Dynamic Implant Surgery—An Accurate Alternative to Stereolithographic Guides—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment: Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
2.5. Definitions of the Outcomes
- -
- Deviation of the implant platform refers to any discrepancy at the most coronal part of the implant (connection) in two spatial dimensions: buccal–lingual and/or mesial–distal direction.
- -
- Apical deviation of the implant refers to any discrepancy at the most apical part of the implant (apex or tip) in two spatial dimensions: buccal–lingual and/or mesial–distal direction.
- -
- Vertical deviation of the implant refers to any apico-coronal discrepancy measured at the most coronal part of the implant (platform). Angular deviation refers to any discrepancy (expressed as degrees) of the whole implant body.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
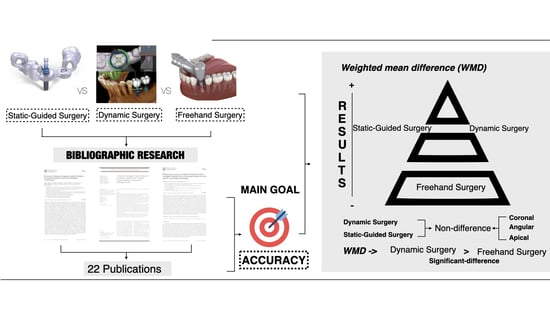
3. Results
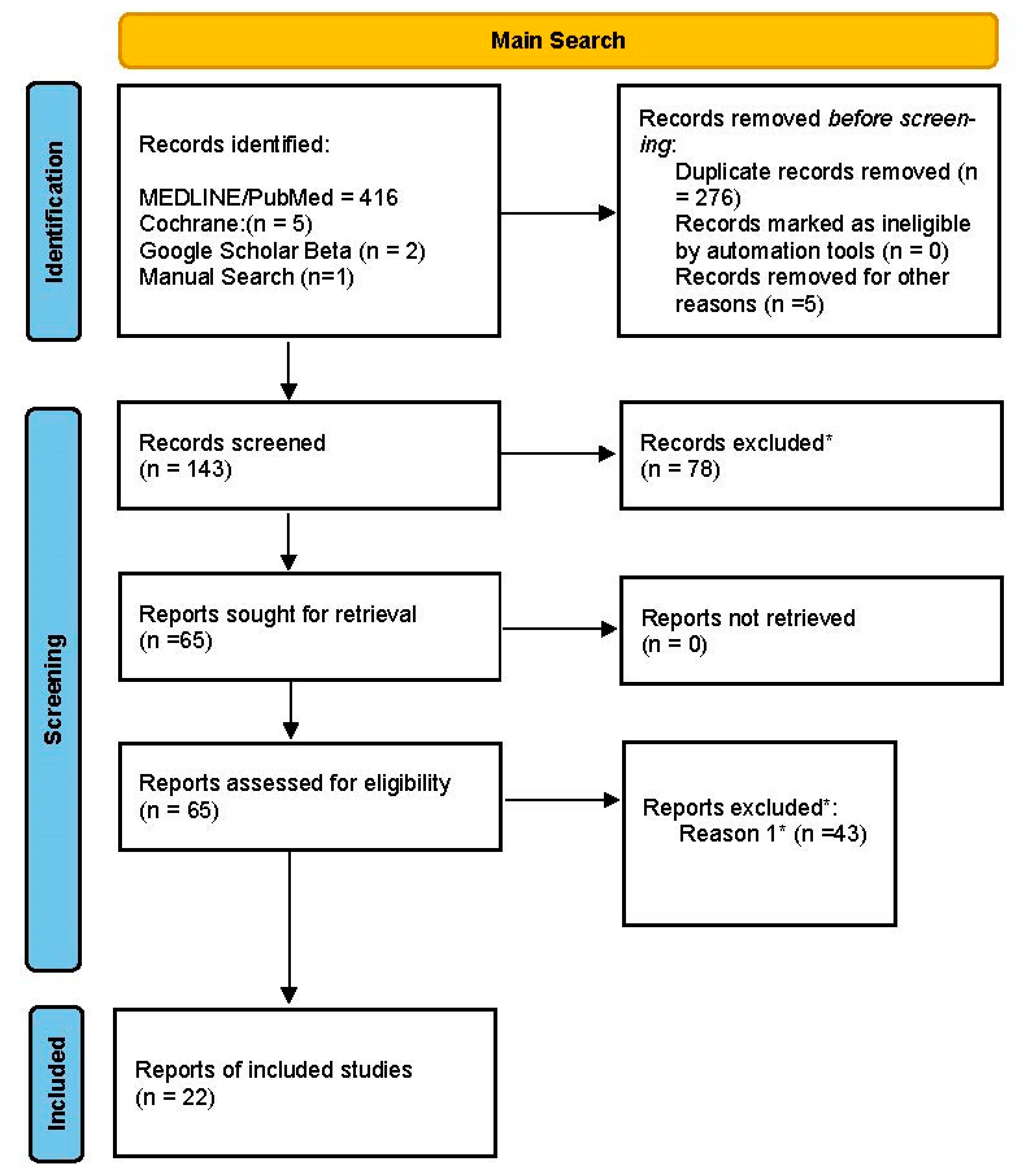
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Qualitative Analyses
3.3. Quantitative Analyses
Platform Deviation
3.4. Angular Deviation
3.5. Apical Deviation
3.6. Apico-Coronal Deviation
3.7. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eliasson, A.; Blomqvist, F.; Wennerberg, A.; Johansson, A. A retrospective analysis of early and delayed loading of full-arch mandibular prostheses using three different implant systems: Clinical results with up to 5 years of loading. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2009, 11, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkfellner, W.; Solar, P.; Gahleitner, A.; Huber, K.; Kainberger, F.; Kettenbach, J.; Homolka, P.; Diemling, M.; Watzek, G.; Bergmann, H. In-vitro assessment of a registration protocol for image guided implant dentistry. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2001, 12, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.R. Hard and soft tissue surgical complications in dental implantology. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 2, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasseh, I.; Al-Rawi, W. Cone beam computed tomography. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 62, 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loubele, M.; Bogaerts, R.; Van Dijck, E.; Pauwels, R.; Vanheusden, S.; Suetens, P.; Marchal, G.; Sanderink, G.; Jacobs, R. Comparison between effective radiation dose of CBCT and MSCT scanners for dentomaxillofacial applications. Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 71, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C. Application of a surgical navigation system in the rehabilitation of maxillary defects using zygoma implants: Report of one case. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2011, 26, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ozan, O.; Turkyilmaz, I.; Yilmaz, B. A preliminary report of patients treated with early loaded implants using computerized tomography-guided surgical stents: Flapless versus conventional flapped surgery. J. Oral Rehabil. 2007, 34, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultin, M.; Svensson, K.G.; Trulsson, M. Clinical advantages of computer-guided implant placement: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, N.; Serrano, C.; van den Brink, H.; Pineau, J.; Prognon, P.; Borget, I.; El Batti, S. Advantages and disadvantages of 3-dimensional printing in surgery: A systematic review. Surgery 2016, 159, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Lee, J.; Lim, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M. Verification of the usability of a navigation method in dental implant surgery: In vitro comparison with the stereolithographic surgical guide template method. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo-Albiol, J.; Barootchi, S.; Salomó-Coll, O.; Wang, H. Advantages and disadvantages of implant navigation surgery. A systematic review. Ann. Anat. 2019, 225, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’haese, J.; Ackhurst, J.; Wismeijer, D.; De Bruyn, H.; Tahmaseb, A. Current state of the art of computer-guided implant surgery. Periodontology 2000 2017, 73, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercruyssen, M.; Laleman, I.; Jacobs, R.; Quirynen, M. Computer-supported implant planning and guided surgery: A narrative review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, A.L.; Mandelaris, G.A.; Tardieu, P.B. Prosthetically directed implant placement using computer software to ensure precise placement and predictable prosthetic outcomes. part 1: Diagnostics, imaging, and collaborative accountability. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2006, 26, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Voulgarakis, A.; Strub, J.R.; Att, W. Outcomes of implants placed with three different flapless surgical procedures: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittwer, G.; Adeyemo, W.L.; Schicho, K.; Figi, M.; Enislidis, G. Navigated flapless transmucosal implant placement in the mandible: A pilot study in 20 patients. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2007, 22, 801–807. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, W.; Luk, W.; Cheung, L. Three-dimensional accuracy of implant placement in a computer-assisted navigation system. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2006, 21, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, K.; White, G.S.; Morea, D.N.; Wright, R.F. Use of stereolithographic templates for surgical and prosthodontic implant planning and placement. part I. the concept. J. Prosthodont. 2006, 15, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casap, N.; Wexler, A.; Eliashar, R. Computerized navigation for surgery of the lower jaw: Comparison of 2 navigation systems. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, K.; White, G.S.; Morea, D.N.; Wright, R.F. Use of stereolithographic templates for surgical and prosthodontic implant planning and placement. part II. A clinical report. J. Prosthodont. 2006, 5, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.S.; Emery, R.W.; Cullum, D.R.; Sheikh, A. Implant placement is more accurate using dynamic navigation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Lan, T.; Pan, C.; Lee, H. Dental implant navigation system guide the surgery future. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, G.; Stoffner, R.; Keiler, M.; Zangerl, A.; Widmann, R.; Puelacher, W.; Bale, R. A laboratory training and evaluation technique for computer-aided oral implant surgery. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2009, 5, 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanelli, L.V.; DeGroot, B.S.; Lipton, D.I.; Mandelaris, G.A. Accuracy of a dynamic dental implant navigation system in a private practice. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 5.1; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses; Ottawa Hospital Research Institute: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, D.; Marquardt, P.; Zwahlen, M.; Jung, R.E. A systematic review on the accuracy and the clinical outcome of computer-guided template-based implant dentistry. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.; Sancho-Puchades, M.; Mir-Marí, J.; Mühlemann, S.; Jung, R.; Hämmerle, C. A randomized controlled clinical trial comparing conventional and computer-assisted implant planning and placement in partially edentulous patients. part 4: Accuracy of implant placement. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2019, 39, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasak, C.; Watzak, G.; Gahleitner, A.; Strbac, G.; Schemper, M.; Zechner, W. Computed tomography-based evaluation of template (NobelGuide™)-guided implant positions: A prospective radiological study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naziri, E.; Schramm, A.; Wilde, F. Accuracy of computer-assisted implant placement with insertion templates. GMS Interdiscip. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. DGPW 2016, 13, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Schnutenhaus, S.; Edelmann, C.; Rudolph, H.; Luthardt, R.G. Retrospective study to determine the accuracy of template-guided implant placement using a novel nonradiologic evaluation method. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 121, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Lee, H.; Lan, T. Comparing accuracy of implant installation with a navigation system (NS), a laboratory guide (LG), NS with LG, and freehand drilling. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, N.E.; Kennedy, K.; McGlumphy, E.A.; Clelland, N.L. Split-mouth comparison of the accuracy of computer-generated and conventional surgical guides. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2013, 28, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydemir, C.A.; Arısan, V. Accuracy of dental implant placement via dynamic navigation or the freehand method: A split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2020, 31, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanelli, L.V.; Mandelaris, G.A.; Franchina, A.; Pranno, N.; Pagliarulo, M.; Cera, F.; Maltese, F.; De Angelis, F.; Di Carlo, S. Accuracy of dynamic navigation system workflow for implant supported full arch prosthesis: A case series. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; An, S.; Hong, M.; Jeon, K.; Lee, K. Accuracy of a direct drill-guiding system with minimal tolerance of surgical instruments used for implant surgery: A prospective clinical study. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2016, 8, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, A.E.; Turkyilmaz, I.; Ozan, O.; McGlumphy, E.A. Reliability of implant placement with stereolithographic surgical guides generated from computed tomography: Clinical data from 94 implants. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, F.; Eghbali, A.; De Bruyckere, T.; Cleymaet, R.; Cosyn, J. A randomized controlled trial on the efficiency of free-handed, pilot-drill guided and fully guided implant surgery in partially edentulous patients. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewsiri, D.; Panmekiate, S.; Subbalekha, K.; Mattheos, N.; Pimkhaokham, A. The accuracy of static vs. dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery in single tooth space: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrin, G.L.; Rafael, S.N.; Passoni, B.B.; Magini, R.S.; Benfatti, C.A.; Gruber, R.; Peruzzo, D.C. Clinical and tomographic comparison of dental implants placed by guided virtual surgery versus conventional technique: A split-mouth randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, G.; Taraschi, V.; Vercellotti, T.; Ben-Nissan, B.; Marchetti, C. Three-dimensional implant positioning with a piezosurgery implant site preparation technique and an intraoral surgical navigation system: Case report. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2017, 32, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smitkarn, P.; Subbalekha, K.; Mattheos, N.; Pimkhaokham, A. The accuracy of single-tooth implants placed using fully digital-guided surgery and freehand implant surgery. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, Y. Accuracy of dynamic navigation compared to static surgical guide for dental implant placement. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2020, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimarj, P.; Subbalekha, K.; Dhanesuan, K.; Siriwatana, K.; Mattheos, N.; Pimkhaokham, A. Comparison of the accuracy of implant position for two-implants supported fixed dental prosthesis using static and dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Zhao, J.; Fan, L.; Qiu, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Kim, Y. Accuracy evaluation of computer-designed surgical guide template in oral implantology. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 2189–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elian, N.; Jalbout, Z.N.; Classi, A.J.; Wexler, A.; Sarment, D.; Tarnow, D.P. Precision of flapless implant placement using real-time surgical navigation: A case series. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2008, 23, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Ozan, O.; Turkyilmaz, I.; Ersoy, A.E.; McGlumphy, E.A.; Rosenstiel, S.F. Clinical accuracy of 3 different types of computed tomography-derived stereolithographic surgical guides in implant placement. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Assche, N.; Van Steenberghe, D.; Quirynen, M.; Jacobs, R. Accuracy assessment of computer-assisted flapless implant placement in partial edentulism. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2010, 37, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzer, S.; Bertha, G.; Heschl, A.; Wegscheider, W.A.; Lorenzoni, M. Three-dimensional accuracy of guided implant placement: Indirect assessment of clinical outcomes. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, L.V.; Mandelaris, G.A.; DeGroot, B.S.; Gambarini, G.; De Angelis, F.; Di Carlo, S. Accuracy of a novel trace-registration method for dynamic navigation surgery. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2020, 40, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanelli, L.V.; Mandelaris, G.A.; Franchina, A.; Di Nardo, D.; Galli, M.; Pagliarulo, M.; Testarelli, L.; Di Carlo, S.; Gambarini, G. Accuracy evaluation of 14 maxillary full arch implant treatments performed with da vinci bridge: A case series. Materials 2020, 22, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürhauser, R.; Mailath-Pokorny, G.; Haas, R.; Busenlechner, D.; Watzek, G.; Pommer, B. Esthetics of flapless single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla using guided surgery: Association of three-dimensional accuracy and pink esthetic score. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, e427–e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, A.; Wanschitz, F.; Birkfellner, W.; Zauza, K.; Klug, C.; Schicho, K.; Kainberger, F.; Czerny, C.; Bergmann, H.; Ewers, R. Computer-aided placement of endosseous oral implants in patients after ablative tumour surgery: Assessment of accuracy. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2003, 14, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.S.; Emery, R.W.; Lank, K.; Ryan, J. Implant placement accuracy using dynamic navigation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2017, 32, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittwer, G.; Adeyemo, W.L.; Schicho, K.; Gigovic, N.; Turhani, D.; Enislidis, G. Computer-guided flapless transmucosal implant placement in the mandible: A new combination of two innovative techniques. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somogyi-Ganss, E.; Holmes, H.I.; Jokstad, A. Accuracy of a novel prototype dynamic computer-assisted surgery system. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, G.; Keiler, M.; Zangerl, A.; Stoffner, R.; Longato, S.; Bale, R.; Puelacher, W. Computer-assisted surgery in the edentulous jaw based on 3 fixed intraoral reference points. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppin, J.; Popovic, A.; Strauss, M.; Spüntrup, E.; Steiner, A.; Stoll, C. Evaluation of the accuracy of three different computer-aided surgery systems in dental implantology: Optical tracking vs. stereolithographic splint systems. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, R.W.; Merritt, S.A.; Lank, K.; Gibbs, J.D. Accuracy of dynamic navigation for dental implant placement–model-based evaluation. J. Oral Implantol. 2016, 42, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Westendorff, C.; Gomez-Roman, G.; Reinert, S. Accuracy of navigation-guided socket drilling before implant installation compared to the conventional free-hand method in a synthetic edentulous lower jaw model. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, G.; Bale, R.J. Accuracy in computer-aided implant surgery—A review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2006, 21, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marques-Guasch, J.; Rodriguez-Bauzá, R.; Satorres-Nieto, M.; Wang, H.; Hernández-Alfaro, F.; Gargallo-Albiol, J. Accuracy of dynamic implant navigation surgery performed by a novice operator. A preliminary study in a cadaveric model. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2022, 25, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tahmaseb, A.; Wismeijer, D.; Coucke, W.; Derksen, W. Computer technology applications in surgical implant dentistry: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2014, 29, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, R.E.; Schneider, D.; Ganeles, J.; Wismeijer, D.; Zwahlen, M.; Hämmerle, C.H.; Tahmaseb, A. Computer technology applications in surgical implant dentistry: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2009, 24, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]




| Author (Year) | Study Design | Groups Analyzed | No. of Patients | No. of Implants | Location | Flap/Flapless | Dynamic Guided Navigation System | Surgical Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dechawat Kaewsiri et al. [42] (2019) | RCT | DGS vs. SGS | 30 | 30 | Max and mand | Flap and flapless | Iris-100 software (EPED Inc., Taiwan) | NR |
| Paweena Yimarj et al. [47] (2020) | RCT | DGS vs. SGS | 30 | 60 | NS | NS | Iris-100 software (EPED Inc., Taiwan) | NR |
| Aktolun Aydemir et al. [37] (2020) | RCT | DGS vs. FH | 32 | 86 | Max | Flap | Navident (ClaroNav Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada) | Not satisfactory stability of the radiopaque stent in 2 patients |
| Palita Smitkarn et al. [45] (2019) | RCT | SGS vs. FH | 52 | 60 | Max and mand | Flap | CoDiagnostics | |
| Faris Younes et al. [41] (2018) | RCT | SGS vs. FH | 33 | 71 | Max | Flap and flapless | Simplant | NR |
| Pei Shen et al. [48] (2015) | RCT | SGS vs. FH | 60 | 109 | NS | Flapless | Simplant | NR |
| Farley et al. [36] (2013) | RCT | SGS vs. FH | 10 | 20 | Max and mand | Flap | Implant master software (iDent Imaging) | NR |
| Magrin et al. [43] (2019) | RCT | SGS vs. FH | 16 | 24 | Mand | Flap and flapless | DentalSlice, Bioparts | 4 implants lacked osseointegration |
| Pellegrino et al. [44] (2017) | CS (prosp) | DGS | 5 | 5 | Max and mand | Flap and flapless | Navident (ClaroNav Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada) | NR |
| Elian et al. [49] (2008) | CS (prosp) | DGS | 6 | 14 | Max and Mand | Flapless | Software DenX Advanced Dental Systems, (Moshav Ora, Israel). | NR |
| Block et al. [21] | CS (prosp) | DGS vs. FH | 478 | 714 | Max and mand | NS | X-Guide, X-Nav Technologies | NR |
| Ting-Mao Sun et al. [35] (2020) | CS (prosp) | DGS vs. FH | NS | 96 | Max and mand | Flapless | AQNavi, (TITC Ltd., Kaohsiung, Taiwan) | NR |
| Stefanelli et al. [38] (2020) | CS (prosp) | DGS | 13 | 77 | Max and mand | NS | Navident (ClaroNav Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada) | 4 implants lost through lack of osseointegration. |
| Du-Hyeong Lee et al. [39] (2016) | CS (prosp) | SGS | 11 | 21 | Max and mand | Flapless | R2GATE 1.0; MegaGen Implant, Gyeongbuk, Korea | NR |
| Oguz Ozan et al. [50] (2009) | CS (prosp) | SGS | 30 | 30 | NR | Flapless | Stent Cad; Media Lab Software, La Spezia, Italy | NR |
| Van Assche et al. [51] (2010) | CS (prosp) | SGS | 8 | 21 | Max and mand | Flapless | Procera (Nobel Biocare AB, Göteburg, Sweden) | NR |
| Platzer et al. [52] (2011) | CS (prosp) | SGS | 5 | 15 | Mand | Flapless | Simplant Materialise Dental, Leuven, Belgium | NR |
| Ahmet Ersan Ersoy et al. [40] (2008) | CS (prosp) | SGS | 14 | 29 | Max and mand | Flap and flapless | Stent Cad, Media Lab Software, La Spezia, Italy | NR |
| Dong Wu et al. [46] (2020) | CS (retrosp) | DGS vs. SGS | 54 | 95 | NR | Flap | DHC-DI3E, Suzhou Digital-health Care Co., Ltd., China | NR |
| Stefanelli et al. [53] | CS (retrosp) | DGS | 59 | 136 | Max and mand | NS | Navident (ClaroNav Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada) | NR |
| Stefanelli et al. [54] | CS (retrosp) | DGS | 14 | 56 | Max | NS | Navident (ClaroNav Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada) | |
| Fürhauser et al. [55] | CS (retrosp) | SGS | 27 | 27 | Max | Flapless | NobelClinician (Nobel Biocare, Gothenburg, Sweden) | NR |
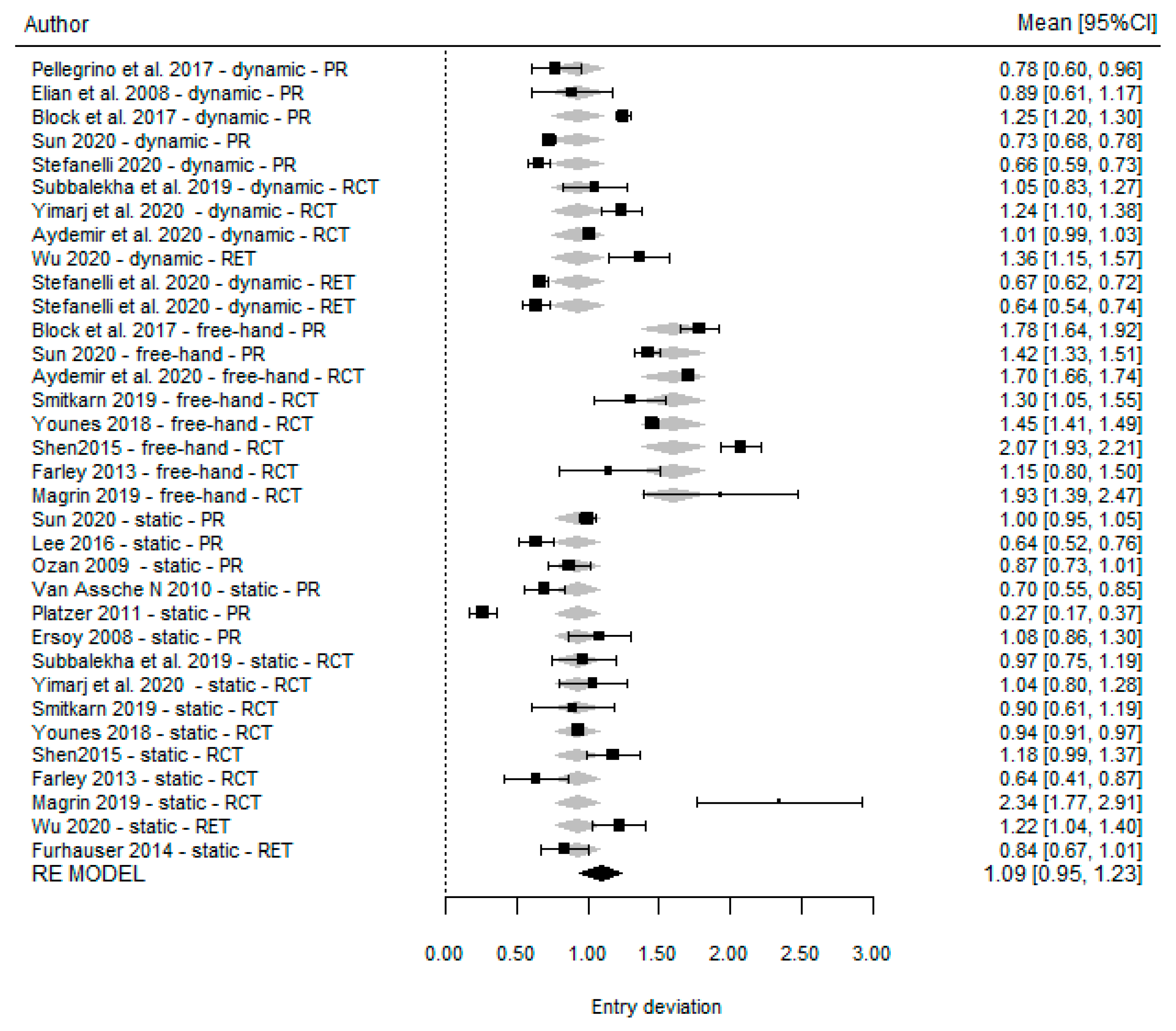
| Dynamic Guided | Static Guided | Freehand | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Platform Deviation (SD) | Angular Deviation (SD) | Apical Deviation (SD) | Vertical Deviation (SD) | Platform Deviation (SD) | Angular Deviation (SD) | Apical Deviation (SD) | Vertical Deviation (SD) | Platform Deviation (SD) | Angular Deviation (SD) | Apical Deviation (SD) | Vertical Deviation (SD) |
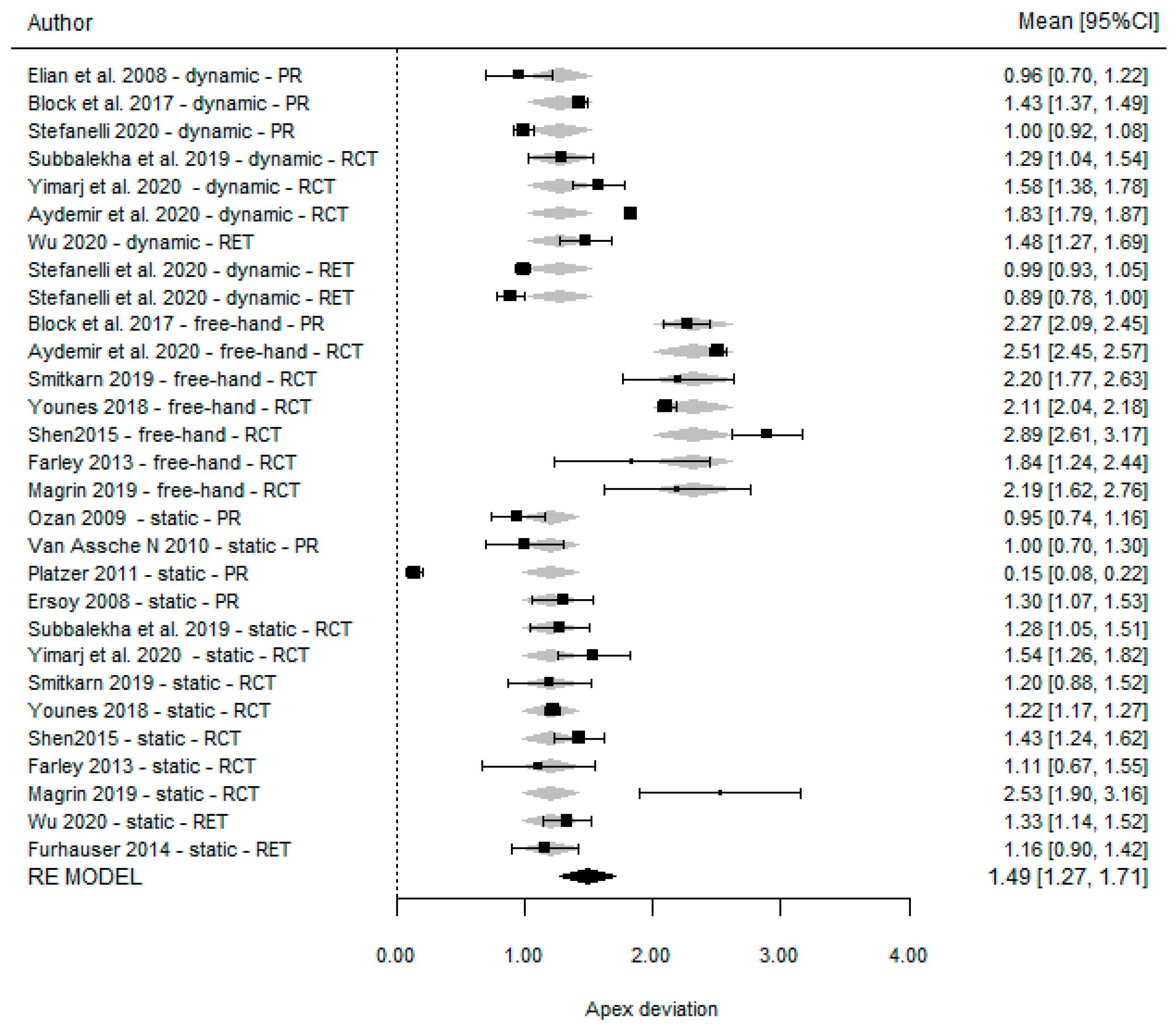
| Dechawat Kaewsiri et al. [42] (2019) | 1.05 (0.44) | 3.06 (1.37) | 1.29 (0.50) | NA | 0.97 (0.44) | 2.84 (1.71) | 1.28 (0.46) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Paweena Yimarj et al. [47] (2020) | 1.24 (0.39) | 3.78 (1.84) | 1.58 (0.56) | NA | 1.04 (0.67) | 4.08 (1.69) | 1.54 (0.79) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Aktolun Aydemir et al. [37] (2020) | 1.01 (0.07) | 5.59 (0.39) | 1.83 (0.12) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.70 (0.13) | 10.04 (0.83) | 2.51 (0.21) | NA |
| Palita Smitkarn et al. [45] (2019) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.9 (0.8) | 2.8 (2.6) | 1.2 (0.9) | NA | 1.3 (0.7) | 7.0 (7.0) | 2.2 (1.2) | NA |
| Faris Younes et al. [41] (2018) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.94 (0.1) | 4.25 (0.89) | 1.22 (0.18) | NA | 1.45 (0.1) | 6.99 (0.87) | 2.11 (0.18) | NA |
| Pei Shen et al. [48] (2015) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.18 (0.72) | 4.21 (1.91) | 1.43 (0.74) | 0.54 (0.29) | 2.07 (0.51) | 8.84 (4.64) | 2.89 (1.02) | 0.78 (0.33) |
| Farley et al. [36] (2013) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.64 (0.37) | 4.26 (NA) | 1.11 (0.71) | (−) 1.20 (0.70) | 1.15 (0.57) | 7.14 (NA) | 1.84 (0.97) | (−) 1.51 (1.02) |
| Magrin et al. [43] (2019) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2.34 (1.01) | 2.2 (1.1) | 2.53 (1.11) | NA | 1.93 (0.95) | 3.5 (1.6) | 2.19 (1.00) | NA |
| Pellegrino et al. [44] (2017) | 0.78 (0.20) | NA | 1.04 (0.29) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Elian et al. [49] (2008) | 0.89 (0.53) | 3.78 (2.76) | 0.96 (0.50) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Block et al. [21] (2017) | 1.25 (0.65) | 3.26 (2.24) | 1.43 (0.73) | 0.84 (0.68) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.78 (0.77) | 6.50 (4.21) | 2.27 (1.02) | 1.12 (0.83) |
| Ting-Mao Sun et al. [35] (2020) | 0.73 (0.13) | 3.24 (0.36) | NA | NA | 1.00 (0.15) | 4.54 (0.29) | NA | NA | 1.42 (0.25) | 6.12 (0.12) | NA | NA |
| Stefanelli et al. [38] (2020) | 0.66 (0.32) | 2.7 (0.99) | 1 (0.35) | 0.57 (0.29) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Du-Hyeong Lee et al. [39] (2016) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.64 (0.29) | 2.21 (1.04) | NA | 0.93 (0.38) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Oguz Ozan et al. [50] (2009) | NA | NA | NA | NA | O.87 (0.4) | 2.91 (1.3) | 0.95 (0.6) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Van Assche et al. [51] (2010) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.7 (0.34) | 2.7 (1.9) | 1.0 (0.7) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Platzer et al. [52] (2011) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.27 (0.19) | 14 (11.6) | 0.15 (0.13) | 0.28 (0.19) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Ahmet Ersan Ersoy et al. [40] (2008) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.08 (0.6) | 4.45 (1.64) | 1.3 (0.64) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Dong Wu et al. [43] (2020) | 1.36 (0.65) | 3.71 (1.32) | 1.48 (0.65) | NA | 1.22 (0.70) | 4.34 (2.22) | 1.33 (0.73) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Luigi V. Stefanelli et al. [53] (2020) | 0.67 (0.29) | 2.5 (1.04) | 0.99 (0.33) | 0.55 (0.25) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Stefanelli et al. [54] (2020) | 0.64 (0.37) | 2.49 (1.14) | 0.89 (0.42) | 0.46 (0.26) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Fürhauser et al. [55] (2014) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.84 (0.44) | 2.7 (2.6) | 1.16 (0.69) | 0.52 (0.39) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Study | Mean (SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic | Static | Mean Difference, % (CI) | |
| DGS vs. SGS | |||
| Ting-Mao Sun et al. [35] (2020) | 0.73 (0.13) | 1.00 (0.15) | −0.27 (−0.34, −0.20) |
| Dechawat Kaewsiri et al. [42] (2019) | 1.05 (0.44) | 0.97 (0.44) | 0.08 (−0.23, 0.39) |
| Paweena Yimarj et al. [47] (2020) | 1.24 (0.39) | 1.04 (0.67) | 0.20 (−0.08, 0.48) |
| Dong Wu et al. [46] (2020) | 1.36 (0.65) | 1.22 (0.70) | 0.14 (−0.14, 0.42) |
| Model for all studies | 0.02 (−0.27, 0.31) | ||
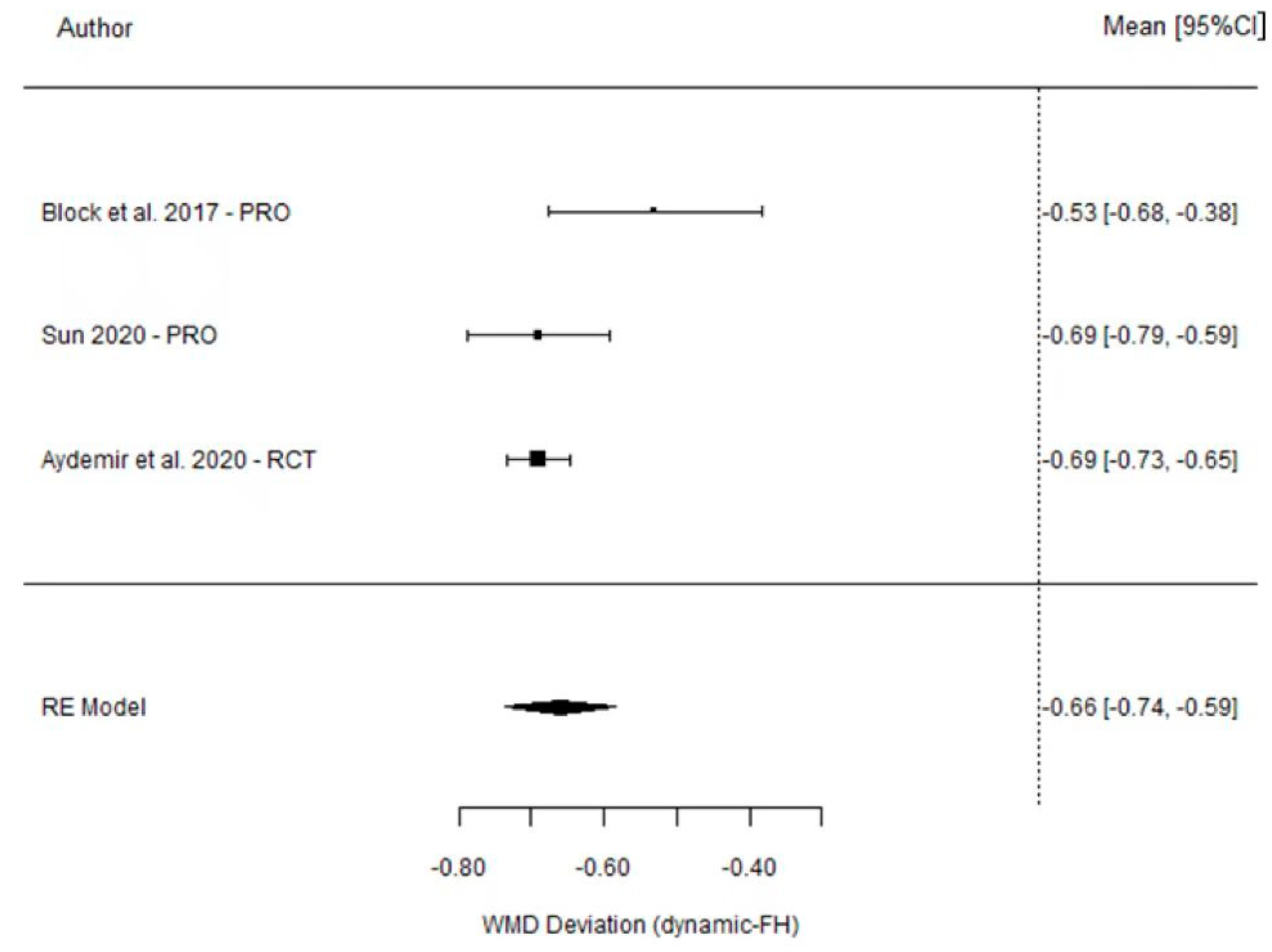
| DGS vs. freehand | Dynamic | Freehand | |
| Block et al. [21] (2017) | 1.25 (0.65) | 1.78 (0.77) | −0.53 (−0.68, −0.38) |
| Ting-Mao Sun et al. [35] (2020) | 0.73 (0.13) | 1.42 (0.25) | −0.69 (−0.79, −0.59) |
| Aktolun Aydemir et al. [37] (2020) | 1.01 (0.07) | 1.70 (0.13) | −0.69 (−0.73, −0.65) |
| Model for all studies | −0.66 (−0.74, −0.59) | ||
| Study | Mean (SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic | Static | Mean Difference, % (CI) | |
| DGS vs. SGS | |||
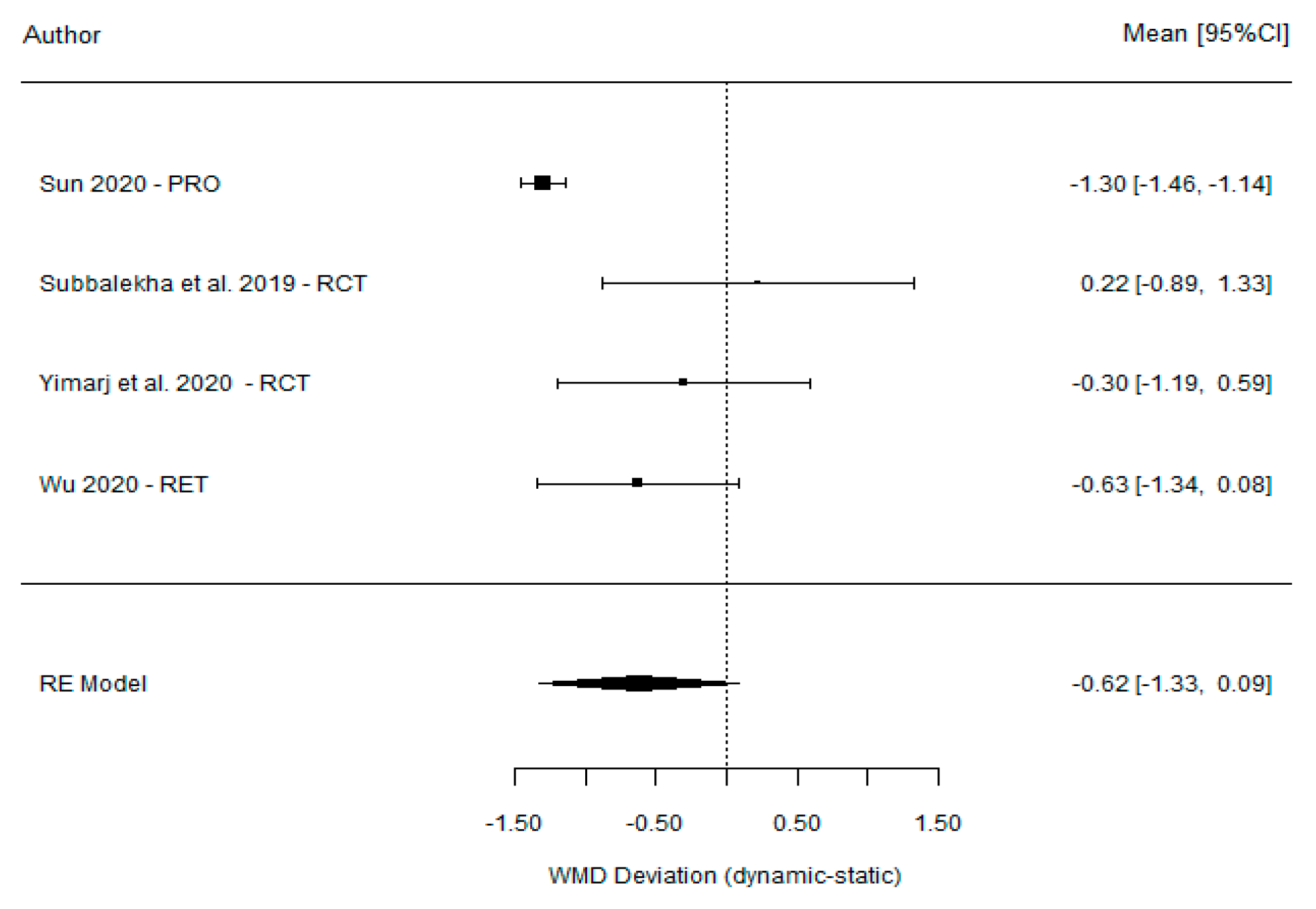
| Ting-Mao Sun et al. [35] (2020) | 3.24 (0.36) | 4.54 (0.29) | −1.30 (−1.46, −1.14) |
| Dechawat Kaewsiri et al. [42] (2019) | 3.06 (1.37) | 2.84 (1.71) | 0.22 (−0.89, 1.33) |
| Paweena Yimarj et al. [47] (2020) | 3.78 (1.84) | 4.08 (1.69) | −0.30 (−1.19, 0.59) |
| Dong Wu et al. [46] (2020) | 3.71 (1.32) | 4.34 (2.22) | −0.63 (−1.34, 0.08) |
| Model for all studies | −0.62 (−1.33, 0.09) | ||
| DGS vs. freehand | Dynamic | Freehand | |
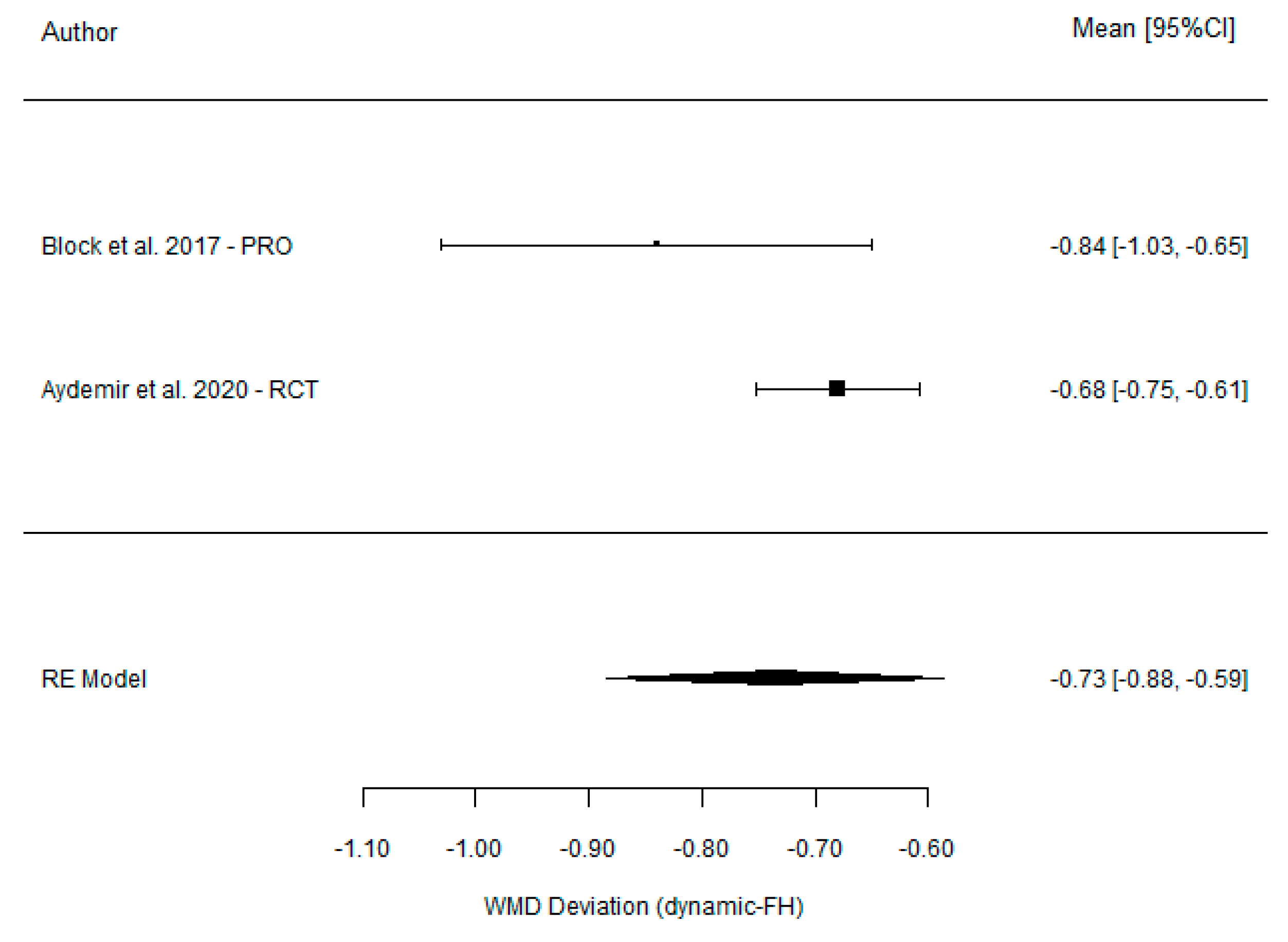
| Block et al. [21] (2017) | 3.26 (2.24) | 6.5 (4.21) | −3.24 (−4.01, −2.47) |
| Ting-Mao Sun et al. [35] (2020) | 3.24 (0.36) | 6.12 (0.12) | −2.88 (−3.01, −2.75) |
| Aktolun Aydemir et al. [37] (2020) | 5.59 (0.39) | 10.04 (0.83) | −4.41 (−4.68, −4.14) |
| Model for all studies | −3.52 (−4.69, −2.35) | ||
| Study | Mean (SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic | Static | Mean Difference, % (CI) | |
| DGS vs. SGS | |||
| Dechawat Kaewsiri et al. [42] (2019) | 1.29 (0.50) | 1.28 (0.46) | 0.01 (−0.33, 0.35) |
| Paweena Yimarj et al. [47] (2020) | 1.58 (0.56) | 1.54 (0.79) | 0.04 (−0.31, 0.39) |
| Dong Wu et al. [46] (2020) | 1.48 (0.65) | 1.33 (0.73) | 0.15 (−0.13, 0.43) |
| Model for all studies | 0.08 (−0.11, 0.26) | ||
| DGS vs. freehand | Dynamic | Freehand | |
| Block et al. [21] (2017) | 1.43 (0.73) | 2.27 (1.02) | −0.84 (−1.03, −0.65) |
| Aktolun Aydemir et al. [37] (2020) | 1.83 (0.12) | 2.51 (0.21) | −0.68 (−0.75, −0.61) |
| Model for all studies | −0.73 (−0.88, −0.59) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques-Guasch, J.; Bofarull-Ballús, A.; Giralt-Hernando, M.; Hernández-Alfaro, F.; Gargallo-Albiol, J. Dynamic Implant Surgery—An Accurate Alternative to Stereolithographic Guides—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11060150
Marques-Guasch J, Bofarull-Ballús A, Giralt-Hernando M, Hernández-Alfaro F, Gargallo-Albiol J. Dynamic Implant Surgery—An Accurate Alternative to Stereolithographic Guides—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dentistry Journal. 2023; 11(6):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11060150
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques-Guasch, Jordi, Anna Bofarull-Ballús, Maria Giralt-Hernando, Federico Hernández-Alfaro, and Jordi Gargallo-Albiol. 2023. "Dynamic Implant Surgery—An Accurate Alternative to Stereolithographic Guides—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Dentistry Journal 11, no. 6: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11060150
APA StyleMarques-Guasch, J., Bofarull-Ballús, A., Giralt-Hernando, M., Hernández-Alfaro, F., & Gargallo-Albiol, J. (2023). Dynamic Implant Surgery—An Accurate Alternative to Stereolithographic Guides—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dentistry Journal, 11(6), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11060150