A Comparative Study of the Clonal Diversity and Virulence Characteristics of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolated from Australian and Turkish (Turkey) Children and Adults with Urinary Tract Infections
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
UPEC strains and their sources
Typing of the isolates
- a)
- PhP typing with the PhPlate-RE system
- b)
- Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis
DNA extraction
Phylogenetic grouping and PCR detection of VAGs
VAG scores
Statistical analyses
Results
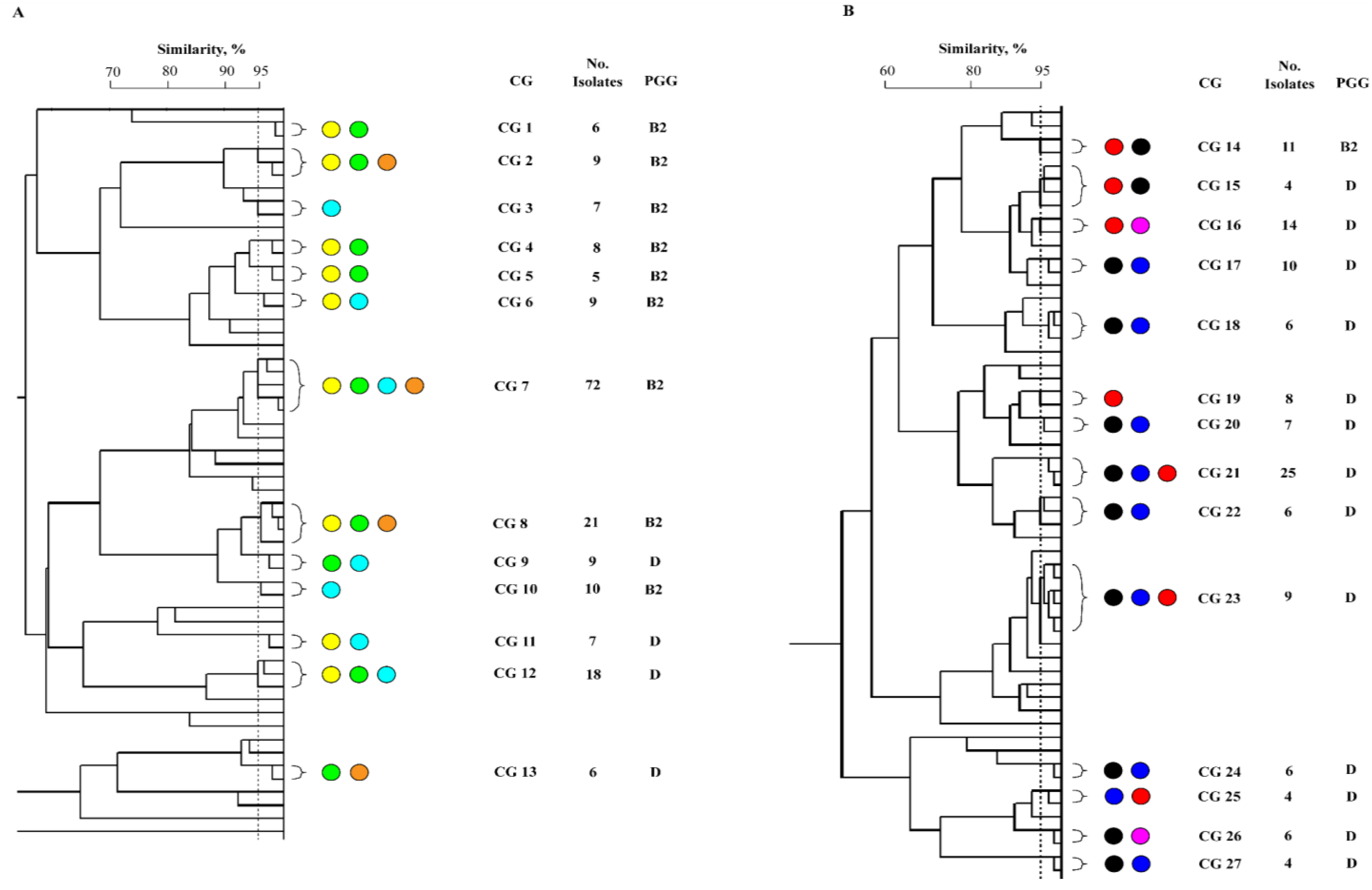
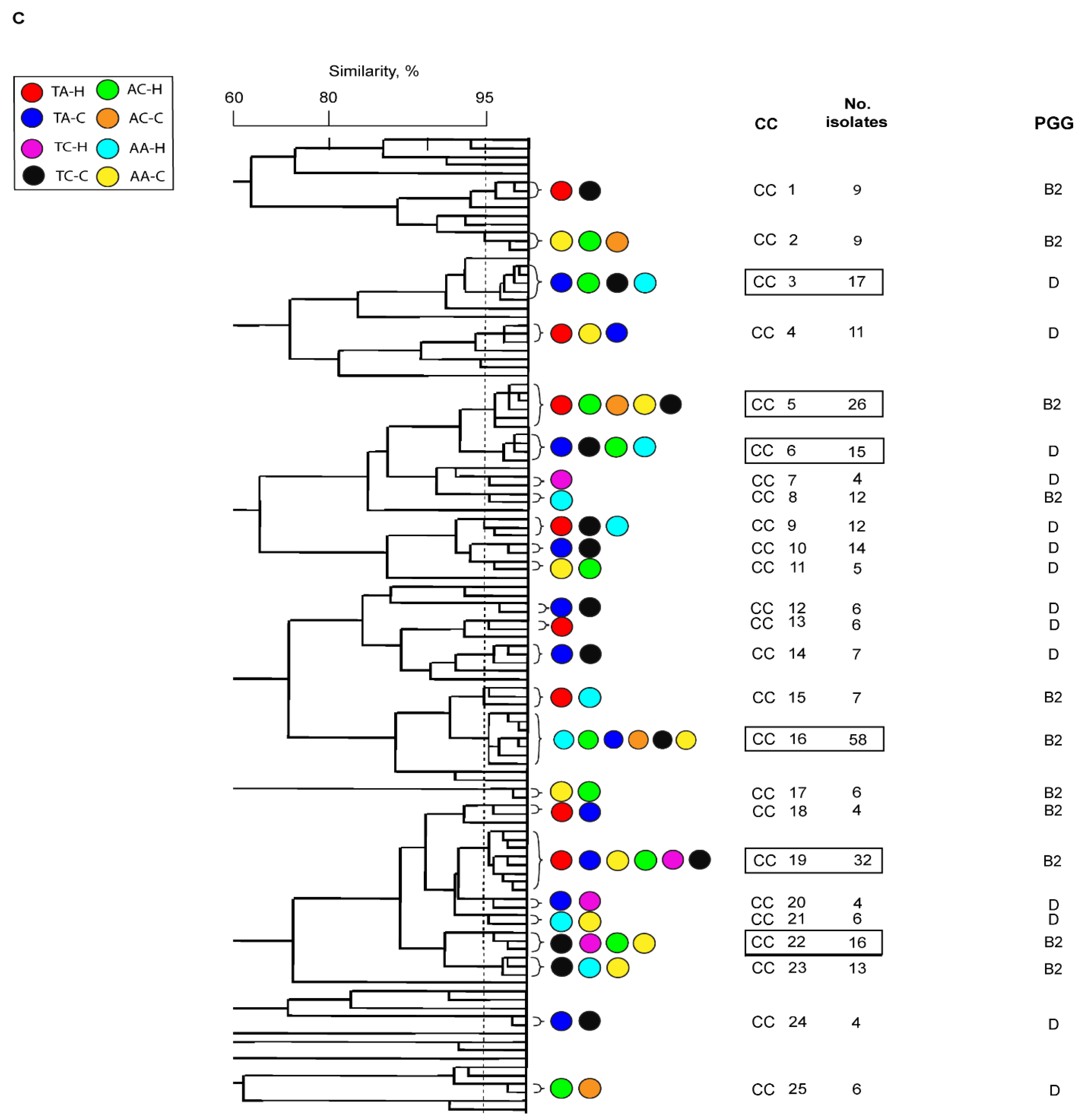
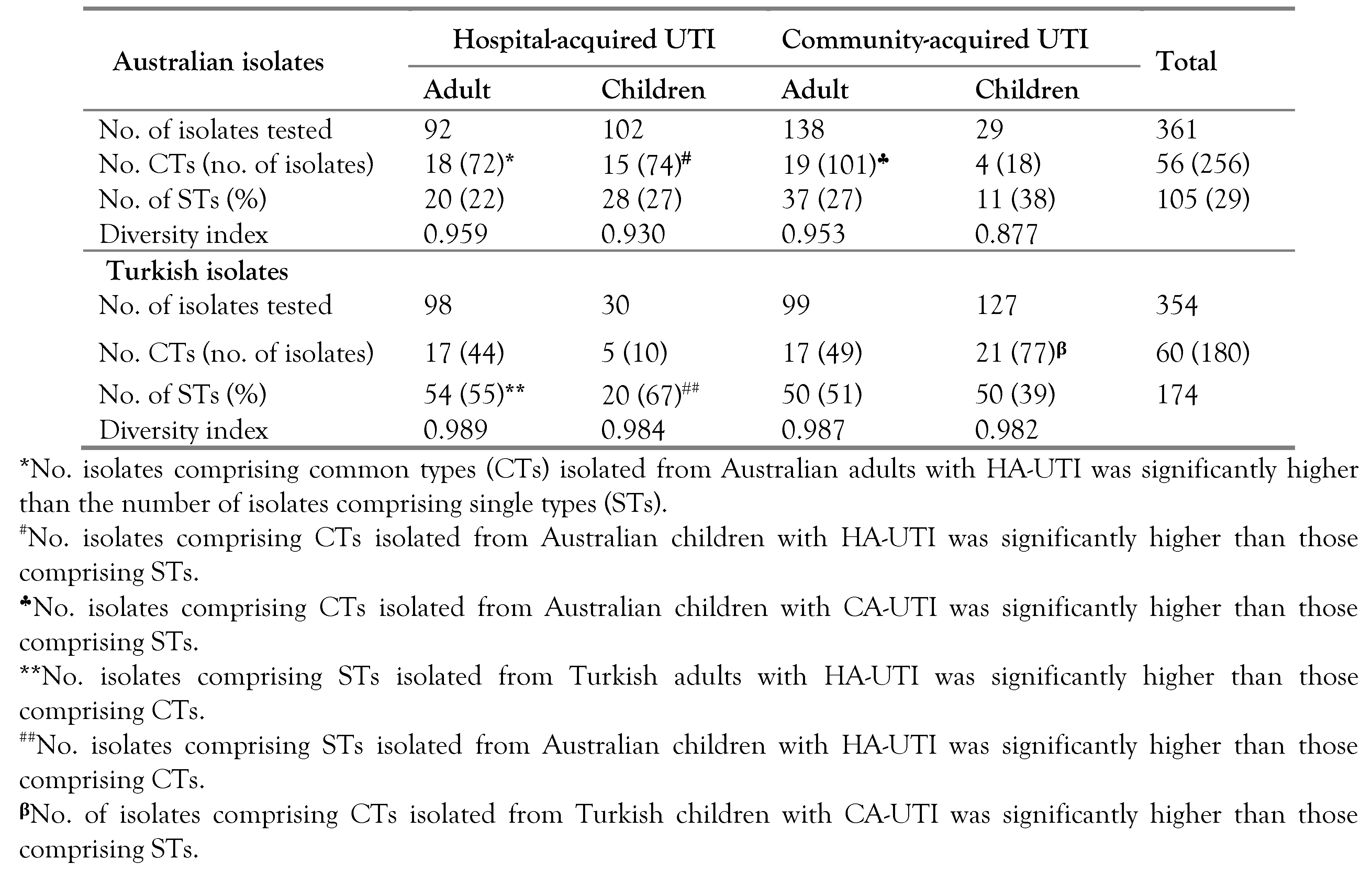
Distribution of UPEC among Australian and Turkish patients with UTI
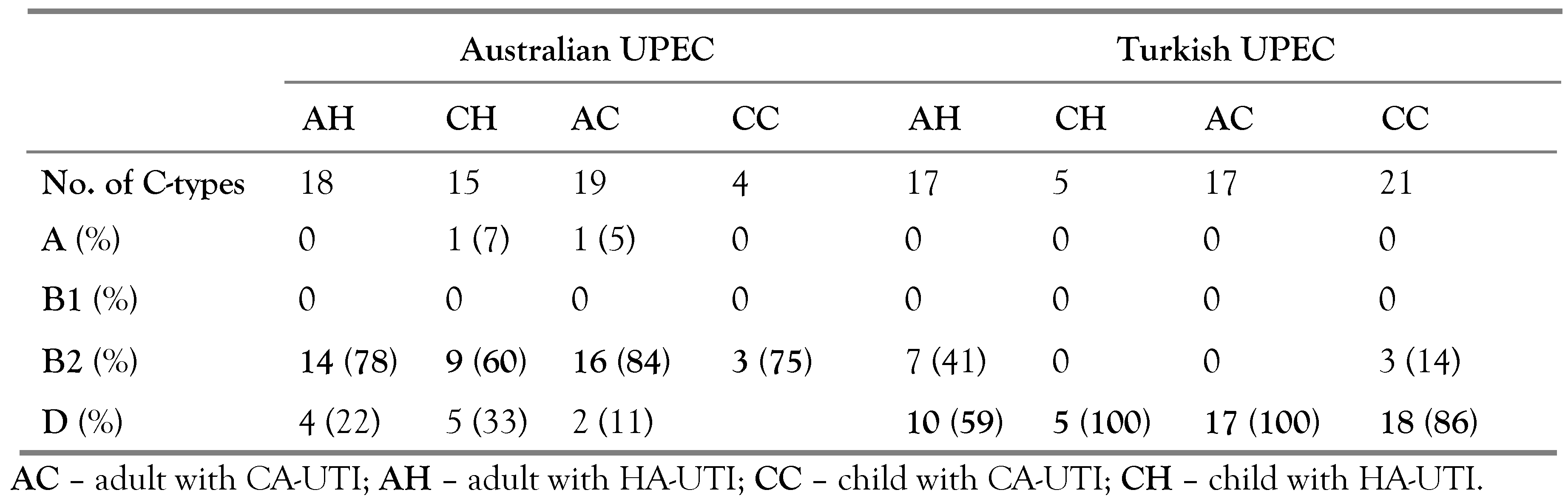
Phylogeny
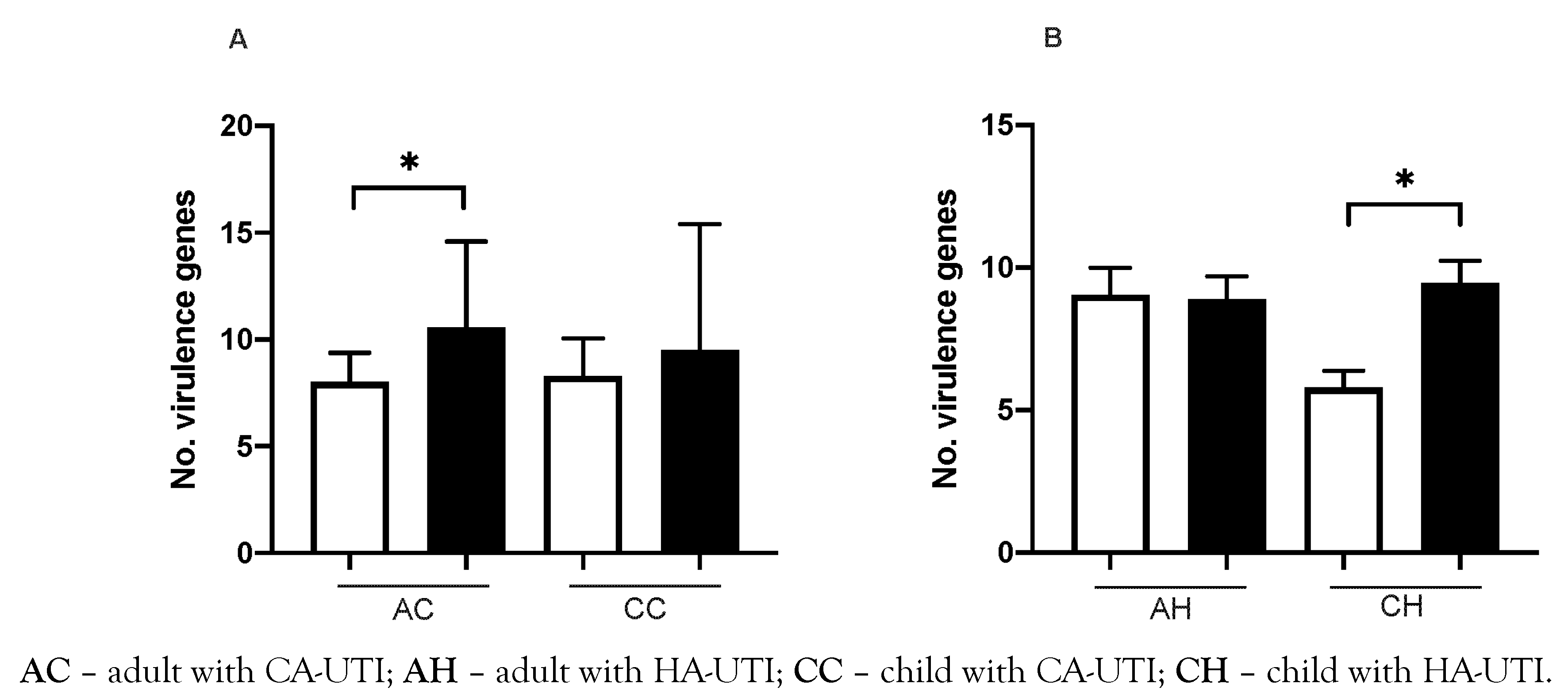
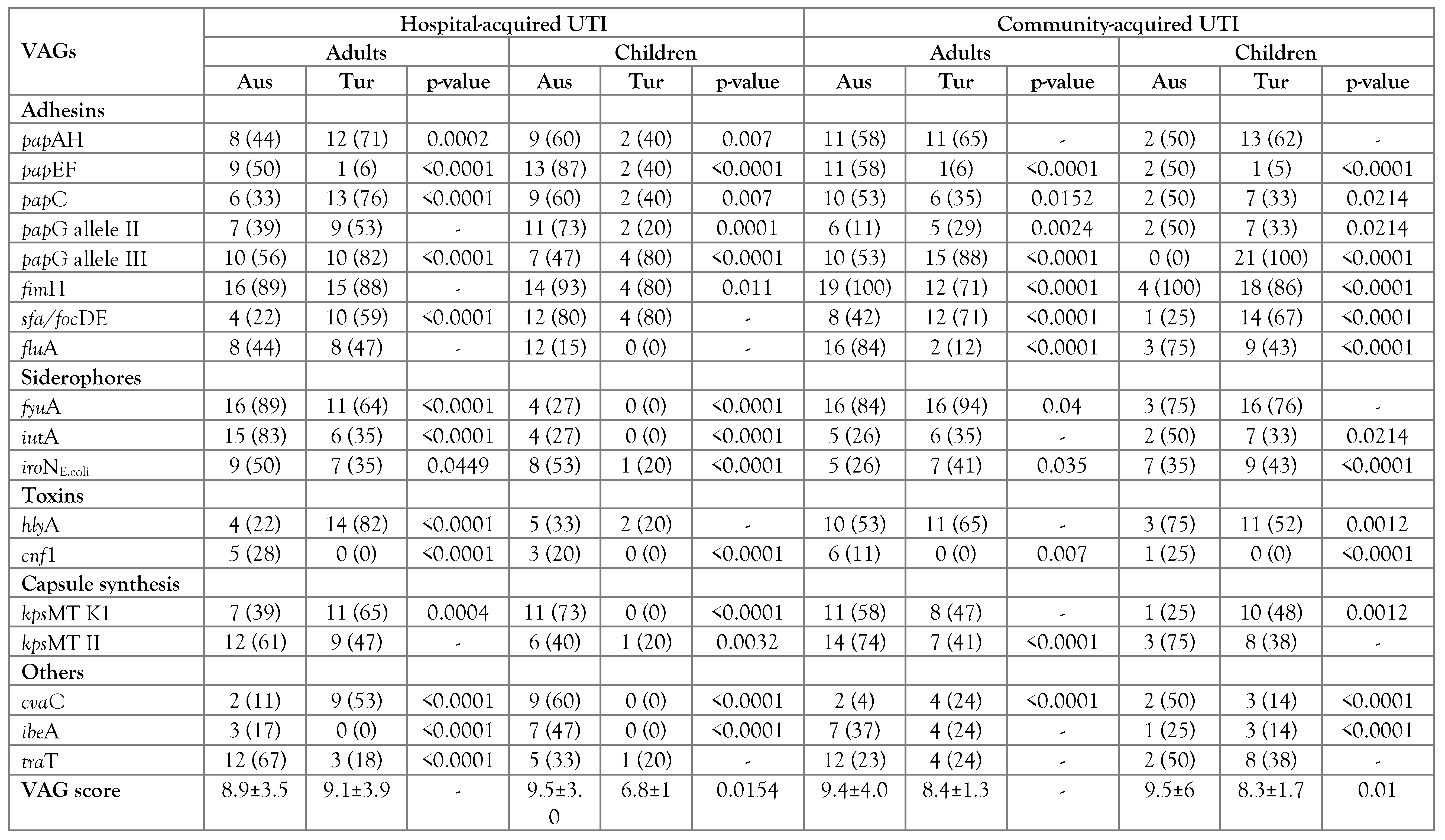
VAG scores
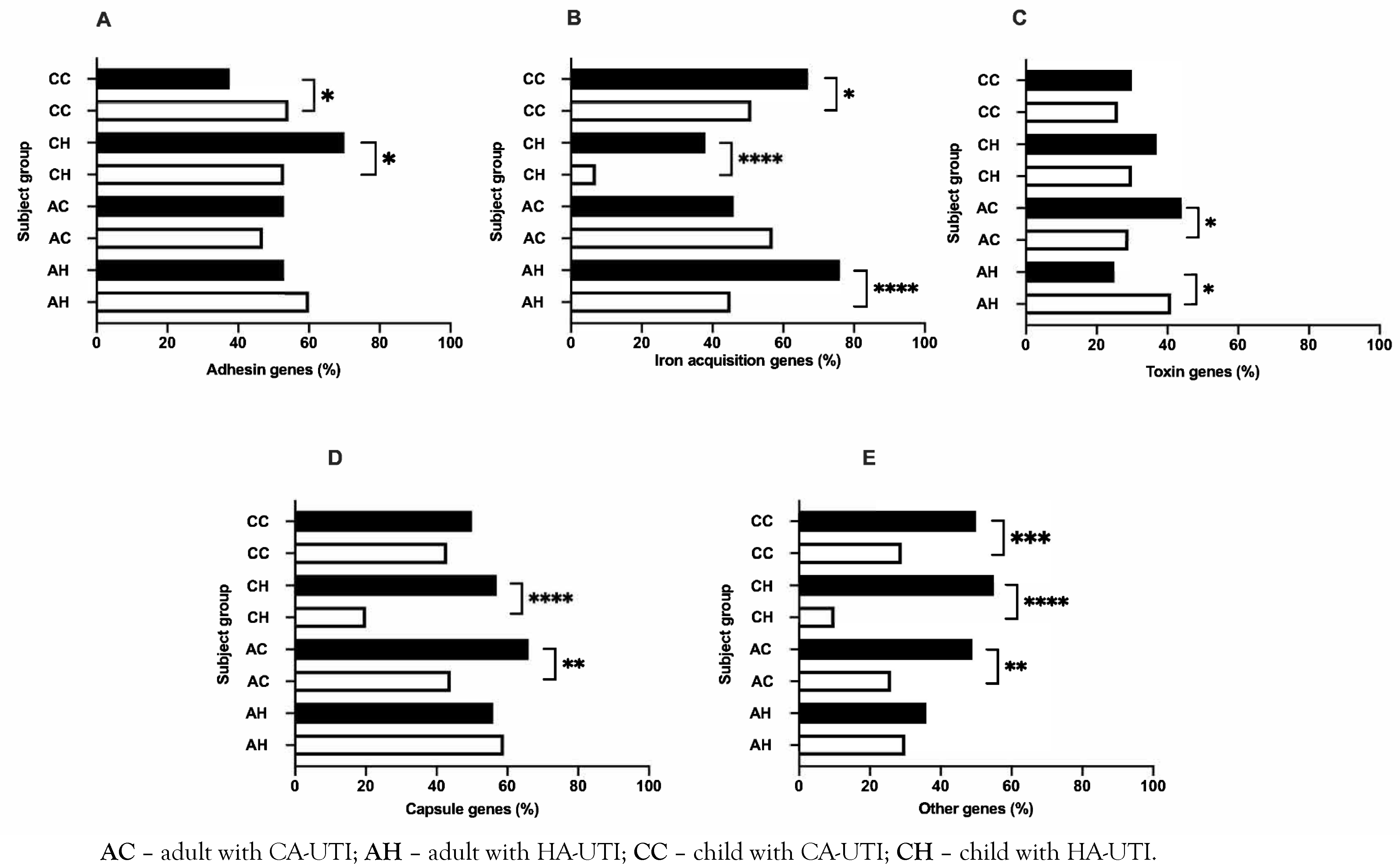
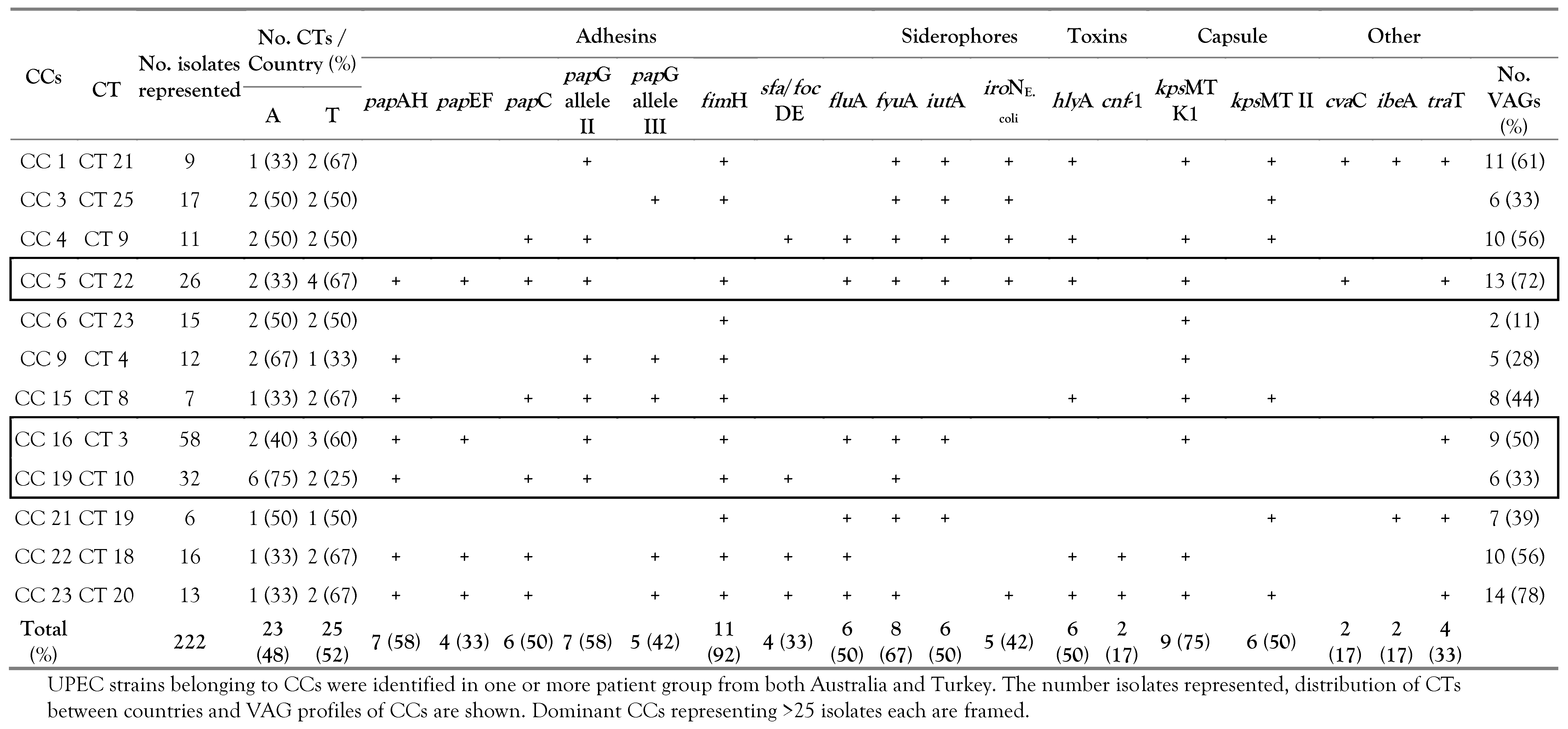
Prevalence of VAG functional groups
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
References
- Behzadi, P.; Urbán, E.; Matuz, M.; Benkő, R.; Gajdács, M. The role of Gram-negative bacteria in urinary tract infections: Current concepts and therapeutic options. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021, 1323, 35–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Johnson, J.R. Medical and economic impact of extraintestinal infections due to Escherichia coli: Focus on an increasingly important endemic problem. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulett, G.C.; Totsika, M.; Schaale, K.; Carey, A.J.; Sweet, M.J.; Schembri, M.A. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence and innate immune responses during urinary tract infection. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013, 16, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Wong, A.H.C.; Leung, A.A.M.; Hon, K.L. Urinary tract infection in children. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2019, 13, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, M.; Vehreschild, M.; Wagenlehner, F. Management of uncomplicated recurrent urinary tract infections. BJU Int. 2022, 129, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroumand, M.; Sharifi, A.; Manzouri, L.; Khoramrooz, S.S.; Khosravani, S.A. Evaluation of pap and sfa genes relative frequency P and S fimbriae encoding of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from hospitals and medical laboratories; Yasuj City, Southwest Iran. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2019, 21, e89499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozzari, A.; Behzadi, P.; Kerishchi Khiabani, P.; Sholeh, M.; Sabokroo, N. Clinical cases, drug resistance, and virulence genes profiling in uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Appl Genet. 2020, 61, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Andreu, A.; Pigrau, C.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Johnson, J.R.; Prats, G. Relationship between Escherichia coli strains causing acute cystitis in women and the fecal E. coli population of the host. J Clin Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2529–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarshar, M.; Behzadi, P.; Ambrosi, C.; Zagaglia, C.; Palamara, A.T.; Scribano, D. FimH and anti-adhesive therapeutics: A disarming strategy against uropathogens. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, P. Classical chaperone-usher (CU) adhesive fimbriome: Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Folia Microbiol 2020, 65, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.A. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli-associated exotoxins. In Urinary Tract Infections, 2nd ed.; Mulvey, M.A., Klumpp, J.D., Stapleton, A.E., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulett, G.C.; Valle, J.; Beloin, C.; Sherlock, O.; Ghigo, J.M.; Schembri, M.A. Functional analysis of antigen 43 in uropathogenic Escherichia coli reveals a role in long-term persistence in the urinary tract. Infect Immun. 2007, 75, 3233–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoetendal, E.G.; Akkermans, A.D.; Akkermans-van Vliet, W.M.; de Visser, J.A.G.; de Vos, W.M. The host genotype affects the bacterial community in the human gastronintestinal tract. Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2001, 13, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Johnson, J.R.; Pérez, T.; Prats, G.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Andreu, A. Structure and urovirulence characteristics of the fecal Escherichia coli population among healthy women. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Duran, S.; Horcajada, J.P.; Sorlí, L.; et al. Community-onset healthcare-related urinary tract infections: Comparison with community and hospital- acquired urinary tract infections. J Infect. 2012, 64, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmerhausen, T.; Katouli, M. Molecular characterisation of Escherichia coli isolated from hospitalised children and adults with urinary tract infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014, 33, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmerhausen, T.L.; Woods, J.L.; Faoagali, J.; Katouli, M. Interactions of uroseptic Escherichia coli with renal (A- 498) and gastrointestinal (HT-29) cell lines. J Med Microbiol. 2014, 63 Pt 12, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owrangi, B.; Masters, N.; Kuballa, A.; O’Dea, C.; Vollmerhausen, T.L.; Katouli, M. Invasion and translocation of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from urosepsis and patients with community-acquired urinary tract infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018, 37, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astley, D.; Masters, N.; Kuballa, A.; Katouli, M. Commonality of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli isolated from patients with extraintestinal infections, healthy individuals and the environment. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021, 40, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumuk, Z.; Afacan, G.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P. Turkey: A further country concerned by community-acquired Escherichia coli clone O25-ST131 producing CTX-M-15. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008, 62, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozcal, E.; Eldem, V.; Aydemir, S.; Skurnik, M. The relationship between phylogenetic classification, virulence and antibiotic resistance of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli in İzmir province, Turkey. PeerJ. 2018, 6, e5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manges, A.R.; Johnson, J.R.; Foxman, B.; O’Bryan, T.T.; Fullerton, K.E.; Riley, L.W. Widespread distribution of urinary tract infections caused by a multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli clonal group. N Eng J Med. 2001, 345, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Stell, A.L.; O’Bryan, T.T.; et al. Global molecular epidemiology of the O15:K52:H1. extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli clonal group: Evidence of distribution beyond Europe. J Clin Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.R.; Murray, A.C.; Kuskowski, M.A.; et al. Distribution and characteristics of Escherichia coli clonal group A. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005, 11, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Griffiths, M.W. PCR differentiation of Escherichia coli from other Gram-negative bacteria using primers derived from the nucleotide sequences flanking the gene encoding the universal stress protein. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1998, 27, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmerhausen, T.L.; Ramos, N.L.; Gündoğdu, A.; Robinson, W.; Brauner, A.; Katouli, M. Population structure and uropathogenic virulence-associated genes of faecal Escherichia coli from healthy young and elderly adults. J Med Microbiol. 2011, 60, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, E.M.; Matthews, B.; Gundogdu, A.; et al. Prevalence and persistence of Escherichia coli strains with uropathogenic virulence characteristics in sewage treatment plants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5882–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corney, B.G.; Colley, J.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Whittington, R.; Graham, G.C. Rapid identification of some Leptospira isolates from cattle by random amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2927–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M. Diversity of microbial communities. In Advances in Microbial Ecology; Advances in Microbial, Ecology, Marshall, K.C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1984; Volume 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Env. Microbiol Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bingen, E. Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4555–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Stell, A.L. Extended virulence genotypes of Escherichia coli strains from patients with urosepsis in relation to phylogeny and host compromise. J Infect Dis. 2000, 181, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, T.A.; Wu, X.Y.; Barchia, I.; et al. Comparison of virulence gene profiles of Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy and diarrheic swine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4782–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restieri, C.; Garriss, G.; Locas, M.C.; Dozois, C.M. Autotransporter-encoding sequences are phylogenetically distributed among Escherichia coli clinical isolates and reference strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.R.; Kuskowski, M.A.; O’bryan, T.T.; Colodner, R.; Raz, R. Virulence genotype and phylogenetic origin in relation to antibiotic resistance profile among Escherichia coli urine sample isolates from Israeli women with acute uncomplicated cystitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platell, J.L.; Johnson, J.R.; Cobbold, R.N.; Trott, D.J. Multidrug-resistant extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli of sequence type ST131 in animals and foods. Vet Microbiol. 2011, 153, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.R.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; DebRoy, C.; et al. Comparison of Escherichia coli ST131 pulsotypes, by epidemiologic traits, 1967-2009. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012, 18, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, N.L.; Saayman, M.L.; Chapman, T.A.; et al. Genetic relatedness and virulence gene profiles of Escherichia coli strains isolated from septicaemic and uroseptic patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010, 29, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, E.; Matthews, B.; Stratton, H.M.; Katouli, M. Pathogenic Escherichia coli found in sewage treatment plants and environmental waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5536–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manges, A.R.; Tabor, H.; Tellis, P.; Vincent, C.; Tellier, P.P. Endemic and epidemic lineages of Escherichia coli that cause urinary tract infections. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008, 14, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, R.S. Urinary tract infections attributed to diverse ExPEC strains in food animals: Evidence and data gaps. Front Microbiol. 2015, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manges, A.R.; Johnson, J.R.J. Food-borne origins of Escherichia coli causing extraintestinal infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2012, 55, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avasthi, T.S.; Kumar, N.; Baddam, R.; et al. Genome of multidrug-resistant uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain NA114 from India. J Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 4272–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Stanton-Cook, M.; et al. Global dissemination of a multidrug resistant Escherichia coli clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014, 111, 5694–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiles, T.J.; Kulesus, R.R.; Mulvey, M.A. Origins and virulence mechanisms of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Exp Mol Pathol. 2008, 85, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.H.; Tsau, Y.K.; Kuo, C.Y.; Su, L.H.; Lin, T.Y. Comparison of extended virulence genotypes for bacteria isolated from pediatric patients with urosepsis, acute pyelonephritis, and acute lobar nephronia. Paed Infect Dis J. 2010, 29, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozeh, F.; Saffari, M.; Neamati, F.; Zibaei, M. Detection of virulence genes in Escherichia coli isolated from patients with cystitis and pyelonephritis. Int J Infect Dis. 2014, 29, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, N.L.; Dzung, D.T.; Stopsack, K.; et al. Characterisation of uropathogenic Escherichia coli from children with urinary tract infection in different countries. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011, 30, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.G.; Palermo, J.J.; Schilling, J.D.; Roth, R.; Heuser, J.; Hultgren, S.J. Intracellular bacterial biofilm-like pods in urinary tract infections. Science. 2003, 301, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.G.; Redford, P.; Welch, R.A.; Payne SMJI, immunity. TonB-dependent systems of uropathogenic Escherichia coli: Aerobactin and heme transport and TonB are required for virulence in the mouse. Infect Immun. 2001, 69, 6179–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashchandrabose, S.; Mobley, H.L. Back to the metal age: Battle for metals at the host-pathogen interface during urinary tract infection. Metallomics. 2015, 7, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassat, J.E.; Skaar, E.P. Iron in Infection and Immunity. Cell Host Microbe. 2013, 13, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.C.; Garcia-Herrero, A.; Johanson, T.H.; et al. Siderophore uptake in bacteria and the battle for iron with the host; a bird’s eye view. Biometals. 2010, 23, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, N.; Saayman, M.L.; Chapman, T.; et al. Genetic relatedness and virulence gene profiles of Escherichia coli strains isolated from septicaemic and uroseptic patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010, 29, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, E.C.; Brumbaugh, A.R.; Mobley, H.L. Redundancy and specificity of Escherichia coli iron acquisition systems during urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 2011, 79, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bien, J.; Sokolova, O.; Bozko, P. Role of uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence factors in development of urinary tract infection and kidney damage. Int J Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 681473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, B.K.; Mulvey, M.A. The UPEC pore-forming toxin α-hemolysin triggers proteolysis of host proteins to disrupt cell adhesion, inflammatory, and survival pathways. Cell Host Microbe. 2012, 11, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, K.; Hannan, T.J.; Guest, R.L.; et al. Dysregulation of Escherichia coli α-hemolysin expression alters the course of acute and persistent urinary tract infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015, 112, E871–E880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, S.J.; Snyder, I.S. Effect of Escherichia coli alpha- hemolysin on human peripheral leukocyte function in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982, 37, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, T.J.; Bower, J.M.; Redd, M.J.; Mulvey, M.A. Use of zebrafish to probe the divergent virulence potentials and toxin requirements of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Davidson, B.A.; Genagon, S.A.; et al. E. coli virulence factor hemolysin induces neutrophil apoptosis and necrosis/lysis in vitro and necrosis/lysis and lung injury in a rat pneumonia model. Am J Physiol. 2005, 289, L207–L216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erjavec, M.S.; Žgur-Bertok, D. Extended Characterization of Human Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolates from Slovenia; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, S.M.; Hull, S.I. Loss of resistance to ingestion and phagocytic killing by O− and K− mutants of a uropathogenic Escherichia coli O75:K5 strain. Infect Immun. 1999, 67, 3757–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 |
 |
 |
 |
© GERMS 2022.
Share and Cite
Astley, D.J.; Spang, L.; Parnian, F.; Vollmerhausen, T.; Kilic, H.; Hora, M.; Gundogdu, A.; Katouli, M. A Comparative Study of the Clonal Diversity and Virulence Characteristics of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolated from Australian and Turkish (Turkey) Children and Adults with Urinary Tract Infections. GERMS 2022, 12, 214-230. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1324
Astley DJ, Spang L, Parnian F, Vollmerhausen T, Kilic H, Hora M, Gundogdu A, Katouli M. A Comparative Study of the Clonal Diversity and Virulence Characteristics of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolated from Australian and Turkish (Turkey) Children and Adults with Urinary Tract Infections. GERMS. 2022; 12(2):214-230. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1324
Chicago/Turabian StyleAstley, Dylan John, Labolina Spang, Fatemeh Parnian, Tara Vollmerhausen, Huseyin Kilic, Mehmet Hora, Aycan Gundogdu, and Mohammad Katouli. 2022. "A Comparative Study of the Clonal Diversity and Virulence Characteristics of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolated from Australian and Turkish (Turkey) Children and Adults with Urinary Tract Infections" GERMS 12, no. 2: 214-230. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1324
APA StyleAstley, D. J., Spang, L., Parnian, F., Vollmerhausen, T., Kilic, H., Hora, M., Gundogdu, A., & Katouli, M. (2022). A Comparative Study of the Clonal Diversity and Virulence Characteristics of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolated from Australian and Turkish (Turkey) Children and Adults with Urinary Tract Infections. GERMS, 12(2), 214-230. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1324



