Abstract
Background: Burn victims admitted in burn intensive care units (ICU) are at a high risk of nosocomial infections generated by methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). This systematic review aims to estimate the incidence of MRSA among burn patients admitted to the ICU setting, with an emphasis on the incidence rate and antibiotic resistance profile of the MRSA strains. Methods: A systematic literature search was performed in five electronic databases limited to publication dates from 1st January 2000 until 31st August 2017. After screening n=481 articles, n=21 were found to meet the inclusion criteria of this systematic review. Results: Results from the meta-analysis revealed that the risk for MRSA isolates in the burn ICU was 55.0% higher (OR 0.55, 95%CI 0.32-0.94). Therefore, timely testing, appropriate hygiene practice and suggested wound care must be practiced while handling such patients. Conclusion: Further studies are needed to identify the risk factors of MRSA infections among burn patients and to develop new antimicrobial agents for MRSA infections.
Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a prevalent pathogen globally, and one of the most frequent causes of nosocomial infections in high risk units such as the burn intensive care unit (ICU). Due to irrational use of broad-spectrum antibiotics over the years, methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has become one of the predominant pathogens in the burn units, causing invasive infections in burn patients globally, with reported infection rates of greater than 50% [1]. Burn ICU has become a major reservoir for MRSA in the hospital setting with reported MRSA outbreaks in several hospitals, which resulted in complications such as pneumonia, sepsis and bacteremia in burn patients [1,2]. Burn patients are more susceptible to bacterial infection due to physical deprivation of the skin barrier and reduction in cell-mediated immunity [3]. Overall, 75% of deaths occurring in patients with severe burns are due to sepsis from burn wound infections or other infectious complications [3]. Since the emergence of MRSA isolates, which are becoming more multidrug resistant, the prevalence of MRSA infections in healthcare settings has continued to pose a major challenge for infection control professionals [3]. Emergence of antibiotic resistance limits the availability of therapeutic options for effective treatment of infections and this contributes to the rise in economic burden [4].
There are limited data available regarding the prevalence of MRSA infections among burn patients in the recent years. Most studies focused on the proportion of MRSA among the population in the general ICU and there is currently no review which assesses the global prevalence of MRSA infections among burn patients in the burn ICU. This gap in the existing literature needs to be addressed, particularly in burn patients who pose a greater risk of infection than other patients. Understanding the extent of MRSA infections among burn patients is important in highlighting the need to take appropriate action to minimize transmission, infection and mortality in this vulnerable population. This study aims to determine the risk of MRSA and incidence rate difference of MRSA and MSSA in burn ICU. This information will be of assistance in developing effective infection control programs, guidelines and preventive measures to reduce MRSA infections in these high-risk units in the current healthcare setting.
Methods
A systematic search on PubMed, EMBASE (Ovid), Cochrane, CINAHL Plus and Scopus was performed to identify studies that assessed the risk of MRSA and MSSA isolates and the resistance pattern of MRSA in burn ICU. The search was limited to publication dates from 1st January 2000 until 31st August 2017. Titles and abstracts were searched using search terms such as methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus OR (MRSA) OR Meth resis S aureus AND burn ICU OR burn intensive care unit, to identify the research papers. The following MeSH terms were used in PubMed, connected with Boolean operator AND: “sepsis, cross infection, nosocomial infection”, “burn unit, burn centre”. This systematic review was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [5]. The references of review articles retrieved from the databases were reviewed for articles that may be relevant to the objectives of this research. All titles and abstracts of retrieved articles were screened for relevance to the aim of the study and full texts were obtained for review if appropriate.
Population intervention comparator and outcome
P = burn patients admitted in the ICU.
I = None/not applicable.
C = active MRSA or MSSA infection.
O = Culture and sensitivity pattern.
Study selection
Articles were selected based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Studies which fulfilled the following criteria were eligible for inclusion: 1) a quantitative study that assesses the prevalence of MRSA and S. aureus infection in burn intensive care unit; 2) a study that examines the resistance pattern of MRSA; 3) the study design is a randomized controlled trial, cohort or cross-sectional study.
The eligibility was determined by title, abstract and full text of the paper. All systematic literature reviews, case reports, case control studies, letter to editors, conference proceedings and research briefs were excluded from the study. However, their reference lists were screened to identify any other article from grey literature that might not have appeared in the main search.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Abstracts of retrieved articles with relevant content were chosen for full text review. Data extraction was performed for selected studies by using a data extraction form on a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. The data extraction form included name of first author, title of study, year of publication, country, study design, study objective, study population, number of patients, criteria for selection of patients, number of isolates, resistance profile and study limitations. The quality of each selected study was assessed by using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale, which is a quality assessment tool for observational studies.
Data synthesis and analysis
Analysis was carried out carried out using Stata Statistical Software: Release 14 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA). Data (i.e., the total number of S. aureus isolates was further categorized into MSSA cases and MRSA cases) were extracted from the selected research article and data, i.e., number of MRSA and MSSA isolates was utilized for analysis. Random effect model was used to estimate the effect size of proportions to estimate the incidence of MRSA isolates among burn patients at a confidence interval of 95%. Furthermore, subgroup analysis was performed to estimate the risk of MRSA infections among burn patients across different regions. In the case if there was a higher heterogeneity, Tau-squared value was used to interpret the heterogeneity among the studies.
Results
Study selection
From the systematic literature search of five electronic databases, 481 studies were identified as shown in Table 1. After screening of titles and abstracts, 72 potentially relevant articles were selected for full-text review for eligibility. Of the 72 studies, 21 studies were included in this systematic review. The PRISMA flow diagram of study selection is presented in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Number of records found in each database.
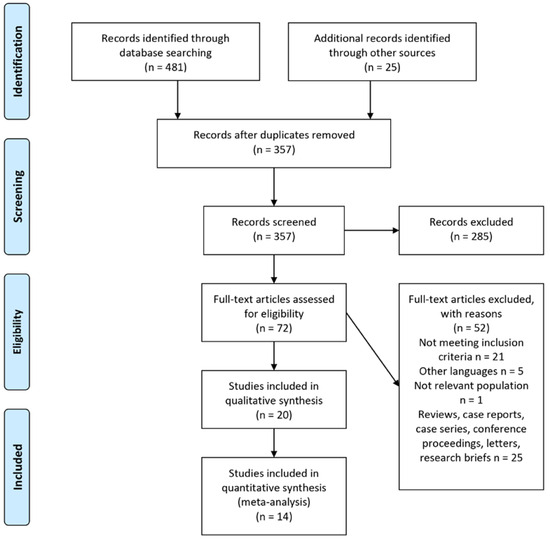
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of study selection.
Study characteristics
Of the 21 included studies, 13 were cross-sectional studies and eight were cohort studies. These studies involved at least 8455 patients, primarily located in India (four studies) [2,6,7,8], the USA (three studies) [9,10,11], China (two studies) [12,13], Iraq (two studies) [14,15], Kuwait (two studies) [16,17], and Sweden (two studies) [18,19]. The other study populations were located in Ghana [20], Iran [21], Israel [22], Lithuania [23], Pakistan [24], and Korea, [25]. Numbers of patients were not specified in three of the included studies [7,11,21]. In most of the studies MRSA infections were investigated/treatment among the group of patients diagnosed with burns wound infections, followed by nosocomial infection, sepsis/septicemia. A summary of the study characteristics is presented in Table A1 (Appendix A).
Quality assessment
Two separate Newcastle-Ottawa Scale forms were used for cohort studies and cross-sectional studies. The mean Newcastle-Ottawa Scale quality score for included cohort studies was 7.25 out of 9, with a range of 6-8. Four of the cohort studies were rated as good quality and the remaining four were rated as fair quality. The mean Newcastle-Ottawa Scale score for 13 selected cross-sectional studies was 7 out of 10, with a range of 6-8. Four cross-sectional studies were rated as fair quality and nine of the studies were rated as good quality.
Overall risk of MRSA in burn ICU
A total of 14 studies reported data that was relevant to the outcomes of interest for this systematic review. With respect to risk of MRSA, only studies which determined the total number of isolates obtained and number of MRSA isolates were included in the analysis. A total of 22,722 isolates and 3,106 MRSA isolates from 20 studies were included in determining the risk of MRSA among burn patients in burn ICU as shown in Figure 2 [2,6,7,8,9,10,11,13,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Upon performing an overall meta-analysis it was revealed that the risk of MRSA infections among burn ICU patients was 55% more likely in comparison to MSSA (0.55, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.32-0.94)—Figure 2.
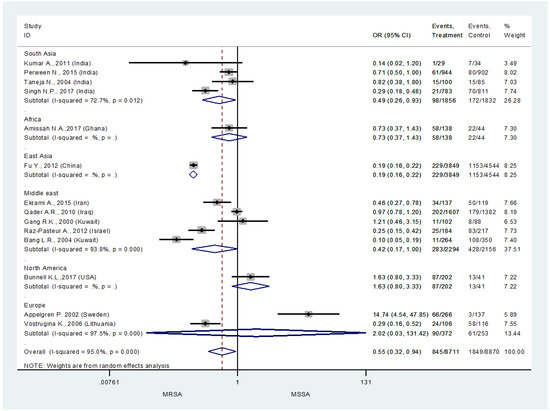
Figure 2.
Risk of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections among ICU burn patients.
Furthermore, a subgroup analysis was performed to see the situation based on the World Health Organization (WHO) regional classification. It was revealed that the risk of MRSA among ICU burn patients was highest among the South Asian region 49.0% (OR 0.49, 95%CI 0.26-0.93). Overall, all the four studies included in this analysis were from India, where Taneja et al., 2004 [28], and Perween et al., 2015 [2], were the two studies from the South Asian region reporting 82% and 71% risk of MRSA infections among ICU burn patients. The Middle East region was observed to be the second with the highest rate of MRSA infections among ICU burn patients. Overall, for the Middle Eastern region the risk of MRSA infections was 42.0% (OR 0.42, 95%CI 0.17-1.00). Studies from Iraq (Qader AR & Muhamad JA., 2010) (OR 0.97, 95%CI 0.78-1.20) were observed to be reporting the highest MRSA infection among the ICU burn patients, followed by Iran (Ekrami, Montazeri, Kaydani, & Shokoohizadeh, 2015) (OR 0.46, 95%CI 0.27-0.78) and Israel (Raz-Pasteur et al., 2013) (OR 0.25, 95%CI 0.15-0.42). Overall, in the Middle Eastern region there were two studies from Kuwait and only one of them was reporting 10% risk of MRSA among ICU burn patients. The analysis for the African and East Asian region was inconclusive due to only one study in each of these regions. Based on the results of these single studies from these region we can see that the risk of MRSA infection in Ghana [20] was 73% and in China it was 0.19% among ICU burn patients.
Similarly, there was only one study from the North American region [10], which reported very minor rates of MRSA infection among their burn population (OR 1.63, 95%CI 0.80-3.33). Among the regions it was noticed that Europe (OR 2.02, 95%CI 0.03-131.42) had the lowest risk of MRSA infections among their ICU burn patients. Overall, it is revealed that Sweden has the lowest risk of MRSA infection among their ICU burn patients (OR 14.74, 95%CI 4.54-47.85) in the European region, and in comparison to other regions as well.
Discussion
This study is the first systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the risk of MRSA in burn ICU. In some developed countries, nosocomial infections were mostly caused by multidrug resistant S. aureus strains particularly MRSA [29], Based on the findings of this review, the overall likelihood of MRSA among burn patients admitted into burn ICU is 55.0% (OR 0.55, 95%CI 0.32-0.94). The high incidence of bacteremia caused by MRSA in this burn center is due to severe injury of the patients admitted, early necretomies and enteral feeding as well as prolonged hospitalization and antibiotic treatment [23], Studies that were conducted in India showed high incidence of MRSA infections, which may be due to poor hygienic conditions of hospitals and prevalence of low-level socioeconomic groups of patients often associated with poor sanitation, malnutrition and inadequate hygiene habits [15], Crowding of patients with high levels of disease acuity and healthcare workers in a relatively small area further increases the risk of S. aureus infections in this group of patients.
Lower incidence of MRSA in developed countries such as those located in the Middle East and Europe could be attributed to active surveillance and treatment of MRSA associated cases [30], Routine screening of hospitalized patients and healthcare workers for MRSA has shown promising results in Europe and Scandinavian countries [31], Poor hygiene and irrational use of antibiotics are considered main factors for high risk of MRSA prevalence as indicated in our results from low- and middle-income countries, such as India.
Based on our findings, glycopeptide antibiotics remain the drug of choice for treatment of MRSA infections. All MRSA isolates in studies conducted in China, India, Pakistan and USA were highly susceptible to glycopeptide antibiotics, teicoplanin and vancomycin [2,6,9,13,14,24]. This increased resistance of MRSA further limits the availability of therapeutic options for treatment of infections in burn patients. MRSA isolates were often obtained at high rates from early stages of burn injury, in patients admitted to the burn ICU [25]. Administration of antibiotics to burn patients at admission before microbial culture and sensitivity test is carried out may have contributed to the development of these multidrug resistant pathogens. The development of resistance in these pathogens can be minimized by applying de-escalation therapy in the early stage of burn injury, once microbiological culture test results have been obtained [25].
The global epidemic of MRSA correlates with the development of public health policies that encourage higher patient flow in hospitals, which has resulted in a high number of hospitals to be operating at full or near-full capacity [32]. Overcrowding of hospitals in addition to understaffing has led to the failure of MRSA infection control programs due to inefficient isolation of infected patients, decreased compliance with hygiene rules and increased movement of patients and hospital staff between hospital units [33]. Burn patients who commonly have surgical or open wounds and indwelling devices such as IV catheter, have an increased risk of acquisition of bacterial infections as these wounds act as a good media for growth of pathogens.
The presence of MRSA and other multidrug-resistant pathogens on burn wounds is often associated with the patient’s poor response to antibiotic treatment and severe clinical manifestations [4]. Hence, clinicians should develop and reemphasize clinical practice protocols for hand hygiene, environmental cleaning and disinfection to minimize transmission of MRSA and reduce the risk of infection in intensive care settings [34]. In addition, the implementation of antibiotic stewardship programs should be considered to promote appropriate selection of empirical antibiotic therapy regimen, dose and duration of therapy and route of administration to optimize therapy, reduce cost of treatment, improve clinical outcomes and reduce development of microbial resistance [35].
Limitations of this review include the exclusion of non-English publications and the fact that only observational cohort and cross-sectional studies were included in this review. Unreported comorbidities among patients in the study could have contributed to the higher risk of infections among burn patients in the burn ICU. High heterogeneity among the studies can be another issue, which should be kept in consideration while interpreting the results. Overall, Tau [2] was 0.8827, however, statistically significant heterogenity was observed among the studies from Middle East and Europe, where Tau [2] was 0.9142 and 8.8605.
Conclusions
In summary, the overall risk of MRSA isolates/infections among burn patients admitted into burn ICU was 55.0% (OR 0.55, 95%CI 0.32-0.94). Epidemiological studies and introduction of strict infection control measures could reduce the prevalence of MRSA infections but may be insufficient for the prevention of MRSA outbreaks. Hence, further research is encouraged to focus on assessing and monitoring the drug resistance profile of MRSA for development of new antibiotics to prevent infection and outbreaks in this high-risk population.
Authors Contributions
TMK and YLK conceived the study. YLK performed data extraction. LHL and BHG verified data extraction. TMK and YLK performed data analysis. YLK TMK wrote the initial draft. AB, KGC, LHL and BHG finalized the draft. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Monash Library staff for their kind support in providing access to the full text of the included papers.
Conflicts of interest
All authors—none to disclose.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Characteristics of included studies.
Table A1.
Characteristics of included studies.
| First author, country, year (ref) | Study design | Study year | Recruitment site | Condition /diagnosis | No. of participants | Total no. of isolates | S. aureus | MSSA | MRSA | Antibiotic resistance profile of MRSA isolates | Quality score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant | Susceptible | |||||||||||
| Kumar A, India, 2011 | Cohort study | 2009-2010 | Burn ward of Guru Teg Bahadur Hospital | Sepsis/septicemia | 80 | 28 | 8 | 1 | 7 | Cephalexin (62.5%), erythromycin (62.5%), amoxicillin (62.5%), ciprofloxacin (62.5%), cefoxitin (87.5%), co-trimoxazole (75%), gentamicin (50%) | Vancomycin (100%) | 7 |
| Perween N, India, 2015 | Cross-sectional study | 2012 | Burn ward of a tertiary care hospital | Burn wound infection | 1294 | 883 | 141 | 61 | 80 | Penicillin (100%), cephalexin (100%), cefazolin (100%), erythromycin (98.7%), clindamycin (97.4%), gentamicin (97.4%), amikacin (84.6%), ofloxacin (96.2%), ciprofloxacin (100%) | Vancomycin (100%), teicoplanin (100%), linezolid (97.4%), chloramphenicol (85.9%), rifampicin (88.5%) | 6 |
| Amissah NA, Ghana, 2017 | Cross- sectional study | 2014-2015 | Burn unit, Reconstructive Plastic Surgery and Burn Center of Korle Bu Teaching Hospital | Nosocomial infections/burn wound infection | 62 | 80 | 80 | 58 | 22 | N/A | N/A | 7 |
| Fu Y, China, 2012 | Cross-sectional study | 1998-2009 | Burn center, Changhai Hospital | Burn wound infection | 114 | 3620 | 1382 | 229 | 1153 | N/A | Vancomycin (100%) | 7 |
| Taneja N, India, 2004 | Cohort study | 2000-2001 | Burn unit of a tertiary care referral center | Hospital-acquired infections/burn wound infection | 74 | 85 | 30 | 15 | 15 | Erythromycin (66.6%), netilmicin (22.2%), cefotaxime (55.5%), ciprofloxacin (44.4%), gentamicin (77.7%) | N/A | 8 |
| Ekrami A, Iran, 2015 | Cross-sectional study | 2013-2014 | Burn center, Taleghani burn hospital | Burn wound infection | N/A | 103 | 96 | 34 | 50 | Penicillin (100%), cefoxitin (93%), ampicillin (89%), erythromycin (71%), tetracycline (75%), gentamicin (64%), ciprofloxacin (71%), ampicillin-sulbactam (57%), ceftazidime (79%) | N/A | 7 |
| Cen H, China, 2015 | Cross-sectional study | 2011-2013 | Burn ward of Zhejiang University of Medicine | Hospital-acquired infections/ burn wound infection | 1942 | 2212 | 410 | N/A | 324 | N/A | N/A | 6 |
| Qader AR, Iraq, 2010 | Cross-sectional study | 2008-2009 | Sulaimani Burn, Reconstructive and Plastic Surgery Hospital | Nosocomial infections/ burn wound infection | 760 | 1405 | 462 | 202 | 179 | N/A | N/A | 7 |
| Bunnell KL, USA, 2017 | Cohort study | 2012-2015 | Trauma and burn ICU at Rhode Island Hospital, a level I trauma center | Nosocomial infections | 80 | 115 | N/A | 87 | 13 | N/A | N/A | 6 |
| Gang RK, Kuwait, 2000 | Cohort study | 1992-1998 | Burn Unit of the Al-Babtain Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery of the Ibn Sina Hospital | Sepsis/septicemia | 80 | 91 | N/A | 11 | 8 | N/A | N/A | 6 |
| DiMuzio EE, USA, 2012 | Cross-sectional study | 2004-2011 | Cincinnati Shriners Hospital for Children | Burn wound infection | N/A | 7217 | 1790 | N/A | 806 | N/A | N/A | 8 |
| Raz-Pasteur A, Israel, 2012 | Cross-sectional study | 2001-2009 | Rambam Healthcare Campus (RHC) Burn Unit and ICU | Sepsis | 159 | 159 | N/A | 25 | 83 | N/A | N/A | 8 |
| Ronat J, Iraq, 2014 | Cross-sectional study | 2008-2009 | Sulaymaniyah burn center | Systemic infections due to burns | 1169 | 65 | 17 | N/A | N/A | Penicillin G (100%), oxacillin (100%), gentamicin (88%), fusidic acid (71%), levofloxacin (59%), clindamycin (35%), minocycline (29%), rifampin (29%) | Quinupristin-dalfopristin (88%), nitrofurantoin (100%), vancomycin (100%) | 7 |
| Appelgren P, Sweden, 2002 [19] | Cohort study | 1993-1995 | Burn unit of Karolinska Hospital | Nosocomial/community acquired infections | 230 | 200 | 69 | 66 | 3 | N/A | N/A | 8 |
| Bang LR, Kuwait, 2004 | Cohort study | 1992-2001 | Burns Unit, Al-Babtain Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery | Sepsis/septicemia | 166 | 253 | 119 | 11 | 108 | N/A | N/A | 6 |
| Vostrugina K, Lithuania, 2006 | Cohort study | 1999-2003 | Department of Plastic Surgery and Burns of Kaunas University of Medicine Hospital | 82 | 82 | N/A | 24 | 58 | N/A | N/A | 7 | |
| Schweizer M, USA, 2012 | Cohort study | 2009-2010 | BTU of a teaching hospital with a level-1 trauma center | Sepsis/bacteremia | 144 | 144 | N/A | N/A | 24 | Erythromycin (91%) | Linezolid (100%), daptomycin (100%), quinupristin-dalfopristin (100%), rifampin (100%), co-trimoxazole (100%), gentamicin (100%), vancomycin (100%) | 6 |
| Naqvi Z.A., Pakistan, 2007 | Cross-sectional study | 2002-2003 | Department of Microbiology, Basic Medical Sciences Institute, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi | Burn wound infection | 52 | 190 | 41 | N/A | 10 | Clindamycin (70%), amikacin (90%), ciprofloxacin (100%), gentamicin (80%), clarithromycin (80%) | Vancomycin (100%), chloramphenicol (100%) | 6 |
| Lee H.G., Korea, 2013 | Cross-sectional study | 2007-2011 | Burn intensive care unit | Nosocomial infections/burn wound infection | 397 | 562 | 81 | N/A | 78 | N/A | N/A | 8 |
| Singh N.P., India, 2017 | Cross-sectional study | 2010-2014 | Burn wards and intensive care unit | Nosocomial infections/burn wound infection | N/A | 762 | N/A | 21 | 70 | N/A | N/A | 6 |
| Fransen J., Sweden, 2016 | Cross-sectional study | 1994-2012 | The Burn Center, Department of Hand, Plastic and Burn Surgery, University Hospital of Linko Ping | Burn wound infection | 1570 | 4531 | 851 | N/A | 15 | N/A | N/A | 8 |
References
- Norbury, W.; Herndon, D.N.; Tanksley, J.; Jeschke, M.G.; Finnerty, C.C. Infection in burns. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2016, 17, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perween, N.; Krishanprakash, S.; Bharara, T. Bacteriological profile of burn wound infection in a tertiary care hospital in North India with special reference to methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int Multispec J Health 2015, 1, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Church, D.; Elsayed, S.; Reid, O.; Winston, B.; Lindsay, R. Burn wound infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 2006, 19, 403–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alebachew, T.; Yismaw, G.; Derabe, A.; Sisay, Z. Staphylococcus aureus burn wound infection among patients attending Yekatit 12 Hospital burn unit, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci 2012, 22, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kashyap, B.; Mishra, S.; Agarwal, V.; Kaur, I.R. Bacteriological analysis and antibacterial resistance pattern in burn sepsis: An observation at a tertiary care hospital in East Delhi. Infect Dis Clin Pract 2011, 19, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Rani, M.; Gupta, K.; Sagar, T.; Kaur, I.R. Changing trends in antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of bacterial isolates in a burn unit. Burns 2017, 43, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, N.; Emmanuel, R.; Chari, P.S.; Sharma, M. A prospective study of hospital-acquired infections in burn patients at a tertiary care referral centre in North India. Burns 2004, 30, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, M.; Ward, M.; Cobb, S.; et al. The epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on a burn trauma unit. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2012, 33, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnell, K.L.; Zullo, A.R.; Collins, C.; Adams, C.A., Jr. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia in critically ill trauma and burn patients: A retrospective cohort study. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2017, 18, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMuzio, E.E.; Healy, D.P.; Durkee, P.; Neely, A.N.; Kagan, R.J. Trends in bacterial wound isolates and antimicrobial susceptibility in a pediatric hospital. J Burn Care Res 2014, 35, e304–e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangard-Rafsanjani, Z.; Sarayani, A.; Nosrati, M.; et al. Effect of a community pharmacist-delivered diabetes support program for patients receiving specialty medical care: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Educ 2015, 41, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xie, B.; Ben, D.; et al. Pathogenic alteration in severe burn wounds. Burns 2012, 38, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronat, J.B.; Kakol, J.; Khoury, M.N.; et al. Highly drug-resistant pathogens implicated in burn-associated bacteremia in an Iraqi burn care unit. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qader, A.R.; Muhamad, J.A. Nosocomial infection in Sulaimani Burn Hospital, Iraq. Ann Burns Fire Disasters 2010, 23, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bang, R.L.; Sharma, P.N.; Sanyal, S.C.; Bang, S.; Ebrahim, M.K. Burn septicaemia in Kuwait: Associated demographic and clinical factors. Med Princ Pract 2004, 13, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, R.K.; Sanyal, S.C.; Bang, R.L.; Mokaddas, E.; Lari, A.R. Staphylococcal septicaemia in burns. Burns 2000, 26, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransén, J.; Huss, F.R.; Nilsson, L.E.; Rydell, U.; Sjöberg, F.; Hanberger, H. Surveillance of antibiotic susceptibility in a Swedish Burn Center 1994-2012. Burns 2016, 42, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelgren, P.; Björnhagen, V.; Bragderyd, K.; Jonsson, C.E.; Ransjö, U. A prospective study of infections in burn patients. Burns 2002, 28, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amissah, N.A.; van Dam, L.; Ablordey, A.; et al. Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in a burn unit of a tertiary care center in Ghana. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, T.; Briceño, M.; Mayan, I.; et al. The impact of phenotypic and genotypic G6PD deficiency on risk of Plasmodium vivax infection: A case-control study amongst Afghan refugees in Pakistan. PLoS Med 2010, 7, e1000283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz-Pasteur, A.; Hussein, K.; Finkelstein, R.; Ullmann, Y.; Egozi, D. Blood stream infections (BSI) in severe burn patients—early and late BSI: A 9-year study. Burns 2013, 39, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vostrugina, K.; Gudaviciene, D.; Vitkauskiene, A. Bacteremias in patients with severe burn trauma. Medicina (Kaunas) 2006, 42, 576–579. [Google Scholar]
- Naqvi, Z.A.; Hashmi, K.; Kharal, S.A. Methicillin resistant S. aureusin burn patients. Pak J Pharmacol 2007, 24, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.G.; Jang, J.; Choi, J.E.; et al. Blood stream infections in patients in the burn intensive care unit. Infect Chemother 2013, 45, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, F.; Han, C. Pathogen distribution and drug resistance in a burn ward: A three-year retrospective analysis of a single center in China. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015, 8, 19188–19199. [Google Scholar]
- Ekrami, A.; Montazeri, E.A.; Kaydani, G.A.; Shokoohizadeh, L. Methicillin resistant staphylococci: Prevalence and susceptibility patterns in a burn center in Ahvaz from 2013-2014. Iran J Microbiol 2015, 7, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taneja, N.; Emmanuel, R.; Chari, P.; Sharma, M. A prospective study of hospital-acquired infections in burn patients at a tertiary care referral centre in North India. Burns 2004, 30, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. The Staphylococcus aureus “superbug”. J Clin Invest 2004, 114, 1693–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.S.; Otto, M. Improved understanding of factors driving methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus epidemic waves. Clin Epidemiol 2013, 5, 205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, A.; Loeffen, F.; Bakker, J.; Klaassen, C.; Wulf, M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pig farming. Emerg Infect Dis 2005, 11, 1965–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, C.; Labarca, J.; Salles, M. Prevention strategies for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Latin America. Braz J Infect Dis 2010, 14 Suppl 2, S107–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.; Halton, K.; Graves, N.; et al. Overcrowding and understaffing in modern health-care systems: Key determinants in meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus transmission. Lancet Infect Dis 2008, 8, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerden, B.; Fry, C.; Johnson, A.P.; Wilcox, M.H. The control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus blood stream infections in England. Open Forum Infect Dis 2015, 2, ofv035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Cho, I.H.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Strategies to minimize antibiotic resistance. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2013, 10, 4274–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2018.