Abstract
Introduction: Klebsiella pneumoniae is a significant nosocomial pathogen. We aimed to assess the clinical success following high-dose ciprofloxacin for recurrent bacteremia from biofilm-forming multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in a liver transplanted patient. Case report: A 55-year-old male had undergone liver transplantation and at day 10 he developed fever and dysuria. Two blood cultures became positive and were identified by Vitek2 (BioMérieux, USA) as K. pneumoniae. From his urine K. pneumoniae was isolated. Based on antimicrobial susceptibility (AST) panel (Vitek2), i.v. meropenem 1 g 8 hourly and i.v. amikacin 15 mg/kg/daily (5 days) were started (the isolate was ciprofloxacin-resistant). Following 14 days of meropenem he was discharged and 3 days later he was readmitted with fever and dysuria. Since the blood and urine isolate was K. pneumoniae, based on AST 21 days of meropenem were given, the patient was discharged and 3 days later he was readmitted with fever and dysuria. Since this was the 3rd episode with K. pneumoniae bacteremia, to exclude the focus of infection contrast-enhanced computed tomography and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography were done but both were normal. Based on multilocus sequence typing (MLST) and microtiter plate assay, biofilm forming magA(K1)- positive (+) K. pneumoniae CC23 was found. The patient was having continuous asymptomatic bacteriuria with similar (magA(K1)-positive (+) K. pneumoniae CC23) isolate; we opted for high dose oral ciprofloxacin (800 mg, 8 hourly) for 7 days. Conclusions: Following a high dose of oral ciprofloxacin, we were able to achieve urinary microbial clearance and a permanent cure following (magA(K1)-positive (+) K. pneumoniae CC23) bacteremia. This could be a promising therapy to achieve microbial clearance from biofilm-forming multidrug- resistant K. pneumoniae.
Introduction
Nowadays, orthotropic liver transplantation (OLT) is performed commonly. Bacterial infections are common following OLT and often associated with transplant failure and a high burden. Due to prolonged immunosuppression, the risk for infections is high, but symptoms are often masked, thus leading to delay in diagnosis [1]. Most bacterial infections are nosocomial in origin and associated with invasive medical devices. By performing microbial culture, the majority of etiological agents are isolated, and opting for antimicrobials in proper dosage, patients tend to get a permanent cure. However, when a patient gets recurrent infections in addition to opting for proper antimicrobial dosage, offending source identification and clearance are of utmost importance to prevent further recurrences [2].
Klebsiella pneumoniae is regarded as the second most common cause of Gram-negative bacteremia. It also is a significant nosocomial pathogen and it is particularly common among immunocompromised patients. Relative to planktonic K. pneumoniae infections, infections following biofilm-forming (BF) K. pneumoniae strains are more difficult to treat [3]. We report a case with recurrent bacteremia from biofilm- forming multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae in a liver transplanted patient.
Case report
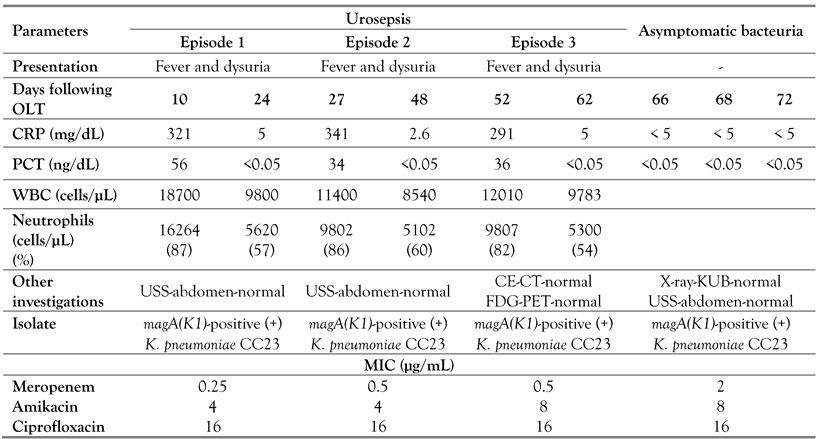
A 55-year-old male had undergone OLT following non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and he had remained well following the acute stage of liver transplantation (on day 9, C-reactive protein (CRP) was 6 mg/dL, and procalcitonin (PCT) was <0.5 ng/L). He was on cyclosporine and steroids. The 16 Fr latex urine catheter was removed at day 7 following OLT. On day 10 following OLT, he developed high spikes of fever and dysuria. Two blood cultures following 12 and 14 h of incubation became positive and identified by Vitek2 (BioMérieux, USA) as K. pneumoniae with 99% probability. He had significant (>105 CFU) bacteriuria and later it was identified as K. pneumoniae using CLED and Vitek2 platform. Based on the antimicrobial susceptibility panel testing (AST) Vitek2, we commenced i.v. meropenem 1 g 8 hourly and i.v. amikacin 15 mg/kg daily (his serum creatinine was normal). The isolate was resistant to all cephalosporins, beta-lactam/beta-lactamase combinations, penicillins, quinolones (the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of ciprofloxacin was 16 µg/mL), chloramphenicol, nitrofurantoin and aminoglycosides, except for amikacin. On day 10 following OLT, CRP was 321 mg/dL, PCT was 56 ng/L, and a full blood count showed neutrophil leukocytosis (16264 cells/µL) with left shift. Both cyclosporine and steroids doses were reduced.
Both ultrasound scan of the abdomen and pelvis and chest X-ray did not reveal any particular foci of infection. He was treated 14 days with i.v. meropenem and five days of i.v. amikacin; at day 24 following OLT, fever subsided, indicating a clinical cure, and CRP and PCT came down to 5 mg/dL and <0.05 ng/L, respectively, indicating response with inflammatory markers. He was discharged on day 25 following OLT with immunomodulators (low doses of cyclosporine and steroids) and 3 days later again he developed a fever with dysuria. He was admitted to the same care facility, blood and urine cultures were performed and empirically i.v. meropenem and i.v. amikacin were started. Subsequently, two blood cultures and urine culture became positive, and K. pneumoniae was isolated. All other investigations were unremarkable except for CRP (341 mg/dL) and PCT (34 ng/L). On this occasion, he was treated with meropenem for 21 days, and amikacin was given for seven days. On day 49 following OLT, clinically well, and all markers of inflammation (day 48 following OLT: CRP 2.6 mg/dL and PCT<0.05 ng/dL) were negative, he was discharged with similar doses of immunomodulators (given at day 25 following OLT).
Following the third day of discharge, he again developed fever and dysuria and was admitted to the same unit for further care. We further reduced the dose of both immunomodulators. All other systems were insignificant. Similarly, his blood and urine cultures became positive, and K. pneumoniae was isolated. Since this was the 3rd episode of K. pneumoniae bacteremia, we did a full body contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CE-CT) and a 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) to detect any active focus of infection. Both CECT and FDG-PET scans were negative and excluded active infectious/inflammatory foci, and all investigations except for CRP (291 mg/dL) and PCT (36 ng/L) remained negative. On all 3 occasions, he had not had features of pyelonephritis and clinical features were consistent with lower urinary tract infections. He was treated 10 days with i.v. meropenem and five days of i.v. amikacin, fever subsided, indicating a clinical cure, and CRP and PCT came down to 5 mg/dL and <0.05 ng/L (measured on day 62 following OLT)—Table 1. Since the patient was free of invasive devices except for i.v. access (which also applied following each admission) and latex urinary catheter kept from day 0 to day 7 following OLT, we thought about the possibility of formation of BF in the lower urinary tract. An urodynamic test was done and excluded functional bladder pathology.

Table 1.
Timeline of urosepsis and asymptomatic bacteriuria following biofilm forming magA(K1)- positive (+) K. pneumoniae CC23 infection.
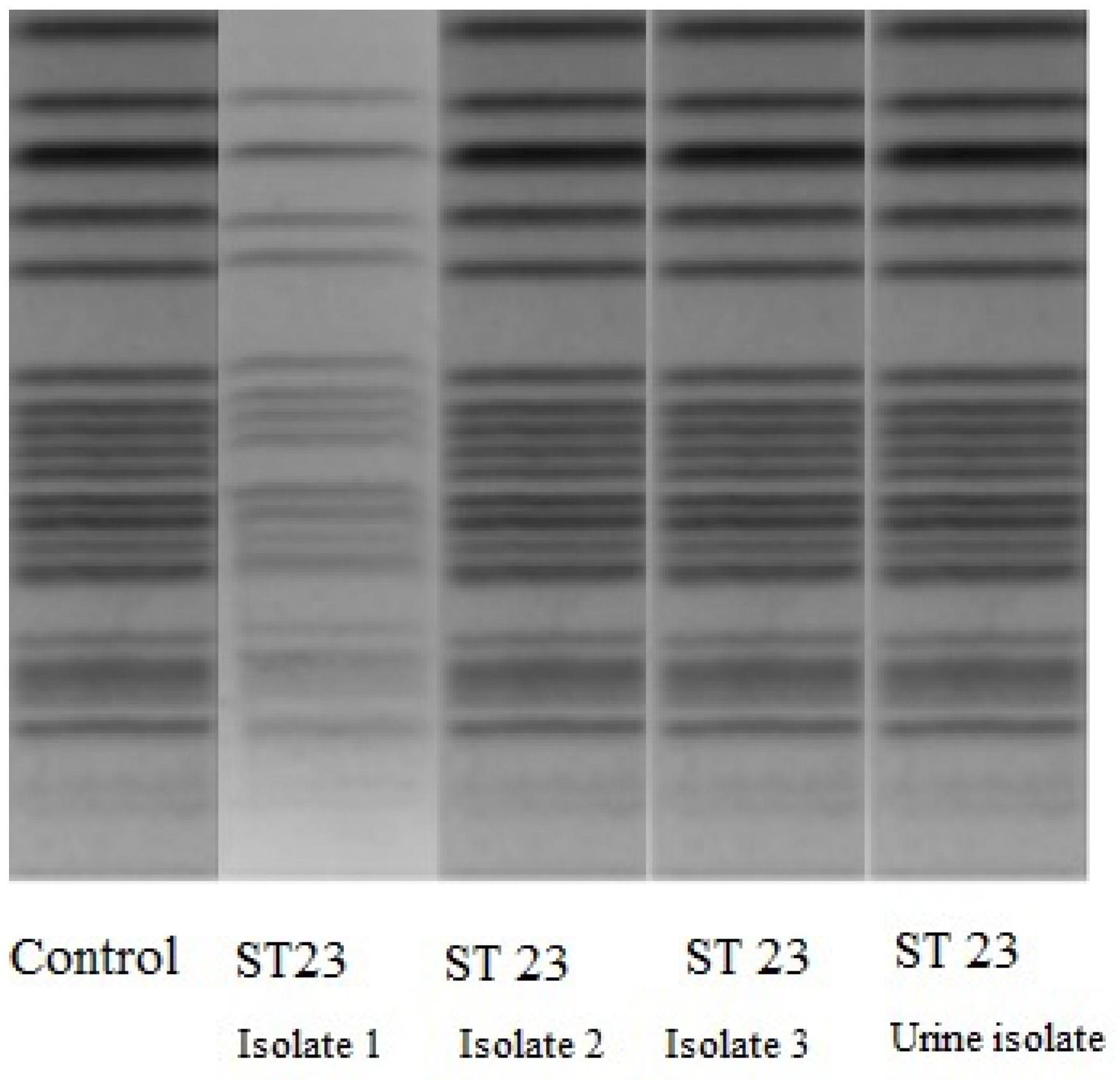
All K. pneumoniae isolates were further analyzed. Based on multilocus sequence typing (MLST), seven housekeeping genes (gapA, infB, mdh, pgi, phoE, rpoB, and tonB) were PCR- amplified and sequenced from all isolates according to the K. pneumoniae MLST protocol [4]. Alleles and sequence types (STs) were assigned by the MLST database. All had ST23 indicating a common origin and pulse field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) proved that the same micro-organisms were responsible for the bacteremia and lower urinary tract infections (Figure 1). Further, we found that all isolates were biofilm-forming K. pneumoniae [5]. Further, we performed PCR for megA and rmpA using forward, 5′-GGTGCTCTTTACATCATTGC-3′ and, for magA reverse, 5′- GCAATGGCCATTTGCGTTAG-3′ and for rmpA forward, 5′-ACTGGGCTACCTCTGCTTCA-3′, and for rmpA reverse, 5′- CTTGCATGAGCCATCTTTCA-3′ [6,7]. Biofilm was detected by microtiter plate assay using crystal violet staining. The test median optical density (OD) 550 value was 2.18, (for control—0.23) a value indicative of strong biofilm formation. Each assay was performed in triplicate. All isolates were similar and we found BF forming magA(K1)-positive (+) K. pneumoniae ST23 isolate [7]. The string test was positive indicating that all isolates were of the hypermucoviscosity phenotype.
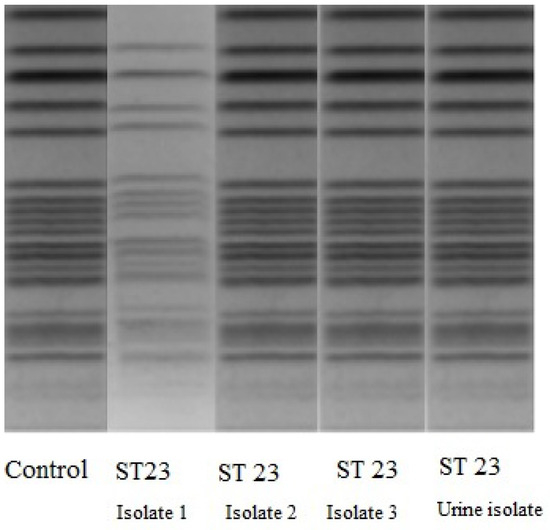
Figure 1.
PFGE of bloodstream and urinary K. pneumoniae isolates.
We did urine cultures every other day to assess the microbial clearance. The patient was having continuous asymptomatic bacteriuria for 5 days with similar (magA(K1)-positive (+) K. pneumoniae CC23) isolate; we opted for high dose oral ciprofloxacin (800 mg, 8 hourly) for 7 days (K. pneumoniae was resistant to ciprofloxacin). The minimal biofilm inhibitory concentration, minimal biofilm eradication concentration and biofilm bactericidal concentration were determined observing the color change of p- iodonitrotetrazolium violet in the microplate wells and ciprofloxacin for our isolate, and were 16 µg/mL, 32 µg/mL and 32 µg/mL, respectively. Subsequent urine cultures (on days 3, 5, and 10) became negative, and the patient remained well up to now (15 months following the third episode of bacteremia).
Discussion
Recurrent urinary tract infections leading to bacteremia are common among immunocompromised patients with anatomically and physiologically abnormal urinary tracts. When recurrent bacteremia develops in a patient with anatomically and physiologically normal urinary tract, the identification of the source could be problematic [8].
Recently, K. pneumoniae has emerged globally as a multidrug-resistant nosocomial pathogen with limited available treatment options [9]. BF forming K. pneumoniae has increased the burden and is often associated with device-related infections, infections on body surfaces, and chronic infections [10]. Use of PFGE has confirmed both bacteremia and lower UTI caused by same isolate and MLST has confirmed responsive pathogens (ST23) in each episode having a similar origin.
In a patient with OLT, recurrent bacteremia following biofilm-forming K. pneumoniae is a great problem. The patient required multiple hospital admissions and prolonged parenteral antimicrobial therapy. Here, the patient would harbor K. pneumoniae from a biofilm at the lower urinary tract. When an invasive device is kept for prolonged period, formation of BF in that anatomical vicinity is well documented [10]. In our case, the urine catheter was kept for a short period (7 days) following OLT and it could be the possible nidus for BF within the lower urinary tract [8].−[10] The patient was on immunomodulators and this could be a risk factor to develop recurrences. Since the patient was having asymptomatic bacteriuria with the same isolate, there was an important risk of developing another episode of bacteremia. Even with prolonged antimicrobials, a complete cure was doubtful. Following each episode, meropenem MIC creep was observed suggesting prolonged exposure leading to K. pneumoniae meropenem resistance.
High dose ciprofloxacin can develop tendinitis, tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, hepatotoxicity, aortic aneurysm and dissection. Also, eradication of human gut and urethral microbiome can be considered as an adverse effect [11]. In this case, we have not observed any of these known adverse effects following the use of high-dose ciprofloxacin. In vitro concentration-dependent killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm was observed following use of ciprofloxacin [12]. Although the isolate remained resistant to ciprofloxacin, based on high renal penetration and excretion we have opted for ciprofloxacin in a high-dose. At present, biofilm lytic agents are less available, and most are at different stages of development [9]. High dose antibiotics showed a promising effect on biofilms [8].−[10] Following high-dose ciprofloxacin therapy, the patient has not developed more recurrences and his asymptomatic bacteriuria was also resolved.
The development of ciprofloxacin resistance in K. pneumoniae is a stepwise process. The sequential genetic mutations would lead to development of gradual resistance. In the current case, we were not able to assess the mechanisms of ciprofloxacin resistance among our isolate.
Conclusions
Following a high dose of oral ciprofloxacin, we were able to achieve urinary microbial clearance and a permanent cure of bacteremia from a (magA(K1)-positive (+) K. pneumoniae ST23) isolate. This could be useful to achieve microbial clearance in a patient with recurrent infections from biofilm-forming K. pneumoniae. A large sample study is required to justify this.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report and the accompanying images.
Author Contributions
MK and JAASJ conducted the clinical examination and treatment intervention. MK and JAASJ performed the microscopy and identification of blood culture isolate. JAASJ drafted the manuscript; MK reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors—none to declare.
References
- Vera, A.; Contreras, F.; Guevara, F. Incidence and risk factors for infections after liver transplant: Single-center experience at the University Hospital Fundacion Santa Fe de Bogotá, Colombia. Transpl Infect Dis. 2019, 13, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epp, A.; Larochelle, A.; Urogynaecology Committee, Family Physicians Advisory Committee. Recurrent urinary tract infection. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2010, 32, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuyama, H.; Yamashiro, S.; Kinjo, K.; Tamaki, H.; Kishaba, T. Validation of sputum Gram stain for treatment of community-acquired pneumonia and healthcare-associated pneumonia: A prospective observational study. BMC Infect Dis 2018, 14, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubMLST. MLST schemes. Available online: https://pubmlst.org/mlst (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- Hunter, S.B.; Vauterin, P.; Lambert-Fair, M.A.; et al. Establishment of a universal size standard strain for use with the PulseNet standardized pulsedfield gel electrophoresis protocols: Converting the national databases to the new size standard. J Clin Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.H.; Wu, A.M.; Tsai, C.G.; Chang, X.Y.; Tsai, S.F.; Wu, T.S. Contribution of fucose-containing capsules in Klebsiella pneumoniae to bacterial virulence in mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008, 233, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, J.S.; Bakaletz, L.O.; Wozniak, D.J. What’s on the outside matters: The role of the extracellular polymeric substance of gram-negative biofilms in evading host immunity and as a target for therapeutic intervention. J Biol Chem. 2016, 291, 12538–12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, A.; Yousefi Mashouf, R.; Ebrahimzadeh Namvar, A.M.; Alikhani, M.Y. Detection of magA gene in Klebsiella spp. isolated from clinical samples. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2013, 16, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hummers-Pradier, E.; Ohse, A.M.; Koch, M.; Heizmann, W.R.; Kochen, M.M. Urinary tract infection in men. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004, 42, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wnorowska, U.; Piktel, E.; Durnaś, B.; Fiedoruk, K.; Savage, P.B.; Bucki, R. Use of ceragenins as a potential treatment for urinary tract infections. BMC Infect Dis. 2019, 19, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Service (NHS). Ciprofloxacin. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/ciprofloxacin/ (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Song, Z.; Høiby, N. Ciprofloxacin shows concentration dependent killing of P. aeruginosa biofilm in vitro. J Cyst Fibros. 2010, 9, S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© GERMS 2021.