Disruption of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Protein Synthesis by Tannins
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Tannins preparation
Bacterial strains and materials
Antimicrobial assays
Scanning electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy
Total RNA isolation
Next-generation sequencing
Next-generation sequencing analysis
Results
Antimicrobial effects of tannins on MRSA
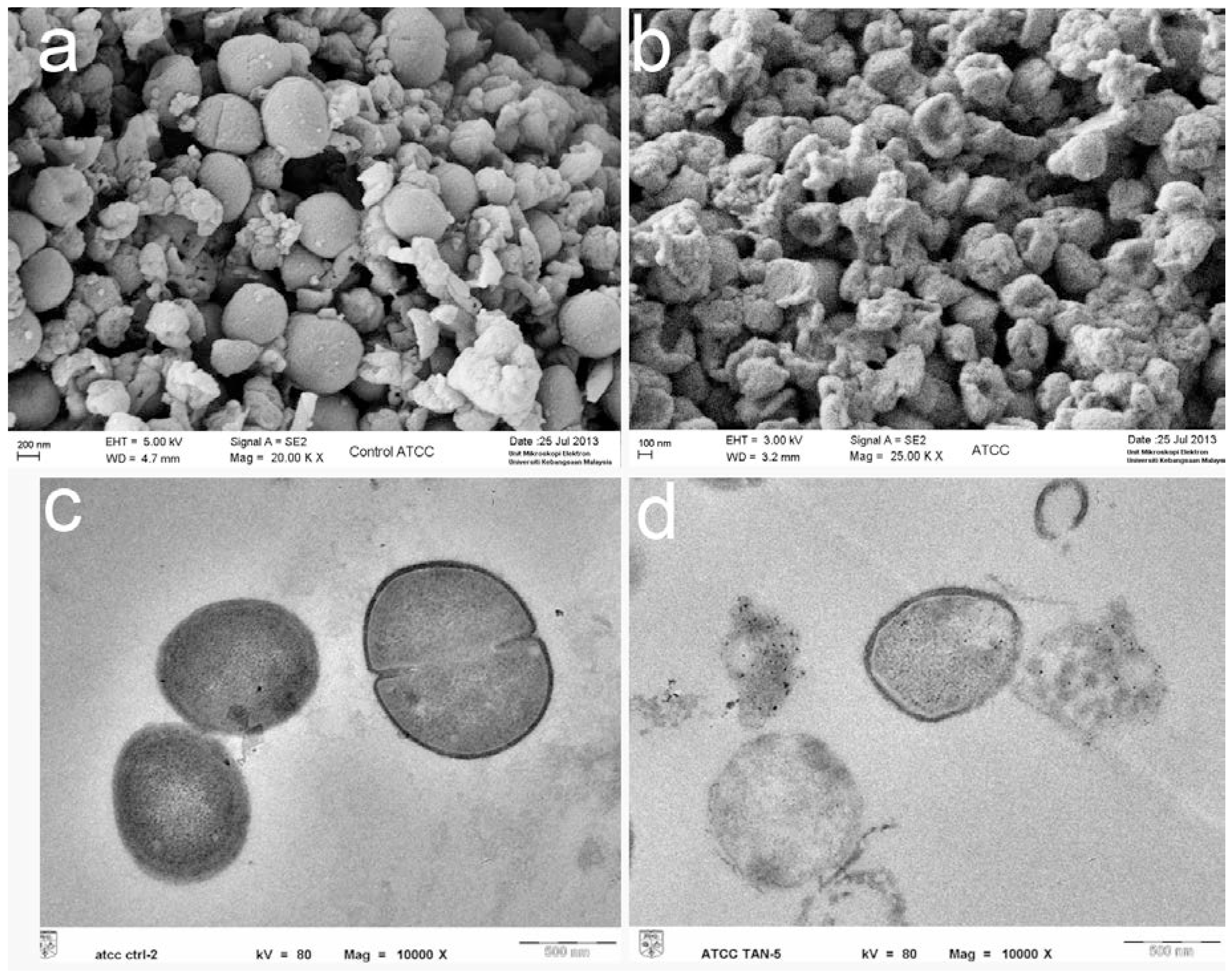
Electron microscopy study
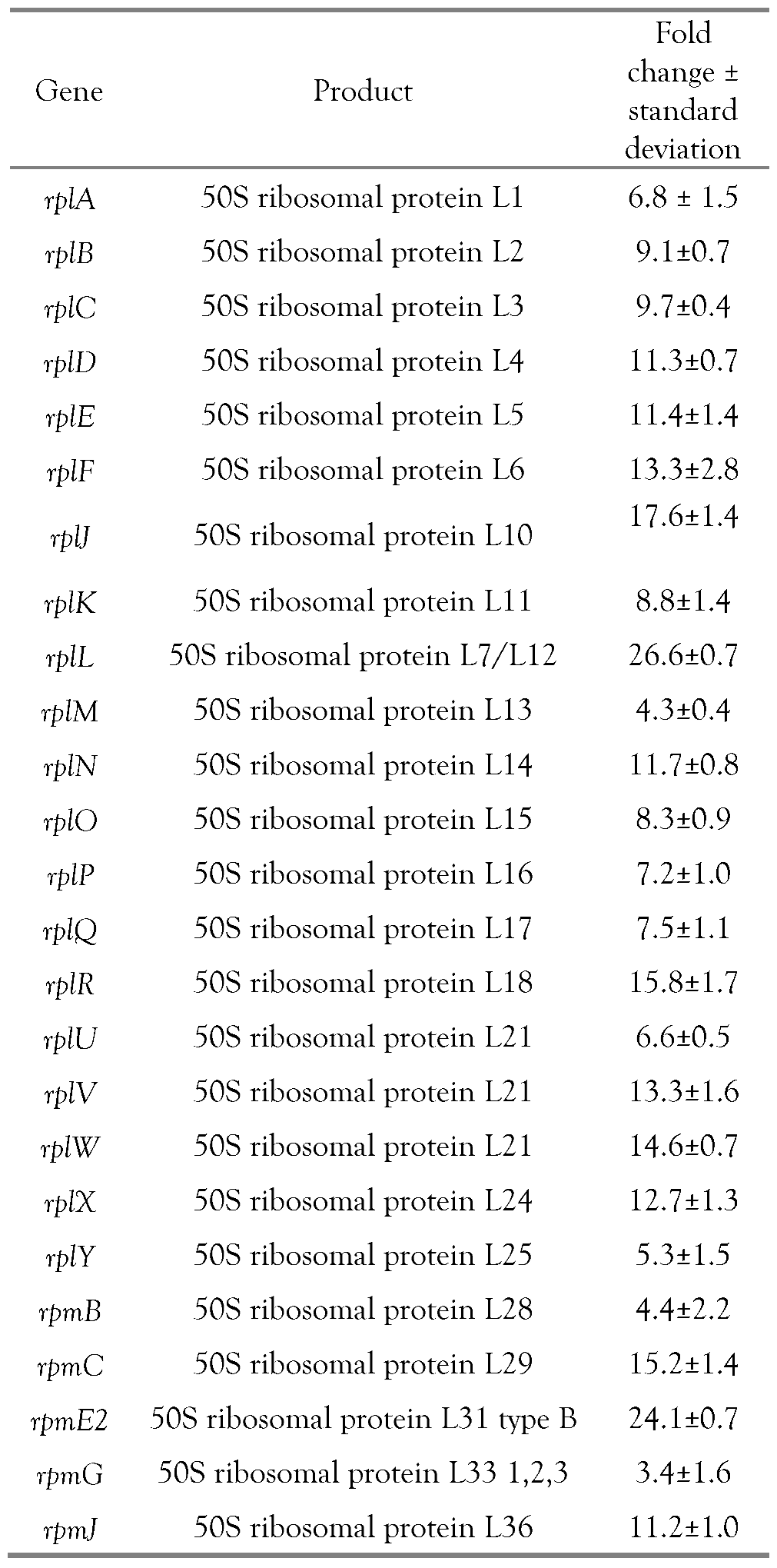
Effects of tannins on MRSA protein synthesis
Discussion
Antimicrobial activity of tannins on MRSA
Molecular effects of tannins on inhibition of MRSA ribosomal protein synthesis
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, H.M.; Graber, C.J. Limitations of antibiotic options for invasive infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: is combination therapy the answer? J Antimicrob Chemother 2010, 65, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Durai, R.; Ng, P.C.H.; Hoque, H. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an update. AORN J 2010, 91, 599–609; quiz 607–609. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Miro, J.M.; Hoen, B.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: a consequence of medical progress. JAMA 2005, 293, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, J.P.; Clark, C.C.; Hackman, B.O. Nosocomial and community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteremias from 1980 to 1993: impact of intravascular devices and methicillin resistance. Clin Infect Dis 1996, 23, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanafani, Z.A.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. [Staphylococcus aureus infections: new challenges from an old pathogen]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 2006, 24, 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Shakil, S.; Akram, M.; Khan, A.U. Tigecycline: a critical update. J Chemother 2008, 20, 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Sorlozano, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Martinez, T.; et al. Detection of new mutations conferring resistance to linezolid in glycopeptide-intermediate susceptibility Staphylococcus hominis subspecies hominis circulating in an intensive care unit. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2010, 29, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Mahady, G.B. Medicinal plants for the prevention and treatment of bacterial infections. Curr Pharm Des 2005, 11, 2405–2427. [Google Scholar]
- Harborne, J.B. Plant polyphenols: vegetable tannins revisited; Haslam, E., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Jeon, B.T.; et al. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of tannins extracted from agricultural by-products. J Med Plants Res 2012, 6, 3072–3079. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Harbi, R.; Al-wegaisi, R.; Moharram, F.; Shaaban, M.; El-Rahman, O.A. Antibacterial and anti-hemolytic activity of tannins from Pimenta dioica against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Bangladesh J Pharmacol 2017, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, S.N.A.; Ibrahim, N.; Yaacob, W.A. Isolation and identification of anti-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus compounds from Phyllanthus columnaris stem bark. Malays J Microbiol 2014, 10, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, P.R. Manual of Clinical Microbiology; ASM Press: Washington DC, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Method for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility test, for bacteria that grow aerobically; Approved Standard. 10th ed. 2015; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 1999. Methods for determining bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents; Approved Guideline. 1999; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Scalbert, A. Antimicrobial properties of tannins. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3875–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanbabaee, K.; Van Ree, T. Tannins: classification and definition. Nat Prod Rep 2001, 18, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.T.; Wong, T.Y.; Wei, C.I.; Huang, Y.W.; Lin, Y. Tannins and human health: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 1998, 38, 421–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shingare, P.; Chaugule, V. Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial activity of miswak, propolis, sodium hypochlorite and saline as root canal irrigants by microbial culturing and quantification in chronically exposed primary teeth. Germs 2011, 1, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, P.Y.; Chung, L.Y.; Navaratnam, P. Transcriptional profiles of the response of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to pentacyclic triterpenoids. PLoS One 2013, 8, e56687. [Google Scholar]
- Champney, W.S. The other target for ribosomal antibiotics: inhibition of bacterial ribosomal subunit formation. Infect Disord Drug Targets 2006, 6, 377–390. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, B.A. Inhibition of bacterial ribosome assembly: a suitable drug target? Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2009, 73, 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Champney, W.S. Bacterial ribosomal subunit assembly is an antibiotic target. Curr Top Med Chem 2003, 3, 929–947. [Google Scholar]
- Ikigai, H.; Nakae, T.; Hara, Y.; Shimamura, T. Bactericidal cathechins damage the lipid bilayer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1993, 1147, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Viljoen, A.; van Vuuren, S.; Ernst, E.; et al. Osmitopsis asteriscoides (Asteraceae)-the antimicrobial activity and essential oil composition of a Cape-Dutch remedy. J Ethnopharmacol 2003, 88, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.S.; Ibrahim, D.; Kassim, J. Assessment of in vivo and in vitro cytotoxic activity of hydrolysable tannin extracted from Rhizophora apiculata barks. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2011, 27, 2737–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, L.M.; Chacana, P.A.; Dominguez, J.E.; Fernandez Miyakawa, M.E. Perspectives in the use of tannins as alternative to antimicrobial growth promoter factors in poultry. Front Microbiol 2014, 5, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| MRSA isolates | 1 | 7 |
| Oxacillin 1 mg | R | R |
| Vancomycin 30 mg | S | S |
| Chloramphenicol 30 mg | S | S |
| Tetracycline 30 mg | S | R |
| Ampicillin 10 mg | R | R |
| Penicillin 10 mg | R | R |
| Cefoxitin 30 mg | R | R |
| Erythromycin 15 mg | R | R |
| Kanamycin 30 mg | S | R |
| Rifampicin 5 mg | S | S |
| Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 23.75/ 1.25 mg | S | S |
 |
 |
© GERMS 2017.
Share and Cite
Adnan, S.-N.-A.; Ibrahim, N.; Yaacob, W.A. Disruption of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Protein Synthesis by Tannins. Germs 2017, 7, 186-192. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2017.1125
Adnan S-N-A, Ibrahim N, Yaacob WA. Disruption of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Protein Synthesis by Tannins. Germs. 2017; 7(4):186-192. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2017.1125
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdnan, Siti-Noor-Adnalizawati, Nazlina Ibrahim, and Wan Ahmad Yaacob. 2017. "Disruption of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Protein Synthesis by Tannins" Germs 7, no. 4: 186-192. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2017.1125
APA StyleAdnan, S.-N.-A., Ibrahim, N., & Yaacob, W. A. (2017). Disruption of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Protein Synthesis by Tannins. Germs, 7(4), 186-192. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2017.1125




