Experienced vs. Novice Participants Perception of Overall Quality and Intention to Join in Future Sport Trials: Case European Duathlon Championship
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling
3.2. Measures
3.3. Statistical Procedure
4. Results
4.1. Structural Model: Experienced Participants
4.2. Structural Model: Novice Participants
4.3. Fuzzy-Set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA): Experienced Participants
4.4. Fuzzy-Set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA): Novice Participants
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almeida, A.M. Economic impact of sporting events—Evaluation criteria and indicators of interest in the case of Madeira. Rev. Mot. 2019, 15 (Suppl. S2), 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, M.A. Sports Management and Sponsorship; Towards a New Paradigm. J. Sports Econ. Manag. 2018, 8, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.W.; Lu, H.F. A longitudinal assessment on the economic effects of hosting major sporting events. Appl. Econ. 2018, 50, 6085–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Kim, E.; Mastromartino, B.; Qian, T.Y.; Nauright, J. The sport industry in growing economies: Critical issues and challenges. Int. J. Sports Mark. Spons. 2018, 19, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhu, L.; Cai, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, H. Examining the Impacts of Mega-Events on Urban Development using Coupling Analysis: A Case Study of the Boao Forum for Asia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richelieu, A. A sport-oriented place branding strategy for cities, regions and countries. Sport Bus. Manag. Int. J. 2018, 8, 354–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candrea, A.N.; Ispas, A. Promoting tourist destinations through sport events. The case of Brasov. J. Tour. 2010, 10, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Higham, J. Commentary—Sport as an Avenue of Tourism Development: An Analysis of the Positive and Negative Impacts of Sport Tourism. Curr. Issues Tour. 1999, 2, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplanidou, K.; Gibson, H.J. Predicting Behavioral Intentions of Active Event Sport Tourists: The Case of a Small-scale Recurring Sports Event. J. Sport Tour. 2010, 15, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, D.; Dehe, B. Service quality at the London 2012 games—A paralympics athletes survey. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2016, 33, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolyperas, D.; Maglaras, G.; Sparks, L. Sport fans’ roles in value co-creation. Eur. Sport Manag. Q. 2019, 19, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabuig-Moreno, F.; Burillo, P.; Crespo-Hervás, J.; Mundina, J.J.; Gallardo, L. Satisfacción, Calidad y Valor Percibido en espectadores de atletismo. Rev. Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Física Deporte 2010, 10, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jae, K.Y.; Kyoum Kim, Y.; Kil Kim, M.; Hak Lee, J. The role of involvement and identification on event quality perceptions and satisfaction. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2010, 22, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hightower, R.; Brady, M.K.; Baker, T.L. Investigating the role of the physical environment in hedonic service consumption: An exploratory study of sporting events. J. Bus. Res. 2002, 55, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.J.; Brady, M.K.; Hult, G.T.M. Assessing the effects of quality, value, and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioral intentions in service environments. J. Retail. 2000, 76, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.D.; Alexandris, K.; Tsigilis, N.; Karvounis, S. Predicting spectators’ behavioural intentions in professional football: The role of satisfaction and service quality. Sport Manag. Rev. 2013, 16, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angosto Sánchez, S.; Morán-Navarro, R.; Martínez-Cava, A.; López-Gullón, J.M. Calidad percibida en una prueba de triatlón. SPORT TK-Rev. EuroAmericana Cienc. Deporte 2016, 5, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bernthal, M.J.; Sawyer, L.L. The importance of expectations on participatory sport event satisfaction: An exploration into the effect of athlete skill level on service expectations. Sport J. 2004, 7. Available online: https://thesportjournal.org/article/the-importance-of-expectations-on-participatory-sport-event-satisfaction/ (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Bi, T.; Bianchi-Berthouze, N.; Singh, A.; Costanza, E. Understanding the shared experiences of runners and spectators in long-distance running events. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow Scotland, UK, 4–9 May 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo-Hervás, J.; Calabuig-Moreno, F.; Prado-Gascó, V.; Añó-Sanz, V.; Núñez-Pomar, J. The role of passion in the quality-value-satisfaction-intentions chain: Linear models and the QCA approach for athletes. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraživanja 2019, 32, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.; Hill, T. Essential Operations Management; Macmillan International Higher Education: London, UK; Red Globe Press: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyama, S.; Greenwell, T.C. Examining similarities and differences in consumer motivation for playing and watching soccer. Sport Mark. Q. 2011, 20, 148–156. Available online: https://fitpublishing.com/content/examining-similarities-and-differences-consumer-motivation-playing-and-watching-soccer-p-148 (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Du, J.; Jordan, J.S.; Funk, D.C. Managing Mass Sport Participation: Adding a Personal Performance Perspective to Remodel Antecedents and Consequences of Participant Sport Event Satisfaction. J. Sport Manag. 2015, 29, 688–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaz-González, A.M.; Sahelices-Pinto, C.; Mendaña-Cuervo, C.; García-Tascón, M. Overall Quality of Sporting Events and Emotions as Predictors of Future Intentions of Duathlon Participants. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakis, N.D.; Kaplanidou, K.; Karabaxoglou, I. Effect of Event Service Quality and Satisfaction on Happiness Among Runners of a Recurring Sport Event. Leis. Sci. 2015, 37, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.; Howat, G. The Relationships among Service Quality, Value, Satisfaction, and Future Intentions of Customers at an Australian Sports and Leisure Centre. Sport Manag. Rev. 2008, 5, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Yoh, T.; Shonk, D.J. Antecedents and consequences of satisfaction among participants in health-affiliated charity sport events. Int. J. Event Festiv. Manag. 2021, 12, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woratschek, H.; Horbel, C.; Popp, B. Value co-creation in sport management. Eur. Sport Manag. Q. 2014, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisheng, C.; Doyeon, W.; Jung-sup, B. Customer value co-creation behaviour in fitness centres: How does it influence customers’ value, satisfaction, and repatronage intention? Manag. Sport Leis. 2019, 24, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Saura, E.; Vegara-Ferri, J.M.; Morales-Baños, V.; López-Gullón, J.M.; López-Sánchez, G.F.; Angosto, S. Perceived quality, perceived value, satisfaction and future intentions in participants in swimming crossings. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2018, 18, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonk, D.J.; Chelladural, P. Service Quality, Satisfaction, and Intent to Return in Event Sport Tourism. J. Sport Manag. 2008, 22, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerbeek, H.M.; Shilbury, D. A Conceptual Model for Sport Services Marketing Research: Integrating Quality, Value and Satisfaction. Int. J. Sports Mark. Spons. 2003, 5, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. A Conceptual Model of Service Quality and Its Implications for Future Research. J. Mark. 1985, 49, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. SERVQUAL: A multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. J. Retail. 1988, 64, 12–40. [Google Scholar]
- Rust, R.T.; Oliver, R.L. Service Quality: Insights and Managerial Implications from the Frontier. In Service Quality: New Directions in Theory and Practice; Rust, R.T., Oliver, R.L., Eds.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, M.K.; Cronin, J.J. Some New Thoughts on Conceptualizing Perceived Service Quality: A Hierarchical Approach. J. Mark. 2001, 65, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemes, M.D.; Brush, G.J.; Collins, M.J. Analysing the professional sport experience: A hierarchical approach. Sport Manag. Rev. 2011, 14, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jae Ko, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cattani, K.; Pastore, D. Assessment of event quality in major spectator sports. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2011, 21, 304–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; James, J.D. Service quality at sporting events: Is aesthetic quality a missing dimension? Sport Manag. Rev. 2011, 14, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.; Kambitsis, C.; Laios, A. Relationship between measures of service quality and satisfaction of spectators in professional sports. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2001, 11, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabuig-Moreno, F.; Crespo Hervàs, J. Uso del método Delphi para la elaboración de una medida de la calidad percibida de los espectadores de eventos deportivos. Retos 2009, 15, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuviala-Nuviala, A.; Tamayo-Fajardo, J.A.; Iranzo-Llopis, J.; Falcón-Miguel, D. Creación, diseño, validación y puesta en práctica de un instrumento de medición de la satisfacción de usuarios de organizaciones que prestan servicios deportivos. Retos 2008, 14, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuviala, A.; Grao-Cruces, A.; Tamayo, J.A.; Nuviala, R.; Álvarez, J.; Fernández-Martínez, A. Diseño y análisis del cuestionario de valoración de servicios deportivos (EPOD2). Rev. Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Física Deporte 2013, 13, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabuig-Moreno, F.; Prado-Gascó, V.; Crespo-Hervás, J.; Núñez-Pomar, J.; Añó-Sanz, V. Predicting future intentions of basketball spectators using SEM and fsQCA. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Greenwell, C.; Lee, K. Effects of service quality, perceived value, and consumer satisfaction on behavioral intentions in Virtual Golf. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2018, 18, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar]
- García-Fernández, J.; Gálvez-Ruiz, P.; Vélez-Colon, L.; Ortega-Gutiérrez, J.; Fernández-Gavira, J. Exploring fitness centre consumer loyalty: Differences of non-profit and low-cost business models in Spain. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraživanja 2018, 31, 1042–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.J.; Kwon, H.H.; Kim, T.; Park, C.; Song, K. Assessment of Event Quality in Major Spectator Sports: Single-Item Measures. J. Glob. Sport Manag. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burillo, P.; De la Riva, L.; García-Unanue, J.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; Felipe, J.L. Spectator spending and satisfaction analysis in the 2017 Madrid Tennis Open according to the attendee profile. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2018, 18, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo-Hervás, J.; Pérez-Campos, C.; Mundina-Gómez, J. Calidad de servicio percibida por los espectadores de fútbol. Análisis de diferencias entre grupos [Spectators perceived service quality of a football event. Analysing differences between groups]. J. Sports Econ. Manag. 2012, 2, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, S.W.; Turley, L.W. Consumer perceptions of service quality attributes at sporting events. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 54, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Chen, M.Y.; Ye, Y.C.; Tung, I.W.; Cheng, C.F.; Tung, S. Perceived service quality and life satisfaction: The mediating role of the actor’s satisfaction-with-event. Int. J. Sports Mark. Spons. 2012, 13, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Campos, C. Análisis de la Calidad del Servicio en los Eventos Deportivos. Calidad Percibida y Satisfacción de los Espectadores y de los Deportistas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de València, Valencia, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cevallos, D.; Proaño-Grijalva, A.; Alguacil, M.; Duclos-Bastías, D.; Parra-Camacho, D. Segmentation of Participants in a Sports Event Using Cluster Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.A.; Ko, Y.J.; Martínez, L. An Application of Fuzzy Logic to Service Quality Research: A Case of Fitness Service. J. Sport Manag. 2010, 24, 502–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angosto-Sánchez, S. Diseño y Validación de un Cuestionario Sobre Calidad Percibida en Eventos Deportivos Populares (CAPPEP) [Design and Validation a Questionnaire of Perceived Quality in Popular Sport Event (CAPPEP)]. Master’s Thesis, University of Murcia, Murcia, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Byon, K.; Huang, H. Service Quality, Perceived Value, and Fan Engagement: Case of Shanghai Formula One Racing. Sport Mark. Q. 2019, 28, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C. Influence of Multiple Interactions in Value CoCreation on Sports Spectators’ Perceived Value of Sports Events. Complexity 2021, 2021, 9972225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boksberger, P.E.; Melsen, L. Perceived value: A critical examination of definitions, concepts and measures for the service industry. J. Serv. Mark. 2011, 25, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeithaml, V.A. Consumer Perceptions of Price, Quality, and Value: A Means-End Model and Synthesis of Evidence. J. Mark. 1988, 52, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo Hervás, J.; Prado-Gascó, V.; González-Serrano, M.H. Perceived Value in Sporting Events (PVSP): A Further Step for the Strategic Management. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, J.; Martelo-Landroguez, S.; Vélez-Colon, L.; Cepeda-Carrión, G. An explanatory and predictive PLS-SEM approach to the relationship between organizational culture, organizational performance and customer loyalty. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2018, 9, 438–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuviala, A.; Grao-Cruces, A.; Fernández-Ozcorta, E.; Nuviala, R. Asociación entre calidad del servicio deportivo, valor y satisfacción de usuarios en España. Univ. Psychol. 2015, 14, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayduk, T.; Brison, N.; Drayer, J. The Effect of Partitioned Ticket Prices on Sport Consumer Perceptions and Enduring Attitudes. J. Sport Manag. 2021, 35, 522–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.; Parasuraman, A. The Behavioral Consequences of Service Quality. J. Mark. 1996, 60, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C. A National Customer Satisfaction Barometer: The Swedish Experience. J. Mark. 1992, 56, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.W.; Fornell, C.; Lehmann, D.R. Customer Satisfaction, Market Share, and Profitability: Findings from Sweden. J. Mark. 1994, 58, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Dos-Santos, M.; Pérez-Campos, C. Do emotions influence the intention of attending a sporting event? Differences by gender. J. Sports Econ. Manag. 2015, 5, 2–16. [Google Scholar]
- Fleshman, S.F.; Kaplanidou, K. Predicting Active Sport Participant’s Approach Behaviors from Emotions and Meaning Attributed to Sport Event Experience. Event Manag. 2023, 27, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, M.; Jordan, J.S. Athletic goal achievement: A critical antecedent of event satisfaction, re-participation intention, and future exercise intention in participant sport events. Sport Manag. Rev. 2020, 23, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. Measurement and evaluation of satisfaction processes in retail settings. J. Retail. 1981, 57, 25–48. [Google Scholar]
- Alguacil, M.; Núñez-Pomar, J.; Pérez-Campos, C.; Prado-Gascó, V. Perceived value, satisfaction and future intentions in sport services. Acad. Rev. Latinoam. Adm. 2019, 32, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabuig Moreno, F.; Prado-Gascó, V.; Crespo Hervás, J.; Núñez-Pomar, J.; Añó Sanz, V. Spectator emotions: Effects on quality, satisfaction, value, and future intentions. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, M.; Knight, G.; Croninjr, J.; Tomas, G.; Hult, M.; Keillor, B. Removing the contextual lens: A multinational, multi-setting comparison of service evaluation models. J. Retail. 2005, 81, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, A.; Gálvez-Ruiz, P.; Vélez-Colón, L.; Bernal-García, A. Service convenience, perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty: A study of consumers from low-cost fitness centers in Spain. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2016, 16, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, G.H.G.; Levesque, T. Customer satisfaction with services: Putting perceived value into the equation. J. Serv. Mark. 2000, 14, 392–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-García, A.; García-Fernández, J.; Grao-Cruces, A.; Teva-Villén, R.; Nuviala, A. Escala de intenciones futuras de comportamiento a servicios deportivos [Behavioral intentions of sports services consumers according to the social and demographic variables]. Rev. Mex. Psicol. 2018, 35, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscaia, R.; Correia, A.; Rosado, A.; Maroco, J.; Ross, S. The effects of emotions on football spectators’ satisfaction and behavioural intentions. Eur. Sport Manag. Q. 2012, 12, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscaia, R.; Correia, A.; Rosado, A.; Ross, S.; Maroco, J. Sport Sponsorship: The Relationship Between Team Loyalty, Sponsorship Awareness, Attitude Toward the Sponsor, and Purchase Intentions. J. Sport Manag. 2013, 27, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzel, S.; Yassim, M. The effect of joy on the behaviour of cricket spectators: The mediating role of satisfaction. Manag. Leis. 2007, 12, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, H.; Chelladurai, P.; Harada, M. Direct and Interaction Effects of Team Identification and Satisfaction on Intention to Attend Games. Sport Mark. Q. 2003, 12, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, M.; James, J.D. Customer Satisfaction With Game and Service Experiences: Antecedents and Consequences. J. Sport Manag. 2010, 24, 338–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madruga-Vicente, M.; Cerro-Herrero, D.; Angosto-Sánchez, S.; Prieto-Prieto, J. Perceived quality and future intentions in sport events: Segmentation of participants of trail running. Cult. Cienc. Deporte 2021, 16, 605–615. [Google Scholar]
- Avourdiadou, S.; Theodorakis, N.D. The development of loyalty among novice and experienced customers of sport and fitness centres. Sport Manag. Rev. 2014, 17, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, J.O.; DiClemente, C.C. Transtheoretical therapy: Toward a more integrative model of change. Psychother. Theory Res. Pract. 1982, 19, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Alejos Gómez, C. Análisis de la Calidad Percibida, Satisfacción, Valor Percibido e Intenciones Futuras de los Usuarios de los Servicios Deportivos Públicos Gestionados por Logroño Deporte; Universidad de La Rioja: Logroño, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos-Sánchez, J.J.; Ruiz-Juan, F.; Villarreal-Angeles, M.A.; Rivera, J.I.Z. Etapas de cambio en la práctica de actividad física de tiempo libre en estudiantes de secundaria de Victoria de Durango, México. (Change stages to practice of physical activity within free time in high school students of Victoria of Durango, Mexico). Retos 2018, 35, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, Y. Application of the transtheoretical model to identify predictors of physical activity transition in university students. J. Sport Psychol. 2017, 26, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Leyton, M.; Batista, M.; Lobato, S.; Jiménez, R. Validación del cuestionario del modelo transteórico del ejercicio físico [Validation of the questionnaire of the Transtheoretical Model of change of Physical Exercise]. Rev. Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Física Deporte 2019, 19, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.T.; Kueh, Y.C.; Arifin, W.N.; Kim, Y.; Kuan, G. Application of Transtheoretical Model on Behavioral Changes, and Amount of Physical Activity Among University’s Students. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuah, N.A.; Amiel, C.; Qureshi, S.; Car, J.; Kaur, B.; Majeed, A. Transtheoretical model for dietary and physical exercise modification in weight loss management for overweight and obese adults. In Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; Tuah, N.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Sampieri, R.; Fernández-Collado, C.; Baptista-Lucio, M.P. Research Methodology, 5th ed.; McGrawhill Iberoamericana: Irvine, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Muñiz, J.; Fonseca-Pedrero, E. Ten steps for test development. Psicothema 2019, 31, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjong, R.; Wentworth, B. Expert judgment and risk perception. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Stavanger, Norway, 17–22 June 2001; Available online: https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/ISOPE-I-01-423 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Hyrkäs, K.; Appelqvist-Schmidlechner, K.; Oksa, L. Validating an instrument for clinical supervision using an expert panel. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2003, 40, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunnally, J.C.; Bernstein, I.H. Psychometric Theory, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, D.; Higgins, C.; Thompson, R. The partial least squares (PLS) approach to causal modeling: Personal computer adoption and use as an illustration. Technol. Stud. 1995, 2, 285–309. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W. The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. In Modern Methods for Business Research; George, A., Ed.; Laurence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Ringle, C.M.; Wende, S.; Will, A. SmartPLS 2.0 (Beta); University of Hamburg: Hamburg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Bookstein, F.L. Two Structural Equation Models: LISREL and PLS Applied to Consumer Exit-Voice Theory. J. Mark. Res. 1982, 19, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W.; Marcolin, B.L.; Newsted, P.R. A Partial Least Squares Latent Variable Modeling Approach for Measuring Interaction Effects: Results from a Monte Carlo Simulation Study and an Electronic-Mail Emotion/Adoption Study. Inf. Syst. Res. 2003, 14, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragin, C.C. Redesigning Social Inquiry: Fuzzy Sets and Beyond; Bibliovault OAI Repository; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA; London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragin, C.C.; Davey, S. Fuzzy-Set/Qualitative Comparative Analysis 4.0.; Department of Sociology, University of California: Irvine, CA, USA, 2022; Available online: http://www.socsci.uci.edu/~cragin/fsQCA/software.shtml (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Falk, R.F. A Primer for Soft Modeling; University of Akron Press: Akron, OH, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Woodside, A.G. Moving beyond multiple regression analysis to algorithms: Calling for a paradigm shift from symmetric to asymmetric thinking in data analysis and crafting theory. J. Bus. Res. 2013, 66, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiss, P.C. Building better causal theories: A fuzzy set approach to typologies in organizational research. Acad. Manag. J. 2011, 54, 393–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodet, G. Investigating Customer Satisfaction in a Health Club Context by an Application of the Tetraclasse Model. Eur. Sport Manag. Q. 2006, 6, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.A.; Sharland, A.; Cronin, J.J.; Bullard, W. Recreational Service Quality in the International Setting. Int. J. Serv. Ind. Manag. 1993, 4, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, R.N. A Dynamic Model of the Duration of the Customer’s Relationship with a Continuous Service Provider: The Role of Satisfaction. Mark. Sci. 1998, 17, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
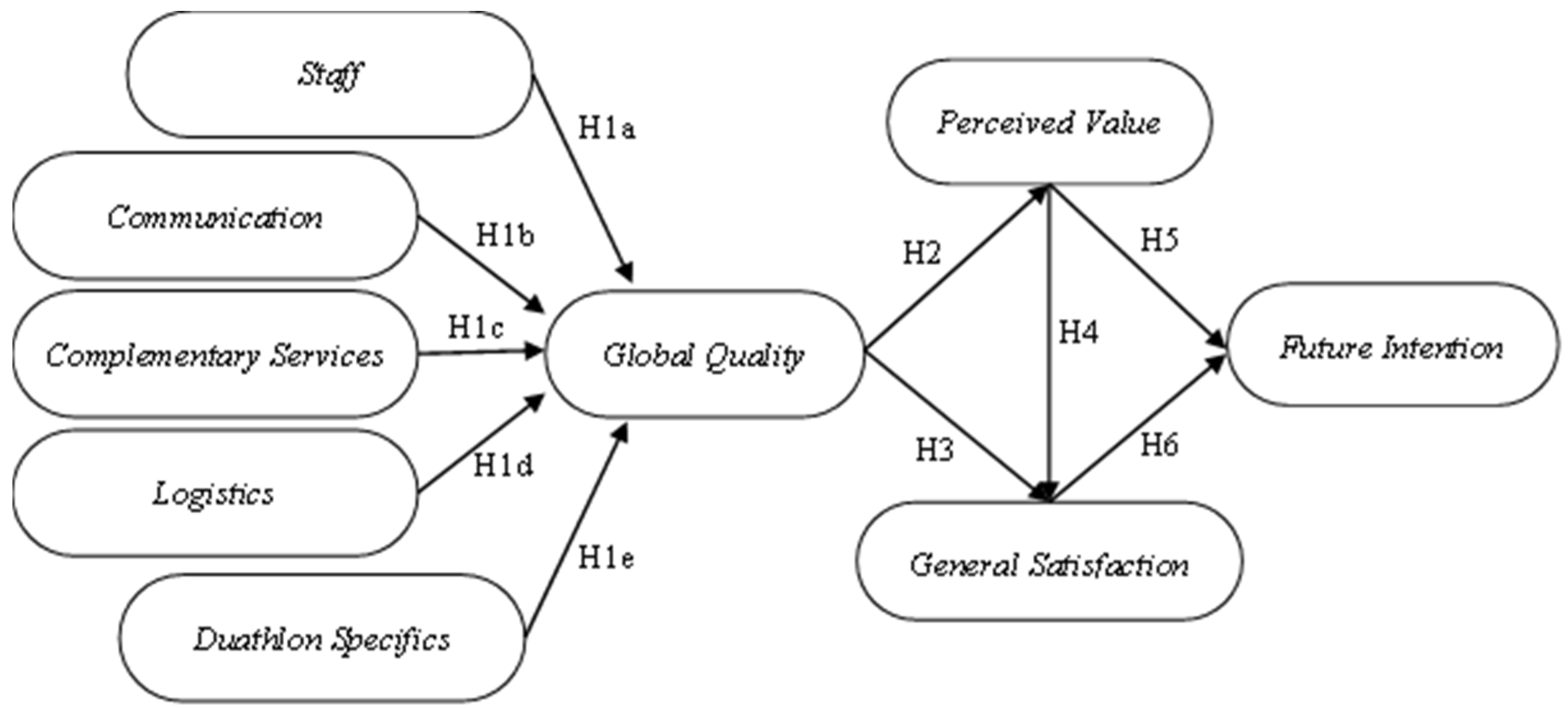

| Hypothesis | Relations (Path Coefficients) | Experienced β(t) | Novice β(t) | Experienced Test | Novice Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1a | S → GQ | 0.2753 *** (3.0402) | 0.3636 *** (4.1485) | Supported | Supported |
| H1b | C → GQ | 0.1969 ** (2.3891) | −0.0535 (0.5960) | Supported | Not supported |
| H1c | CS → GQ | 0.0803 (0.9522) | 0.0569 (0.4203) | Not Supported | Not Supported |
| H1d | L → GQ | 0.0965 (0.8605) | 0.0504 (0.3707) | Not Supported | Not Supported |
| H1e | DS → GQ | 0.3513 *** (3.8040) | 0.5503 *** (3.3000) | Supported | Supported |
| H2 | GQ → PV | −0.0051 (0.0214) | 0.5685 *** (8.7856) | Not Supported | Supported |
| H3 | GQ → GS | 0.8427 *** (18.2806) | 0.7469 *** (8.6920) | Supported | Supported |
| H4 | PV → GS | −0.0075 (0.1102) | 0.0625 (0.7200) | Not Supported | Not Supported |
| H5 | PV → FI | 0.0914 (1.1054) | 0.1948 *** (3.4959) | Not Supported | Supported |
| H6 | GS → FI | 0.8044 *** (9.8137) | 0.7607 *** (14.5086) | Supported | Supported |
| Frequency Cut-Off: 2 | Future Intentions (FI) | Future Intentions (~FI) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consistency Cut-Off | E = 0.826 | N = 0.826 | E = 0.808 | N = 0.805 | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| GQ | • | • | • | ○ | ○ | ||||
| PV | • | • | • | ○ | |||||
| GS | • | • | • | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Raw coverage | 0.843 | 0.644 | 0.707 | 0.743 | 0.640 | 0.828 | 0.679 | 0.795 | 0.824 |
| Unique coverage | 0.266 | 0.067 | 0.091 | 0.127 | 0.023 | 0.193 | 0.044 | 0.089 | 0.117 |
| Consistency | 0.819 | 0.880 | 0.895 | 0.892 | 0.923 | 0.851 | 0.912 | 0.835 | 0.863 |
| Overall solution coverage | 0.910 | 0.858 | 0.872 | 0.913 | |||||
| Overall solution consistency | 0.807 | 0.848 | 0.820 | 0.784 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magaz-González, A.-M.; Sahelices-Pinto, C.; Mendaña-Cuervo, C.; García-Tascón, M. Experienced vs. Novice Participants Perception of Overall Quality and Intention to Join in Future Sport Trials: Case European Duathlon Championship. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2023, 13, 1395-1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13080102
Magaz-González A-M, Sahelices-Pinto C, Mendaña-Cuervo C, García-Tascón M. Experienced vs. Novice Participants Perception of Overall Quality and Intention to Join in Future Sport Trials: Case European Duathlon Championship. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education. 2023; 13(8):1395-1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13080102
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagaz-González, Ana-María, César Sahelices-Pinto, Cristina Mendaña-Cuervo, and Marta García-Tascón. 2023. "Experienced vs. Novice Participants Perception of Overall Quality and Intention to Join in Future Sport Trials: Case European Duathlon Championship" European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education 13, no. 8: 1395-1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13080102
APA StyleMagaz-González, A.-M., Sahelices-Pinto, C., Mendaña-Cuervo, C., & García-Tascón, M. (2023). Experienced vs. Novice Participants Perception of Overall Quality and Intention to Join in Future Sport Trials: Case European Duathlon Championship. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education, 13(8), 1395-1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13080102










