Basaloid Cell Hyperplasia Overlying Dermatofibroma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
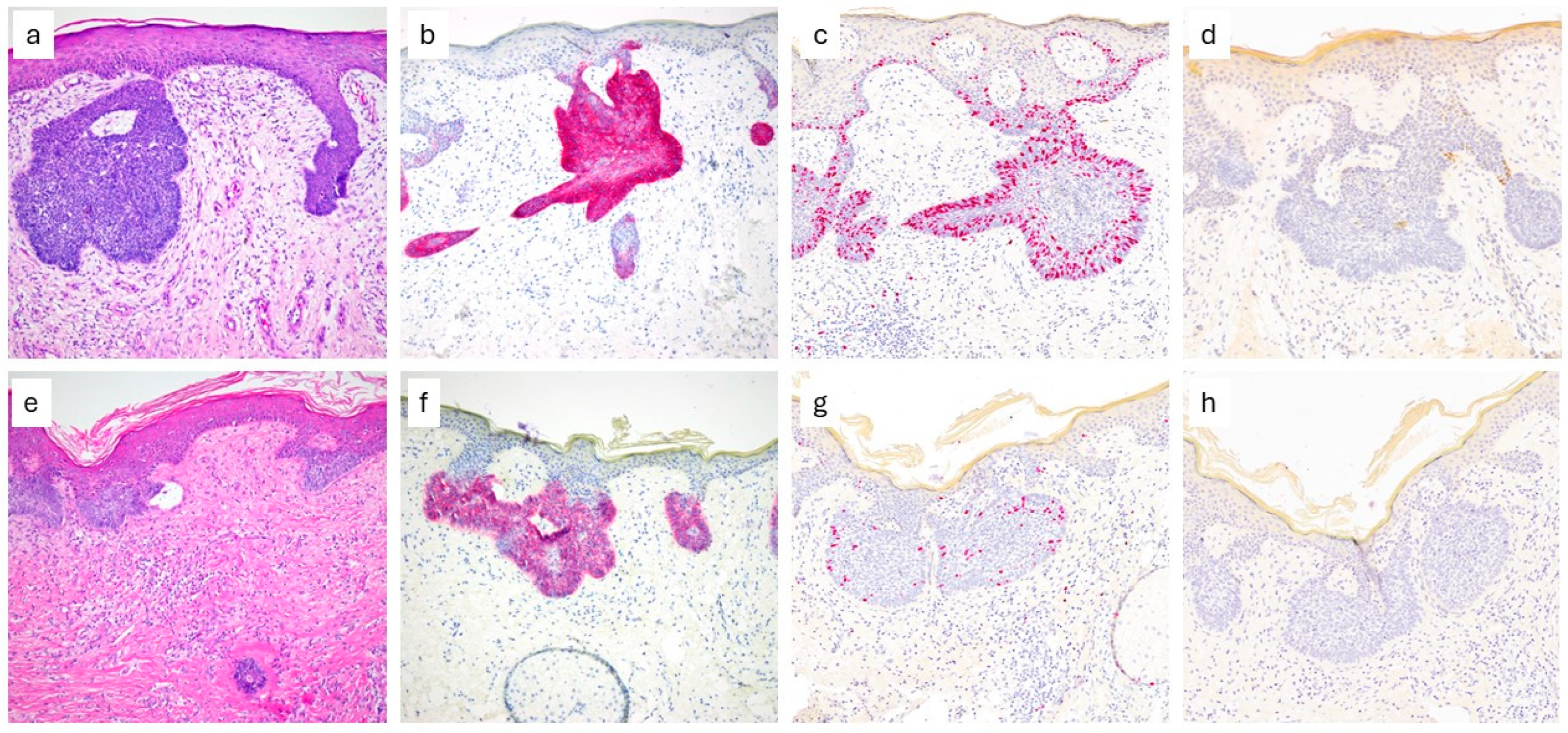
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCC | Basal Cell Carcinoma |
| BCH | Basaloid Cell Hyperplasia |
| CISH | Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization |
| CK20 | Cytokeratin 20 |
| DF | Dermatofibroma |
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| HE | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| MT | Metallothionein |
| SCC | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| SCF | Stem Cell Factor |
References
- Myers, D.J.; Fillman, E.P. Dermatofibroma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470538/ (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Han, T.Y.; Chang, H.S.; Lee, J.H.K.; Lee, W.M.; Son, S.J. A clinical and histopathological study of 122 cases of dermatofibroma (benign fibrous histiocytoma). Ann. Dermatol. 2011, 23, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenel, E.; Yuyucu Karabulut, Y.; Doğruer Şenel, S. Clinical, histopathological, dermatoscopic and digital microscopic features of dermatofibroma: A retrospective analysis of 200 lesions. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerslev, T.; Rossen, K.; Hou-Jensen, K.; Jacobsen, G.K. Immunohistochemical detection of p53 in epidermal proliferationsoverlying dermatofibromas. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1995, 75, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Amini, S.B.; Zaim, M.T. Follicular Basal Cell Hyperplasia Overlying Dermatofibroma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1997, 21, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stashower, M.E.; Smith, K.; Corbett, D.; Skelton, H.G. Basaloid/follicular hyperplasia overlying connective tissue/mesenchymal hamartomas simulating basal cell carcinomas. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehregan, D.R.; Thomas, L.; Thomas, J.E. Epidermal basaloid proliferation in cutaneous myxomas. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2003, 30, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flordelis, J.O.; Shen, Y.C.; Wu, Y.H. Basaloid tumors arising from seborrheic keratosis: Malignant basal cell carcinoma or benign basaloid follicular hamartomatous proliferation? J. Cutan. Pathol. 2020, 47, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.B.; Howard, H.G.; Everett, M.A. Epithelial induction in dermatofibroma: A role for the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 1997, 19, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.; Googe, P.B.; Page, R.N.; Mihm, M.C. Melanocytic lesions associated with dermatofibromas: A spectrum of lesions ranging from junctional nevus to malignant melanoma in situ. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuweiter, M.; Böer, A. Spectrum of follicular and sebaceous differentiation induced by dermatofibroma. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2009, 31, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena, L.; Yus, E.S.; Simón, P.; del Rio, E. Induction of cutaneous hyperplasias by altered stroma. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 1996, 18, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.H.; Huh, C.H.; Cho, K.H. Proliferation and Differentiation of the Keratinocytes in Hyperplastic Epidermis Overlying Dermatofibroma: Immunohistochemical Characterization. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2001, 23, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindboe, C.F.; Løvdal, L. Epidermal basaloid cell hyperplasia overlying dermatofibromas. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2011, 33, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Asad, H.; Salim, S.; Kantor, G.; Minimo, C. Anti-cytokeratin 20 staining of Merkel cells helps differentiate basaloid proliferations overlying dermatofibromas from basal cell carcinoma. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2005, 32, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanoszek, L.M.; Wang, G.Y.; Harms, P.W. Histologic Mimics of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, M.C.; Lee, E.; Hibler, B.P.; Barker, C.A.; Mori, S.; Cordova, M.; Nehal, K.S.; Rossi, A.M. Basal cell carcinoma: Epidemiology; pathophysiology; clinical and histological subtypes; and disease associations. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackiewicz-Wysocka, M.; Bowszyc-Dmochowska, M.; Strzelecka-Węklar, D.; Dańczak-Pazdrowska, A.; Adamski, Z. Basal cell carcinoma—Diagnosis. Contemp. Oncol. 2013, 17, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Niculet, E.; Bobeica, C.; Craescu, M.; Nicolescu, A.C.; Tocu, G.; Onisor, C.; Arbune, M.; Tatu, A.L. Multimodal Considerations Concerning Basal Cell Carcinoma Clefting—Profile of Structural and Aggressive Traits—Perspectives. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernick, N. BerEP4/EpCAM. PathologyOutlines.com. Available online: https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsepcam.html (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Sunjaya, A.P.; Sunjaya, A.F.; Tan, S.T. The Use of BEREP4 Immunohistochemistry Staining for Detection of Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Skin. Cancer 2017, 2017, 2692604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossen, K.; Haerslev, T.; Hou-Jensen, K.; Jacobsen, G.K. Bcl-2 overexpression in basaloid proliferations overlying dermatofibromas and basal cell carcinomas. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 1997, 105, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernick, N. Cytokeratin 20 (CK20, K20). PathologyOutlines.com. Available online: https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsck20.html (accessed on 18 September 2014).
- Shin, M.K.; Choi, C.M.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, N.I. CK20 Positive Large-cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Presenting with Skin Metastases. Ann. Dermatol. 2011, 23, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairatchaneeboon, M.; Elenitsas, R.; Nguyen, J.V. Follicular induction and CK20+ Merkel cells overlying cutaneous focal mucinosis. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2019, 46, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitakis, J.; Bourchany, D.; Faure, M.; Claudy, A. Merkel cells in hyperplastic and neoplastic lesions of the skin. An immunohistochemical study using an antibody to keratin 20. Dermatology 1998, 196, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Roshani, D.; Gao, B.; Li, P.; Shang, N. Metallothionein: A comprehensive review of its classification, structure, biological functions, and applications. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, P.; Philcox, J.C.; Carey, L.C.; Rofe, A.M. Metallothionein: The multipurpose protein. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 627–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossen, K.; Haerslev, T.; Hou-Jensen, K.; Jacobsen, G.K. Metallothionein expression in basaloid proliferations overlying dermatofibromas and in basal cell carcinomas. Br. J. Dermatol. 1997, 136, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neinaa, Y.M.E.H.; El-Ashmawy, A.A.; Alshenawy, H.A.S.; Dorgham, W.L. The Prognostic Value of Podoplanin Expression in Nonmelanoma Skin Cancers: Correlation with Lymphatic Vessel Density. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2020, 42, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Kushima, R.; Okabe, H. Immunohistochemical demonstration of D2-40 in basal cell carcinomas of the skin. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2008, 35, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebcherani, A.J.; Andrade HFde Sotto, M.N. Diagnostic utility of immunohistochemistry in distinguishing trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma: Evaluation using tissue microarray samples. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, F.; Forrester, S.J.; Eguchi, S.; Zhang, M.Z.; Harris, R.C. Expression and function of the epidermal growth factor receptor in physiology and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1025–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnidar, H.; Eberl, M.; Klingler, S.; Mangelberger, D.; Kasper, M.; Hauser-Kronberger, C.; Regl, G.; Kroismayr, R.; Moriggl, R.; Sibilia, M.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling synergizes with Hedgehog/GLI in oncogenic transformation via activation of the MEK/ERK/JUN pathway. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biray Avci, C.; Kaya, I.; Ozturk, A.; Ozates Ay, N.P.; Sezgin, B.; Kurt, C.C.; Akyildiz, N.S.; Bozan, A.; Yaman, B.; Akalin, T.; et al. The role of EGFR overexpression on the recurrence of basal cell carcinomas with positive surgical margins. Gene 2019, 687, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, T.D.; Durgin, J.S.; Hrycaj, S.M.; Brent, A.A.; Patel, R.M.; Harms, P.W.; Fullen, D.R.; Chan, M.P.; Bresler, S.C. Utility of GLI1 RNA chromogenic in situ hybridization in distinguishing basal cell carcinoma from histopathologic mimics. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walling, H.W.; Fosko, S.W.; Geraminejad, P.A.; Whitaker, D.C.; Arpey, C.J. Aggressive basal cell carcinoma: Presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004, 23, 89–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample Nr | Lobules | Basaloid Cells | Palisade | Clefting | BerEp4 | Ki67 | CK20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | + | − |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | + |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | pos (weak) | +++ | − |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | pos | ++ | + |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | pos | ++ | − |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | +++ | + |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | pos | + | + |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | − |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | pos | +++ | − |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos (weak) | ++ | + |
| 11 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | pos | ++ | + |
| 12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | − |
| 13 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | + |
| 14 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | pos | ++ | − |
| 15 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | + |
| 16 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | pos (focal) | + | + |
| 17 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | − |
| 18 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | − |
| 19 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | pos (focal) | ++ | − |
| 20 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos (focal) | ++ | + |
| 21 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | + |
| 22 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos (focal) | ++ | + |
| 23 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | − |
| 24 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | +++ | − |
| 25 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | ++ | − |
| 26 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos (focal) | nd | nd |
| 27 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos (focal) | nd | nd |
| 28 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | pos (focal) | nd | nd |
| 29 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | nd | nd |
| 30 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos (focal) | nd | nd |
| 31 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | pos | nd | nd |
| 32 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 33 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 34 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 35 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 36 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 37 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 38 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 39 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 40 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | neg | nd | nd |
| 41 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 42 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
| 43 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | neg | nd | nd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the European Society of Dermatopathology. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pablo, I.; Marwa, Z.; Helmut, B.; Laurence, F. Basaloid Cell Hyperplasia Overlying Dermatofibroma. Dermatopathology 2025, 12, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040036
Pablo I, Marwa Z, Helmut B, Laurence F. Basaloid Cell Hyperplasia Overlying Dermatofibroma. Dermatopathology. 2025; 12(4):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040036
Chicago/Turabian StylePablo, Izarra, Zohdy Marwa, Beltraminelli Helmut, and Feldmeyer Laurence. 2025. "Basaloid Cell Hyperplasia Overlying Dermatofibroma" Dermatopathology 12, no. 4: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040036
APA StylePablo, I., Marwa, Z., Helmut, B., & Laurence, F. (2025). Basaloid Cell Hyperplasia Overlying Dermatofibroma. Dermatopathology, 12(4), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040036







