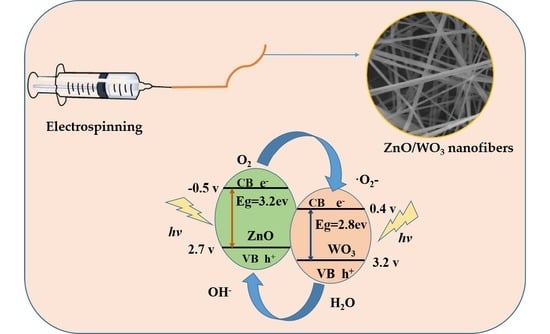
Application of ZnO/WO3 Composite Nanofiber Photocatalysts in Textile Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Yan, H.; Chen, T. Application of ZnO/WO3 Composite Nanofiber Photocatalysts in Textile Wastewater Treatment. Separations 2023, 10, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060339
Xu Y, Yan H, Chen T. Application of ZnO/WO3 Composite Nanofiber Photocatalysts in Textile Wastewater Treatment. Separations. 2023; 10(6):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060339
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yongxin, Hui Yan, and Tiwei Chen. 2023. "Application of ZnO/WO3 Composite Nanofiber Photocatalysts in Textile Wastewater Treatment" Separations 10, no. 6: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060339
APA StyleXu, Y., Yan, H., & Chen, T. (2023). Application of ZnO/WO3 Composite Nanofiber Photocatalysts in Textile Wastewater Treatment. Separations, 10(6), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060339