Anti-Virulence Therapeutic Strategies Against Bacterial Infections: Recent Advances
Abstract
Introduction
Review criteria
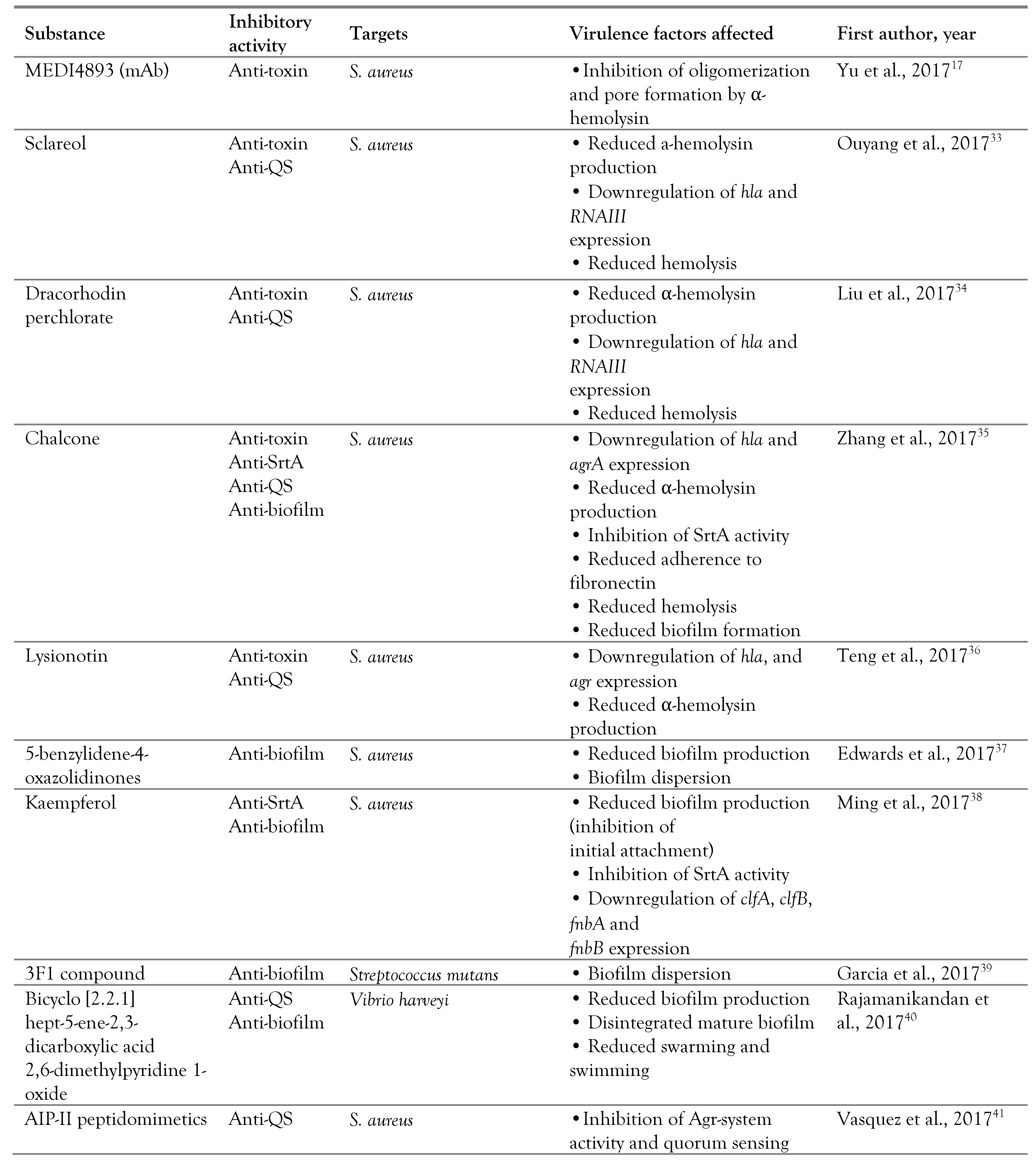
Antivirulence strategies
Antiadherence strategies
Targeting toxins and secretion systems
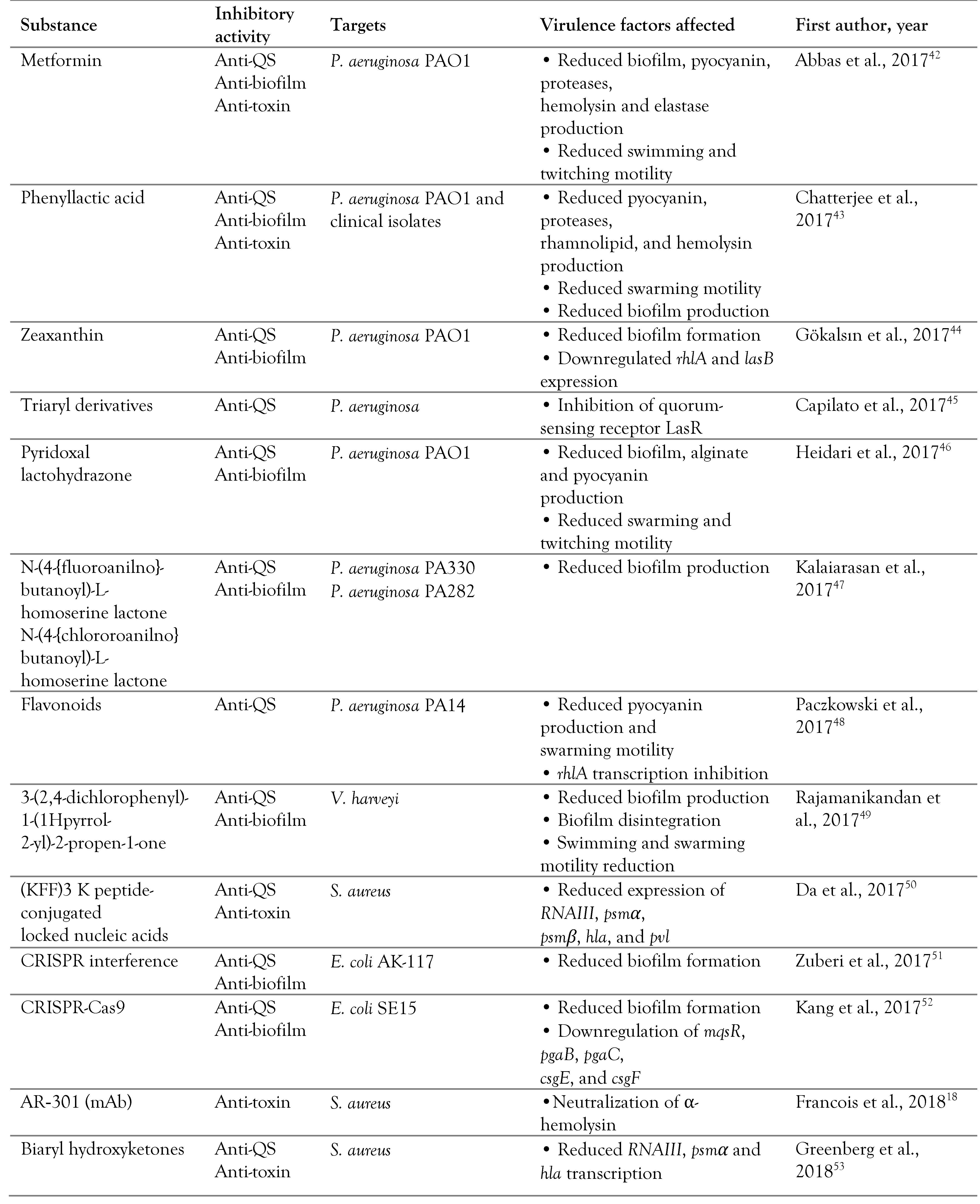
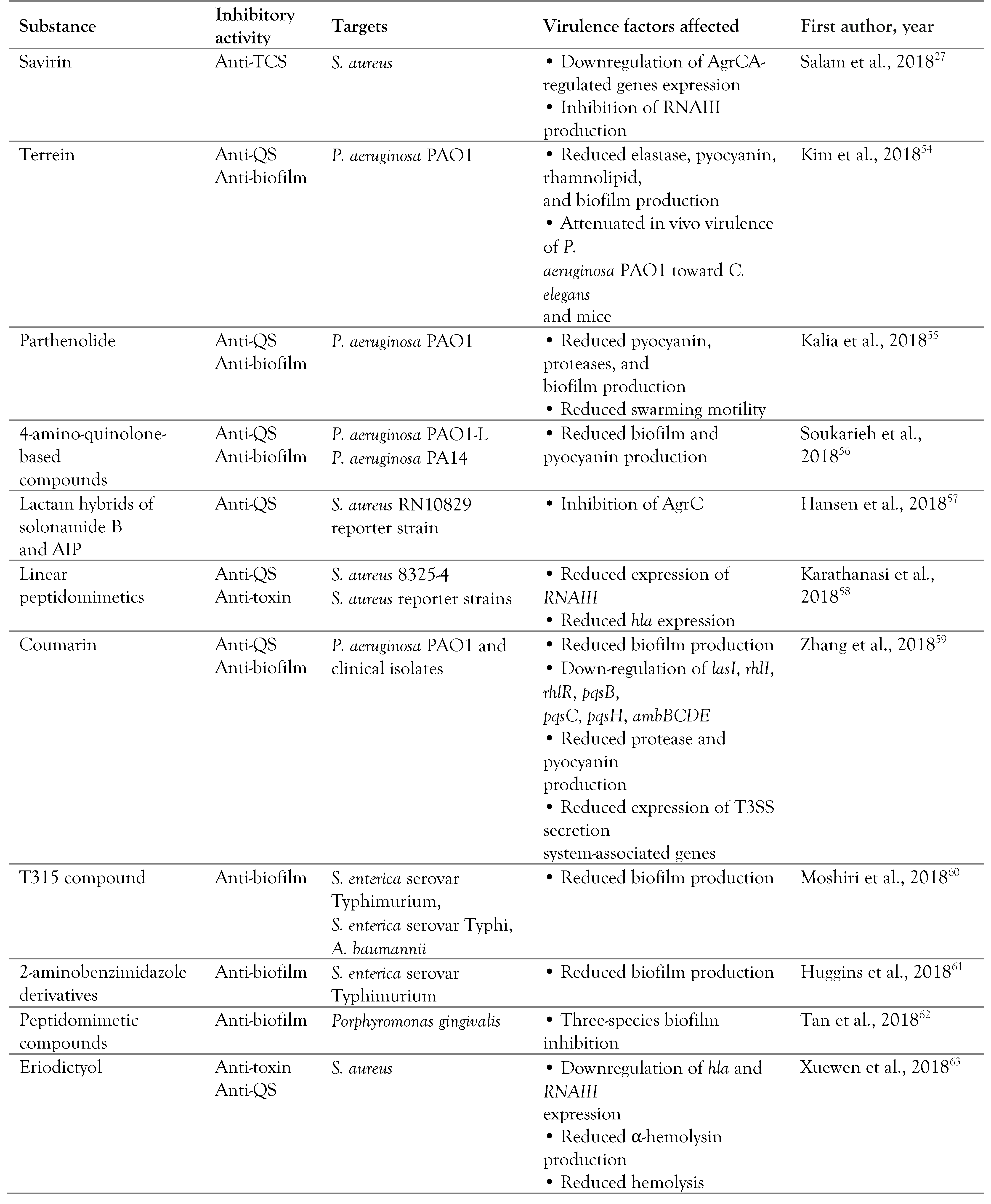
Targeting quorum sensing
Targeting two-component systems
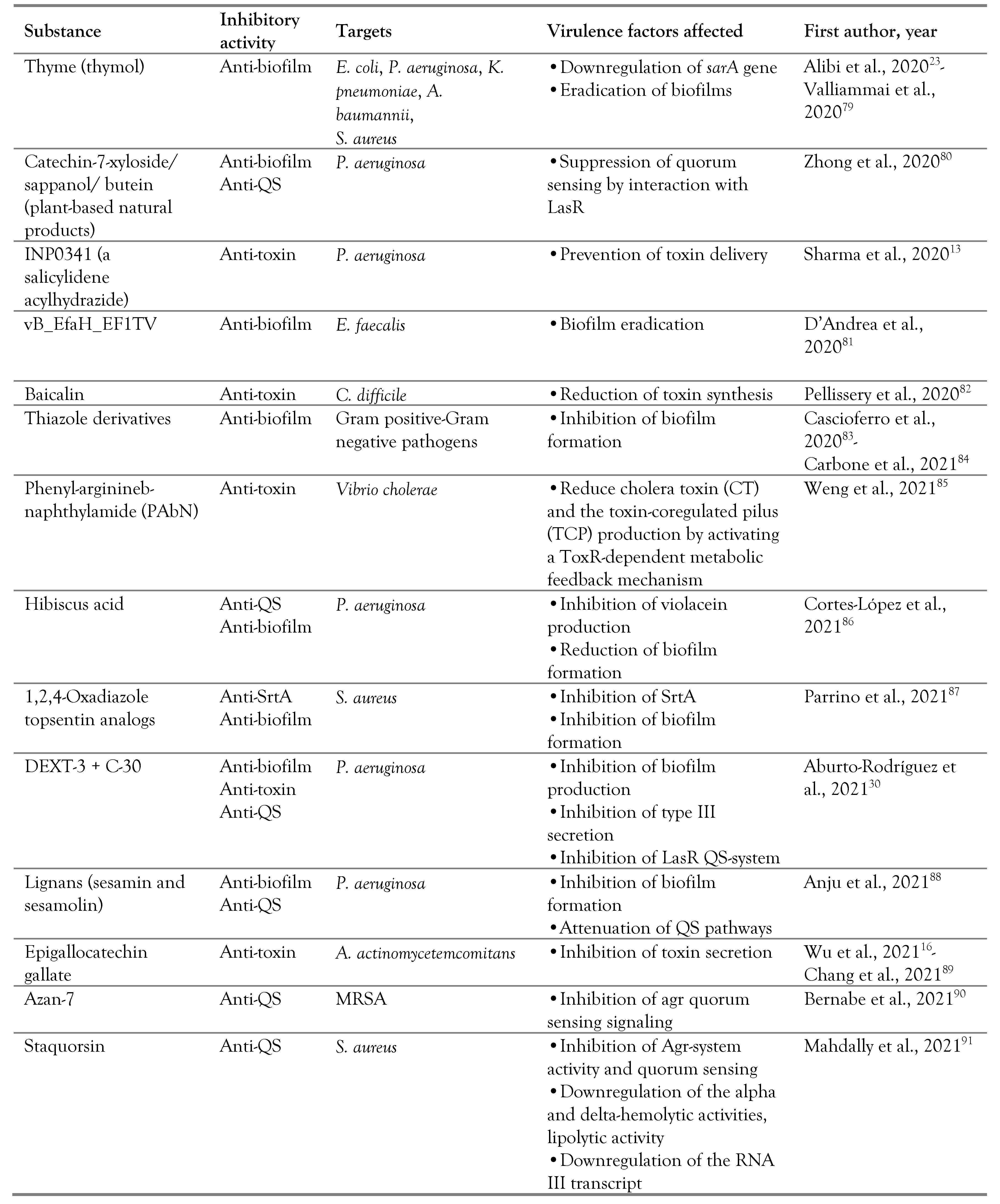
Non-coding RNAs as novel antimicrobial targets
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest
References
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2475067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatkin, A.J.; Bening, S.C.; Manson, A.L.; et al. Clinically relevant mutations in core metabolic genes confer antibiotic resistance. Science 2021, 371, eaba0862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Dhasmana, N.; Dubey, N.; et al. Bacterial virulence factors: Secreted for survival. Indian. J. Microbiol. 2017, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, M.B.; Jumde, V.R.; Titz, A. Pathoblockers or antivirulence drugs as a new option for the treatment of bacterial infections. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.K.; Meysick, K.C.; O’Brien, A.D. Bacterial toxins: Friends or foes? Emerg Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.A.; Stiehm, E.R. Passive immunity in prevention and treatment of infectious diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, S.W.; Cheung, G.Y.; Otto, M. Different drugs for bad bugs: Antivirulence strategies in the age of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Totsika, M.; Schillaci, D. Sortase A: An ideal target for anti-virulence drug development. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 77, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrelovs, N.; Kurbatska, V.; Rudevica, Z.; Leonchiks, A.; Fridmanis, D. Sorting out the superbugs: Potential of sortase A inhibitors among other antimicrobial strategies to tackle the problem of antibiotic resistance. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruén, C.; Chopo-Escuin, G.; Tommassen, J.; Mainar-Jaime, R.C.; Arenas, J. Biofilms as promoters of bacterial antibiotic resistance and tolerance. Antibiotics 2020, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrino, B.; Schillaci, D.; Carnevale, I.; et al. Synthetic small molecules as anti-biofilm agents in the struggle against antibiotic resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 154–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horna, G.; Ruiz, J. Type 3 secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 246, 126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Elofsson, M.; Roy, S. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection by INP0341, asalicylidene acylhydrazide, in a murine model of keratitis. Virulence 2020, 11, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharara, S.L.; Tayyar, R.; Kanafani, Z.A.; Kanj, S.S. HACEK endocarditis: A review. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, P.; Pormohammad, A.; Eslami, H.; Shokouhi, B.; Fakhrzadeh, V.; Kafil, H.S. Oral pathogenesis of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Brown, A.C. Applications of catechins in the treatment of bacterial infections. Pathogens 2021, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Q.; Robbie, G.J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of MEDI4893, an investigational, extended-half-life, anti-Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin human monoclonal antibody, in healthy adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016, 61, e01020–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, B.; Mercier, E.; Gonzalez, C.; et al. Safety and tolerability of a single administration of AR-301, a human monoclonal antibody, in ICU patients with severe pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus: First-in- human trial. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 44, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C.A.; Hurford, I.M.; Cassat, J.E. Antivirulence strategies for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections: A mini review. Front Microbiol. 2021, 11, 632706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing signal- response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.; Naik, M.; Manerikar, V. Quorum sensing- controlled gene expression systems in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In Implication of Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Medicine, Agriculture and Food Industry; Bramhachari, P., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prateeksha Singh, B.R.; Shoeb, M.; Sharma, S.; Naqvi, A.H.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, B.N. Scaffold of selenium nanovectors and honey phytochemicals for inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing and biofilm formation. Front Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibi, S.; Ben Selma, W.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; et al. Anti- oxidant, antibacterial, anti-biofilm, and anti-quorum sensing activities of four essential oils against multidrug- resistant bacterial clinical isolates. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2020, 68, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, A.; Seif, Y.; Choudhary, K.S.; et al. Pangenome analytics reveal two-component systems as conserved targets in ESKAPEE pathogens. mSystems. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlen, S.; Dersch, P. Anti-virulence strategies to target bacterial infections. In How to Overcome the Antibiotic Crisis; Stadler, M., Dersch, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; 2016; Volume 398, pp. 147–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Williams, J.T.; Aleiwi, B.; Ellsworth, E.; Abramovitch, R.B. Inhibiting Mycobacterium tuberculosis DosRST signaling by targeting response regulator DNA binding and sensor kinase heme. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.M.; Quave, C.L. Targeting virulence in Staphylococcus aureus by chemical inhibition of the accessory gene regulator system in vivo. mSphere 2018, 3, e00500–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, T.; Qin, C.; Xu, H.; Qiao, M. A novel non- coding RNA CsiR regulates the ciprofloxacin resistance in Proteus vulgaris by interacting with emrB mRNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Xia, W.; Li, S.; et al. Identification and expression of small non-coding RNA, L10-Leader, in different growth phases of Streptococcus mutans. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2012, 22, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto-Rodríguez, N.A.; Muñoz-Cázares, N.; Castro-Torres, V.A.; et al. Anti-pathogenic properties of the combination of a T3SS inhibitory halogenated pyrrolidone with C-30 furanone. Molecules. 2021, 26, 7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzoagli, C.; Archetti, M.; Mignot, I.; Baumgartner, M.; Kümmerli, R. Combining antibiotics with antivirulence compounds can have synergistic effects and reverse selection for antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Rodríguez, M.M.; Cortes-López, H.; García-Contreras, R.; et al. Tetradecanoic acids with anti-virulence properties increase the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a murine cutaneous infection model. Front Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 597517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, O.; Mao, S.; Xuewen, H.; et al. Sclareol protects Staphylococcus aureus-induced lung cell injury via inhibiting alpha-hemolysin expression. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, D.; Guo, Y.; et al. Dracorhodin perochlorate attenuates Staphylococcus aureus USA300 virulence by decreasing α-toxin expression. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Teng, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Chalcone attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence by targeting sortase A and alpha-hemolysin. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Z.; Shi, D.; Liu, H.; et al. Lysionotin attenuates Staphylococcus aureus pathogenicity by inhibiting α-toxin expression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, G.A.; Shymanska, N.V.; Pierce, J.G. 5-Benzylidene- 4-oxazolidinones potently inhibit biofilm formation in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Chem Commun. 2017, 53, 7353–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, D.; Wang, D.; Cao, F.; et al. Kaempferol inhibits the primary attachment phase of biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.; Blackledge, M.; Michalek, S.; et al. Targeting of Streptococcus mutans biofilms by a novel small molecule prevents dental caries and preserves the oral microbiome. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanikandan, S.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Srinivasan, P. Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, computational screening to design quorum sensing inhibitors targeting LuxP of Vibrio harveyi and its biological evaluation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 192–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, J.K.; Tal-Gan, Y.; Cornilescu, G.; Tyler, K.A.; Blackwell, H.E. Simplified AIP-II peptidomimetics are potent inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus AgrC quorum sensing receptors. Chembiochem 2017, 18, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Elsherbini, A.M.; Shaldam, M.A. Repurposing metformin as a quorum sensing inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Afr. Health Sci. 2017, 17, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; D’Morris, S.; Paul, V.; et al. Mechanistic understanding of phenyllactic acid mediated inhibition of quorum sensing and biofilm development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 8223–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökalsın, B.; Aksoydan, B.; Erman, B.; Sesal, N.C. Reducing virulence and biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by potential quorum sensing inhibitor carotenoid: Zeaxanthin. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capilato, J.N.; Philippi, S.V.; Reardon, T.; et al. Development of a novel series of non-natural triaryl agonists and antagonists of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR quorum sensing receptor. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, A.; Noshiranzadeh, N.; Haghi, F.; Bikas, R. Inhibition of quorum sensing related virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by pyridoxal lactohydrazone. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 112, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaiarasan, E.; Thirumalaswamy, K.; Harish, B.N.; Gnanasambandam, V.; Sali, V.K.; John, J. Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by quorum-sensing inhibitors. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczkowski, J.E.; Mukherjee, S.; McCready, A.R.; et al. Flavonoids suppress Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence through allosteric inhibition of quorum-sensing receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4064–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanikandan, S.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Srinivasan, P. Discovery of potent inhibitors targeting Vibrio harveyi LuxR through shape and e-pharmacophore based virtual screening and its biological evaluation. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 103, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, F.; Yao, L.; Su, Z.; et al. Antisense locked nucleic acids targeting agrA inhibit quorum sensing and pathogenesis of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuberi, A.; Misba, L.; Khan, A.U. CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) inhibition of luxS gene expression in E. coli: An approach to inhibit biofilm. Front Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Hur, J.K.; Lee, S.S. CRISPR-based genome editing of clinically important Escherichia coli SE15 isolated from indwelling urinary catheters of patients. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.; Kuo, D.; Jankowsky, E.; et al. Small-molecule AgrA inhibitors F12 and F19 act as antivirulence agents against Gram-positive pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, J.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Yoon, S.S.; Kim, W.G. Terrein is an inhibitor of quorum sensing and c-di-GMP in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A connection between quorum sensing and c-di-GMP. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Yadav, V.K.; Singh, P.K.; Sharma, D.; Narvi, S.S.; Agarwal, V. Exploring the impact of parthenolide as anti- quorum sensing and anti-biofilm agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sci. 2018, 199, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukarieh, F.; Vico Oton, E.; Dubern, J.F.; et al. In silico and in vitro-guided identification of inhibitors of alkylquinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules. 2018, 23, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, A.M.; Peng, P.; Baldry, M.; et al. Lactam hybrid analogues of solonamide B and autoinducing peptides as potent S. aureus AgrC antagonists. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karathanasi, G.; Bojer, M.S.; Baldry, M.; et al. Linear peptidomimetics as potent antagonists of Staphylococcus aureus agr quorum sensing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sass, A.; Van Acker, H.; et al. Coumarin reduces virulence and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by affecting quorum sensing, type III secretion and c-di-GMP levels. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, J.; Kaur, D.; Hambira, C.M.; et al. Identification of a small molecule anti-biofilm agent against Salmonella enterica. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, W.M.; Vu Nguyen, T.; Hahn, N.A.; et al. 2- Aminobenzimidazoles as antibiofilm agents against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Medchemcomm 2018, 9, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Patil, P.C.; Luzzio, F.A.; Demuth, D.R. In vitro and in vivo activity of peptidomimetic compounds that target the periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00400–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuewen, H.; Ping, O.; Zhongwei, Y.; et al. Eriodictyol protects against Staphylococcus aureus-induced lung cell injury by inhibiting alpha-hemolysin expression. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, O.; Ruixue, Y.; Jiaqiang, D.; et al. Subinhibitory concentrations of prim-o-glucosylcimifugin decrease the expression of alpha-hemolysin in Staphylococcus aureus (USA300). Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2018, 2018, 7579808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanissery, R.; Zeng, D.; Doyle, R.G.; Theriot, C.M. A small molecule-screening pipeline to evaluate the therapeutic potential of 2-aminoimidazole molecules against Clostridium difficile. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, E.; Hayes, S.; Chang, E.H.; Yutuc, S.; Brown, A.C. Receptor-based peptides for inhibition of leukotoxin activity. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Li, M.; Hao, Z.; et al. Subinhibitory concentrations of resveratrol reduce alpha-hemolysin production in Staphylococcus aureus isolates by downregulating saeRS. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Meng, X.M.; et al. Inhibition of alpha- hemolysin expression by resveratrol attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.H.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; Brown, A.C. Catechin- mediated restructuring of a bacterial toxin inhibits activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Parrino, B.; Petri, G.L.; et al. 2, 6- Disubstituted imidazo [2, 1-b][1, 3, 4] thiadiazole derivatives as potent staphylococcal biofilm inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 167, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zai, Y.; Xi, X.; et al. A novel membrane-disruptive antimicrobial peptide from frog skin secretion against cystic fibrosis isolates and evaluation of anti-MRSA effect using Galleria mellonella model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Dietz, M.J.; Li, B. Antimicrobial peptide LL-37 is bactericidal against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Qu, K.; Tan, D.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriophage and its potential to disrupt multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mi, Z.; Mi, L.; et al. Identification and characterization of capsule depolymerase Dpo48 from Acinetobacter baumannii phage IME200. PeerJ. 2019, 7, e6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, S.; Sharma, D.; Bisht, D.; Khan, A.U. Identification of factors involved in Enterococcus faecalis biofilm under quercetin stress. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, V.C.; Patel, S.K.S.; Kang, Y.C.; Lee, J.K. Quorum sensing inhibitors as antipathogens: Biotechnological applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 68–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namivandi-Zangeneh, R.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wong, E.H.; Boyer, C. Antibiofilm platform based on the combination of antimicrobial polymers and essential oils. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abutaleb, N.S.; Seleem, M.N. Antivirulence activity of auranofin against vancomycin-resistant enterococci: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2020, 55, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valliammai, A.; Selvaraj, A.; Yuvashree, U.; Aravindraja, C.; Karutha Pandian, S. sarA-dependent antibiofilm activity of thymol enhances the antibacterial efficacy of rifampicin against Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Ravichandran, V.; Zhang, N.; et al. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing by natural products: Virtual screening, evaluation and biomolecular interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, M.M.; Frezza, D.; Romano, E.; et al. The lytic bacteriophage vB_EfaH_EF1TV, a new member of the Herelleviridae family, disrupts biofilm produced by Enterococcus faecalis clinical strains. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissery, A.J.; Vinayamohan, P.G.; Venkitanarayanan, K. In vitro antivirulence activity of baicalin against Clostridioides difficile. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Parrino, B.; Carbone, D.; et al. Thiazoles, their benzofused systems, and thiazolidinone derivatives: Versatile and promising tools to combat antibiotic resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 7923–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Cascioferro, S.; Parrino, B.; et al. Thiazole analogues of the marine alkaloid nortopsentin as inhibitors of bacterial biofilm formation. Molecules. 2020, 26, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Bina, T.F.; Bina, X.R.; Bina, J.E. ToxR mediates the antivirulence activity of phenyl-arginine-β-naphthylamide to attenuate Vibrio cholerae virulence. Infect Immun. 2021, 89, e0014721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-López, H.; Castro-Rosas, J.; García-Contreras, R.; et al. Antivirulence activity of a dietary phytochemical: Hibiscus acid isolated from Hibiscus sabdariffa L. reduces the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a mouse infection model. J. Med. Food. 2021, 24, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrino, B.; Carbone, D.; Cascioferro, S.; et al. 1,2,4-Oxadiazole topsentin analogs as staphylococcal biofilm inhibitors targeting the bacterial transpeptidase sortase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anju, V.T.; Busi, S.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. Sesamin and sesamolin rescues Caenorhabditis elegans from Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection through the attenuation of quorum sensing regulated virulence factors. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 155, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.H.; Brown, A.C. Epigallocatechin gallate alters leukotoxin secretion and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans virulence. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabè, G.; Dal Pra, M.; Ronca, V.; et al. A novel aza- derivative inhibits agr quorum sensing signaling and synergizes methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to clindamycin. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 610859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdally, N.H.; George, R.F.; Kashef, M.T.; Al-Ghobashy, M.; Murad, F.E.; Attia, A.S. Staquorsin: A novel Staphylococcus aureus agr-mediated quorum sensing inhibitor impairing virulence in vivo without notable resistance development. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 700494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
© GERMS 2022.
Share and Cite
Dehbanipour, R.; Ghalavand, Z. Anti-Virulence Therapeutic Strategies Against Bacterial Infections: Recent Advances. Germs 2022, 12, 262-275. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1328
Dehbanipour R, Ghalavand Z. Anti-Virulence Therapeutic Strategies Against Bacterial Infections: Recent Advances. Germs. 2022; 12(2):262-275. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1328
Chicago/Turabian StyleDehbanipour, Razieh, and Zohreh Ghalavand. 2022. "Anti-Virulence Therapeutic Strategies Against Bacterial Infections: Recent Advances" Germs 12, no. 2: 262-275. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1328
APA StyleDehbanipour, R., & Ghalavand, Z. (2022). Anti-Virulence Therapeutic Strategies Against Bacterial Infections: Recent Advances. Germs, 12(2), 262-275. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1328




