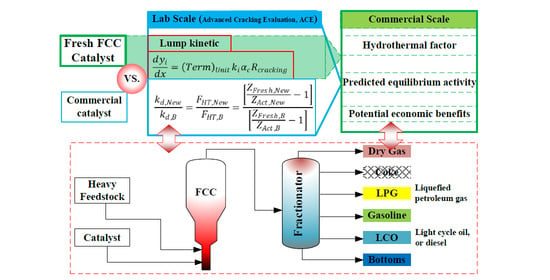
A Novel Method to Investigate the Activity Tests of Fresh FCC Catalysts: An Experimental and Prediction Process from Lab Scale to Commercial Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Evaluation Method and Experimental Description
2.1. Simulated Industrial Evaluation Method
2.2. Recommended Experimental and Device Requirements
2.3. Catalysts to Be Evaluated
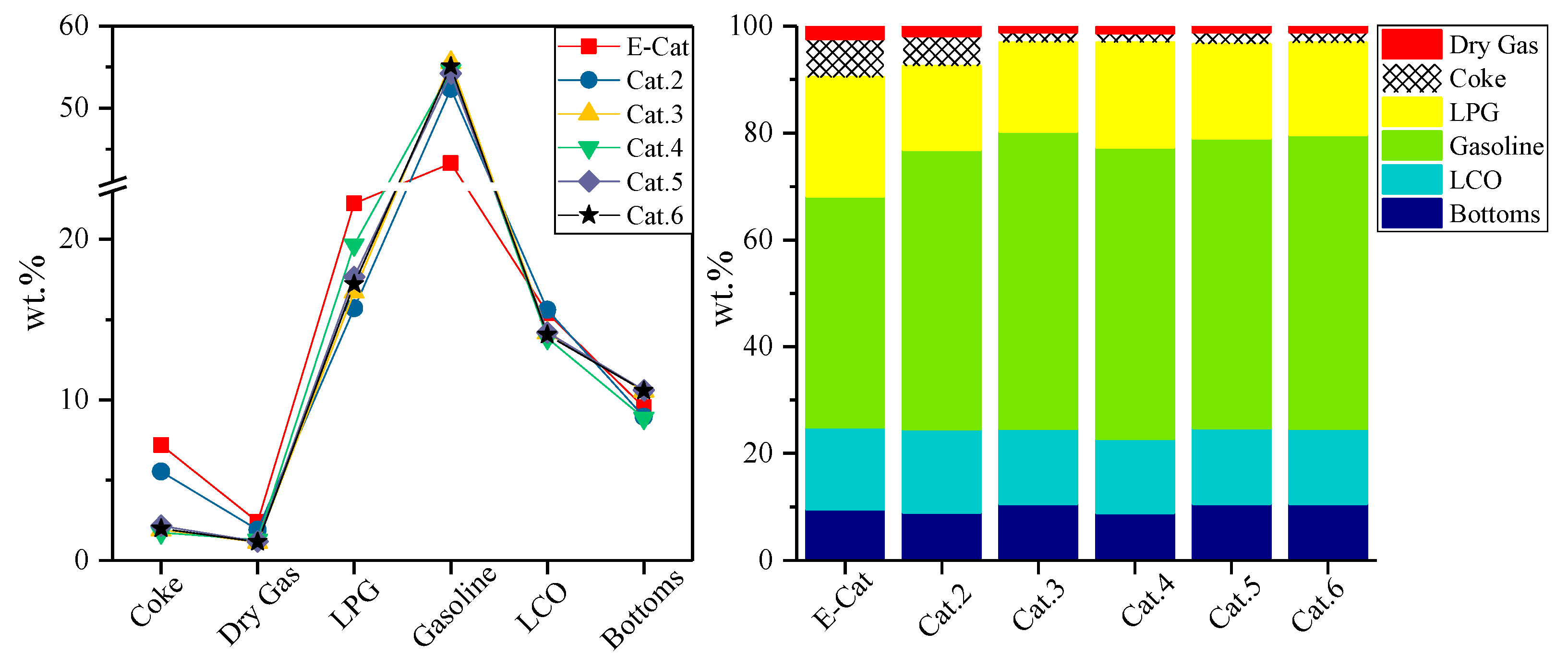
3. Results and Discussion
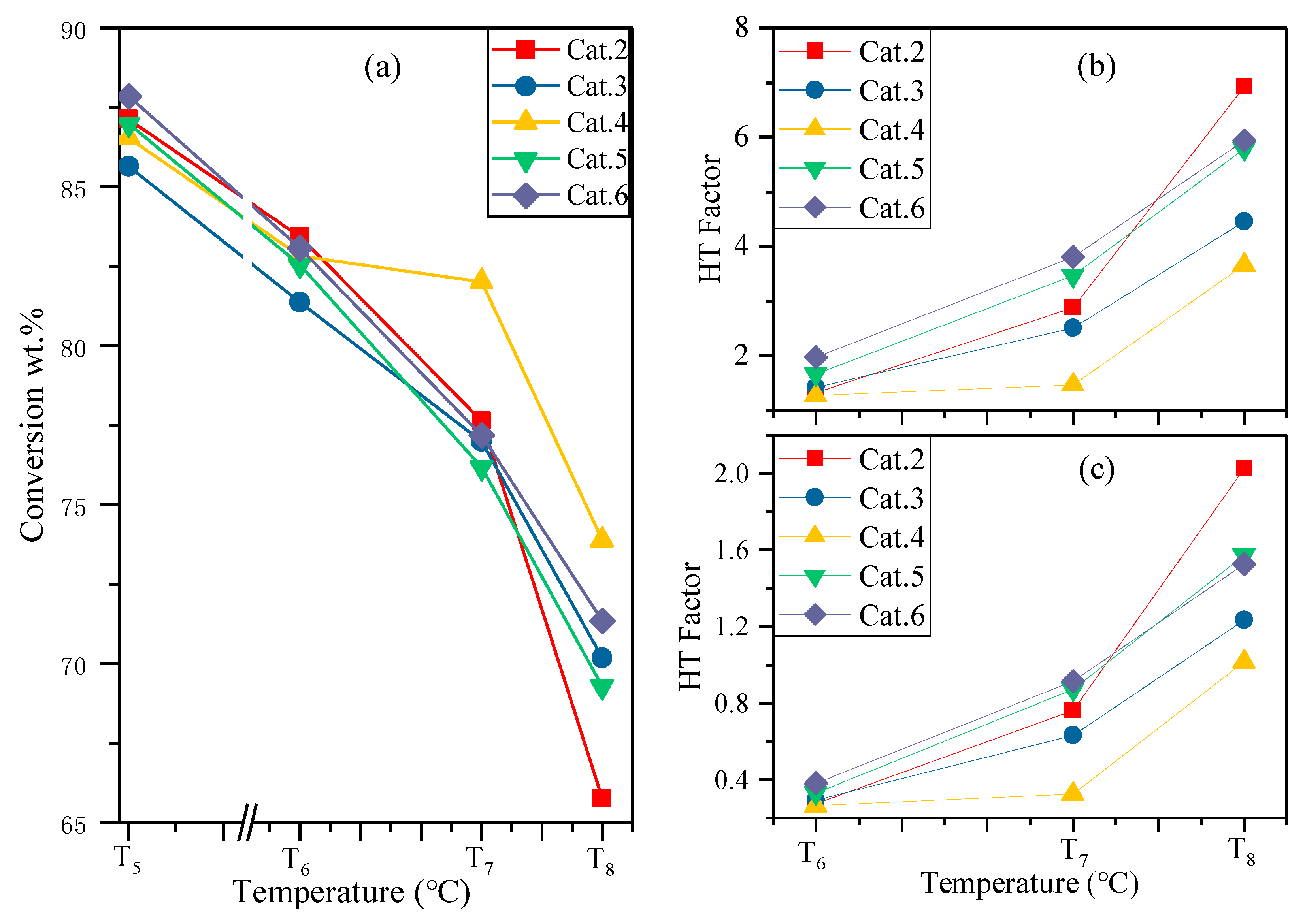
3.1. Modification for Hydrothermal Conditions
3.2. Predicted Equilibrium Activity
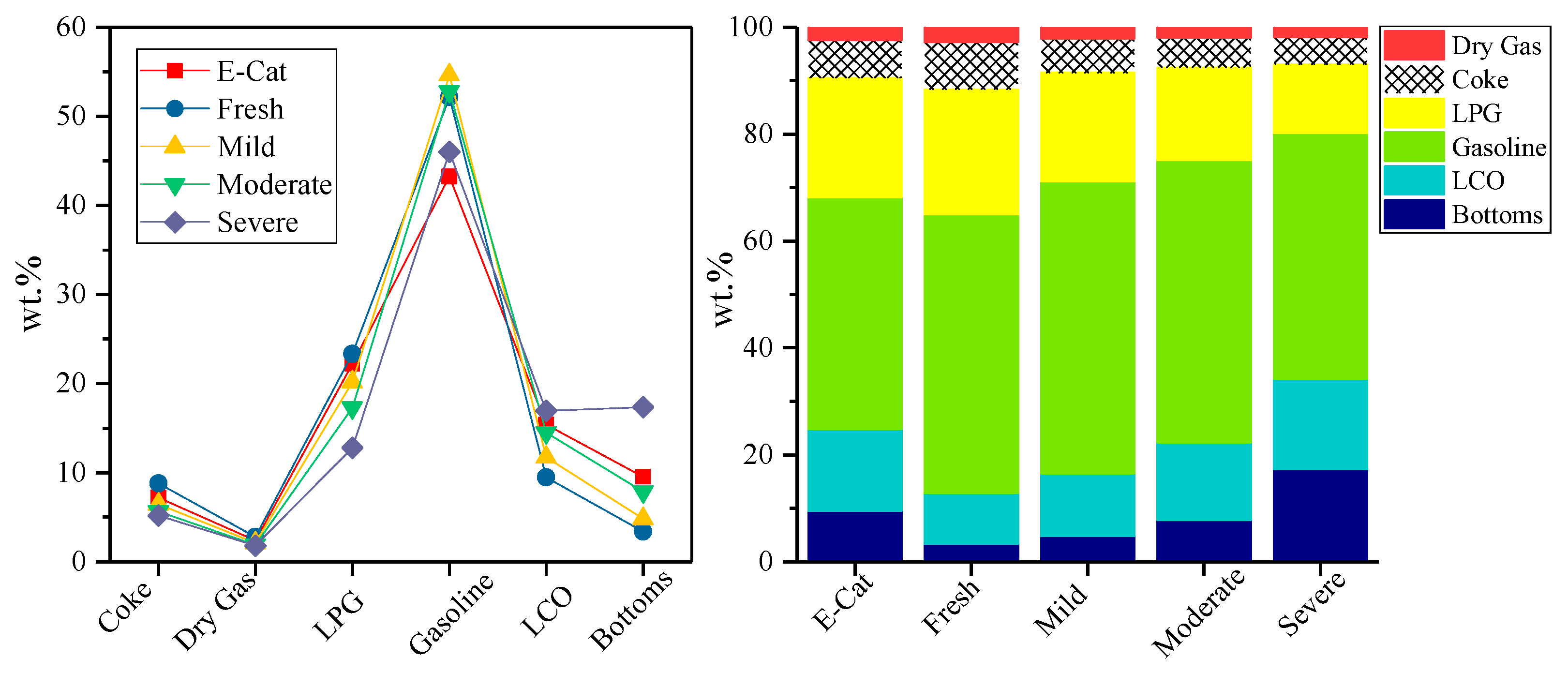
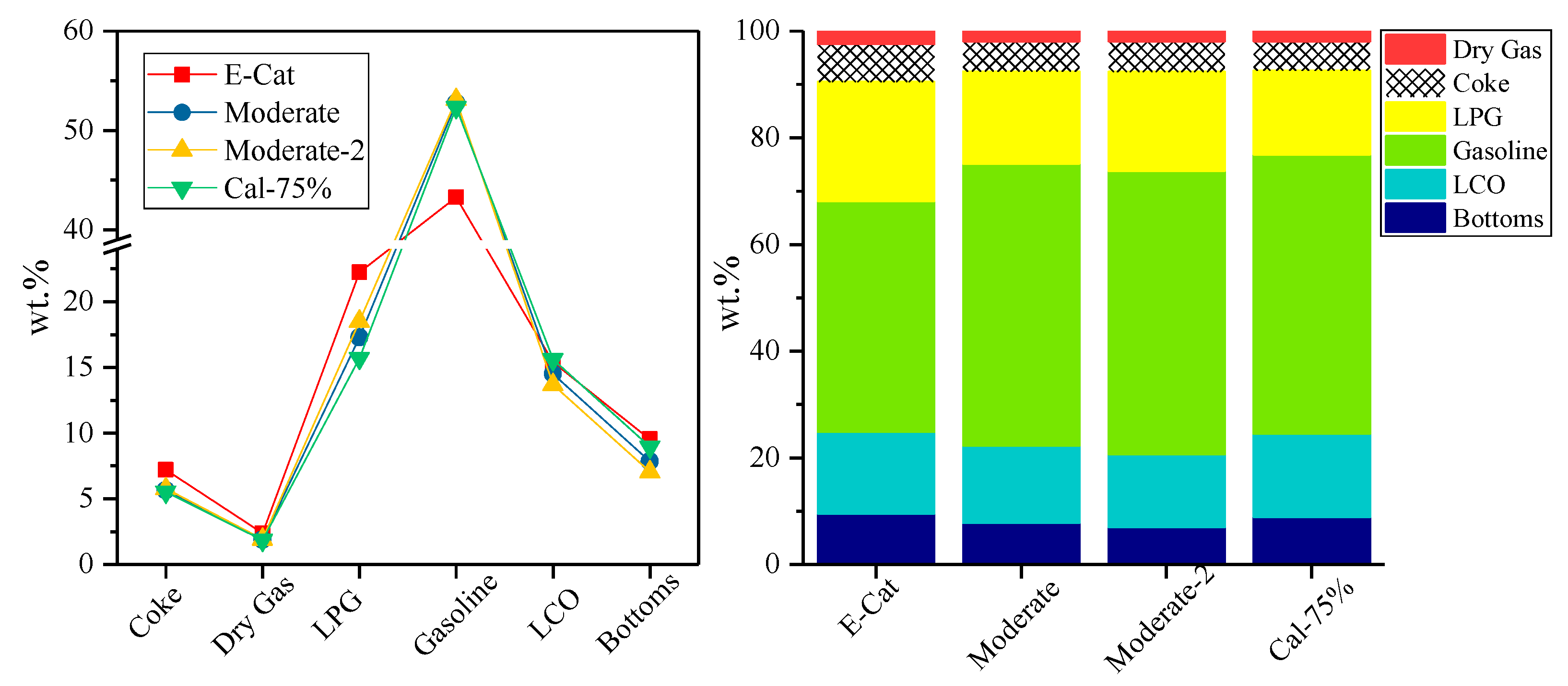
3.3. Industrial Evaluation for FCC Catalysts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, S. Enhancing Transient Event Trigger Real-Time Optimization for Fluid Catalytic Cracking Unit Operation with Varying Feedstock. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20340–20356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yu, M.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Li, C. Conceptual Fluid Catalytic Cracking Process with the Additional Regenerated Catalyst Circulation Path for Gasoline Reprocessing and Upgrading with Minimum Loss. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhou, L.; Ji, X.; He, G.; Dai, Y.; Dang, Y. Adaptive Modeling Strategy Integrating Feature Selection and Random Forest for Fluid Catalytic Cracking Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 11265–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Etim, U.J.; Yan, Z.; Mintova, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Gao, X. Fluid catalytic cracking technology: Current status and recent discoveries on catalyst contamination. Catal. Rev. 2018, 61, 333–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, B.; Zhang, R.; Gu, T.; Ji, X.; Zhong, L.; Chen, G.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Li, X. Co-upgrading of raw bio-oil with kitchen waste oil through fluid catalytic cracking (FCC). Appl. Energy 2018, 217, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tian, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, L.; Li, S. Experimental Study on Spent FCC Catalysts for the Catalytic Cracking Process of Waste Tires. Processes 2019, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, D.V.; Karthik, V.; Kumar, V.; Prasad, B.; Garg, M.O. Kinetic modeling for catalytic cracking of pyrolysis oils with VGO in a FCC unit. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 170, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Siddiqui, M.B.; Hussain, A.; Aitani, A.; Al-Khattaf, S. Catalytic cracking of crude oil to light olefins and naphtha: Experimental and kinetic modeling. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 120, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Husein, M.M.; Gao, C.; Gao, J. Pilot-scale evaluation of hydrotreating inferior coker gas oil prior to its fluid catalytic cracking. Fuel 2018, 226, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Sauvanaud, L.; Mathieu, Y.; Al-Bogami, S.; Bourane, A.; Al-Ghrami, M. Direct crude oil cracking for producing chemicals: Thermal cracking modeling. Fuel 2018, 211, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Yuan, M.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y. Fundamental study of hierarchical millisecond gas-phase catalytic cracking process for enhancing the production of light olefins from vacuum residue. Fuel 2019, 237, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etim, U.J.; Xu, B.; Peng, B.; Ullah, R.; Subhan, F.; Yan, Z. Role of nickel on vanadium poisoned FCC catalyst: A study of physiochemical properties. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Livi, K.J.; Kundu, S.; Cheng, W.-C. Characterization of iron contamination on equilibrium fluid catalytic cracking catalyst particles. J. Catal. 2018, 361, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etim, U.J.; Xu, B.; Bai, P.; Ullah, R.; Subhan, F.; Yan, Z. Vanadium and nickel deposition on FCC catalyst: Influence of residual catalyst acidity on catalytic products. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 273, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Sauvanaud, L. FCC testing at bench scale: New units, new processes, new feeds. Catal. Today 2013, 218–219, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, A.G.; Ebrahim, H.A.; Azarhoosh, M.J. 8-Lump kinetic model for fluid catalytic cracking with olefin detailed distribution study. Fuel 2018, 225, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, Y.M.; Mustafa, M.; Patel, R.; Mujtaba, I.M. Parameter estimation of a six-lump kinetic model of an industrial fluid catalytic cracking unit. Fuel 2019, 235, 1436–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occelli, M.L. Advances in Fluid Catalytic Cracking: Testing, Characterization, and Environmental Regulations; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Alvira, J.I.; Del Olmo, I.H.; Rodríguez, E.; Arandes, J.M.; Castano, P. A Data-Driven Reaction Network for the Fluid Catalytic Cracking of Waste Feeds. Processes 2018, 6, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.petro-sim.com.
- Available online: http://www.kaysertech.com.
- Liu, X.; Duan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, G. Commercial application of LDO-70 efficient conversion catalyst for heavy oil. Pet. Refin. Chem. Ind. 2013, 44, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, K.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tian, A.; Zhang, H. Effect of propylene-enhancing promoter on performance of catalyst LB-5 in heavy oil catalytic pyrolysis for light olefins. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2015, 44, 1710–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Xiong, X.; Ma, M.; Gao, W. Industrial application of FCC catalyst LPC-70 for improving gasoline yield. Pet. Refin. Chem. Ind. 2018, 49, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Wang, J.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Shen, M. Catalytic deactivation mechanism research over Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts for NH3-SCR (I): The impact of 950 °C hydrothermal aging time. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 176, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenstein, D.; Farmer, D.; Knoell, J.; Fougret, C.; Brandt, S. Progress in the deactivation of metals contaminated FCC catalysts by a novel catalyst metallation method. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 462–463, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etim, U.J.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Bai, P.; Qiao, K.; Yan, Z. Improved catalytic cracking performance of USY in the presence of metal contaminants by post-synthesis modification. Fuel 2016, 178, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Description | Recommended Conditions | Assumed Regeneration Temp | Modified Conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp | Hours | Temp | Hours | |||
| 1 | Fresh activity | T1 (705) | 6 | - | T5 | H2 |
| 2 | Mild deactivation | T2 (760) | 6 | 660 | T6 | H2 |
| 3 | Moderate deactivation | T3 (775) | 6 | 705 | T7 | H2 |
| 4 | Severe deactivation | T4 (795) | 6 | 750 | T8 | H2 |
| No. | Catalysts | Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| Cat.1 | LDO-70 | - |
| Cat.2 | YN-20, YN-E-Cat | - |
| Cat.3 | LDO-70 + LB-5 | 4.25:1 |
| Cat.4 | LPC-70 + LHG | 5:1 |
| Cat.5 | LDO-70 + LB-5 | 6:1 |
| Cat.6 | LDO-70 + LHG | 5:1 |
| Program | Property | Metal | Content/(μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight /(g/mol) | 374 | Ni | 9.57 |
| Viscosity (100 °C)/(mm2/s) | 12.27 | V | 10.09 |
| Density (70 °C)/(Kg/m3) | 867.3 | Na | 16 |
| ω (Conradson Carbon Residue)/% | 4.17 | Ca | 18.11 |
| Flash Point/°C | 204 | Fe | 10.22 |
| ω (Paraffin)/% | 68.9 | Pb | 0.03 |
| ω (Aromatics)/% | 21.7 | Cu | 0.87 |
| ω (Gelatin)/% | 9.4 |
| Deactivation | Reference Conversion | Recommended Conditions | Modified Conditions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat.1 | Δ | Cat.2 | Δ | Cat.1 | Cat.2 | ||
| Fresh | 76.74 | 87.01 | 10.27 | 89.14 | 12.40 | 86.98 | 87.13 |
| Mild | 71.85 | 84.10 | 12.25 | 85.45 | 13.60 | 82.53 | 83.44 |
| Moderate | 69.13 | 83.03 | 13.90 | 84.45 | 15.32 | 76.17 | 77.63 |
| Severe | 67.1 | 79.05 | 11.95 | 81.50 | 14.40 | 69.27 | 65.75 |
| Description | E-Cat | YN-20 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T5 | T6 | T7 | T7 | T8 | ||
| Recovery, wt% | 101.0 | 101.1 | 101.0 | 100.4 | 100.7 | 100.6 |
| Conversion, wt% | 75.08 | 87.13 | 83.44 | 77.63 | 79.28 | 65.75 |
| Yields, wt%: | ||||||
| Coke | 7.20 | 8.83 | 6.48 | 5.67 | 5.77 | 5.18 |
| Dry Gas | 2.40 | 2.82 | 2.14 | 1.90 | 1.91 | 1.83 |
| Hydrogen | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 |
| Methane | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.64 | 0.60 |
| Ethane | 0.47 | 0.68 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.47 |
| Ethylene | 0.65 | 0.83 | 0.57 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.41 |
| Propane | 1.16 | 1.94 | 1.10 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.53 |
| Propylene | 7.69 | 5.98 | 5.62 | 5.07 | 5.37 | 3.98 |
| n-Butane | 0.84 | 1.87 | 1.16 | 0.75 | 0.81 | 0.43 |
| Isobutane | 3.69 | 7.35 | 5.13 | 3.45 | 3.85 | 1.82 |
| C4 Olefins | 8.85 | 6.19 | 7.19 | 7.26 | 7.65 | 6.00 |
| 1-Butene | 1.66 | 1.39 | 1.56 | 1.47 | 1.56 | 1.15 |
| Isobutylene | 3.04 | 1.31 | 1.80 | 2.22 | 2.28 | 2.13 |
| c-2-Butene | 1.76 | 1.49 | 1.64 | 1.52 | 1.63 | 1.15 |
| t-2-Butene | 2.35 | 1.97 | 2.16 | 2.01 | 2.15 | 1.52 |
| Butadiene | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Gasoline | 43.27 | 52.16 | 54.64 | 52.77 | 53.10 | 45.99 |
| LCO | 15.39 | 9.50 | 11.72 | 14.51 | 13.68 | 16.92 |
| Bottoms | 9.53 | 3.37 | 4.84 | 7.86 | 7.04 | 17.33 |
| TOTAL | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Liao, Y.; Su, Y.; Ji, D.; Li, H.; Yang, Y. A Novel Method to Investigate the Activity Tests of Fresh FCC Catalysts: An Experimental and Prediction Process from Lab Scale to Commercial Scale. Processes 2021, 9, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020209
Ma Y, Liao Y, Su Y, Ji D, Li H, Yang Y. A Novel Method to Investigate the Activity Tests of Fresh FCC Catalysts: An Experimental and Prediction Process from Lab Scale to Commercial Scale. Processes. 2021; 9(2):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020209
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yanqing, Yitao Liao, Yi Su, Dong Ji, Hongwei Li, and Yong Yang. 2021. "A Novel Method to Investigate the Activity Tests of Fresh FCC Catalysts: An Experimental and Prediction Process from Lab Scale to Commercial Scale" Processes 9, no. 2: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020209
APA StyleMa, Y., Liao, Y., Su, Y., Ji, D., Li, H., & Yang, Y. (2021). A Novel Method to Investigate the Activity Tests of Fresh FCC Catalysts: An Experimental and Prediction Process from Lab Scale to Commercial Scale. Processes, 9(2), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020209