Abstract
Sample preparation has been recognized as a major step in the chemical analysis workflow. As such, substantial efforts have been made in recent years to simplify the overall sample preparation process. Major focusses of these efforts have included miniaturization of the extraction device; minimizing/eliminating toxic and hazardous organic solvent consumption; eliminating sample pre-treatment and post-treatment steps; reducing the sample volume requirement; reducing extraction equilibrium time, maximizing extraction efficiency etc. All these improved attributes are congruent with the Green Analytical Chemistry (GAC) principles. Classical sample preparation techniques such as solid phase extraction (SPE) and liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) are being rapidly replaced with emerging miniaturized and environmentally friendly techniques such as Solid Phase Micro Extraction (SPME), Stir bar Sorptive Extraction (SBSE), Micro Extraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS), Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction (FPSE), and Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Micro Extraction (DLLME). In addition to the development of many new generic extraction sorbents in recent years, a large number of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) created using different template molecules have also enriched the large cache of microextraction sorbents. Application of nanoparticles as high-performance extraction sorbents has undoubtedly elevated the extraction efficiency and method sensitivity of modern chromatographic analyses to a new level. Combining magnetic nanoparticles with many microextraction sorbents has opened up new possibilities to extract target analytes from sample matrices containing high volumes of matrix interferents. The aim of the current review is to critically audit the progress of microextraction techniques in recent years, which has indisputably transformed the analytical chemistry practices, from biological and therapeutic drug monitoring to the environmental field; from foods to phyto-pharmaceutical applications.
1. Introduction
The development of analytical methods for quantitative analyses in environmental water, biological sample matrices, and in food or food supplements with a reduced amount of toxic solvents, and the replacing with non-toxic ones, without loss of efficacy in the extraction procedure, are important aims for contemporary researchers [1,2]. These aspects are deeply valued during method development and validation in all fields [3].
Often, these aspects lead to the development of new approaches for analyte extraction and clean-up involved in the development of better sorbent coating technology for solid phase microextraction and stir bar sorptive extraction. The use of novel devices, like packed sorbent (in microextraction by packed sorbent, MEPS), fabric phase sorptive extraction media (in fabric phase sorbent extraction, FPSE), and imprinted polymer (in molecularly imprinted polymer extraction), as well as the use of combined strategies with magnetic elements, can enhance the efficiency and the recovery of the target analyte.
Liquid phase microextraction methods have demonstrated important innovations for the extraction and pre-concentration of analytes from different matrices. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) and its modifications, such as ultrasound-assisted DLLME (UA-DLLME), ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (IL-DLLME), deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DES-DLLME), and sugaring-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction (SULLE), can offer unique benefits, such as a high pre-concentration factor for the target analytes, low cost, simplicity and combined use with almost every analytical measurement technique [4].
A large number of solvent microextraction techniques, including single-drop microextraction, DLLME, and liquid-phase microextraction (LPME), have been reported. Implementation of these techniques can vary widely, but common features remain the same, including the use of only a small amount of organic solvents and a high sample-to-acceptor volume ratio. The organic phase, which extracts and pre-concentrates the target analyte(s), can be used for quantification by means of different types of instrument configurations [5]. LPME is usually performed to analyze water samples or aqueous solutions. Analysis of solid samples is commonly done in two steps: the solid sample is converted to aqueous solution using a suitable pretreatment procedure, and then the LPME is applied. Direct analysis of solid samples is somewhat exceptional, rather than common. Several works have been reported for the determination of different analytes in complex matrices, such as phenolic compounds in plant materials [6] and food samples [7,8] by using DLLME in combination with High Performance Liquid Chromatography-UltraViolet/Visible detector (HPLC-UV/Vis) [6] and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry detector (GC-MS) [7] instrument configurations.
Replacing hazardous solvents with ionic liquids (IL) or natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) is another important task available in DLLME, and was recently reviewed by Shishov and co-workers [9]. It is possible to modify the IL’s properties depending on the analytical purpose, due to the cation’s fine structure and the anion’s identity [10], but high cost and toxicity remain as the main disadvantages [11]. Recently, NADESs have been rapidly developed as a new type of green solvents, as an alternative to ILs. NADESs are based on primary metabolites, such as organic acids, amino acids and sugars, but limited data are available for these solvents’ properties.
The aim of this review is to report the recently applied protocols and devices used in the extraction (and clean-up) procedures for quantitative analyses in complex matrices, with the main goal being the reduction of time, sample manipulation, solvent consumption and use of non-toxic solvents, in accordance with Green Analytical Chemistry (GAC) concepts.
2. Sorbent-Based Sorptive Microextraction Techniques
Sorbent-based sorptive microextraction techniques utilize a solid/semi-solid organic polymer as the sorbent, immobilized on a substrate (such as fused silica fiber, silica particles, glass-coated bar magnet, cellulose/polyester/fiber glass fabric etc.), and include solid phase microextraction (SPME) and its different modifications and implementations, stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE), microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS), thin film microextraction (TFME), and fabric phase sorptive extraction (FPSE). Sampling and sample preparation using these techniques are often carried out either by (1) headspace extraction; or by (2) direct immersion extraction. Due to the glue-like, highly viscous polymeric sorbents are prone to irreversibly adsorb matrix interferents from the sample matrix, direct immersion extraction can only be done when the aqueous sample is free from particulates or macromolecules. As such, biological, environmental and food samples require rigorous sample pretreatment prior to analyte extraction such as filtration, centrifugation, protein precipitation, etc. Once the analytes are extracted into these devices, desorption can be carried out by applying thermal shock or by exposing to an organic solvent. Due to the special geometrical advantage (fiber retractable inside a syringe needle), SPME fiber can be introduced directly into GC inlet or into the HPLC system via a special interface. For SBSE or FPSE, a thermal desorption unit can be used. Alternatively, solvent mediated desorption can be used followed by injecting an aliquot into GC or HPLC for chromatographic separation and analysis.
2.1. Fiber-Based Solid-Phase Microextraction, Capillary Solid-Phase Microextraction, and Related Techniques
Solid-phase microextraction (SPME), invented by J. Pawliszyn in 1987, undoubtedly deserves the credit for beginning a new era in analytical sample preparation characterized by solvent-free extraction, miniaturization and automation. SPME integrates sampling, extraction and analyte preconcentration into a single step. Due to this ease of interfacing with other analytical systems, as well as many other advantages, SPME has been enjoying exponential growth in applications in many different areas since its inception.
The miniaturization of sample preparation techniques and the integration, particularly in on-line configuration, of chromatographic instruments that could allow a reduction in labor-intensive manual operation and help to enhance the overall analytical performance [12] still remain the major focus in academic and industrial research. In this scenario, even if MEPS is more easily automated than SPE, and more robust than solid-phase microextraction (SPME) [13], sorbent-based techniques and their different formats certainly represent a valid choice. These techniques provide simplicity in their operation, consume no solvent or minimize solvent usage, allow the separation and pre-concentration of the analytes using different commercial fibers, and the possibility of automating the entire process could be successfully applied in food, environmental, clinical, pharmaceutical and bioanalysis applications [14,15,16], as recently reviewed by Silva and co-workers [17].
The fibers, which are commercially available, may be different based on their type:
- -
- non-bonded phases: stable with some water-miscible organic solvents, although some swelling may occur when used with non-polar solvents,
- -
- bonded phases: stable with all organic solvents, except for some non-polar solvents,
- -
- partially cross-linked phases: stable in most water-miscible organic solvents and some polar solvents,
- -
- highly cross-linked phases: similar to the partially cross-linked phases, except that some bonding to the core may occur.
All of these phases have been strongly and deeply studied and implemented for analysis of volatile components and in different applications—e.g., food, food supplements, and bioanalysis—but all show the same limitation with regard to handling of large sample volumes as for the main SPE/SPME procedure. These procedures (also capillary-like) could easily be used in biological and food analyses due to the relatively low sample volume, but in environmental applications, where large sample volumes are required in order to obtain higher pre-concentration factors, their limitations are highlighted.
Even if these “limitations” are present, fiber-based solid-phase microextraction and capillary solid-phase microextraction represent valid alternatives to conventional approaches due to the wide range of phases commercially available, their better stability and reproducibility (both between lots and analyses), and their unique characteristic of being solvent-less.
The latter techniques, capillary solid-phase microextraction, consist of an inert liner with a packet of coated open capillary tubes inside. The main advantage in comparison to the other reported microextraction procedures is that the surface areas of the extraction phase are more than two orders and one order of magnitude higher, respectively, than that of fiber-SPME. Hence, an equal extraction quantity can be obtained in a lower time. Another advantage is represented by the large cross-section area, resulting in a lower flow resistance; consequently, water samples are able to flow through the cartridge independently, without the need for an auxiliary apparatus. Using capillary solid-phase microextraction, the extraction phase is protected from damage in the liner, so no heightened precautions are needed during application. Furthermore, the cartridge shows a small-bore diameter, which ensures the retention of trace and ultra-trace compounds using limited sample amounts, allowing high absolute recovery. The advances in SPME in terms of new coatings, formants and applications have been reviewed in a large number of articles; only a few are referenced here [18,19,20,21].
Although SPME offers numerous advantages over conventional sample preparation techniques, it suffers from significant shortcomings, including (1) relatively low operating temperature; (2) instability and swelling of the coating if exposed to organic solvents; (3) low sorbent loading results and poor extraction sensitivity; (4) high run-to-run and batch-to-batch variability; (5) the fact that the slow diffusion of the analyte(s) into viscous sorbents often leads to a long extraction equilibrium time; and (6) the fact that physically holding sorbent to the inert support results in a short life time for the SPME fiber. The majority of the shortcomings stem from the sorbent coating technology used in manufacturing the SPME fibers. However, the coating-related deficiency has been duly addressed by the sol-gel-based coating technology developed by Malik and his research groups [22]. This technology subsequently aided in the development of hundreds of sorbents possessing unique selectivity, as well as unprecedented thermal, solvent and chemical stability. A large number of review articles have critically evaluated these SPME coatings [23,24,25,26,27].
2.2. Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction (SBSE)
Stir bar sorptive extraction was developed by Pat Sandra and his research group [28] with the aim of increasing the extraction sensitivity of SPME by incorporating substantially higher sorbent loading compared to SPME. In the original invention, poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) was coated onto a glass-coated magnetic bar. The unique design of SBSE makes it an independent sample preparation device, capable of diffusing the sample matrix by itself on a magnetic stirrer without requiring any external magnet. Extraction and preconcentration of the analyte is carried out by introducing the SBSE device directly into the aqueous sample. The analytes are extracted and preconcentrated when the SBSE spins inside the solution. Following the analyte extraction (driven by equilibrium), the SBSE device is withdrawn from the sample, rinsed with deionized water to clean matrix interferents, and dried with a Kim wipe. Subsequently, the extracted analytes are desorbed using a thermal desorption unit coupled to gas chromatography, or can be subjected to solvent desorption by exposing it to a small volume of a suitable organic solvent. The eluent is typically dried under nitrogen, and the sample is reconstituted in smaller-volume solvent. The sample can be analyzed in a gas or liquid chromatographic system. SBSE devices are commercially available under the trade name Twister®. Among others, a major drawback of this technique is the availability of only two phases: PDMS and Poly(ethylene glycol) in PDMS [29]. The high viscosity of both of these phases slows down analyte diffusion during extraction, resulting in a long extraction equilibrium time. As such, the extraction sensitivity in SBSE has not been improved proportionately with the sorbent loading, compared to SPME. Several review articles have discussed recent developments in SBSE [29,30,31,32,33]. As in the case of SPME, the efficiency of SBSE has been substantially improved by adopting sol-gel coating technology [34,35,36,37,38].
2.3. Micro Extraction by Packed Sorbent Procedures (MEPS)
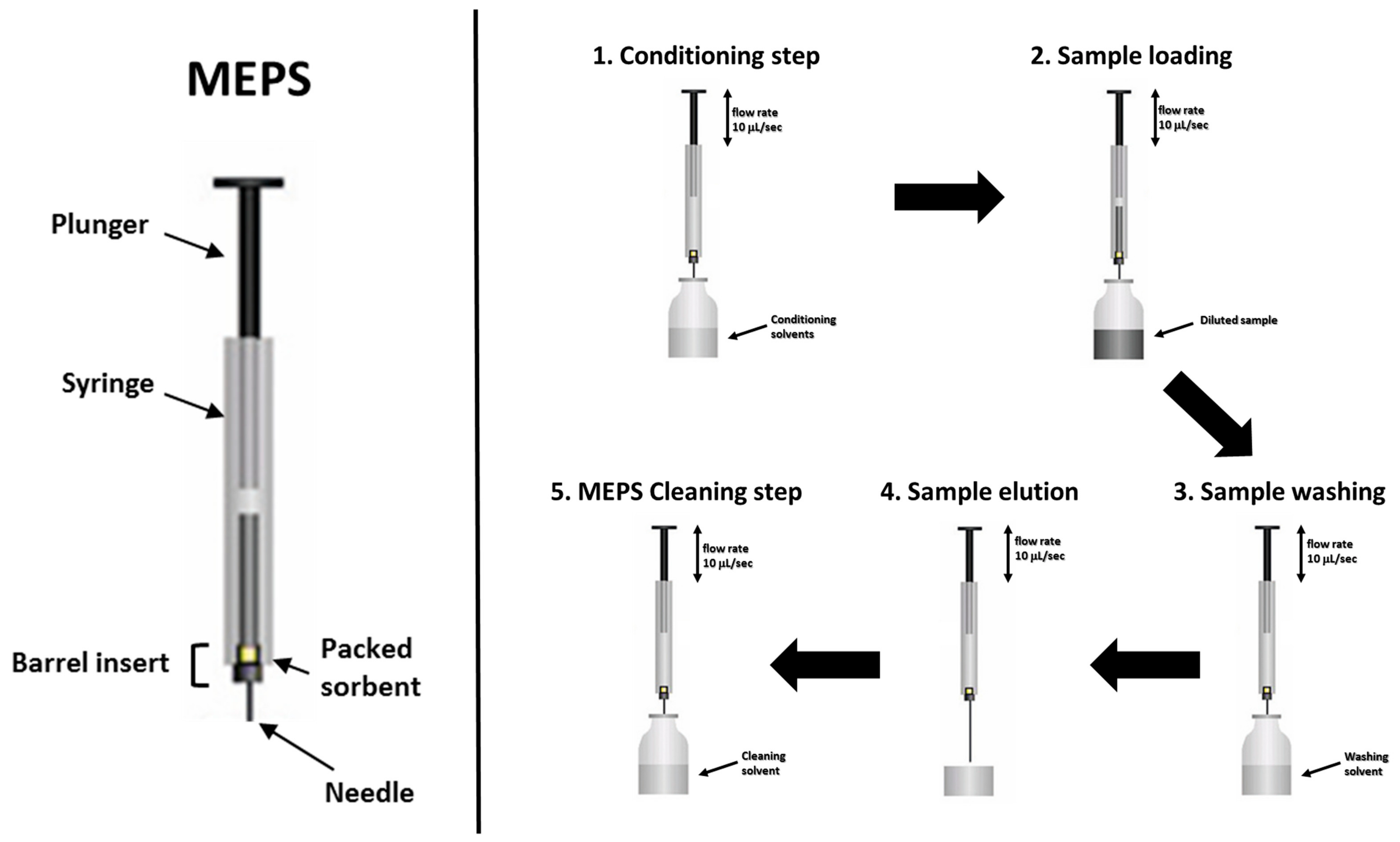
Recently, Abdel-Rehim and coworkers [39] reviewed the literature published on Micro Extraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS) methods. This extraction procedure shows some very interesting potential benefits, such as low solvent consumption, small sample volume (10–250 μL), and the ability to be directly injected into the HPLC system without further treatments, with solvent volumes being compatible with several instrumental configurations and analyses. Figure 1 shows the device and the general procedure applied in MEPS extraction.
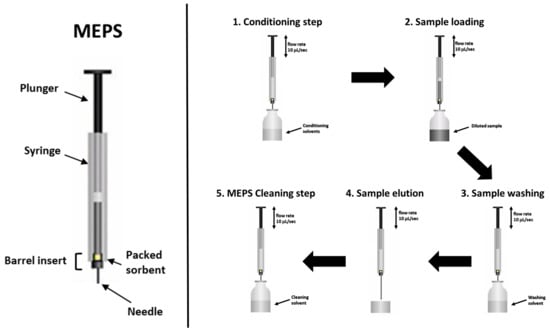
Figure 1.
Device (left) and general procedure (right) applied in MEPS extraction.
This device is used in different fields, from biological applications to food and food supplement analyses. The main drawback is also related to its advantages. In fact, the possibility of using small sample volumes permits its application in analyses where only small volumes are available, for example plasma. In the case of higher volumes (such as in the environmental field), this device often shows its limitations.
Nowadays, several types of packing materials are available, including:
- -
- Silica-based sorbents SIL (unmodified silica),
- -
- C2(ethyl),
- -
- C8 (octyl),
- -
- C18 (octadecyl);
- -
- Mixed-mode C8 and ion exchange (SCX),
- -
- Mixed-mode M1 (80% C8 and 20% SCX with sulfonic acid bonded silica);
- -
- Polystyrene-divinylbenzene (PS-DVB),
- -
- Porous graphitic carbon,
- -
- Molecular imprinted polymers (MIPs) based on different templates,
- -
- Metal organic framework (MOF)-based MIPs [40,41],
- -
- Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) for immunoaffinity sorbents production.
Additionally, other commercial sorbents, such as new kinds of graphitic sorbent, polypyrrole/polyamide, polyaniline nanowires, CMK-3 nanoporous materials, functionalized silica monoliths, APS (amino-propyl silane), and cyanopropyl hybrid silica have been successfully applied in MEPS devices to extract different groups of analytes, as recently reviewed [39,42].
To aid and improve the reproducibility during the extraction process, MEPS devices are also coupled to syringes in semi-automated and/or fully automated configurations. In fact, the main critical point during extraction relates to the reproducibility of the flow rate (generally μL s−1) used in the different steps (Figure 1). A MEPS syringe and a one-way check valve [43] was used for the realization of automated or semi-automated MEPS extraction, both for on-line and off-line instrument configurations.
Table 1 presents selected MEPS applications in different fields and the performances obtained when applying this device.

Table 1.
Some recent MEPS applications (2012–2017, not previously reviewed) [39,43] in different fields, and the performances obtained when applying this device.
As previously mentioned, applications in environmental fields are very limited due to the large volumes that are necessary for the trace analysis of pollutants, both organic and inorganic. Additionally, applications are relatively limited for foods and food supplements due to difficult application of MEPS, which requires a longer time in the pre-analytical steps.
2.4. Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Procedures (FPSE)
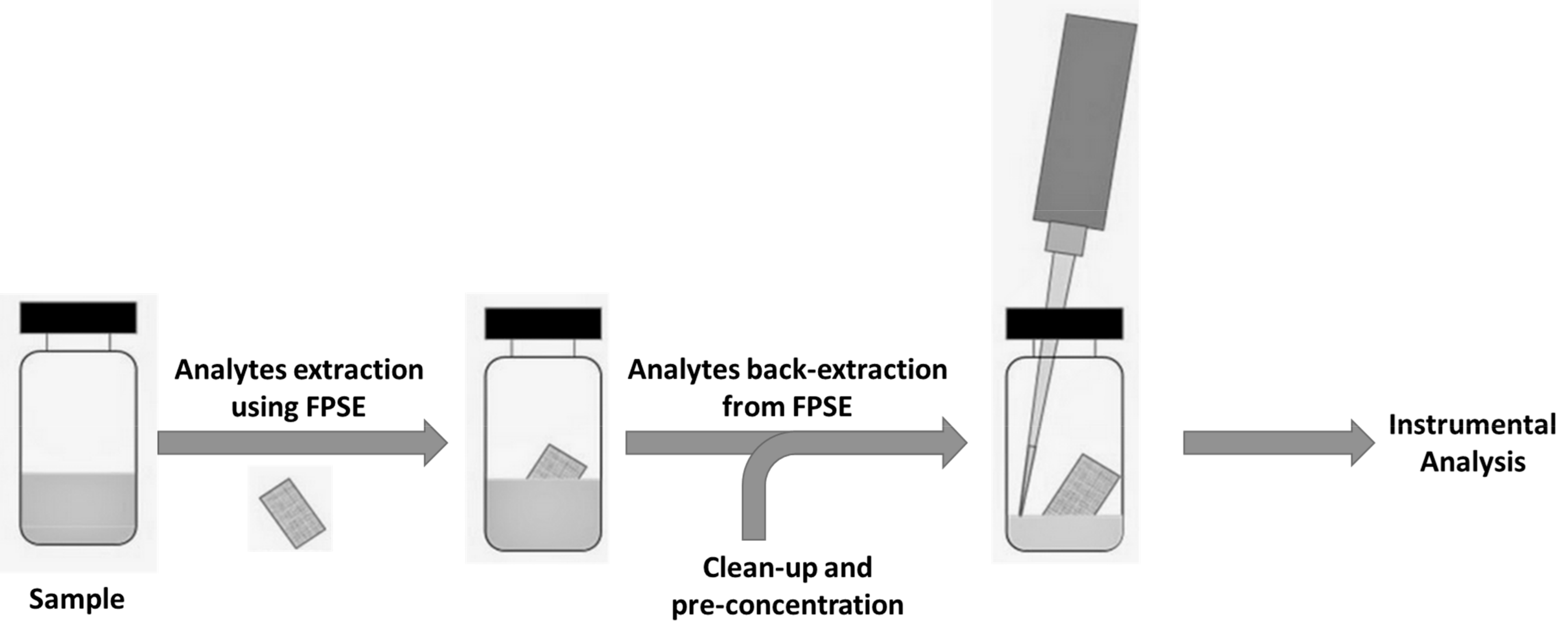
Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction (FPSE) is a novel sample preparation procedure that mitigates the drawbacks of MEPS. In fact, it allows small and large volumes to be treated, and could be usefully applied in all fields where a very high pre-concentration factor is required, from environmental to biological, from toxicological to food and food supplement quality control. The common drawbacks encountered in conventional sample preparation techniques can be conveniently overcome by using FPSE—developed by Kabir and Furton [59], and recently reviewed by the inventors [60]—which does not require any matrix modifications or clean-up. FPSE successfully integrates the advantages of equilibrium-based extraction (SPME/SBSE) and exhaustive extraction (SPE) without the necessity of time-consuming sample pretreatment procedures such as protein precipitation. The sorbent is covalently bonded to the substrate surface, and therefore offers high chemical, physical, and thermal stability. In addition, the open geometry of the media facilitates fast analyte sorption and desorption. The substrate used in FPSE is not inert, and contributes synergistically to the overall polarity of the FPSE media. Fabric phase sorptive extraction substantially simplifies the sample preparation workflow in comparison to other available and recent techniques, as demonstrated in Figure 2.
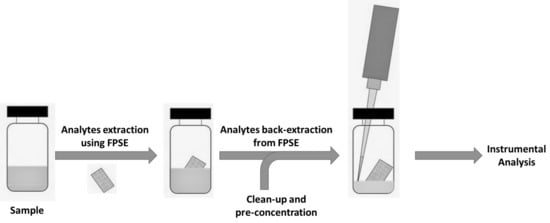
Figure 2.
General procedure (right) applied in FPSE extraction.
Using FPSE devices, both large sample volumes (such as in the environmental field) and small sample volumes (generally applicable in the biological and pharmaceutical fields) can be easily handled, maintaining very good analytical performances in terms of LOQ, linearity and low pre-analytical steps, as reported in Table 2.

Table 2.
Some recent FPSE applications in different fields, and the performances obtained when applying this device.
2.5. Magnetic Nanoparticle Extraction
Recently these applications were reviewed [9], and in particular, a review focused on using magnetic nanoparticles for the selective extraction of trace species from a complex matrix was reported [83].
The main advantage of this last configuration is the possibility of retaining the analytes adsorbed on magnetic stationary phase directly in the tube, cleaning the sample from the matrix and the interference compounds, and analyzing the extract directly for trace species.
To date, no other innovative applications—except for those reported in very recent review papers—have been reported in the literature for food analysis [84], for drugs in biological matrices [85], or in other research fields [86,87].
All of these papers clearly report the great advantages in using magnetic devices to allow the total recovery of the extracted analytes by using a strong magnet during the cleaning process. In this way, it could be possible to retain the analytes without any loss related to the wash step.
Additionally, it is also possible to dry the extracted samples and re-suspend them in a mobile phase more suitable for the instrumental analysis, thus also obtaining a great pre-concentration factor for trace analyses.
3. Solvent-Based Microextraction Techniques
Due to its high toxicity, expensive disposal requirements, and contribution to further environmental pollution, liquid-liquid extraction and its various modifications have undergone critical evaluation during the last decade, leading to the introduction of liquid phase microextraction (LPME). In a very short period, a number of techniques evolved, with the common goal of minimizing solvent consumption in the sample preparation process.
3.1. Liquid-Liquid Micro Extraction (LPME)
Considering the principles of Green Analytical Chemistry [88], the development of analytical methods that reduce the amount of toxic solvents, or replace them with non-toxic alternatives without sacrificing the efficacy of the extraction procedure, is a major aim for researchers.
Liquid phase microextraction methods (LPME), in comparison to solid phase (micro) extraction, have shown important innovations for trace analytes in different matrices. LPME is utilized for organic compounds and inorganic trace elements in several application fields, such as the environmental, biological, and food fields. LPME can be divided into three different procedure modes: headspace LPME (HS-LPME), direct-immersed LPME (DI-LPME), and hollow fiber LPME (HF-LPME). In HS-LPME, a drop of extraction solvent—which can be either an organic solvent or a water solution—is suspended at the tip of a micro-syringe needle and exposed to the headspace of the sample; this is very suitable for analyses of volatile compounds. DI-LPME is very similar, except that the extraction solvent must be immiscible with aqueous solutions, and is directly immersed into a stirred sample solution. HF-LPME uses a hollow fiber in order to stabilize and protect the extraction solvent, while the small fiber pore size avoids the interference of large molecules and particles, which could result in a more extensive clean-up of the sample during the extraction process. Sharifi and co-workers [89] recently reviewed the principal applications in which these LPME techniques are applied.
3.2. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction (DLLME)
Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) and its modifications—such as ultrasound-assisted DLLME (UA-DLLME), ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (IL-DLLME), deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DES-DLLME), and sugaring-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction (SULLE)—offer unique benefits, such as a high pre-concentration factor for the target analytes, low cost, simplicity, and the possibility of combined use with almost every analytical measurement technique [4,90,91]. A large number of solvent microextraction techniques, including single drop microextraction, DLLME, liquid phase microextraction (LPME), have been reported. This extraction procedure allows a better analytical performance in comparison to HF-LPME, as reported by Xiong and Hu [92]. The organic phase, which contains the target analyte(s), can be used for quantification by means of different types of instrument configurations [5]. LPME is usually performed to analyze water samples or aqueous solutions. Analysis of solid samples is commonly done in two steps; the solid sample is converted to aqueous solution using a suitable pretreatment procedure, and then LPME is applied.
4. Conclusions
As is clearly highlighted in this review paper, the extraction (and clean-up) procedures applied to complex matrices are the real rate-limiting step in sample preparation, particularly related to the overall analytical performance of the developed (and validated) method. Several procedures that have recently been applied, their main aim being the reduction of time, sample manipulation, solvent consumption, and use of toxic solvents, in accordance with the Green Analytical Chemistry (GAC) concepts. A good idea of the advantages/disadvantages of the different procedures treated herein is reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
A comparison of some characteristics of sample preparation techniques [17,93,94].
These innovative procedures also allow analytical performance to be improved by using well-known instrument configurations—such as HPLC-UV/Vis—while avoiding the use of more complex and expensive ones (HPLC-MS, UPLC-MS, etc.). Additionally, these instrumentations can also be used by non-expert operators in routine analyses, both in clinical and in quality-control procedures.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by University “G. d’Annunzio” of Chieti-Pescara, Chieti, Italy.
Author Contributions
All Authors contributed equally to the present work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kabir, A.; Furton, K.J. Sample preparation in Food Analysis: Practices, Problems and Future Outlook. In Analytical Chemistry: Developments, Applications and Challenges in Food Analysis; Locatelli, M., Celia, C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 23–54. ISBN 978-1-53612-267-1. [Google Scholar]
- Locatelli, M.; Cifelli, R.; Vitalei, S.; Santini, P.; De Luca, E.; Bellagamba, G.; Celia, C.; Carradori, S.; Di Marzio, L.; Mollica, A. Method validation and hyphenated techniques: Recent trends and future perspectives. In Analytical Chemistry: Developments, Applications and Challenges in Food Analysis; Locatelli, M., Celia, C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–22. ISBN 978-1-53612-267-1. [Google Scholar]
- Locatelli, M.; Sciascia, F.; Cifelli, R.; Malatesta, L.; Bruni, P.; Croce, F. Analytical methods for the endocrine disruptor compounds determination in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1434, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campillo, N.; Viñas, P.; Šandrejová, J.; Andruch, V. Ten years of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and derived techniques. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2017, 52, 267–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, H. Recent development and applications of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1295, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, S.; Bai, X.; Gu, D. Utilization of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with HPC-UV as a sensitive and efficient method for the extraction and determination of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in Chinese medicinal herbs. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 3, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Han, F.; Jing, S.; Yuan, C.; Guo, A.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method for HPLC determination of phenolic compounds in wine. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariña, L.; Boido, E.; Carrau, F.; Dellacassa, E. Determination of volatile phenols in red wines by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1157, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishov, A.; Bulatov, A.; Locatelli, M.; Carradori, S.; Andruch, V. Application of deep eutectic solvents in analytical chemistry. A review. Microchem. J. 2017, 135, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Bi, W.; Tian, M.; Row, K.H. Application of ionic liquid for extraction and separation of bioactive compounds from plants. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 904, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khezeli, T.; Daneshfar, A.; Sahraei, R. A green ultrasonic-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for the HPLC-UV determination of ferulic, caffeic and cinnamic acid from olive, almond, sesame and cinnamon oil. Talanta 2016, 150, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, G.; Rodrigues, M.; Fortuna, A.; Falcão, A.; Queiroz, J. A critical review of microextraction by packed sorbent as a sample preparation approach in drug bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 1409–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J.; Li, C. Determination of eight quinolones in milk using immunoaffinity microextraction in a packed syringe and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1064, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira e Silva, H.; de Pinho, P.G.; Machado, B.P.; Hogg, T.; Marques, J.; Câmara, J.S.; Albuquerque, F.; Silva Ferreira, A.C. Impact of forced-aging process on madeira wine flavor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11989–11996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perestrelo, R.; Caldeira, M.; Rodrigues, F.; Camara, J.S. Volatile flavour constituent patterns of terras madeirenses red wines extracted by dynamic headspace solid-phase microextraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Câmara, J.; Marques, J.; Alves, A.; Ferreira, A.S. Heterocyclic acetals in madeira wines. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.; Cavaco, C.; Perestrelo, R.; Pereira, J.; Câmara, J.S. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS) and Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) as Sample Preparation Procedures for the Metabolomic Profiling of Urine. Metabolites 2014, 4, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulra’uf, L.B.; Hammed, W.A.; Tan, G.H. SPME Fibers for the Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 42, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.D.; Wang, L.C.; Guo, Y. Recent Developments in Solid-phase Microextraction Coatings for Environmental and Biological Analysis. Chem. Lett. 2017, 46, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri-Moghadam, H.; Alam, M.N.; Pawliszyn, J. Review of geometries and coating materials in solid phase microextraction: Opportunities, limitations, and future perspectives. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 984, 42–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Zhou, L.D.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.Z.; Xia, Z.N.; Yuan, C.S. Solid-phase microextraction technology for in vitro and in vivo metabolite analysis. TrAC 2016, 80, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.X.; Chong, S.L.; Malik, A. Sol-gel column technology for single-step deactivation, coating, and stationary-phase immobilization in high-resolution capillary gas chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4566–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A. Solid-phase microextraction-based sol–gel technique. TrAC 2016, 75, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Piri-Moghadam, H.; Naderi, M. Towards greater mechanical, thermal and chemical stability in solid-phase microextraction. TrAC 2012, 34, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, C.; Sanz, J.; Camara, C. Recent developments in solid-phase microextraction coatings and related techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1103, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Malik, A. Innovations in sol-gel microextraction phases for solvent-free sample preparation in analytical chemistry. TrAC 2013, 45, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A. Advances in sol-gel based columns for capillary electrochromatography: Sol-gel open-tubular columns. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 3973–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltussen, E.; Sandra, P.; David, F.; Cramers, C. Stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE), a novel extraction technique for aqueous samples: Theory and principles. J. Microcolumn Sep. 1999, 11, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilart, N.; Marce, R.M.; Borrull, F.; Fontanals, N. New coatings for stir-bar sorptive extraction of polar emerging organic contaminants. TrAC 2014, 54, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, S.; Lucena, R. Recent Advances in Extraction and Stirring Integrated Techniques. Separations 2017, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazyropoulou, C.; Samanidou, V. Stir bar sorptive extraction applied to the analysis of biological fluids. Bioanalysis 2014, 7, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Chen, B.B.; Hu, B. Recent developments in stir bar sorptive extraction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 2001–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, A.; Basauri, O.; Rodil, R.; Usobiaga, A.; Fernandez, L.A.; Etxebarria, N.; Zuloaga, O. Stir-bar sorptive extraction: A view on method optimisation, novel applications, limitations and potential solutions. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2642–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amlashi, N.E.; Hadjmohammadi, M.R. Sol-gel coating of poly(ethylene glycol)-grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes for stir bar sorptive extraction and its application to the analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 3445–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Mao, X.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Development of novel sol-gel coatings by chemically bonded ionic liquids for stir bar sorptive extraction-application for the determination of NSAIDS in real samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7261–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Mao, X.J.; He, M.; Chen, B.B.; Hu, B. Stir bar sorptive extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet/inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for analysis of thyroxine in urine samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1318, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duy, S.V.; Fayad, P.B.; Barbeau, B.; Prevost, M.; Sauve, S. Using a novel sol-gel stir bar sorptive extraction method for the analysis of steroid hormones in water by laser diode thermal desorption/atmospheric chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 101, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.M.; Wang, H.M.; Guan, Y.F. Preparation of stir bars for sorptive extraction using sol-gel technology. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1045, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Said, R.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Sorbent, device, matrix and application in microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS): A review. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1043, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskierko, Z.; Sharma, P.S.; Prochowicz, D.; Fronc, K.; D’Souza, F.; Toczydłowska, D.; Stefaniak, F.; Noworyta, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Film with Improved Surface Area Developed by Using Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) for Sensitive Lipocalin (NGAL) Determination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19860–19865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Fang, G.; Wang, S. A novel core-shell molecularly imprinted polymer based on metal-organic frameworks as a matrix. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10118–10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Maia, A.S.; Gonçalves, V.M.; Tiritan, M.E. New trends in sample preparation techniques for environmental analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 44, 142–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmongy, H.; Ahmed, H.; Wahbi, A.-A.; Amini, A.; Colmsjö, A.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Determination of metoprolol enantiomers in human plasma and saliva samples utilizing microextraction by packed sorbent and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, M.; Ferrone, V.; Cifelli, R.; Barbacane, R.C.; Carlucci, G. MicroExtraction by Packed Sorbent and HPLC determination of seven non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in human plasma and urine. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1367, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, M.; Ciavarella, M.T.; Paolino, D.; Celia, C.; Fiscarelli, E.; Ricciotti, G.; Pompilio, A.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Grande, R.; Zengin, G.; et al. Determination of Ciprofloxacin and Levofloxacin in Human Sputum Collected from Cystic Fibrosis Patients using Microextraction by Packed Sorbent-High Performance Liquid Chromatography PhotoDiode Array Detector. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1419, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, V.; Tessari, F.; Bellagamba, G.; De Luca, E.; Cifelli, R.; Celia, C.; Primavera, R.; Di Francesco, M.; Paolino, D.; Di Marzio, L.; et al. MicroExtraction by Packed Sorbent and HPLC-PDA quantification of multiple anti-inflammatory drugs and fluoroquinolones in human plasma and urine. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campestre, C.; Locatelli, M.; Guglielmi, P.; De Luca, E.; Bellagamba, G.; Menta, S.; Zengin, G.; Celia, C.; Di Marzio, L.; Carradori, S. Analysis of imidazoles and triazoles in biological samples after MicroExtraction by Packed Sorbent. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ares, A.M.; Fernández, P.; Regenjo, M.; Fernández, A.M.; Carro, A.M.; Lorenzo, R.A. A fast bioanalytical method based on microextraction by packed sorbent and UPLC-MS/MS for determining new psychoactive substances in oral fluid. Talanta 2017, 174, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, E.; Bahrami, A.; Afkhami, A.; Shahna, F.G. Determination of urinary trans,trans-muconic acid using molecularly imprinted polymer in microextraction by packed sorbent followed by liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1061–1062, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, S.N.; Santos-Neto, A.J.; Lancas, F.M. Development and optimization of a fast method for the determination of statins in human plasma using microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS) followed by ultra high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS). Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.; González, M.; Regenjo, M.; Ares, A.M.; Fernández, A.M.; Lorenzo, R.A.; Carro, A.M. Analysis of drugs of abuse in human plasma using microextraction by packed sorbents and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1485, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, T.; Gonçalves, A.; Margalho, C.; Barroso, M.; Gallardo, E. Rapid analysis of cocaine and metabolites in urine using microextraction in packed sorbent and GC/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 2051–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercolini, L.; Mandrioli, R.; Raggi, M.A. Content of melatonin and other antioxidants in grape-related foodstuffs: Measurementusing a MEPS-HPLC-F method. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 53, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Moral, M.P.; Tena, M.T. Use of microextraction bypacked sorbents following selective pressurised liquid extraction for thedetermination of brominated diphenyl ethers in sewage sludge by gaschromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1364, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, R.M.G.; Pinto, C.G.; Pavón, J.L.P.; Cordero, B.M. In situ derivatization combined to automatedmicroextraction by packed sorbents for the determination of chlorophenolsin soil samples by gas chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1359, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salami, F.H.; Queiroz, M.E.C. Microextraction inpacked sorbent for analysis of sulfonamides in poultry litter wastewatersamples by liquid chromatography and spectrophotometric detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2014, 37, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Ghaemi, F. Microextraction in packed syringe by using a three-dimensional carbon nanotube/carbon nanofiber-graphene nanostructure coupled to dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of phthalate esters in water samples. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3851–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumes, B.H.; Lanças, F.M. Use of graphene supported on aminopropyl silica for microextraction of parabens from water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1487, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric Phase Sorptive Extractor (FPSE). U.S. Patent US 20140274660 A1, 18 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kabir, A.; Mesa, R.; Jurmain, J.; Furton, K.G. Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Explained. Separations 2017, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, M.; Kabir, A.; Innosa, D.; Lopatriello, T.; Furton, K.G. A Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Photo Diode Array Detection Method for the Determination of Twelve Azole Antimicrobial Drug Residues in Human Plasma and Urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1040, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; D’Ovidio, C.; Grossi, R.; Innosa, D.; Macerola, D.; Tartaglia, A.; Di Donato, V.; Locatelli, M. Fabric phase sorptive extraction-high performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array detection method for triple therapy in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Locatelli, M.; Kabir, A.; Tinari, N.; Macerola, D.; Tartaglia, A.; Furton, K.G. A Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Photo Diode Array Detection Method for the Determination of three antitumoral Drugs. Sci. Rep. 2017. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Samanidou, V.; Kaltzi, I.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Simplifying sample preparation using fabric phase sorptive extraction technique for the determination of benzodiazepines in blood serum by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Gaurav; Heena; Malik, A.K.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Efficient analysis of selected estrogens using fabric phase sorptive extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1359, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes-Alonso, R.; Ciofi, L.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J.; Del Bubba, M.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Determination of androgens and progestogens in environmental and biological samples using fabric phase sorptive extraction coupled to ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1437, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aznar, M.; Alfaro, P.; Nerin, C.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric phase sorptive extraction: An innovative sample preparation approach applied to the analysis of specific migration from food packaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanidou, V.; Galanopoulos, L.-D.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fast extraction of amphenicols residues from raw milk using novel fabric phase sorptive extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 855, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karageorgou, E.; Manousi, N.; Samanidou, V.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric phase sorptive extraction for the fast isolation of sulfonamides residues from raw milk followed by high performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aznar, M.; Úbeda, S.; Nerin, C.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric phase sorptive extraction as a reliable tool for rapid screening and detection of freshness markers in oranges. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1500, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanidou, V.; Michaelidou, K.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric phase sorptive extraction of selected penicillin antibiotic residues from intact milk followed by high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanidou, V.; Filippou, O.; Marinou, E.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Sol-gel-graphene-based fabric-phase sorptive extraction for cow and human breast milk sample cleanup for screening bisphenol A and residual dental restorative material before analysis by HPLC with diode array detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 2612–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakade, S.S.; Borrull, F.; Furton, K.G.; Kabir, A.; Marcé, R.M.; Fontanals, N. Dynamic fabric phase sorptive extraction for a group of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from environmental waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1456, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Gaurav; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Malik, A.K. Development of a fabric phase sorptive extraction with high-performance liquid chromatography and ultraviolet detection method for the analysis of alkyl phenols in environmental samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3228–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racamonde, I.; Rodil, R.; Quintana, J.B.; Sieira, B.J.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Cela, R. Fabric phase sorptive extraction: A new sorptive microextraction technique for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from environmental water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 865, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldán-Pijuán, M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Stir fabric phase sorptive extraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in environmental waters by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1376, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesdeoca-Esponda, S.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J. Fabric phase sorptive extraction followed by UHPLC-MS/MS for the analysis of benzotriazole UV stabilizers in sewage samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8137–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Guerra, R.B.; Montesdeoca-Esponda, S.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J. Rapid monitoring of residual UV-stabilizers in seawater samples from beaches using fabric phase sorptive extraction and UHPLC-MS/MS. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakade, S.S.; Borrull, F.; Furton, K.G.; Kabir, A.; Fontanals, N.; Marcé, R.M. Comparative study of different fabric phase sorptive extraction sorbents to determine emerging contaminants from environmental water using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2015, 144, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthemidis, A.; Kazantzi, V.; Samanidou, V.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. An automated flow injection system for metal determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry involving on-line fabric disk sorptive extraction technique. Talanta 2016, 156–157, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heena; Kaur, R.; Rani, S.; Malik, A.K.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Determination of cobalt(II), nickel(II) and palladium(II) Ions via fabric phase sorptive extraction in combination with high-performance liquid chromatography-UV detection. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcudia-León, M.C.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Integrated sampling and analysis unit for the determination of sexual pheromones in environmental air using fabric phase sorptive extraction and headspace-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1488, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulusoy, H.I. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles for the selective extraction of trace species from a complex matrix. In Analytical Chemistry: Developments, Applications and Challenges in Food Analysis; Locatelli, M., Celia, C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 55–76. ISBN 978-1-53612-267-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Hernández, A.A.; Álvarez-Romero, G.A.; Contreras-López, E.; Aguilar-Arteaga, K.; Castañeda-Ovando, A. Food Analysis by Microextraction Methods Based on the Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles as Supports: Recent Advances. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2974–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, I.; Fernandes, C. Magnetic solid phase extraction for determination of drugs in biological matrices. TrAC 2017, 89, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; González-Hernández, P.; Pino, V.; Pasán, J.; Afonso, A.M. Metal-organic frameworks as novel sorbents in dispersive-based microextraction approaches. TrAC 2017, 90, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, Á.; Zougagh, M. Recent advances in magnetic nanomaterials for improving analytical processes. TrAC 2017, 84, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Owczarek, K.; Namieśnik, J. Modern solutions in the field of microextraction using liquid as a medium of extraction. TrAC 2016, 85, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, V.; Abbasi, A.; Nosrati, A. Application of hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction techniques in analytical toxicology. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Latest trends, green aspects, and innovations in liquid-phase-based microextraction techniques: A review. Turkish J. Chem. 2016, 40, 868–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diuzheva, A.; Carradori, S.; Andruch, V.; Locatelli, M.; De Luca, E.; Tiecco, M.; Germani, R.; Menghini, L.; Nocentini, A.; Gratteri, P.; et al. Use of innovative (micro)extraction techniques to characterize harpagophytum procumbens root and its commercial food supplements. Phytochem. Anal. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Hu, B. Comparison of hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of organosulfur pesticides in environmental and beverage samples by gas chromatography with flame photometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1193, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rehim, M. Recent advances in microextraction by packed sorbent for bioanalysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rehim, M. New trend in sample preparation: On-line microextraction in packed syringe for liquid and gas chromatography applications: I. Determination of local anaesthetics in human plasma samples using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 801, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).