Abstract
Introduction: At present, strongyloidiasis is considered by the World Health Organizaiton (WHO) as one of the most neglected diseases. Case report: A husband and a wife, both born in the Moscow region and never having traveled, initially presented with fever and unexplained peripheral eosinophilia. Parasitological examination revealed Strongyloides stercoralis in feces samples. Helminth infection was strongly associated with poor sanitary conditions. While albendazole was ineffective, after the treatment with ivermectin, both patients were asymptomatic, their ELISA tests were negative, and no larvae of S. stercoralis were found in the feces. Conclusions: We concluded that patients with unexplained eosinophilia must be checked for the presence of parasites before steroid or immunosuppressive therapy. These patients, if infected, may develop the highly fatal hyperinfective syndrome. The cases reported here raise concern about possible hidden strongyloidiasis in the Moscow region and re-emergence of this infection in this and other temperate regions in Russia.
Introduction
At present, strongyloidiasis is considered by the World Health Organizaiton (WHO) as one of the most neglected diseases. Millions of people, predominantly in tropical countries, are infected with Strongyloides stercoralis [1]. Cases of strongyloidiasis are also described in the regions with moderate climate. In Moscow region, local cases of strongyloidiasis were documented in 1982 in 17 patients and in 2004 in two patients [2]. After that, there were no cases of autochthonous strongyloidiasis in the region.
Case report
The observations below describe autochthonous cases of strongyloidiasis in a family of Moscow region residents detected in 2017.
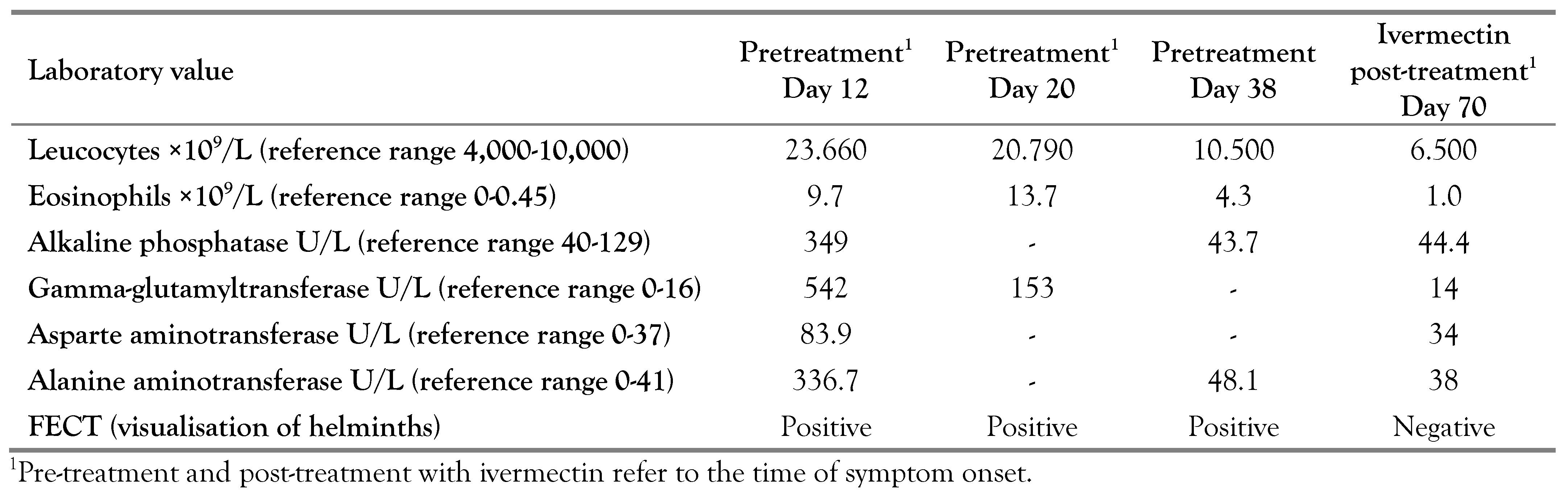
A 57-year-old male was born and lived in one of the villages of Shatursky district, Moscow region. In 2005, he started building a house and spent considerable time in the vegetable garden. On 04.06.2017 he visited a doctor with a fever (37.8 °C), cough, abdominal pain and weakness. On 16.06.2017, following lack of improvement, he was admitted to the hospital and diagnosed with renal colic. In the next several days, his body temperature normalized, the cough and pain in the abdomen stopped and he felt healthy. Blood test revealed leukocytosis, eosinophilia, and increased level of blood sedimentation rate and biochemical markers of liver damage (Table 1). The ultrasound examination of the abdomen was normal. At the same time, formol-ether concentration technique (FECT) revealed rhabditiform larvae S. stercoralis infection in the feces. No other pathologies were detected. Anti- Strongyloides immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Elisa DRG Instruments GmbH, Germany) using the manufacturer's protocols and cut-off value for positive sera. The patients had a positive S. stercoralis serology with OD for S. stercoralis IgG antibodies value of 0.33. Tests for HIV, syphilis, yersiniosis, viral hepatitis and rotaviruses were negative. No pathogenic bacteria were found in stool.

Table 1.
Summary of clinical and laboratory details of patient A.
Albendazole (400 mg, 2 times per day for 3 days) was prescribed on 20.06.2017. FECT revealed larvae of S. stercoralis after treatment with albendazole (Table 1), so ivermectin was prescribed: 12 mg per day for three days.
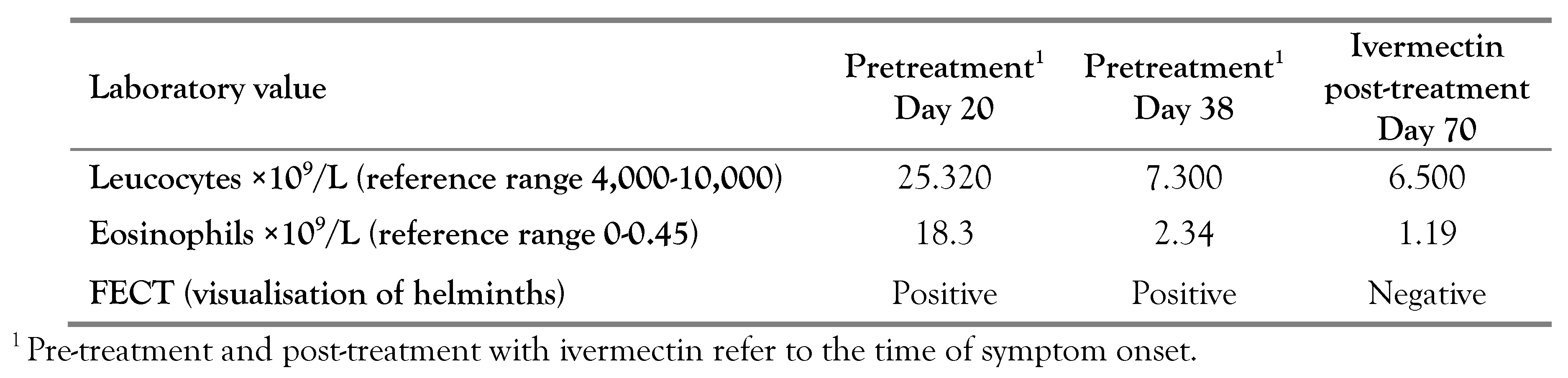
After that, his wife was examined. The 56- year-old female patient presented with the same clinical findings at the beginning of the disease and subsequent progress, as her husband. She did not contact doctors earlier and was examined first on the 20th day from the time of symptom onset (Table 2). At that time she had no complains and was examined strictly because of the epidemiological context.

Table 2.
Summary of clinical and laboratory details of patient B.
The ultrasound examination revealed enlarged lymph nodes in the lesser omentum plane; the nodes were oblong, sized 24×15 mm. The FECT revealed larvae of S. stercoralis. The patient was positive for IgG antibodies to S. stercoralis with OD of 0.42. Albendazole (as above) was prescribed on 25.06.2017, but the FECT revealed larvae of S. stercoralis after the treatment with albendazole. At this point, the treatment was switched to ivermectin (12 mg per day for three days) from 02.08.2017 to 04.08.2017. After three weeks from the symptom onset (and before treatment with ivermectin), the tendency for normalization of blood laboratory parameters (numbers of leucocytes and eosinophils, biochemical values for alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyltransferase, asparte aminotransferase, and alanine aminotransferase) was observed, suggesting the end of S. stercoralis migration. In a month after treatment with ivermectin, further normalization of laboratory values was documented (Table 1 and Table 2).
Blood count, biochemical markers of liver damage, strongyloides IgG antibody (ELISA) and stool were examined after 3, 6 and 12 months. Blood tests were within normal range, and no larvae of S. stercoralis were found in the feces. ELISA test for Strongyloides IgG antibody was positive prior to treatment and then became negative with treatment in both patients after 6 months (OD 0).
Discussion
At present, there are no reliable methods for diagnosing strongyloidiasis. Microscopic examination of stool is not sensitive enough, and enrichment techniques (FECT, for instance) and examination of multiple samples can only partially improve the performance of the method. PCR has not proven to be diagnostically superior to other parasitological techniques in low-density infections, where the larval output is low and irregular [3]. Our observations raise serious concern about possible ongoing autochthonous transmission in Moscow region, and it appears that not all autochthonous cases are being detected. Lifelong infection with S. stercoralis through larval autoinfection and development of potentially lethal hyperinfection syndrome highlights the importance of proper diagnosis of this neglected disease [4].
A number of studies established that a full developmental cycle of S. stercoralis can occur in the zones with moderate climate. The distribution of strongyloidiasis depends on the climate factors, such as humidity and soil temperature, and autochthonous cases were identified in Russia, Spain, Italy and France [2,5,6,7]. In northern Italy, strongyloidiasis is now considered a reemerging disease [8]. Poor sanitary conditions are also very important. In this observation, there was only an outhouse toilet, and patients took feces as a fertilizer from it to the vegetable garden without preliminary composting.
Albendazole was inefficient and the patients were treated with ivermectin confirming previous observations that ivermectin is highly effective for strongyloidiasis treatment [9]. Ivermectin is a drug of choice for strongyloidiasis treatment. Because of the ability of S. stercoralis to autoinfect and its long persistence in the human body, as well as its life cycle that alternates between free-living in moist soil and parasitic stages in the host, eradication of strongyloidiasis and prevention of infection are extremely difficult. The local residents that use feces as fertilizer should be advised to compost and take other necessary disinfection measures.
Conclusions
In previous publications describing cases of strongyloidiasis imported to Moscow from tropical and subtropical regions, the authors supposed that cases of local infection will be found again in Moscow region, and this is just a matter of time [10]. The cases reported here confirm this hypothesis. Due to the global warming, some experts claim that prevalence of helminthiasis is increasing around the globe. Strongyloidiasis in Moscow region, where this infection is endemic, must be considered as a re-emerging disease.
Consent: The patients consented to the publication this case report.
Author Contributions
AMB contributed to manuscript writing. AMB, ANL, MSM and TVS contributed to data collection and manuscript editing. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Conflicts of interest
All authors – none to declare.
References
- Schär, F.; Trostdorf, U.; Giardina, F.; et al. Strongyloides stercoralis: global distribution and risk factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013, 7, e2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstein, A.M.; Malishev, N.A.; Milonova, H.G.; Alautdina, L.V. [Cases of S. stercoralis infection in Moscow region and review of literature]. Med Parazitol (Mosk).
- Buonfrate, D.; Requena-Mendez, A.; Angheben, A. Accuracy of molecular biology techniques for the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection - a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018, 12, e0006229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejia, R.; Nutman, T.B. Screening, prevention, and treatment for hyperinfection syndrome and disseminated infections caused by Strongyloides stercoralis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2012, 25, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, L.; Roure, S.; Fernández-Rivas, G. Strongyloides stercoralis, the hidden worm. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 70 cases diagnosed in the North Metropolitan Area of Barcelona, Spain, 2003-2012. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2013, 107, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Perez, A.; Lopez-Velez, R. Is strongyloidiasis endemic in Spain? PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015, 9, e0003482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Duvignaud, A.; Pistone, T.; Malvy, D. Strongyloidiasis in a young French woman raises concern about possible ongoing autochthonous transmission in Spain. Int J Infect Dis. 2016, 42, 43–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrescia, F.F.; Falda, A.; Caramaschi, G.; et, al. Reemergence of strongyloidiasis, Northern Italy. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009, 15, 1534–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suputtamongkol, Y.; Premasathian, N.; Bhumimuang, K. Efficacy and safety of single and double doses of ivermectin versus 7-day high dose albendazole for chronic strongyloidiasis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011, 5, e1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstein, A.M.; Fedyanina, L.V.; Malyshev, N.A. [Acute and chronic strongyloidiasis in Russian tourists travelled to Thailand, the coast of Black sea in Russia and Abkhazia: problems of diagnosis and treatment. Analysis of cases and review]. Epidemiol Infect Dis (Mosk). 2017, 3, 156–61. [Google Scholar]
© GERMS 2021.