Prevalence of Clostridioides difficile Contamination in the Healthcare Environment and Instruments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Search strategy
Inclusion/exclusion criteria and studies selection
Analysis of data
Results
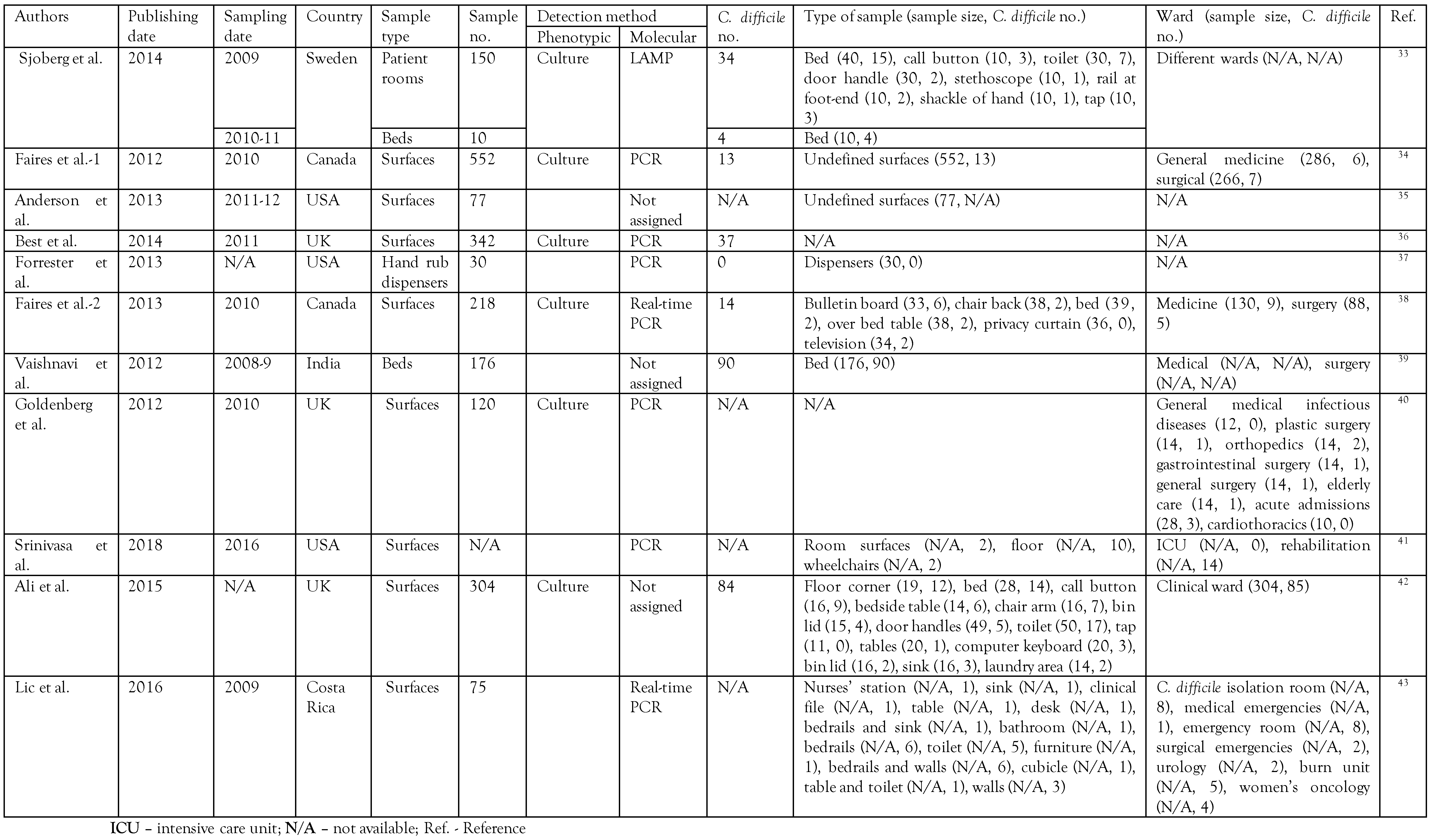
Search results
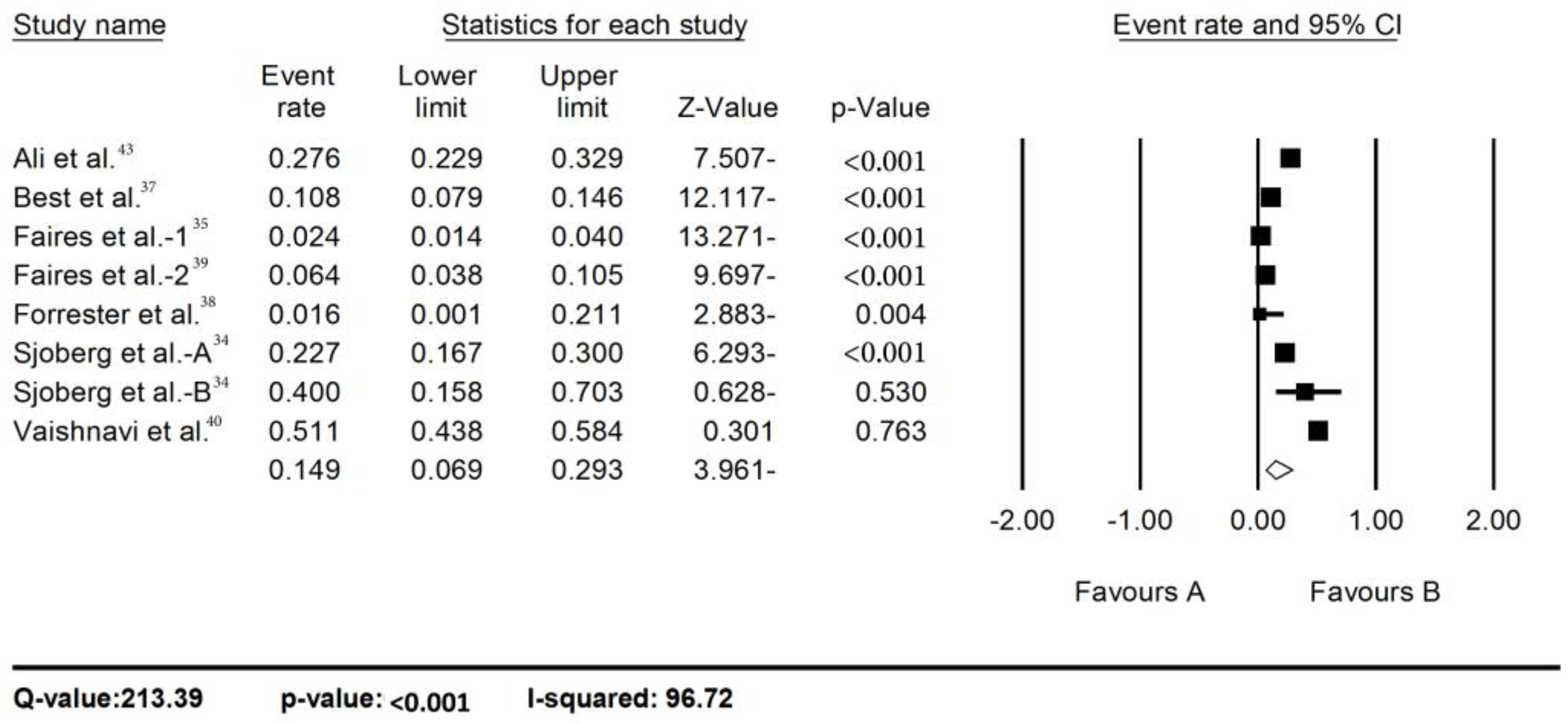
Pooled prevalence of C. difficile in hospital environments
Subgroup analysis of C. difficile prevalence in hospital environments based on the study country
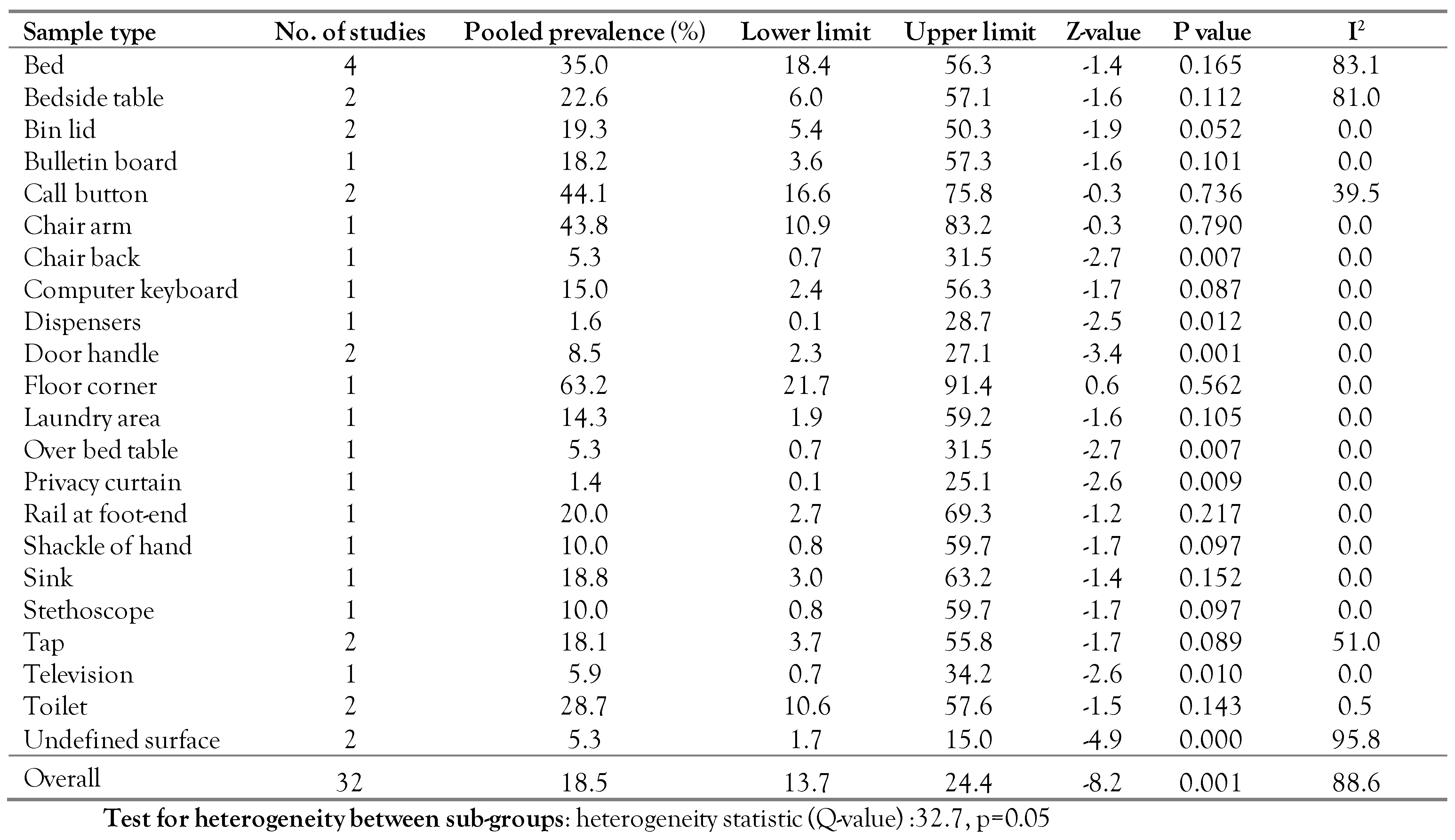
Subgroup analysis of C. difficile prevalence in hospital environments based on the study sample types
The C. difficile prevalence in each sample
Publication bias
Discussion
Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yakob, L.; Riley, T.V.; Paterson, D.L.; Clements, A.C. Clostridium difficile exposure as an insidious source of infection in healthcare settings: An epidemiological model. BMC Infect Dis. 2013, 13, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, M.; Marra, A.R.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Al-Maani, A.S.; Abbas, S.; Rosenthal, V.D. Prevention of Clostridioides difficile in hospitals: A position paper of the International Society for Infectious Diseases. Int J Infect Dis. 2021, 102, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czepiel, J.; Dróżdż, M.; Pituch, H.; et al. Clostridium difficile infection: Review. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019, 38, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.A.; Anderson, D.J. Hospital infection control: Clostridioides difficile. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2020, 33, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, J.P.C.; Liu, X.; Lo, S.H.S.; Chien, W.T.; Wan, X. Effects of environmental cleaning bundles on reducing healthcare-associated Clostridioides difficile infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hosp Infect. 2020, 106, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motamedi, H.; Fathollahi, M.; Abiri, R.; Kadivarian, S.; Rostamian, M.; Alvandi, A. A worldwide systematic review and meta-analysis of bacteria related to antibiotic-associated diarrhea in hospitalized patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kociolek, L.K.; Crews, J.D.; Schwenk, H.T. Recent advances in Clostridioides difficile infection epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment in children. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2021, 34, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Roo, A.C.; Regenbogen, S.E. Clostridium difficile infection: An epidemiology update. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2020, 33, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J. Are room decontamination units needed to prevent transmission of environmental pathogens? Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.J.; Chen, L.F.; Weber, D.J.; et al. Enhanced terminal room disinfection and acquisition and infection caused by multidrug-resistant organisms and Clostridium difficile (the Benefits of Enhanced Terminal Room Disinfection study): A cluster-randomised, multicentre, crossover study. Lancet 2017, 389, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yui, S.; Ali, S.; Muzslay, M.; Jeanes, A.; Wilson, A.P.R. Identification of Clostridium difficile reservoirs in the patient environment and efficacy of aerial hydrogen peroxide decontamination. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2017, 38, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Reprint-preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Phys Ther. 2009, 89, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsells, E.; Shi, T.; Leese, C.; et al. Global burden of Clostridium difficile infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Glob Health. 2019, 9, 010407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, D.M.; Nerandzic, M.M.; Jury, L.A.; Jinno, S.; Chang, S.; Donskey, C.J. Acquisition of spores on gloved hands after contact with the skin of patients with Clostridium difficile infection and with environmental surfaces in their rooms. Am J Infect Control. 2012, 40, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janezic, S.; Potocnik, M.; Zidaric, V.; Rupnik, M. Highly divergent Clostridium difficile strains isolated from the environment. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigaglia, P. Recent advances in the understanding of antibiotic resistance in Clostridium difficile infection. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2016, 3, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Collins, D.; Riley, T. Environmental sources of Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile in the hospital. Int J Infect Dis. 2020, 101, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.P.; Kuijper, E.J. Potential sources of Clostridium difficile in human infection. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015, 29, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenheim, M.; Zbinden, R.; Handschin, A.E.; Gohritz, A.; Altintas, M.A.; Giovanoli, P. Changes in bacterial isolates from burn wounds and their antibiograms: A 20-year study (1986–2005). Burns. 2009, 35, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Compte, D.; Camacho-Ortiz, A.; Ponce-de-León, S. Infection control in limited resources countries: Challenges and priorities. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2017, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegranzi, B.; Pittet, D. Healthcare-associated infection in developing countries: Simple solutions to meet complex challenges. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2007, 28, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.J.; Rutala, W.A. The role of the environment in transmission of Clostridium difficile infection in healthcare facilities. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samore, M.H.; Venkataraman, L.; DeGirolami, P.C.; Arbeit, R.D.; Karchmer, A.W. Clinical and molecular epidemiology of sporadic and clustered cases of nosocomial Clostridium difficile diarrhea. Am J Med. 1996, 100, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, K.; Lawrence, J.; Berry, C.; et al. Risk Factors for primary Clostridium difficile infection; results from the observational study of risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection in hospitalized patients with infective diarrhea (ORCHID). Front Public Health. 2020, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumford, D.M., III; Nerandzic, M.M.; Eckstein, B.C.; Donskey, C.J. What is on that keyboard? Detecting hidden environmental reservoirs of Clostridium difficile during an outbreak associated with North American pulsed-field gel electrophoresis type 1 strains. Am J Infect Control. 2009, 37, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, E.A.; Ulrich, D.; Brooks, D. Successful removal of Clostridioides difficile spores and pathogenic bacteria from a launderable barrier using a commercial laundry process. Infect Dis. 2020, 13, 1178633720923657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrant, J.; Jenkins, R.O.; Laird, K.T. From ward to washer: The survival of Clostridium difficile spores on hospital bed sheets through a commercial UK NHS healthcare laundry process. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2018, 39, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, E.A.; Bochan, M.; Reiff, T.T.; Blackwell, C.; Webb, K.W.; Hart, K.W. Decreasing Clostridium difficile health care-associated infections through use of a launderable mattress cover. Am J Infect Control. 2015, 43, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajravelu, R.K.; Guerrero, D.M.; Jury, L.A.; Donskey, C.J. Evaluation of stethoscopes as vectors of Clostridium difficile and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012, 33, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, W.F.; Kalra, S.; Vasudevan, R.S.; Torriani, F. Aseptic stethoscope barriers prevent C difficile transmission in vitro. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021, 5, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, T.; Earlywine, M.; Breeding, V. Environmental services impact on healthcare-associated Clostridium difficile reduction. Am J Infect Control. 2019, 47, 400–405.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Vossebein, L.; Zille, A. Efficacy of disinfectant-impregnated wipes used for surface disinfection in hospitals: A review. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2019, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöberg, M.; Eriksson, M.; Andersson, J.; Norén, T. Transmission of Clostridium difficile spores in isolation room environments and through hospital beds. APMIS 2014, 122, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faires, M.C.; Pearl, D.L.; Ciccotelli, W.A.; et al. A prospective study to examine the epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium difficile contamination in the general environment of three community hospitals in southern Ontario, Canada. BMC Infect Dis. 2012, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.J.; Gergen, M.F.; Smathers, E.; et al. Decontamination of targeted pathogens from patient rooms using an automated ultraviolet-C-emitting device. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2013, 34, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, E.L.; Parnell, P.; Thirkell, G.; et al. Effectiveness of deep cleaning followed by hydrogen peroxide decontamination during high Clostridium difficile infection incidence. J Hosp Infect. 2014, 87, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.D.; Banaei, N.; Buchner, P.; Spain, D.A.; Staudenmayer, K.L. Environmental sampling for Clostridium difficile on alcohol-based hand rub dispensers in an academic medical center. Surg Infect 2014, 15, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faires, M.C.; Pearl, D.L.; Berke, O.; Reid-Smith, R.J.; Weese, J.S. The identification and epidemiology of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium difficile in patient rooms and the ward environment. BMC Infect Dis. 2013, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnavi, C.; Singh, M. Preliminary investigation of environmental prevalence of Clostridium difficile affecting inpatients in a north Indian hospital. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2012, 30, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, S.D.; Patel, A.; Tucker, D.; French, G.L. Lack of enhanced effect of a chlorine dioxide-based cleaning regimen on environmental contamination with Clostridium difficile spores. J Hosp Infect. 2012, 82, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, V.R.; Hariri, R.; Frank, L.R.; et al. Hospital-associated Clostridium difficile infection and reservoirs within the hospital environment. Am J Infect Control. 2019, 47, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Muzslay, M.; Wilson, P. A novel quantitative sampling technique for detection and monitoring of Clostridium difficile contamination in the clinical environment. J Clin Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2570–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, L.; Rodríguez, C.; Gamboa-Coronado, M.D.M. Molecular detection of Clostridium difficile on inert surfaces from a Costa Rican hospital during and after an outbreak. Am J Infect Control. 2016, 44, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 |
 |
 |
© GERMS 2022.
Share and Cite
Borji, S.; Rostamian, M.; Kadivarian, S.; Kooti, S.; Dashtbin, S.; Hosseinabadi, S.; Abiri, R.; Alvandi, A. Prevalence of Clostridioides difficile Contamination in the Healthcare Environment and Instruments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Germs 2022, 12, 361-371. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1340
Borji S, Rostamian M, Kadivarian S, Kooti S, Dashtbin S, Hosseinabadi S, Abiri R, Alvandi A. Prevalence of Clostridioides difficile Contamination in the Healthcare Environment and Instruments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Germs. 2022; 12(3):361-371. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1340
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorji, Soroush, Mosayeb Rostamian, Sepide Kadivarian, Sara Kooti, Shirin Dashtbin, Somayeh Hosseinabadi, Ramin Abiri, and Amirhooshang Alvandi. 2022. "Prevalence of Clostridioides difficile Contamination in the Healthcare Environment and Instruments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Germs 12, no. 3: 361-371. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1340
APA StyleBorji, S., Rostamian, M., Kadivarian, S., Kooti, S., Dashtbin, S., Hosseinabadi, S., Abiri, R., & Alvandi, A. (2022). Prevalence of Clostridioides difficile Contamination in the Healthcare Environment and Instruments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Germs, 12(3), 361-371. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1340




