Fabrication of Modified Random Phase Masks with Phase Modulation Elements Exhibiting Gaussian Profiles Using Molecular Migration under Photopolymerization
Abstract
1. Introduction
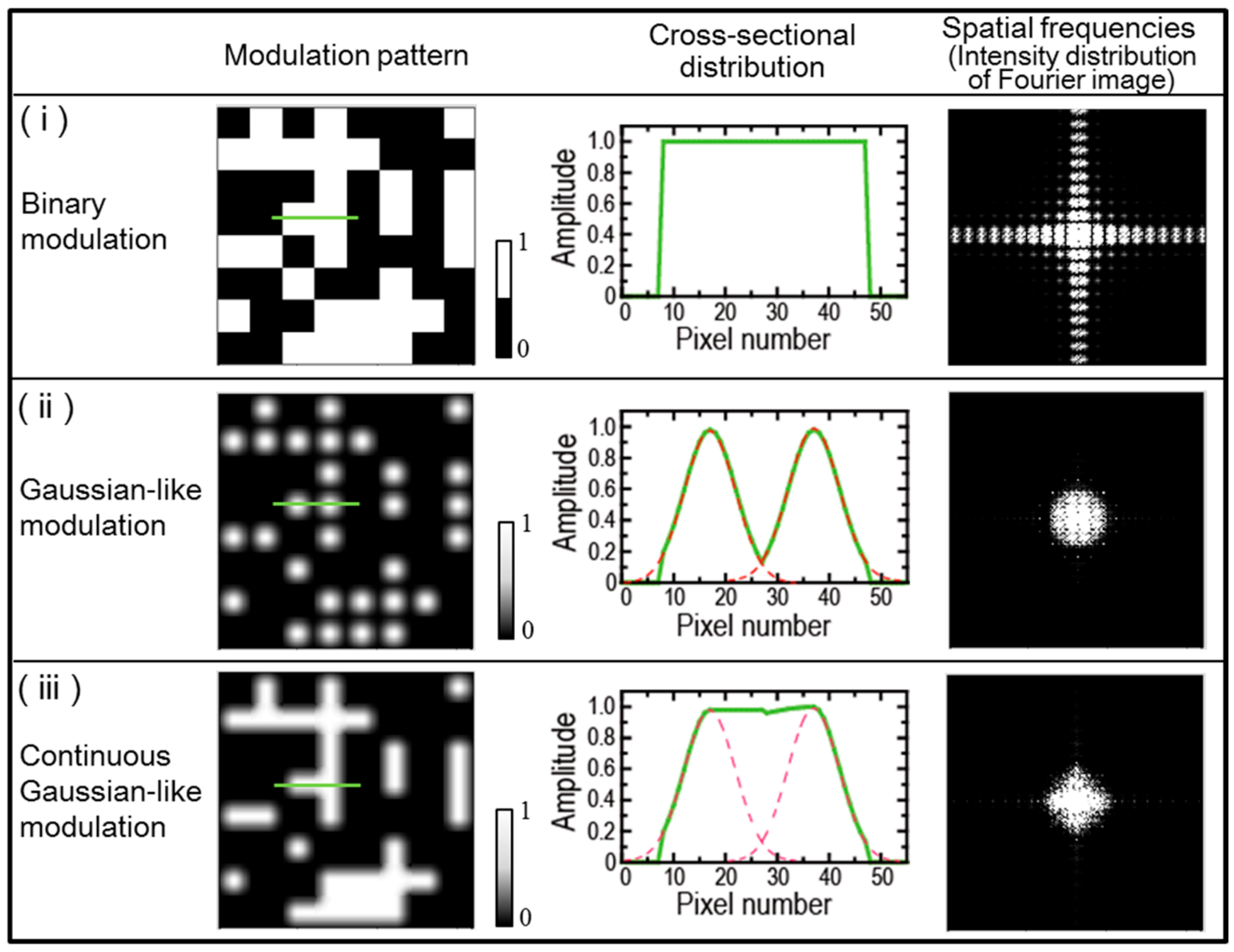
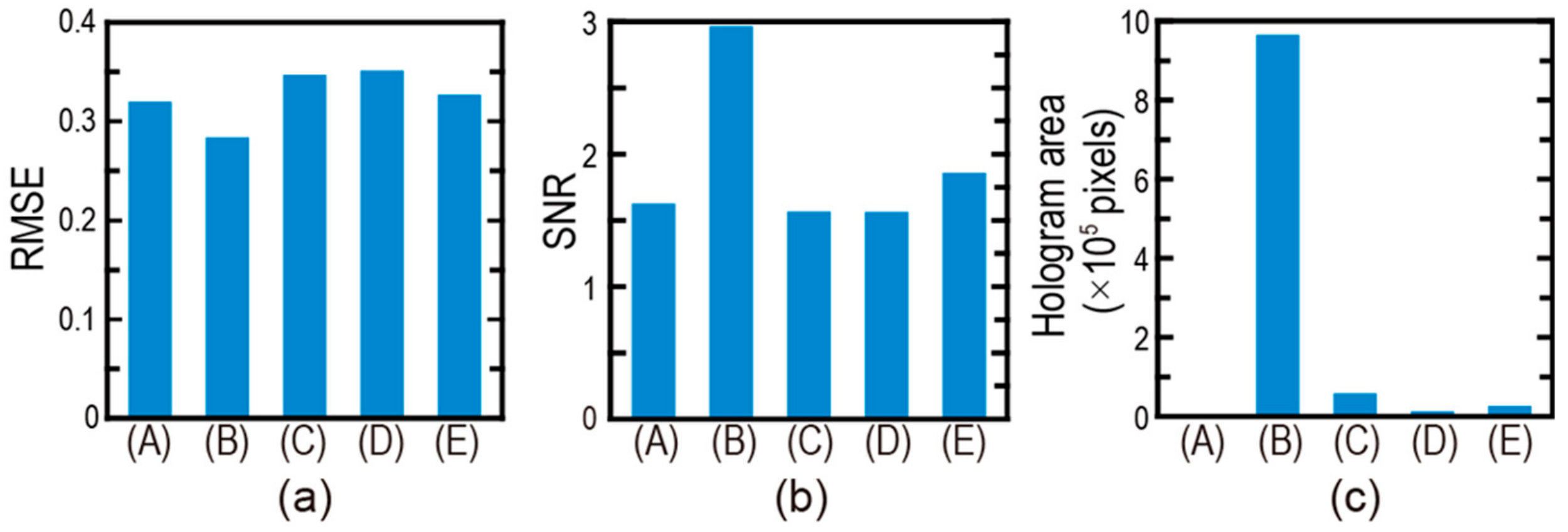
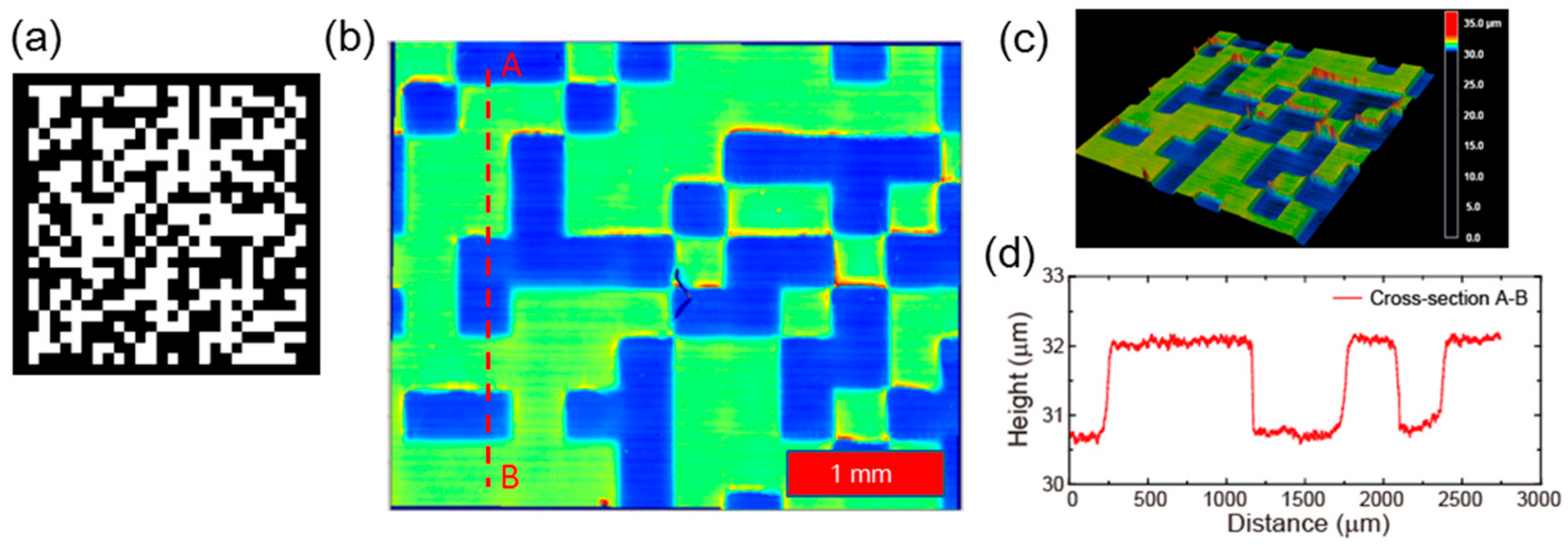
2. Preliminary Investigation on the Effectiveness of the Proposed Random Phase Mask
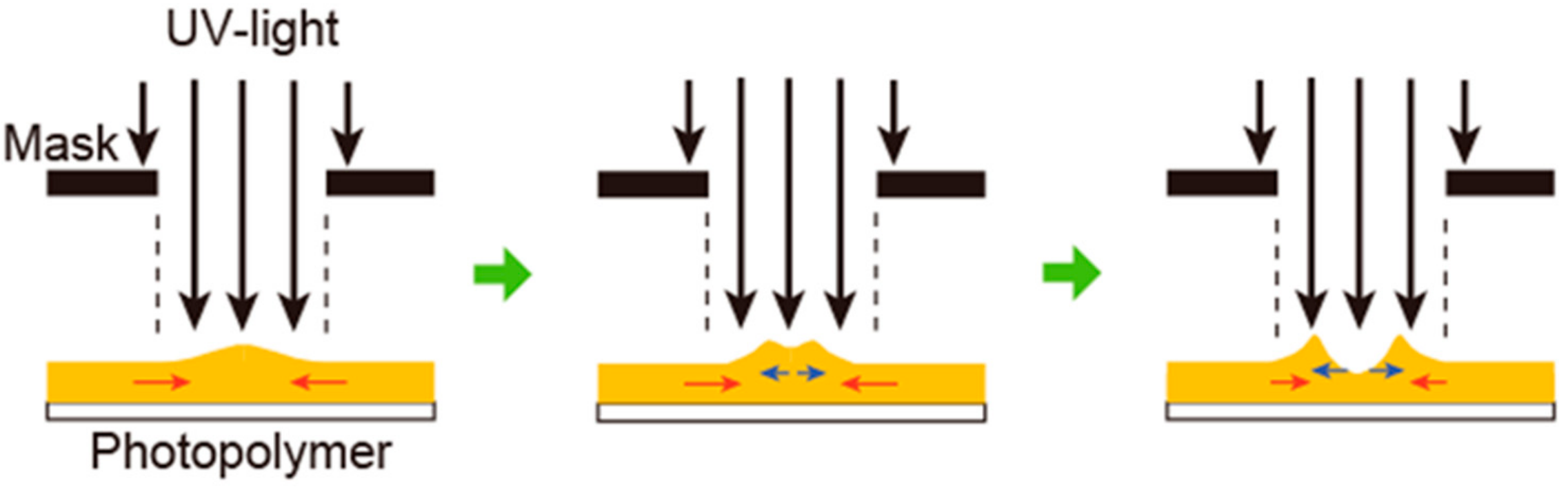
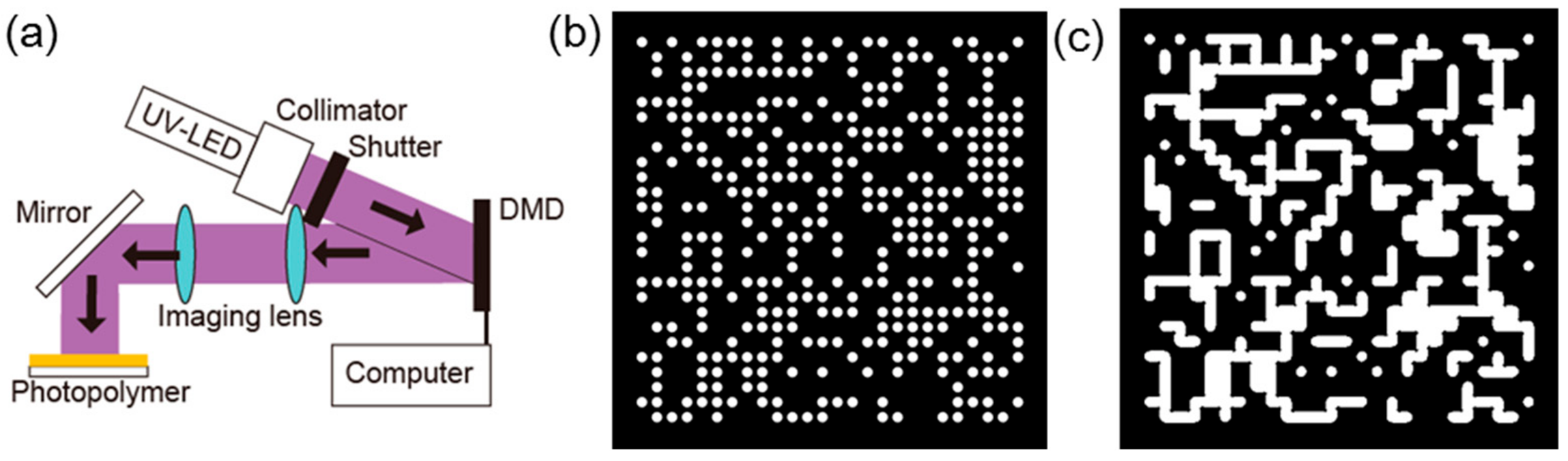
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Conventional Fabrication of a Random Phase Mask
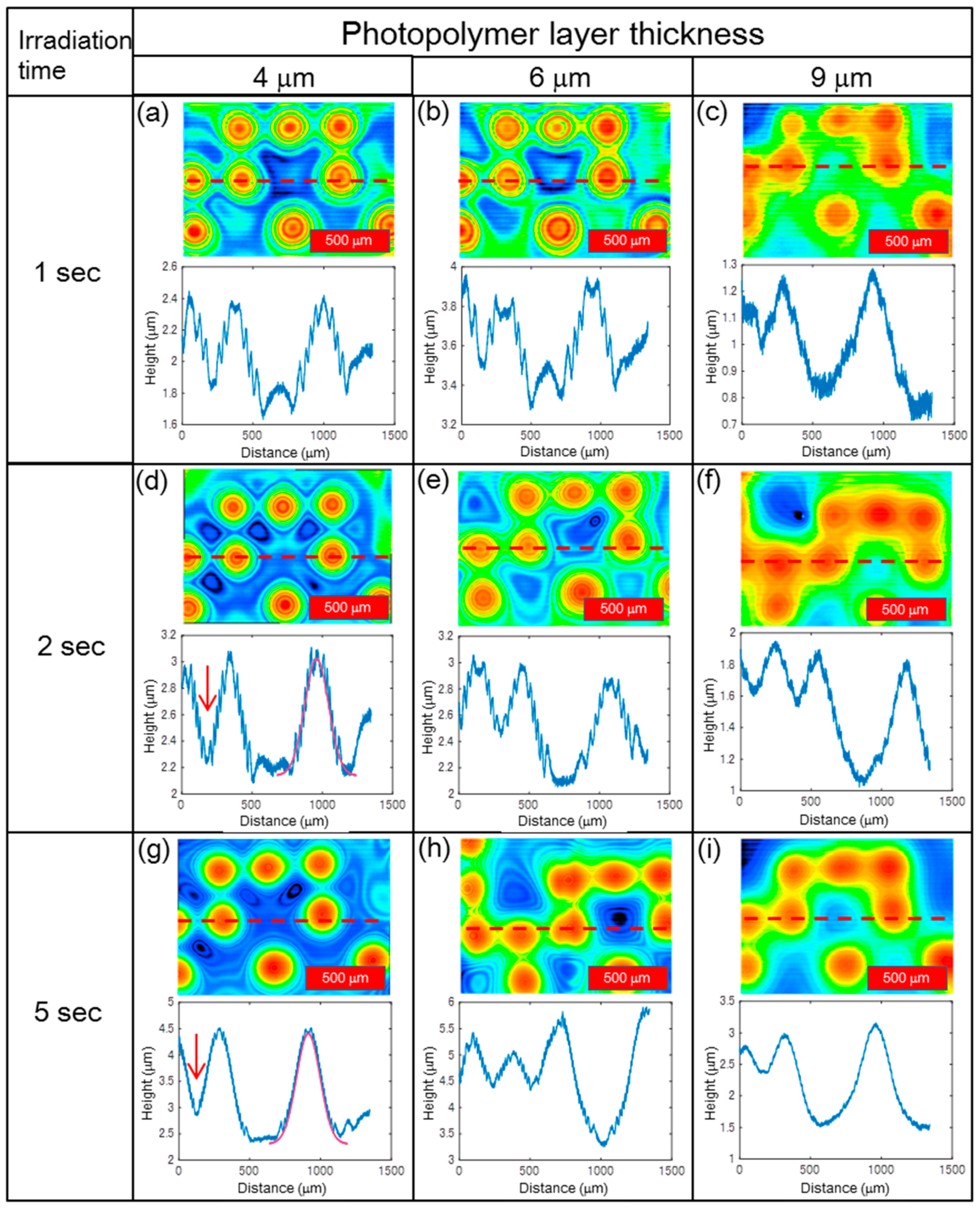
4.2. Gaussian-Like Random Phase Modulation Mask
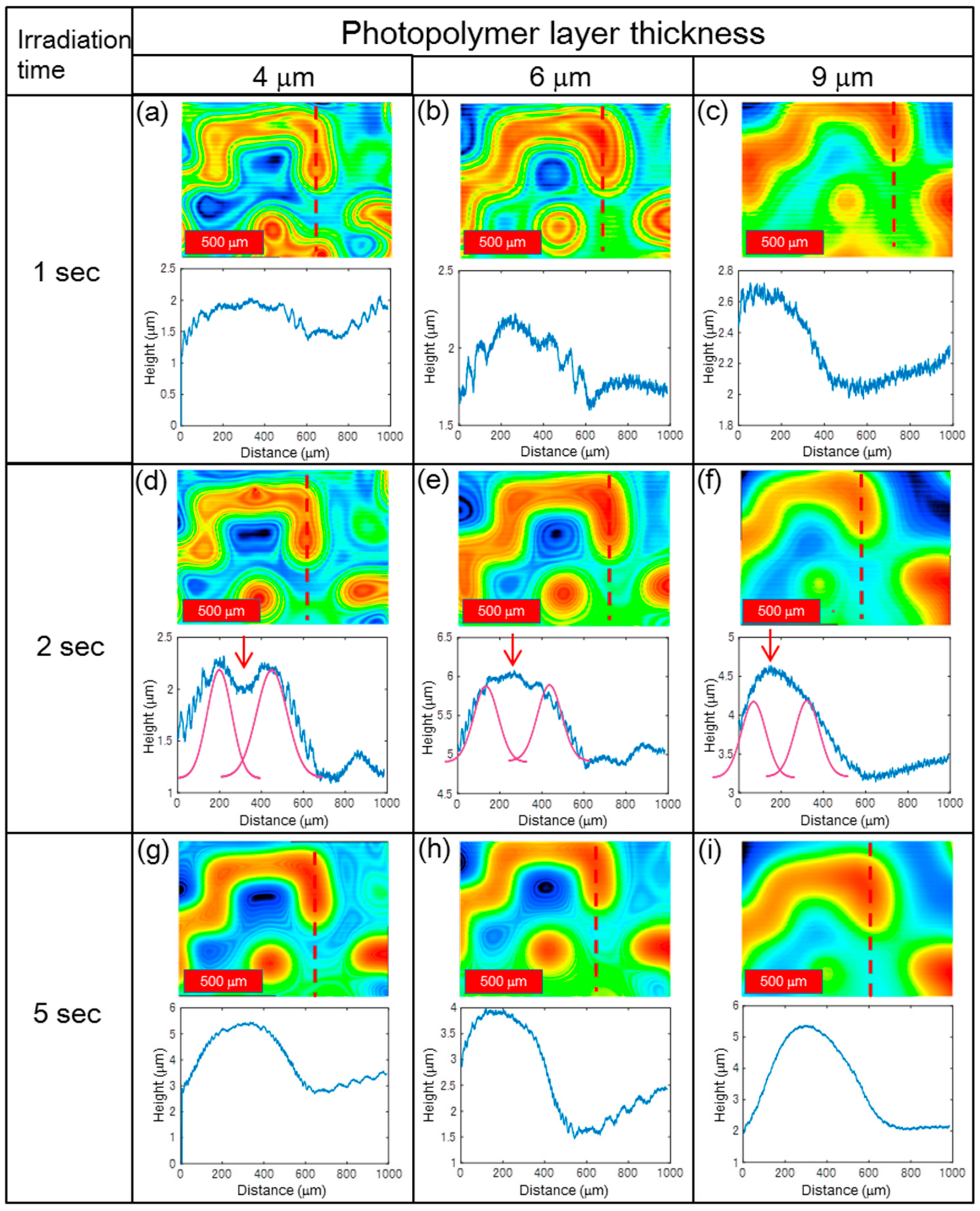
4.3. Continuous Gaussian-Like Random Phase Modulation Mask
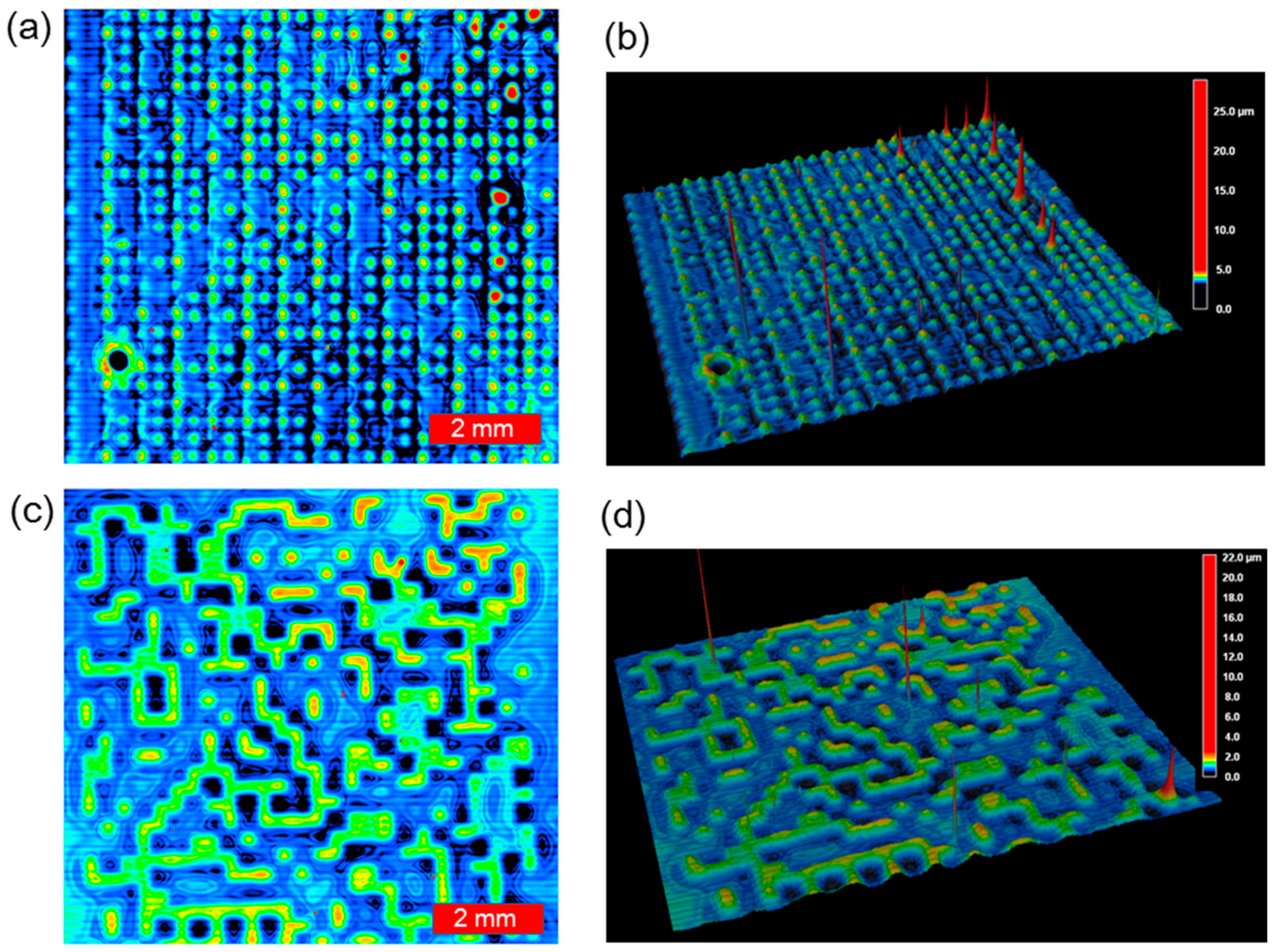
4.4. Large-Area Formation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, B. Some aspects of a large capacity holographic memory. Appl. Opt. 1972, 11, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, A.; Psaltis, D. High-density recording in photopolymer-based holographic three-dimensional disks. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; Jefferson, C.M.; Bernal, M.-P.; Marcus, B.; Burr, G.W.; Macfarlane, R.M.; Coufal, H.; Shelby, R.M.; Guenther, H.; Sincerbox, G.T.; et al. Holographic data storage. IBM J. Res. Develop. 2000, 44, 341–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Oshida, Y.; Miyamura, Y. Random phase shifters for Fourier transformed holograms. Appl. Opt. 1972, 11, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, F.H. Angle-multiplexed storage of 5000 holograms in lithium niobate. Opt. Lett. 1993, 18, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psaltis, D.; Levene, M.; Allen, P.; Barbastathis, G. Holographic storage using shift multiplexing. Opt. Lett. 1995, 20, 782–784. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; McMichael, I.; Ma, J. Influence of phase masks on cross talk in holographic memory. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1694–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashaw, M.C.; Hesselink, L. Digital wavelength-multiplexed holographic data storage system. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1780–1782. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Kostuk, R. Improvement to holographic digital data-storage system with random and pseudorandom phase masks. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 4853–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder, F.-K.; Hagen, R.; Rölle, T.; Weiser, M.-S.; Fäcke, T. From the surface to volume: Concepts for the next generation of optical-holographic data-storage materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4552–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimobaba, T.; Ito, T. Random phase-free computer-generated hologram. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 9549–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, K.; Hosaka, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Onoe, S.; Ide, T. Technique for positioning hologram for balancing large data capacity with fast readout. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 56, 09NA04-1–09NA04-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Kang, L.; Han, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y. UV-resistant holographic data storage in noble-metal/semiconductor nanocomposite films with electron acceptors. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horimai, H.; Tan, X.; Li, J. Collinear holography. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 2575–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Hara, M.; Tokuyama, K.; Hirooka, K.; Ishioka, K.; Fukumoto, A.; Watanabe, K. Improved performance in coaxial holographic data recording. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 16196–16209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-C.; Yu, Y.-W.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Teng, T.-C.; Tsai, M.-F. Point spread function of a collinear holographic storage system. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 18111–18118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Sun, C.-C. Increase of signal-to-noise ratio of a collinear holographic storage system with reference modulated by a ring lens array. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobukawa, T.; Nomura, T. Design of high-resolution and multilevel reference pattern for improvement of both light utilization efficiency and signal-to-noise ratio in coaxial holographic data storage. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 3773–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Horimai, H.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y.; Tan, X. Phase modulated high density collinear holographic data storage system with phase retrieval reference beam locking and orthogonal reference encoding. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioka, A.; Kurahashi, K. Holographic image formation using phase plates with incoherent imaging property. Appl. Opt. 1976, 15, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal, M.-P.; Burr, G.W.; Coufal, H.; Grygier, R.K.; Hoffnagle, J.A.; Jefferson, C.M.; Oesterschulze, E.; Shelby, R.M.; Sincerbox, G.T.; Quintanilla, M. Effects of multilevel phase masks on interpixel cross talk in digital holographic storage. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Várhegyi, P.; Koppa, P.; Ujhelyi, F.; Lőrincz, E. System modeling and optimization of Fourier holographic memory. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 3024–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, M.; Tanaka, K.; Tokuyama, K.; Toishi, M.; Hirooka, K.; Fukumoto, A.; Watanabe, K. Linear reproduction of a holographic storage channel using coherent addition of optical DC components. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 5885–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Yin, S.; Tan, Q.; Cao, L.; He, Q.; Jin, G. Improving signal-to-noise ratio by use of a cross-shaped aperture in the holographic data storage system. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 6234–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Fujimura, R. Interpixel crosstalk cancellation on holographic memory. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 56, 09NA10-1–09NA10-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobukawa, T.; Barada, D.; Nomura, T.; Fukuda, T. Orthogonal polarization encoding for reduction of interpixel cross talk in holographic data storage. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 22425–22439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, S.; Nobukawa, T.; Barada, D.; Fukuda, T.; Emoto, A. Suppression of inter-pixel cross talk and reduction of recording spot size for high-density holographic memory. Opt. Rev. 2019, 26, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emoto, A.; Fukuda, T. Randomly displaced phase distribution design and its advantage in page-data recording of Fourier transform holograms. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramoto, S.; Fukuda, T.; Emoto, A. Randomly displaced phase distribution design for computer generated binary holograms with narrow recording spots. Opt. Rev. 2018, 25, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burckhardt, C.B. Use of a random phase mask for the recording of Fourier transform holograms of data masks. Appl. Opt. 1970, 9, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croutxé-Barghorn, C.; Lougnot, D.J. Use of self-processing dry photopolymers for the generation of relief optical elements: a photochemical study. Pure Appl. Opt. 1996, 5, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Tamoto, T.; Emoto, A.; Kawatsuki, N. Holographic recording in photoreactive monomer/polym composites. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 1781–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, L.; Sakhno, O.; Stumpe, J. Application of Norland adhesive for holographic recording. Opt. Mater. 2005, 27, 1379–13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, C.; de Gans, B.-J.; Kozodaev, D.; Alexeev, A.; Escuti, M.J.; van Heesch, C.; Bel, T.; Schubert, U. Polymerization-induced diffusion as a tool to generate periodic relief structures: A combinatorial study. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6136, 61360H-1–61360H-12. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, K.; Ichimura, K. Self-developable surface relief photoimaging generated by anionic UV-curing of epoxy resins. Polym. J. 2009, 41, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emoto, A.; Baharim, S.B.; Sasaki, T.; Shioda, T.; Ogiwara, A.; Ono, H. Chronological investigations of Raman-Nath diffraction grating inscribed by direct laser writing in photoreactive monomer base mixtures. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 122502-1–122502-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, A.W.; Paris, D.P. Binary Fraunhofer holograms, generated by computer. Appl. Opt. 1967, 6, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.; Lemonnier, O.; Laulagnet, F.; Fargeix, A.; Tissot, F.; Armand, F. Complementary computer generated holography for aesthetic watermarking. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 5547–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Ishii, Y. Computer-generated hologram fabricated by electron-beam lithography for noise reduction. Opt. Rev. 2012, 19, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wägli, Ph.; Homsy, A.; de Rooij, N.F. Norland optical adhesive (NOA81) microchannels with adjustable wetting behavior and high chemical resistance against a range of mid-infrared-transparent organic solvents. Sen. Actuators B 2011, 156, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baten’kin, M.A.; Mensov, S.N. Optical formation of polymeric materials with heterogeneously distributed nanopores from a photopolymerizable composite. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 64-1–64-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.K.; Dominguez, R.B.; Bhand, S.; Muñoz, R.; Marty, J.-L. A novel automated flow-based biosensor for the determination of organophosphate pesticides in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emoto, A.; Noguchi, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Fukuda, T. Fabrication of submicrometer pores with an outer shell using modified poly(vinyl alcohol) and the molecular or particle collection effect. Langmuir 2013, 29, 12601–12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossipov, D.A.; Hilborn, J. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-based hydrogels formed by “Click Chemistry”. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emoto, A.; Honda, J.; Suzuki, K.; Kimoto, T.; Fukuda, T. Fabrication of Modified Random Phase Masks with Phase Modulation Elements Exhibiting Gaussian Profiles Using Molecular Migration under Photopolymerization. Photonics 2019, 6, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6020062
Emoto A, Honda J, Suzuki K, Kimoto T, Fukuda T. Fabrication of Modified Random Phase Masks with Phase Modulation Elements Exhibiting Gaussian Profiles Using Molecular Migration under Photopolymerization. Photonics. 2019; 6(2):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6020062
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmoto, Akira, Junya Honda, Kou Suzuki, Takumi Kimoto, and Takashi Fukuda. 2019. "Fabrication of Modified Random Phase Masks with Phase Modulation Elements Exhibiting Gaussian Profiles Using Molecular Migration under Photopolymerization" Photonics 6, no. 2: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6020062
APA StyleEmoto, A., Honda, J., Suzuki, K., Kimoto, T., & Fukuda, T. (2019). Fabrication of Modified Random Phase Masks with Phase Modulation Elements Exhibiting Gaussian Profiles Using Molecular Migration under Photopolymerization. Photonics, 6(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6020062




