In Vitro Screening of the Apatite-Forming Ability, Biointeractivity and Physical Properties of a Tricalcium Silicate Material for Endodontics and Restorative Dentistry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Biointeractivity: Alkalizing Activity (pH of Soaking Water) and Calcium Release
2.3. Physical Properties: Porosity, Water Sorption, Solubility, and Setting Time
2.4. Surface Characterization
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
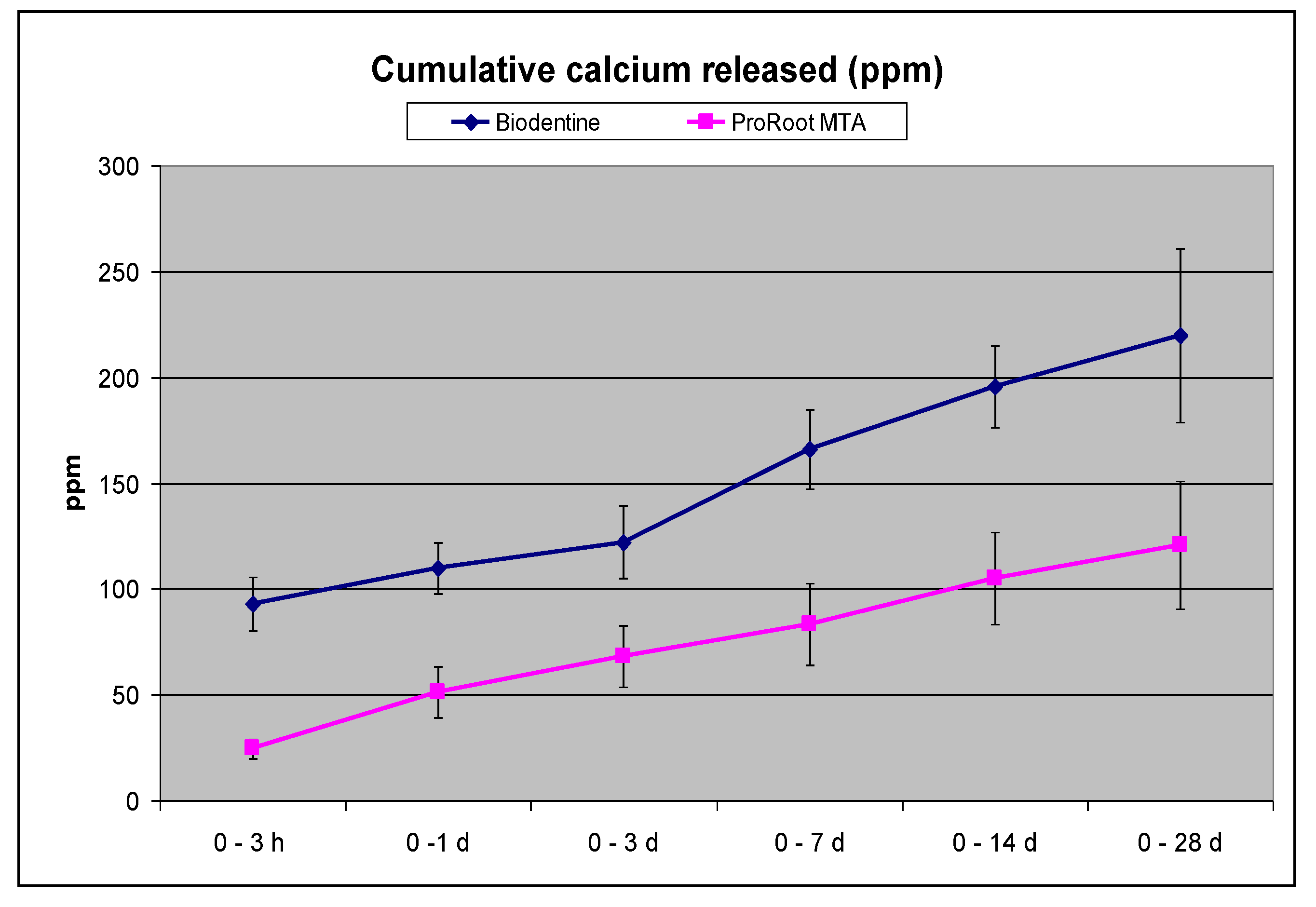
3.1. Biointeractivity: Alkalizing Activity (pH of Soaking Water) and Calcium Release
| pH of soaking water | ||
|---|---|---|
| Biodentine | ProRoot MTA | |
| 3 h | 11.62 ± 0.13 A a | 10.89 ± 0.67 A b |
| 1 day | 11.65 ± 0.53 A a | 10.52 ± 0.60 A b |
| 3 days | 10.90 ± 0.59 B a | 9.09 ± 0.40 B b |
| 7 days | 9.19 ± 0.59 C a | 8.87 ± 0.14 B a |
| 14 days | 9.56 ± 0.27 C a | 8.33 ± 1.15 C b |
| 28 days | 9.48 ± 0.74 C a | 7.88 ± 0.46 C b |
| Calcium released (ppm) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Biodentine | ProRoot MTA | |
| 0 - 3 h | 92.83 ± 12.73 A a | 24.48 ± 4.62 A b |
| 3 h - 1 d | 17.13 ± 4.82 B a | 37.63 ±13.80 A b |
| 1 - 3 d | 18.76 ± 8.38 B a | 17.40 ± 4.5 A a |
| 3 - 7 d | 43.58 ± 3.03 C a | 16.50 ± 6.19 A b |
| 7 - 14 d | 28.85 ± 9.73 B a | 30.00 ±7.30 A a |
| 14 - 28 d | 42.4 ± 4.37 C a | 20.52 ± 6.05 A b |
| Porosity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Biodentine | ProRoot MTA | |
| Volume of Open Pores (Vop, cm3) | 0.02324 ± 0.0010 a | 0.0312 ± 0.0025 b |
| Volume of Impervious Portion (Vip, cm3) | 0.0778 ± 0.0033 a | 0.0755 ± 0.0054 a |
| Exterior Volume (V, cm3) | 0.1010 ± 0.0050 a | 0.1067 ± 0.0076 a |
| Apparent Porosity (Vop/V, %) | 22.98 ± 0.23 a | 29.24 ± 0.84 b |
| Physical properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| Biodentine | ProRoot MTA | |
| Setting time (min) | 12 ± 1 a | 170 ± 3 b |
| Water sorption (%) | 12.64 ± 0.15 a | 14.55 ± 0.44 a |
| Solubility (%) | 11.93 ± 0.43 a | 10.70 ± 0.33 a |
3.2. Physical Properties
3.2.1. Porosity
3.2.2. Setting Time, Solubility and Water Sorption
3.3. Apatite-Forming Ability: ESEM-EDX Morphological and Chemical Surface Analysis
Biodentine

ProRoot MTA

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parirokh, M.; Torabinejad, M. Mineral trioxide aggregate: A comprehensive literature review - Part I: Chemical, physical, and antibacterial properties. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; van Landuyt, K.; Taddei, P.; Modena, E.; van Meerbeek, B.; Prati, C. ESEM-EDX and Raman techniques to study MTA calcium-silicate cements in wet conditions and in real-time. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabinejad, M.; White, D.J. Tooth filling material and method of use. Patent US 1998/5769638 and WO 94/24955, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri, J.; Gandolfi, M.G. Evaluation of the radiopacity of calcium silicate cements containing different radiopacifiers. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 43, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primus, C. Dental Material. Patent WO 02/056838, US 2004/0226478; (provisional application filed in 2001), 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Parirokh, M.; Torabinejad, M. Mineral trioxide aggregate: A comprehensive literature review - Part III: Clinical applications, drawbacks, and mechanism of action. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mente, J.; Geletneky, B.; Ohle, M.; Koch, M.J.; Ding, P.G.; Wolff, D.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Martin, N.; Staehle, H.J.; Pfefferle, T. Mineral trioxide aggregate or calcium hydroxide direct pulp capping: An analysis of the clinical treatment outcome. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabinejad, M.; Parirokh, M. Mineral trioxide aggregate: A comprehensive literature review - Part II: Leakage and biocompatibility investigations. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okiji, T.; Yoshiba, K. Reparative dentinogenesis induced by mineral trioxide aggregate: A review from the biological and physicochemical points of view. Int. J. Dent. 2009, 2009, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Shah, S.N.; Feng, R.; Prati, C.; Akintoye, S.O. Biomimetic calcium-silicate cements support differentiation of human orofacial mesenchymal stem cells. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Ciapetti, G.; Taddei, P.; Perut, F.; Tinti, A.; Cardoso, M.; van Meerbek, B.; Prati, C. Apatite formation on bioactive calcium-silicate cements for dentistry affects surface topography and human marrow stromal cells proliferation. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 974–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Ciapetti, G.; Perut, F.; Taddei, P.; Modena, E.; Rossi, P.L.; Prati, C. Biomimetic calcium-silicate cements aged in simulated body solutions. Osteoblasts response and analyses of apatite coating. J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2009, 7, 160–170. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadame-Jafari, S.; Mantellini, M.G.; Botero, T.M.; McDonald, N.J.; Nor, J.E. Effect of ProRoot MTA on pulp cell apoptosis and proliferation in vitro. J. Endod. 2005, 31, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Nakano, T.; Tomokiyo, A.; Fujii, S.; Wada, N.; Monnouchi, S.; Hori, K.; Akamine, A. Mineral trioxide aggregate induces bone morphogenetic protein-2 expression and calcification in human periodontal ligament cells. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Rabeah, E.; Perinpanayagam, H.; MacFarland, D. Human alveolar bone cells interact with ProRoot and tooth-colored MTA. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjpe, A.; Smoot, T.; Zhang, H.; Johnson, J.D. Direct contact with mineral trioxide aggregate activates and differentiates human dental pulp cells. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakki, S.S.; Bozkurt, S.B.; Hakki, E.E.; Belli, S. Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate on cell survival, gene expression associated with mineralized tissues, and biomineralization of cementoblasts. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Taddei, P.; Siboni, F.; Modena, E.; Ciapetti, G.; Prati, C. Development of the foremost light-curable calcium-silicate MTA cement as root-end in oral surgery. Chemical-physical properties, bioactivity and biological behaviour. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, e134–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G. A new method for evaluating the pulpward diffusion of Ca and OH ions through coronal dentin into the pulp. Iran. Endod. J. 2012, 7, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Taddei, P.; Modena, E.; Siboni, F.; Prati, C. Biointeractivity-related vs. chemi/physisorption-related apatite precursor-forming ability of current root end filling materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2013, 101B, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Taddei, P.; Tinti, A.; Prati, C. Apatite-forming ability of ProRoot MTA. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 43, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Taddei, P.; Tinti, A.; Dorigo De Stefano, E.; Rossi, P.L.; Prati, C. Kinetics of apatite formation on a calcium-silicate cement for root-end filling during ageing in physiological-like phosphate solutions. Clin. Oral Investig. 2010, 14, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, C.; Siboni, F.; Polimeni, A.; Bossù, M.; Gandolfi, M.G. Use of calcium-containing endodontic sealers as apical barrier in fluid contaminated wide-open apices. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2014, 2. in press. [Google Scholar]
- Pelliccioni, G.A.; Vellani, C.P.; Gatto, M.R.; Gandolfi, M.G.; Marchetti, C.; Prati, C. ProRoot mineral trioxide aggregate cement used as a retrograde filling without addition of water: An in vitro evaluation of its microleakage. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Iacono, F.; Agee, K.; Siboni, F.; Tay, F.; Pashley, D.H.; Prati, C. Setting time and expansion in different soaking media of experimental accelerated calcium-silicate cements and ProRoot MTA. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 108, e39–e45. [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Prati, C. MTA and F-doped MTA cements used as sealers with warm gutta-percha. Long-term sealing ability study. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 43, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, R.; Olivier, M. Dental composition. Patent WO 2011/124841, US 2013/0025498, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Koubi, G.; Colon, P.; Franquin, J.C.; Hartmann, A.; Richard, G.; Faure, M.O.; Lambert, G. Clinical evaluation of the performance and safety of a new dentine substitute, Biodentine, in the restoration of posterior teeth—a prospective study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, A.; Lipski, M.; Parafiniuk, M.; Sporniak-Tutak, K.; Lichota, D.; Kosierkiewicz, A.; Kaczmarek, W.; Buckowska-Radlinska, J. Response of human dental pulp capped with Biodentine and mineral trioxide aggregate. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.V.; Gorin, C.; Willig, C.; Baroukh, B.; Pellat, B.; Decup, F.; Opsahl Vital, S.; Chaussain, C.; Boukpessi, T. Effect of a calcium-silicate-based restorative cement on pulp repair. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, P.; Camps, J.; de Méo, M.; Déjou, J.; About, I. Induction of specific cell responses to a Ca3SiO5-based posterior restorative material. J. Dent. Res. 2008; 24, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar]
- The International Organization for Standardization. Implants for Surgery—In vitro Evaluation for Apatite-Forming Ability of Implant Materials. ISO/FDIS 23317:2007(E). Available online: http://www3.chubu.ac.jp/documents/faculty/kokubo_tadashi/home/33/33_5e3f7c01288352282eca51295fc47f1a.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2013).
- Rashid, F.; Shiba, H.; Mizuno, N.; Mouri, Y.; Fujita, T.; Shinohara, H.; Ogawa, T.; Kawaguchi, H.; Kurihara, H. The effect of extracellular calcium ion on gene expression of bone-related proteins inhuman pulp cells. J. Endod. 2003, 29, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, U. Effects of calcium hydroxide-containing pulp-capping agents on pulp cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. J. Dent. Res. 1985, 64, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, M.; Banzai, Y. Calcium ion release from calcium hydroxide stimulated fibronectin gene expression in dental pulp cells and the differentiation of dental pulp cells to mineralized tissue forming cells by fibronectin. Int. Endod. J. 2008, 41, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Hayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Maeno, M.; Ogiso, B. Calcium ions released from mineral trioxide aggregate convert the differentiation pathway of C2C12 Cells into osteoblast lineage. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Han, J.S. Effects of HA released calcium ion on osteoblast differentiation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyckmans, J.; Roberts, S.J.; Bolander, J.; Schrooten, J. Mapping calcium phosphate activated gene networks as a strategy for targeted osteoinduction of human progenitors. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4612–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Sasaki, J.; Egusa, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Nakano, T.; Sohmura, T.; Nakahira, A. Effect of calcium ion concentrations on osteogenic differentiation and hematopoietic stem cell niche-related protein expression in osteoblasts. Tissue Eng. Part A 2010, 16, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takita, T.; Hayashi, M.; Takeichi, O.; Ogiso, B.; Suzuki, N.; Otsuka, K.; Ito, K. Effect of mineral trioxide aggregate on proliferation of cultured human dental pulp cells. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium signaling. Cell 1995, 80, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, C.; Holland, R. Calcium hydroxide study based on scientific evidences. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2003, 11, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonson, S.; Jeansonne, B.G.; Lallier, T.E. Root-end filling materials alter fibroblast differentiation. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, M.; Sautier, J.M.; Berdal, A.; Simon, S. Biodentine induces immortalized murine pulp cell differentiation into odontoblast-like cells and stimulates biomineralization. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Wu, T.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Jiang, L.; Peng, W.; Chang, J.; Zhu, Y. Role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway in driving tricalcium silicate-induced proliferation and biomineralization of human dental pulp cells in vitro. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérard, M.; Le Clerc, J.; Meary, F.; Pérez, F.; Tricot-Doleux, S.; Pellen-Mussi, P. Spheroid model study comparing the biocompatibility of Biodentine and MTA. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakki, S.S.; Bozkurt, B.S.; Gandolfi, M.G.; Prati, C.; Belli, S. The response of cementoblasts to calcium phosphate resin-based and calcium silicate-based commercial sealers. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, D.; Ford, T.R.; Papaioannou, S.; Nicholson, J.; McDonald, F. An evaluation of accelerated Portland cement as a restorative material. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4001–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, C.; Miao, B.; Bareille, R.; Rey, C. Preparation, physical-chemical characterisation and cytocompatibility of calcium carbonate cements. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; de With, G.; Sommerdijk, N.A. In situ techniques in biomimetic mineralization studies of calcium carbonate. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Siboni, F.; Prati, C. Chemical-physical properties of TheraCal, a novel light-curable MTA-like material for pulp-capping. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, G.; Dammaschke, T.; Gerth, H.U.V.; Zandbiglari, T.; Schafer, E. A comparative study of selected properties of ProRoot mineral trioxide aggregate and two Portland cements. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogue, R.H.; Lerch, W. Hydration of Portland cement compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1934, 26, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.F.W.; Barret, P.; Brown, P.W.; Double, D.D.; Frohnsdorff, G.; Johansen, V.; Ménétrier-Sorrentino, D.; Odler, I.; Parrott, L.J.; Pommersheim, J.M.; Young, J.F. The hydration of tricalcium silicate. RILEM Technical Committees 68-MMH, Task Group 3. Mater. Struct. 1984, 6, 457–468. [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Parrilli, A.P.; Fini, M.; Prati, C.; Dummer, P.M.H. 3D micro-CT analysis of the interface voids associated with Thermafil root fillings used with AH Plus or a flowable MTA sealer. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gandolfi, M.G.; Siboni, F.; Polimeni, A.; Bossù, M.; Riccitiello, F.; Rengo, S.; Prati, C. In Vitro Screening of the Apatite-Forming Ability, Biointeractivity and Physical Properties of a Tricalcium Silicate Material for Endodontics and Restorative Dentistry. Dent. J. 2013, 1, 41-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj1040041
Gandolfi MG, Siboni F, Polimeni A, Bossù M, Riccitiello F, Rengo S, Prati C. In Vitro Screening of the Apatite-Forming Ability, Biointeractivity and Physical Properties of a Tricalcium Silicate Material for Endodontics and Restorative Dentistry. Dentistry Journal. 2013; 1(4):41-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj1040041
Chicago/Turabian StyleGandolfi, Maria Giovanna, Francesco Siboni, Antonella Polimeni, Maurizio Bossù, Francesco Riccitiello, Sandro Rengo, and Carlo Prati. 2013. "In Vitro Screening of the Apatite-Forming Ability, Biointeractivity and Physical Properties of a Tricalcium Silicate Material for Endodontics and Restorative Dentistry" Dentistry Journal 1, no. 4: 41-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj1040041
APA StyleGandolfi, M. G., Siboni, F., Polimeni, A., Bossù, M., Riccitiello, F., Rengo, S., & Prati, C. (2013). In Vitro Screening of the Apatite-Forming Ability, Biointeractivity and Physical Properties of a Tricalcium Silicate Material for Endodontics and Restorative Dentistry. Dentistry Journal, 1(4), 41-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj1040041









