COVID-19 in Nigeria: Account of Epidemiological Events, Response, Management, Preventions and Lessons Learned
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
- Confirmed cases/cumulative confirmed cases: This refers to the total number of confirmed COVID-19 cases within the period of study. It is represented as frequency.
- Deaths/cumulative deaths: This refers to the total number of deaths that resulted owing to COVID-19 infection within the study period. It is represented as frequency.
- Percentage of deaths: This refers to the proportion of COVID-19 deaths recorded in a particular State to the cumulative deaths recorded in all the States assessed within the study period. It is represented in percentage.
- Attack rate / Attack rate per 100,000 of population: The index refers to the number of persons infected with COVID-19 per 100,000 of the country’s population. It is represented as frequency per 100,000 of population.
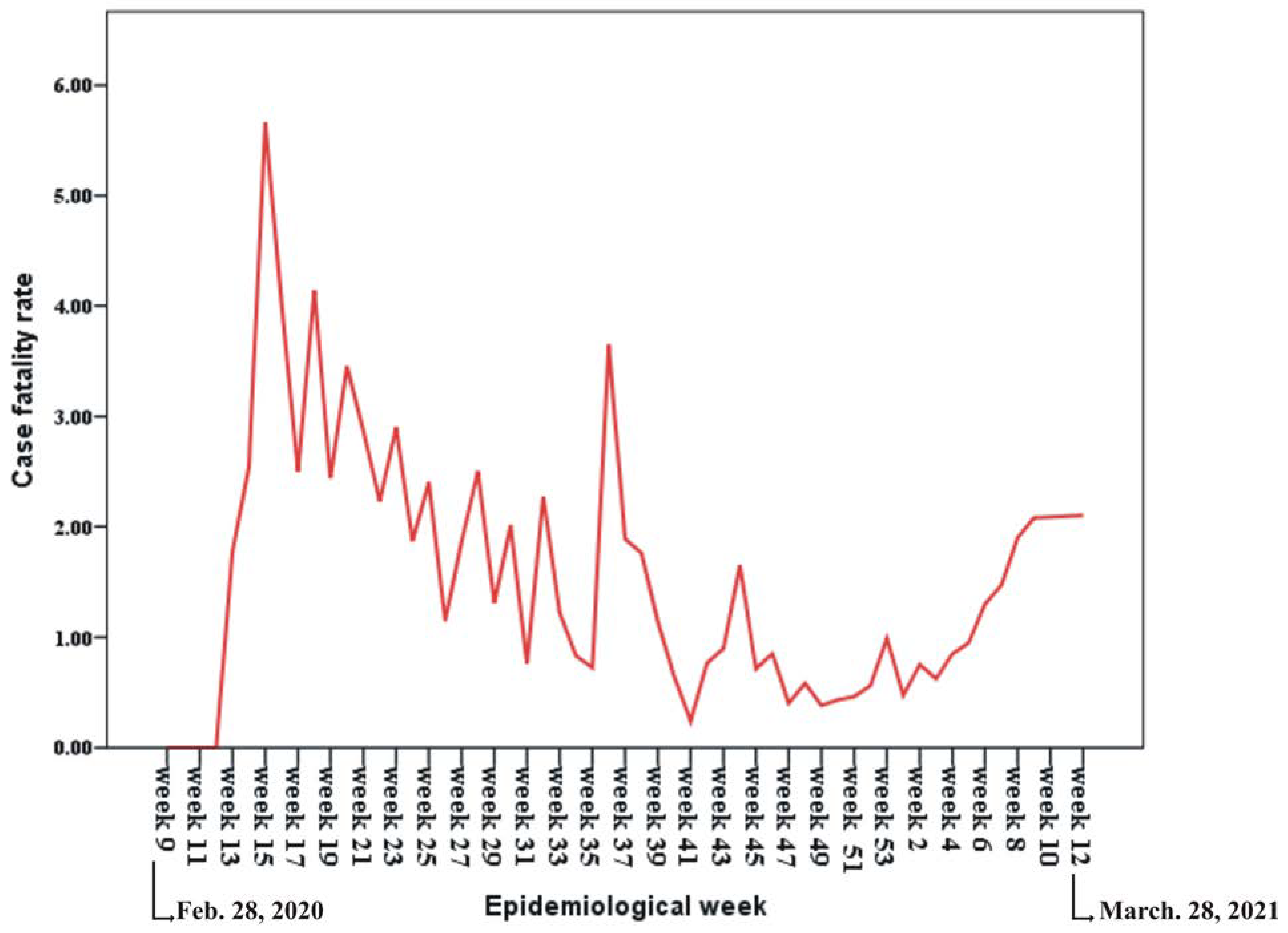
- Case fatality rate: It refers to the proportion of cumulative deaths recorded in a state/country to the cumulative confirmed cases. It is represented in percentage.
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Conflicts of interest
References
- World Health Organization. Impact of COVID-19 on people's livelihoods, their health and our food systems: Joint statement by ILO, FAO, IFAD and WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/13-10-2020-impact-of- covid-19-on-people's-livelihoods-their-health-and-our- food-systems (accessed on 16 May 2021).
- Okafor, U.G.; Olalaye, M.A.; Asobara, H.C.; Umeodinka, E.F. Global impact of COVID-19 pandemic on public health supply chains. IntechOpen. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ogar, C.O.; Okoroiwu, H.U.; Obeagu, E.I.; Etura, J.E.; Abunimye, D.A. Assessment of blood supply and usage pre- and during COVID-19 pandemic: A lesson from non-voluntary donation. Transfus Clin Biol. 2021, 28, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoroiwu, H.U.; Okafor, I.M.; Asemota, E.A.; Ogar, C.O.; Uchenna, I.K. Coping with COVID-19 pandemic in blood transfusion services in West Africa: The need to restrategize. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2021, 43, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pley, C.M.; McNaughton, A.L.; Matthews, P.C.; Lourenço, J. The global impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. BMJ Global Health. 2021, 6, e004275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Andam, K.; Edeh, H.; Oboh, V.; Pauw, K.; Thurlow, J. Impacts of COVID-19 on food systems and poverty in Nigeria. Adv Food Secur Sustain. 2020, 5, 145–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigeria Centre for Disease Control. An update of COVID-19 outbreak in Nigeria. Available online: https://ncdc.gov.ng/diseases/sitreps/?cat=14&name=A n%20update%20of%20COVID- 19%20outbreak%20in%20Nigeria (accessed on 6 April 2021).
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update: Data as received by WHO from national authorities, as of 28 March 2021, 10 am CET.
- Okoroiwu, H.U.; Uchendu, I.K.; Ogar, C.O.; Okafor, I.M. COVID-19 in Nigeria: Situation update and combative measures taken by the government. Germs. 2020, 10, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC). Government Laboratories. Available online: https://covid19.ncdc.gov.ng/laboratory/ (accessed on 6 April 2021).
- Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC). Fee paying laboratories. Available online: https://covid19.ncdc.gov.ng/privatelabs/ (accessed on 6 April 2021).
- Nigeria Center for Disease Control (NCDC). National Interim guidelines for Clinical Management of COVID-19. Version 3; Nigeria Center for Disease Control, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 vaccines shipped by COVAX arrived Nigeria. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/news/covid-19-vaccines- shipped-covax-arrive-nigeria (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- Enitan, S.S.; Oyekale, O.A.; Akele, R.Y.; et al. Assessment of knowledge, perception and readiness to participate in COVID-19 vaccine trial. Int J Vaccine Immun. 2020, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eniade, O.D.; Olarinmoye, A.; Otovwe, A.; Akintunde, F.E.; Okedare, O.O.; Aniyeloye, A.O. Willingness to accept COVID-19 vaccine and its determinants among Nigerian citizens: A web based cross sectional study. J Adv Med Med Res. 2021, 33, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Nigeria Youth call for action to improve adolescent's health: Deliberations center on revitalizing healthcare services threatened by COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/pmnch/media/news/2021/nigeri a-adolescent-health/en/ (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Balasubramanian, S.; Rao, N.M.; Goenka, A.; Roderick, M.; Ramanan, A.V. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in children - what we know so far and what we do not. Indian Pediatr. 2020, 57, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elimian, K.O.; Ochu, C.L.; Ilori, E.; et al. Descriptive epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019 in Nigeria, 27 February - 6 June 2020. Epidemiol Infect. 2020, 14, e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Africa. Weekly bulletin on outbreaks and other emergencies. 2020, 23, 1–7.
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasseli, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Zanela, A.; et al. Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SaRS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA. 2020, 323, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Velkoska, E.; Burrell, L.M. Emerging markers in cardiovascular disease: Where does angiotensin- converting enzymes 2 fit? Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013, 40, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, S.A.; Ahmed, A. COVID-19 pandemic in African perspective. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Economic Forum. Why Sub-Sahara Africa needs a unique response to COVID-19. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/03/17/world/africa/c oronavirus-africa-burkina-faso.html (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- David, J.B.; Andriano, L.; Brazel, D.M.; et al. Demographic science aids in understanding the spread and fatality rates of COVID-19. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020, 117, 9696–9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaji, M.M.; Habibzabeh, P.; Vintzileos, A.; Shokouli, S.; Miralles-Wilhelm Amoroso, A. Temperature, humidity, latitude analysis to estimate potential spread and seasonality of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Netw Open. 2020, 3, e2011834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, L.E.; Molina-Crus, A.; Barillas-Murry, C. BCG vaccine protection from severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020, 117, 17720–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayomi, A.; Balogun, M.R.; Bankole, M.; et al. From Ebola to COVID-19: Emergency preparedness and response plans and actions in Lagos, Nigeria. Global Health 2021, 17, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otu, A.; Ameh, S.; Osifo-Dawodu, E.; Alade, E.; Ekuri, S.; Idris, J. An account of the Ebola virus disease outbreak in Nigeria: Implications and lessons learnt. BMC Public Health. 2017, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Epidemiological indices | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Cumulative confirmed cases | 162,593 |
| Cumulative recoveries | 150,308 |
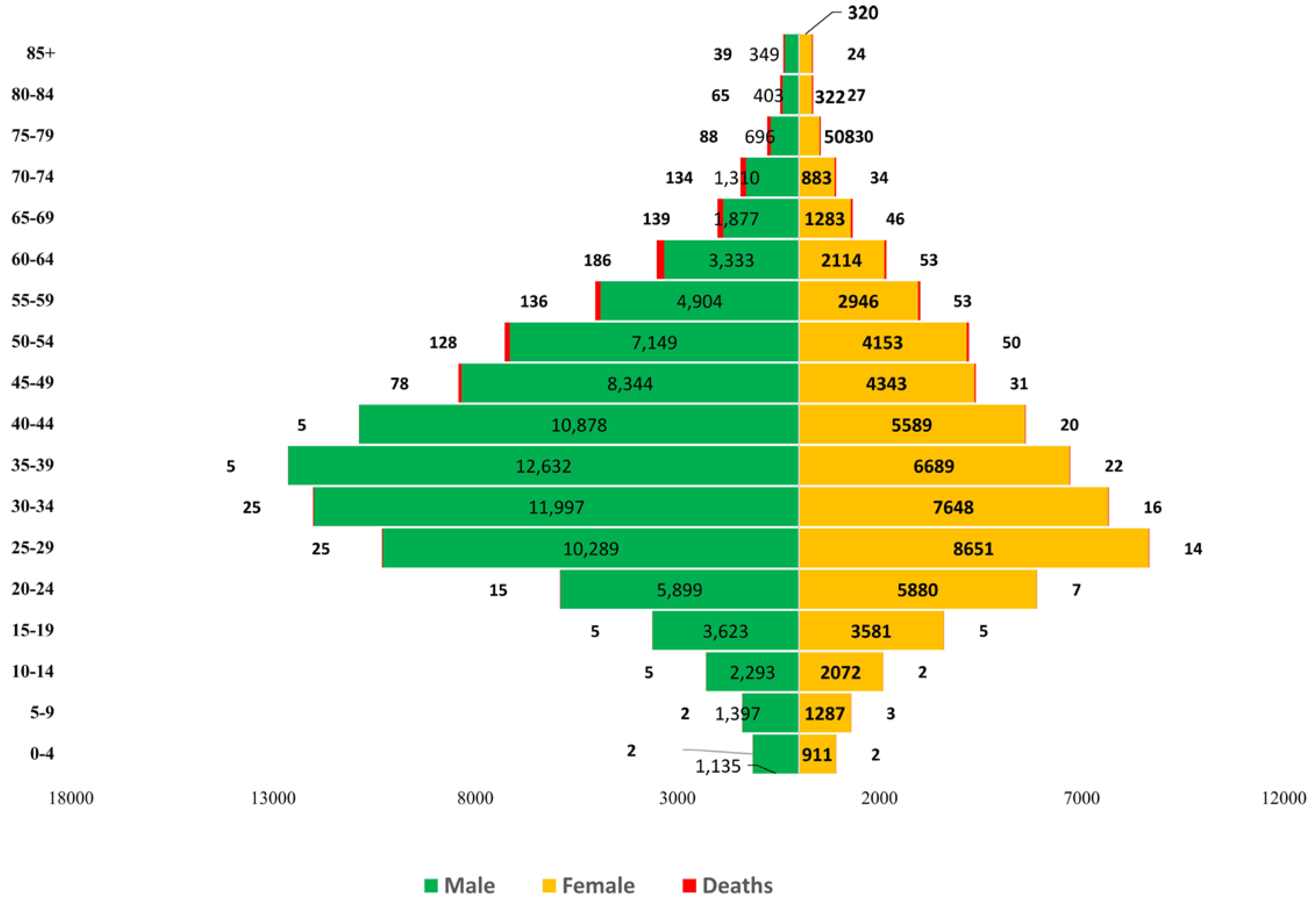
| Cumulative deaths | 2,048 |
| Total active cases | 10,237 |
| Attack rate per 100,000 of population | 78.8 |
| Cumulative deaths per 100,000 of population | 1.0 |
| Case fatality rate | 1.3 |
| Total tests performed | 1,778,105 |
| PCR | 1,608,186 (90.4%) |
| RDT | 169,919 (9.6%) |
| Total dose of vaccines administered | 923,623 |
| Vaccine approved for use | AstraZeneca/Oxford vaccine |
| State | No. of cases | % of cases | No. of deaths | % of deaths | CFR | No. of tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lagos | 57,581 | 35.41 | 439 | 21.43 | 0.76 | 428,499 |
| FCT | 19,617 | 12.06 | 156 | 7.62 | 0.75 | 242,845 |
| Plateau | 9,024 | 5.55 | 57 | 2.78 | 0.63 | 66,908 |
| Kaduna | 8,914 | 5.48 | 65 | 3.17 | 0.73 | 77,538 |
| Rivers | 6,909 | 4.25 | 100 | 4.88 | 1.45 | 160,199 |
| Oyo | 6,838 | 4.20 | 123 | 6.00 | 1.80 | 56,286 |
| Edo | 4,875 | 3.00 | 185 | 9.03 | 3.79 | 33,739 |
| Ogun | 4,617 | 2.84 | 49 | 2.39 | 1.06 | 69,821 |
| Kano | 3,902 | 2.40 | 110 | 5.37 | 2.82 | 91,948 |
| Ondo | 3,168 | 1.95 | 62 | 3.03 | 1.96 | 23,566 |
| Kwara | 3,078 | 1.89 | 55 | 2.68 | 1.79 | 23,684 |
| Delta | 2,599 | 1.60 | 71 | 3.47 | 2.73 | 34,499 |
| Osun | 2,524 | 1.55 | 52 | 2.54 | 2.06 | 18,352 |
| Nasarawa | 2,318 | 1.42 | 13 | 0.63 | 0.56 | 22,546 |
| Enugu | 2,237 | 1.37 | 29 | 1.42 | 1.30 | 22,183 |
| Katsina | 2,083 | 1.28 | 34 | 1.66 | 1.63 | 37,909 |
| Gombe | 2,030 | 1.25 | 44 | 2.15 | 2.17 | 43,517 |
| Ebonyi | 2,007 | 1.23 | 32 | 1.56 | 1.59 | 14,959 |
| Anambra | 1,909 | 1.17 | 19 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 23,999 |
| Akwaibom | 1,762 | 1.08 | 14 | 0.68 | 0.79 | 16,708 |
| Abia | 1,665 | 1.02 | 21 | 1.02 | 1.26 | 21,141 |
| Imo | 1,642 | 1.01 | 37 | 1.81 | 2.25 | 33,517 |
| Bauchi | 1,521 | 0.93 | 17 | 0.83 | 1.12 | 24,498 |
| Borno | 1,327 | 0.82 | 38 | 1.85 | 2.86 | 19,760 |
| Benue | 1,188 | 0.73 | 22 | 1.07 | 1.85 | 16,639 |
| Adamawa | 1,051 | 0.64 | 32 | 1.56 | 3.04 | 18,255 |
| Niger | 930 | 0.57 | 17 | 0.83 | 1.83 | 17,505 |
| Taraba | 910 | 0.56 | 22 | 1.07 | 2.42 | 12,578 |
| Ekiti | 865 | 0.53 | 11 | 0.54 | 1.27 | 16,090 |
| Bayelsa | 852 | 0.52 | 26 | 1.27 | 3.05 | 16,735 |
| Sokoto | 774 | 0.48 | 28 | 1.37 | 3.62 | 18,749 |
| Jigawa | 518 | 0.32 | 16 | 0.78 | 3.09 | 8,987 |
| Kebbi | 442 | 0.27 | 16 | 0.78 | 3.62 | 14,878 |
| Cross River | 366 | 0.22 | 17 | 0.83 | 4.64 | 6,871 |
| Yobe | 313 | 0.19 | 9 | 0.44 | 2.87 | 10,410 |
| Zamfara | 232 | 0.14 | 8 | 0.39 | 3.45 | 7,392 |
| Kogi | 5 | 0.003 | 2 | 0.10 | 40.00 | 4,600 |
© GERMS 2021.
Share and Cite
Okoroiwu, H.U.; Ogar, C.O.; Nja, G.M.E.; Abunimye, D.A.; Ejemot-Nwadiaro, R.I. COVID-19 in Nigeria: Account of Epidemiological Events, Response, Management, Preventions and Lessons Learned. Germs 2021, 11, 391-402. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1276
Okoroiwu HU, Ogar CO, Nja GME, Abunimye DA, Ejemot-Nwadiaro RI. COVID-19 in Nigeria: Account of Epidemiological Events, Response, Management, Preventions and Lessons Learned. Germs. 2021; 11(3):391-402. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1276
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkoroiwu, Henshaw Uchechi, Christopher Ogar Ogar, Glory Mbe Egom Nja, Dennis Akongfe Abunimye, and Regina Idu Ejemot-Nwadiaro. 2021. "COVID-19 in Nigeria: Account of Epidemiological Events, Response, Management, Preventions and Lessons Learned" Germs 11, no. 3: 391-402. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1276
APA StyleOkoroiwu, H. U., Ogar, C. O., Nja, G. M. E., Abunimye, D. A., & Ejemot-Nwadiaro, R. I. (2021). COVID-19 in Nigeria: Account of Epidemiological Events, Response, Management, Preventions and Lessons Learned. Germs, 11(3), 391-402. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1276




