A Rare Case of Transient Acantholytic Dermatosis (AKA. Grover’s Disease) with Concomitant Pediculosis Pubis: An Atypical Presentation and First Documented Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
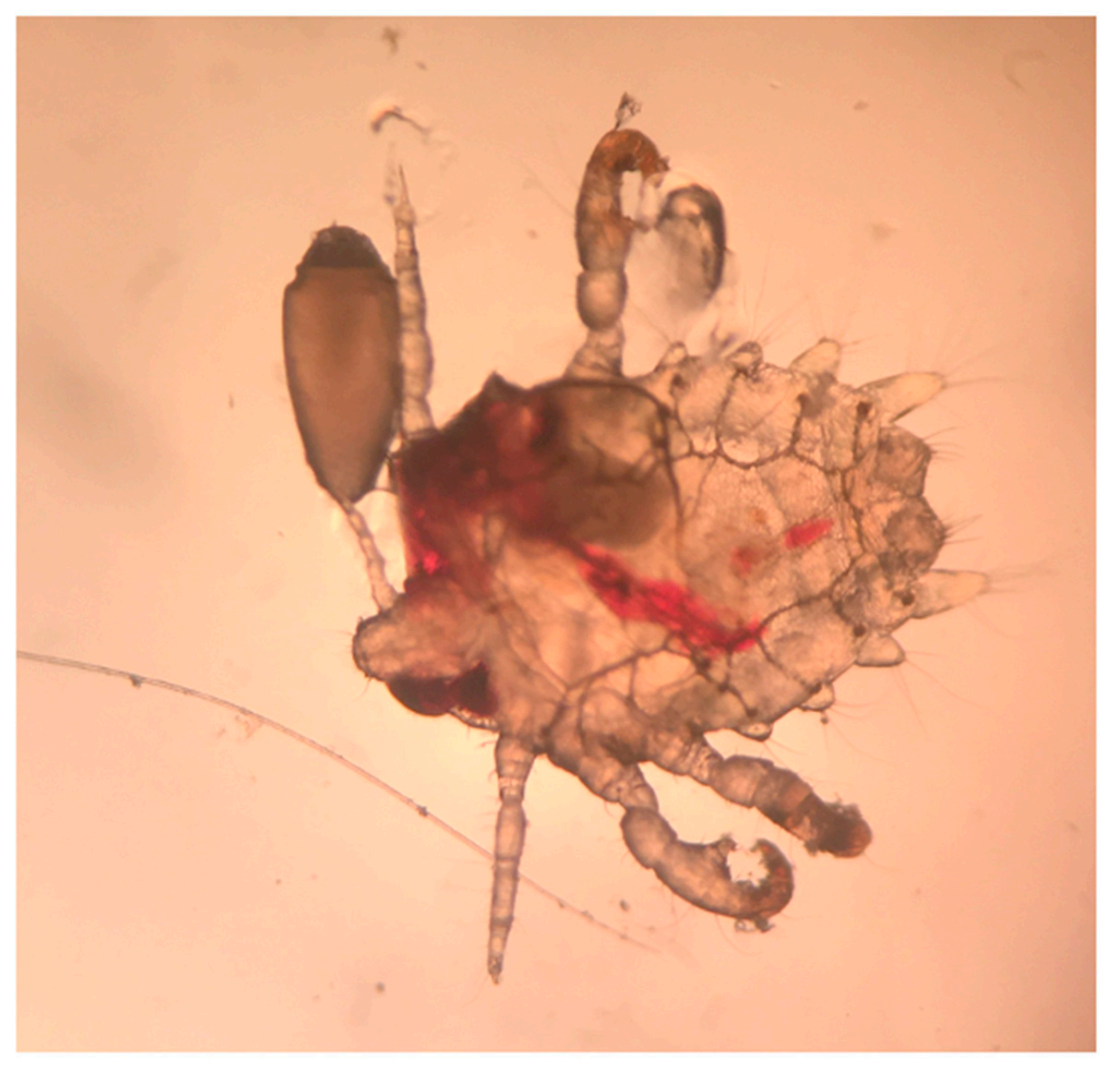
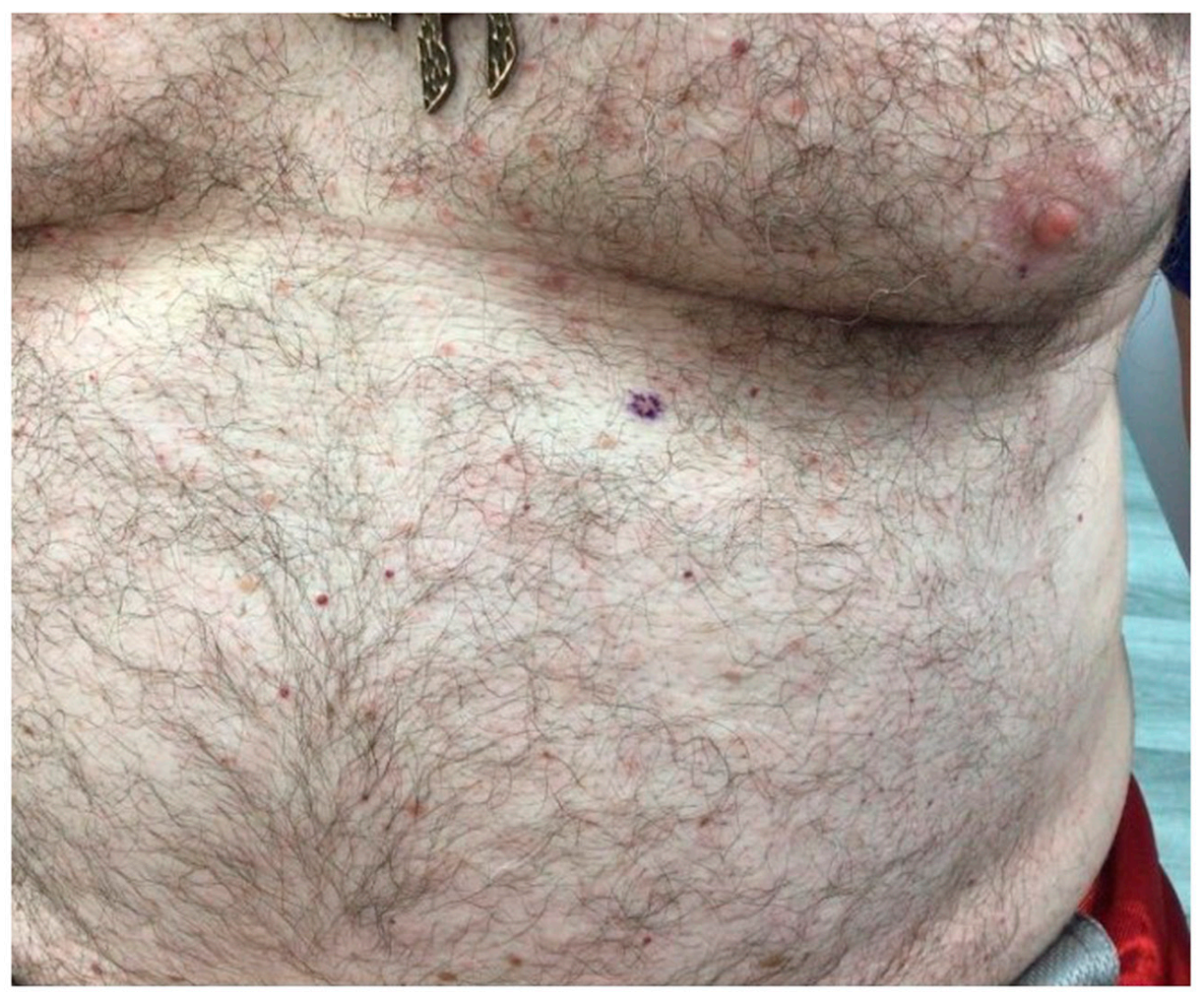
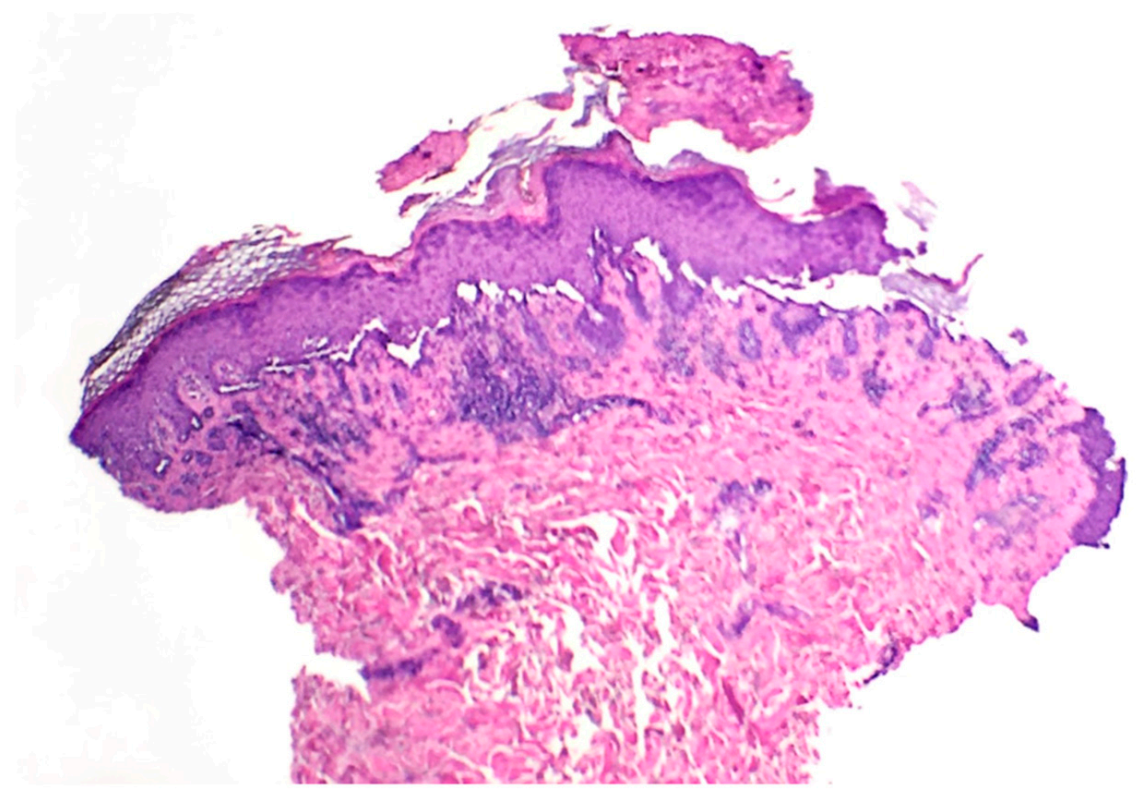
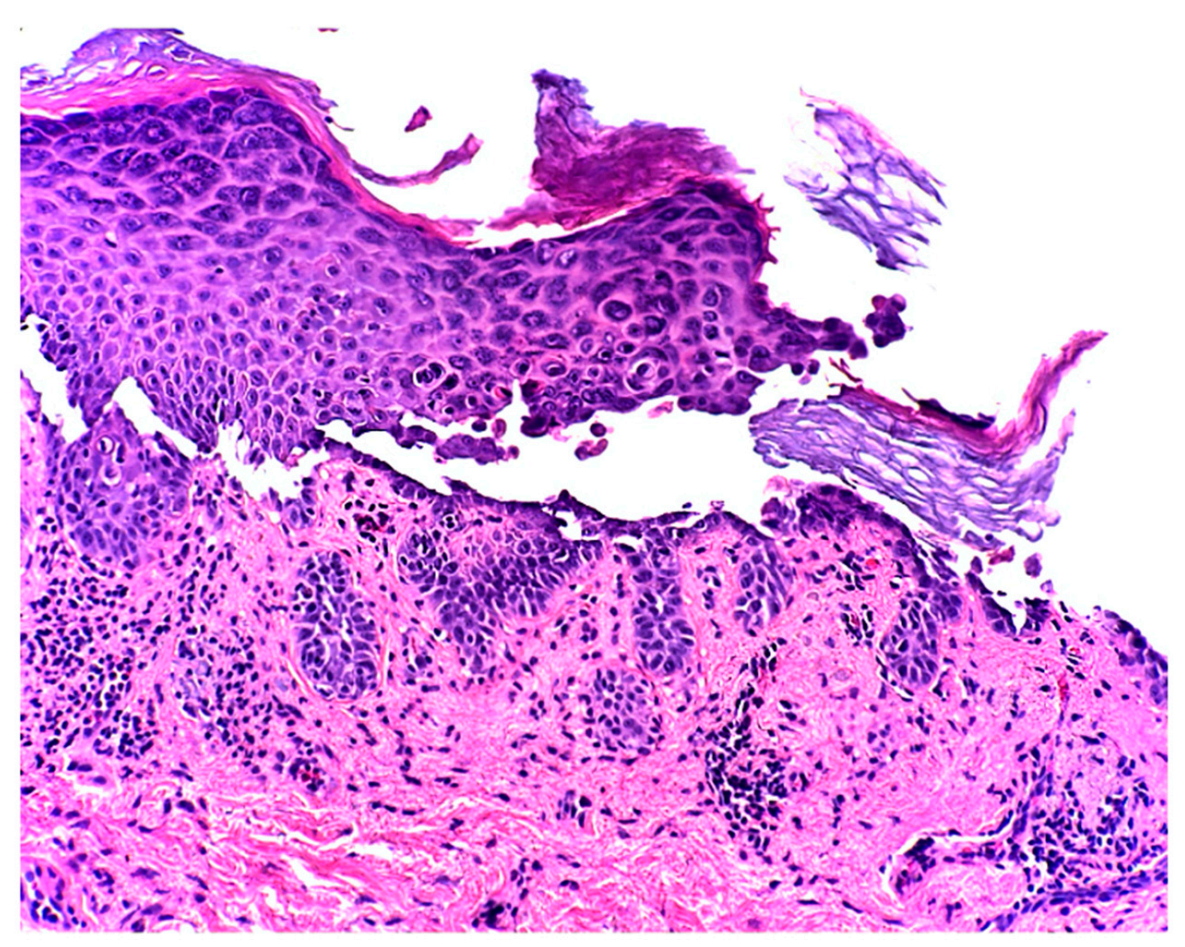
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grover, R.W. Transient acantholytic dermatosis. Arch. Dermatol. 1970, 101, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacarrubba, F.; Boscaglia, S.; Nasca, M.R.; Caltabiano, R.; Micali, G. Grover’s disease: Dermoscopy, reflectance confocal microscopy and histopathological correlation. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2017, 7, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streit, M.; Paredes, B.E.; Braathen, L.R.; Brand, C.U. Transitorische akantholytische Dermatose (M. Grover). Eine Analyse des klinischen Spektrums anhand von 21 histologisch erfassten Fällen [Transitory acantholytic dermatosis (Grover disease). An analysis of the clinical spectrum based on 21 histologically assessed cases]. Hautarzt 2000, 51, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragg, B.N.; Simon, L.V. Pediculosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Specchio, F.; Argenziano, G.; Tiodorovic-Zivkovic, D.; Moscarella, E.; Lallas, A.; Zalaudek, I.; Longo, C. Dermoscopic clues to diagnose acantholytic dyskeratosis. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2015, 5, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomel, J.; Zalaudek, I.; Argenziano, G. Dermatoscopy of Grover’s disease and solitary acantholytic dyskeratoma shows a brown, star-like pattern. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2012, 53, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaddu, S.; Müllegger, R.R.; Kerl, H. Grover’s disease associated with Sarcoptes scabiei. Dermatology 2001, 202, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köstler, E. Transitorische akantholytische Dermatose (Grover) bei Sarcoptes-scabiei-Infektion. Hautarzt 1997, 48, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordaan, H.F.; du Toit, M.J.; Whitaker, D. Stellungnahme zur Arbeit von E. Köstler: ‘Transitorische akantholytische Dermatose (Grover) bei Sarcoptes-scabiei-Infektion’ in Hautarzt (1997) 48:915–917. Hautarzt 1999, 50, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.D.; Dinneen, A.M.; Landa, N.; Gibson, L.E. Grover’s disease: Clinicopathologic review of 72 cases. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1999, 74, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouqui, P.; Stein, A.; Dupont, H.T.; Gallian, P.; Badiaga, S.; Rolain, J.-M.; Mege, J.L.; La Scola, B.; Berbis, P.; Raoult, D. Ectoparasitism and vector-borne diseases in 930 homeless people from Marseilles. Medicine 2005, 84, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, C.G. Relationship of treatment-resistant head lice to the safety and efficacy of pediculicides. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2004, 79, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, A.J.; Rogers, A.T. Glutamate-gated chloride channels and the mode of action of the avermectin/milbemycin anthelmintics. Parasitology 2005, 131, S85–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Ci, X.; An, N.; Ju, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Han, C.; Cui, J.; Deng, X. Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice. Inflamm. Res. 2008, 57, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Moiin, A.; Chang, M.W.; Tada, J. Sudoriferous acrosyringeal acantholytic disease. A subset of Grover’s disease. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1996, 23, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinfeld, N.; Mones, J. Seasonal variation of transient acantholytic dyskeratosis (Grover’s disease). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.J.; Clark, L.N.; Deloney, L.A.; McDonald, J.E. Grover disease (transient acantholytic dermatosis) in acute myeloid leukemia on FDG PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 39, e173–e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, L.E.; Piletta, P.A.; Etienne, A.; Salomon, D.; Saurat, J.H. Incidence of transient acantholytic dermatosis (Grover’s disease) in a hospital setting. Dermatology 1999, 198, 410–411. [Google Scholar]
- Boutli, F.; Voyatzi, M.; Lefaki, I.; Chaidemenos, G.; Kanitakis, J. Transient acantholytic dermatosis (Grover’s disease) in a renal transplant patient. J. Dermatol. 2006, 33, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippoliti, G.; Paulli, M.; Lucioni, M.; D’Armini, A.M.; Lauriola, M.; Saaleb, R.M.H. Grover’s Disease after Heart Transplantation: A Case Report. Case Rep. Transplant. 2012, 2012, 126592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Parsons, J.M. Transient acantholytic dermatosis (Grover’s disease): A global perspective. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1996, 35, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, I.; Azevedo, F.; Mesquita-Guimarães, J.; Resende, C.; Fernandes, N.; MacEdo, G. Grover’s disease secondary to ribavirin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 142, 1257–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, J.S.; Burkemper, N.M. Grover disease (transient acantholytic dermatosis) induced by anastrozole. Cutis 2011, 88, 175–177. [Google Scholar]
- Mahler, S.J.; De Villez, R.L.; Pulitzer, D.R. Transient acantholytic dermatosis induced by recombinant human interleukin 4. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1993, 29, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscharner, G.G.; Bühler, S.; Borner, M.; Hunziker, T. Grover’s disease induced by cetuximab. Dermatology 2006, 213, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anforth, R.; Fernandez-Peñas, P.; Long, G.V. Cutaneous toxicities of RAF inhibitors. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e11–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelzer, V.H.; Buser, T.; Willi, N.; Rothschild, S.I.; Wicki, A.; Schiller, P.; Cathomas, G.; Zippelius, A.; Mertz, K.D. Grover’s-like drug eruption in a patient with metastatic melanoma under ipilimumab therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pendlebury, G.A.; Oro, P.; Merideth, D.; Rudnick, E. A Rare Case of Transient Acantholytic Dermatosis (AKA. Grover’s Disease) with Concomitant Pediculosis Pubis: An Atypical Presentation and First Documented Case Report. Dermatopathology 2021, 8, 502-508. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology8040052
Pendlebury GA, Oro P, Merideth D, Rudnick E. A Rare Case of Transient Acantholytic Dermatosis (AKA. Grover’s Disease) with Concomitant Pediculosis Pubis: An Atypical Presentation and First Documented Case Report. Dermatopathology. 2021; 8(4):502-508. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology8040052
Chicago/Turabian StylePendlebury, Gehan A., Peter Oro, Drew Merideth, and Eric Rudnick. 2021. "A Rare Case of Transient Acantholytic Dermatosis (AKA. Grover’s Disease) with Concomitant Pediculosis Pubis: An Atypical Presentation and First Documented Case Report" Dermatopathology 8, no. 4: 502-508. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology8040052
APA StylePendlebury, G. A., Oro, P., Merideth, D., & Rudnick, E. (2021). A Rare Case of Transient Acantholytic Dermatosis (AKA. Grover’s Disease) with Concomitant Pediculosis Pubis: An Atypical Presentation and First Documented Case Report. Dermatopathology, 8(4), 502-508. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology8040052