Leaching of Different Clear Aligner Systems: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mi, H.-Y.; Jing, X.; Turng, L.-S.; Peng, X.-F. Microcellular injection molding and particulate leaching of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) scaffolds. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Nuremberg, Germany, 15 May 2014; pp. 392–396. [Google Scholar]
- Eliades, T.; Eliades, G.; Watts, D.C. Structural conformation of in vitro and in vivo aged orthodontic elastomeric modules. Eur. J. Orthod. 1999, 21, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, T. Clear aligners in orthodontic treatment. Aust. Dent. J. 2017, 62, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Align-Technology. Invisalign® Clear Aligners. Available online: https://www.invisalign.com/the-invisalign-difference/smarttrack-aligner-material (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Eon-holdings. Eon Clear Aligners®. Available online: https://eonaligner.com (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- 3M. Clarity® Aligners. Available online: https://www.3m.com/3M/en_US/orthodontics-us/featured-products/clarity-eos/ (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Dentsply-Sirona. SureSmile® Clear Aligners. Available online: https://www.dentsplysirona.com/en/explore/orthodontics/suresmile-aligner.html (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Schuster, S.; Eliades, G.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, T.; Bradley, T.G. Structural conformation and leaching from in vitro aged and retrieved Invisalign appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 126, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, J.H.; Giampaolo, E.T.; Machado, A.L.; Vergani, C.E. Cytotoxicity of denture base acrylic resins: A literature review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2003, 90, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioka, C.; Bourauel, C.; Hiskia, A.; Kletsas, D.; Eliades, T.; Eliades, G. Light-cured or chemically cured orthodontic adhesive resins? A selection based on the degree of cure, monomer leaching, and cytotoxicity. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 127, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotyk, M.W.; Wiltshire, W.A. An investigation into bisphenol-A leaching from orthodontic materials. Angle Orthod. 2014, 84, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliades, T.; Hiskia, A.; Eliades, G.; Athanasiou, A.E. Assessment of bisphenol-A release from orthodontic adhesives. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2007, 131, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Aslam Khan, M.U.; Abdullah, A.M.; Abd Razak, S.I. A review on current trends of polymers in orthodontics: BPA-free and smart materials. Polymers 2021, 13, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levrini, L.; Mangano, A.; Margherini, S.; Tenconi, C.; Vigetti, D.; Muollo, R.; Marco Abbate, G. ATP bioluminometers analysis on the surfaces of removable orthodontic aligners after the use of different cleaning methods. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.-M.; Tai, K.-W.; Hu, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-C. Cytotoxic effects of denture base materials on a permanent human oral epithelial cell line and on primary human oral fibroblasts in vitro. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2001, 14, 439–443. [Google Scholar]
- Thavarajah, R.; Thennukonda, R.A. Analysis of adverse events with use of orthodontic sequential aligners as reported in the manufacturer and user facility device experience database. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2015, 26, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, H.; Hoshino, Y.; Tajima, K.; Takagi, N. Leaching and cytotoxicity of formaldehyde and methyl methacrylate from acrylic resin denture base materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1994, 71, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Goncalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Goncalves, A.M.M. Impacts of plastic products used in daily life on the environment and human health: What is known? Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 72, 103239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, A.S.; Pottipalli Sathyanarayana, H.; Kailasam, V.; Padmanabhan, S. Comparative evaluation of salivary bisphenol A levels in patients wearing vacuum-formed and Hawley retainers: An in-vivo study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 151, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO; FAO. Toxicological and Health Aspects of Bisphenol A; FAO: Ottawa, OT, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- NIST. National Institute of Standard and Technology. Available online: https://www.nist.gov (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Walele, A.P.S.; Chaudhari, A.; Patil, C.; Yaragamblimath, P.; Survase, R. Leaching from thermoplastic sheets-a quantitative assessment. Int. J. Contemp. Med. 2016, 3, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. Facts about Benzene. Available online: https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/benzene/basics/facts.asp (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- PubChem. National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 17 October 2021).
- ChEBI. Chemical Entities of Biological Interest. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/init.do (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Mojarrab, M.; Delazar, A.; Esnaashari, S.; Afshar, F.H. Chemical composition and general toxicity of essential oils extracted from the aerial parts of Artemisia armeniaca Lam. and A. incana (L.) Druce growing in Iran. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.-A.; Jeong, T.-S.; Park, D.-S.; Xu, M.-Z.; Oh, H.-W.; Song, K.-B.; Lee, W.S.; Park, H.-Y. Antioxidant effects of quinoline alkaloids and 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol isolated from Scolopendra subspinipes. J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 29, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amudha, M.; Rani, S. Assessing the bioactive constituents of Cadaba fruticosa (L.) Druce through GC-MS. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 6, 383–385. [Google Scholar]
- Material Safety Data Sheet. Available online: https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/64655.htm (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Matasa, C.G. Screening orthodontic polymers for leaching. World J. Orthod. 2003, 4, 157–161. [Google Scholar]

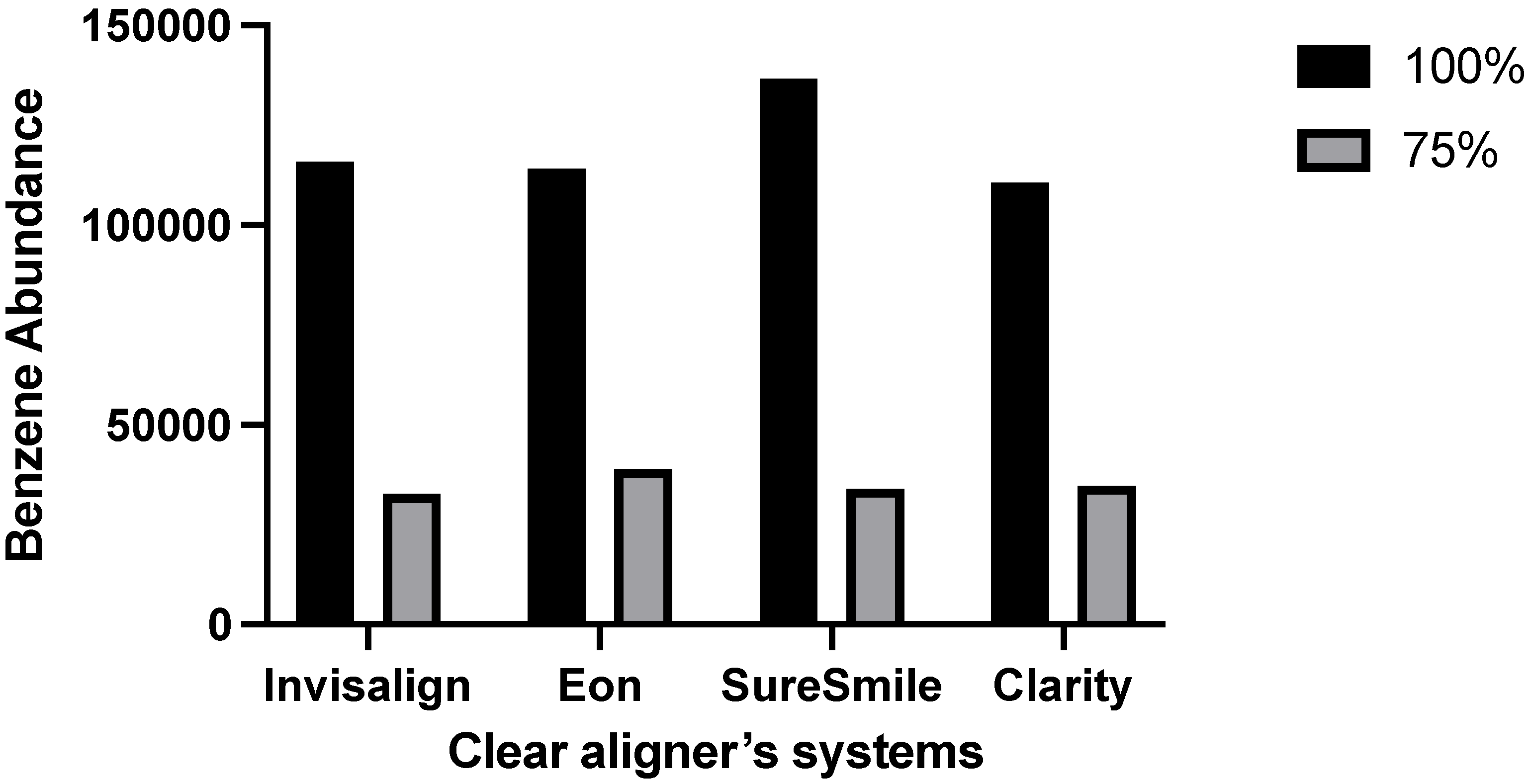
| Immersion Solution Concentration | Chemical Compound | Substance Concentration % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invisalign® | Eon® | Sure Smile® | Clarity® | ||
| 100% Ethanol | Benzene, 1,3-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) | 42% | 16.1% | 37% | 32% |
| Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) | ND | 11% | 25% | 16% | |
| Undecane, 4,6-dimethyl | ND | 5.4% | ND | 8% | |
| Heptadecane, 2,6,10,14-tetramethyl | ND | 2.1% | 6% | ND | |
| Octane, 3,5-dimethyl | ND | 4.3% | ND | ND | |
| Nonadecane | ND | 5.3% | ND | ND | |
| Dodecanoic acid, ethyl ester | ND | 16% | ND | ND | |
| 1-Octadecanesulphonyl chloride | ND | ND | 8.1% | ND | |
| Methoxyacetic acid, 2-tridecyl ester | ND | ND | ND | 8% | |
| Ether, hexyl pentyl | ND | ND | ND | 7.6% | |
| 75% Ethanol | Benzene, 1,3-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) | 20.3% | 74.2% | 80% | 58% |
| 50% Ethanol | Phenol, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) | ND | ND | 95% | 94% |
| Immersion Solution Concentration | Aligner’s System | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error | F | p-Value | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||||||
| 100% Ethanol | Invisalign® | 11 | 10,535.82 | 34,943.36 | 10,535.82 | 0.961 | 0.42 | −12,939.45 | 34,011.08 |
| Eon® | 11 | 39,547.09 | 43,964.78 | 13,255.88 | 10,011.15 | 69,083.03 | |||
| SureSmile® | 11 | 24,809.27 | 46,290.84 | 13,957.21 | −6289.34 | 55,907.88 | |||
| Clarity® | 11 | 22,472.73 | 34,562.63 | 10,421.02 | −746.76 | 45,692.22 | |||
| 75% Ethanol | Invisalign® | 11 | 2981.27 | 9887.76 | 2981.27 | 0.006 | 0.999 | −3661.42 | 9623.96 |
| Eon® | 11 | 3548.27 | 11,768.29 | 3548.27 | −4357.77 | 11,454.32 | |||
| SureSmile® | 11 | 3093.64 | 10,260.43 | 3093.64 | −3799.42 | 9986.69 | |||
| Clarity® | 11 | 3164.82 | 10,496.51 | 3164.82 | −3886.84 | 10,216.47 | |||
| 50% Ethanol | Invisalign® | 11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.667 | 0.577 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Eon® | 11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||
| SureSmile® | 11 | 3137.64 | 10,406.36 | 3137.64 | −3853.45 | 10,128.73 | |||
| Clarity® | 11 | 2966.91 | 9840.12 | 2966.91 | −3643.78 | 9577.59 | |||
| Aligner’s System | Immersion Solution Concentration | Mean Difference | Std. Error | F | p-Value | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||||
| Invisalign® | 100% | 75% | 7554.55 | 8940 | 0.738 | 0.487 | −14,486 | 29,595 |
| 50% | 10,535.82 | 8940 | −11,504 | 32,576 | ||||
| 75% | 100% | −7554.55 | 8940 | −29,595 | 14,486 | |||
| 50% | 2981.27 | 8940 | −19,059 | 25,021 | ||||
| 50% | 100% | −10,535.82 | 8940 | −32,576 | 11,504 | |||
| 75% | −2981.27 | 8940 | −25,021 | 19,059 | ||||
| Eon® | 100% | 75% | 35,998.81818 * | 11204 | 7.627 | 0.002 * | 8377 | 63,621 |
| 50% | 39,547.09091 * | 11204 | 11,925 | 67,169 | ||||
| 75% | 100% | −35,998.81818 * | 11204 | −63,621 | −8377 | |||
| 50% | 3548.27 | 11204 | −24,074 | 31,170 | ||||
| 50% | 100% | −39,547.09091 * | 11204 | −67,169 | −11,925 | |||
| 75% | −3548.27 | 11,204 | −3,1170 | 24,074 | ||||
| SureSmile® | 100% | 75% | 21,715.64 | 11,950 | 2.197 | 0.129 | −7745 | 51,177 |
| 50% | 21,671.64 | 11,950 | −7789 | 51,133 | ||||
| 75% | 100% | −21,715.64 | 11,950 | −51,177 | 7745 | |||
| 50% | −44.00 | 11,950 | −29,505 | 29,417 | ||||
| 50% | 100% | −21,671.64 | 11,950 | −51,133 | 7789 | |||
| 75% | 44.00 | 11,950 | −29,417 | 29,505 | ||||
| Clarity® | 100% | 75% | 19,307.91 | 9217 | 2.956 | 0.067 | −3413 | 42,029 |
| 50% | 19,505.82 | 9217 | −3215 | 42,227 | ||||
| 75% | 100% | −19,307.91 | 9217 | −42,029 | 3413 | |||
| 50% | 197.91 | 9217 | −22,523 | 22919 | ||||
| 50% | 100% | −19,505.82 | 9217 | −42,227 | 3215 | |||
| 75% | 0 | 9217 | −22,919 | 22,523 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhendi, A.; Khounganian, R.; Almudhi, A.; Ahamad, S.R. Leaching of Different Clear Aligner Systems: An In Vitro Study. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10020027
Alhendi A, Khounganian R, Almudhi A, Ahamad SR. Leaching of Different Clear Aligner Systems: An In Vitro Study. Dentistry Journal. 2022; 10(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhendi, Aseel, Rita Khounganian, Abdullazez Almudhi, and Syed Rizwan Ahamad. 2022. "Leaching of Different Clear Aligner Systems: An In Vitro Study" Dentistry Journal 10, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10020027
APA StyleAlhendi, A., Khounganian, R., Almudhi, A., & Ahamad, S. R. (2022). Leaching of Different Clear Aligner Systems: An In Vitro Study. Dentistry Journal, 10(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10020027






