A Revisit to Effervescence-Assisted Microextraction of Non-Polar Organic Compounds Using Hydrophobic Magnetic Nanoparticles—Application to the Determination of UV Filters in Natural Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Synthesis of Stearic Acid-Coated Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.4. Preparation of Effervescent Tablets
2.5. Experimental Procedure
2.6. Real Samples
3. Results
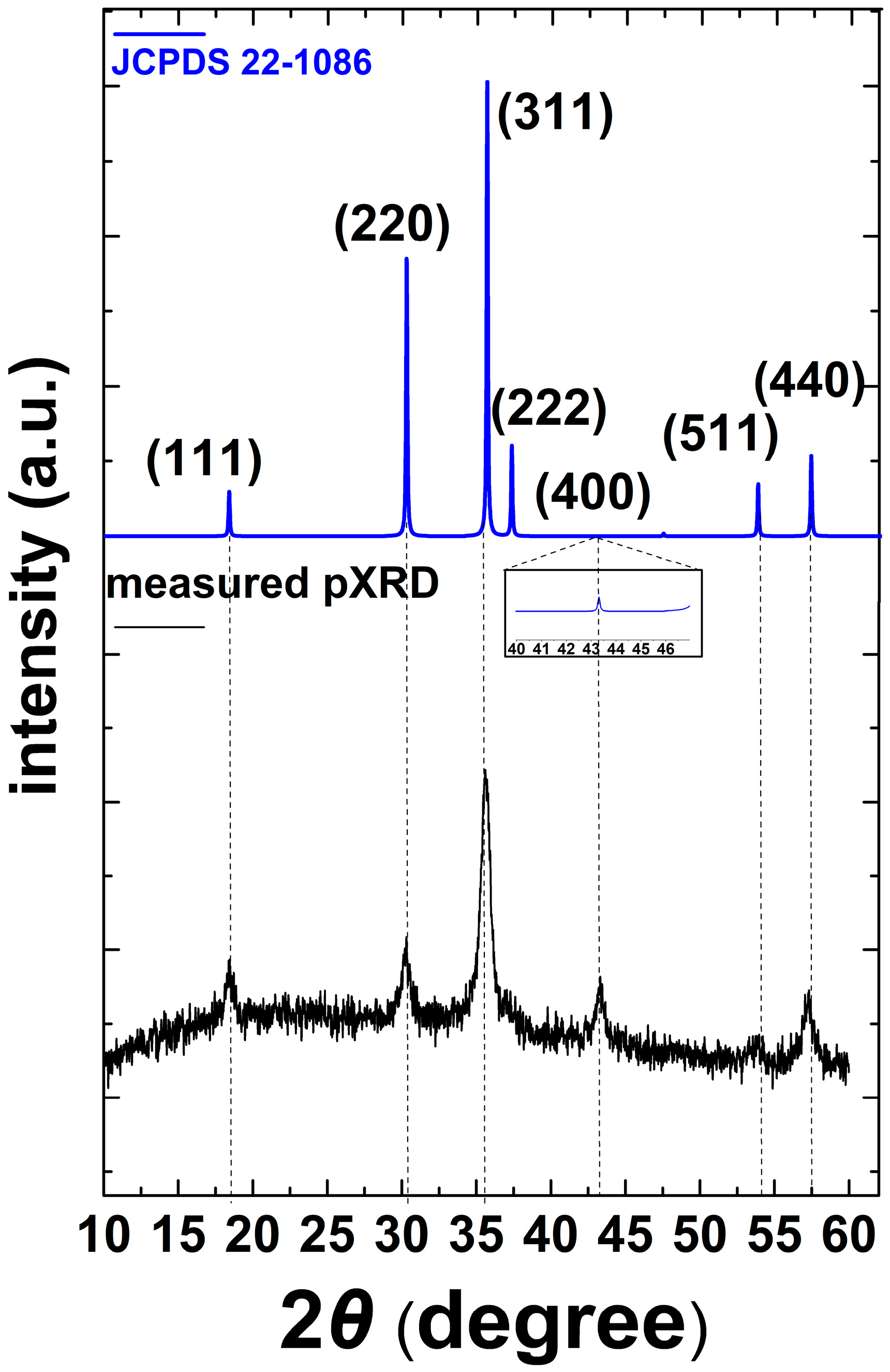
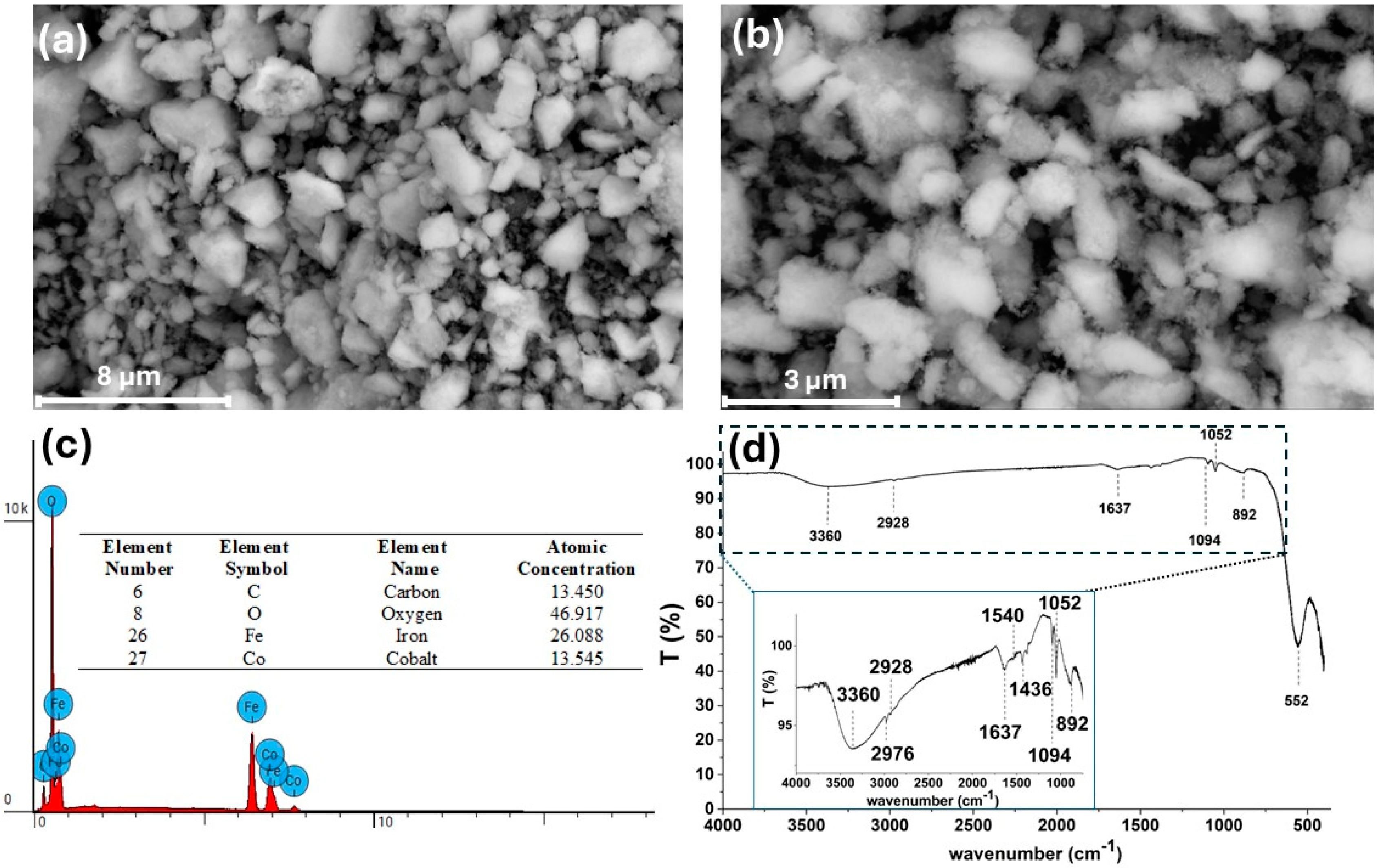
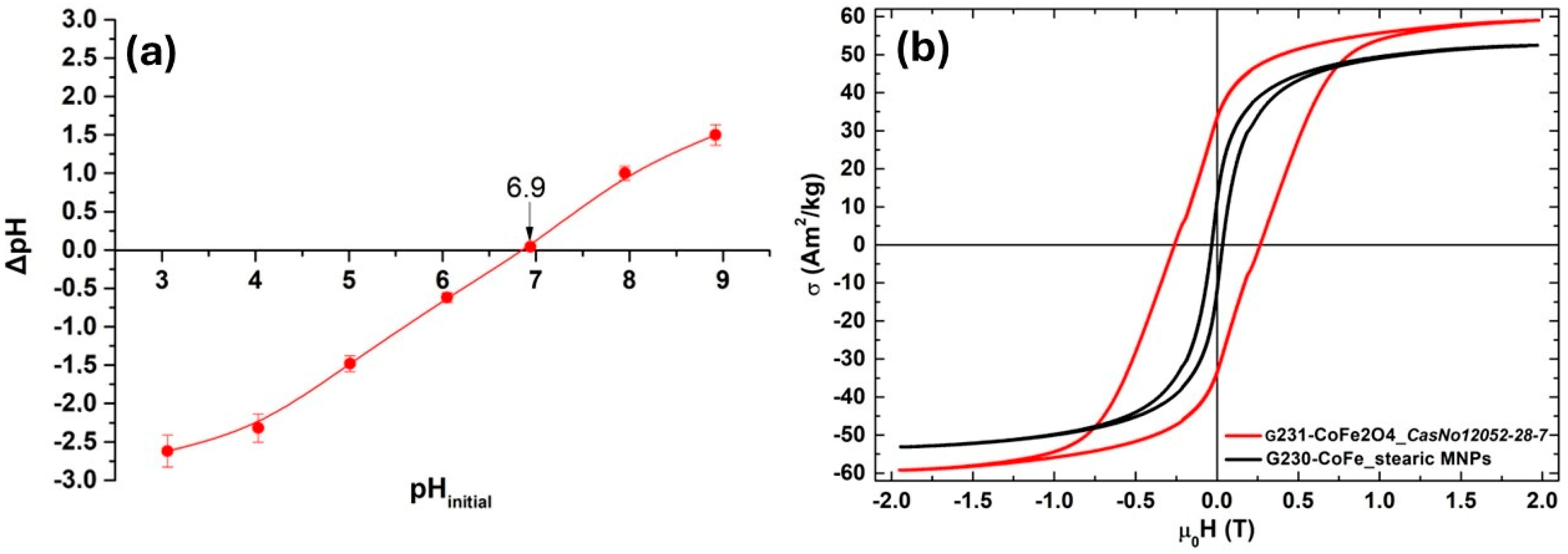
3.1. Characterization of CoFe2O4@Stearic Acid Magnetic Nanoparticles
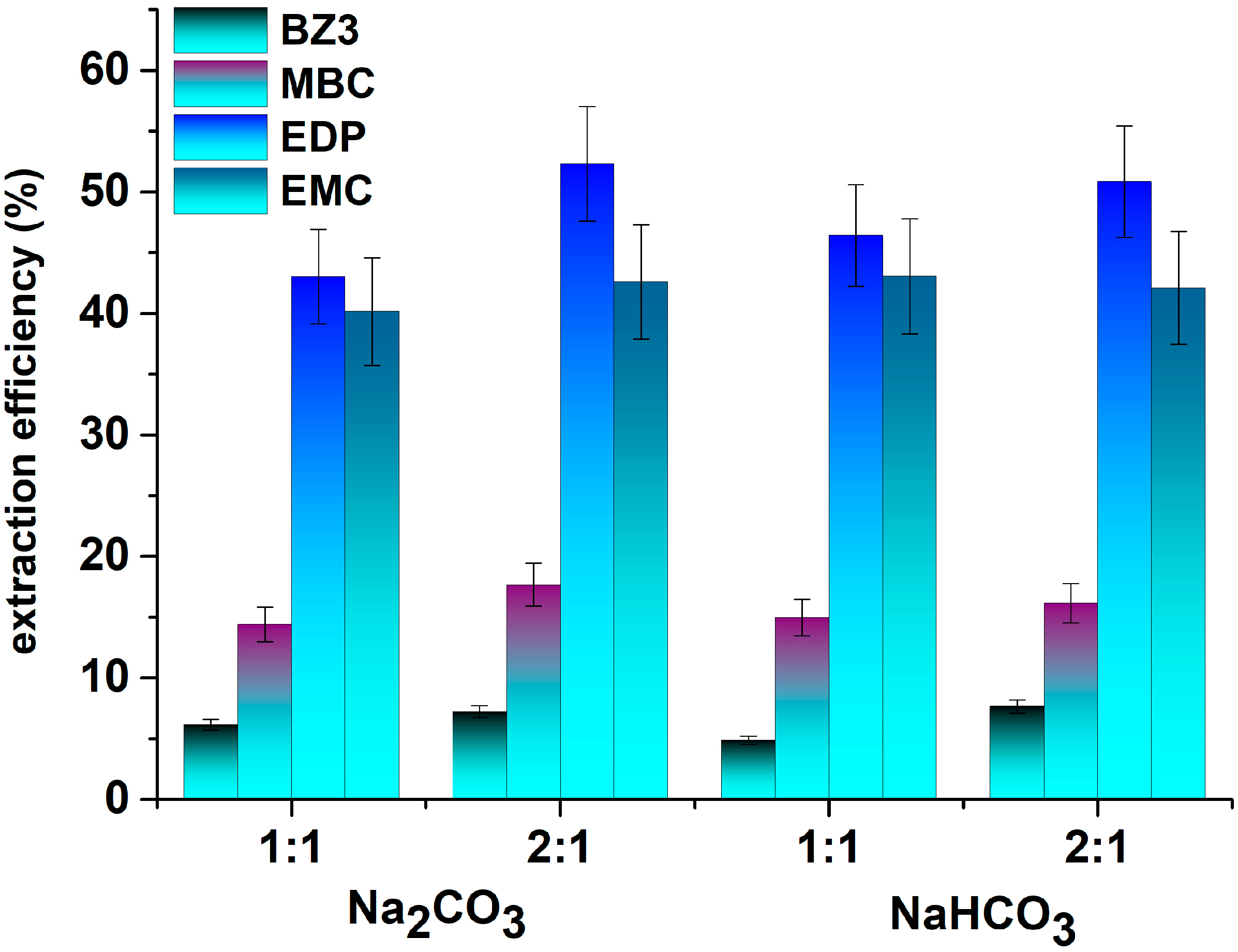
3.2. Effect of Effervescence on the Extraction Efficiency
3.3. Effect of Sorbent Mass
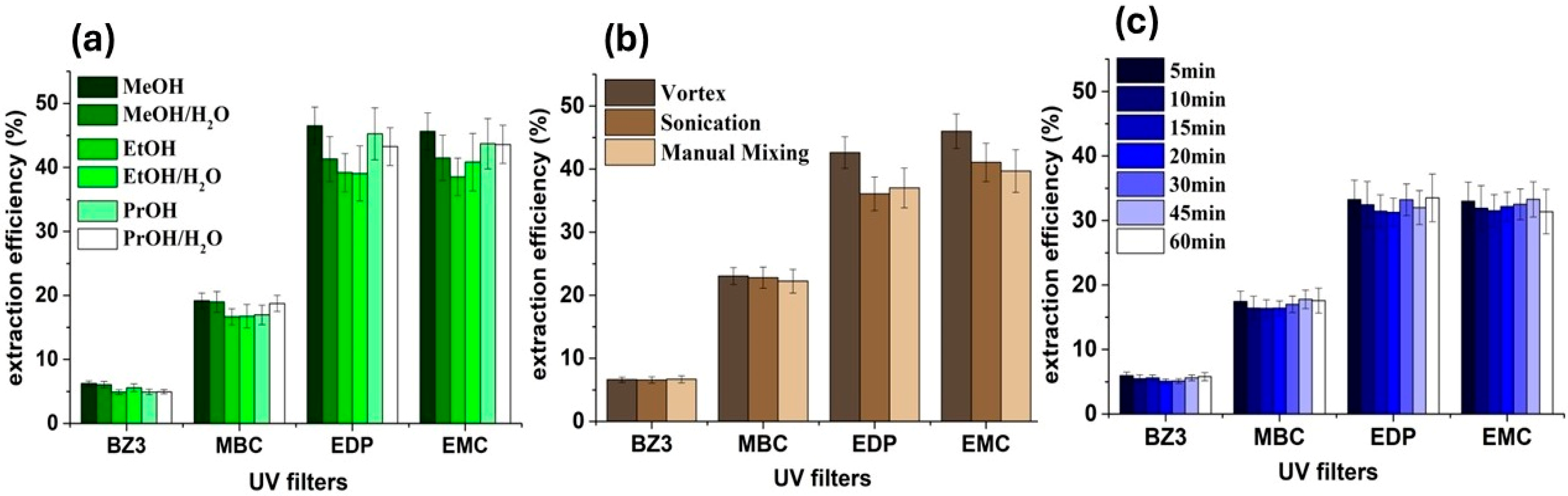
3.4. Optimization of the Desorption Process
3.5. Analytical Characteristics of the Method
3.6. Application to the Analysis of Genuine Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lasarte-Aragonés, G.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Effervescence-assisted dispersive micro-solid phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 9128–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasarte-Aragonés, G.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S. Effervescence-Assisted Microextraction—One Decade of Developments. Molecules 2020, 25, 6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasarte-Aragonés, G.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Effervescence-assisted carbon nanotubes dispersion for the micro-solid-phase extraction of triazine herbicides from environmental waters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3269–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, D. Effervescence assisted on-site liquid phase microextraction for the determination of five triazine herbicides in water. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1371, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Jin, L.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y. Magnetic effervescent tablet-assisted ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in liquid matrix samples. Talanta 2019, 195, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Chen, K.; Gao, M.; Qu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, X. Magnetic effervescent tablets containing ionic liquids as a non-conventional extraction and dispersive agent for determination of pyrethroids in milk. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Enhanced adsorption/extraction of five typical polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from meat samples using magnetic effervescent tablets composed of dicationic ionic liquids and NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-H.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Ye, L.-H.; Yang, J.; Dong, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, J.; Cao, J. Effervescent salt and crown ether-assisted matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction of coumarins from Cortex fraxini. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 141, 111752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Guo, X.; Chen, X.; Duan, J.; Gao, Z.; Zheng, B.; Shen, Q. Effervescent tablets containing magnetic ionic liquids as a non-conventional extraction and dispersive agent for speciation of arsenite and arsenate in vegetable samples. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Jing, X.; Tian, Y.; Feng, C. Magnetic Fe3O4 @ Porous Activated Carbon Effervescent Tablet-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction of Phenolic Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Environmental Water. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Hu, L.; Gao, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Lu, R. Effervescence-Assisted β-Cyclodextrin/Attapulgite Composite for the in-Syringe Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Pyrethroids in Environmental Water Samples. Talanta 2016, 153, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wu, X.; Jia, Y.; Xi, X.; Yang, X.; Lu, R.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Zhou, W. Use of Magnetic Effervescent Tablet-Assisted Ionic Liquid Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction to Extract Fungicides from Environmental Waters with the Aid of Experimental Design Methodology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 906, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; He, J.; Zhao, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, X. Effervescent Tablet-Assisted Switchable Hydrophilicity Solvent-Based Microextraction with Solidification of Floating Organic Droplets for HPLC Determination of Phenolic Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Bottled Beverages. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimirad, B.; Rajabi, M.; Elhampour, A. A rapid and simple extraction of anti-depressant drugs by effervescent salt-assisted dispersive magnetic micro solid-phase extraction method using new adsorbent Fe3O4@SiO2@N3. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1047, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, S.; Lucena, R. Recent Advances in Extraction and Stirring Integrated Techniques. Separations 2017, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Wang, R.; Fan, R.; Yang, X.; Mei, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Magnetic amino-functionalized metal-organic frameworks as a novel solid support in ionic liquids-based effervescent tablets for efficient extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in milks. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Na, Y.; Liang, N.; Zhao, L. Magnetic effervescent tablets containing deep eutectic solvent as a green microextraction for removal of polystyrene nanoplastics from water. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 188, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, R.H.; Mills, R.; Armstrong, H.L. Viscosity of Electrolytes and Related Properties. Am. J. Phys. 1966, 34, 280–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawliszyn, J.; Bayona, J.M.; Dugo, P.; Le, X.C.; Lee, H.K.; Li, X.F.; Lord, H. Comprehensive Sampling and Sample Preparation: Analytical Techniques for Scientists; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9780123813732. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, A.; Purkait, M.K. Effect of fatty acid chain length and concentration on the structural properties of the coated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 24, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel Rashin, M.; Hemalatha, J. Magnetic and ultrasonic studies on stable cobalt ferrite magnetic nanofluid. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, F.; Pellutiè, L.; Sordello, F.; Minero, C.; Ortel, E.; Hodoroaba, V.-D.; Maurino, V. Influence of agglomeration and aggregation on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 216, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, B.; Ozcelik, S.; Icin, K.; Senturk, K.; Ozcelik, B.; Arda, L. Structural, optical, magnetic, photocatalytic activity and related biological effects of CoFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 13068–13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, M.; Manouchehri, S.; Yousefi, M.H.; Amighian, J. The effect of solution temperature on crystallite size and magnetic properties of Zn substituted Co ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Fu, L.; Su, M.; Aslam, M.; Wong, K.C.; Dravid, V.P. Interaction of Fatty Acid Monolayers with Cobalt Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, T.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Denardin, J.C.; Varaprasad, K. The effect of capping agents on the structural and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 11774–11782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.T.; Suppiah, D.D.; Muhd Julkapli, N. Fatty acid coated iron oxide nanoparticle: Effect on stability, particle size and magnetic properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 606, 125371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiivanov, K.I.; Panayotov, D.A.; Mihaylov, M.Y.; Ivanova, E.Z.; Chakarova, K.K.; Andonova, S.M.; Drenchev, N.L. Power of Infrared and Raman Spectroscopies to Characterize Metal-Organic Frameworks and Investigate Their Interaction with Guest Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1286–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, V.; Pratap, A.; Raval, H. Studies on Poly (Hydroxy Alkanoates)/(Ethylcellulose) Blends. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2000, 23, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, P.J.; Jackson, A. Interpretation of the Infrared Spectra of Metal-Stearate Salts. Appl. Spectrosc. Pract. 2024, 2, 27551857241253834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjia, M.; Baroutaji, A.; Olabi, A.G. The Introduction of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles as a Solution for Magnetostrictive Applications. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giokas, D.L.; Zhu, Q.; Pan, Q.; Chisvert, A. Cloud point–dispersive μ-solid phase extraction of hydrophobic organic compounds onto highly hydrophobic core–shell Fe2O3 @C magnetic nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1251, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouma, V.; Pournara, A.D.; Manos, M.J.; Giokas, D.L. Fabric phase sorpitive extraction and passive sampling of ultraviolet filters from natural waters using a zirconium metal organic framework-cotton composite. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1670, 462945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A.; Giokas, D.L.; Salvador, A. Development of stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction mediated by magnetic nanoparticles and its analytical application to the determination of hydrophobic organic compounds in aqueous media. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1362, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieddu, M.; Pasciu, V.; Demontis, M.P.; Baralla, E. The Application of Liquid Chromatography for the Analysis of Organic UV Filters in Environmental and Marine Biota Matrices. Separations 2024, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A.; Salvador, A.; Sánchez-Quiles, D.; Tovar-Sánchez, A. Determination of UV filters in both soluble and particulate fractions of seawaters by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 812, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Kong, X.; Liu, S.; Che, D.; Sun, Z.; Li, G.; Ping, M.; Tang, J.; You, J. Determination of Ultraviolet Filters in Domestic Wastewater by LC–MS Coupled with Polydopamine-Based Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction and Isotope-Coded Derivatization. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Acid:Base Ratio | Acid | Base | Solution pH | Duration of Effervescence (s) | Ionic Strength (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | Citric Acid | Na2CO3 | 5.6 | 40 | 0.54 |
| NaHCO3 | 5.3 | 120 | 0.57 | ||
| Tartaric acid | Na2CO3 | 5.8 | 40 | 0.42 | |
| NaHCO3 | 4.6 | 60 | 0.18 | ||
| Oxalic acid | Na2CO3 | 5.3 | 50 | 0.34 | |
| NaHCO3 | 5.3 | 240 | 0.35 | ||
| Ascorbic acid | Na2CO3 | 8.0 | 60 | 0.25 | |
| NaHCO3 | 6.5 | 50 | 0.18 | ||
| NaH2PO4 | Na2CO3 | 7.4 | 60 | 0.80 | |
| NaHCO3 | 6.7 | 30 | 0.43 | ||
| Fumaric acid | Na2CO3 | 4.8 | 180 | 0.42 | |
| NaHCO3 | 4.2 | 180 | 0.24 | ||
| 2:1 | Citric acid | Na2CO3 | 4.5 | 60 | 0.38 |
| NaHCO3 | 3.9 | 210 | 0.64 | ||
| Tartaric acid | Na2CO3 | 4.6 | 60 | 0.36 | |
| NaHCO3 | 3.3 | 60 | 0.12 | ||
| Oxalic acid | Na2CO3 | 2.6 | 40 | 0.22 | |
| NaHCO3 | 2.4 | 60 | 0.34 | ||
| Ascorbic acid | Na2CO3 | 6.9 | 90 | 0.10 | |
| NaHCO3 | 5.6 | 40 | 0.12 | ||
| NaH2PO4 | Na2CO3 | 6.8 | 60 | 0.62 | |
| NaHCO3 | 6.4 | 180 | 0.41 | ||
| Fumaric acid | Na2CO3 | 3.9 | 60 | 0.24 | |
| NaHCO3 | 3.2 | 60 | 0.24 |
| 1:1 Acid:Base Ratio | pH | Effervescence Time | Ionic Strength | BZ3 | MBC | EDP | EMC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.00 | ||||||
| Effervescence time | −0.54 * | 1.00 | |||||
| Ionic strength | 0.12 | 0.11 | 1.00 | ||||
| BZ3 | −0.38 | 0.28 | −0.25 | 1.00 | |||
| MBC | −0.39 | 0.25 | −0.34 | 0.82 * | 1.00 | ||
| EDP | −0.15 | 0.15 | −0.31 | 0.11 | 0.42 | 1.00 | |
| EMC | −0.57 * | 0.48 * | −0.21 | 0.31 | 0.56 * | 0.28 | 1.00 |
| 2:1 Acid:Base Ratio | pH | Effervescence Time | Ionic Strength | BZ3 | MBC | EDP | EMC |
| pH | 1.00 | ||||||
| Effervescence time | 0.20 | 1.00 | |||||
| Ionic strength | 0.05 | 0.54 * | 1.00 | ||||
| BZ3 | −0.21 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 1.00 | |||
| MBC | −0.20 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.85 * | 1.00 | ||
| EDP | 0.18 | 0.09 | −0.09 | 0.66 * | 0.77 * | 1.00 | |
| EMC | −0.44 | −0.08 | −0.16 | 0.46 | 0.60 * | 0.44 | 1.00 |
| UV Filter | Slope ± sb ×103 (μg mL−1) a | Regression Coefficient R2 a | Linearity (μg mL−1) | LOD b (μg mL−1) | (%RSD) c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repeatability | Reproducibility | |||||
| BZ3 | 105 ± 4.4 | 0.995 | 0.5–10 | 0.5 | 9.2 | 10.4 |
| MBC | 323 ± 4.0 | 0.999 | 0.1–10 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 11.1 |
| EDP | 394 ± 9.0 | 0.998 | 0.1–10 | 0.1 | 8.6 | 4.2 |
| EMC | 101 ± 4.9 | 0.998 | 0.1–10 | 0.1 | 3.4 | 10.1 |
| UV Filter | Tap Water | River Water | Lake Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| BZ3 | 78.4 ± 7.1 | 105.2 ± 5.8 | 84.7 ± 6.3 |
| MBC | 102.1 ± 9.8 | 102.8 ± 7.9 | 127.1 ± 10.4 |
| EDP | 98.0 ± 8.4 | 105.0 ± 9.0 | 117.3 ± 12.4 |
| EMC | 101.6 ± 7.3 | 107.5 ± 9.2 | 112.4 ± 8.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toti, E.; Gouma, V.; Karagianni, V.I.; Giokas, D.L. A Revisit to Effervescence-Assisted Microextraction of Non-Polar Organic Compounds Using Hydrophobic Magnetic Nanoparticles—Application to the Determination of UV Filters in Natural Waters. Separations 2024, 11, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110315
Toti E, Gouma V, Karagianni VI, Giokas DL. A Revisit to Effervescence-Assisted Microextraction of Non-Polar Organic Compounds Using Hydrophobic Magnetic Nanoparticles—Application to the Determination of UV Filters in Natural Waters. Separations. 2024; 11(11):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110315
Chicago/Turabian StyleToti, Efthymia, Vasiliki Gouma, Vasiliki I. Karagianni, and Dimosthenis L. Giokas. 2024. "A Revisit to Effervescence-Assisted Microextraction of Non-Polar Organic Compounds Using Hydrophobic Magnetic Nanoparticles—Application to the Determination of UV Filters in Natural Waters" Separations 11, no. 11: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110315
APA StyleToti, E., Gouma, V., Karagianni, V. I., & Giokas, D. L. (2024). A Revisit to Effervescence-Assisted Microextraction of Non-Polar Organic Compounds Using Hydrophobic Magnetic Nanoparticles—Application to the Determination of UV Filters in Natural Waters. Separations, 11(11), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110315








