Incidence and Predictors of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate-Induced Renal Impairment in HIV Infected Nigerian Patients
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Study design
Study setting
Source of data
Operational definition
Statistical analysis
Ethical approval
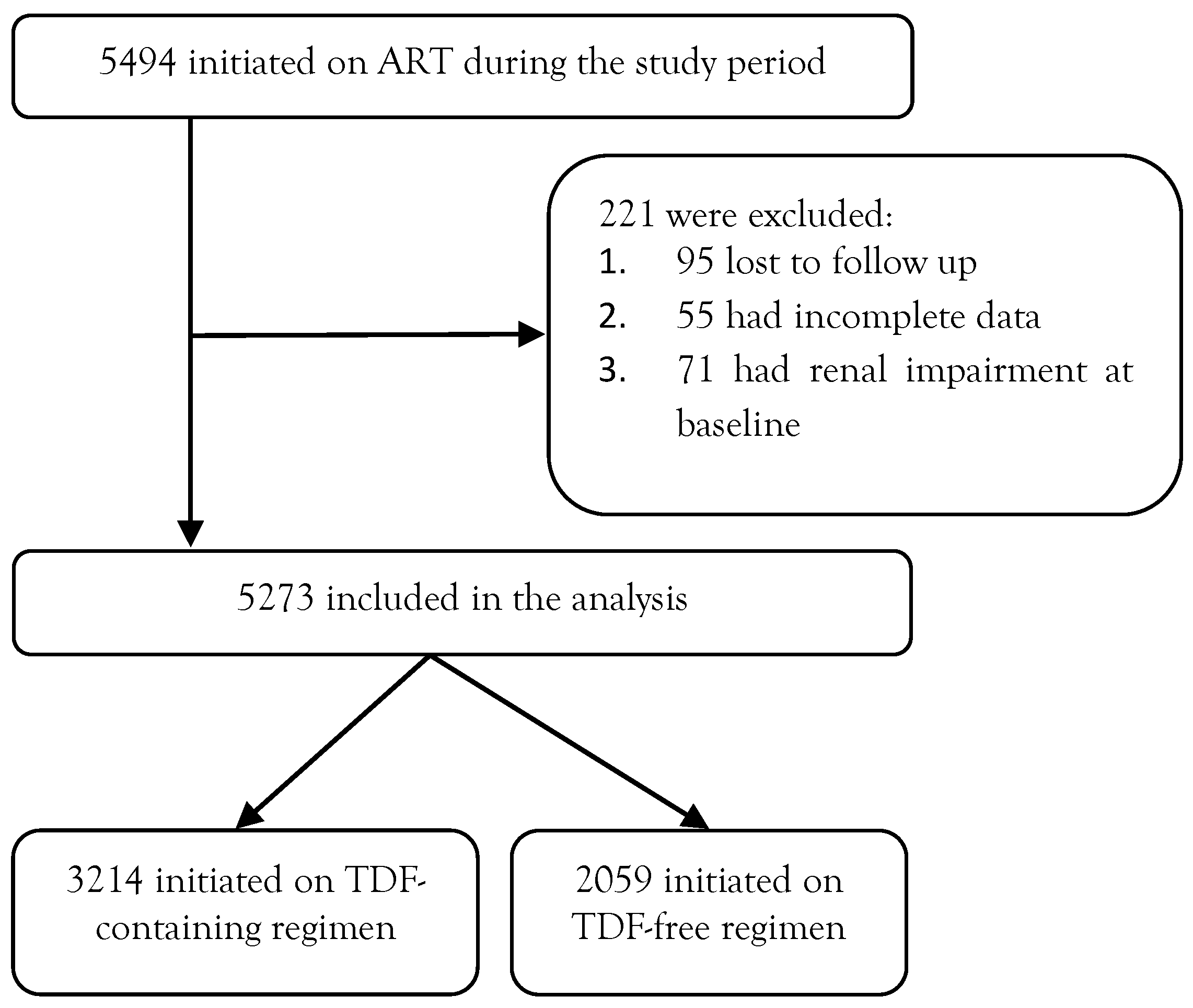
Results
Demographic and baseline characteristics
Characteristics of patients according to TDF exposure status
Cumulative incidence of renal impairment among TDF exposed/unexposed HIV infected individuals
Bivariate analysis of risk factors associated with renal impairment
Logistic regression analysis of risk factors associated with renal impairment
Discussion
Cumulative incidence of renal impairment in the study population
Other factors independently associated with renal impairment
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
Note
References
- Tourret, J.; Deray, G.; Isnard-Bagnis, C. Tenofovir effect on the kidneys of HIV-infected patients: a double-edged sword? J Am Soc Nephrol 2013, 24, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squires, K.; Pozniak, A.L.; Pierone G., Jr.; et al. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in nucleoside-resistant HIV-1 infection: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2003, 139, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkus, G.; Hitchcock, M.J.; Cihlar, T. Assessment of mitochondrial toxicity in human cells treated with tenofovir: comparison with other nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2002, 46, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.M.; Ofotokun, I.; Sheth, A.; Acosta, E.P.; King, J.R. Tenofovir: once-daily dosage in the management of HIV infection. Clin Med Insights Ther 2012, 4, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.D.; Wiebe, N.; Smith, N.; Keiser, P.; Naicker, S.; Tonelli, M. Systematic review and meta-analysis: renal safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in HIV-infected patients. Clin Infect Dis 2010, 51, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, P.; Hemalatha, R.; Isaac, B. A reliable and reproducible rodent model of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) (anti-HIV drug) nephrotoxicity that resembles human TDF tubulopathy. Biomed Res 2016, 27, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, A.; Ijeoma, O.; Edikpo, N.J.; Oputiri, D.; Geoffrey, O.B.P. Tenofovir renal toxicity: evaluation of cohorts and clinical studies—Part 2. Pharmacol Pharm 2014, 5, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patel, K.K.; Patel, A.K.; Ranjan, R.R.; Patel, A.R.; Patel, J.K. Tenofovir-associated renal dysfunction in clinical practice: an observational cohort from western India. Indian J Sex Transm Dis 2010, 31, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.M.; Suresh, K. Tenofovir-induced nephrotoxicity: a retrospective cohort study. Med J Malaysia 2016, 71, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, E.P.; Scarsi, K.K.; Darin, K.M.; Gerzenshtein, L.; Postelnick, M.J.; Palella, F.J., Jr. Low incidence of renal impairment observed in tenofovir-treated patients. J Antimicrob Chemother 2011, 66, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quesada, P.R.; Esteban, L.L.; García, J.R.; et al. Incidence and risk factors for tenofovir-associated renal toxicity in HIV-infected patients. Int J Clin Pharm 2015, 37, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, N.T.; Harries, A.D.; Chinnakali, P.; et al. Low incidence of renal dysfunction among HIV-infected patients on a tenofovir-based first line antiretroviral treatment regimen in Myanmar. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0135188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachor, H.; Machekano, R.; Estrella, M.M.; et al. Incidence of stage 3 chronic kidney disease and progression on tenofovir-based antiretroviral therapy regimens: a cohort study in HIV-infected adults in Cape Town, South Africa. AIDS 2016, 30, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahar, E.; Mugrabi, F.; Kedem, E.; Hassoun, G.; Pollack, S. [Crucial risk factors for renal function deterioration of HIV-infected patients at the AIDS Clinic in Rambam Hospital]. Harefuah 2013, 152, 207–210, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kooij, K.W.; Vogt, L.; Wit, F.W.N.M.; et al. Higher prevalence and faster progression of chronic kidney disease in human immunodeficiency virus-infected middle-aged individuals compared with human immunodeficiency virus-uninfected controls. J Infect Dis 2017, 216, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calza, L.; Trapani, F.; Tedeschi, S.; et al. Tenofovir-induced renal toxicity in 324 HIV-infected, antiretroviral-naïve patients. Scand J Infect Dis 2011, 43, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Raboud, J.; Walmsley, S.; et al. Hepatitis C co-infection is associated with an increased risk of incident chronic kidney disease in HIV-infected patients initiating combination antiretroviral therapy. BMC Infect Dis 2017, 17, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mweemba, A.; Zanolini, A.; Mulenga, L.; et al. Chronic hepatitis B virus coinfection is associated with renal impairment among Zambian HIV-infected adults. Clin Infect Dis 2014, 59, 1757–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nelson, M.R.; Katlama, C.; Montaner, J.S.; et al. The safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HIV infection in adults: the first 4 years. AIDS 2007, 21, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waal, R.; Cohen, K.; Fox, M.P.; et al. Changes in estimated glomerular filtration rate over time in South African HIV-1-infected patients receiving tenofovir: a retrospective cohort study. J Int AIDS Soc 2017, 20, 21317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Summary of New Recommendations. Consolidated ARV Guidelines, June 2013. 2013. Available online: http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/arv2013/intro/rag/en/index4.html (accessed on day month year).
- Levey, A.S.; Bosch, J.P.; Lewis, J.B.; Greene, T.; Rogers, N.; Roth, D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med 1999, 130, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Greene, T.; et al. Expressing the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate with standardized serum creatinine values. Clin Chem 2007, 53, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 2002, 39, S1–S266. [Google Scholar]
- Mulenga, L.; Musonda, P.; Mwango, A.; et al. Effect of baseline renal function on tenofovir-containing antiretroviral therapy outcomes in Zambia. Clin Infect Dis 2014, 58, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, T.; Gatanaga, H.; Komatsu, H.; et al. Renal function declines more in tenofovir- than abacavir-based antiretroviral therapy in low-body weight treatment-naïve patients with HIV Infection. PLoS One 2012, 7, e29977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, R.; Calza, L. Assessment of kidney safety parameters among HIV-Infected patients starting a tenofovir-containing antiretroviral therapy. Open Drug Safety J 2011, 2, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzer, R.; Estrella, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Association of tenofovir exposure with kidney disease risk in HIV Infection. AIDS 2012, 26, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Montoya-Ferrer, A.; Sanz, A.B.; et al. Tenofovir nephrotoxicity: 2011 Update. AIDS Res Treat 2011, 2011, 354908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.R.; Katlama, C.; Montaner, J.S.; et al. The safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HIV infection in adults: the first 4 years. AIDS 2007, 21, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzedine, H.; Isnard-Bagnis, C.; Hulot, J.S.; et al. Renal safety of tenofovir in HIV treatment-experienced patients. AIDS 2004, 18, 1074–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agbaji, O.O.; Agaba, P.A.; Idoko, J.A.; et al. Temporal changes in renal glomerular function associated with the use of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in HIV-infected Nigerians. West Afr J Med 2011, 30, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salome, T.; Kasamba, I.; Mayanja, B.N.; et al. The effect of tenofovir on renal function among Ugandan adults on long term antiretroviral therapy: a cross sectional enrolment analysis. AIDS Res Ther 2016, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpondo, B.C.; Kalluvya, S.E.; Peck, R.N.; et al. Impact of antiretroviral therapy on renal function among HIV-infected Tanzanian adults: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS One 2014, 9, e89573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, G.M.; Lau, B.; Atta, M.G.; Fine, D.M.; Keruly, J.; Moore, R.D. Chronic kidney disease incidence, and progression to end-stage renal disease, in HIV-infected individuals: a tale of two races. J Infect Dis 2008, 197, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzels, J.F.M.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Swinkels, D.W.; Willems, H.L.; den Heijer, M. Age- and gender-specific reference values of estimated GFR in Caucasians: the Nijmegen Biomedical Study. Kidney Int 2007, 72, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.S.; Fordyce, M.W.; Hitchcock, M.J. Tenofovir alafenamide: a novel prodrug of tenofovir for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus. Antiviral Res 2016, 125, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, N. The efficacy and safety of tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in antiretroviral regimens for HIV-1 therapy. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Frequency/ Mean/Median | %/SD/(IQR) |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 1737 | 32.9 |
| Female | 3536 | 67.1 |
| Total | 5273 | 100.0 |
| Age (years), mean | 39.13 | 9.0 |
Weight (kg), mean | 58.67 | 11.8 |
| CD4 (baseline) (cells/cmm), median | 184.0 | (106.0, 260.0) |
| CD4 (48 weeks) (cells/cmm), median | 314.0 | (180.0, 469.0) |
| HIV RNA viral load (baseline) (log10 copies/mL), median | 4.62 | (4.0, 5.2) |
| HIV RNA viral load (48 weeks) (log10 copies/mL), median | 3.02 | (2.3, 4.51) |
| Creatinine clearance (baseline) (mL/min), median | 75.0 | (63.6, 91.0) |
| Creatinine clearance (48 weeks) (mL/min), median | 68.5 | (53.1, 83.5) |
| GFR (baseline) (mL/min/1.73 sqm), median | 107.5 | (102.5, 113.6) |
| GFR (48 weeks) (mL/min/1.73 sqm), median | 103.5 | (88.3, 126.1) |
| Factors | All patients | N (%)/Median (IQR) TDF exposure | Statistic/p value | |
| Yes (n=3214) | No (n=2059) | |||
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 1737 (32.9%) | 1214 (69.9%) | 523 (30.1%) | Chi-square=91.341 |
| Female | 3536 (67.1%) | 1995 (56.4%) | 1541 (43.6%) | p<0.001 |
| Age (years), mean | 39.8±9.2 | 38.02±8.7 | T=7.0 | |
| p<0.001 | ||||
| ≤39 years | 1735 (57.2%) | 1298 (42.8%) | Chi-square=42.138 | |
| >39 years | 1479 (66.0%) | 761 (34.0%) | p<0.001 | |
| Weight | ||||
| <57 kg | 1458 (63.6%) | 834 (36.4%) | Chi-square=12.058 | |
| ≥57 kg | 1756 (58.9%) | 1225 (41.1%) | p<0.001 | |
| CD4 at baseline | 173.0 (86.0, 1349.0) | 196.0 (131.0, 268.0) | K.Wallis H=24.2530 | |
| (cells/cmm), median | p<0.001 | |||
| ≤184 cells/cmm | 572 (59.8%) | 385 (40.2%) | Chi-square=0.686 | |
| >184 cells/cmm | 2642 (61.2%) | 1674 (38.8%) | p=0.407 | |
| HIV RNA viral load at baseline (log10 copies/mL), median | 4.7 (4.04, 5.2) | 4.6 (3.8, 5.1) | K.Wallis H=4.507 p=0.033 | |
| <4.62 (log10 copies/mL) | 417 (52.9%) | 371 (47.1%) | Chi-square=25.120 p<0.001 | |
| ≥4.62 (log10 copies/mL) | 2797 (62.4%) | 1688 (37.6%) | ||
| Creatinine clearance (mL/min), median | 83.7 (70.09, 97.7) | 90.3 (77.2, 106.5) | K.Wallis H=129.1 p<0.001 | |
| GFR (mL/min/1.73 sqm), median | 106.9 (102.0, 112.4) | 108.3 (103.5, 113.9) | K.Wallis H=39.34 p<0.001 | |
| HBsAg | ||||
| Positive | 680 (82.9%) | 140 (17.1%) | Chi-square=197.657 | |
| Negative | 2614 (56.9%) | 1979 (43.1%) | p<0.001 | |
| HCV Ab | ||||
| Positive | 384 (72.2%) | 148 (27.8%) | Chi-square=31.775 | |
| Negative | 2910 (59.6%) | 1971 (40.4%) | p<0.001 | |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Yes | 120 (2.2%) | 78 (1.4%) | Chi-square=0.005 | |
| No | 3174 (58.6%) | 2041 (37.7%) | p=0.942 | |
| Renal Impairment | TDF exposure | Odds ratio (95%CI) | Statistics/ p value | |
| Yes | No | |||
| Yes | 148 (4.6%) | 3066 (95.4%) | 2.0 (1.48- 2.89) | Chi-square=19.0 p<0.001 |
| No | 47 (2.3%) | 2012 (97.7%) | ||
| Factors | Unadjusted OR (95%CI) | p value |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 1.27 (0.93-1.68) | 0.130 |
| Female (Ref) | ||
| Age (years) | 1.07 (1.06-1.09) | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 1.01 (0.99-1.02) | 0.283 |
| TDF exposure | ||
| Yes | ||
| No (Ref) | 2.07 (1.48-2.88) | <0.001 |
| Baseline log VL (median) | ||
| <log 4.62 | ||
| >log 4.62 (Ref) | 1.34 (0.69-2.59) | 0.383 |
| Baseline CD4 count (cells/cmm) | 0.99 (0.98-1.01) | 0.226 |
| Baseline GFR (mL/min/1.73 sqm) | 0.98 (0.97-0.99) | 0.001 |
| HBsAg | ||
| Positive | ||
| Negative (Ref) | 1.13 (0.77-1.66) | 0.523 |
| HCV Ab | ||
| Positive | ||
| Negative (Ref) | 1.62 (1.08-2.42) | 0.020 |
| Nephrotoxic drug exposure | ||
| Yes | ||
| No (Ref) | 1.46 (1.06-1.99) | 0.018 |
| Comorbid conditions | ||
| Yes | ||
| No (Ref) | 4.47 (2.94-6.80) | <0.001 |
| Factors | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p value |
| Gender | ||
| Male | ||
| Female (Ref) | 0.75 (0.55-1.04) | 0.082 |
| Age (years) | 1.06 (1.05-1.08) | <0.001 |
| TDF exposure | ||
| Yes | ||
| No (Ref) | 1.85 (1.31-2.60) | <0.001 |
| Baseline GFR | 0.99 (0.98-1.01) | 0.077 |
| (mL/min/1.73 sqm) | ||
| HCV Ab | ||
| Positive | ||
| Negative (Ref) | 1.2 (0.79-1.83) | 0.398 |
| Nephrotoxic drug exposure | ||
| Yes | ||
| No (Ref) | 1.14 (0.82-1.58) | 0.426 |
| Comorbid conditions | ||
| Yes | ||
| No (Ref) | 2.71 (1.72-4.25) | <0.001 |
© GERMS 2018.
Share and Cite
Ojeh, B.V.; Abah, I.O.; Ugoagwu, P.; Agaba, P.A.; Agbaji, O.O.; Gyang, S.S. Incidence and Predictors of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate-Induced Renal Impairment in HIV Infected Nigerian Patients. Germs 2018, 8, 67-76. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2018.1133
Ojeh BV, Abah IO, Ugoagwu P, Agaba PA, Agbaji OO, Gyang SS. Incidence and Predictors of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate-Induced Renal Impairment in HIV Infected Nigerian Patients. Germs. 2018; 8(2):67-76. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2018.1133
Chicago/Turabian StyleOjeh, Bazim V., Isaac O. Abah, Placid Ugoagwu, Patricia A. Agaba, Oche O. Agbaji, and Steven S. Gyang. 2018. "Incidence and Predictors of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate-Induced Renal Impairment in HIV Infected Nigerian Patients" Germs 8, no. 2: 67-76. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2018.1133
APA StyleOjeh, B. V., Abah, I. O., Ugoagwu, P., Agaba, P. A., Agbaji, O. O., & Gyang, S. S. (2018). Incidence and Predictors of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate-Induced Renal Impairment in HIV Infected Nigerian Patients. Germs, 8(2), 67-76. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2018.1133




