Application of the Modified Fuzzy-PID-Smith Predictive Compensation Algorithm in a pH-Controlled Liquid Fertilizer System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. pH Control Equipment and Control Model
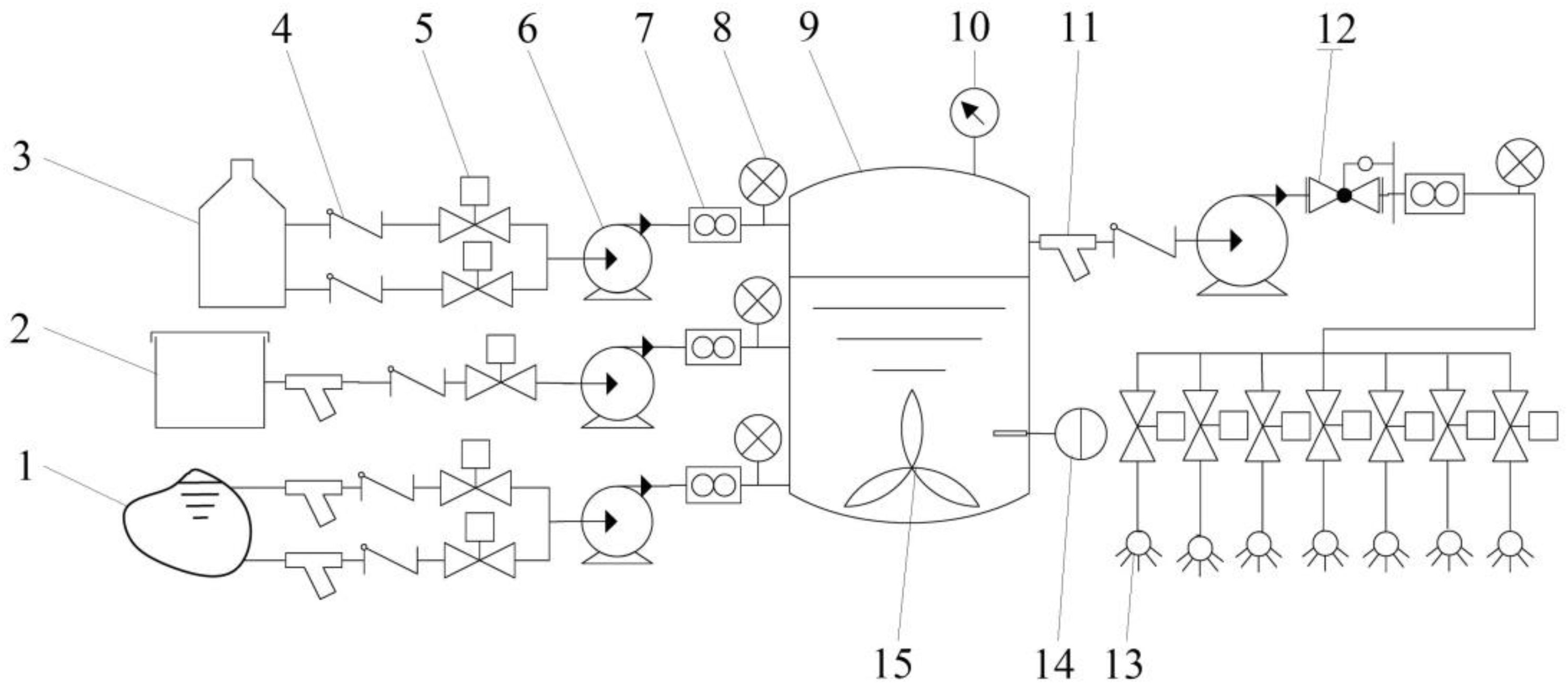
2.1. pH Control Equipment
2.2. Description of the Mixed Fertilizer pH Adjustment Process
2.2.1. Static Model
2.2.2. pH Dynamic Governance Model
2.3. System Identification
3. pH Control System Controller Design Research and Simulation
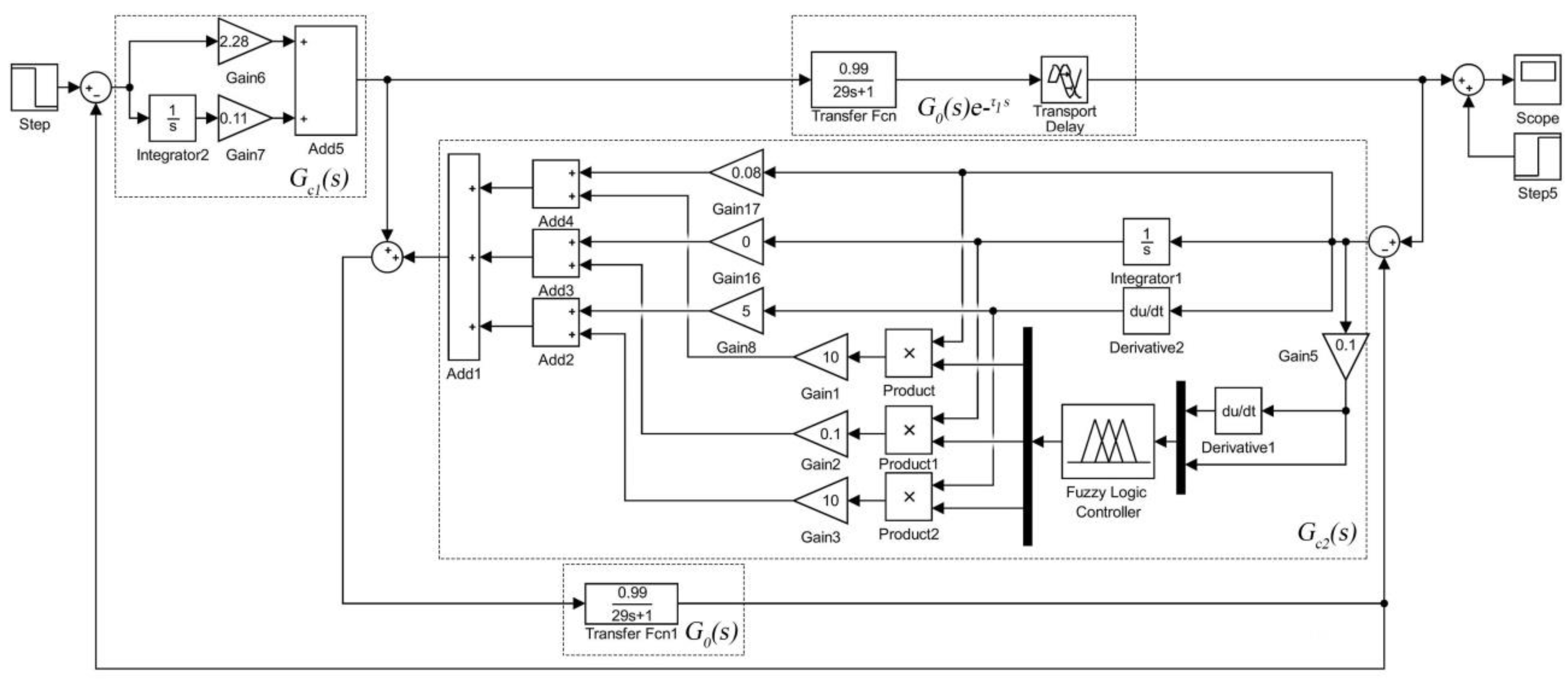
3.1. Design of the Fuzzy-PID Controller
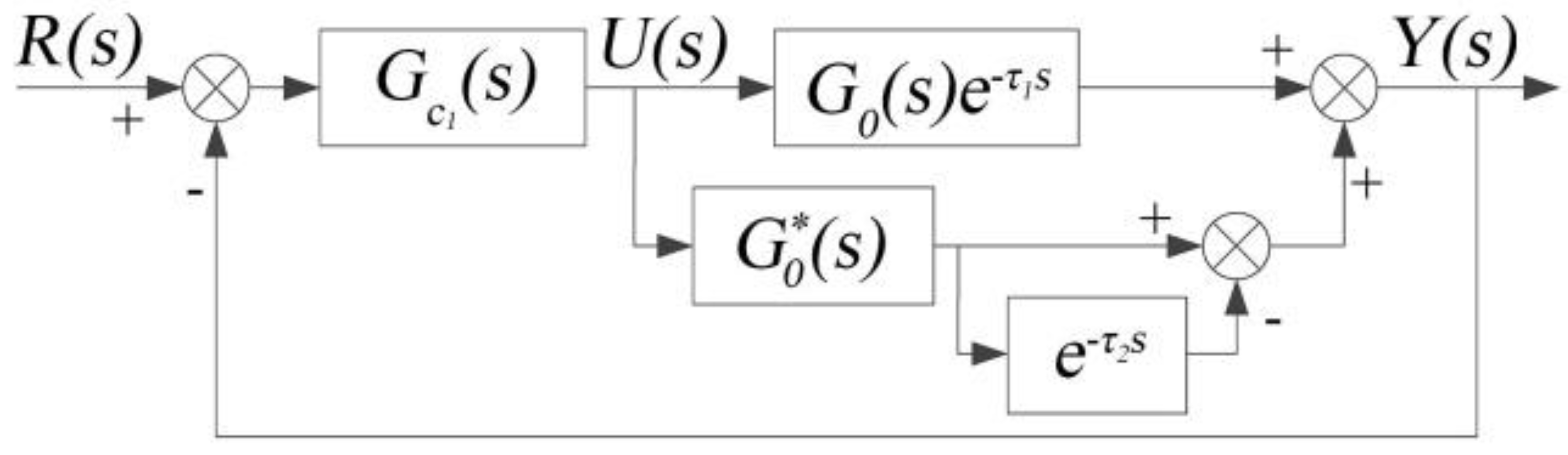
3.2. Design of the Smith Predictor
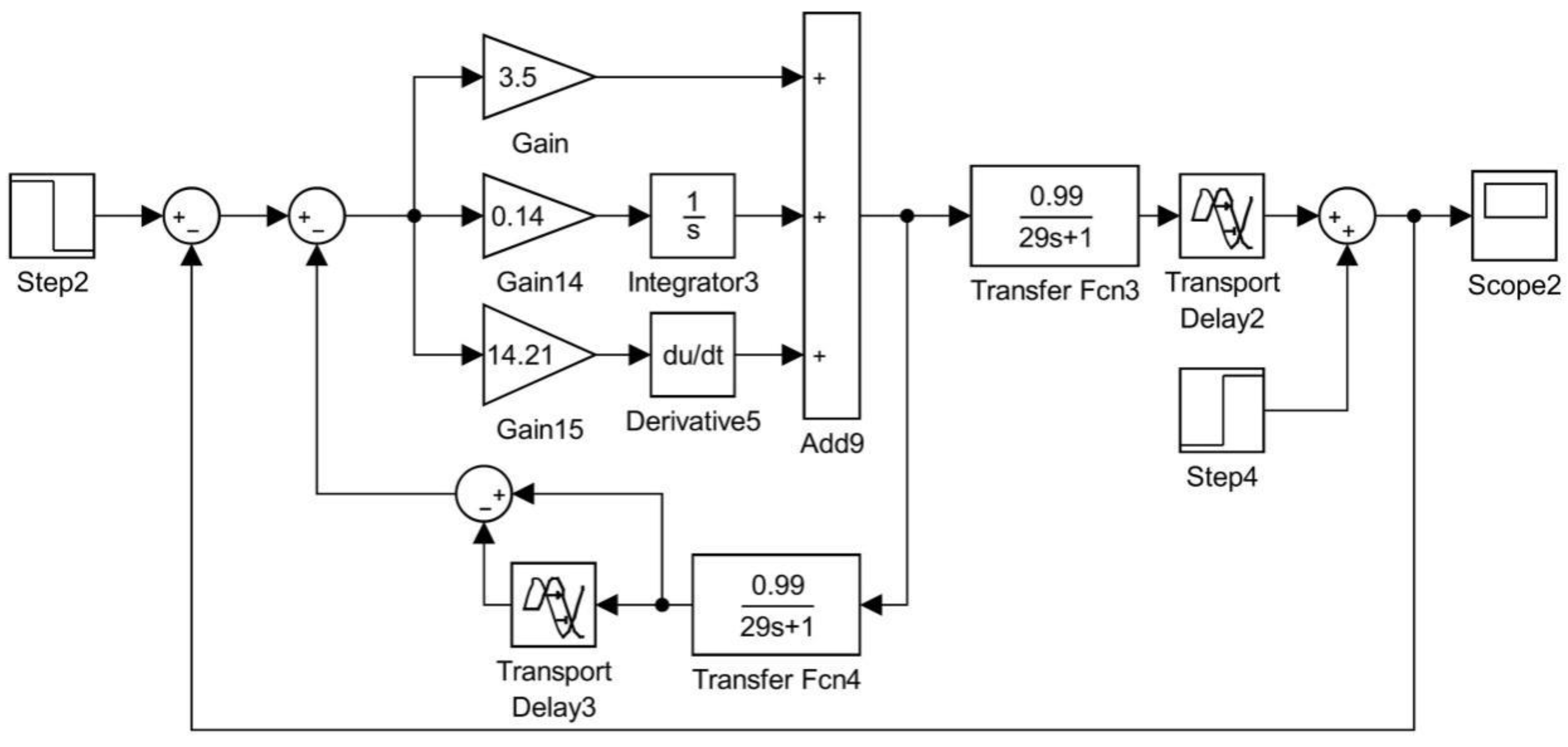
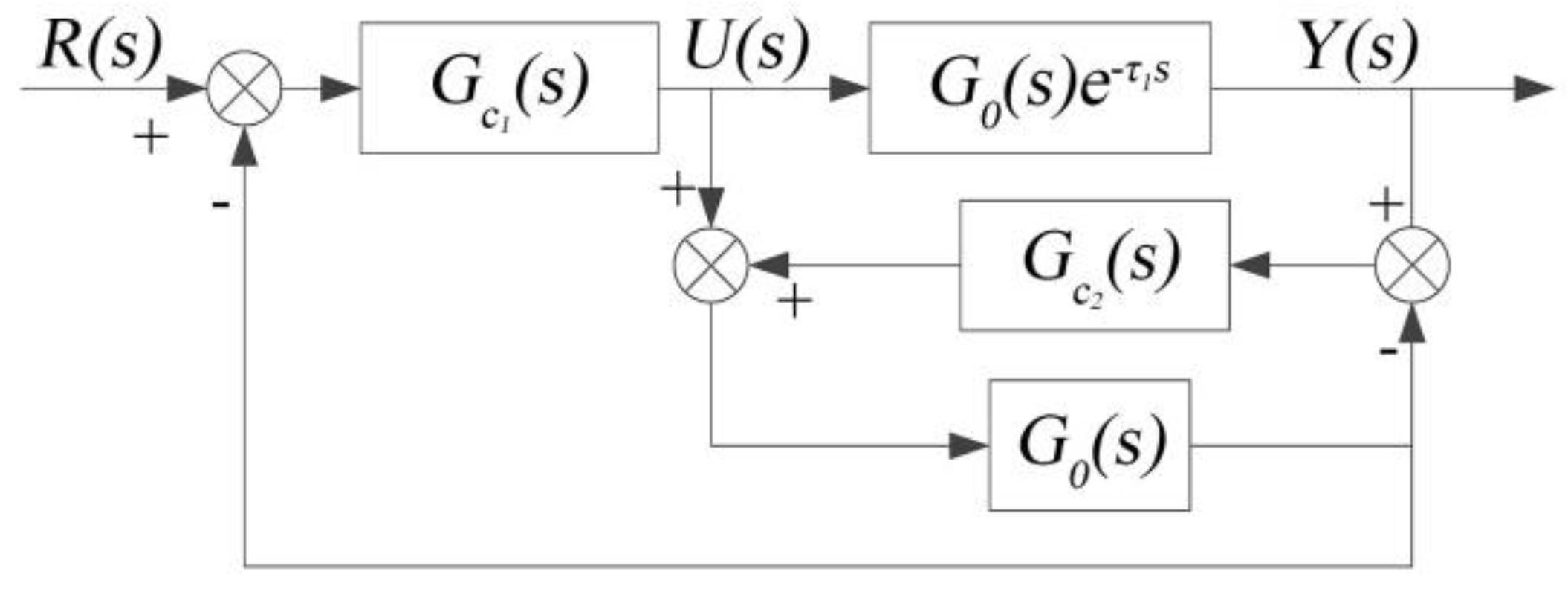
3.3. Design of the Fuzzy-PID-Smith (FP-Smith) Predictive Compensator
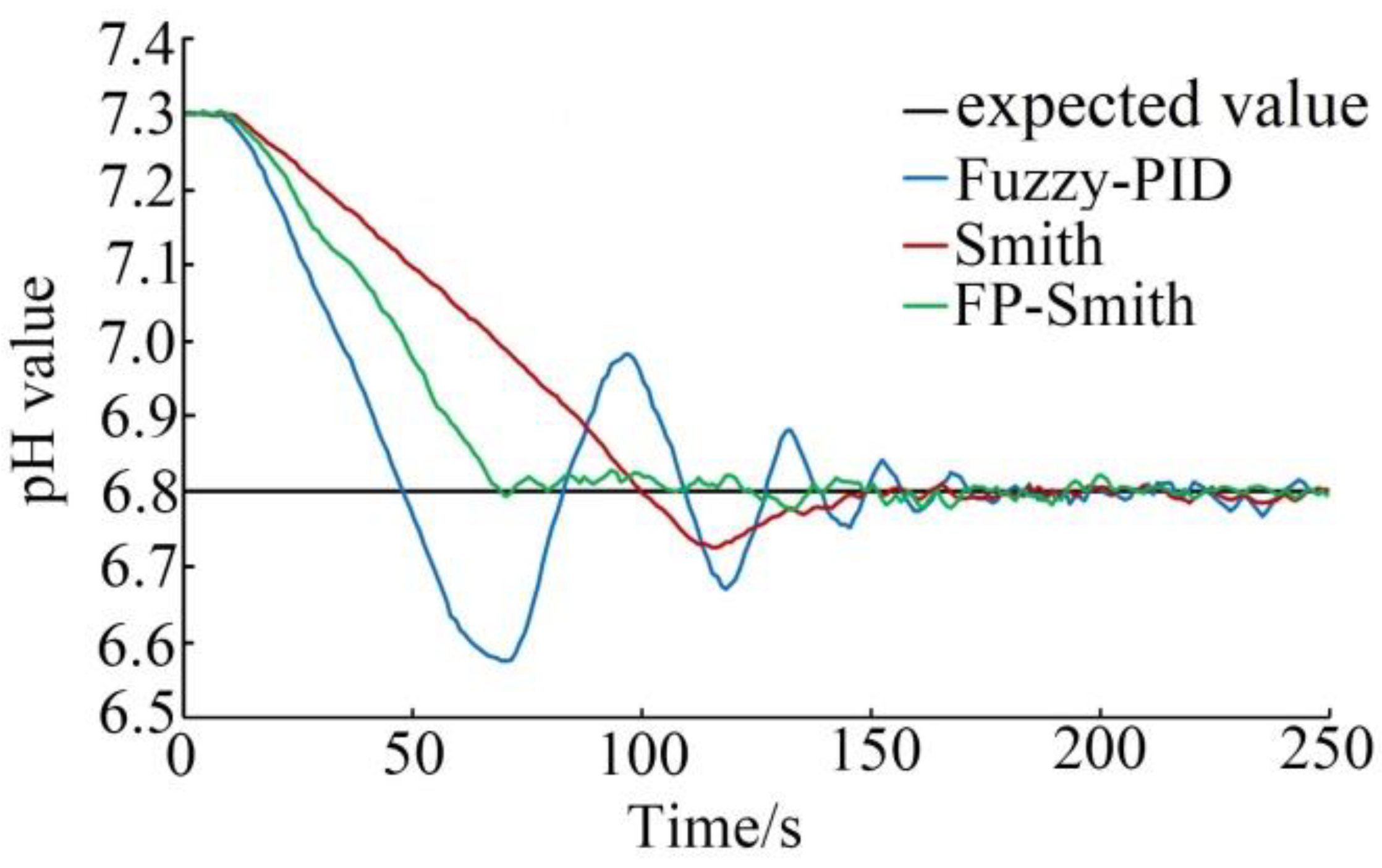
4. Simulation Results
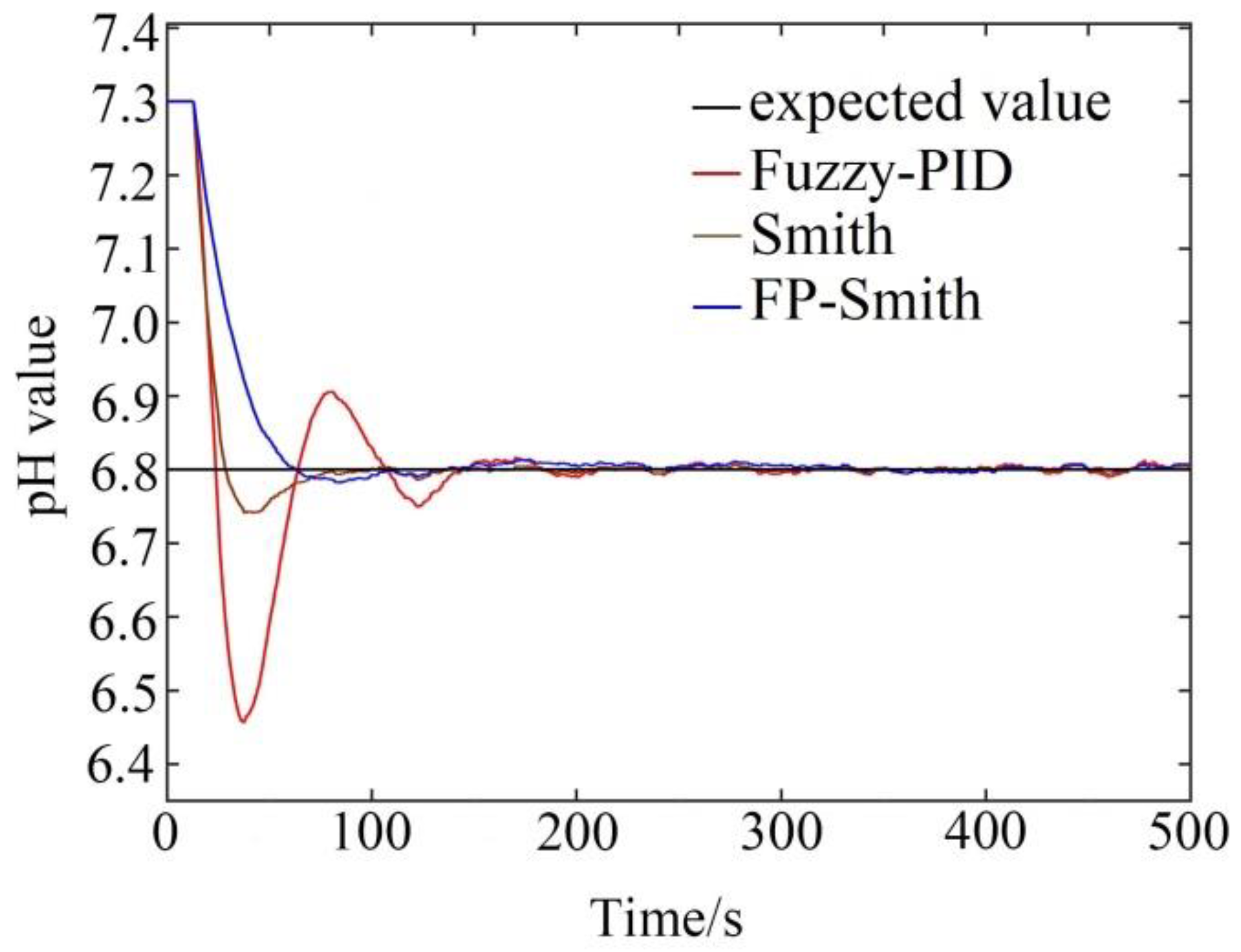
4.1. The Model Is Accurate
4.2. Model Mismatch
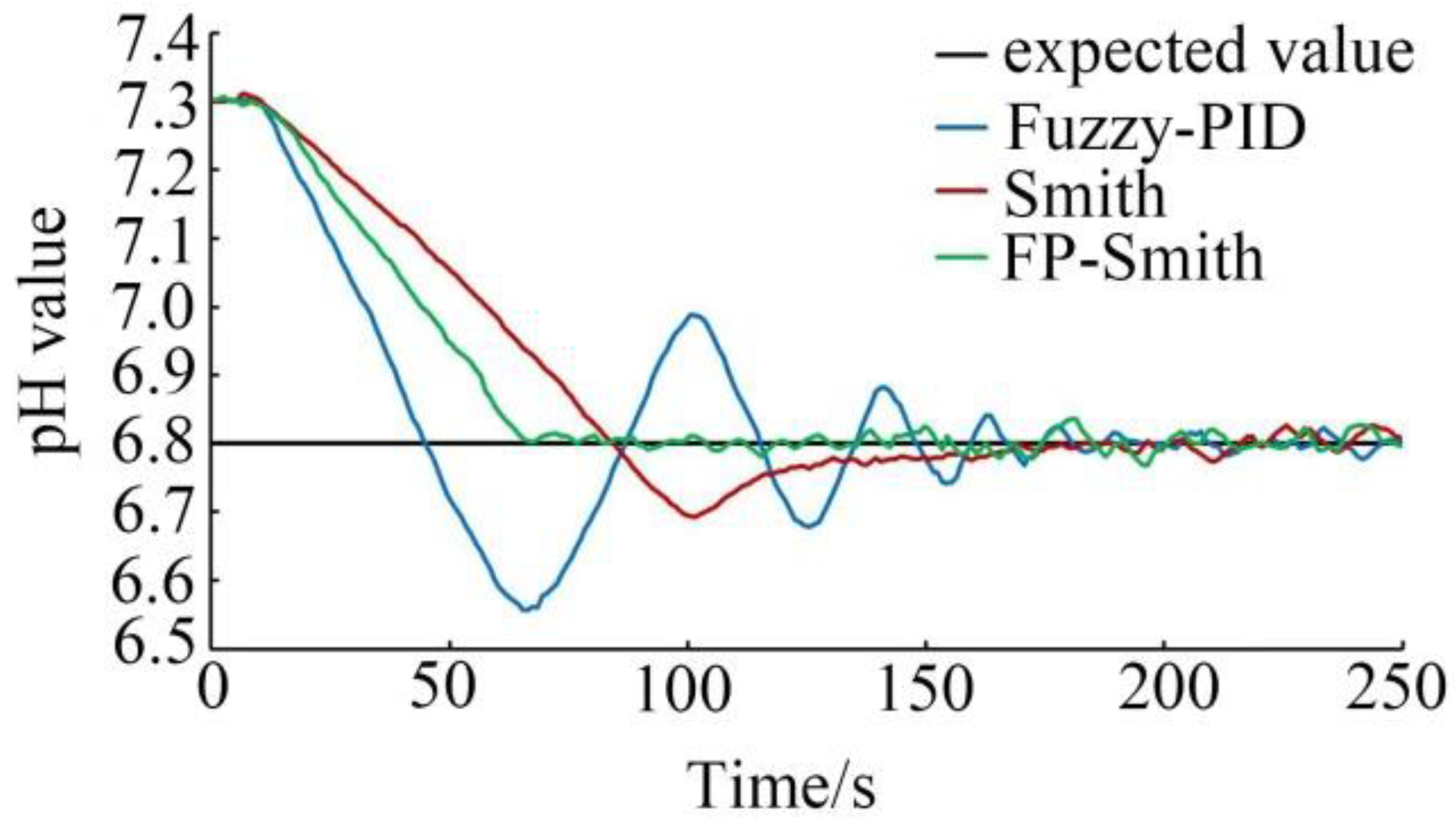
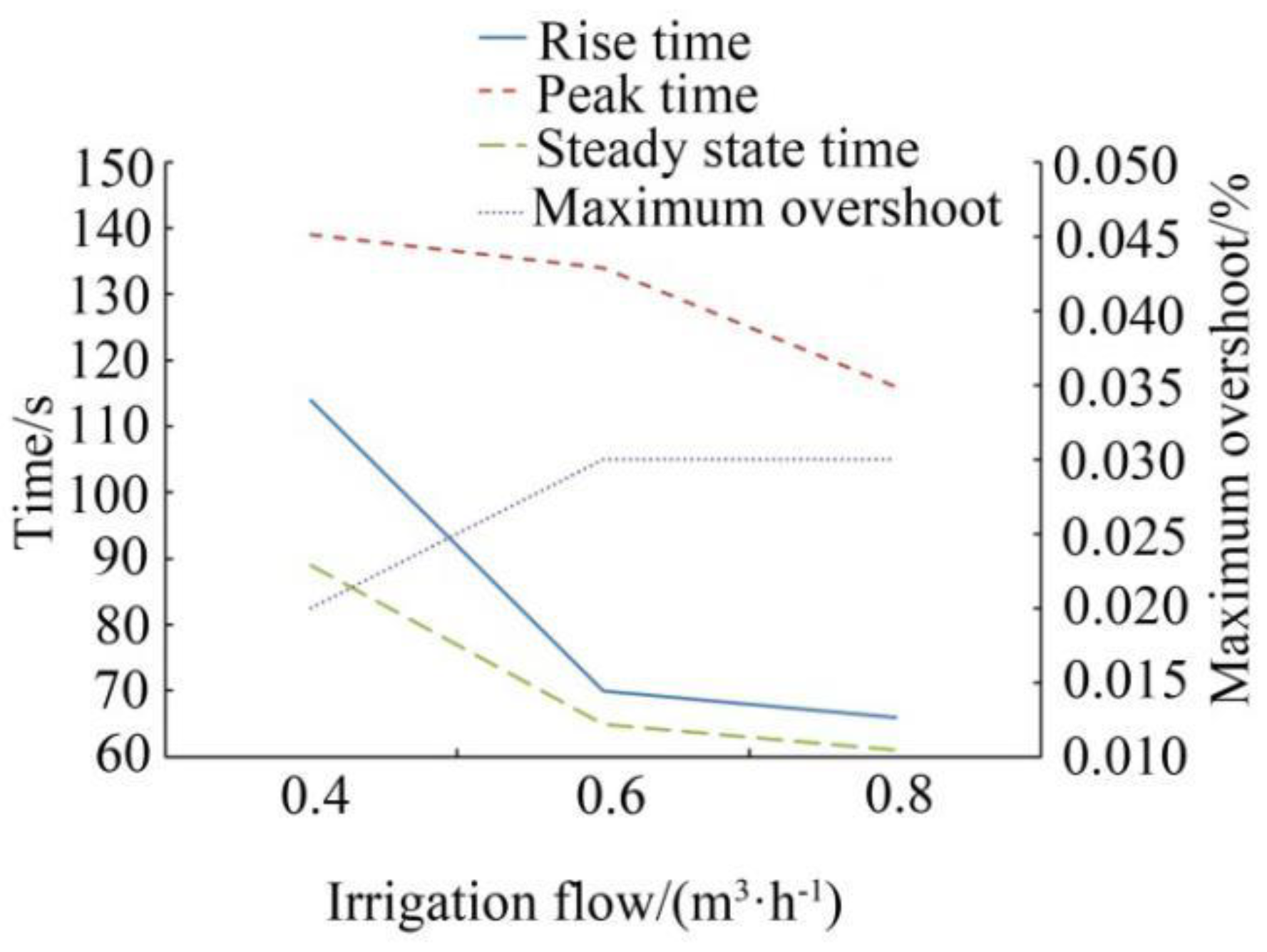
5. Analysis of Experimental Results
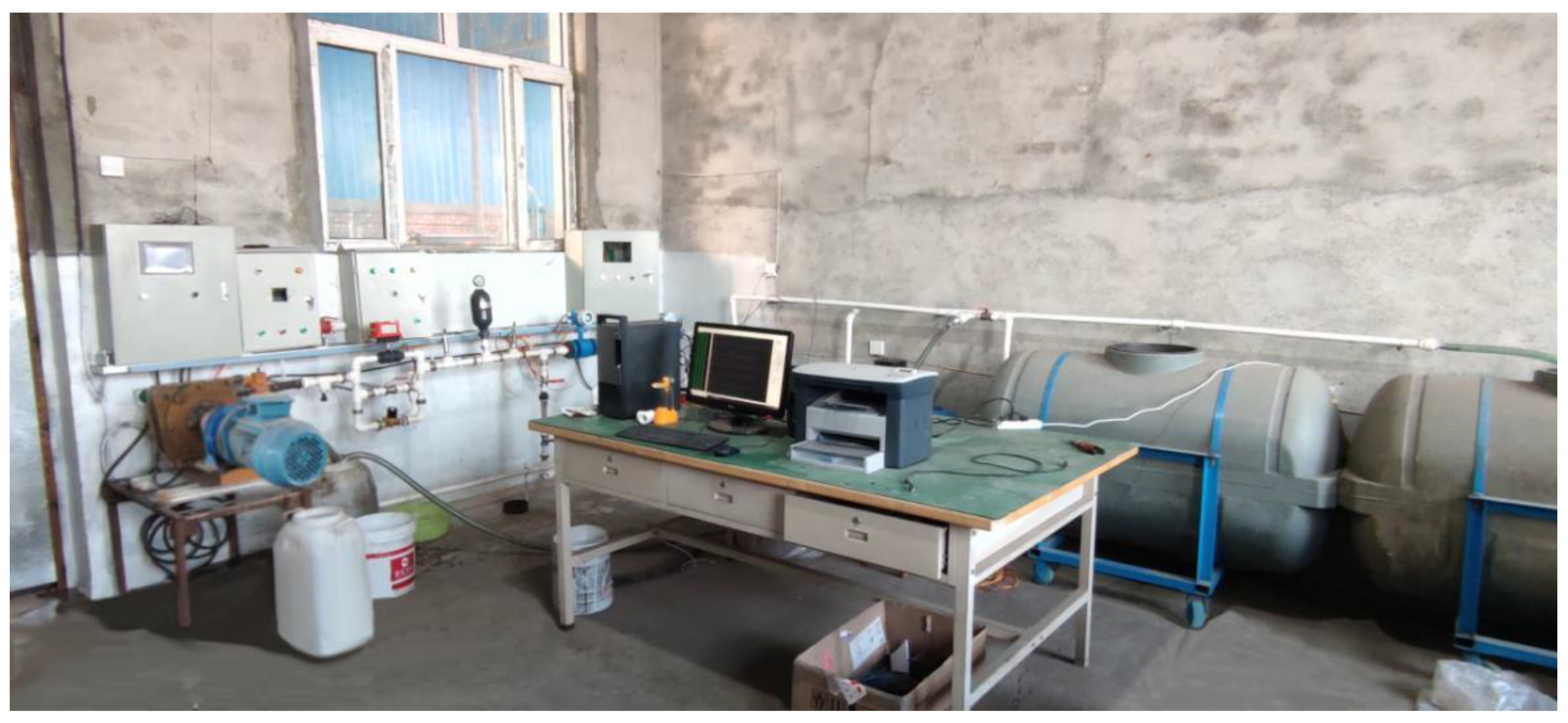
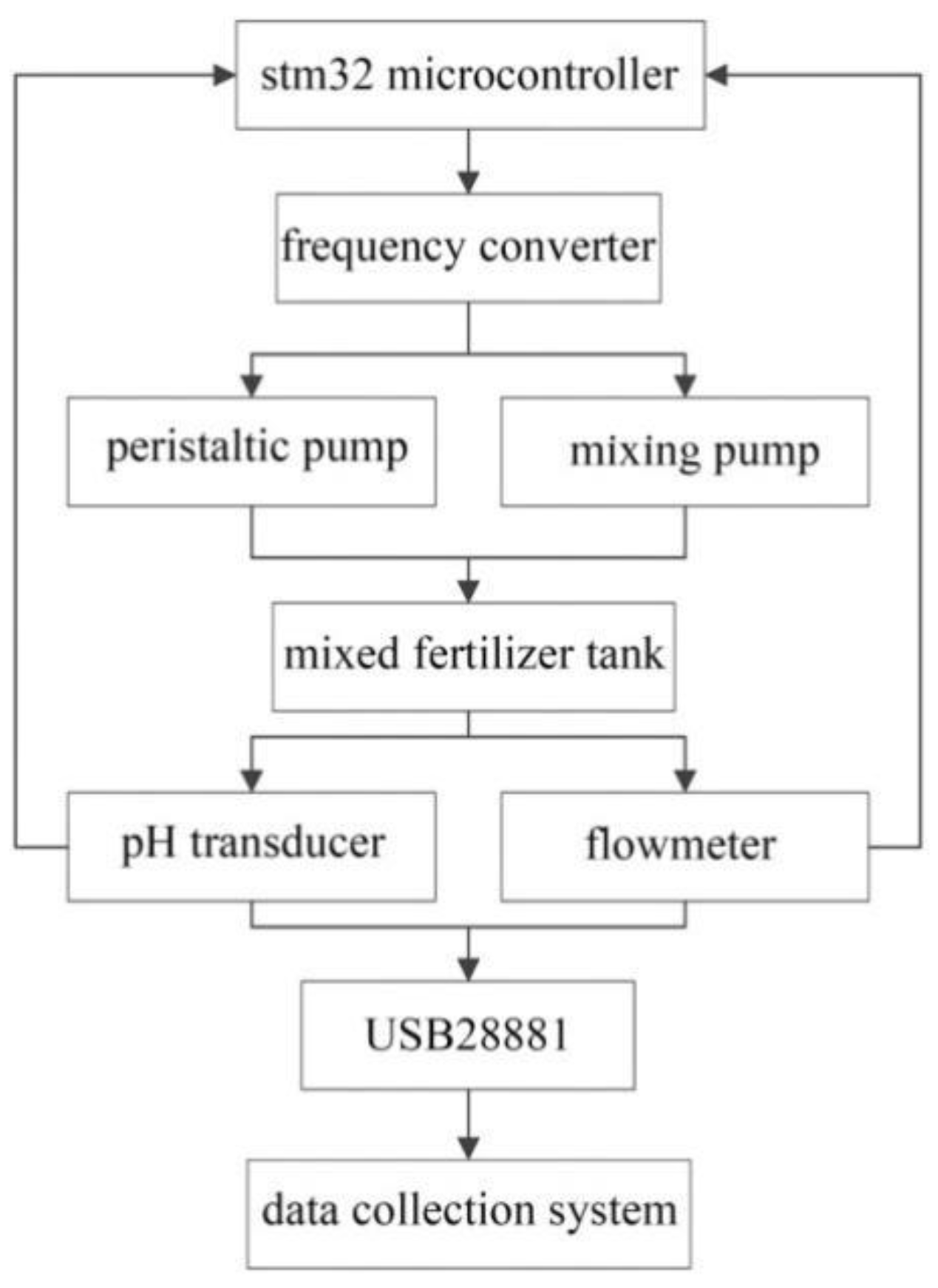
5.1. Experimental Device and System Design
5.2. Analysis of Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuzman, B.; Petković, B.; Denić, N.; Petković, D.; Ćirković, B.; Stojanović, J.; Milić, M. Estimation of optimal fertilizers for optimal crop yield by adaptive neuro fuzzy logic. Rhizosphere 2021, 18, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, F. Effect of fertilizer solution concentrations on filter clogging in drip fertigation systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlRassas, A.M.; Al-qaness, M.A.; Ewees, A.A.; Ren, S.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Damaševičius, R.; Krilavičius, T. Optimized ANFIS Model Using Aquila Optimizer for Oil Production Fore-casting. Processes 2021, 9, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Li, G.; Deng, F. Gain-Scheduled Model Predictive Control for a Commercial Vehicle Air Brake System. Processes 2021, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansson, A.W.; Syafiie, S. Model predictive control of pH neutralization processes: A review. Control Eng. Pract. 2015, 45, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.W.; Lu, F.; Loh, A.P.; Tan, K.C. Modeling and control of a pilot pH plant using genetic algorithm. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2005, 18, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yu, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guo, N. Nonlinear Model Algorithmic Control of a pH Neutralization Process. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 21, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, H.J.; Silva, F.V.D.; Fileti, A.M.F. ANN model adaptation algorithm based on extended Kalman filter applied to pH control using MPC. J. Process Control 2021, 102, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, S.; Poshtan, J.; Jahed-Motlagh, M.R.; Montazeri, A. Nonlinear model predictive control of a pH neutralization process based on Wiener–Laguerre model. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 146, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E. pH Control Using PI Control Algorithms with Automatic Tuning Method. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2001, 79, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaya, R.B.; Palm, S.; Boverie, A. Multilevel qualitative and numerical optimization of fuzzy controllers. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 20–24 March 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Nalovsky, T. Optimization of Fuzzy Controller Parameters for the Temperature Control of Superheated Steam. Procedia Eng. 2015, 100, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, S.; Ahmed, M.A.; Lee, K.-B.; Kim, Y.-C. Fuzzy Logic Weight Based Charging Scheme for Optimal Distribution of Charging Power among Electric Vehicles in a Parking Lot. Energies 2020, 13, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Lee, K.-B.; Ahmed, M.A.; Hayes, B.; Kim, Y.-C. Two-Stage Fuzzy Logic Inference Algorithm for Maximizing the Quality of Performance under the Operational Constraints of Power Grid in Electric Vehicle Parking Lots. Energies 2020, 13, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Ahmed, M.A.; Kim, Y.-C. Efficient Power Management Algorithm Based on Fuzzy Logic Inference for Electric Vehicles Parking Lot. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 65467–65485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zouaoui, Z.; Chen, Z. Neuro-Fuzzy Modified Smith predictor for IPDT and FOPDT Processes Control. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2013, 46, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Xu, J.; Cheng, Y. A Novel Smith Predictive Linear Active Disturbance Rejection Control Strategy for the First-Order Time-Delay Inertial System. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, Z.; Hao, S.; Leng, J.; Wei, Y. Modified Smith fuzzy PID temperature control in an oil-replenishing device for deep-sea hydraulic system. Ocean Eng. 2017, 149, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliu-Batlle, V.; Rivas-Perez, R. Control of the temperature in a petroleum refinery heating furnace based on a robust modified Smith predictor. ISA Trans. 2020, 112, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, K.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, J.; Jing, P. Simulation of hydraulic transplanting robot control system based on fuzzy PID controller. Measurement 2020, 164, 108023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.L.; Díez, J.L.; Valera, A.; Valera, A.; Vallés, M. Remote Fuzzy Control of a DC Motor. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2008, 41, 13652–13658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domanski, P.D.; Lawrynczuk, M. Control Quality Assessment for Processes With Asymmetric Properties and its Application to pH Reactor. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 94535–94546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.A.; Kravaris, C. Nonlinear control of pH processes using the strong acid equivalent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1991, 30, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiącek, J. Geometrical parameters of binary granular mixtures with size ratio and volume fraction: Experiments and DEM simulations. Granul. Matter 2016, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salehi, S.; Shahrokhi, M.; Nejati, A. Adaptive nonlinear control of pH neutralization processes using fuzzy approximators. Control Eng. Pract. 2009, 17, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, G.-B. A Modified 2-DOF Control Framework and GA Based Intelligent Tuning of PID Controllers. Processes 2021, 9, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chen, G.; Ying, H. Predictive fuzzy PID control: Theory, design and simulation. Inf. Sci. 2001, 137, 157–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrea, C.; Páez, F. Design and Comparison of Strategies for Level Control in a Nonlinear Tank. Processes 2021, 9, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSabbah, S.; Aldhaifallah, M.; Al-Jarrah, M. Design of Multiregional Supervisory Fuzzy PID Control of pH Reactors. J. Control Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Z.; Wu, P.; Wu, D. Application of fuzzy adaptive control to a MIMO nonlinear time-delay pump-valve system. ISA Trans. 2015, 57, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.-Y.; Wang, W.-Q. Research on fuzzy self-adaptive PI-Smith control in long time-delay system. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2011, 18, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, Y. Decoupling Adaptive Smith Prediction Model of Flatness Closed-Loop Control and its Application. Processes 2020, 8, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, I.S.; Barbosa, R.S. Smith-fuzzy fractional control of systems with time delay. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 78, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinow, S.I.; Keller, J.B. The transverse force on a spinning sphere moving in a viscous fluid. J. Fluid Mech. 1961, 11, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, D.-H.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Du, D.-S. Smith prediction monitor AGC system based on fuzzy self-tuning PID control. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2010, 17, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

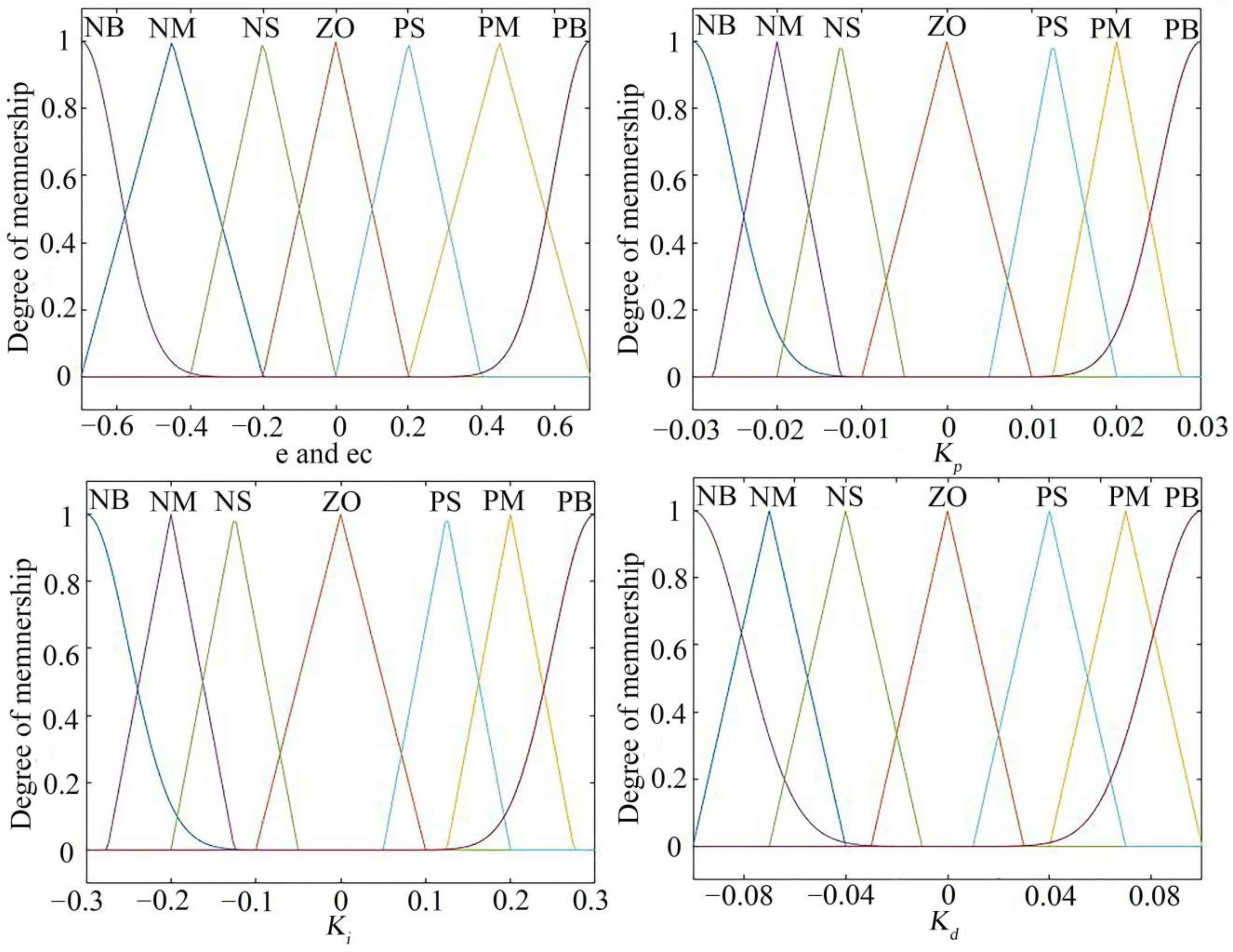




| ec | e | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PB | |
| NB | PB/NB/NB | PB/NB/NB | PM/NM/NM | PM/NM/NM | PS/NS/NS | ZO/ZO/ZO | ZO/ZO/ZO |
| NM | PB/NB/NB | PB/NB/NB | PM/NM/NM | PS/NS/NS | PS/NS/NS | ZO/ZO/ZO | NS/ZO/ZO |
| NS | PM/NB/NB | PM/NB/NB | PM/NS/NS | PS/NS/NS | ZO/ZO/ZO | NS/PS/PS | NS/PS/PS |
| ZO | PM/NM/NM | PS/NS/NS | PS/NS/NS | ZO/ZO/ZO | NS/PS/PS | NM/PM/PM | NM/PM/PM |
| PS | PS/NS/NS | PS/NS/NS | ZO/ZO/ZO | NS/PS/PS | NS/NS/NM | NM/NM/NM | NM/PB/PB |
| PM | ZO/ZO/ZO | ZO/ZO/ZO | NS/PS/PS | NM/PS/PS | NS/PS/PS | NM/PB/PB | NB/PB/PB |
| PB | ZO/ZO/ZO | NS/ZO/ZO | NM/PS/PS | NM/PM/PM | NM/PS/PS | NB/PB/PB | NB/PB/PB |
| the Controller Type | Rise Time(s) | Peak Time(s) | Steady-State Time(s) | Maximum Over-Conditioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy-PID | 20.201 | 29.373 | 87.926 | 4.9% |
| Smith | 41.430 | 60.227 | 77.135 | 0.4% |
| FP-Smith | 45.632 | 56.816 | 37.951 | 0.1% |
| the Controller Type | Rise Time(s) | Peak Time(s) | Steady-State Time(s) | Maximum Over-Conditioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy-PID | 23.855 | 34.479 | 134.732 | 5.1% |
| Smith | 28.639 | 38.479 | 62.124 | 0.9% |
| FP-Smith | 63.272 | 84.440 | 55.135 | 0.3% |
| the Controller Type | Rise Time(s) | Peak Time(s) | Steady-State Time(s) | Maximum Over-Conditioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy-PID | 60 | 80 | 132 | 2.6% |
| Smith | 112 | 132 | 149 | 1.5% |
| FP-Smith | 114 | 139 | 89 | 0.2% |
| the Controller Type | Rise Time(s) | Peak Time(s) | Steady-State Time(s) | Maximum Over-Conditioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy-PID | 49 | 71 | 146 | 3.3% |
| Smith | 101 | 115 | 125 | 01% |
| FP-Smith | 70 | 134 | 65 | 0.3% |
| the Controller Type | Rise Time(s) | Peak Time(s) | Steady-State Time(s) | Maximum Over-Conditioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy-PID | 46 | 67 | 157 | 3.6% |
| Smith | 86 | 102 | 116 | 1.6% |
| FP-Smith | 66 | 116 | 61 | 0.2% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Hu, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, H.; Du, C.; Meng, Z. Application of the Modified Fuzzy-PID-Smith Predictive Compensation Algorithm in a pH-Controlled Liquid Fertilizer System. Processes 2021, 9, 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091506
Shan Y, Zhang L, Ma X, Hu X, Hu Z, Li H, Du C, Meng Z. Application of the Modified Fuzzy-PID-Smith Predictive Compensation Algorithm in a pH-Controlled Liquid Fertilizer System. Processes. 2021; 9(9):1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091506
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Yongchao, Lixin Zhang, Xiao Ma, Xue Hu, Zhizheng Hu, He Li, Chanchan Du, and Zihao Meng. 2021. "Application of the Modified Fuzzy-PID-Smith Predictive Compensation Algorithm in a pH-Controlled Liquid Fertilizer System" Processes 9, no. 9: 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091506
APA StyleShan, Y., Zhang, L., Ma, X., Hu, X., Hu, Z., Li, H., Du, C., & Meng, Z. (2021). Application of the Modified Fuzzy-PID-Smith Predictive Compensation Algorithm in a pH-Controlled Liquid Fertilizer System. Processes, 9(9), 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091506






