Abstract
One of the Korean endemic plants, Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai (Oleaceae), contains acteoside, which is a glycoside exhibiting neuroprotective, anti-inflammation effects and antibacterial capacities. We conducted an investigation on the effects of the callus of A. distichum (cultivar Okhwang 1, CAO) on pro-inflammatory mediators released following nuclear factor-кB (NF-кB), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt (PI3K-Akt) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal activation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Immunoblotting was employed to find out the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), inducible nitric oxide (iNOS), and activation of MAPK molecules, NF-κB and Akt. Cytokines, COX-2, and iNOS gene expression were assessed using polymerase chain reaction techniques. Cytokines, COX-2, and iNOS gene expression were assessed using polymerase chain reaction techniques. High-performance liquid chromatography revealed that CAO was rich in acteoside and isoacteoside. As a result, CAO inhibited the generation of NO, cytokines, COX-2, and iNOS expression. Further, translocation to the nuclear of NF-κB p65 and degradation of the inhibitor of NF-кB (IкB) were alleviated by suppressing phosphorylation. Additionally, CAO significantly impacted MAPK pathway activation by potentially reducing phosphorylation of MAPKs. These results indicate that the anti-inflammatory effect of CAO is mediated via the inhibition of MAPK, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB signaling pathways, probably via glycosides, phenolics, and flavonoids bioactivity derived from plants. CAO can serve as a potential anti-inflammatory agent, which alleviates inflammation factors and act through specific cell signaling pathways.
1. Introduction
Inflammation serves as a response to harmful stimuli. The stimuli are caused by injured cells, pathogens, and endogenous signals, which result in cellular healing to restore normal function [1]. These reactions may repair injured tissues and maintain homeostasis, which is regulated by numerous cytokines and inflammatory mediators, which includes the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, nitric oxide (NO), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) [2,3]. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the main ligand of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), disproportionately initiates the response of innate immunity, resulting in enhanced inflammatory states and causing cell death [4]. LPS activates macrophages to secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxidative species (ROS) [5,6]. Under these stimulations, the pro-inflammatory mediators, including NO and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), are generated in large amounts by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), respectively [7]. COX-2 and iNOS are expressed in responses to various pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can contribute to growing tumors by relating them with angiogenesis and apoptosis [8,9,10,11,12]. The nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is involved in regulating the expression of various genes’ inflammation [13]. In unstimulated cells, this complex is maintained in an inactive structure in the cytoplasm by binding with the NF-κB inhibitor (IκB) [14]. The common NF-κB signaling pathway is activated within stimulation to pro-inflammatory mediators, such as molecular stimulus, pathogens, and cytokines. Activation of NF-κB occurs through ubiquitination of IκB proteins [13,15]. Phosphorylation of IκB protein is followed by its degradation and ubiquitination, which results in releasing NF-κB p50:p65 dimers [16,17]. The released p65 is then translocated to the nucleus, where it binds to target genes and brings about the transcription of related mediators [18,19]. According to recent studies, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt (PI3K-Akt) signaling pathways are related to the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators through IκB degradation and phosphorylation of NF-κB in LPS-induced macrophages. Hence, investigating PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways will contribute to providing an effective therapeutic approach for alleviating inflammation [20]. Thus, the modulation of inflammatory cytokines and mediators could alleviate various inflammatory diseases. Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai, the deciduous shrub of the flowering plants in Oleaceae, is regarded as a unique plant resource as only one species exists worldwide [21]. Okhwang 1 (light yellow-colored corolla), the first official cultivar of A. distichum, displays in contrast to the ivory color of the natural isolate [22]. A. distichum contains glycosides (e.g., acteoside, isoacteoside, rutin, and hirsutrin) and phenolic compounds (e.g., rutin, gentisic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, and quercetin) [23,24]. In particular, acteoside possesses several pharmacological properties, including anti-hepatotoxic [25], anti-inflammatory [26], and antioxidant activities [27]. In plants, acteoside is known to be present only in low concentrations [28,29]. Reportedly, isoacteoside demonstrates anti-cancer [30] and anti-inflammatory effects. When seeking for alternatives to selectively produce useful compounds from plant resources, plant tissue cultures have shown continuous potential in the production of bioactive plant metabolites [31,32]. Both cultured plant cells and whole plant cells synthesize compounds in a qualitatively similar manner [33]. This processing provides an effective alternative source for extracting worthy compounds from plants [34]. Previously, the antioxidant activity, as well as the inhibitory effects on oxidative DNA damage, of the callus of A. distichum have been reported [35]. However, the anti-inflammatory effect of A. distichum Okhwang 1 (CAO) callus and its mechanism are still unclear. Thus, to determine the mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effects of CAO, we investigated whether CAO inhibits the expression of inflammatory mediators and the MAPK, NF-κB, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. As CAO demonstrated the capability to improve LPS-induced inflammatory responses in macrophages, we speculate that the CAO can be developed as a potential resource for reducing inflammation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material of A. distichum Nakai Cultivar OkHwang 1
A. distichum Nakai was collected from GoesanBun-jae-Nongwon (Goesan-gun, Republic of Korea, voucher in InfoBoss Cyber Herbarium (IN); Y. Kim, IB-00589, Figure 1a).

Figure 1.
The representative image of (a) A. distichum var. Okhwang 1 and (b) callus of A. distichum var. Okhwang 1.
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
All chemicals were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA) unless otherwise specified. Acteoside and isoacteoside were purchased from Sigma. Acetonitrile, chloroform, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), ethyl acetate, methanol, and petroleum ether (HPLC-grade) were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). DMEM, FBS, penicillin/streptomycin, and trypsin were purchased from Hyclone (Logan, UT, USA). The antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, UK), Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA), and Cell Signaling Technology (Boston, MA, USA).
2.3. Callus Induction
To induce callus formation [36], a 1 cm2 piece of leaf explants were placed on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium (containing 0.9% agar and 4% saccharose, pH 5.7), supplemented with NAA and 2,4-D, which cultured at 25 °C for 14~21 days. Subsequently, a sufficient amount of calli were obtained through subculture in the same medium (Figure 1b).
2.4. Extraction and Fractionation
The callus from A. distichum (cultivar Okhwang 1, 100 g) were extracted with 80% methanol using a sonicator for 3 days. The extracts were concentrated using a rotary vacuum evaporator (EYELA, Shanghai, China), and then the extracts were fractionated using petroleum ether and ethyl acetate three times. The ethyl acetate fraction of callus from A. distichum (CAO, 254 mg) was in DMSO for the experiment.
2.5. HPLC Analysis
A Waters 2695 system equipped with the Waters 2996 Photodiode array detector (PDA, MA, USA) was used to analyze CAO. The separation was performed using an Xbridge-C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm). The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile (solvent A) and water containing 1% acetic acid (solvent B). The sample injection volume was 10 µL. The flow rate was 1.0 mL/min, for a total run time of 20 min. The system was run using a gradient program: 0–20 min: 90% B to 50% B. The peaks of interest were monitored at 190–380 nm using a PDA detector and compared with the standard substances (acteoside and isoacteoside).
2.6. Cell Culture
The mouse RAW 264.7 macrophages (passage no. 27) were obtained from ATCC (ATCC CRL-2278™, Manassas, VA, USA). The cells were cultured in DMEM, supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% p/s, and maintained under 37 °C, 5% CO2.
2.7. Cell Viability
The effect of CAO on cell viability was measured using the MTS assay kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), following the manufacturer’s protocols. RAW 264.7 cells were seeded in 96-well plates for 24 h in complete medium. The cells were treated with CAO extracts (12.5–400 µg/mL) for 24 h, then exposed to the reagent for 2 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Next, the reduction was measured using the ELx808 plate reader (Biotek, Korea) at 490 nm.
2.8. NO Assay
RAW 264.7 cells were seeded for 24 h. The cells were then treated with CAO for 2 h with 1 µg/mL of LPS. The media were collected for NO analysis. The NO concentrations were analyzed using the Griess reagent (Sigma). Supernatants and the Griess reagent were mixed for 10 min. The absorbance was spectrophotometrically measured using a HumanCorp Xma-3000PC at 540 nm.
2.9. Western Blotting Analysis
The cells were lysed in a RIPA buffer with a 1 × protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Scientific, MA, USA). Total protein in the sample was determined using the Bradford protein assay (Bio-Rad). The proteins were then separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane (Bio-Rad). Next, the membranes were incubated with an appropriate primary antibody, maintained overnight at 4 °C. The primary antibodies included a dilution of an anti-iNOS polyclonal antibody (ab3523), an anti-COX-2 polyclonal antibody (ab52237), a phosphospecific anti-PI3K (Y607) polyclonal antibody (ab182651), an anti-GAPDH (6C5) monoclonal antibody (ab8245, Abcam), a phosphospecific anti-NF-κB p65 (Ser536) (93H1) monoclonal antibody (#3033), a phosphospecific anti-p38 MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182) polyclonal antibody (#9211), an anti-p38 MAPK polyclonal antibody (#8690S1), a phosphospecific anti-p44/p42 MAPK (Thr202/Tyr204) polyclonal antibody (#9101), an anti-p44/p42 MAPK polyclonal antibody (#9102), a phosphospecific anti-SAPK/JNK MAPK (Thr183/Tyr185) polyclonal antibody (#9251), an anti-SAPK/JNK MAPK polyclonal antibody (#9252S), a phosphospecific anti-IκB-α (Ser32) (14D4) monoclonal antibody (#2859), an anti-IκB-α monoclonal antibody (#4812S), a phosphospecific anti-Akt (Ser473) (D9E) monoclonal antibody (#4060, Cell signaling), and an anti-NF-κB p65 (F-6) monoclonal antibody (sc-8008, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) (1:1000). After, the membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies; anti-rabbit IgG-HRP monoclonal antibody (18-8816-33) and anti-mouse IgG-HRP monoclonal antibody (18-8817-33, Rockland) (1:5000) for 1 h. The immunoreactive bands were visualized using an Luminol/enhancer solution (Bio-Rad). The bands were analyzed using the ImageJ software (developed at the National Institutes of Health, USA, http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij, 2020).
2.10. RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from RAW 264.7 cells using Nucleo Spin® RNA Plus (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany), and cDNA was synthesized using Rever Tra Ace –α- (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan) following the manufacturer’s protocol. PCR was performed using Quick Taq® HS Dye Mix (Toyobo). The transcription levels were normalized to those of GAPDH.
2.11. Quantitative PCR Analysis
The cDNAs obtained in the previous experiment were used as templates for qPCR, employing the Quanti Tect® SYBR Green PCR kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). To quantify the mRNA expression, the qPCR analysis was performed using a 7500 Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA). The primers were designed using the Primer 3 program (Table 1). Datasets were analyzed using the ABI 7500 Software version 2.3 (Applied Biosystems). The transcription levels were normalized to those of GAPDH.

Table 1.
Sequences of primers used in the RT-PCR and RT-qPCR analysis.
2.12. Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence was performed to visualize localization of NF-κB, IκB-α, and phosphorylation of Akt upon LPS stimulation. RAW 264.7 cells seeded on glass coverslips were treated with the CAO extract for 24 h with 1 µg/mL of LPS. After treatment, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (Biosesang) Next, the cells were blocked with 3% BSA for 1 h. The cells were then incubated with the appropriate primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C. The primary antibodies included an anti-NF-κB p65 antibody (1:500), an anti-IκB-α antibody (1:500), and a phosphospecific anti-Akt antibody (1:500). After, cells were incubated with the appropriate secondary antibodies at a 1:1000 dilution of an anti-mouse IgG (Alexa Fluor® 488) polyclonal antibody (ab150113) and an anti-rabbit IgG (Alexa Fluor® 568) polyclonal antibody (ab175471, Abcam) or 300 nM of DAPI (D1306, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) for 5 min in the dark. Finally, sample coverslips were mounted using Fluorescence Mounting Medium (S3023, Dako, Carpinteria, CA, USA). The observations were performed using a fluorescence microscope and a CKX53 microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) with 400× magnification, and micrographs were captured with a Digital Single-Lens Reflex Camera (DS126271, Canon, Tokyo, Japan).
2.13. Statistical Analysis
All the data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 5.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) and are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. The data were analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance, with Tukey’s multiple-comparisons post-hoc test employed for comparing mean values among multiple groups.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Acteoside and Isoacteoside in CAO
To identify and quantify acteoside and isoacteoside of CAO, the major chemical constituents were analyzed by HPLC and compared with its standards. The chromatogram of CAO was identified by comparing the retention time (RT) to that of standard acteoside and isoacteoside at 330 nm. The HPLC results revealed acteoside and isoacteoside contained in CAO (RT = 19.87 and 22.85) (Figure 2A), and it was compared with that of standard acteoside and isoacteoside (RT = 20.10 and 22.83) (Figure 2B). Compared with the standard curve, the amount of acteoside was analyzed to be 399.27 ± 2.3 mg/g (39.93% w/w), and isoacteoside was analyzed to be 56.69 ± 1.1 mg/g (5.67% (w/w) in CAO. These results confirmed that acteoside and isoacteoside, with chemical structures shown in Figure 2C,D, are the major compounds in CAO.
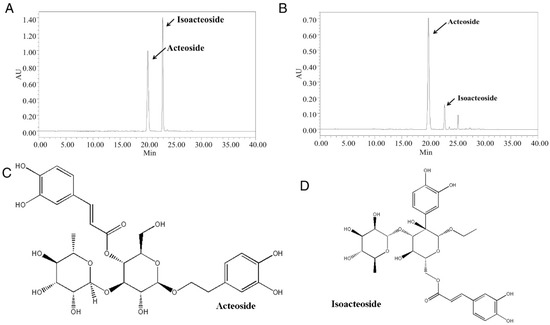
Figure 2.
HPLC chromatogram of CAO and chemical structures of two glycosides. (A) HPLC chromatogram of CAO in 330 nm. (B) HPLC chromatogram of acteoside and isoacteoside standard in 330 nm. (C) The chemical structure of acteoside. (D) The chemical structure of isoacteoside. AU, arbitrary units; CAO = callus of A. distichum var. Okhwang 1.
3.2. Effects of CAO on Cell Viability
To conduct cell viability assay, RAW 264.7 macrophages were cultured with CAO (0–400 μg/mL). After 24 h, cell viability was assayed using MTS assay. In macrophages, the CAO was non-cytotoxic below 400 μg/mL and did not significantly suppress cell growth. The results demonstrated that the CAO extract was non-cytotoxic in RAW 264.7 cells below 400 μg/mL and did not significantly suppress cell growth (Figure 3A).
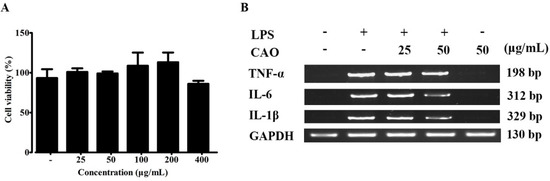
Figure 3.
(A) Effect of CAO on cell viability in macrophages. Cells were treated with CAO for 24 h. Cell viability was measured using MTS assay. (B) Inhibitory effects of CAO on pro-inflammatory cytokine secretions by RT-PCR. Data are expressed as means ± SD (n ≥ 3). CAO = callus of A. distichum var. Okhwang 1.
3.3. Effects of CAO on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Secretions
As shown in Figure 3B, the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) increased under LPS treatment. However, treatments with CAO (25 and 50 µg/mL) showed inhibitory effects against LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretions in macrophages. In particular, CAO at 50 µg/mL significantly down-regulated the released levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and IL-1β) compared with the LPS-treated group.
3.4. Effects of CAO on NO Production, COX-2 and iNOS Expression
NO production is shown in Figure 4A. LPS-induced macrophages produced significant amounts of NO (1443.9 ± 31.6%) when compared to the control (100%). However, the production of NO was significantly attenuated following CAO treatment at 25 (1166.7 ± 46.8%) and 50 μg/mL (753.8 ± 68.6%) compared with CAO alone treatment (107.61 ± 6.1%). To investigate the mechanisms by which CAO suppressed the production of NO, the expression of COX-2 and iNOS was measured. As shown in Figure 4, western blotting analysis demonstrated that 24 h of LPS stimulation significantly upregulated iNOS (4.16 ± 0.12-fold) and COX-2 (1.52 ± 0.03-fold) protein expression (Figure 4B,D). CAO treatments at 50 μg/mL significantly attenuated the expression (1.82 ± 0.12-fold and 0.98 ± 0.04-fold). Additionally, we investigated whether CAO inhibited iNOS (Figure 4C,E) and COX-2 (Figure 4C,F) mRNA levels. The significantly increased iNOS (12.21 ± 0.08-fold) mRNA expression was attenuated following CAO treatments (9.57 ± 0.15-fold at 50 μg/mL) when compared to the control. As detected by RT-qPCR, the expression levels of iNOS followed a similar pattern as those detected by RT-PCR (Figure 4e). Furthermore, the significantly increased COX-2 (6.46 ± 0.04-fold) mRNA expression was attenuated following CAO treatments (5.59 ± 0.09-fold at 50 μg/mL); the COX-2 expression levels detected by RT-qPCR followed a similar pattern (Figure 4f).
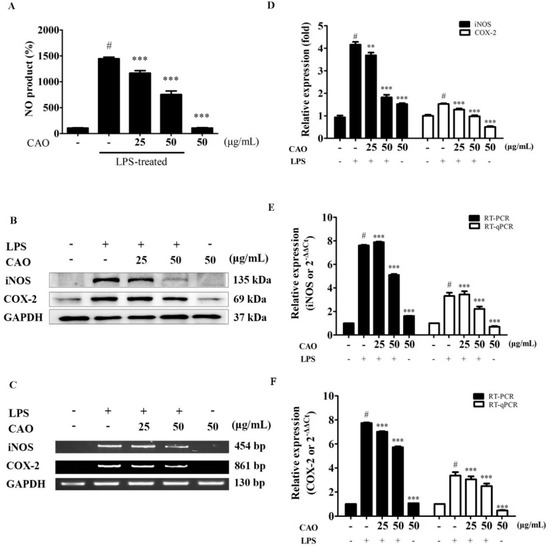
Figure 4.
Effect of CAO on NO production, COX-2, and iNOS expression in macrophages. (A) released NO production to the medium was evaluated using a Griess reagent assay. (B) The expressions of COX-2 and iNOS protein were subjected to immunoblotting. (C) The COX-2 and iNOS mRNA levels were subjected to RT-PCR. (D) The bar graphs of the protein expression. (E) The bar graphs of RT-PCR and RT-qPCR for iNOS. (F) The bar graphs of RT-PCR and RT-qPCR for COX-2. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n ≥ 3). # p < 0.001 vs. non-treated cells. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. LPS-treated cells. NO = nitric oxide; CAO = callus of A. distichum var. Okhwang 1.
3.5. Effects of CAO on IκB/NF-κB Signaling Pathways
To demonstrate the effects of CAO on the signaling pathway of IκB/NF-κB, focuses on the inhibited inflammatory response, immunoblotting was carried out to confirm the inhibitory effect of CAO on the phosphorylation of NF-κB and degradation of IκB. Our results demonstrated that CAO suppresses the NF-κB signaling mechanisms by inhibiting the phosphorylation of IκB-α. CAO significantly blocked the degradation of IκB-α in a concentration-dependent manner. Furthermore, CAO significantly attenuated p-p65 without altering the total level of p65 (Figure 5B,D). Next, we performed an immunofluorescence investigation to monitor the expression of the NF-κB subunit. Immunofluorescence data obtained from individual cells confirmed our finding that CAO treatment at 50 µg/mL potentially inhibited the translocation of phosphorylated NF-κB (subunit p65) and the degradation of IκB-α (Figure 6A,B).
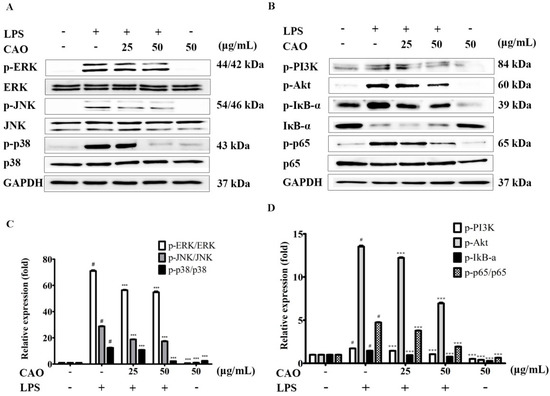
Figure 5.
Effect of CAO on MAPK phosphorylations and PI3K/Akt/IκB/NF-κB signaling pathways in macrophages. (A) The expression of MAPK phosphorylations was subjected to immunoblotting. (B) The expression of PI3K/Akt/IκB/NF-κB phosphorylations was subjected to immunoblotting. (C) The levels of p-ERK, p-JNK, and p-p38 phosphorylations compared to the value of each non-treated group. (D) The levels of PI3K, Akt, IκB-α, and p65 phosphorylations compared to the value of each non-treated group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n ≥ 3). # p < 0.001 vs. non-treated cells. *** p < 0.001 vs. LPS-treated cells. CAO = callus of A. distichum var. Okhwang 1.
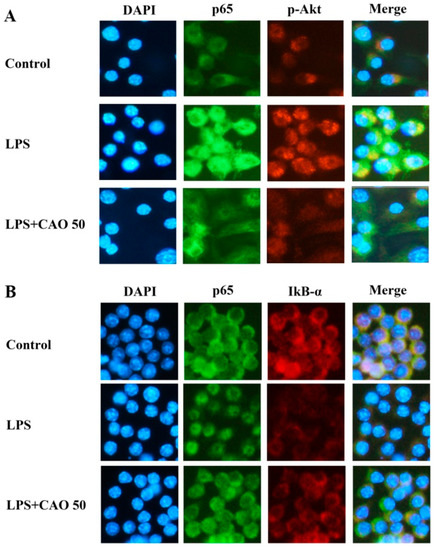
Figure 6.
Effects of CAO on the expression of NF-κB and p-Akt in macrophages. (A) The immunofluorescence images show NF-κB staining (green), p-Akt staining (red), and Nuclei (blue). (B) The immunofluorescence images show Nuclei (blue), NF-κB staining (green), and IκB-α staining (red). Each image was captured at 400× magnification. CAO = 50 μg/mL of callus of A. distichum var. Okhwang 1.
3.6. Effects of CAO on PI3K-Akt Activation and MAPKs Pathway
The activation of the MAPK (ERK1/2, JNK1/2, and p38) and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is crucial for initiating the NF-κB signal transduction pathway. We sought to identify the activities of action by which CAO reduces the production of inflammatory cytokines. LPS induction significantly increased Akt phosphorylation; this enhanced phosphorylation was suppressed by CAO. Furthermore, CAO demonstrated that the ERK1/2 (except 25 μg/mL), JNK1/2, and p38 phosphorylation levels induced by LPS were significantly inhibited (Figure 5A,C). Additionally, we confirmed the effect of CAO on the phosphorylation of Akt through immunoblotting (Figure 5B) and immunofluorescence investigations (Figure 6A). These results demonstrated that CAO suppressed the expression and detection of phospho-Akt in individual cells. Collectively, our results suggest that CAO reduced the production of NO, COX-2, and iNOS expression by down-regulating the LPS-induced ERK, JNK, p38 MAPKs, IκB-α/NF-κB, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.
4. Discussion
According to a study on chemotaxonomy of the Oleaceae [37], the Oleaceae family synthesizes and distributes iridoid glucosides. Abeliophyllum, one of the Oleaceae family, synthesizes caffeoyl phenylethanoid glycosides (cornoside and acteoside). In particular, A. distichum Nakai is known to predominantly contain acteoside and isoacteoside [24]. Regarding A. distichum, which consists of only one species worldwide, several researchers have investigated its environmental and ecological characteristics, genome sequences, and bioactivities [21,22,38,39,40,41]. Reportedly, a previous study has proved that the inhibitory effects on the inflammation of the A. distichum leaf are facilitated via the inhibition of ERK-mediated NF-κB phosphorylation in mouse monocytes [42]. However, research on Okhwang 1, a new official cultivar of A. distichum, is lacking, except for studies regarding the genetic characteristics. Moreover, the study on the pharmacological properties of the callus induced by plant cell culture remains insufficient. In the present study, we tried to assess whether the treatment of RAW 264.7 macrophages with CAO may affect the expression on selected pro-inflammatory factors. To analyze the chemicals present in CAO, HPLC analyses were performed to identify major phytochemicals. As a result of HPLC analysis, two components are predominant in CAO, which are analyzed to acteoside and isoacteoside compared to purchased standard products. Macrophages/monocytes can be stimulated by LPS to produce pro-inflammatory molecules (NO, PGE2, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, etc.) by leading signaling pathways (including IκB/NF-κB, PI3K/Akt, and MAPKs) in cells [43,44,45]. In these processes, the immune system adjusts macrophages, which play a crucial role in responding immune or participating in inflammatory responses [46,47,48,49]. COX-2 and iNOS are important factors involved in the production of excess PGE2 and NO at the inflammatory sites and are known to play important roles during the pathogenesis of chronic diseases [47,50,51]. Therefore, the strong inhibitory effects on iNOS and COX-2 expression, documented by several reports, are immensely worthy in treating and preventing inflammatory disorders [49]. Results of cell viability indicate that CAO did not significantly affect cell proliferation. In LPS-induced macrophages, CAO significantly inhibited producing NO. NO production levels are related to the expression of COX-2 and iNOS. CAO significantly inhibited LPS-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression at the transcriptional levels. These findings suggest that the suppression of NO release by CAO could be due to the inhibition of COX-2 and iNOS. MAPKs are involved in directing cellular responses to pro-inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, they control cellular functions, including gene expression, apoptosis, proliferation, mitosis, differentiation, and cell survival [52]. The MAPKs, which control cellular signal transduction to the nucleus, consist of serine/threonine kinases, such as JNK, p38 MAPK, and ERK [53]. The phosphorylation of MAPKs has been involved in signaling pathways linked to LPS-induced inflammation, which suggests that MAPKs are a major molecular for regulating inflammation [54,55]. We identified the mechanism of action by which CAO reduces the production of inflammatory mediators. CAO significantly inhibited LPS-induced ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPKs. The ability of CAO to regulate the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 may also affect a reduction in COX-2 and iNOS expression. These results are supported by the fact that MAPKs are involved in the regulation of COX-2 and iNOS genes, as inhibition of MAPK activity results in the suppression of COX-2 and iNOS gene expression [56]. Based on the inhibitory effects of CAO on COX-2 and iNOS expression, we investigated whether CAO could suppress the phosphorylation IκB/NF-κB pathway under LPS stimulation. Furthermore, we confirmed the expression of NF-κB by an immunofluorescence investigation. NF-κB that controls the transcription of DNA regulates the expression of target genes coding for pro-inflammatory mediators involved in immune and inflammatory responses, including cytokines [57,58]. Therefore, NF-κB is regarded as a target molecular for inflammatory treatment strategies [59,60]. The degradation of IκB and phosphorylation of MAPKs are the upstream regulatory signaling pathways for the transcriptional activation of NF-κB [13]. CAO reduced LPS-stimulated inflammation through the inhibition of phosphorylation of NF-κB. Furthermore, phosphorylation and degradation of IκB were inhibited following CAO treatment. Based on immunofluorescence data detected in individual cells, we confirmed our discovery that the LPS-induced phosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus of NF-κB was potentially inhibited by CAO treatment. These findings verify that CAO might regulate the production of cytokines, chemokines, and NO through suppressing IκB degradation, thus inhibiting translocation to the nucleus of NF-κB. Therefore, the inhibition of these signaling pathways could demonstrate the potential of CAO as a suppressor of inflammatory mediators. Additionally, IκB/NF-κB, MAPKs, and PI3K/Akt is another signaling pathway that controls the expression of inflammatory factors by activating the NF-κB signal transduction pathway [61]. Thus, suppression of phosphorylation is known to be a main target to modulate inflammatory disorders. CAO significantly suppressed LPS-induced PI3K/Akt phosphorylation. Furthermore, immunofluorescence data from cells confirmed that the phosphorylation of Akt was inhibited by CAO treatment, leading to the retention of p65 in the cytoplasm. Additionally, correlation among the expression of IκB and the penetration to the nuclear of p65 was shown. In the present study, we demonstrated that the suppression of NO production and iNOS and COX-2 expression by CAO was mediated through the down-regulation of MAPKs, NF-κB, and PI3K/Akt pathways. In conclusion, we suggest that CAO has anti-inflammatory effects and could be a superior candidate for an anti-inflammation agent derived from natural resources.
5. Conclusions
In summary, treatment of CAO can reduce the levels of cytokines, iNOS, and COX-2 in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Moreover, CAO affected particular proteins regulating MAPK, NF-κB, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways. In conclusion, the present study suggests that the treatment of CAO could be a potential resource for alleviating inflammatory diseases by significantly attenuating specific factors in LPS-induced signaling pathways.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, T.-W.J. and J.-H.P.; supervision, project administration, J.-H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- A current view on inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 825. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Hattori, S.; Kasai, K. Lipopolysaccharide activates Akt in vascular smooth muscle cells resulting in induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase through nuclear factor-kappa B activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 481, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Bowie, A.G. The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savva, A.; Roger, T. Targeting toll-like receptors: Promising therapeutic strategies for the management of sepsis-associated pathology and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.Y.; Wen, M.H. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated reactive oxygen species and signal transduction in the regulation of interleukin-1 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22131–22139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, R.Z.; Stow, J.L. Cytokine secretion in macrophages: SNAREs, Rabs, and membrane trafficking. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, I.; Terencio, M.C.; Guillén, I.; Ferrándiz, M.L.; Coloma, J.; Payá, M.; Alcaraz, M.J. Co-regulation between cyclo-oxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the time-course of murine inflammation. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 361, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, S. Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991, 43, 109–142. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, H.Y.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Neurobiology of nitric oxide. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 1996, 10, 291–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop-Bailey, D.; Calatayud, S.; Warner, T.D.; Hla, T.; Mitchell, J.A. Prostaglandins and the regulation of tumor growth. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2002, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S.; Rumi, M.A.; Okuyama, T.; Kinoshita, Y. Effect of prostaglandins on the regulation of tumor growth. Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents 2004, 4, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vane, J.R.; Botting, R.M. Mechanism of action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am. J. Med. 1998, 104, 2S–8S, discussion 21S–22S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-κB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, S.; Kestler, H.; Lasar, A.; Wirth, T. NF-κB controls the global pro-inflammatory response in endothelial cells: Evidence for the regulation of a pro-atherogenic program. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5308–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Wang, Q.M. The IKK NF-κB system: A treasure trove for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, F.; Smith, E.L.; Carmody, R.J. The regulation of NF-κB subunits by phosphorylation. Cells 2016, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.E.; Mitxitorena, I.; Carmody, R.J. The ubiquitination of NF-κB subunits in the control of transcription. Cells 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanarek, N.; London, N.; Schueler-Furman, O.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Ubiquitination and degradation of the inhibitors of NF-kappaB. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Baltimore, D. NF-κB: Ten years after. Cell 1996, 87, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Chien, S.Y.; Chan, Y.L.; Lu, M.K.; Wu, C.H.; Kong, Z.L.; Wu, C.J. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses by Sargassum hemiphyllum sulfated polysaccharide extract in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, U.; Chang, C.S.; Kim, Y.S. Genetic structure and conservation considerations of rare endemic Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai (Oleaceae) in Korea. J. Plant Res. 2000, 113, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Xi, H.; Jang, T.; Park, J.H. The complete chloroplast genome of Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai (Oleaceae), cultivar Ok Hwang 1ho: Insights of cultivar specific variations of A. distichum. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 1640–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Seo, E.J.; Sung, J.; Choi, K.M.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.; Efferth, T.; Hyun, T.K. Polyphenolic compounds, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai extract. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2017, 90, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.; Kang, D.G.; Kwon, T.O.; Jang, K.K.; Chai, K.Y.; Yun, Y.G.; Chung, H.T.; Lee, H.S. Four glycosides from the leaves of Abeliophyllum distichum with inhibitory effects on angiotensin converting enzyme. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Hase, K.; Tezuka, Y.; Tani, T.; Namba, T.; Kadota, S. Hepatoprotective activity of phenylethanoids from Cistanche deserticola. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesier, K.; Harwat, M.; Böhm, V.; Bitsch, R. Assessment of antioxidant activity by using different in vitro methods. Free Radic. Res. 2002, 36, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.D.; Lau, K.M.; Xu, H.X.; Li, P.C.; But, P.P.H. Antioxidant activity of phenylethanoid glycosides from Brandisia hancei. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 71, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imakura, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Mima, A. Bitter phenyl propanoid glycosides from campsis chinensis. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, S.; Nishibe, S.; Benecke, R.; Thieme, H. Phenolic compounds from Forsythia leaves. II. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 3667–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Guo, F.; Peng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B. Suppression of in vitro and in vivo human ovarian cancer growth by isoacteoside is mediated via sub-G1 cell cycle arrest, ROS generation, and modulation of AKT/PI3K/m-TOR signalling pathway. J. BUON 2019, 24, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, A.; Narasu, M.L. Production of podophyllotoxin from Podophyllum hexandrum: A potential natural product for clinically useful anticancer drugs. Cytotechnology 2000, 34, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.R.; Ravishankar, G. Plant cell cultures: Chemical factories of secondary metabolites. Biotechnol. Adv. 2002, 20, 101–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hellwig, S.; Drossard, J.; Twyman, R.M.; Fischer, R. Plant cell cultures for the production of recombinant proteins. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanpour-Ardestani, N.; Sharifi, M.; Behmanesh, M. Establishment of callus and cell suspension culture of Scrophularia striata Boiss.: An in vitro approach for acteoside production. Cytotechnology 2015, 67, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, T.W.; Park, J.H. Antioxidant activity and inhibitory effects on oxidative DNA damage of callus from Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai. Kor. J. Plant Res. 2018, 31, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, D.; Seo, B.; Lee, C. Studies on the in vitro induction of callus from another culture of Abeliophyllum distichum. J. Chonbuk Nat. Univ. 1989, 31, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, S.R.; Franzyk, H.; Wallander, E. Chemotaxonomy of the Oleaceae: Iridoids as taxonomic markers. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Lee, H.Y. Effect of antioxidant and skin whitening of ethanol extracts from ultrasonic pretreated Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai. Kor. J. Med. Crop. Sci. 2015, 23, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Lee, H.L.; Lee, D.K.; Kim, K.J. Complete plastid genome sequences of Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai (Oleaceae), a Korea endemic genus. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2016, 1, 596–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Kim, Y.; Xi, H.; Jang, T.; Kim, G.; Park, J.; Park, J.H. The complete chloroplast genome of a new candidate cultivar, Sang Jae, of Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai (Oleaceae): Initial step of A. distichum intraspecies variations atlas. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 3716–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Min, J.; Kim, Y.; Xi, H.; Kwon, W.; Jang, T.; Kim, G.; Park, J.H. The complete chloroplast genome of a new candidate cultivar, Dae Ryun, of Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai (Oleaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 3713–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.H.; Park, J.H.; Eo, H.J.; Song, H.M.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.R.; Jeong, J.B. Anti-inflammatory effect of the extracts from Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai in LPS-stimulated RAW264. 7 cells. Kor. J. Plant Res. 2014, 27, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Jantan, I.; Harikrishnan, H. Zerumbone suppresses the activation of inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated U937 macrophages through MyD88-dependent NF-κB/MAPK/PI3K-Akt signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 55, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Jantan, I.; Harikrishnan, H.; Wahab, S.M.A. Magnoflorine enhances LPS-activated pro-inflammatory responses via MyD88-dependent pathways in U937 macrophages. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, K.B.; Kim, H.; Shin, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.A.; Kim, M.O.; Jung, E.; Lee, J.; Park, D. Anti-inflammatory effects of Zea mays L. husk extracts. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.J.; Mellouk, S.; Hoffman, S.L.; Meltzer, M.S.; Nacy, C.A. Cellular mechanisms of nonspecific immunity to intracellular infection: Cytokine-induced synthesis of toxic nitrogen oxides from L-arginine by macrophages and hepatocytes. Immunol. Lett. 1990, 25, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.; Nacy, C.; Schreiber, R.; Granger, D.; Crawford, R.; Meltzer, M.; Fortier, A. Neutralization of gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha blocks in vivo synthesis of nitrogen oxides from L-arginine and protection against Francisella tularensis infection in Mycobacterium bovis BCG-treated mice. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, R.; Gerecitano, J.; Shapiro, D.; Green, S.J.; Aguet, M.; Le, J.; Vilcek, J. Generation of nitric oxide and clearance of interferon-gamma after BCG infection are impaired in mice that lack the interferon-gamma receptor. J. Inflamm. 1995, 46, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Green, S.J.; Scheller, L.F.; Marletta, M.A.; Seguin, M.C.; Klotz, F.W.; Slayter, M.; Nelson, B.J.; Nacy, C.A. Nitric oxide: Cytokine-regulation of nitric oxide in host resistance to intracellular pathogens. Immunol. Lett. 1994, 43, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.I.A.; Jantan, I.; Haque, M.A. Naturally occurring immunomodulators with antitumor activity: An insight on their mechanisms of action. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 50, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers Gibson, T.; Xu, B.-E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, E.; Gotoh, Y. The MAP kinase cascade is essential for diverse signal transduction pathways. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1993, 18, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, K.L.; Rossa, C., Jr. The potential of p38 MAPK inhibitors to modulate periodontal infections. Curr. Drug Metab. 2009, 10, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, B. MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy—From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1754, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, C. Inhibition of LPS-induced NO production by taurine chloramine in macrophages is mediated though Ras-ERK-NF-κB. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, T.D. Introduction to NF-κ B: Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasier, A.R. The NF-κB regulatory network. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2006, 6, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surh, Y.J.; Chun, K.S.; Cha, H.H.; Han, S.S.; Keum, Y.S.; Park, K.K.; Lee, S.S. Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: Down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-κB activation. Mutat. Res. 2001, 480, 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, S.S. NF-κB as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammation: Recent advances. Mol. Med. Today 2000, 6, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, M.H.; Rhee, S.H.; Perkins, D.J.; Medvedev, A.E.; Piao, W.; Fenton, M.J.; Vogel, S.N. TLR4/MyD88/PI3K interactions regulate TLR4 signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).