Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV): A Review
Abstract
Introduction
Literature review
Virology and pathogenesis
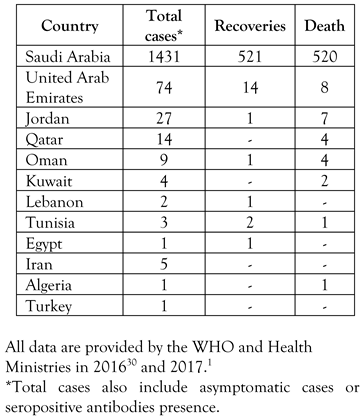
Epidemiology
Sources and transmission
Clinical manifestation and diagnosis
Treatment and prevention
Discussion
One Health approach
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV)-Lebanon. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/don/04-july-2017-mers-lebanon/en/ (accessed on 05 July 2017).
- Bauerfeind, R.; von Graevenitz, A.; Kimmig, P.; et al. Zoonoses: Infectious Diseases Transmissible from Animals to Humans, 4th Ed. ed; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, K.; Hirsch, M.; Thorner, A. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: Virology, pathogenesis, and epidemiology. In UpToDate; Post, T.W., Ed.; . UpToDate Inc: Waltham, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, J. Patient with new strain of coronavirus is treated in intensive care at London hospital. BMJ 2012, 345, e6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tawfiq, A. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-coronavirus infection: An overview. J Infect Public Health 2013, 6, 319–322. [Google Scholar]
- Azhar, E.I.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Farraj, S.A.; Hassan, A.M.; Al-Saeed, M.S.; Hashem, A.M. Evidence for camel-to-human transmission of MERS coronavirus. N Engl J Med. 2014, 370, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV). 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/middle-east-respiratory-syndrome-coronavirus-(mers-cov) (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol Biol 2015, 1282, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, P.C.; Huang, Y.; Lau, S.K.; Yuen, K.Y. Coronavirus genomics and bioinformatics analysis. Viruses 2010, 2, 1804–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif-Yakan, A.; Kanj, S.S. Emergence of MERS-CoV in the Middle East: origins, transmission, treatment, and perspectives. PLoS Pathog 2014, 10, e1004457. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, J.F.; Lau, S.K.; To, K.K.; Cheng, V.C.; Woo, P.C.; Yuen, K.Y. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: another zoonotic betacoronavirus causing SARS-like disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 2015, 28, 465–522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.S.; Mou, H.; Smits, S.L.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 2013, 495, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindler, E.; Jónsdóttir, H.R.; Muth, D.; et al. Efficient replication of the novel human betacoronavirus EMC on primary human epithelium highlights its zoonotic potential. MBio 2013, 4, e00611–2. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, R.W.; Hemida, M.G.; et al. Tropism and replication of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus from dromedary camels in the human respiratory tract: an in-vitro and ex-vivo study. Lancet Respir Med 2014, 2, 813–822. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.A.; Raj, V.S.; Muth, D.; et al. Human coronavirus EMC does not require the SARS-coronavirus receptor and maintains broad replicative capability in mammalian cell lines. MBio 2012, 3, e00515–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, J.F.; Choi, G.K.; Tsang, A.K.; et al. Development and evaluation of novel real-time reverse transcription-PCR assays with locked nucleic acid probes targeting leader sequences of human-pathogenic coronaviruses. J Clin Microbiol 2015, 53, 2722–2726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Widagdo, W.; Raj, V.S.; Schipper, D.; et al. Differential expression of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus receptor in the upper respiratory tracts of humans and dromedary camels. J Virol 2016, 90, 4838–4842. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E. MERS coronavirus: diagnostics, epidemiology and transmission. Virol J 2015, 12, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, L.; Gu, X. Evolutionary dynamics of MERS-CoV: potential recombination, positive selection and transmission. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 25049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Fan, R.Y.Y.; Luk, H.K.H.; et al. Replication of MERS and SARS coronaviruses in bat cells offers insights to their ancestral origins. Emerg Microbes Infect 2018, 7, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Dromedary Camels and MERS-CoV: Filling Knowledge Gaps. 2017. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i7350e.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2018).
- Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy. Camel with MERS-CoV Had Signs of Illness. 2013. Available online: http://www.cidrap.umn.edu/news-perspective/2013/11/camel-mers-cov-had-signs-illness (accessed on 25 November 2018).
- Chan, J.F.; Chan, K.H.; Choi, G.K.; et al. Differential cell line susceptibility to the emerging novel human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012: implications for disease pathogenesis and clinical manifestation. J Infect Dis 2013, 207, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar]
- van Boheemen, S.; de Graaf, M.; Lauber, C.; et al. Genomic characterization of a newly discovered coronavirus associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans. MBio 2012, 3, e00473–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Ge, X.; Wang, L.F.; Shi, Z. Bat origin of human coronaviruses. Virol J 2015, 12, 221. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Shi, X.; Jiang, L.; et al. Structure of MERS-CoV spike receptor-binding domain complexed with human receptor DPP4. Cell Res 2013, 23, 986–993. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; et al. Discovery of seven novel mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J Virol 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar]
- Cauchemez, S.; Fraser, C.; Van Kerkhove, M.D.; et al. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: quantification of the extent of the epidemic, surveillance biases, and transmissibility. Lancet Infect Dis 2014, 14, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijawi, B.; Abdallat, M.; Sayaydeh, A.; et al. Novel coronavirus infections in Jordan, April 2012: epidemiological findings from a retrospective investigation. East Mediterr Health J 2013, 19 (Suppl. 1), S12–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MERS Corona Map. 23017. Available online: http://coronamap.com (accessed on day month year).
- Banerjee, A.; Rawat, R.; Subudhi, S. Outbreak control policies for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS): the present and the future. J Trop Dis Public Health. 2015, 3, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus outbreak in the Republic of Korea. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2015, 6, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV)—Update. 2014. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/don/2014_05_15_mers/en/ (accessed on 29 June 2017).
- Hemida, M.G.; Perera, R.A.; Wang, P.; et al. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) coronavirus seroprevalence in domestic livestock in Saudi Arabia, 2010 to 2013. Euro Surveill 2013, 18, 20659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS). Transmission. 2016. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/mers/about/transmission.html (accessed on 29 June 2017).
- Meyer, B.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Wernery, U.; et al. Serologic assessment of possibility for MERS-CoV infection in equids. Emerg Infect Dis 2015, 21, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusken, C.B.; Ababneh, M.; Raj, V.S.; et al. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) serology in major livestock species in an affected region in Jordan, June to September 2013. Euro Surveill 2013, 18, 20662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusken, C.B.; Schilp, C.; Raj, V.S.; et al. MERS-CoV infection of alpaca in a region where MERS-CoV is endemic. Emerg Infect Dis 2016, 22, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, J.S.; Lam, T.T.; Ahmed, M.M.; et al. Co-circulation of three camel coronavirus species and recombination of MERS-CoVs in Saudi Arabia. Science 2016, 351, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, M.M.; Chu, D.K.; Gomaa, M.R.; et al. Surveillance for coronaviruses in bats, Lebanon and Egypt, 2013-2015. Emerg Infect Dis 2016, 22, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, A.L.; Goutard, F.L.; Miguel, E.; et al. MERS-CoV at the animal–human interface: inputs on exposure pathways from an expert-opinion elicitation. Front Vet Sci 2016, 3, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkema, R.S.; Farag, E.A.B.A.; Himatt, S.; et al. Risk factors for primary Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in camel workers in Qatar during 2013-2014: A case-control study. J Infect Dis 2017, 215, 1702–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumla, A.; Rustomjee, R.; Ntoumi, F.; et al. Middle East respiratory syndrome—need for increased vigilance and watchful surveillance for MERS-CoV in Sub-Saharan Africa. Int J Infect Dis 2015, 37, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Whitaker, B.; Sakthivel, S.K.; et al. Real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay panel for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J Clin Microbiol 2014, 52, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Arifi, A.A.; Balkhy, H.H.; et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Ann Intern Med 2014, 160, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hameed, F.; Wahla, A.S.; Siddiqui, S.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus patients admitted to an intensive care unit in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. J Intensive Care Med 2016, 31, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Harthi, A.; Hussein, J.; et al. Severe neurologic syndrome associated with Middle East respiratory syndrome corona virus (MERS-CoV). Infection 2015, 43, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excler, J.L.; Delvecchio, C.J.; Wiley, R.E.; et al. Toward developing a preventive MERS-CoV vaccine—Report from a workshop organized by the Saudi Arabia Ministry of Health and the International Vaccine Institute, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, November 14-15, 2015. Emerg Infect Dis 2016, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaneri, A.B.; Johnson, R.F.; Wada, J.; Bollinger, L.; Jahrling, P.B.; Kuhn, J.H. Middle East respiratory syndrome: obstacles and prospects for vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 2015, 14, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.; Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C. The emerging novel Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: the “knowns” and “unknowns”. J Formos Med Assoc 2013, 112, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© GERMS 2019.
Share and Cite
Ramadan, N.; Shaib, H. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV): A Review. GERMS 2019, 9, 35-42. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2019.1155
Ramadan N, Shaib H. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV): A Review. GERMS. 2019; 9(1):35-42. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2019.1155
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamadan, Nour, and Houssam Shaib. 2019. "Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV): A Review" GERMS 9, no. 1: 35-42. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2019.1155
APA StyleRamadan, N., & Shaib, H. (2019). Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV): A Review. GERMS, 9(1), 35-42. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2019.1155




