A Compendium of the Principal Stationary Phases Used in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography: Where Have We Arrived?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Achiral Stationary Phases in HILIC
2.1. Commercial Stationary Phases
2.2. Non-Commercial Stationary Phases
| Phase Type | Phase Name | Functional Groups | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral | Alkylurea | 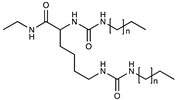 | [50] |
| Pentafluorobenzamide | 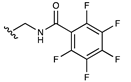 | [53] | |
| Polyacrylamide | 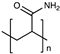 | [47] | |
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone | 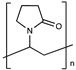 | [49] | |
| Polyglycerol | 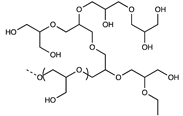 | [48] | |
| Anionic | Dicarboxylic cellulose | 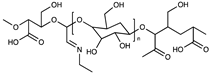 | [55] |
| Poly(itaconic acid) | 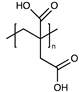 | [56] | |
| Sulfonated chitooligosaccharide | 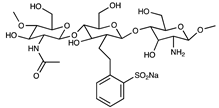 | [57] | |
| Cationic | Butanediol/dopamine dendrimer |  | [58] |
| Dodecyl/hydroxyethyl/ quaternary amine | 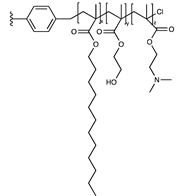 | [59] | |
| Polyethyleneimine embedded | 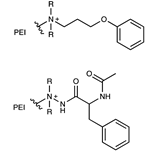 | [60,61] | |
| PVA-cationic cellulose | 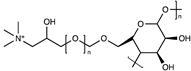 | [62] | |
| Zwitterionic | Amino acids | 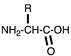 | [63,64,65,66,67,68,69] |
| Peptides (Glutathione, glycylalanine) | 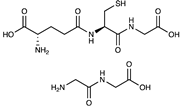 | [70,71,72,73] | |
| Sulfonate/pyridinium | 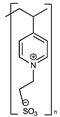 | [74] | |
| Carboxylate or sulfonate/tertiary amine | 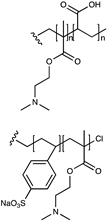 | [75] |
3. Chiral Stationary Phases in HILIC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alpert, A.J. Hydrophilic-Interaction Chromatography for the Separation of Peptides, Nucleic Acids and Other Polar Compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 1990, 499, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandera, P.; Janás, P. Recent Advances in Stationary Phases and Understanding of Retention in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 967, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, L.; Havlíková, L.; Vlčková, H. Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography of Polar and Ionizable Compounds by UHPLC. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 63, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyler, A.R.; Armstrong, B.L.; Cha, J.Y.; Zhou, M.X.; Yang, Q.; Robinson, R.I.; Dunphy, R.; Burinsky, D.J. Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography on Amino-Silica Phases Complements Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Capillary Electrophoresis for Peptide Analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 724, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbis, S.D.; Melse-Boonstra, A.; West, C.E.; Van Breemen, R.B. Determination of Folates in Human Plasma Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5358–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, B.A. Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Using Amino and Silica Columns for the Determination of Polar Pharmaceuticals and Impurities. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 913, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Huang, J. Chromatographic Behavior of Epirubicin and Its Analogues on High-Purity Silica in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1041, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gaiki, S. Retention Behavior of Small Polar Compounds on Polar Stationary Phases in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1074, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandera, P. Stationary and Mobile Phases in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 692, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Noga, S. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC)-a Powerful Separation Technique. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandera, P.; Hájek, T.; Škeříková, V.; Soukup, J. Dual Hydrophilic Interaction-RP Retention Mechanism on Polar Columns: Structural Correlations and Implementation for 2-D Separations on a Single Column. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemström, P.; Irgum, K. Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 1784–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkmen, C.; Gebrehiwot, W.H.; Uslu, B. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC): Latest Applications in the Pharmaceutical Researches. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 17, 316–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargano, A.F.G.; Roca, L.S.; Fellers, R.T.; Bocxe, M.; Domínguez-Vega, E.; Somsen, G.W. Capillary HILIC-MS: A New Tool for Sensitive Top-Down Proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6601–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P.G.; Mnatsakanyan, M.; Francis, A.R.; Shalliker, R.A. A Discussion on the Process of Defining 2-D Separation Selectivity. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilar, M.; Olivova, P.; Daly, A.E.; Gebler, J.C. Orthogonality of Separation in Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6426–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Patterson, D.G.; Lee, M.L. Geometric Approach to Factor Analysis for the Estimation of Orthogonality and Practical Peak Capacity in Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Separations. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 3840–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, P.F.; Duarte, A.C.; Duarte, R.M.B.O. Comprehensive Multidimensional Liquid Chromatography for Advancing Environmental and Natural Products Research. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugo, P.; Cacciola, F.; Kumm, T.; Dugo, G.; Mondello, L. Comprehensive Multidimensional Liquid Chromatography: Theory and Applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1184, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairchild, J.N.; Horváth, K.; Guiochon, G. Approaches to Comprehensive Multidimensional Liquid Chromatography Systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, W.; Rasmussen, H.T. Orthogonal Method Development Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography and Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for the Determination of Pharmaceuticals and Impurities. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1083, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yang, B.; Dasgupta, P.K. Low-Bleed Silica-Based Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8750–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, B.; Liang, X. Preparation of a Low Bleeding Polar Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography. Talanta 2018, 182, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Richards, M.A.; Zha, Y.; Francis, R.; Lozano, R.; Ruan, J. Determination of Inorganic Pharmaceutical Counterions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Coupled with a Corona® CAD Detector. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.; Kwon, S.W. Comparison of Two Aerosol-Based Detectors for the Analysis of Gabapentin in Pharmaceutical Formulations by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. Talanta 2011, 85, 2301–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wahab, M.F.; Breitbach, Z.S.; Armstrong, D.W. Carboxylated Cyclofructan 6 as a Hydrolytically Stable High Efficiency Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography and Mixed Mode Separations. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6038–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, J.C.; Lawhead, C.L. Liquid Chromatography of Saccharides. J. Chromatogr. A 1975, 105, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalley, D.V. Is Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography with Silica Columns a Viable Alternative to Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography for the Analysis of Ionisable Compounds? J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1171, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pack, B.W.; Risley, D.S. Evaluation of a Monolithic Silica Column Operated in the Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Mode with Evaporative Light Scattering Detection for the Separation and Detection of Counter-Ions. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1073, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T. Silica Hydride: A Separation Material Every Analyst Should Know About. Molecules 2021, 26, 7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnier, F.E.; Noel, R. Glycerolpropylsilane Bonded Phases in the Steric Exclusion Chromatography of Biological Macromolecules. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1976, 14, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandera, P.; Hájek, T. Utilization of Dual Retention Mechanism on Columns with Bonded PEG and Diol Stationary Phases for Adjusting the Separation Selectivity of Phenolic and Flavone Natural Antioxidants. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 3603–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazourek, J. Monitoring of Mutarotation of Monosaccharides by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandera, P.; Hájek, T. A New Definition of the Stationary Phase Volume in Mixed-mode Chromatographic Columns in Hydrophilic Liquid Chromatography. Molecules 2021, 26, 4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnarova, K.; Kozlík, P. Comparison of Different HILIC Stationary Phases in the Separation of Hemopexin and Immunoglobulin G Glycopeptides and Their Isomers. Molecules 2020, 25, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Bhalodia, N.; Fattal, B. Evaluating Relative Retention of Polar Stationary Phases in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. Separations 2019, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.W.; Jin, H.L. Evaluation of the Liquid Chromatographic of monosaccharides, disaccharides, trisaccharides, tetrasaccharides, deoxysaccharides and sugar alcohols with stable cyclodextrin bonded phase columns. J. Chromatogr. A 1989, 462, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, A.; Chang, S.S.C.; Kullman, J.P.S.; Armstrong, D.W. Practice and Mechanism of HPLC Oligosaccharide Separation with a Cyclodextrin Bonded Phase. Talanta 1998, 47, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T. Peptide Separation in Normal Phase Liquid Chromatography. Sci. Instrum. Div. 1997, 69, 3038–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, T.; Taniguchi, A.; Okada, T.; Horie, K.; Arase, S.; Ikegami, Y. Functionalization Using Polymer or Silane? A Practical Test Method to Characterize Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Phases in Terms of Their Functionalization Method. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1638, 461850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, G.; Winge, S.; Sandberg, H. Separation of Monosaccharides by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography with Evaporative Light Scattering Detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1092, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturrospe, E.; Da Silva, K.M.; Andújar, B.T.; Cuykx, M.; Boeckmans, J.; Vanhaecke, T.; Covaci, A.; van Nuijs, A.L.N. An Exploratory Approach for an Oriented Development of an Untargeted Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Platform for Polar Metabolites in Biological Matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1637, 461807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shen, G.; Yang, B. A Hyperbranched Polyethylenimine Functionalized Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 3633–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Irgum, K. Covalently Bonded Polymeric Zwitterionic Stationary Phase for Simultaneous Separation of Inorganic Cations and Anions. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Fischer, G.; Girmay, Y.; Irgum, K. Zwitterionic Stationary Phase with Covalently Bonded Phosphorylcholine Type Polymer Grafts and Its Applicability to Separation of Peptides in the Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography Mode. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1127, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y. A Survey of Polar Stationary Phases for Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography and Recent Progress in Understanding Retention and Selectivity. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2022, 36, e5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, C.; Guillarme, D.; Spörri, A.S.; Cognard, E.; Ortelli, D.; Edder, P.; Rudaz, S. Aminoglycoside Analysis in Food of Animal Origin with a Zwitterionic Stationary Phase and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 882, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Geng, H.; Yang, B. A Hydrolytically Stable Amide Polar Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. Talanta 2021, 231, 122340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Jing, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, F.; Yang, B. A Polar Stationary Phase Obtained by Surface-Initiated Polymerization of Hyperbranched Polyglycerol onto Silica. Talanta 2020, 209, 120525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Wan, L.; Wu, R. One-Pot Hydrothermal Cross-Linking Preparation of Poly(Vinylpyrrolidone) Immobilized Silica Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1633, 461656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, A.K.; Guragain, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Takafuji, M.; Ihara, H. L-Lysine-Derived Highly Selective Stationary Phases for Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography: Effect of Chain Length on Selectivity, Efficiency, Resolution, and Asymmetry. Sep. Sci. Plus 2019, 2, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moni, L.; Ciogli, A.; D’Acquarica, I.; Dondoni, A.; Gasparrini, F.; Marra, A. Synthesis of Sugar-Based Silica Gels by Copper-Catalysed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition via a Single-Step Azido-Activated Silica Intermediate and the Use of the Gels in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. Chem.A Eur. J. 2010, 16, 5712–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Liang, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Liang, X. Chemically Bonded Maltose via Click Chemistry as Stationary Phase for HILIC. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ferreira, C.C.; Gama, M.R.; da Silva, G.S.; Almeida, W.P.; Collins, C.H.; Jardim, I.C.S.F. Synthesis and Evaluation of a Pentafluorobenzamide Stationary Phase for HPLC Separations in the Reversed Phase and Hydrophilic Interaction Modes. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3855–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCalley, D.V. Understanding and Manipulating the Separation in Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1523, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Luo, G.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H. A New Strategy for the Preparation of Mixed-Mode Chromatographic Stationary Phases Based on Modified Dialdehyde Cellulose. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1618, 460885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cai, T.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Qiu, H. Poly(Itaconic Acid)-Grafted Silica Stationary Phase Prepared in Deep Eutectic Solvents and Its Unique Performance in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. Talanta 2019, 191, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Yang, H.; Huang, S.; Bai, Z. A Sulfonated Chitooligosaccharide Modified Silica Material for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography and Its Chromatographic Evaluation. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zeng, J.; Fu, Q.; Gao, D.; Zhang, K.; Ren, X.; Zhou, K.; Xia, Z.; Wang, L. Preparation and Evaluation of a Reversed-Phase/Hydrophilic Interaction/Ion-Exchange Mixed-Mode Chromatographic Stationary Phase Functionalized with Dopamine-Based Dendrimers. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, C.; Jia, Z.; Dai, X.; Wei, Y. Facile Preparation of Polymer-Brush Reverse-Phase/Hydrophilic Interaction/Ion-Exchange Tri-Mode Chromatographic Stationary Phases by Controlled Polymerization of Three Functional Monomers. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1619, 460966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Hu, C.; Gao, D.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zu, F.; Zeng, J.; Wang, L.; Xia, Z. Preparation of a Poly(Ethyleneimine) Embedded Phenyl Stationary Phase for Mixed-Mode Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1042, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Luo, Q.; Ren, X.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, D.; Fu, Q.; Zu, F.; Xia, Z.; Wang, L. Preparation and Performance of a Poly(Ethyleneimine) Embedded N-Acetyl-L-Phenylalanine Mixed-Mode Stationary Phase for HPLC. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Pan, X.; Hou, Y.; Yang, B. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Cationic Cellulose Copolymer Encapsulated SiO2 Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 21336–21341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Guo, Z.; Cai, X.; Xue, X.; Liang, X. Preparation and Chromatographic Evaluation of a Cysteine-Bonded Zwitterionic Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1228, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, A.; Guo, Z.; Yu, L.; Cao, L.; Liang, X. A Novel Zwitterionic HILIC Stationary Phase Based on “Thiol-Ene” Click Chemistry between Cysteine and Vinyl Silica. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4550–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciogli, A.; Buonsenso, F.; Proietti, N.; Mazzoccanti, G.; Manetto, S.; Calcaterra, A.; De Angelis, M.; Gasparrini, F. Preparation of a High-Density Vinyl Silica Gel to Anchor Cysteine via Photo-Click Reaction and Its Applications in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1675, 463173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcaterra, A.; Manetto, S.; Buonsenso, F.; Francioso, A.; Pierini, M.; Villani, C. Separation of Monosaccharide Anomers on Photo-Click Cysteine-Based Stationary Phase: The α/β Interconversion Process Studied by Dynamic Hydrophilic Liquid Chromatography. Separations 2022, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Geng, H.; Yang, B. A Polymer-Based Zwitterionic Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography. Talanta 2020, 216, 120927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadpour, M.; Maghari, S.; Rezadoost, H.; Bagheri, M.; Ghassempour, A. A Click Tyrosine Zwitterionic Stationary Phases for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1621, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, C.; Miao, Y.; Deng, Z.; Ba, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, S. Tetra-Proline Modified Calix[4]Arene Bonded Silica Gel: A Novel Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography. Talanta 2019, 193, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aral, H.; Çelik, K.S.; Altındağ, R.; Aral, T. Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of a Novel Multifunctional Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction/Reversed Phase Mixed-Mode Chromatography. Talanta 2017, 174, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Wang, X.; Peng, J.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, S. Preparation and Evaluation of Surface-Bonded Phenylglycine Zwitterionic Stationary Phase. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5941–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Wei, J.; Guo, Z.; Liang, X. Glutathione-Based Zwitterionic Stationary Phase for Hydrophilic Interaction/Cation-Exchange Mixed-Mode Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1314, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Liu, Y.; Shen, A.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, L.; Liang, X. Preparation of Glutathione-Functionalized Zwitterionic Silica Material for Efficient Enrichment of Sialylated N-Glycopeptides. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4131–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoczylas, M.; Bocian, S.; Buszewski, B. Dipeptide-Bonded Stationary Phases for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 96389–96397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Skoczylas, M. Multi-Parametric Characterization of Amino Acid- and Peptide-Silica Stationary Phases. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takafuji, M.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Sasahara, K.; Ihara, H. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Hydrophilic Interaction/Ion Exchange Mixed-Mode Chromatographic Stationary Phase with Pyridinium-Based Zwitterionic Polymer-Grafted Porous Silica. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3957–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Preparation of Hydrophilic Interaction/Ion-Exchange Mixed-Mode Chromatographic Stationary Phase with Adjustable Selectivity by Controlling Different Ratios of the Co-Monomers. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1487, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocian, S.; Skoczylas, M.; Buszewski, B. Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins as Chemically Bonded Stationary Phases—A Review. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, O.H.; Ciogli, A.; Villani, C.; De Martino, M.; Pierini, M.; Cavazzini, A.; Bell, D.S.; Gasparrini, F. Ultra-Fast High-Efficiency Enantioseparations by Means of a Teicoplanin-Based Chiral Stationary Phase Made on Sub-2μm Totally Porous Silica Particles of Narrow Size Distribution. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1427, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, O.H.; Antonelli, M.; Ciogli, A.; Villani, C.; Cavazzini, A.; Catani, M.; Felletti, S.; Bell, D.S.; Gasparrini, F. Future Perspectives in High Efficient and Ultrafast Chiral Liquid Chromatography through Zwitterionic Teicoplanin-Based 2-Μm Superficially Porous Particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1520, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, O.H.; Antonelli, M.; Ciogli, A.; De Martino, M.; Catani, M.; Villani, C.; Cavazzini, A.; Ye, M.; Bell, D.S.; Gasparrini, F. Direct Analysis of Chiral Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Their Counterions by Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Macrocyclic Glycopeptide-Based Chiral Stationary Phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1576, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoccanti, G.; Manetto, S.; Ricci, A.; Cabri, W.; Orlandin, A.; Catani, M.; Felletti, S.; Cavazzini, A.; Ye, M.; Ritchie, H.; et al. High–Throughput Enantioseparation of Nα–Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl Proteinogenic Amino Acids through Fast Chiral Chromatography on Zwitterionic-Teicoplanin Stationary Phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1624, 461235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, O.H.; Catani, M.; Mazzoccanti, G.; Felletti, S.; Manetto, S.; De Luca, C.; Ye, M.; Cavazzini, A.; Gasparrini, F. Boosting the Enantioresolution of Zwitterionic-Teicoplanin Chiral Stationary Phases by Moving to Wide-Pore Core-Shell Particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1676, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirilli, R.; Costi, R.; Di Santo, R.; La Torre, F.; Pierini, M.; Siani, G. Perturbing Effects of Chiral Stationary Phase on Enantiomerization Second-Order Rate Constants Determined by Enantioselective Dynamic High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: A Practical Tool to Quantify the Accessible Acid and Basic Catalytic Sites Bonded. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3560–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasa, S.K.M.; Venkatanarayana, M.; Chennuru, L.N.; Rao, B.C.S.; Vemparala, M.; Chaman, A.F.; Talluri, M.V.N.K. Chiral LC Method Development: Stereo-Selective Separation, Characterization, and Determination of Cabotegravir and Related RS, RR, and SS Isomeric Impurities on Coated Cellulose-Based Chiral Stationary Phase by HILIC-LC and LC-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 222, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Baeza, M.; Escuder-Gilabert, L.; Martín-Biosca, Y.; Sagrado, S.; Medina-Hernández, M.J. Comparative Study on Retention Behaviour and Enantioresolution of Basic and Neutral Structurally Unrelated Compounds with Cellulose-Based Chiral Stationary Phases in Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1673, 463073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
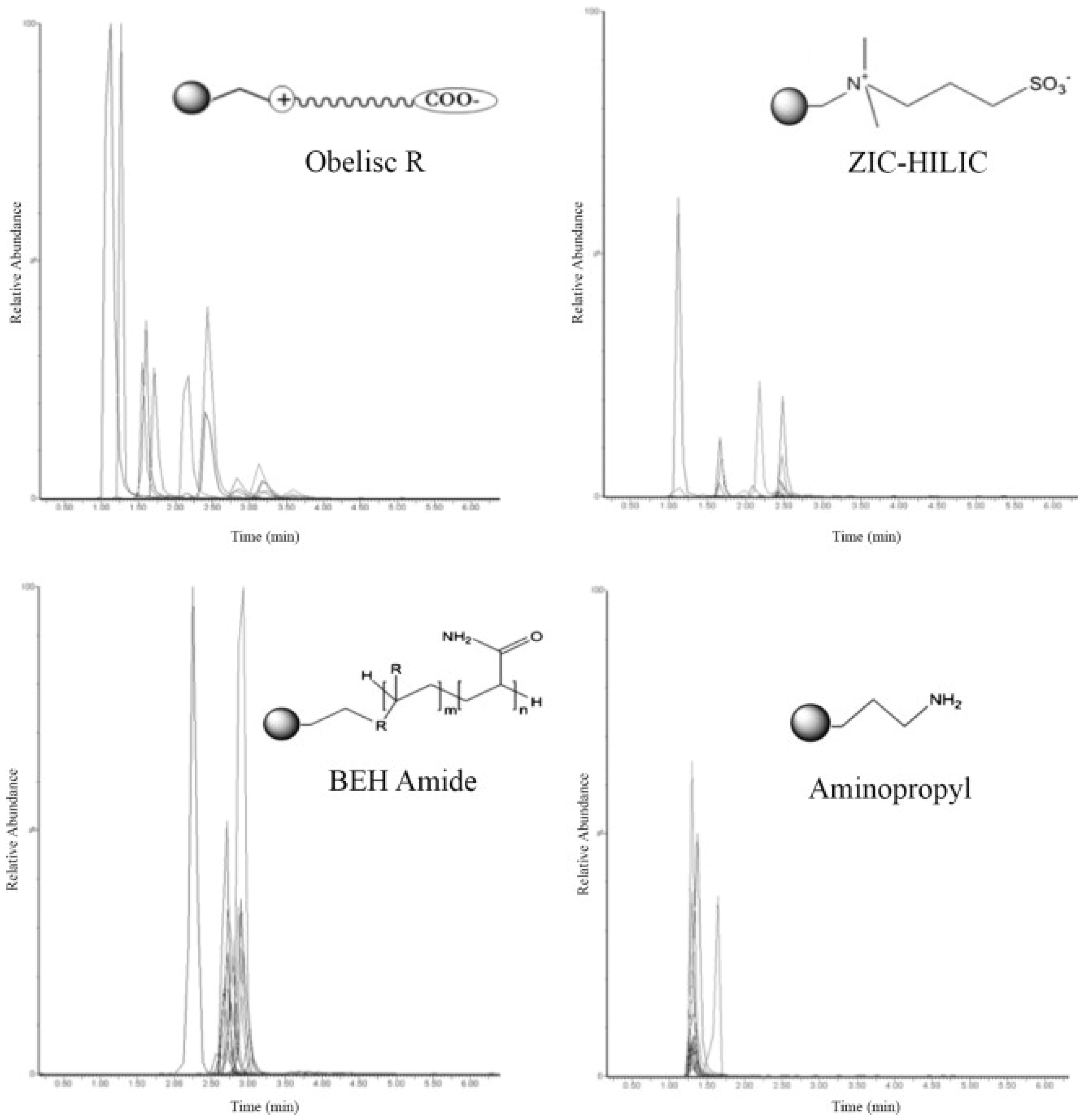
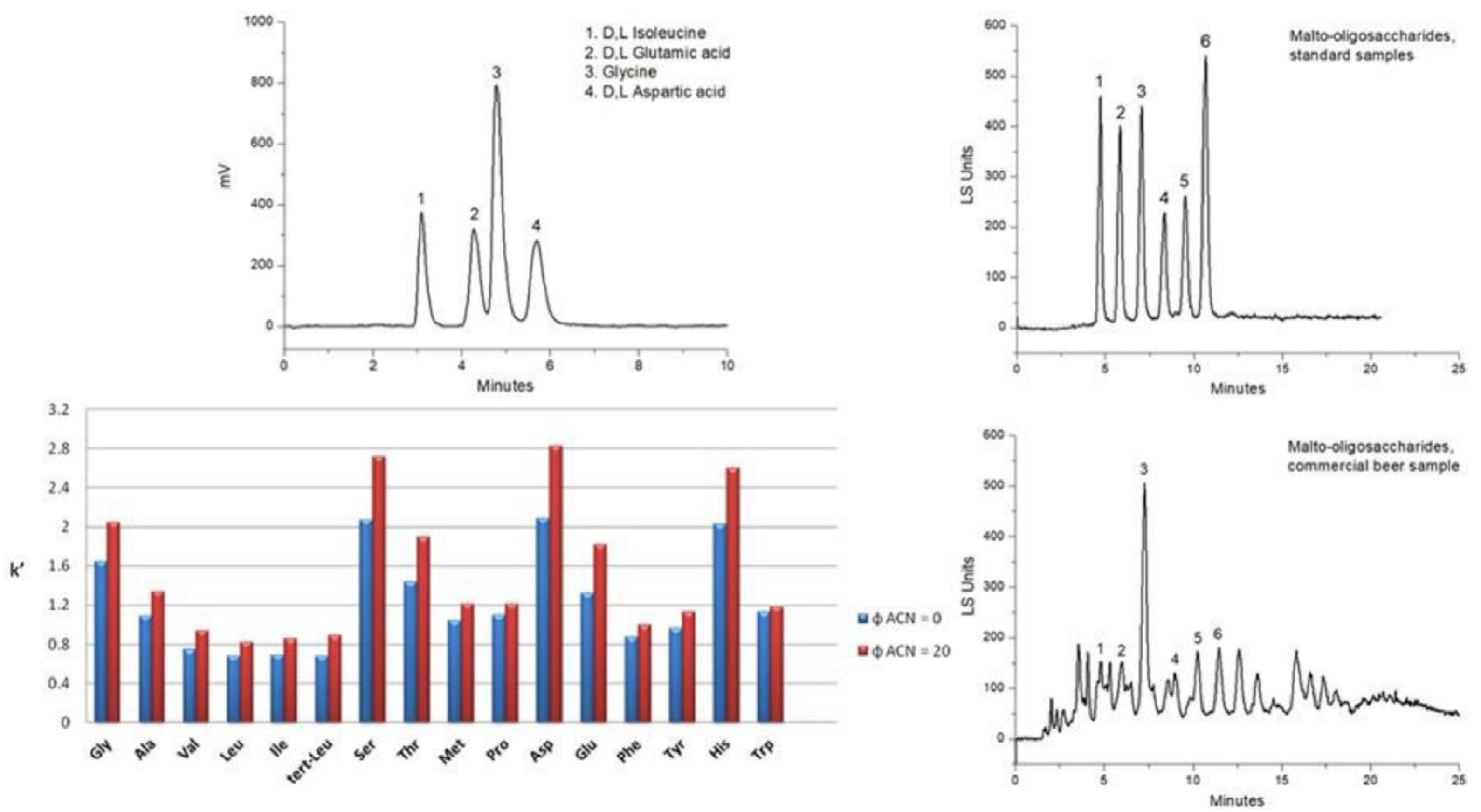
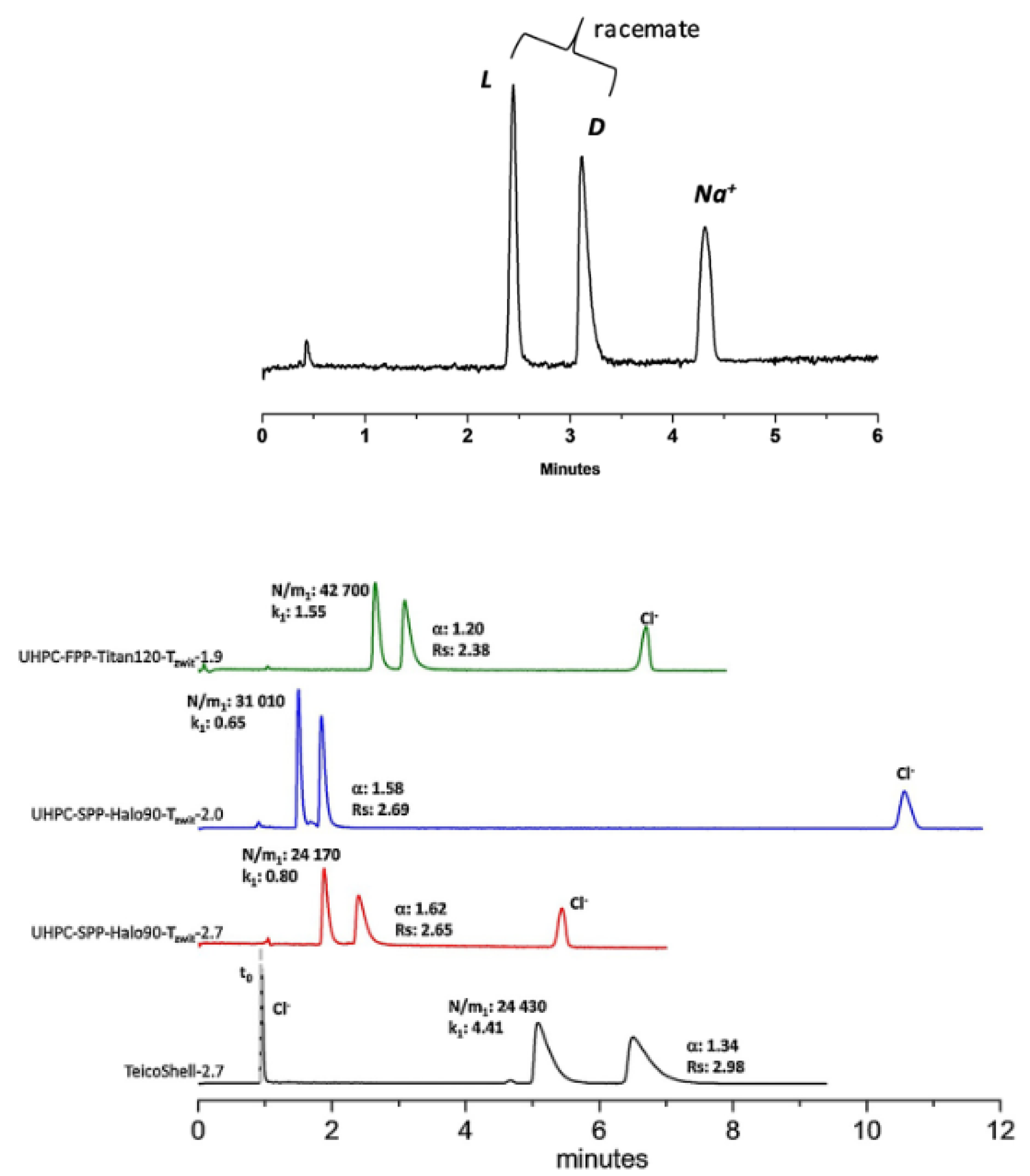
| Phase Type | Phase Name | Functional Group | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral | Amide |  | [12,39,40] |
| Cyclofructan | 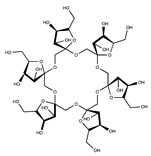 | [37,38] | |
| Cyclodextrin | 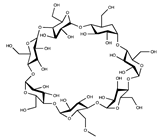 | ||
| Diol | 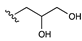 | [31,32,33] | |
| Pentanediol |  | [34,35] | |
| Polyacrylamide | 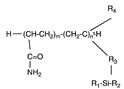 | [8,41] | |
| Polyhydroxy | 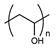 | [36] | |
| Anionic | Aspartic acid | 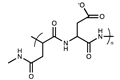 | [1] |
| Carboxylic acid | 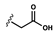 | [1] | |
| Silanol | 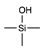 | [29] | |
| Sulfoethyl | 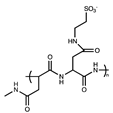 | [1] | |
| Cationic | Amino |  | [4] |
| Tertiary/quaternary amine |  | [9,42] | |
| Polyethyleneimine | 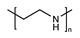 | [43] | |
| Zwitterionic | Phosphocoline | 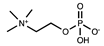 | [36] |
| Sulfobetaine | 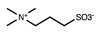 | [36] | |
| Sulfonate, phosphate/quaternary amine | 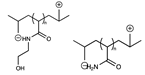 | [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guarducci, M.A.; Fochetti, A.; Ciogli, A.; Mazzoccanti, G. A Compendium of the Principal Stationary Phases Used in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography: Where Have We Arrived? Separations 2023, 10, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10010022
Guarducci MA, Fochetti A, Ciogli A, Mazzoccanti G. A Compendium of the Principal Stationary Phases Used in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography: Where Have We Arrived? Separations. 2023; 10(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuarducci, Maria A., Andrea Fochetti, Alessia Ciogli, and Giulia Mazzoccanti. 2023. "A Compendium of the Principal Stationary Phases Used in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography: Where Have We Arrived?" Separations 10, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10010022
APA StyleGuarducci, M. A., Fochetti, A., Ciogli, A., & Mazzoccanti, G. (2023). A Compendium of the Principal Stationary Phases Used in Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography: Where Have We Arrived? Separations, 10(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10010022








