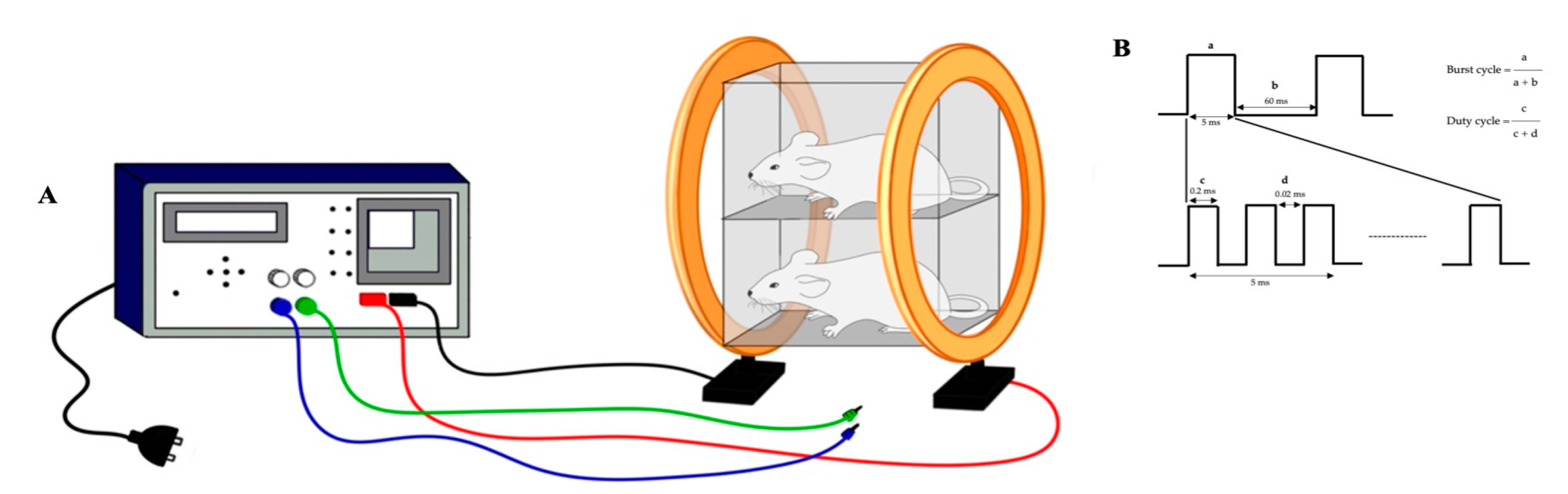
2.4. PEMF Exposure
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Analysis
2.6. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
2.7. Immunohistochemistry Procedures
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Wnt5a mRNA Expressions
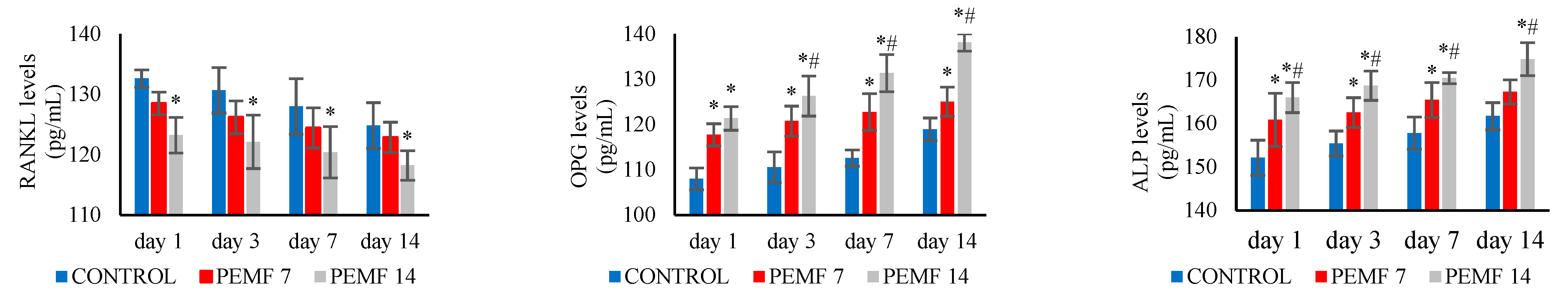
3.2. RANKL, OPG, and ALP Levels
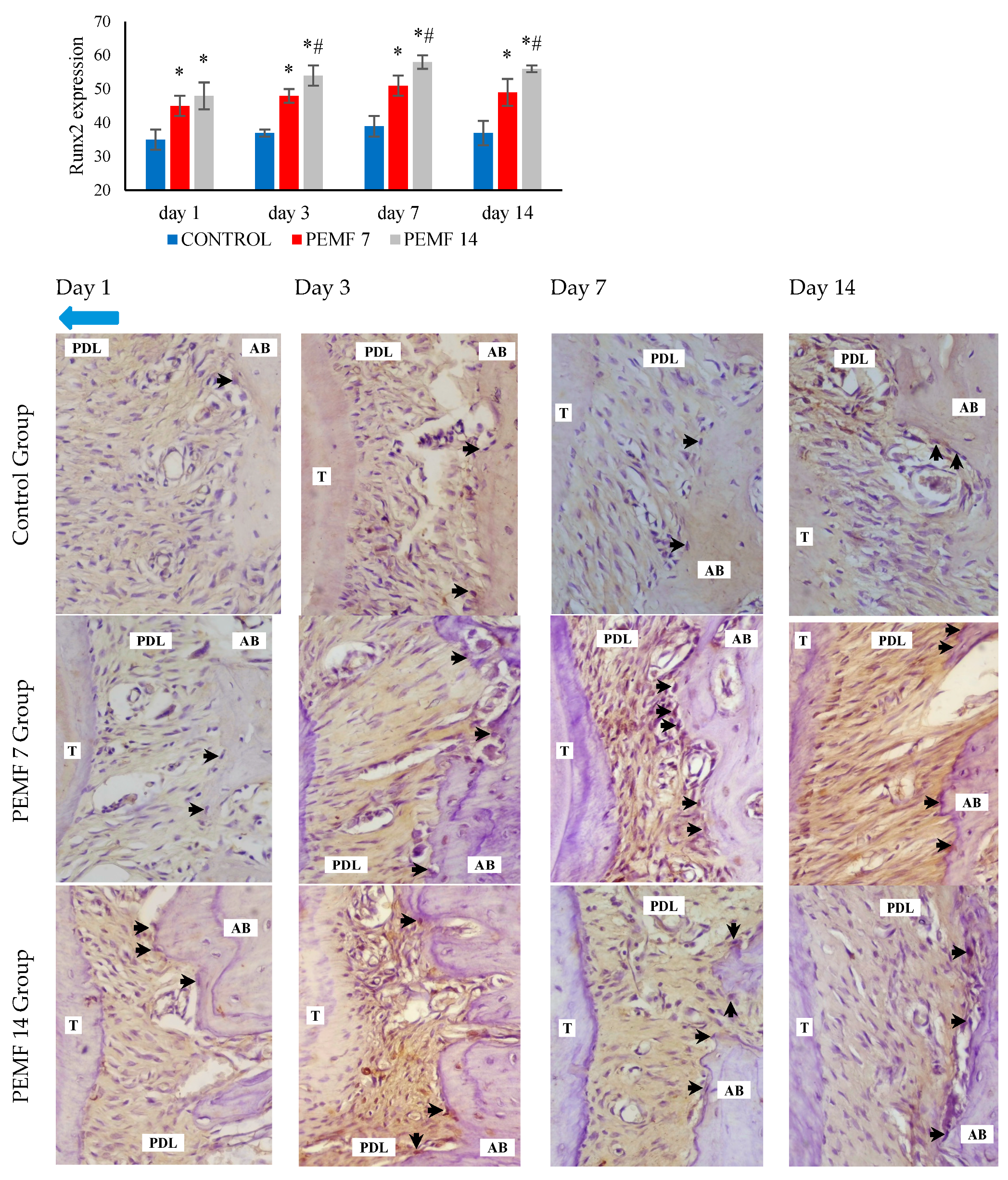
3.3. Runx2 Expressions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alikhani, M.; Sangsuwon, C.; Al-ansari, S.; Nervina, J.M.; Teixeira, C.C. Biphasic theory: Breakthrough understanding of tooth movement. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2018, 3, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Koide, M.; Uehara, S.; Okamoto, M.; Ishihara, A.; Kayama, T.; Saito, M.; Marumo, K. The regulation of bone metabolism and disorders by Wnt signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aonuma, T.; Tamamura, N.; Fukunaga, T.; Sakai, Y.; Takeshita, N.; Shigemi, S.; Yamashiro, T.; Thesleff, I.; Takano-Yamamoto, T. Delayed tooth movement in Runx2+/- mice associated with mTORC2 in stretch-induced bone formation. Bone Rep. 2020, 27, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, M.; Safavi, S.M.; Dianat, O.; Tusi, S.K.; Younessian, F. Acid and alkaline phosphatase levels in GCF during orthodontic tooth movement. J. Dent. Shiraz Univ. Med. Sci. 2015, 16, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Shoji-Matsunaga, A.; Ono, T.; Hayashi, M.; Takayanagi, H.; Moriyama, K.; Nakashima, T. Osteocyte regulation of orthodontic force-mediated tooth movement via RANKL expression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Jeon, H.H.; Alshabab, A.; Lee, Y.J.; Chung, C.H.; Graves, D.T. Rankl deletion in periodontal ligament and bone lining cells blocks orthodontic tooth movement. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arn, M.L.; Dritsas, K.; Pandis, N.; Kloukos, D. The effects of fixed orthodontic retainers on periodontal health: A systematic review. Ajodo 2020, 157, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.F.; Yang, L.; He, H.C.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; He, C.Q. Pulsed electromagnetic fields on postmenopausal osteoporosis in Southwest China: A randomized, active-controlled clinical trial. Bioelectromagnetics 2013, 34, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, A.; Loddo, S.; Bellone, F.; Pecora, C.; Lasco, A.; Morabito, N. Pulsed electromagnetic fields modulate bone metabolism via RANKL/OPG and Wnt/β-catenin pathways in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: A pilot study. Bone 2018, 116, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assiotis, A.; Sachinis, N.P.; Chalidis, B.E. Pulsed electromagnetic fields for the treatment of tibial delayed unions and nonunions. A prospective clinical study and review of the literature. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2012, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.F.; Xiong, J.; Chen, Y.X.; Wang, J.F.; Qiu, X.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Qiu, Y. Early application of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postoperative delayed union of long-bone fractures: A prospective randomized controlled study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajerani, H.; Tabeie, F.; Vossoughi, F.; Jafari, E.; Assadi, M. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic field on mandibular fracture healing: A randomized control trial, (RCT). J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 120, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadossi, R.; Massari, L.; Racine-Avila, J.; Aaron, R.K. Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation of bone healing and joint preservation: Cellular mechanisms of skeletal response. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. Glob. Res. Rev. 2020, 4, e1900155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flatscher, J.; Pavez Loriè, E.; Mittermayr, R.; Meznik, P.; Slezak, P.; Redl, H.; Slezak, C. Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF)-physiological response and its potential in trauma treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferroni, L.; Gardin, C.; Dolkart, O.; Salai, M.; Barak, S.; Piattelli, A.; Amir-Barak, H.; Zavan, B. Pulsed electromagnetic fields increase osteogenetic commitment of MSCs via the mTOR pathway in TNF-α mediated inflammatory conditions: An in-vitro study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Selvamurugan, N.; Warshaw, J.; Partridge, N.C. Pulsed electromagnetic fields inhibit human osteoclast formation and gene expression via osteoblasts. Bone 2018, 106, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androjna, C.; Fort, B.; Zborowski, M.; Midura, R.J. Pulsed electromagnetic field treatment enhances healing callus biomechanical properties in an animal model of osteoporotic fracture. Bioelectromagnetics 2014, 35, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, H.; Xia, L.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y.; He, C. Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulates osteoprotegerin and reduces RANKL expression in ovariectomized rats. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jing, D.; Tang, C.; Ding, Y.; Feng, X. Effects of low-intensity pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone microarchitecture, mechanical strength and bone turnover in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, D.; Cai, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, G.; Li, F.; Xu, Q.; Xie, K.; Tang, C.; Liu, J.; Guo, W.; et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields partially preserve bone mass, microarchitecture, and strength by promoting bone formation in hindlimb-suspended rats. J. Bone Min. Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 2250–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.G.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.C.; Kang, K.H.; Cho, J.H.; Cho, J.W.; Chang, N.Y.; Bay, R.C.; Chae, J.M. Effectiveness of pulsed electromagnetic field for pain caused by placement of initial orthodontic wire in female orthodontic patients: A preliminary single-blind randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 152, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.H.; Vijayalakshmi, D.; Kumar, N.M.V.; Nagachandran, K.S. Effectiveness of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy for pain relief in adult patients during the initial space closure phase of orthodontic treatment using sliding mechanics: A single-blind, split-mouth randomized clinical trial. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2020, 24, 808–828. [Google Scholar]
- Dogru, M.; Akpolat, V.; Dogru, A.G.; Karadede, B.; Akkurt, A.; Karadede, M.I. Examination of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on orthodontic tooth movement in rats. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014, 28, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhad Patil, W.A.; Karemore, A.A. Efficacy of pulsed electromagnetic field in reducing treatment time: A clinical investigation. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 161, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Kako, S.; Miyazawa, K.; Tabuchi, M.; Kimura, F.; Kataoka, K.; Kato, R.; Sato, T.; Goto, S. Dynamics and observations of long-term orthodontic tooth movement and subsequent relapse in C57BL/6 mice. Exp. Anim. 2023, 72, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Kitaura, H.; Shen, W.R.; Kishikawa, A.; Ogawa, S.; Ohori, F.; Noguchi, T.; Marahleh, A.; Nara, Y.; Mizoguchi, I. Establishment of an orthodontic retention mouse model and the effect of anti-c-Fms antibody on orthodontic relapse. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Gou, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; Tian, S.; Yu, L. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic field on bone formation and lipid metabolism of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis rats through canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 4927035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, D.; Zhai, M.; Tong, S.; Xu, F.; Cai, J.; Shen, G.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, K.; Liu, J.; et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote osteogenesis and osseointegration of porous titanium implants in bone defect repair through a Wnt/β-catenin signaling-associated mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, M.; Jing, D.; Tong, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zeng, Z.; Shen, G.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Luo, E. Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote in vitro osteoblastogenesis through a Wnt/β-catenin signaling-associated mechanism. Bioelectromagnetics 2016, 37, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umiatin, U.; Dilogo, I.H.; Wijaya, S.K.; Sari, P.; Djaja, A.D. Design and development of pulse electromagnetic fields (PEMF) as adjuvant therapy for fracture healing: A preliminary study on rats. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2092, 020028. [Google Scholar]
- Millett, D. The rationale for orthodontic retention: Piecing together the jigsaw. Br. Dent. J. 2021, 230, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adawy, M.; Darweesh, S.; Alashwah, A.; Dessoky, N. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic field on the alveolar bone density and its impact on the dental implant osseointegration in osteoporotic patients (a randomized controlled clinical trial). Alex. Dent. J. 2024, 49, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, Q.; Guo, S.; Wu, Y. Role of Wnt5a in periodontal tissue development, maintenance, and periodontitis: Implications for periodontal regeneration. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, M.; Udagawa, N.; Uehara, S.; Maeda, K.; Yamashita, T.; Nakamichi, Y.; Kato, H.; Saito, N.; Minami, Y.; Takahashi, N.; et al. Noncanonical Wnt5a enhances Wnt/β-catenin signaling during osteoblastogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, N.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kikuta, J.; Shimizu, M.; Yoshino, T.; Hikida, T.; Takahashi, M.; Goseki, T.; Kasai, K. Wnt5a stimulates the bone formation in tension side during orthodontic tooth movement. Int. J. Oral Med. Sci. 2015, 13, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umiatin, U.; Dilogo, I.H.; Sari, P.; Wijaya, S.K. The effect of pulsed electromagnetic field exposure on fracture healing through the Wnt signal pathway. OnLine J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 20, 239–249. [Google Scholar]
- Gomathi, K.; Akshaya, N.; Srinaath, N.; Moorthi, A.; Selvamurugan, N. Regulation of Runx2 by post-translational modifications in osteoblast differentiation. Life Sci. 2020, 245, 117389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, N.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Ryaby, J.T.; Waldorff, E.I.; Lee, W.Y.W.; Li, G. A novel pulsed electromagnetic field promotes distraction osteogenesis via enhancing osteogenesis and angiogenesis in a rat model. J. Orthop. Transl. 2020, 25, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Pei, H.; Wang, X.; Bao, T.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, L.; He, C. Pulsed electromagnetic field promotes bone anabolism in postmenopausal osteoporosis through the miR-6976/BMP/Smad4 Axis. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 2023, 8857436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloise, N.; Petecchia, L.; Ceccarelli, G.; Fassina, L.; Usai, C.; Bertoglio, F.; Balli, M.; Vassalli, M.; Cusella De Angelis, M.G.; Gavazzo, P.; et al. The effect of pulsed electromagnetic field exposure on osteoinduction of human mesenchymal stem cells cultured on nano-TiO2 surfaces. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, L.; Jiang, L.; Li, H. Therapeutic effect of pulsed electromagnetic field on bone wound healing in rats. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2020, 40, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi-Sun, J.; Kobayashi, I.; Kashima, M.; Hirayama, J.; Kakikawa, M.; Yamada, S.; Suzuki, N. Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields facilitate both osteoblast and osteoclast activity through Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the zebrafish scale. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 7, 1340089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukasaki, M.; Takayanagi, H. Osteoimmunology: Evolving concepts in bone-immune interactions in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 626–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T.; Hayashi, M.; Sasaki, F.; Nakashima, T. RANKL biology: Bone metabolism, the immune system, and beyond. Inflamm. Regen. 2020, 40, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, V.; Penninger, J.M. The RANKL-RANK story. Gerontology 2015, 61, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimatsu, M.; Kitaura, H.; Morita, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Ukai, T. Effects of anti-mouse RANKL antibody on orthodontic tooth movement in mice. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liao, Y.; Xie, H.; Liao, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, N.; Sun, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, G. Effects of combined treatment with ibandronate and pulsed electromagnetic field on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. Bioelectromagnetics 2017, 38, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Yang, K. Changes in alveolar bone structure during orthodontic tooth movement in adolescent and adult rats: A microcomputed tomography study. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2023, 26, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gen Target | Primer | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Length (bp) | Tm (°C) | Gene Bank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wnt5a | Forward | CGCTGCTGGAGTGGTAAATGC | 148 | 59.90 | NM_022631.3 |
| Reverse | TGCGACCTGCTTCATTGTTG | 60.04 | |||
| Beta-actin | Forward | CCTAAGGCCAACCGTGAAA | 152 | 55.3 | NM_017008.4 |
| Reverse | CAGAGGCATACAGGGACAAC | 55.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maulana, H.; Yueniwati, Y.; Permatasari, N.; Suyono, H. Role of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Alveolar Bone Remodeling during Orthodontic Retention Phase in Rat Models. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12090287
Maulana H, Yueniwati Y, Permatasari N, Suyono H. Role of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Alveolar Bone Remodeling during Orthodontic Retention Phase in Rat Models. Dentistry Journal. 2024; 12(9):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12090287
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaulana, Hafiedz, Yuyun Yueniwati, Nur Permatasari, and Hadi Suyono. 2024. "Role of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Alveolar Bone Remodeling during Orthodontic Retention Phase in Rat Models" Dentistry Journal 12, no. 9: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12090287
APA StyleMaulana, H., Yueniwati, Y., Permatasari, N., & Suyono, H. (2024). Role of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Alveolar Bone Remodeling during Orthodontic Retention Phase in Rat Models. Dentistry Journal, 12(9), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12090287






