Abstract
Mangiferin has been reported to exhibit anti-viral, anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, immunomodulatory and hepatoprotective properties. This study aimed to develop an HPLC method to isolate mangiferin from Salacia chinensis L. root; investigate the impact of solvents on yield; optimise the ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) technique; and compare mangiferin yield with continuously shaking extraction (CSE) and decoction techniques. The results showed that mangiferin, with a purity of over 88%, could be achieved by HPLC using a mixture of solvent A (water: acetonitrile: orthophosphoric acid, 96.8:3:0.2 (v/v/v)) and solvent B (acetonitrile). Solvent type significantly affected the extraction yield of mangiferin, and a mixture of acetone and water gave the highest extraction yield, as compared to other solvents or mixtures. UAE conditions, such as ultrasonic power, temperature, time and concentration of acetone significantly affected the extraction of mangiferin. Optimal UAE conditions were at an ultrasonic power of 250 W, temperature of 50 °C, acetone concentration of 40% and extraction time of 60 min. These optimal conditions could extract approximately 92 mg, whereas CSE and decoction only extracted 89.20 mg and 58.71 mg of mangiferin, respectively, from 1 g of S. chinensis root. Therefore, these UAE conditions are recommended for the extraction of mangiferin from S. chinensis root for further utilisation.
1. Introduction
Mangiferin (1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone-C2-β-d glucoside) is a xanthone glucoside (polyphenol) found primarily in mango (Mangifera indica) [1]. Mangiferin is considered as a “super antioxidant”, and has attracted the interest of researchers around the world. Over 450 articles have been published on its occurrence, chemical nature, synthesis and medicinal properties over the last 50 years [2,3]. It has been found to exhibit anti-viral, anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, anti-aging, immunomodulatory, hepatoprotective and analgesic properties [4].
Mangiferin-containing plant materials, such as mango, honeybush tea (Cyclopia spp.) and Salacia chinensis, have been used as traditional medicine for the prevention and treatment of numerous ailments [1]. S. chinensis in particular has been traditionally used for the treatment of arthritis, inflammation, diabetes, obesity, liver disorder and certain cancers [5,6], with mangiferin reported as one of the major bioactive component in the root of S. chinensis [5,7].
The extraction process is an essential step to separate bioactive compounds from more complex plant materials. According to literature, extraction technique is a key factor that significantly influences the yields of phytochemicals [8,9,10,11,12]. For example, Nayak et al. (2015) found that the employment of different extraction methods resulted in the variation of the recovery efficiency of total phenolics, antioxidant activities as well as concentration of individual compounds in Citrus sinensis peels [13]. In addition, solvent type and concentration have also been reported to play an important role in the extraction process [8,14,15,16].
Although several extraction solvents and extraction techniques have been previously tested for the extraction of mangiferin [7,17,18], optimal conditions for maximum extraction of mangiferin from S. chinensis root have not been reported. Therefore, the aim of this study was to isolate and identify mangiferin in the root of S. chinensis; compare the impact of solvent type and concentration on the extraction efficiency of mangiferin; optimise the ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) conditions; and finally compare the extraction efficiency of UAE, as an advanced extraction technique, with two other common conventional extraction techniques, continuously shaking extraction (CSE) and decoction.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
S. chinensis L. root was collected in Nghe an province (Vietnam) and authenticated by A/Prof Vu Quang Nam, Department of Forest Plant Resources, College of Forestry Biotechnology, Vietnam National University of Forestry in March 2016. The voucher specimen of this plant material can be found in the Herbarium of Institute of Medicinal Materials, Ha Noi (SA 611/04). The root was then cut, sun-dried for 2 days and ground to a fine powder using a commercial cutter. The powder was sieved (steel mesh sieve 1.4 mm, EFL 2000; Endecotts Ltd., London, UK) and stored at −20 °C until required for analysis.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Experimental Design
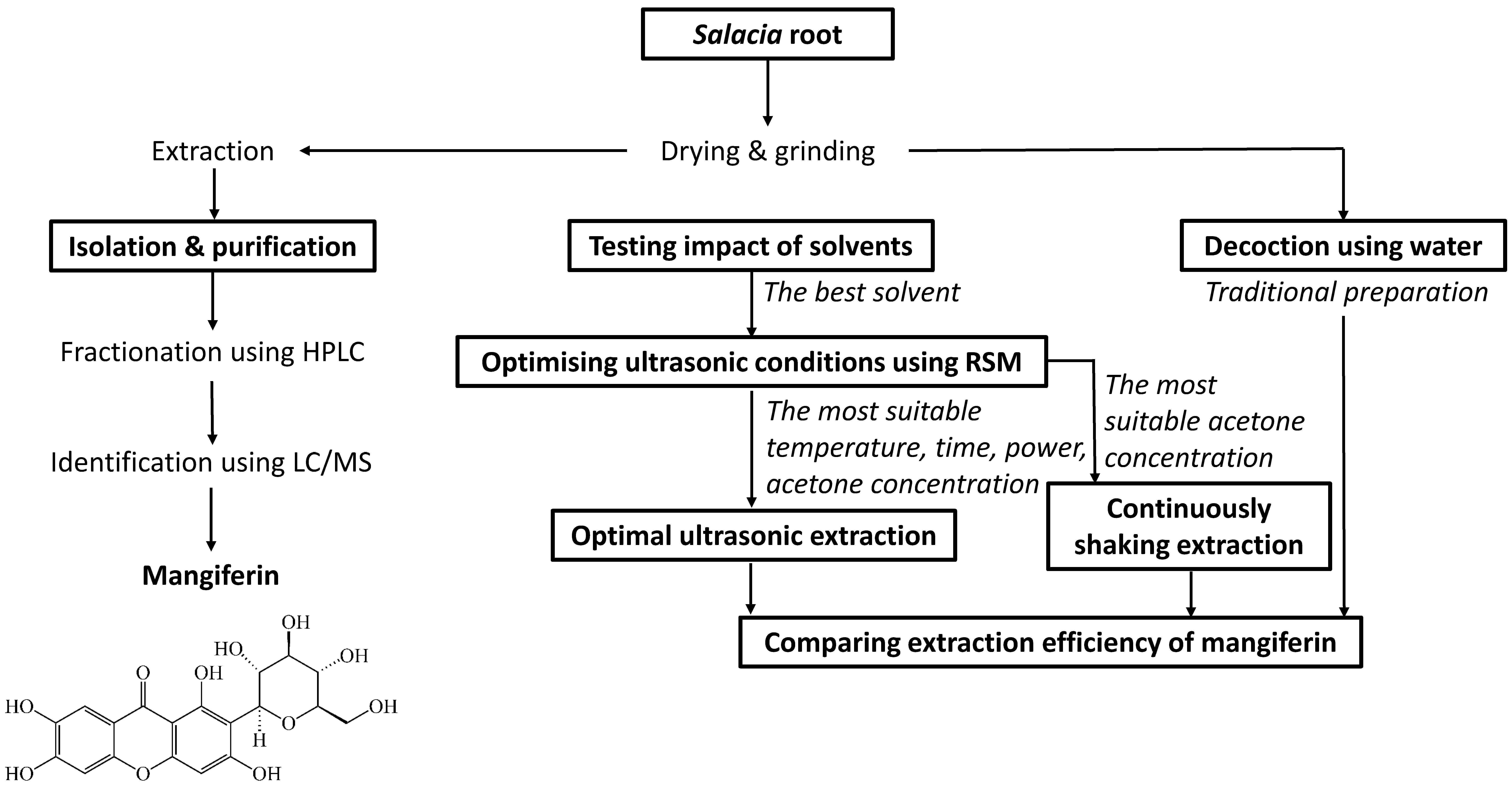
The overall design of this study is shown in Figure 1. Mangiferin was isolated from the UAE extract of the S. chinensis root using HPLC connected with an auto-fraction collector and was then confirmed via LC/MS. A range of solvents were then tested to determine the most suitable solvent for mangiferin extraction. This solvent was then used for optimising extraction conditions using ultrasound-assisted extraction with Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Optimal acetone concentration from RSM was further applied in continuously shaking extraction for comparison. A traditional extraction method, known as decoction using water, was also applied for comparison of the extraction efficiency of mangiferin with optimal ultrasonic extraction and continuously shaking extraction. The best extraction conditions to yield the greatest quantity were then identified for mangiferin from S. chinensis root.
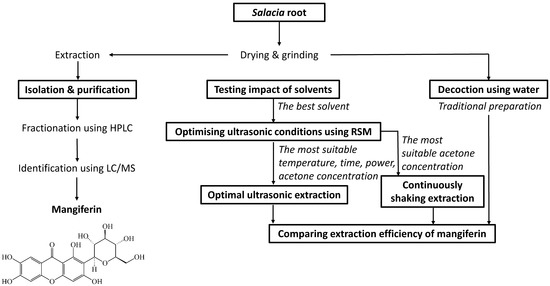
Figure 1.
Experimental design for maximising extraction of mangiferin from S. chinensis root.
2.2.2. Isolation and Identification of Mangiferin in S. chinensis Root Extract
To identify mangiferin in S. chinensis root extract, the S. chinensis root (2 g) was extracted in 100 mL of 50% ethanol using an ultrasonic bath (Soniclean 1000HD, 220 V, 50/60 Hz and 250 W, Soniclean Pty Ltd., Thebarton, SA, Australia) set at 50 °C and 150 W for 60 min. The extract was cooled and then filtered using a Phenex Syringe filter 0.45 µm. The extract was then subjected to the Shimadzu HPLC system (M20, Shimadzu Australia, Rydalmere, NSW, Australia) connected with the EC-C18 reversed-phase column (3.0 × 150, 4 µm, Agilent Technologies Pty Ltd., Santa Clara, CA, USA). The mobile phase consisted of solvent A (a mixture of water: acetonitrile: orthophosphoric acid, 96.8:3:0.2 (v/v/v)) and solvent B (acetonitrile). A gradient elution schedule was used as follows: 100% A from 0 to 3 min; 100% B from 3 to 6 min; a linear gradient from 100% A to 100% B from 6 to 20 min and remained at 100% B to 25 min; and 100% A from 25 to 30 min before the next injection. The volume of injection was 20 µL, and the flow rate was 1 mL/min. The column was kept in an oven with the temperature maintained at 28 °C. The detector was set at 254 nm.
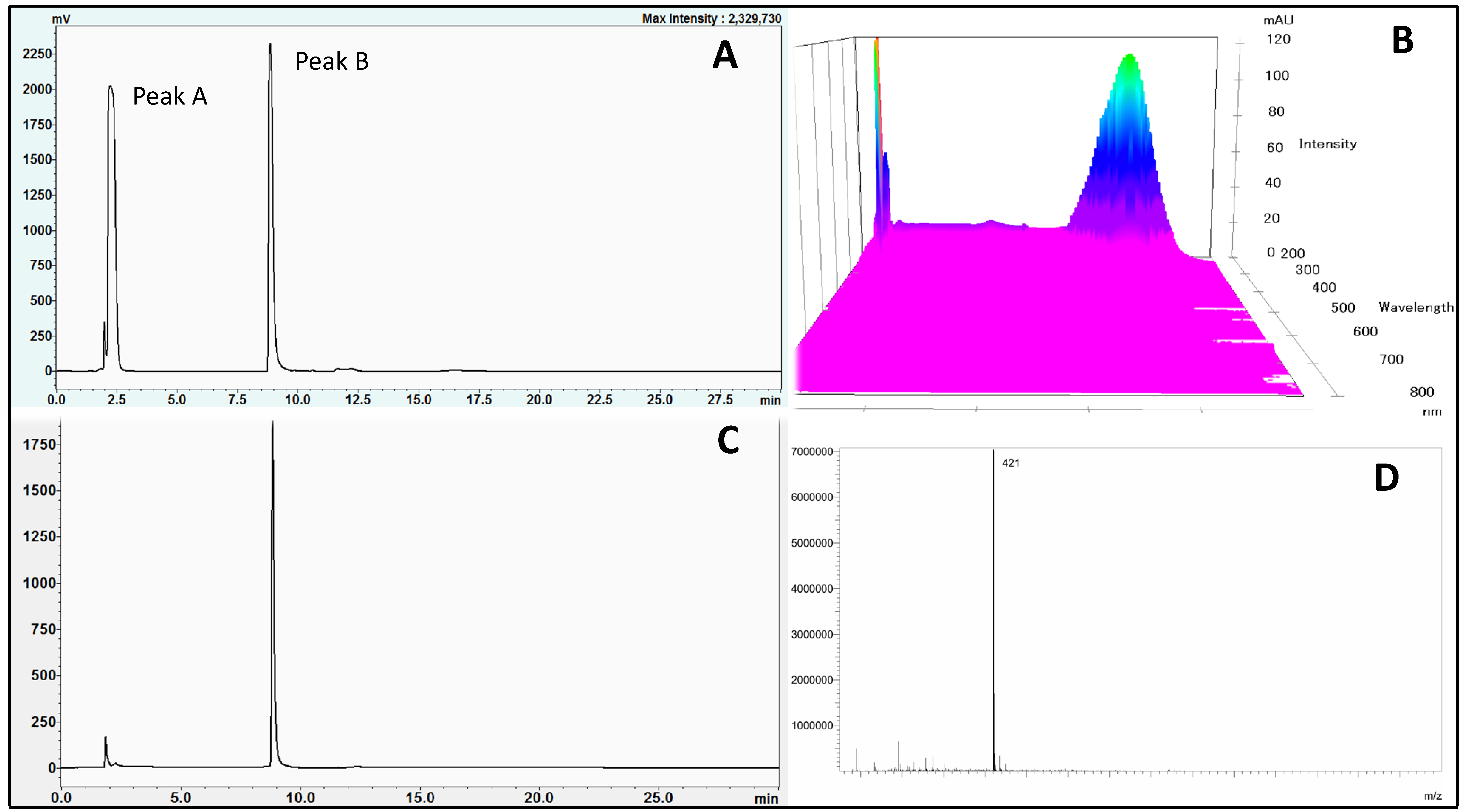
The chromatogram of the S. chinensis root extract with major peaks is shown in Figure 2A. Based on the retention time, peaks A and B were fractionated using an auto-fraction collector and then freeze-dried to a powder form. The fractions A and B (peaks A and B) were then identified according to the method described previously by Muraoka et al. [19] with some minor modifications using a Shimadzu LC/MS (LCMS 2020, Shimadzu Australia, Rydalmere, NSW, Australia) coupled with an electrospray ionization (ESI) interface. The mobile phase including solvents A and B as earlier described was delivered at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min. The volume of injection was 10 µL. The mass spectrometer was operated at negative mode with selected ion monitoring (SIM) and the parameters as follows: nebulizing gas (nitrogen) flow 1.5 L/min, drying gas pressure 0.15 MPa, CDL temperature 250 °C, and block heater temperature 200 °C.
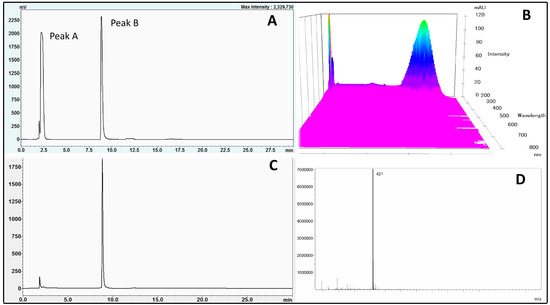
Figure 2.
HPLC chromatogram of S. chinensis crude extract (A), wavelength spectrum (190–700 nm) (B), isolated mangiferin (C) and mass spectrum of mangiferin (D).
2.2.3. Impact of Different Solvents on Recovery of Mangiferin
Seven solvents were used for testing their impact on the extraction efficiency of mangiferin from S. chinensis root. These solvents were water (polarity index, PI 10.2), absolute methanol (PI 5.1), absolute ethanol (PI 4.3), absolute acetone (PI 5.1), methanol 50%, ethanol 50% and acetone 50%.
Extraction was performed by firstly adding 0.5 g of the sample into 25 mL of each solvent (sample/solvent ratio 1:50 g/mL), then extracting using an ultrasonic bath set at the same conditions as described in Section 2.2.2. The extract was then filtered and subjected onto the HPLC system for determination of mangiferin using the HPLC method described in Section 2.2.2. Mangiferin was quantified using a standard curve prepared from mangiferin standard (Sigma Aldrich, Australia) with different concentrations (0.25–2 mM) (Ymangiferin = 0.1507X − 241.368, Ymangiferin is the concentration of mangiferin in mM, X is the area in Volts, R2 = 0.987). The best solvent (acetone 50%) was then used for optimising ultrasonic extraction.
2.2.4. Optimisation of UAE Conditions for Recovery of Mangiferin
To optimise ultrasonic extraction conditions, Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was employed to design, analyse and determine the best conditions for temperature, time, ultrasonic power and water to acetone ratio (acetone concentration). JMP Pro software (version 14.2.0, 64-bit, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was employed for RSM experimental design using a three-level, four-factorial, Box–Behnken methodology design. Four factors were applied with the following ranges: acetone concentration (40–70%), time (30–60 min), extraction temperature (30–50 °C) and power (150–250 W). The sample (2 g) was extracted in 100 mL of solvent with experimental conditions as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Box-Behnken design and experimental results.
For the prediction of the optimal conditions, a second order polynomial Equation (1) was used to evaluate the relationship between variables and mangiferin concentration (Y):
where X1: power; X2: temperature, X3: solvent concentration and X4: time; β0: intercept; β1, β2, β3 and β4: linear regression coefficients; β12, β13, β23, β14, β24 and β34: interaction regression coefficients; and β11, β22, β33 and β44: quadratic regression coefficients.
Y = β0 + β1X1 + β2X2 + β3X3 + β4X4 + β12X1 X2 + β13X1 X3 + β14X1 X4 + β23X2 X3 + β24X2 X4 +
β34X3 X4 + β11X12 + β22X22 + β33X32 + β44X42
β34X3 X4 + β11X12 + β22X22 + β33X32 + β44X42
2.2.5. Continuously Shaking Extraction
Continuously shaking extraction (CSE) was conducted as previously described by Chavan et al. [20] with minor modifications. Optimal acetone concentration (40%) identified from RSM was further applied in CSE. Briefly, 0.5 g of S. chinensis root was added into 25 mL acetone 40%. The extraction was then performed on an orbital shaker for 24 h at ambient temperature. Subsequently, the extract was filtered (Phenex Syringe filter, 0.45 µm, Phenomenex Australia, Lane Cove West NSW, Australia), collected and subjected to HPLC analysis for the determination of mangiferin concentration as described in Section 2.2.2.
2.2.6. Decoction
Decoction of the S. chinensis L. root was conducted similar to a previous study by Karunanayake and Sirimanne [17]. Briefly, 10 g of sample was added into 500 mL DI water (sample/solvent ratio 1:50 g/mL). The mixture was then put in a small container and boiled for 3 h. Subsequently, the extract was filtered (Phenex Syringe filter, 0.45 µm, Phenomenex Australia, Lane Cove West NSW, Australia), collected and subjected to HPLC analysis for determination of the mangiferin concentration.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
JMP Pro version 14.2.0 (64-bit, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was employed for RSM design and statistical analysis in this study. Extraction was conducted in triplicates for each experiment. Data were reported as means ± standard deviations. Differences between the mean levels of the components in the different experiments were taken to be statistically significant at p < 0.05 using Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test. Two-dimensional and 3D contour plots of variable responses, as well as the predictive optimal values and extraction conditions of four independent variables, were generated by the program.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Mangiferin in S. chinensis Root Extract
Figure 2A,B shows the chromatogram and major phytochemical components as well as their major absorbances from the extract of S. chinensis root. These results revealed that S. chinensis root had two major compounds, which were referred to as peak A and peak B. The scanning of absorbance from 190 nm to 700 nm (using PDA detector, Figure 2B) indicated that these compounds had maximum absorbance values in the range of 254 nm. Peak B was then isolated using a Shimadzu auto-fraction collector collected from 8.5 min to 10 min. The fraction was then freeze-dried to get a yellow amorphous powder. Subsequently, the compound was reconstituted in methanol and subjected to LC/MS with negative polarity mode. The chromatogram (Figure 2C) and the mass spectrum (Figure 2D) showed that only a peak was detected with purity of 88.5% and m/z 421. From its physical property (yellow amorphous powder form) and molecular mass (422), the compound (peak B) was identified as mangiferin. Therefore, this study illustrated and confirmed that mangiferin is a major active component in S. chinensis [17,21].
3.2. Impact of Type of Solvent on the Yield of Mangiferin
It was hypothesised that the extraction of mangiferin from S. chinensis root could be influenced by solvent type. Seven common solvents were tested, with the results (Table 2) showing that solvent type did significantly affect the extraction efficiency of mangiferin from S. chinensis root. In general, the mixture of water and organic solvents (at a concentration of 50%, v/v) produced higher extraction efficiency than water or the organic solvents alone. A mixture of water and acetone extracted the highest content of mangiferin (78.76 mg/g of dried sample), followed by ethanol 50%, methanol 50%, methanol, ethanol, and water. By contrast, absolute acetone extracted the lowest level of concentration (10.36 mg/g of dried sample). Since acetone 50% had the highest extraction efficiency, this solvent mixture was used for further experiments. Acetone, or the combination of this organic solvent and water, has also been used effectively by other researchers. For example, while Dailey and Vuong [22] selected acetone 50% as the best solvent for recovery of total phenolics from Macadamia tetraphylla nut skin, absolute ethanol and acetone were chosen by Do et al. [10] for the extraction of TPC from Limnophila aromatic. Of note, Ngo et al. [23] reported that acetone 50% produced the highest yields of extractable solids, phenolics, flavonoids, saponins and antioxidant properties from S. chinensis root.

Table 2.
Impact of type of solvent on recovery of mangiferin from S. chinensis root.
3.3. Optimisation of UAE Conditions for Recovery of Mangiferin
Four ultrasonic extraction factors, including power, temperature, extraction time, and acetone concentration were investigated to identify the optimal conditions using RSM. The second-order polynomial equation for estimation of mangiferin recovery yield was generated as follows:
YMangiferin = −96.60 + 0.46X1 + 3.46X2 + 2.65X3 − 0.07X4 + 0.002X1X2 − 0.0029X1X3 − 0.0185X2X3 +
0.0055X1X4 − 0.0152X2X4 + 0.0027X3X4 − 0.0029X12 − 0.0141X22 − 0.0190X32 + 0.0022X42
0.0055X1X4 − 0.0152X2X4 + 0.0027X3X4 − 0.0029X12 − 0.0141X22 − 0.0190X32 + 0.0022X42
To test the adequacy of the RSM mathematical model for optimisation, variance was analysed (Table 3). The results indicated that the model was significant, PRESS value was high, and the lack of fit was found to be insignificant, meaning that the model fitting was adequate. In addition, the coefficient of determination (R2) was 0.898, revealing that at least 89.8% of the predicted values would match with the actual experimental values, which further confirmed the reliability of the model to predict the content of mangiferin.

Table 3.
Estimated regression coefficients for the model and the analysis of variance.
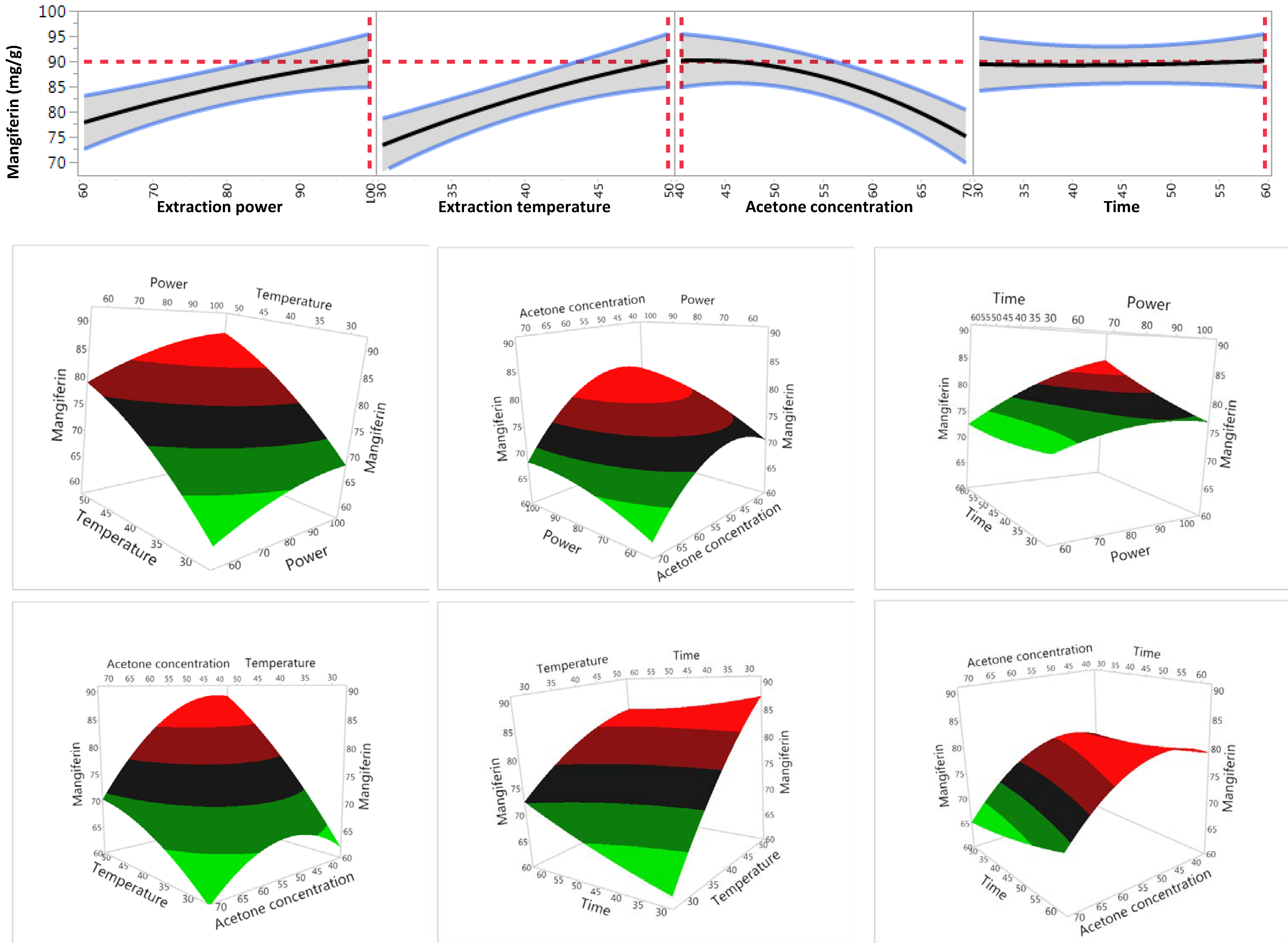
As the model was reliable for prediction, the impact of individual extraction factors on extraction efficiency of mangiferin was further analysed (Table 3 and Figure 3). It was shown that all four variables significantly impact on the recovery yield of mangiferin within their tested ranges (p < 0.05) (Table 3). Recovery yield of mangiferin increased when increasing the ultrasonic power, temperature and time. In contrast, recovery yield of mangiferin decreased when acetone concentration raised from 40% to 70%. These findings were in agreement with our previous study which reported that while extraction time, temperature and irradiative power had a positive correlation on the recovery of total phenolic compounds from S. chinensis root, solvent concentration showed the opposite trend [24].
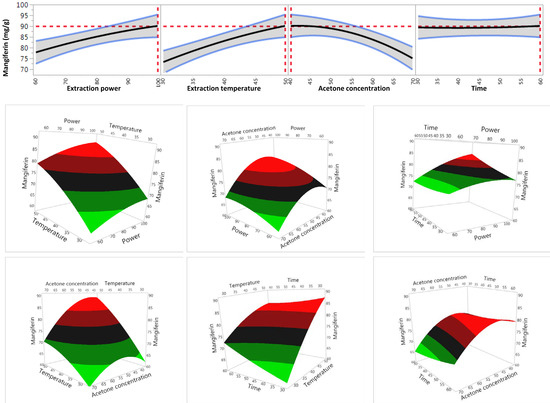
Figure 3.
Effect of variables on the yield of mangiferin.
Table 3 also showed the interaction effects between four variables on the recovery yield of mangiferin. The results indicated that there were significant interactive effects between temperature and acetone concentration, power and extraction time, and temperature and time on the recovery yield of mangiferin. However, no significant interactive effect was observed between extraction power and temperature, extraction power and acetone concentration as well as acetone concentration and extraction time. These results were also confirmed by findings in our previous study which reported that total phenolics in S. chinensis root was influenced significantly by the interactive effect between solvent concentration and temperature, but not affected by the interaction between power and temperature as well as solvent concentration and power [24].
According to this model, the optimal conditions for recovery of mangiferin from S. chinensis root were predicted as follows: extraction power of 250 W, temperature of 50 °C, acetone concentration of 40% and extraction time of 60 min. To validate these predicted optimal conditions, the sample was extracted with similar conditions in triplicate. The actual results were statistically compared with the predicted data using the t-test. The results indicated that the actual experimental data (91.95 ± 0.55 mg/g DW) was not significantly different to the predicted data (91.43 ± 5.30 mg/g DW), revealing that the predicted conditions were reliable and thus these optimal conditions can be used for maximum extraction of mangiferin using UAE.
3.4. Comparison of UAE with CSE and Decoction Extraction Methods
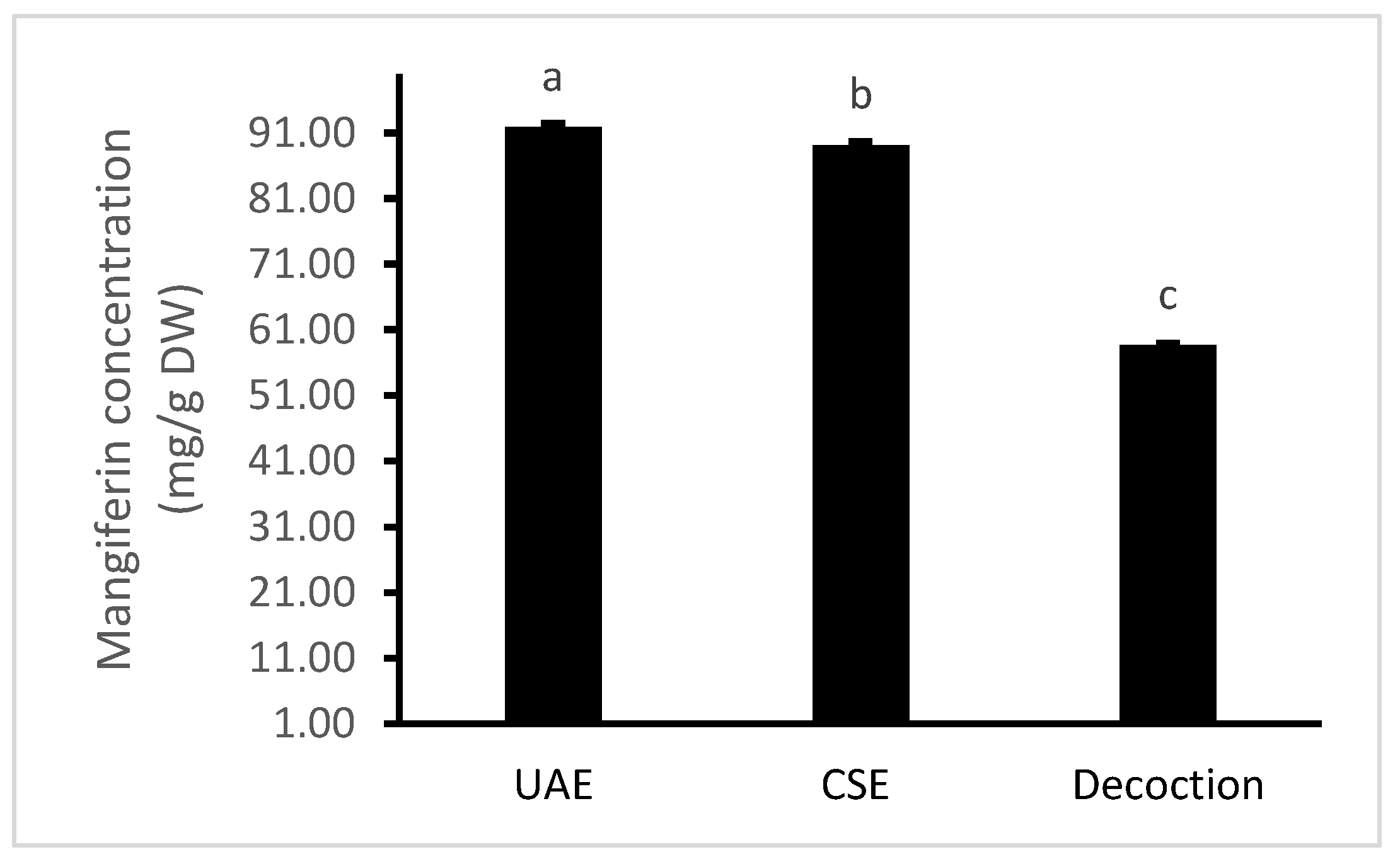
The results obtained from the optimal UAE conditions were further compared with two other conventional extraction methods, including decoction and continuously shaking extraction (CSE). The results are shown in Figure 4.
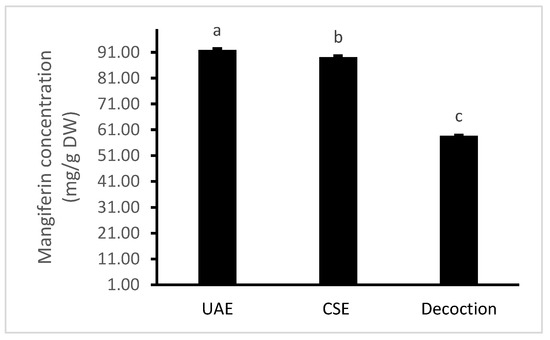
Figure 4.
Comparison levels of mangiferin recovery using the three extraction methods of ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), continuously shaking extraction (CSE) and decoction. Values are means ± standard deviations. Columns with different letters were significantly different at p < 0.05.
It was indicated that UAE yielded the highest content of mangiferin (91.95 mg/g DW), followed by CSE (89.20 mg/g DW). Decoction extracted the lowest content of mangiferin (58.71 mg/g DW), which can be explained by the degradation of mangiferin under high temperatures for longer time periods. These results are supported by our previous study which stated that UAE produced a significantly higher extraction yield of total bioactive compounds as well as antioxidant capacities than other extraction methods [24]. Our results were different to the findings reported by Chavan et al. [7], who found that steam bath-assisted extraction (SBAE) using dimethyl formamide 30% produced a higher yield of mangiferin than UAE, MAE (microwave assisted extraction) and CSE. Differences can be explained by the extraction techniques used in their study which were not under optimised conditions. Moreover, the concentration of acetone (70%), which was used for all methods in that study, produced the lowest yield of mangiferin in the range (40–70%) that we have found in our current research. Therefore, UAE is recommended for the extraction of mangiferin from the root of S. chinensis, as it is more effective, and requires less extraction time.
4. Conclusions
HPLC can effectively isolate mangiferin from S. chinensis root using EC-C18 reversed-phase column and a mixture of solvent A (water: acetonitrile: orthophosphoric acid, 96.8:3:0.2 (v/v/v)) and solvent B (acetonitrile). With an auto-fraction collector, mangiferin with a purity of 88.5% could be achieved. This study further confirmed that mangiferin is a major compound of S. chinensis root. The extraction of mangiferin was significantly affected by solvent type, and a mixture of acetone and water was more effective than absolute acetone, ethanol, methanol, water or mixtures of ethanol or methanol with water. For the application of UAE, ultrasonic power, temperature, time and acetone concentration significantly affected the extraction efficiency of mangiferin. Higher levels of mangiferin were obtained when increasing the ultrasonic power, temperature and time. In contrast, lower levels of mangiferin were achieved when increasing the acetone concentration from 40 to 70%. Optimal UAE conditions were at an ultrasonic power of 250 W, temperature of 50 °C, acetone of 40% and extraction time of 60 min. Under these optimal conditions, approximately 3% higher mangiferin levels were extracted when compared to CSE, and 57% more mangiferin was extracted when compared to the decoction. As UAE requires less time, this technique is recommended for the extraction of mangiferin from S. chinensis root.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.V.N., C.J.S., M.C.B. and Q.V.V.; Formal analysis, T.V.N.; Investigation, T.V.N.; Methodology, T.V.N. and Q.V.V.; Supervision, C.J.S., M.C.B. and Q.V.V.; Writing—original draft, T.V.N.; Writing—review & editing, C.J.S., M.C.B. and Q.V.V.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Vietnam International Education Development (Vietnam) and the University of Newcastle (Australia) for awarding a VIED-TUIT scholarship to Thanh Van Ngo.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gold-Smith, F.; Fernandez, A.; Bishop, K. Mangiferin and cancer: Mechanisms of action. Nutrients 2016, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Sadhukhan, P.; Sil, P.C. Mangiferin: A xanthonoid with multipotent anti-inflammatory potential. Biofactors 2016, 42, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.; Farooq, U.; Akram, K.; Hayat, Z.; Shafi, A.; Sarfraz, F.; Sidhu, M.A.I.; Rehman, H.; Aftab, S. Therapeutic potentials of bioactive compounds from mango fruit wastes. Trend Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Arshad, M.S.; Butt, M.S.; Kwon, J.-H.; Arshad, M.U.; Sultan, M.T. Mangiferin: A natural miracle bioactive compound against lifestyle related disorders. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, J.J.; Ghadage, D.M.; Bhoite, A.S.; Umdale, S.D. Micropropagation, molecular profiling and RP-HPLC determination of mangiferin across various regeneration stages of Saptarangi (Salacia chinensis L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.V.; Scarlett, C.J.; Bowyer, M.C.; Vuong, Q.V. Phytochemical and Antioxidant Properties from Different Parts of Salacia chinensis L. J. Biol. Act. Prod. Nat. 2017, 7, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, J.J.; Ghadage, D.M.; Kshirsagar, P.R.; Kudale, S.S. Optimization of extraction techniques and RP-HPLC analysis of antidiabetic and anticancer drug Mangiferin from roots of ‘Saptarangi’ (Salacia chinensis L.). J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Kumar, B.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, H. Phytochemical screening and extraction: A review. Int. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Azmir, J.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Sharif, K.M.; Mohamed, A.; Sahena, F.; Jahurul, M.H.A.; Ghafoor, K.; Norulaini, N.A.N.; Omar, A.K.M. Techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials: A review. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, Q.D.; Angkawijaya, A.E.; Tran, N.P.L.; Huynh, L.H.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ismadji, S.; Ju, Y.H. Effect of extraction solvent on total phenol content, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity of Limnophila aromatica. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, A.J.; Okoh, A.I. Assessment techniques of antimicrobial properties of natural compounds of plant origin: Current methods and future trends. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, S.S. An overview of extraction techniques for medicinal and aromatic plants. In Extraction Technoloties for Medicinal and Aromatic Plants; Handa, S.S., Khanuja, S.P.S., Longo, G., Rakesh, D.D., Eds.; International Centre for Science and High Technology: Trieste, Italy, 2008; pp. 21–54. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, B.; Dahmoune, F.; Moussi, K.; Remini, H.; Dairi, S.; Aoun, O.; Khodir, M. Comparison of microware, ultrasound and accelerated—Assisted solvent extraction for recovery of polyphenols from Citrus sinensis peels. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libran, C.M.; Mayor, L.; Garcia-Castello, E.M.; Vidal-Brotons, D. Polyphenol extraction from grape wastes: Solvent and pH effect. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Mokrani, A.; Madani, K. Effect of solvent, time and temperature on the extraction of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of peach (Prunus persica L.) fruit. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 162, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kchaou, W.; Abbès, F.; Blecker, C.; Attia, H.; Besbes, S. Effects of extraction solvents on phenolic contents and antioxidant activities of Tunisian date varieties (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanayake, E.H.; Sirimanne, S.R. Mangiferin from the root bark of Salacia reticulata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1985, 13, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, G.V.; Ravi, S.; Tushar, K.V.; Balachandran, I. Quantitative Determination of Mangiferin from the Roots of Salacia fruticosa and the Antioxidant Studies. J. Trop. Med. Plants 2009, 10, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Muraoka, O.; Morikawa, T.; Miyake, S.; Akaki, J.; Ninomiya, K.; Yoshikawa, M. Quantitative determination of potent α-glucosidase inhibitors, salacinol and kotalanol, in Salacia species using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 52, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, J.J.; Jagtap, U.B.; Gaikwad, N.B.; Dixit, G.B.; Bapat, V.A. Total phenolics, flavonoids and antioxidant activity of Saptarangi (Salacia chinensis L.) fruit pulp. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellamuthu, P.S.; Arulselvan, P.; Fakurazi, S. Beneficial effects of mangiferin isolated from Salacia chinensis on biochemical and hematological parameters in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 27, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Dailey, A.; Vuong, V.Q. Effect of extraction solvents on recovery of bioactive compounds and antioxidant properties from macadamia (Macadamia tetraphylla) skin waste. Cogent Food Agric. 2015, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.V.; Scarlett, C.J.; Bowyer, M.C.; Ngo, P.D.; Vuong, Q.V. Impact of Different Extraction Solvents on Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity from the Root of Salacia chinensis L. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.V.; Bowyer, M.C.; Scarlett, C.J.; Vuong, Q.V. Ultrasonic assisted extraction as an advanced technique for the extraction of bioactive compounds from Salacia chinensis root: A comparison with decoction and continuously shaking extraction. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019. under review. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).