A Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedure to Harvest Palate Periosteum as a Source of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Subjects
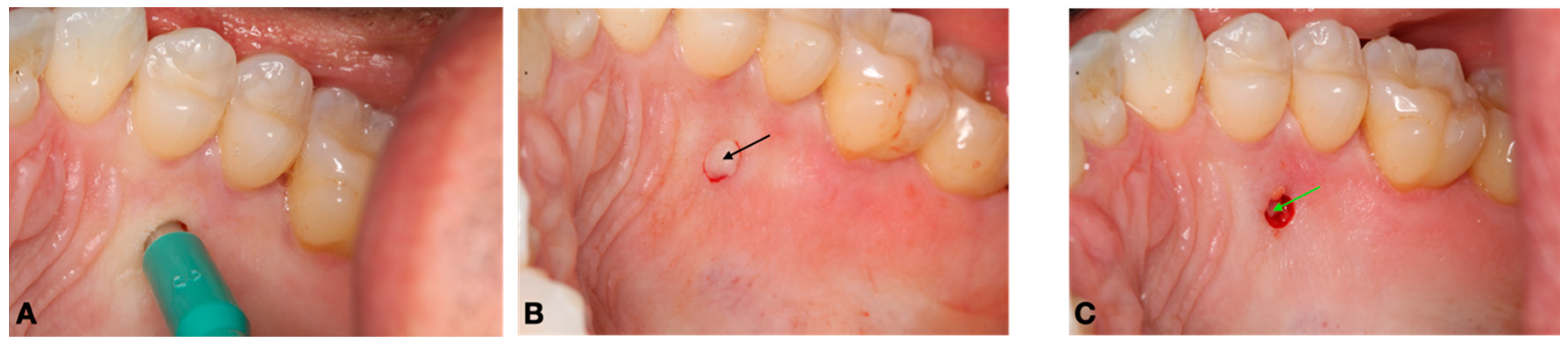
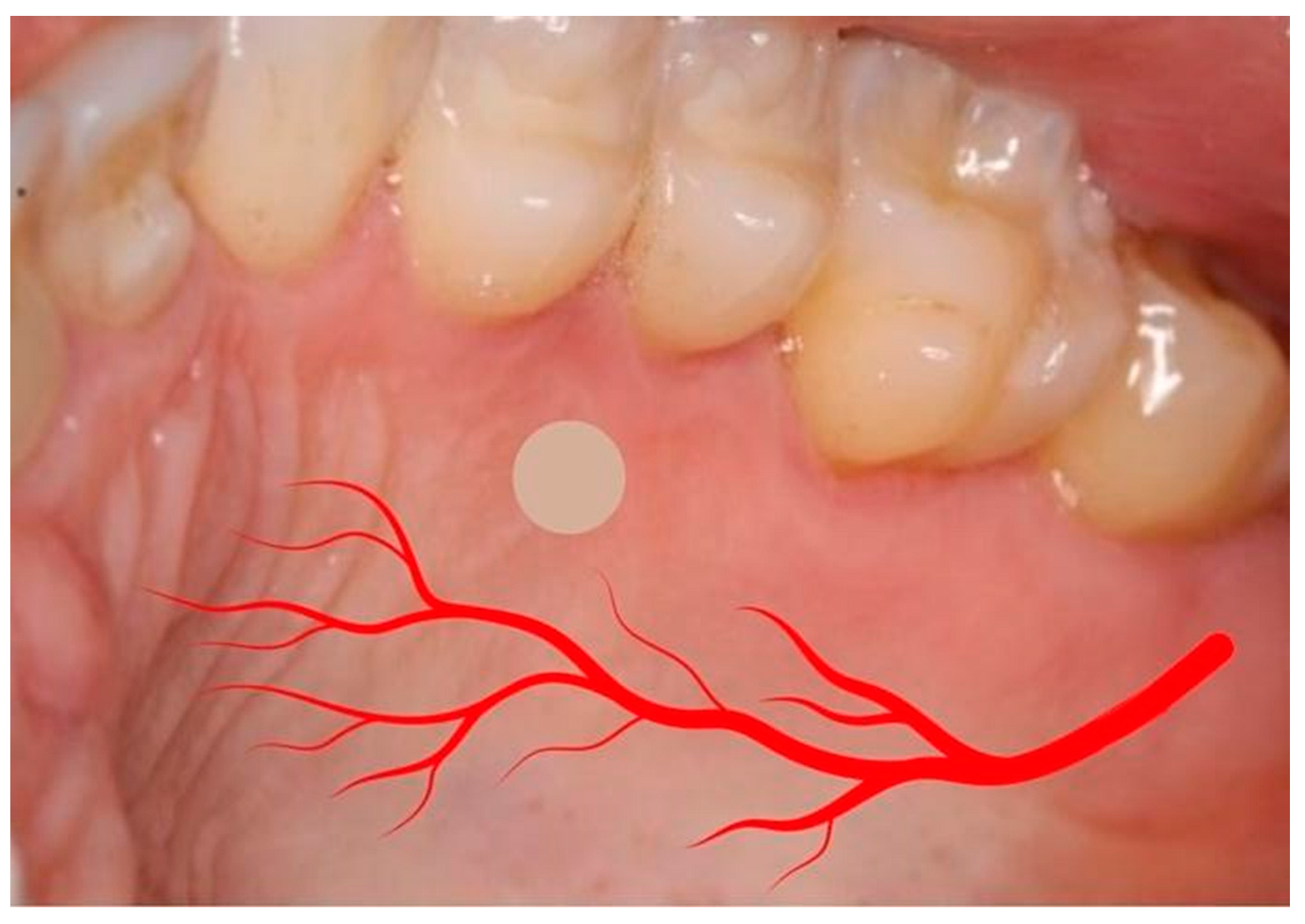
2.2. Surgical Procedure and Pre- and Postoperative Care
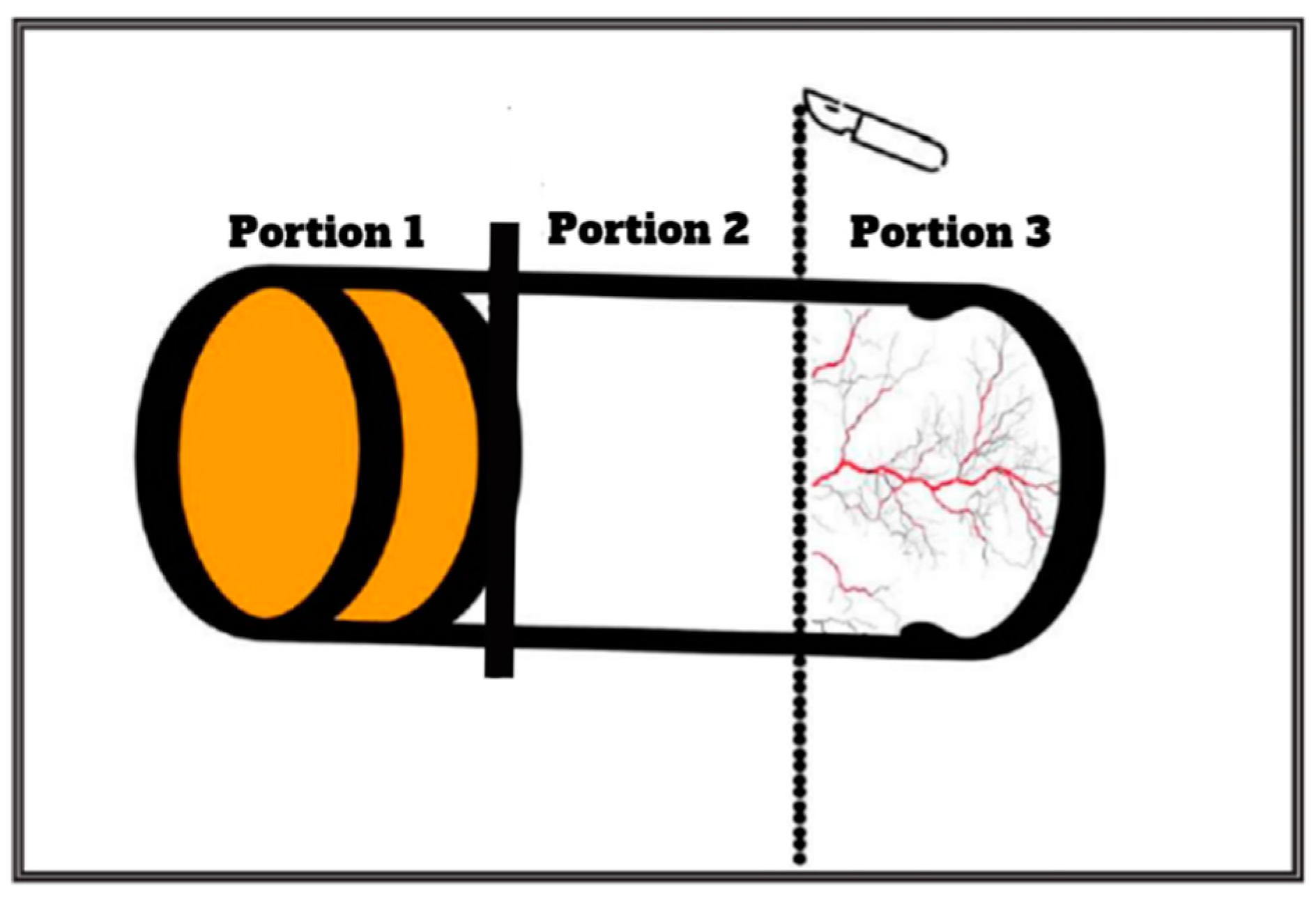
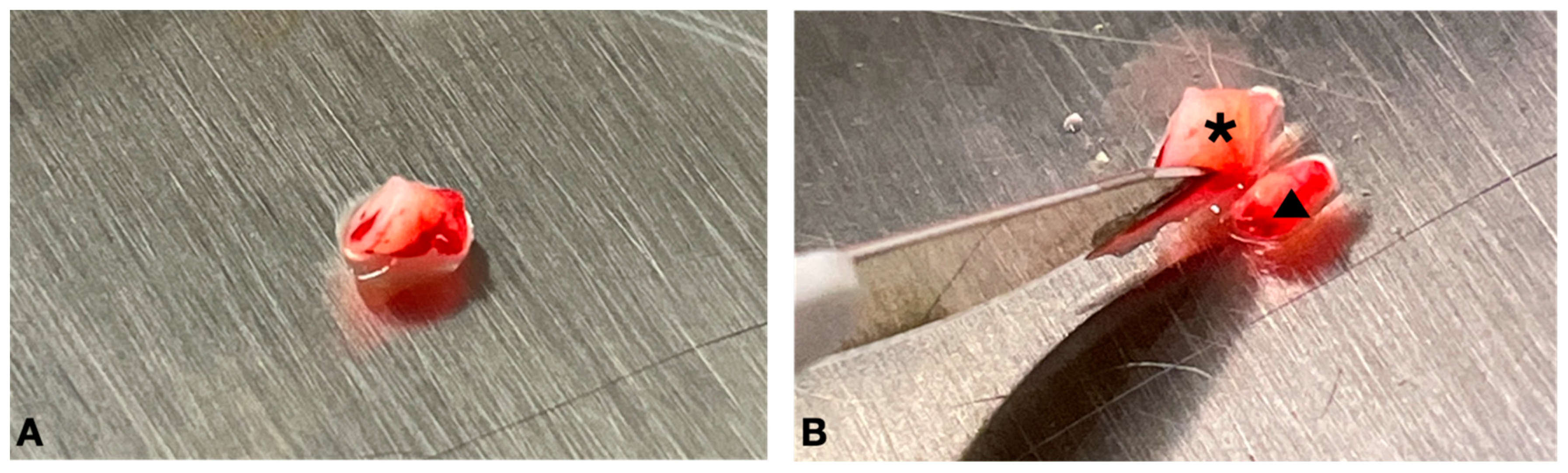
2.3. Tissue Processing and Cell Culture
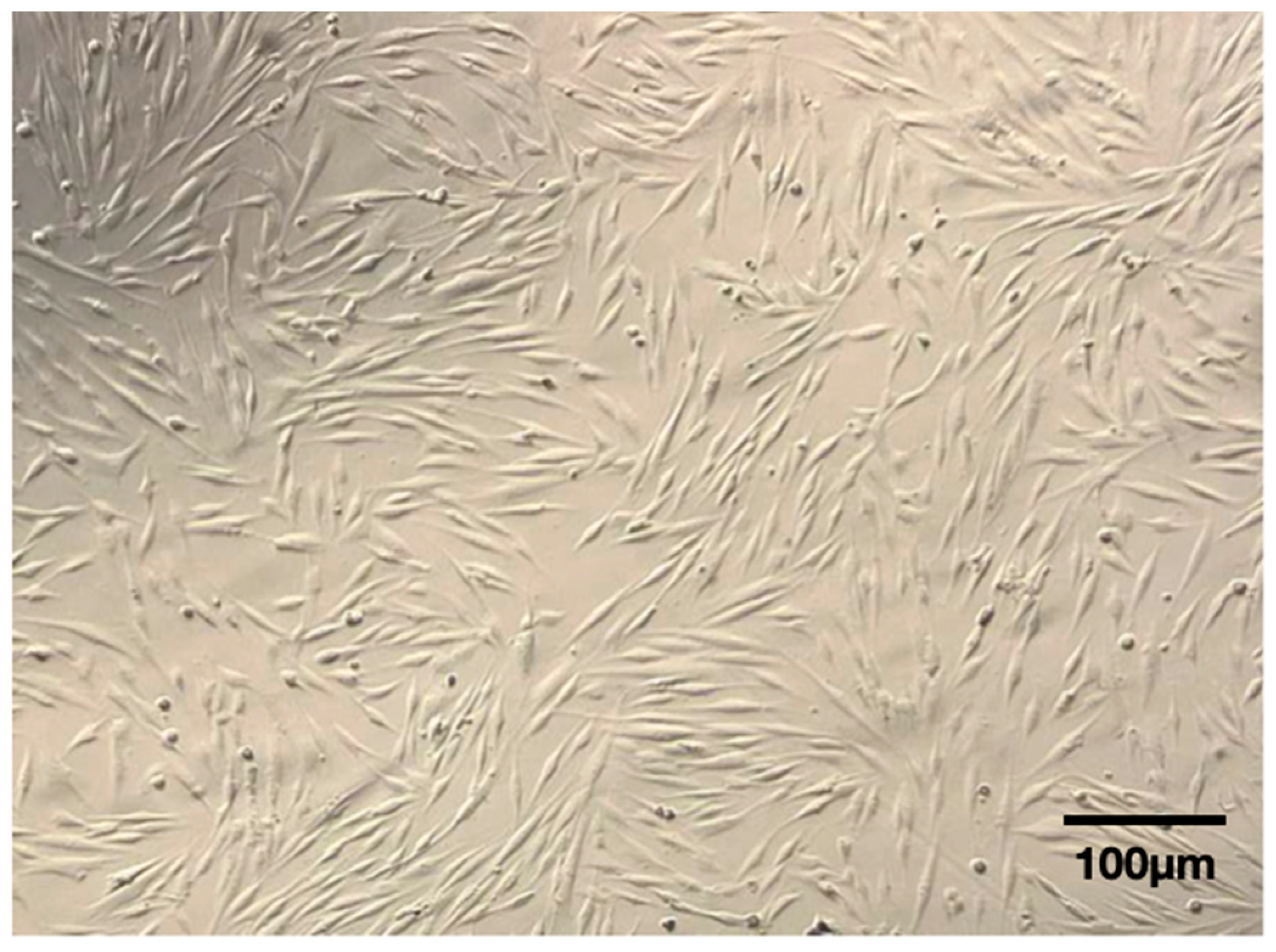
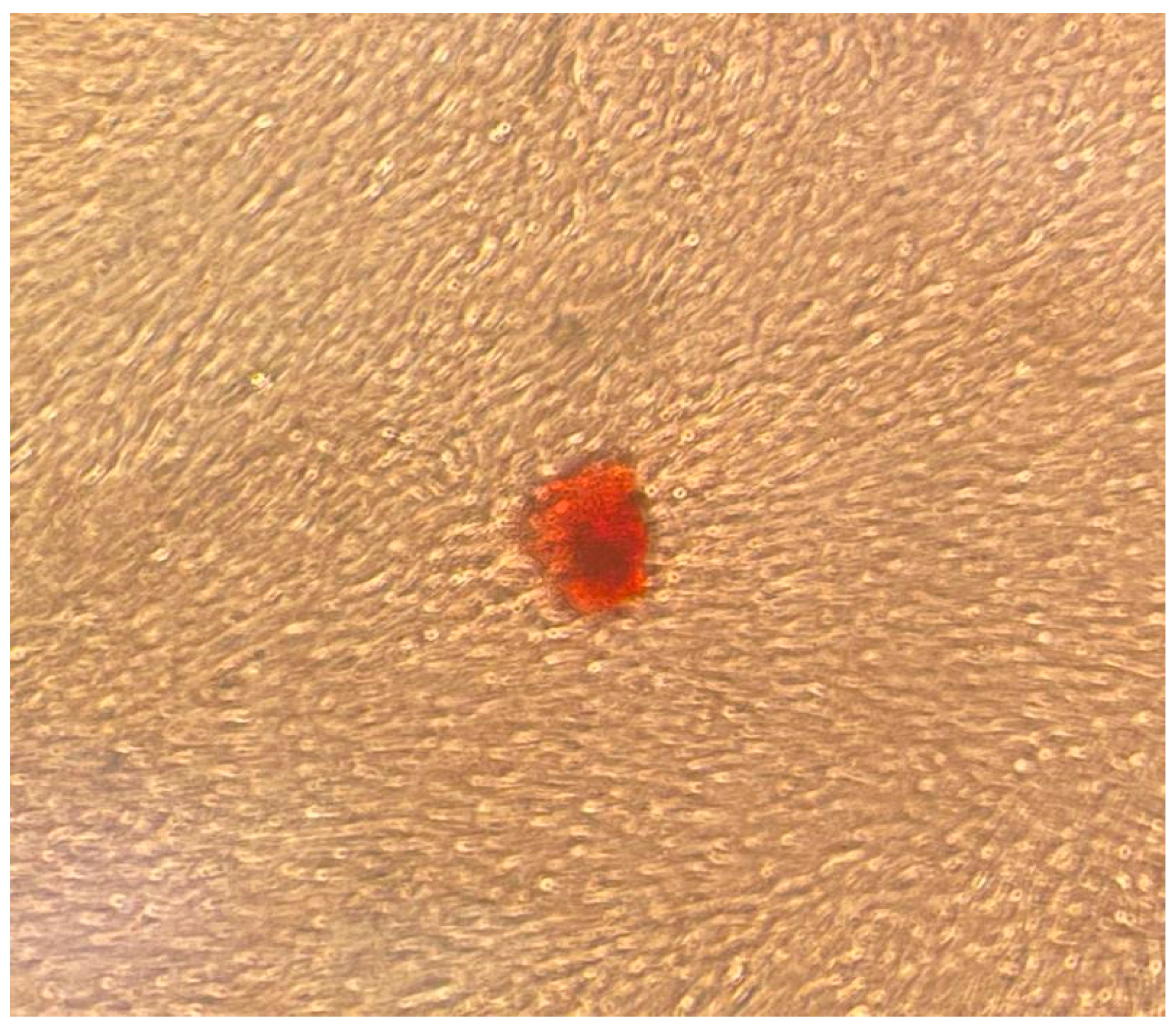
2.4. Adhesion, Morphology, and Viability Assays
2.5. Immunophenotyping
2.6. Osteogenic Differentiation
2.7. Analgesic Intake
3. Results
3.1. Adhesion and Morphology
3.2. Viability Assay and Immunophenotyping
3.3. Osteogenic Differentiation
3.4. Analgesic Intake
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, D.C.; Shyu, W.C.; Lin, S.Z. Mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transpl. 2011, 20, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronthos, S.; Mankani, M.; Brahim, J.; Robey, P.G.; Shi, S. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13625–13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, B.-M.; Miura, M.; Gronthos, S.; Bartold, P.M.; Batouli, S.; Brahim, J.; Young, M.; Robey, P.G.; Wang, C.Y.; Shi, S. Investigation of Multipotent Postnatal Stem Cells from Human Periodontal Ligament. Lancet 2004, 364, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoyama, W.; Liu, Y.; Fang, D.; Yamaza, T.; Seo, B.-M.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Gronthos, S.; Wang, C.-Y.; Shi, S.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Functional Tooth Regeneration in Swine. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsczeck, C.; Götz, W.; Schierholz, J.; Zeilhofer, F.; Kühn, U.; Möhl, C.; Sippel, C.; Hoffmann, K.H. Isolation of Precursor Cells (PCs) from Human Dental Follicle of Wisdom Teeth. Matrix Biol. 2005, 24, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrano, T.I.; Grob, M.S.; Carrión, F.; Nova-Lamperti, E.; Luz, P.A.; Fierro, F.S.; Quintero, A.; Chaparro, A.; Sanz, A. Culture and Characterization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Gingival Tissue. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Benedetto, A.; Brunetti, G.; Posa, F.; Ballini, A.; Grassi, F.R.; Colaianni, G.; Colucci, S.; Rossi, E.; Cavalcanti-Adam, E.A.; Lo Muzio, L.; et al. Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Dental Bud: Role of Integrins and Cadherins. Stem Cell Res. 2015, 15, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrelli, M.; Paduano, F.; Tatullo, M. Cells Isolated from Human Periapical Cysts Express Mesenchymal Stem Cell-like Properties. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naung, N.Y.; Duncan, W.; De Silva, R.; Coates, D. Localization and characterization of human palatal periosteum stem cells in serum-free, xeno-free medium for clinical use. Eur. J. Oral. Sci. 2019, 127, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Hock, J.M.; Burr, D.B. Periosteum: Biology, regulation, and response to osteoporosis therapies. Bone 2004, 35, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lageneste, O.D.; Julien, A.; Abou-Khalil, R.; Frangi, G.; Carvalho, C.; Cagnard, N.; Cordier, C.; Conway, S.J.; Colnot, C. Periosteum contains skeletal stem cells with high bone regenerative potential controlled by Periostin. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Fateh, A.; Salem, D.M.; Intini, G. Periosteum: Biology and application in craniofacial bone regeneration. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Flores, L.; Gutierrez, R.; Lopez-Alonso, A.; Gonzalez, R.; Varela, H. Pericytes as a supplementary source of osteoblasts in periosteal osteogenesis. Clin. Orthop. 1992, 275, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranskunas, M.; Simoliunas, E.; Alksne, M.; Kaupinis, A.; Gintaras, J. Periosteum-derived mesenchymal stem cells secretome—cell-free strategy for endogenous bone regeneration: Proteomic analysis in vitro. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Res. 2021, 12, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Sekiya, I.; Yagishita, K.; Muneta, T. Comparison of human stem cells derived from various mesenchymal tissues: Superiority of synovium as a cell source. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2521–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringe, J.; Leinhase, I.; Stich, S.; Loch, A.; Neumann, K.; Haisch, A.; Häup, T.; Manz, R.; Kaps, C.; Sittinger, M. Human mastoid periosteum-derived stem cells: Promising candidates for skeletal tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2008, 2, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, M.D.; Bonzani, I.C.; Bovis, M.J.; Williams, A.; Stevens, M.M. Human periosteum is a source of cells for orthopaedic tissue engineering: A pilot study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 3085–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Docheva, D.; Knothe, U.R.; Knothe Tate, M.L. Arthritic periosteal tissue from joint replacement surgery: A novel, autologous source of stem cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Graziano, A.; Benedetti, L.; Imbriani, M.; Romano, F.; Ferrarotti, F.; Aimetti, M.; De Angelis, G.M.C. Osteogenic Potential of Human Oral-Periosteal Cells (PCs) Isolated From Different Oral Origin: An In Vitro Study. J. Cell Physiol. 2016, 231, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, M.; Reed, C.R.; Madan, G.; van Aalst, J.A. Osteoinduction in umbilical cord- and palate periosteum-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2010, 64, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Hong, A.; Yen, T.H.; Hong, H.H. Isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Alveolar Periosteum and Effects of Vitamin D on Osteogenic Activity of Periosteum-derived Cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 135, 57166. [Google Scholar]
- Agroya, A.; Khanna, S.S.; Chhabra, P.; Sheth, A.M.; Vattikunta, N.; Kaur, N. Esthetic Root Coverage by Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft with Management of Repeated Rupture of Palatal Arterial Bleeding: A Rare Case Report. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2021, 13 (Suppl. 1), S861–S864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Lorusso, F.; Arcangelo, M.; D’Arcangelo, C.; Celletti, R.; Santos de Oliveira, P. Lateral Sinus Floor Elevation Performed with Trapezoidal and Modified Triangular Flap Designs: A Randomized Pilot Study of Post-Operative Pain Using Thermal Infrared Imaging. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coecke, S.; Balls, M.; Bowe, G.; Davis, J.; Gstraunthaler, G.; Hartung, T.; Hay, R.; Merten, O.W.; Price, A.; Schechtman, L.; et al. Second ECVAM Task Force on Good Cell Culture Practice. Guidance on good cell culture practice. a report of the second ECVAM Task Force Good Cell Cult. Practice. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2005, 33, 261–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho de Faria, A.B.; Chiantia, F.B.; Teixeira, M.L.; Aloise, A.C.; Pelegrine, A.A. Comparative Study Between Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Bone Marrow and from Adipose Tissue, Associated with Xenograft, in Appositional Reconstructions: Histomorphometric Study in Rabbit Calvaria. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, e155–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, W.; Wei, Q.; Wang, H.; He, W.; Wang, B.; et al. Tissue source determines the differentiation potentials of mesenchymal stem cells: A comparative study of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomatto, M.; Gai, C.; Negro, F.; Cedrino, M.; Grange, C.; Ceccotti, E.; Togliatto, G.; Collino, F.; Tapparo, M.; Figliolini, F.; et al. Differential Therapeutic Effect of Extracellular Vesicles Derived by Bone Marrow and Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Wound Healing of Diabetic Ulcers and Correlation to Their Cargoes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeneveldt, L.C.; Herpelinck, T.; Maréchal, M.; Politis, C.; van IJcken, W.F.J.; Huylebroeck, D.; Geris, L.; Mulugeta, E.; Luyten, F.P. The Bone-Forming Properties of Periosteum-Derived Cells Differ Between Harvest Sites. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 554984. [Google Scholar]
- Ho-Shui-Ling, A.; Bolander, J.; Rustom, L.E.; Johnson, A.W.; Luyten, F.P.; Picart, C. Bone regeneration strategies: Engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials 2018, 180, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Xiong, J.; Ji, W. A Systematic Review of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells and Periosteum-Derived Cells for Bone Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2023, 29, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop Dj Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Int. Soc. Cell. Ther. Position Statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar]
- Trovato, L.; Monti, M.; del Fante, C.; Cervio, M.; Lampinen, M.; Ambrosio, L.; Redi, C.A.; Perotti, C.; Kankuri, E.; Ambrosio, G.; et al. A New Medical Device Rigeneracons Allows to Obtain Viable Micro-Grafts From Mechanical Disaggregation of Human Tissues. J. Cell Physiol. 2015, 230, 2299–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, E.; Kim, K.J.; Jun, Y.J.; Rhie, J.W. Cryopreservation of lipoaspirates: In vitro measurement of the viability of adipose-derived stem cell and lipid peroxidation. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narbona-Carceles, J.; Vaquero, J.; Suárez-Sancho, S.; Forriol, F.; Fernández-Santos, M.E. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell aspirates from alternative sources: Is the knee as good as the iliac crest? Injury 2014, 45 (Suppl. 4), S42–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendramini, V.O.; Pouraghaei, S.; Barbosa, R.M.; Aloise, A.C.; Muniz, J.R.F.; Sperandio, M.; Moy, P.K.; Pelegrine, A.A.; Moshaverinia, A. Influence of Dental Pulp Harvesting Method on the Viability and Differentiation Capacity of Adult Dental Pulp-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 9952401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colnot, C. Skeletal cell fate decisions within periosteum and bone marrow during bone regeneration. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 24, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisan, V.; Karabuda, C.Z.; Ozdemir, T. Implant surgery using bone- and mucosa-supported stereolithographic guides in totally edentulous jaws: Surgical and post-operative outcomes of computer-aided vs. standard techniques. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, F.S.; Costa, R.S.A.; Wagner, T.P.; Christofoli, B.R.; Goergen, J.; Izquierdo, C.; Jardim, J.J.; Maltz, M.; Haas, A.N. Incidence and progression of gingival recession over 4 years: A population-based longitudinal study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiser, G.M.; Bruno, J.F.; Mahan, P.E.; Larkin, L.H. The subepithelial connective tissue graft palatal donor site: Anatomic considerations for surgeons. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 1996, 16, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.H.; Hasso, D.G.; Yeh, C.Y.; Leong, D.J.; Chan, H.L.; Wang, H.L. The accuracy of identifying the greater palatine neurovascular bundle: A cadaver study. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, T.; Bosson, J.L.; Isidori, M.; Blanchet, E. Effect of flapless surgery on pain experienced in implant placement using an image-guided system. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2006, 21, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Romandini, M.; Ruales-Carrera, E.; Sadilina, S.; Hammerle, C.H.F.; Sanz, M. Minimal invasiveness at dental implant placement: A systematic review with meta-analyses on flapless fully guided surgery. Periodontol. 2000 2023, 91, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| NUMBER | AGE | GENDER |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 51 | M |
| 2 | 43 | M |
| 3 | 55 | M |
| 4 | 18 | F |
| 5 | 77 | M |
| 6 | 44 | M |
| 7 | 36 | M |
| 8 | 52 | M |
| 9 | 66 | F |
| 10 | 51 | M |
| Mean | 49.30 | - |
| Standard Deviation | 16.03 | - |
| Patient Number | % Viability | % CD 105 | % CD 73 | % CD 90 | % CD 45 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 95 | 68.5 | 100 | 99.8 | 8.6 |
| 2 | 87 | 97.3 | 100 | 100 | 5.9 |
| 3 | 91 | 98.2 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 40.5 |
| 4 | 100 | 99.8 | 100 | 99.7 | 0.3 |
| 5 | 95 | 76.1 | 98.6 | 95.9 | 13.8 |
| 6 | 97 | 92.6 | 100 | 100 | 0.3 |
| 7 | 91 | 97 | 99.9 | 100 | 5.3 |
| 8 | 98 | 92.6 | 100 | 100 | 4.9 |
| 9 | 92 | 98 | 99.9 | 100 | 4.2 |
| 10 | 94 | 72.8 | 100 | 99.5 | 5.8 |
| Mean | 94 | 89.29 | 99.83 | 99.48 | 8.96 |
| Standard Deviation | 3.84 | 9.51 | 0.43 | 1.26 | 11.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelegrine, A.A.; López, D.G.M.; Aloise, A.C.; Zeferino, J.P.G.; Mannina, C.G.; Canal, R.; da Rocha, D.N.; de Castro, T.C.L.; Martinez, E.F.; Holliday, L.S.; et al. A Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedure to Harvest Palate Periosteum as a Source of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12060172
Pelegrine AA, López DGM, Aloise AC, Zeferino JPG, Mannina CG, Canal R, da Rocha DN, de Castro TCL, Martinez EF, Holliday LS, et al. A Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedure to Harvest Palate Periosteum as a Source of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering. Dentistry Journal. 2024; 12(6):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12060172
Chicago/Turabian StylePelegrine, André Antonio, David Gonzalo Montero López, Antonio Carlos Aloise, João Pedro Grandini Zeferino, Carolina Guassi Mannina, Raul Canal, Daniel Navarro da Rocha, Tamara Cristina Lopes de Castro, Elizabeth Ferreira Martinez, Lexie Shannon Holliday, and et al. 2024. "A Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedure to Harvest Palate Periosteum as a Source of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering" Dentistry Journal 12, no. 6: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12060172
APA StylePelegrine, A. A., López, D. G. M., Aloise, A. C., Zeferino, J. P. G., Mannina, C. G., Canal, R., da Rocha, D. N., de Castro, T. C. L., Martinez, E. F., Holliday, L. S., Fanganiello, R. D., & Ferreira, J. R. M. (2024). A Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedure to Harvest Palate Periosteum as a Source of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering. Dentistry Journal, 12(6), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12060172







