Abstract
An Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) is an optical access network that allows a higher data rate with low power consumption. To improve energy savings for an EPON, the sleep and doze modes for the optical network units (ONUs) play a pivotal role. Many prediction schemes have been proposed to control these modes. To increase the prediction accuracy, this study proposes an energy-efficient approach that uses a support vector regression (SVR) model. A dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) scheme called SVR-DBA is designed to allocate bandwidth to ONUs more efficiently and fairly. To determine the effectiveness of the proposed scheme, simulations are performed. The simulation results show that the proposed scheme decreases energy consumption for ONUs by up to 47% and fulfills the quality-of-service (QoS) requirements in terms of delay, jitter, and packet loss.
1. Introduction
Today more than 53.6% of people worldwide have internet access, which causes increasing energy consumption in the access networks. It is predicted that the communication networks consume about 20% of worldwide energy usage [1,2]. Green communications over the past decade have been one of the important topics in academic research and the industry field. Many types of research have been conducted to design and operate access networks in an efficient way to reduce energy consumption worldwide.
In terms of fixed broadband optical access networks, Ethernet passive optical networks (EPONs) are used extensively as deployment cost and power consumption is minimized [3,4]. An EPON system has two major hardware components: an optical line terminal (OLT) at the central office (CO) and several optical network units (ONUs) near the end-user locations that are connected to the OLT via optical fiber links in a tree structure. An EPON uses a point-to-multipoint topology for the downstream direction when the data is broadcast from the OLT to the ONUs and a multipoint-to-point topology for the upstream direction when the data is transmitted from the ONUs to the OLT.
The network medium (feeder fiber) is shared in the upstream direction so the OLT uses a dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) algorithm to calculate the time-slot allocation for transmission for each ONU [5,6] to prevent collisions. Many DBA schemes have been developed to decrease energy consumption for the EPON [7].
The ONU plays a pivotal role for energy saving as it consumes 60% of the energy in a passive optical network (PON) [8]. Since an ONU transceiver can be idle most of the time, turning off the transceiver for the ONU during the idle time reduces energy consumption. Previous software-based energy saving approaches for ONUs involved ONU power shedding, ONU dozing, and ONU sleeping [3]. Power shedding gives the best possible system performance, yet also gives the minimum energy savings. Dozing involves turning off the transmitter for the ONU for a period of time and the receiver is fully functional. Sleeping involves turning off the transmitter and the receiver for an interval. Sleeping gives the maximum energy savings, however the system performance is poor as a longer recovery time is required [9].
The duration of sleep/doze for the ONU significantly affects energy consumption and system performance. A longer sleep/doze period gives greater energy savings, however, it also results in decreased system performance. A short period gives good quality-of-service (QoS) metrics, however, it also results in decreased energy savings. Several schemes have been proposed for ONU sleep/doze time allocation [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. However, most of these studies determine the duration of the sleep/doze by analyzing the current status in the buffers of ONUs and do not consider upcoming traffic from users. Moreover, they use a greedy approach to achieve energy savings by allowing ONUs to enter the sleep/doze mode for a long period. This greedy approach results in an overly long delay and violates the delay restrictions for the different QoS requirements in the optical access networks [14]. Some methods use optimization schemes [16,17] or prediction schemes [11,12,15,16] to decrease energy consumption, however, optimization schemes do not consider the different QoS requirements for network traffic and prediction schemes use overly simple prediction methods.
This study proposes a dynamic bandwidth allocation scheme called SVR-DBA that uses the support vector regression (SVR) model [18,19]. The SVR-DBA scheme extends the period of decreased energy consumption using the SVR model and satisfies the QoS requirements to estimate the arrival time for upcoming high priority traffic. To achieve energy savings, ONUs transit between the active state and the doze state and remain longer in the doze state if the QoS is acceptable. To determine the effectiveness of the SVR-DBA, simulations are used in the experiments. Compared with the IPACT (Interleaved Polling with Adaptive Cycle Time) scheme [5], the Green DBA (GDBA) scheme [13], and the LR-DBA (Logistic Regression DBA) [15], SVR-DBA gives energy savings for ONUs by up to 47% and fulfills QoS requirements in terms of delay, jitter, and packet loss.
The main contributions of this study are as follows. An SVR-based dynamic bandwidth allocation scheme, SVR-DBA, is used to predict the upstream behavior of ONUs. The SVR-DBA controls the bandwidth allocation for ONUs to achieve energy savings by determining the duration of a doze. Secondly, various traffic configurations are simulated and the results show that the SVR-DBA fulfills the QoS requirements for Expedited Forwarding (EF) traffic and Assured Forwarding (AF) traffic. The throughput for the upstream network of the SVR-DBA is maintained for different QoS requirements.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 gives an overview of related work. Section 3 describes the proposed mechanism, the new ONU and OLT architectures, and the working principle of the SVR model. Section 4 details the performance of the proposed scheme and Section 5 gives conclusions.
2. Related Work
Many schemes have been proposed for ONU sleep/doze time allocation [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Liu et al. devised a control scheme that allows the ONU to enter the doze mode if there is no upstream traffic and returns to the active mode if high priority upstream traffic arrives. They also used a downstream-centric algorithm to allow the ONU to send upstream traffic when the OLT forwards the downstream traffic [10]. Nikoukar et al. proposed a two-stage mechanism to increase energy saving efficiency by increasing the doze duration according to the state of the ONU queue and the incoming traffic ratio [11]. This scheme ensures that QoS metrics are satisfied at high traffic loads. Most of the aforementioned schemes achieve maximum energy savings by greedily allowing ONUs to enter the sleep/doze mode for a long period. However, they are of a greedy approach that results in an overly long delay and violates the delay restrictions for different QoS requirements for optical access networks [14].
Liu et al. proposed a dynamic channel assignment scheme to achieve energy savings by dynamically allocating channels to ONUs. The Hungarian method is used to determine the minimum total cost assignment [16]. In [17], Butt et al. proposed an energy-efficient framework called ECS (Efficient Cyclic Sleep) that optimizes the cyclic sleep mode (CSM) using a sleep buffer. These optimization schemes achieve energy savings, however, they do not consider the different QoS requirements for different network traffic.
Some methods predict the next transmission cycle [11,12,15,16]. An ONU-initiated mechanism in SIEPON (Service Interoperability in Ethernet Passive Optical Networks) was proposed to achieve energy savings [12,13] and this scheme also considers the QoS requirements using the sleep duration, the maximum sleep duration boundary, and the estimated upcoming traffic. However, this scheme lacks traffic pattern predictions for more energy savings. Lotfolahi et al. devised a machine learning-based mechanism to increase energy savings for ONUs using a logistic regression model. This scheme decreases power consumption in ONUs by 45% and fulfills QoS requirements [15]. However, the logistic regression model has a potential overfitting problem. The prediction model can be further enhanced.
Other methods are proposed to achieve energy savings for an OLT/ONU with different operation modes or architectures. A watchful sleep mode for the ONU receiver that combines cyclic doze and sleep techniques has been proposed [20,21]. A software-defined networking (SDN) architecture has been integrated into the OLT/ONU to control activation [22,23]. Using appropriate system parameter settings that are determined by the SDN controllers, the SDN-based approach dynamically decides the number of active OLTs and the sleeping configurations for ONUs to achieve energy savings. Lattice theory has been used to model the OLT/ONU network architecture [24,25]. For a lattice structure, fixed-point theory is used to determine sleep/doze durations. To deal with heterogeneous ONU propagation delays, moreover, Lv et al. [2] proposed a postponing scheme that dynamically adjusts the ONU doze/sleep duration, however, this study does not automate the polling cycle time calculation. Since these approaches deal with the energy saving issue from different aspects, future research can be conducted to employ prediction models in these approaches for performance improvements.
3. System Model
3.1. Proposed ONU and OLT Architecture
The proposed ONU and OLT hardware architecture with energy saving functionality are shown in Figure 1. The blocks that are modified to employ the proposed SVR-DBA scheme are highlighted in green color. The ONU architecture is shown with a queue manager and the doze controller in Figure 1a. The dotted line represents the control path from the doze controller to the transmitter. The queue manager groups, and queues, similar incoming network packets from the user network interface (UNI) into three queues to guarantee QoS for three types of network traffic, including EF, AF, and Best Effort (BE) traffic. Among them, the EF traffic is given highest priority, and the BE traffic is given lowest priority. The doze controller manages and controls the doze function.
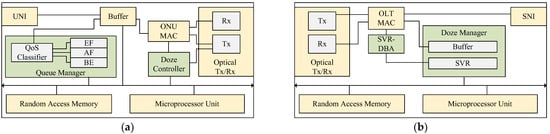
Figure 1.
The proposed architecture for (a) ONU and (b) OLT.
The OLT architecture includes an enhanced SVR-DBA module and a doze manager in Figure 1b. The SVR-DBA module assigns bandwidth to the ONUs depending on whether they are active or dozing and the available bandwidth. The doze manager uses historical data to determine whether an ONU can doze and determines the doze duration using the SVR scheme.
3.2. Determining the Duration of the Doze
The doze duration affects energy consumption and is calculated by the doze manager. The maximum doze duration is defined as the maximum period for which an ONU dozes. According to [14], the maximum allowed delays for EF and AF traffic are 5 ms and the maximum allowed delay for BF traffic is 20 ms to guarantee the QoS requirements. The following equation is used to calculate :
The doze manager uses historical data, such as the high-priority traffic that is reported from the ONUs by REPORT messages, to estimate the ONU queue size for high-priority traffic and to determine the doze duration. The doze manager ensures that the ONU queues do not exceed preset thresholds ( and ) in the doze mode. The ONU’s doze controller monitors the queue sizes during the doze mode. If traffic suddenly increases, it sends an interrupt signal to the OLT to grant bandwidth for the next cycle. The thresholds and guarantee that QoS requirements are fulfilled and are determined using simulation parameters, such as the packet generation model, the transmission cycle times and the number of ONUs.
The operation mode determines the required EF queue length for each cycle as follows:
where is the reported EF queue status if the ONU is in the active mode and is the estimated EF queue status if the ONU is in the doze mode. is calculated as follows:
where is the i-th previous REPORT message, for which and is the binary value that predicts whether the ONU will receive EF traffic () or not () in the doze mode.
The required queue length for AF in each cycle is calculated as:
where is the reported AF queue status if the ONU is in the active mode and is the estimated AF queue status if the ONU is in the doze mode. is calculated as:
where is the i-th previous REPORT message, for which and is the binary value that predicts whether the ONU will receive AF traffic () or not () in the doze mode.
The ONU doze duration is calculated as shown in Figure 2. If is 0 ms, the ONU enters the active mode in the next cycle or the required EF or AF queue length exceeds the QoS constraints; otherwise, is 5 ms or 20 ms, according to the traffic status.
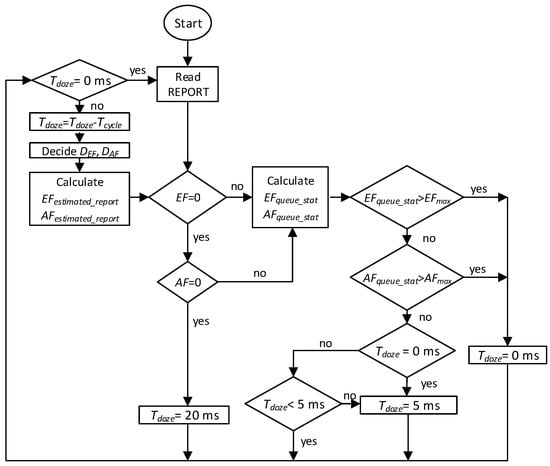
Figure 2.
Calculation for the doze duration .
3.3. Estimating EF and AF Traffic with SVR
The doze duration depends on the estimation of EF and AF traffic. Figure 3 shows the method of calculation for and . The doze manager determines when the ONU sends a REPORT message that contains high-priority traffic status. Using these predictions, it determines and by comparing the estimated time and the next cycle time.
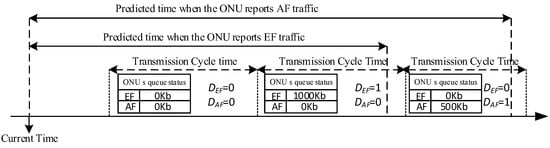
Figure 3.
Calculation for and .
The doze manager uses an SVR model to determine the time at which a REPORT message is sent. The SVR model is trained to capture the temporal characteristics of network traffic. When the traffic pattern is significantly changed, the SVR model is retrained to capture the new temporal characteristics. Historical traffic information is used as the training data. For a training data set , where is a vector of l input variables for the historical traffic information and is the corresponding output value that indicates the presence of high-priority traffic, the ε-SVR model determines the function f(x) (the predictor model) that has the closest values, with a maximum deviation ε, to the target y values for all training cases, such that f(x) is as smooth as possible. For a linear SVR, f(x) is expressed as:
where w is the weight vector with dimensionality l that represents the prediction model and b represents the bias. To ensure that Equation (6) is flat, the ε-SVR model reduces model complexity by minimizing the norm ||w|| for the weight vector w with a deviation of tolerance ε.
For this study, the input variables are the arrival times for the last 10 REPORT messages containing high priority traffic information. However, it may not be possible to determine a function that fits all of the training data with the ε-SVR model. Therefore, a soft-margin uses two slack variables and to determine the deviation in the training data outside the -insensitive area [26,27,28]. These variables are used to determine the number of many data points that are outside the SVR zone. Therefore, the optimization problem is expressed as:
Minimize
Subject to
where the constant C > 0 is used to determine the trade-off between the function flatness and the fitting error. For this study, the kernel function for the SVR model is the radial basis function as it is the most commonly used [27,28,29].
3.4. SVR-Based Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation
When the SVR-DBA module receives the REPORT messages from all active ONUs, it calculates the bandwidth and assigns bandwidth to these ONUs. The bandwidth allocation flowchart for the SVR-DBA is shown in Figure 4. If the ONUs are in the doze mode (), no bandwidth is allocated to them. To allocate bandwidth to active ONUs, the SVR-DBA calculates the initially available bandwidth () and the maximum transmission time () according to the number of active ONUs. The SVR-DBA then allocates bandwidth to each ONU based on the bandwidth request and the available bandwidth.
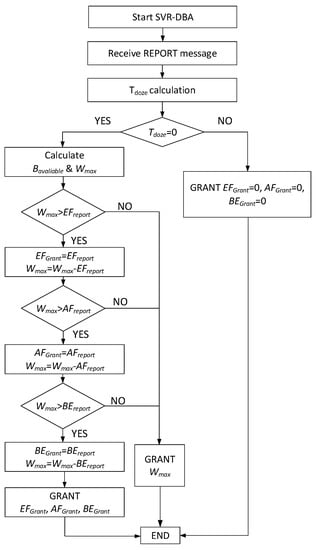
Figure 4.
Bandwidth allocation of SVR-DBA.
This study does not consider the optimization problem for the configuration parameters that are used for the SVR-DBA. The parameter optimization problem is a subject for future research. In practice, optimization schemes [30,31] can be used to optimize the values of these parameters.
3.5. OLT and ONU Operations
When the OLT receives the REPORT messages from the ONUs, it calculates according to the reported queue status and the QoS requirements. If an ONU receives a GATE message, for which the bandwidth assignment is zero, it enters the doze mode; otherwise, it enters the active mode. This mechanism allows a simple ONU architecture as the ONU does not need to monitor the doze duration. The original MPCP can be used without modification as the doze controller depends only on the granted bandwidth. The ONU receiver still receives GATE messages from the OLT during the doze mode.
4. Experiments
To determine the energy saving efficiency in terms of QoS metrics, such as delay, jitter, packet loss, and energy consumption, the proposed system model is implemented with an OPNET (Optimized Network Engineering Tools) simulator [32,33]. For the simulations, the system uses one OLT and 32 ONUs. The capacity of the upstream/downstream channel is 1 Gb/s. The distance between the OLT and the ONUs has a uniform distribution between 10 and 20 km. The buffer size for each ONU is limited to 5 Mb. The wakeup overhead time for each ONU is 0.125 ms. The respective power consumption for the ONU in active mode and the ONU in doze mode is 3.85 W and 1.7 W. The guard time is 5 μs. The DBA computation time is 10 μs.
The generators for AF and BE traffic produce high burst traffic with a burst parameter of 0.8 and the packet size has a uniform distribution between 64 and 1518 bytes. The generator for EF traffic has a Poisson distribution and a packet size that is fixed at 70 bytes. Two QoS parameters are used for the maximum transmission cycle time: 1 ms and 1.5 ms. Table 1 summarizes the simulation parameters.

Table 1.
Simulation parameters.
The simulations involve three different traffic scenarios, which are denoted as 154, 253, and 244, to evaluate the system performance. The notations represent the percentages of network traffic for EF service, AF service, and BE service. Take scenario 154 as an example: 10% of the network bandwidth is occupied by EF packets, 50% by AF packets and 40% by BE packets. The experiments use the IPACT scheme [5], the Green DBA (GDBA) scheme [13], and the LR-DBA scheme [15] to compare performance.
4.1. Mean Packet Delay
The packet delay in the upstream direction includes the polling delay, the queueing delay, and the grant delay [14]. Figure 5 compares the results for the mean packet delay for different traffic loads for two different maximum cycle times of 1.0 ms and 1.5 ms. The results show that if the traffic load is light, the GDBA and SVR-DBA have a longer mean packet delay than the IPACT as the ONUs are often idle and frequently enter the doze mode. The incoming packets from users are buffered in the ONU until the ONU transmitter transits to the active mode. The mean packet delay is decreased in the GDBA and SVR-DBA if the traffic load becomes heavier as the ONUs must transmit many packets so they rarely enter the doze mode. If the traffic load is greater than 80% for a maximum cycle time of 1.0 ms, no ONUs enter the doze mode for any of the schemes. This is also true for a 1.5 ms cycle time if the traffic load is greater than 90%.
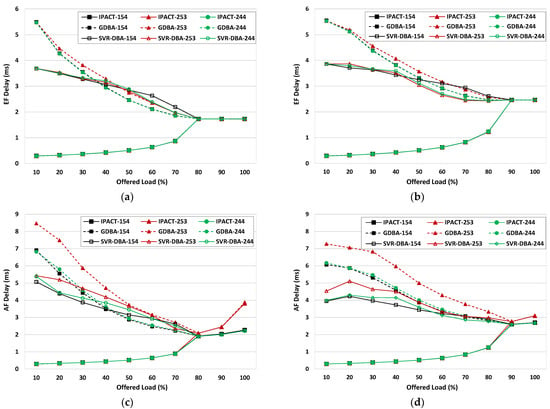
Figure 5.
Packet delay for different scenarios. (a) EF packet delay for 1.0 ms cycle time; (b) EF packet delay for 1.5 ms cycle time; (c) AF packet delay for 1.0 ms cycle time; (d) AF packet delay for 1.5 ms cycle time.
4.2. Jitter
Jitter is one of the most important factors for delivering high quality voice transmission [34]. Jitter is defined as , where N is the total number of received EF packets, is the delay time for the i-th EF packet, and is the average EF packet delay. Figure 6 shows the EF jitter for different traffic loads for two maximum cycle times. If the traffic load is not heavy, the GDBA and SVR-DBA have a higher jitter value than the IPACT. However, the jitter in the SVR-DBA is more stable and less than the jitter for the GDBA. The jitter for the GDBA and SVR-DBA decreases as the traffic load increases.
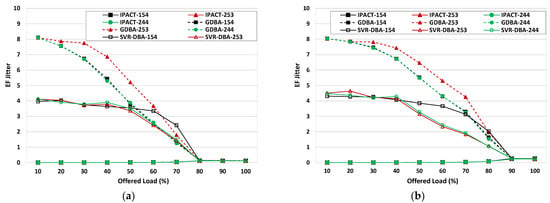
Figure 6.
EF jitter for different scenarios. (a) EF jitter for 1.0 ms cycle time; (b) EF jitter for 1.5 ms cycle time.
4.3. Packet Loss
Packet loss depends on two important factors: the cycle time and the ONU buffer size. A longer cycle time and a larger ONU buffer size decreases packet loss, however, the delay is also increased. For EF and AF traffic, the SVR-DBA and GDBA feature no packet loss for all scenarios as a result of the high priority that is assigned to EF and AF traffic. However, packet loss occurs for BE traffic for the SVR-DBA, GDBA and IPACT as priority is lower. Figure 7 shows the simulation results of the SVR-DBA, GDBA, and IPACT for different traffic loads and maximum cycle times. The SVR-DBA has slightly greater packet loss for all scenarios, however, the packet loss rate is close to the packet loss rates for the other two schemes.
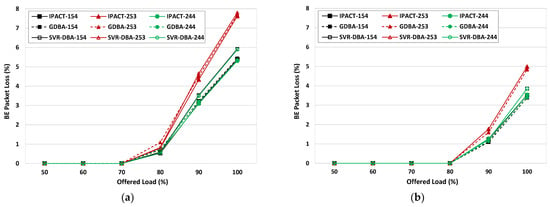
Figure 7.
BE packet loss for different scenarios: (a) BE packet loss for 1.0 ms cycle time; (b) BE packet loss for 1.5 ms cycle time.
4.4. Energy Savings
Figure 8 shows the energy savings for different traffic loads. The SVR-DBA, LR-DBA, and GDBA schemes consume less power than the IPACT for a traffic load of less than 80% and a cycle time of 1.0 ms. The SVR-DBA outperforms the GDBA if the traffic load is between 20% and 80% and it outperforms the LR-DBA for almost all cases. It also consumes 47% less power than the IPACT.
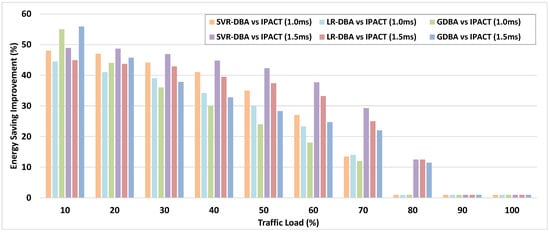
Figure 8.
Average energy consumption improvements of SVR-DBA, LR-DBA, and GDBA for 1.0 ms and 1.5 ms cycle times.
For a cycle time of 1.5 ms, the SVR-DBA also outperforms the GDBA if the traffic load is between 20% and 90% and it outperforms the LR-DBA in all the cases. It consumes 49% less power consumption than the IPACT. The GDBA performs best for a traffic load of less than 20% although the experimental results show that the GDBA has a higher priority packet delay and more jitter than the SVR-DBA. For moderate traffic loads, the experimental results show that the SVR-DBA achieves the best energy savings with a slightly higher packet loss.
The SVR-DBA achieves energy savings as the SVR model accurately predicts the doze mode decisions of and . Therefore, the SVR-DBA outperforms the LR-DBA in nearly all cases as the SVR model more accurately predicts the doze mode than the logistic regression model in the LR-DBA. For a traffic load between 20% and 80%, SVR-DBA also outperforms the GDBA as the SVR model is effectively trained. However, for a traffic load of less than 20%, the effectiveness of the SVR model is compromised as there is a wide variation in the arrival times of the historical REPORT messages. The LR-DBA is also less efficient for the same reason. The GDBA achieves the best energy savings in this situation as its averaging scheme for bandwidth allocation has smoother variations.
5. Conclusions
Energy saving is an important issue for EPONs. This study presents an energy saving doze mechanism for an EPON that uses an SVR model to more accurately predict the presence of high priority traffic and to determine the doze duration. The doze manager trains an SVR model using the historical REPORT messages to determine the doze durations to fulfil the QoS requirements and uses the SVR-DBA to allocate bandwidth to an active ONU. The simulation results show that the proposed mechanism decreases power consumption significantly while fulfilling the QoS requirements in terms of delay, jitter and packet loss. Future study will implement the SVR model in the downstream direction to achieve greater energy savings for the EPON. The proposed scheme requires optimization of the parameters so meta-heuristic optimization schemes will be considered, such as Swarm intelligence algorithms [35] and the Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm [36]. The current system model focuses on three general types of network traffic: EF, AF, and BE. Future study will include various network characteristics for different types of network traffic to determine whether greater energy savings can be achieved. As the EPON technology is developed at high network speeds, the optimization of the predictive models will be further investigated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-Z.Y.; Data curation, M.A.L.; Supervision and Funding, I.-S.H.; Methodology, A.N.; Software and Validation, M.S.A.-R.; Formal Analysis, A.T.L.; Writing—Review and Editing, E.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
MOST 109-2221-E-155-029-MY2.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Van Heddeghem, W.; Lambert, S.; Lannoo, B.; Colle, D.; Pickavet, M.; Demeester, P. Trends in worldwide ICT electricity consumption from 2007 to 2012. Comput. Commun. 2014, 50, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, Y.; Bi, M.; Zhai, Y.; Chi, H.; Wang, Y. Study on the solutions to heterogeneous onu propagation delays for energy-efficient and low-latency EPONs. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193665–193680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaini, A.R.; Ho, P.; Shen, G. Toward green next-generation passive optical networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2011, 49, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaz, S.H.S.; Cuevas, A.; Lee, G.M.; Crespi, N.; Choi, J.K. Improving energy saving in time-division multiplexing passive optical networks. IEEE Internet Comput. 2013, 17, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.; Mukherjee, B.; Pesavento, G. Interleaved polling with adaptive cycle time (IPACT): A dynamic bandwidth distribution scheme in an optical access network. Photonic Netw. Commun. 2002, 4, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.-S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lai, K.R.; Liem, A.T. Generic QoS-aware interleaved dynamic bandwidth allocation in scalable EPONs. IEEE/OSA J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2012, 4, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, R.A.; Idrus, S.M.; Zulkifli, N.; Ashraf, M.W. A survey of energy conservation schemes for present and next generation passive optical networks. J. Commun. 2018, 13, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kani, J. Power saving techniques and mechanisms for optical access networks systems. J. Lightwave Technol. 2013, 31, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirafuji, R.O.C.; da Cunha, K.B.; Campelo, D.R.; Dhaini, A.R.; Khotimsky, D.A. The watchful sleep mode: A new standard for energy efficiency in future access networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-P.; Wu, H.-T.; Ke, K.-W. The QoS provisioning tri-mode energy saving mechanism for EPON networks. Photonic Netw. Commun. 2017, 33, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoukar, A.; Hwang, I.-S.; Su, Y.-M.; Liem, A.T. An adaptive two-stage energy-efficiency mechanism for the doze mode in EPON. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2016, 30, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoukar, A.; Hwang, I.-S.; Wang, C.-J.; Ab-Rahman, M.S.; Liem, A.T. A SIEPON based transmitter sleep mode energy-efficient mechanism in EPON. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2015, 23, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.-S.; Nikoukar, A.; Su, Y.-M.; Liem, A.T. Decentralized SIEPON-based ONU-initiated Tx/TRx energy-efficiency mechanism in EPON. IEEE/OSA J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2016, 8, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoukar, A.; Hwang, I.-S.; Liem, A.T.; Wang, C.-J. QoS-aware energy-efficient mechanism for sleeping mode ONUs in enhanced EPON. Photonic Netw. Commun. 2015, 30, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfolahi, M.; Yang, C.-Z.; Hwang, I.-S.; Nikoukar, A.; Wu, Y.-H. A predictive logistic regression based doze mode energy-efficiency mechanism in EPON. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2018, 101, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-P.; Wu, H.-T.; Yu, P.-Y.; Ke, K.-W. An energy-saving scheme of TWDM-PON system for NG-EPON networks. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Next Generation Electronics (ISNE), Taipei, Taiwan, 7–9 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, R.A.; Idrus, S.M.; Qureshi, K.N.; Shah, P.M.A.; Zulkifli, N. An energy efficient cyclic sleep control framework for ITU PONs. Opt. Switch. Netw. 2018, 27, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, H.; Burges, C.J.C.; Kaufman, L.; Smola, A.J.; Vapnik, V. Support vector regression machines. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denvor, CO, USA, 2–5 December 1996; pp. 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.-H.; Lin, C.-J. Large-scale linear support vector regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 3323–3348. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, R.A.; Ashraf, M.W.; Anwar, M.Y.; Anwar, M. Receiver on time optimization for watchful sleep mode to enhance energy savings of 10-gigabit passive optical network. Tech. J. Univ. Eng. Technol. (UET) 2018, 23, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zin, A.M.; Idrus, S.M.; Ramli, A.; Butt, R.A.; Atan, F.M.; Ismail, N.A. Performance evaluation of XG-PON with DBA based-watchful sleep mode. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Conference on Photonics (ICP 2018), Langkawi, Malaysia, 9–11 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pakpahan, A.F.; Hwang, I.-S. Enabling flexible software-defined energy-efficientorchestration in TWDM-PON. J. Internet Technol. 2020, 21, 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan, E.; Hwang, I.-S.; Liem, A.T.; Ab-Rahman, M.S. 5G-enabled tactile internet resource provision via software-defined optical access networks (SDOANs). Photonics 2021, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SafaeiSisakht, M.; Nikoukar, A.; Goudarzi, H.; Hwang, I.-S.; Liem, A.T. Lattice based EPON energy-saving scheme analysis. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2020, 57, 102243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfias, P.; De Andrade, M.; Tornatore, M.; Buttaboni, A.; Sallent, S.; Gutiérrez, L. Energy-saving mechanism in WDM/TDM-PON based on upstream network traffic. Photonics 2014, 1, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awad, M.; Khanna., R. Support vector regression. In Efficient Learning Machines: Theories, Concepts, and Applications for Engineers and System Designers; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, L.; Tsimhoni, O.; Liu, Y. Using the support vector regression approach to model human performance. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2011, 41, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ameri, A.; Kamavuako, E.N.; Scheme, E.J.; Englehart, K.B.; Parker, P.A. Support vector regression for improved real-time, simultaneous myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Diabat, A. A comprehensive survey of the grasshopper optimization algorithm: Results, variants, and applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 15533–15556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L. Group search optimizer: A nature-inspired meta-heuristic optimization algorithm with its results, variants, and applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 2949–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yang, H. Unlocking the Power of OPNET Modeler; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sethi, A.S.; Hnatyshin, V.Y. The Practical OPNET User Guide for Computer Network Simulation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.; Filsfils, C. Deploying IP and MPLS QoS for Multiservice Networks: Theory and Practice; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Abualigah, L.; Shehab, M.; Diabat, A.; Abraham, A. Selection scheme sensitivity for a hybrid salp swarm algorithm: Analysis and applications. Eng. Comput. 2020, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Diabat, A.; Mirjalili, S.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Gandomi, A.H. The arithmetic optimization algorithm. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 376, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).