Abstract
The emergence and increasing prevalence of multidrug-resistant pathogens has become a major global healthcare problem. According to the World Health Organization if these trends continue, mortality from infection in 2050 will be higher than that from cancer. Microorganisms have various resistance mechanisms against different classes of antibiotics that emphasize the need for discovery of new antimicrobial compounds to treat bacterial infections. An interesting and new strategy for disarming pathogens is antivirulence therapy by blocking bacterial virulence factors or pathogenicity. Therefore, the use of these new pathoblockers could reduce the administration of broad-spectrum antimicrobials and prevalence of resistant strains. This review provides an overview of the antivirulence strategies published studies between years 2017 and 2021. Most antivirulence strategies focused on adhesins, toxins and bacterial communication. Additionally, targeting two-component systems and ncRNA elements were also examined in some studies. These new strategies have the potential to replace traditional antimicrobial agents and can be used to treat infections, especially infections caused by resistant pathogens, by targeting virulence factors.
Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance is a significant global public health threat. The emergence of multidrug resistance in ESKAPE pathogens (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter species), responsible for serious chronic nosocomial infections, has become a serious challenge worldwide. [1] On the other hand, new classes of resistance mechanisms such as metabolic gene alterations may be a new concern to human health. [2] Resistance expansion prevents efficient treatment of infected patients, especially in the hospital setting. All of these threats emphasize the need to identify new strategies for the treatment of bacterial infectious diseases. In this review we highlight antivirulence approaches that are being investigated for the prevention and treatment of bacterial infections. It should be noted that, among the compounds identified and studied for antivirulence therapy, a few have been tested using in vivo models.
Review criteria
This review provides an overview of the antivirulence strategies research. Published works on antivirulence therapy studies from years 2017 to 2021 were identified using the following search terms “antivirulence therapeutics”, “pathoblockers”, “new therapeutic strategies” in Google Scholar, PubMed, Medline and Scopus. The final sample consisted of 77 articles after processing and applying exclusion criteria, and are presented as follows.
Antivirulence strategies
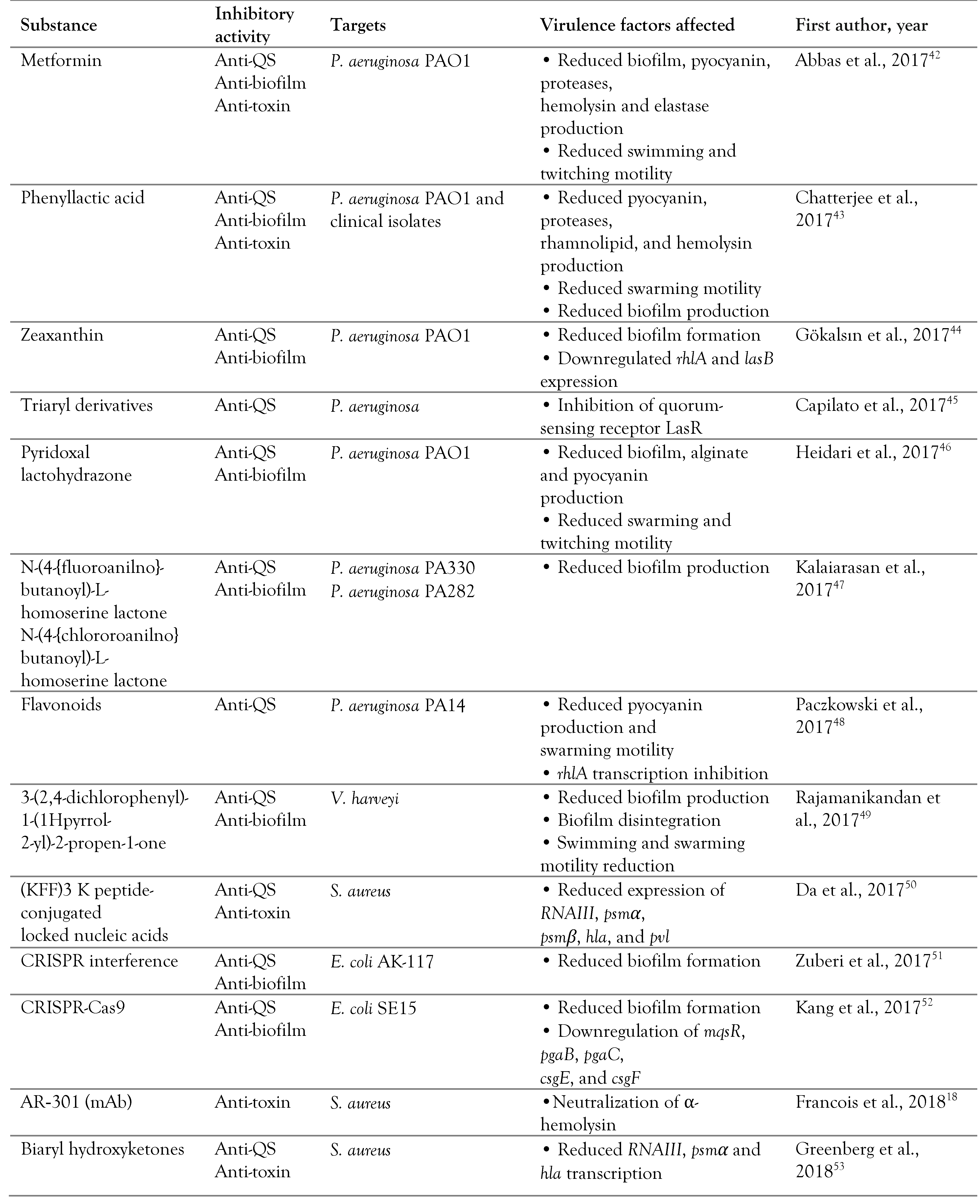
Virulence is a microorganism’s ability to produce disease. Virulence factors are molecules produced by a variety of microbial pathogens that assist in colonization, immunoevasion, immunosuppression, obtaining nutrition and damaging host cells. These factors are often classified in three forms, including membrane associated, secretory or cytosolic. [3] Blocking the activities of virulence factors is a new approach that has emerged over the last decade. Antivirulence drugs, the new class of drugs, target virulence factors of pathogens instead of killing or stopping their growth and consequently disarm infectious pathogens. Bactericidal antibiotics may also cause the selective pressure that drives resistance. Antivirulence drugs interfere with the interaction of the pathogen with its host, and thereby reduce damage to the host and impair the organism’s ability to cause disease without killing it or creating selective pressure. [4] Research on the inactivation of diphtheria and tetanus toxins are the first examples of the antivirulence approach. [5,6] Also, bezlotoxumab is the first antivirulence agent approved by the US food and drug administration (FDA). This agent blocks TcdB in Clostridioides difficile. [7] There are a variety of bacterial targets for antivirulence therapy, however some of the most attractive targets are adhesins, toxins, bacterial communication, two component systems and non-coding RNAs. Studies in recent years have suggested a variety of compounds as candidates for antivirulence therapies (Table 1).

Table 1.
Inhibitors of bacterial adherence, biofilm formation, quorum sensing systems, toxin production and function, and two component systems.
Antiadherence strategies
Adhesion to host tissues is the initial step of infectious diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, inhibiting bacterial adherence by antivirulence drugs can be a promising strategy to prevent infection.
Gram-positive pathogens including staphylococci, enterococci and streptococci can express various surface adhesion proteins known as MSCRAMM (microbial surface component recognizing adhesive matrix molecules). In addition to bacterial adhesion, MSCRAMM play important roles in immune evasion and biofilm formation. On the other hand, sortaseA (SrtA), a membrane-localized cysteine transpeptidase in Gram-positive pathogens, is crucial for the assembly and anchoring of aforementioned cell- surface adhesins to the cell wall envelope. Due to its easy accessibility and lack of homologous sortase in eukaryotes, it is a promising drug target for the development of antivirulence therapeutics against Gram-positive bacterial infections. Additionally, if the selective pressure induced by inhibitors results in mutation in the SrtA gene or an increase in enzyme production to counteract the decrease in enzymatic activity, it finally leads to a reduction in pathogenicity of the pathogen through decreasing enzyme activity and increasing metabolic burden, respectively. To date, various natural products and synthetic small molecules have been discovered as SrtA inhibitory compounds. [8,9]
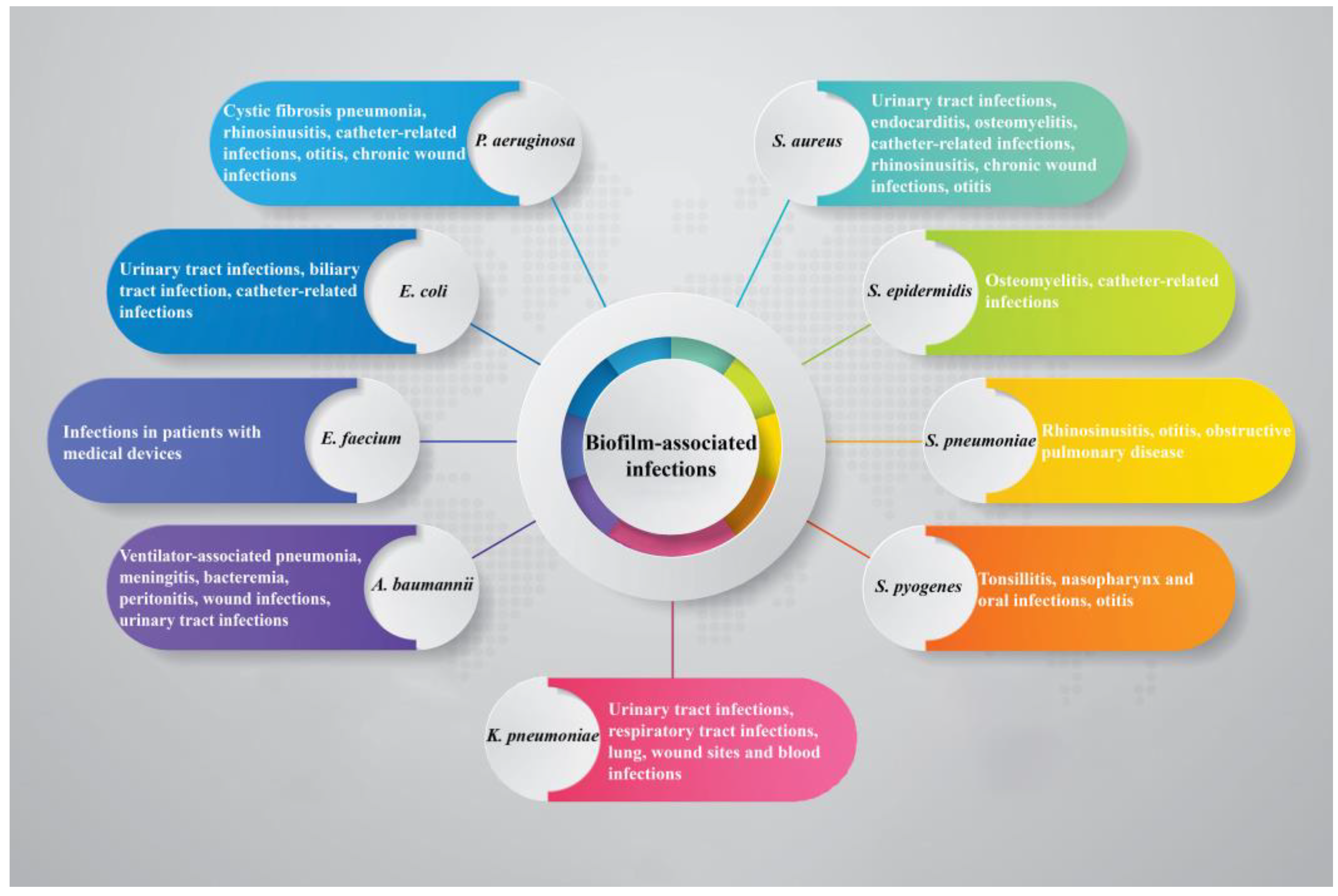
Moreover, one of the most significant strategies for bacteria to counteract antimicrobials is biofilm formation. Bacterial cells are embedded in a self-produced extracellular matrix within biofilms. The antimicrobial resistance of biofilm cells is up to a thousand times higher than that of planktonic forms, and it may be linked to accumulation of resistance mechanisms of single cells within biofilms. Biofilms are involved in chronic and recurrent infections caused by pathogens such as
P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, S. aureus, E. coli, K. pneumoniae and Streptococcus pneumoniae (Figure 1). Furthermore, the presence of bacterial cells in the depth of metabolically inactive cell layers makes it difficult for antibiotics to access them and penetrate the matrix. Given the importance of biofilm in bacterial pathogenicity, it seems to be an attractive target for anti-virulence drug development. The main approach in this regard is based on two strategies: 1) inhibition of biofilm formation by preventing bacterial cells from adhesion to the host tissue and 2) disruption of biofilm communities. To date, various inhibitory compounds have been identified and introduced to achieve these goals. [10] For example, a large number of synthetic small molecules have been identified in recent years that have an interesting capability to target the biofilm formation at different stages [11].

Figure 1.
Biofilm-associated infections.
Targeting toxins and secretion systems
The type III secretion system (T3SS) is one of the most important virulence factors used by some Gram-negative pathogens such as P. aeruginosa, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, Yersinia pestis and Chlamydia spp.
P. aeruginosa is capable to infect a wide host range and lead to high mortality rates, especially in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). This pathogen utilizes the type III secretion system to transport bacterial effectors, ExoS, ExoU, ExoT and ExoY, directly into host cells. T3SS consists of a series of regulated genes that encode components of the secretion apparatus and a translocon, and are important for intoxication of eukaryotic cells. [12] Since the T3SS machinery is evolutionarily conserved, it can be used as a potential target for pathoblockers. In addition, because T3SS is required for pathogenesis but not for survival, the use of inhibitors results in attenuated virulence as well as less selective pressure for resistance. INP0341, a salicylidene acylhydrazide, is a promising substance that has been shown to inhibit T3SS in a range of Gram-negative bacteria, resulting in preventing toxin delivery and, hence, decreasing bacterial virulence. [13]
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is a member of the HACEK group of bacteria together with Haemophilus spp., Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, and Kingella kingae. Although these fastidious Gram-negative organisms are found in the human oral cavity and known as the normal flora, they can cause various invasive infections, particularly endocarditis and localized aggressive periodontitis (LAP). A. actinomycetemcomitans colonizes the gingival sulcus and invades the epithelial tissues and stimulates a pathophysiologic inflammatory response. [14] This organism has different virulence factors including adhesive type IV pili, surface- exposed autotransporter proteins, type V collagen, leukotoxin and lipopolysaccharide. The operon of leukotoxin is comprised of four coding genes including ltxC, ltxA, ltxB, and ltxD. LtxA is a large pore-forming toxin and a key virulence factor, which has the ability to annihilate host immune tissues. [15] Since LtxA has strong affinity for plasma membrane cholesterol-rich lipid rafts, inhibitors such as catechins can prohibit LtxA- mediated cytotoxicity in white blood cells through altering LtxA structure and reducing affinity for cholesterol. Catechin is one group of flavonoids derived from plants, with a variety of health beneficial effects through antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial and antiviral properties. Therefore, catechin and its derivatives are potential compounds to be used as antivirulence agents. [16] In addition, MEDI4893 (suvratoxumab) and AR-301 are two monoclonal neutralizing antibodies against α-hemolysin (Hla) in S. aureus. [17,18] MEDI4893 has completed phase 2 clinical trials and AR-301 had entered phase 3 trials for the prevention of S. aureus pneumonia. [19]
Targeting quorum sensing
Bacterial quorum sensing (QS) is a comprehensive phenomenon that involves the ability to react to cell-population density via gene regulation. QS involves extracellular signaling molecules, also called autoinducers (AIs). This chemical communication is a critical pathway for survival in a competitive environment, for nutrient uptake and cell growth. [20] Gram-positive bacteria use a two-component system that is comprised of membrane-bound sensor kinase receptors and cytoplasmic transcription factors phosphorylated by kinase which then regulate gene expression. Gram-negative bacteria, including Pseudomonas spp., Acinetobacter spp., or Burkholderia spp. employ another type of autoinducers, the acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) which, after binding to a regulatory protein in the cell, operate as a transcription factor for various enzymes and virulence factor secretion genes. [21] Many virulence traits are influenced by QS and thus targeting QS can be a hopeful strategy to inhibit bacterial infections and combat the growing problem of antibiotic resistance. Interference with QS, called quorum quenching (QQ), is a process of obstructing QS by impeding signaling. This process consists of several parts, including inhibition of signaling molecules, blocking the receptor of signaling molecules by mimic molecules, degradation of signaling molecules and amendment of the QS signals by the enzyme activity. The use of nanotechnology in combination with antivirulence therapy in the treatment of diseases seems to be a promising strategy to confront pathogens. Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) as a drug carrier have shown significant effects on the intracellular delivery of antivirulence compounds such as polyphenols of honey with anti-QS activity against P. aeruginosa. [22]
Four essential oils (clove, cinnamon, thyme and marjoram) have been reported to have anti- biofilm and anti-QS activities against Gram- negative and Gram-positive multidrug-resistant pathogens such as E. coli, P. aeruginosa, K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii and S. aureus. [23]
Targeting two-component systems
Two-component systems (TCSs) are involved in sensing environmental changes and expression of genes responding to environmental signals. They consist of a membrane-bound histidine kinase and a corresponding cytoplasmic response regulator that accomplish signal transduction by phosphorylation. TCSs play important roles in bacterial functions including drug resistance and host invasion. Studies characterized some TCSs that control gene networks in reaction to osmolarity, secondary metabolites, temperature, nutrients and ions. These include: DosR/DosS, EnvZ/OmpR, RcsB/RcsC, PhoP/PhoQ, BarA/SirA, CpxR/CpxS, AgrC/AgrA, and QseC/QseB. [24,25]
The DosRST two-component regulatory system has an important role in virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). Studies on two chemical inhibitors including HC104A and HC106A demonstrated that the compounds downregulate the DosR regulon genes and disrupt signal transduction leading to decreased Mtb survival. [26] Savirin, a small molecule inhibitor, reduces the expression of AgrCA- regulated genes and also inhibits RNAIII production in S. aureus, thus leading to a reduction of virulence. However, savarin has no effect on skin commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis. [27]
Non-coding RNAs as novel antimicrobial targets
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA), is a functional RNA molecule that operates without the need for being translated. In general, ncRNAs are involved in biofilm formation, regulation of gene expression responding to extracellular stress and preserving homeostasis of the microbial cell at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional level. Some small non-coding RNAs (sRNAs) function to regulate genes that confer antibiotic resistance. CsiR in Proteus vulgaris were found to regulate EmrB multidrug efflux pump and are involved in the regulation of ciprofloxacin resistance. [28] On the other hand, since sRNAs are expressed in different growth phases of the bacterial life, it is suggested that the presence of sRNAs in the disease progression process is necessary to reconcile with the environmental changes [29].
Since ncRNA can control biofilm formation, antibiotic resistance and bacterial stress responses, targeting the ncRNA pathways is a promising strategy for overcoming bacterial infections.
Discussion
The use of antibiotics has greatly helped in the treatment and control of infections during the 20th century but the widespread usage of conventional antibiotics has led to alarming increases in antibiotic resistance, even last-resort antibiotics like colistin, and failure to treat persistent infections. In recent years, an approach based on antivirulence therapeutics has become a promising strategy to counteract human pathogens. Interestingly, synergy between different antivirulence compounds with distinct targets is an attractive approach to use combination therapy to enhance the anti- pathogenic effect [30].
However, one of the limitations of antivirulence therapies is the inability to completely clear the infection, which is challenging in clinical applications especially for immunocompromised patients. It seems that antivirulence compounds in combination with antibiotics can overcome this limitation. In fact, the use of antivirulence compound makes it possible to use lower concentrations of antibiotics, minimizing side effects and reducing the generation of antibiotic resistance in pathogens as well as effective pathogen removal. A study on the combination of gallium and furanone (as antivirulence compounds) together with antibiotics (colistin, ciprofloxacin, tobramycin and meropenem) in P. aeruginosa showed a significant effect of combination therapy in limiting the spread of antibiotic resistance. Interestingly, it has been suggested that the effectiveness of combination therapy is linked to the molecular mechanism of antibiotic resistance. [31] However, proving this hypothesis requires more detailed and comprehensive studies. Although these studies promise new therapeutic approaches, more research is needed for clinical applications. Since drug interactions are concentration dependent, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics studies are required. In addition, there is evidence that antivirulence compounds may, contrary to expectations, in certain instances act in vivo as signals for activation of virulence factors in pathogens. [32] Hence, animal models must be used to evaluate the effectiveness of antivirulence compounds, alone or in combination with antibiotics, in the host environment.
Conclusions
Here, we reviewed current antivirulence strategies to disarm pathogens by targeting bacterial virulence factors. It should be noted that this strategy, like the use of antibiotics, also has disadvantages including lack of effect on all forms of the disease and low therapeutic effects compared with antibiotics. Because many of the pathogenicity mechanisms in pathogens are unknown, extensive studies on the virulence factors of pathogens and host-pathogen interactions are needed to advance this strategy. Appropriate and ongoing cooperation between governments and pharmaceutical companies can create a great future for new treatment strategies.
Author Contributions
R.D. conceptualized, designed, searched for the review articles, read through, analyzed, interpreted them and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Z.G. read the draft manuscript and revised it for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive funding from an external source, it was self-financed by the authors.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of interest
All authors—none to declare.
References
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2475067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatkin, A.J.; Bening, S.C.; Manson, A.L.; et al. Clinically relevant mutations in core metabolic genes confer antibiotic resistance. Science 2021, 371, eaba0862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Dhasmana, N.; Dubey, N.; et al. Bacterial virulence factors: Secreted for survival. Indian. J. Microbiol. 2017, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, M.B.; Jumde, V.R.; Titz, A. Pathoblockers or antivirulence drugs as a new option for the treatment of bacterial infections. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.K.; Meysick, K.C.; O’Brien, A.D. Bacterial toxins: Friends or foes? Emerg Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.A.; Stiehm, E.R. Passive immunity in prevention and treatment of infectious diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, S.W.; Cheung, G.Y.; Otto, M. Different drugs for bad bugs: Antivirulence strategies in the age of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Totsika, M.; Schillaci, D. Sortase A: An ideal target for anti-virulence drug development. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 77, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrelovs, N.; Kurbatska, V.; Rudevica, Z.; Leonchiks, A.; Fridmanis, D. Sorting out the superbugs: Potential of sortase A inhibitors among other antimicrobial strategies to tackle the problem of antibiotic resistance. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruén, C.; Chopo-Escuin, G.; Tommassen, J.; Mainar-Jaime, R.C.; Arenas, J. Biofilms as promoters of bacterial antibiotic resistance and tolerance. Antibiotics 2020, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrino, B.; Schillaci, D.; Carnevale, I.; et al. Synthetic small molecules as anti-biofilm agents in the struggle against antibiotic resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 154–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horna, G.; Ruiz, J. Type 3 secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 246, 126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Elofsson, M.; Roy, S. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection by INP0341, asalicylidene acylhydrazide, in a murine model of keratitis. Virulence 2020, 11, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharara, S.L.; Tayyar, R.; Kanafani, Z.A.; Kanj, S.S. HACEK endocarditis: A review. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, P.; Pormohammad, A.; Eslami, H.; Shokouhi, B.; Fakhrzadeh, V.; Kafil, H.S. Oral pathogenesis of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Brown, A.C. Applications of catechins in the treatment of bacterial infections. Pathogens 2021, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Q.; Robbie, G.J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of MEDI4893, an investigational, extended-half-life, anti-Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin human monoclonal antibody, in healthy adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016, 61, e01020–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, B.; Mercier, E.; Gonzalez, C.; et al. Safety and tolerability of a single administration of AR-301, a human monoclonal antibody, in ICU patients with severe pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus: First-in- human trial. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 44, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C.A.; Hurford, I.M.; Cassat, J.E. Antivirulence strategies for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections: A mini review. Front Microbiol. 2021, 11, 632706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing signal- response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.; Naik, M.; Manerikar, V. Quorum sensing- controlled gene expression systems in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In Implication of Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Medicine, Agriculture and Food Industry; Bramhachari, P., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prateeksha Singh, B.R.; Shoeb, M.; Sharma, S.; Naqvi, A.H.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, B.N. Scaffold of selenium nanovectors and honey phytochemicals for inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing and biofilm formation. Front Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibi, S.; Ben Selma, W.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; et al. Anti- oxidant, antibacterial, anti-biofilm, and anti-quorum sensing activities of four essential oils against multidrug- resistant bacterial clinical isolates. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2020, 68, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, A.; Seif, Y.; Choudhary, K.S.; et al. Pangenome analytics reveal two-component systems as conserved targets in ESKAPEE pathogens. mSystems. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlen, S.; Dersch, P. Anti-virulence strategies to target bacterial infections. In How to Overcome the Antibiotic Crisis; Stadler, M., Dersch, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; 2016; Volume 398, pp. 147–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Williams, J.T.; Aleiwi, B.; Ellsworth, E.; Abramovitch, R.B. Inhibiting Mycobacterium tuberculosis DosRST signaling by targeting response regulator DNA binding and sensor kinase heme. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.M.; Quave, C.L. Targeting virulence in Staphylococcus aureus by chemical inhibition of the accessory gene regulator system in vivo. mSphere 2018, 3, e00500–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, T.; Qin, C.; Xu, H.; Qiao, M. A novel non- coding RNA CsiR regulates the ciprofloxacin resistance in Proteus vulgaris by interacting with emrB mRNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Xia, W.; Li, S.; et al. Identification and expression of small non-coding RNA, L10-Leader, in different growth phases of Streptococcus mutans. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2012, 22, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto-Rodríguez, N.A.; Muñoz-Cázares, N.; Castro-Torres, V.A.; et al. Anti-pathogenic properties of the combination of a T3SS inhibitory halogenated pyrrolidone with C-30 furanone. Molecules. 2021, 26, 7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzoagli, C.; Archetti, M.; Mignot, I.; Baumgartner, M.; Kümmerli, R. Combining antibiotics with antivirulence compounds can have synergistic effects and reverse selection for antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Rodríguez, M.M.; Cortes-López, H.; García-Contreras, R.; et al. Tetradecanoic acids with anti-virulence properties increase the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a murine cutaneous infection model. Front Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 597517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, O.; Mao, S.; Xuewen, H.; et al. Sclareol protects Staphylococcus aureus-induced lung cell injury via inhibiting alpha-hemolysin expression. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, D.; Guo, Y.; et al. Dracorhodin perochlorate attenuates Staphylococcus aureus USA300 virulence by decreasing α-toxin expression. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Teng, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Chalcone attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence by targeting sortase A and alpha-hemolysin. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Z.; Shi, D.; Liu, H.; et al. Lysionotin attenuates Staphylococcus aureus pathogenicity by inhibiting α-toxin expression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, G.A.; Shymanska, N.V.; Pierce, J.G. 5-Benzylidene- 4-oxazolidinones potently inhibit biofilm formation in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Chem Commun. 2017, 53, 7353–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, D.; Wang, D.; Cao, F.; et al. Kaempferol inhibits the primary attachment phase of biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.; Blackledge, M.; Michalek, S.; et al. Targeting of Streptococcus mutans biofilms by a novel small molecule prevents dental caries and preserves the oral microbiome. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanikandan, S.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Srinivasan, P. Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, computational screening to design quorum sensing inhibitors targeting LuxP of Vibrio harveyi and its biological evaluation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 192–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, J.K.; Tal-Gan, Y.; Cornilescu, G.; Tyler, K.A.; Blackwell, H.E. Simplified AIP-II peptidomimetics are potent inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus AgrC quorum sensing receptors. Chembiochem 2017, 18, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Elsherbini, A.M.; Shaldam, M.A. Repurposing metformin as a quorum sensing inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Afr. Health Sci. 2017, 17, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; D’Morris, S.; Paul, V.; et al. Mechanistic understanding of phenyllactic acid mediated inhibition of quorum sensing and biofilm development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 8223–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökalsın, B.; Aksoydan, B.; Erman, B.; Sesal, N.C. Reducing virulence and biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by potential quorum sensing inhibitor carotenoid: Zeaxanthin. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capilato, J.N.; Philippi, S.V.; Reardon, T.; et al. Development of a novel series of non-natural triaryl agonists and antagonists of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR quorum sensing receptor. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, A.; Noshiranzadeh, N.; Haghi, F.; Bikas, R. Inhibition of quorum sensing related virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by pyridoxal lactohydrazone. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 112, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaiarasan, E.; Thirumalaswamy, K.; Harish, B.N.; Gnanasambandam, V.; Sali, V.K.; John, J. Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by quorum-sensing inhibitors. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczkowski, J.E.; Mukherjee, S.; McCready, A.R.; et al. Flavonoids suppress Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence through allosteric inhibition of quorum-sensing receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4064–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanikandan, S.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Srinivasan, P. Discovery of potent inhibitors targeting Vibrio harveyi LuxR through shape and e-pharmacophore based virtual screening and its biological evaluation. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 103, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, F.; Yao, L.; Su, Z.; et al. Antisense locked nucleic acids targeting agrA inhibit quorum sensing and pathogenesis of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuberi, A.; Misba, L.; Khan, A.U. CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) inhibition of luxS gene expression in E. coli: An approach to inhibit biofilm. Front Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Hur, J.K.; Lee, S.S. CRISPR-based genome editing of clinically important Escherichia coli SE15 isolated from indwelling urinary catheters of patients. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.; Kuo, D.; Jankowsky, E.; et al. Small-molecule AgrA inhibitors F12 and F19 act as antivirulence agents against Gram-positive pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, J.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Yoon, S.S.; Kim, W.G. Terrein is an inhibitor of quorum sensing and c-di-GMP in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A connection between quorum sensing and c-di-GMP. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Yadav, V.K.; Singh, P.K.; Sharma, D.; Narvi, S.S.; Agarwal, V. Exploring the impact of parthenolide as anti- quorum sensing and anti-biofilm agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sci. 2018, 199, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukarieh, F.; Vico Oton, E.; Dubern, J.F.; et al. In silico and in vitro-guided identification of inhibitors of alkylquinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules. 2018, 23, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, A.M.; Peng, P.; Baldry, M.; et al. Lactam hybrid analogues of solonamide B and autoinducing peptides as potent S. aureus AgrC antagonists. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karathanasi, G.; Bojer, M.S.; Baldry, M.; et al. Linear peptidomimetics as potent antagonists of Staphylococcus aureus agr quorum sensing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sass, A.; Van Acker, H.; et al. Coumarin reduces virulence and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by affecting quorum sensing, type III secretion and c-di-GMP levels. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, J.; Kaur, D.; Hambira, C.M.; et al. Identification of a small molecule anti-biofilm agent against Salmonella enterica. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, W.M.; Vu Nguyen, T.; Hahn, N.A.; et al. 2- Aminobenzimidazoles as antibiofilm agents against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Medchemcomm 2018, 9, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Patil, P.C.; Luzzio, F.A.; Demuth, D.R. In vitro and in vivo activity of peptidomimetic compounds that target the periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00400–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuewen, H.; Ping, O.; Zhongwei, Y.; et al. Eriodictyol protects against Staphylococcus aureus-induced lung cell injury by inhibiting alpha-hemolysin expression. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, O.; Ruixue, Y.; Jiaqiang, D.; et al. Subinhibitory concentrations of prim-o-glucosylcimifugin decrease the expression of alpha-hemolysin in Staphylococcus aureus (USA300). Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2018, 2018, 7579808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanissery, R.; Zeng, D.; Doyle, R.G.; Theriot, C.M. A small molecule-screening pipeline to evaluate the therapeutic potential of 2-aminoimidazole molecules against Clostridium difficile. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, E.; Hayes, S.; Chang, E.H.; Yutuc, S.; Brown, A.C. Receptor-based peptides for inhibition of leukotoxin activity. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Li, M.; Hao, Z.; et al. Subinhibitory concentrations of resveratrol reduce alpha-hemolysin production in Staphylococcus aureus isolates by downregulating saeRS. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Meng, X.M.; et al. Inhibition of alpha- hemolysin expression by resveratrol attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.H.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; Brown, A.C. Catechin- mediated restructuring of a bacterial toxin inhibits activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Parrino, B.; Petri, G.L.; et al. 2, 6- Disubstituted imidazo [2, 1-b][1, 3, 4] thiadiazole derivatives as potent staphylococcal biofilm inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 167, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zai, Y.; Xi, X.; et al. A novel membrane-disruptive antimicrobial peptide from frog skin secretion against cystic fibrosis isolates and evaluation of anti-MRSA effect using Galleria mellonella model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Dietz, M.J.; Li, B. Antimicrobial peptide LL-37 is bactericidal against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Qu, K.; Tan, D.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriophage and its potential to disrupt multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mi, Z.; Mi, L.; et al. Identification and characterization of capsule depolymerase Dpo48 from Acinetobacter baumannii phage IME200. PeerJ. 2019, 7, e6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, S.; Sharma, D.; Bisht, D.; Khan, A.U. Identification of factors involved in Enterococcus faecalis biofilm under quercetin stress. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, V.C.; Patel, S.K.S.; Kang, Y.C.; Lee, J.K. Quorum sensing inhibitors as antipathogens: Biotechnological applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 68–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namivandi-Zangeneh, R.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wong, E.H.; Boyer, C. Antibiofilm platform based on the combination of antimicrobial polymers and essential oils. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abutaleb, N.S.; Seleem, M.N. Antivirulence activity of auranofin against vancomycin-resistant enterococci: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2020, 55, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valliammai, A.; Selvaraj, A.; Yuvashree, U.; Aravindraja, C.; Karutha Pandian, S. sarA-dependent antibiofilm activity of thymol enhances the antibacterial efficacy of rifampicin against Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Ravichandran, V.; Zhang, N.; et al. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing by natural products: Virtual screening, evaluation and biomolecular interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, M.M.; Frezza, D.; Romano, E.; et al. The lytic bacteriophage vB_EfaH_EF1TV, a new member of the Herelleviridae family, disrupts biofilm produced by Enterococcus faecalis clinical strains. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissery, A.J.; Vinayamohan, P.G.; Venkitanarayanan, K. In vitro antivirulence activity of baicalin against Clostridioides difficile. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Parrino, B.; Carbone, D.; et al. Thiazoles, their benzofused systems, and thiazolidinone derivatives: Versatile and promising tools to combat antibiotic resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 7923–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Cascioferro, S.; Parrino, B.; et al. Thiazole analogues of the marine alkaloid nortopsentin as inhibitors of bacterial biofilm formation. Molecules. 2020, 26, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Bina, T.F.; Bina, X.R.; Bina, J.E. ToxR mediates the antivirulence activity of phenyl-arginine-β-naphthylamide to attenuate Vibrio cholerae virulence. Infect Immun. 2021, 89, e0014721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-López, H.; Castro-Rosas, J.; García-Contreras, R.; et al. Antivirulence activity of a dietary phytochemical: Hibiscus acid isolated from Hibiscus sabdariffa L. reduces the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a mouse infection model. J. Med. Food. 2021, 24, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrino, B.; Carbone, D.; Cascioferro, S.; et al. 1,2,4-Oxadiazole topsentin analogs as staphylococcal biofilm inhibitors targeting the bacterial transpeptidase sortase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anju, V.T.; Busi, S.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. Sesamin and sesamolin rescues Caenorhabditis elegans from Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection through the attenuation of quorum sensing regulated virulence factors. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 155, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.H.; Brown, A.C. Epigallocatechin gallate alters leukotoxin secretion and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans virulence. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabè, G.; Dal Pra, M.; Ronca, V.; et al. A novel aza- derivative inhibits agr quorum sensing signaling and synergizes methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to clindamycin. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 610859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdally, N.H.; George, R.F.; Kashef, M.T.; Al-Ghobashy, M.; Murad, F.E.; Attia, A.S. Staquorsin: A novel Staphylococcus aureus agr-mediated quorum sensing inhibitor impairing virulence in vivo without notable resistance development. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 700494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© GERMS 2022.