Alexandrian Laurel for Biodiesel Production and its Biodiesel Blends on Performance, Emission and Combustion Characteristics in Common-Rail Diesel Engine
Abstract
1. Introduction
Purpose of Study
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fuel Properties Test and Analysis
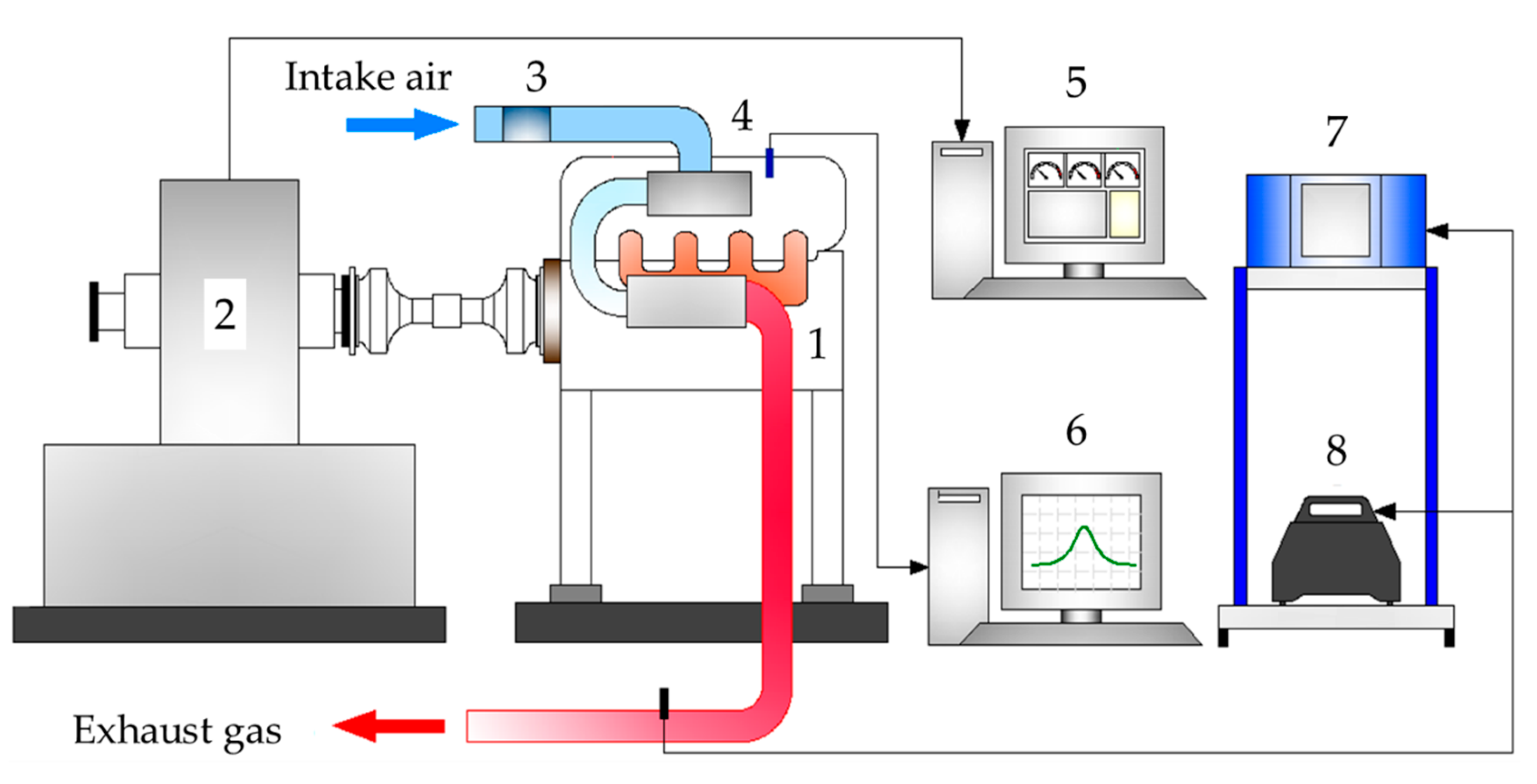
2.3. Engine Setup and Instrumentation
2.4. Heat Release Rate (HRR) Analysis
2.5. Statistical and Equipment Uncertainty Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
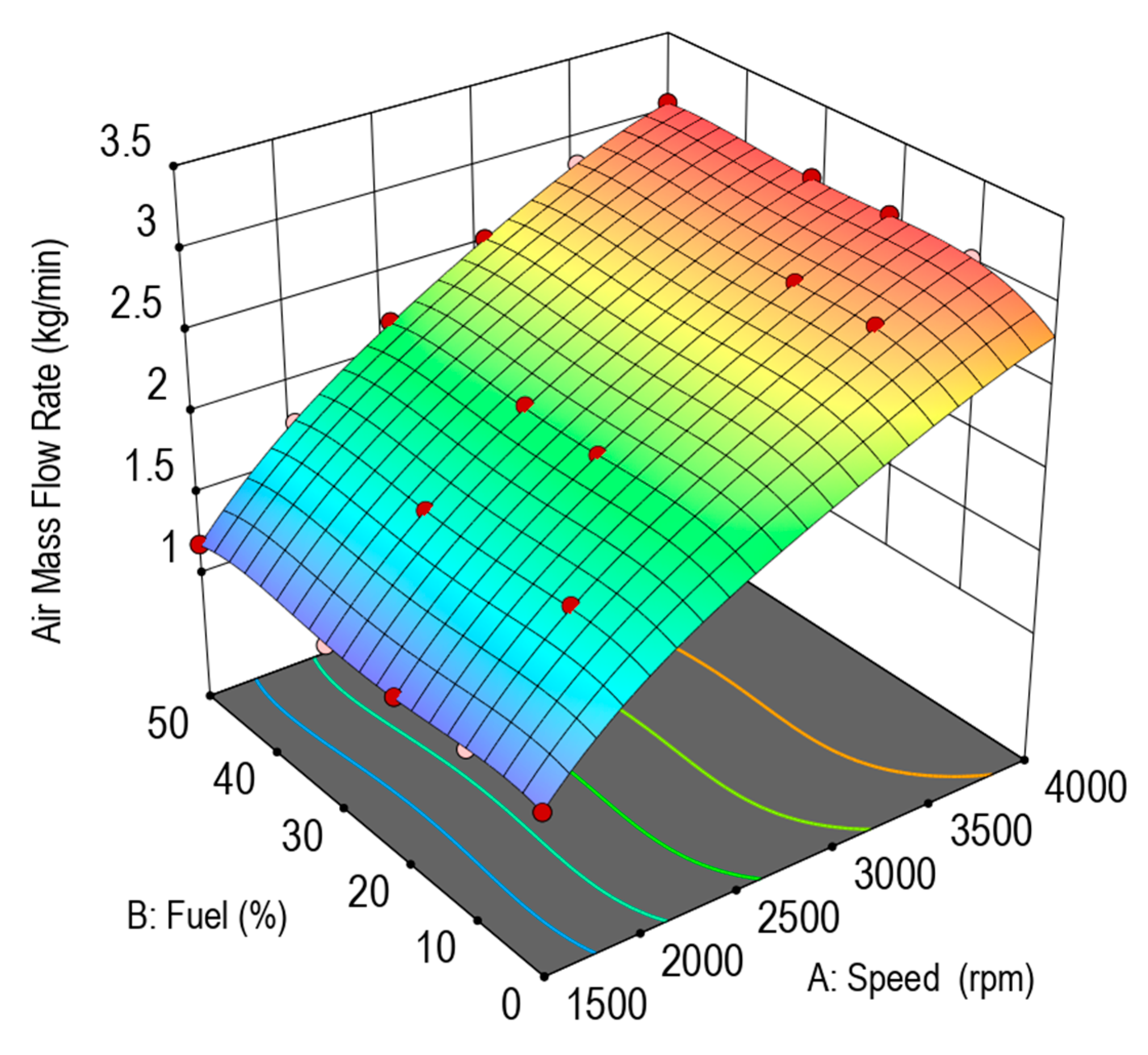
3.1. Engine Performance
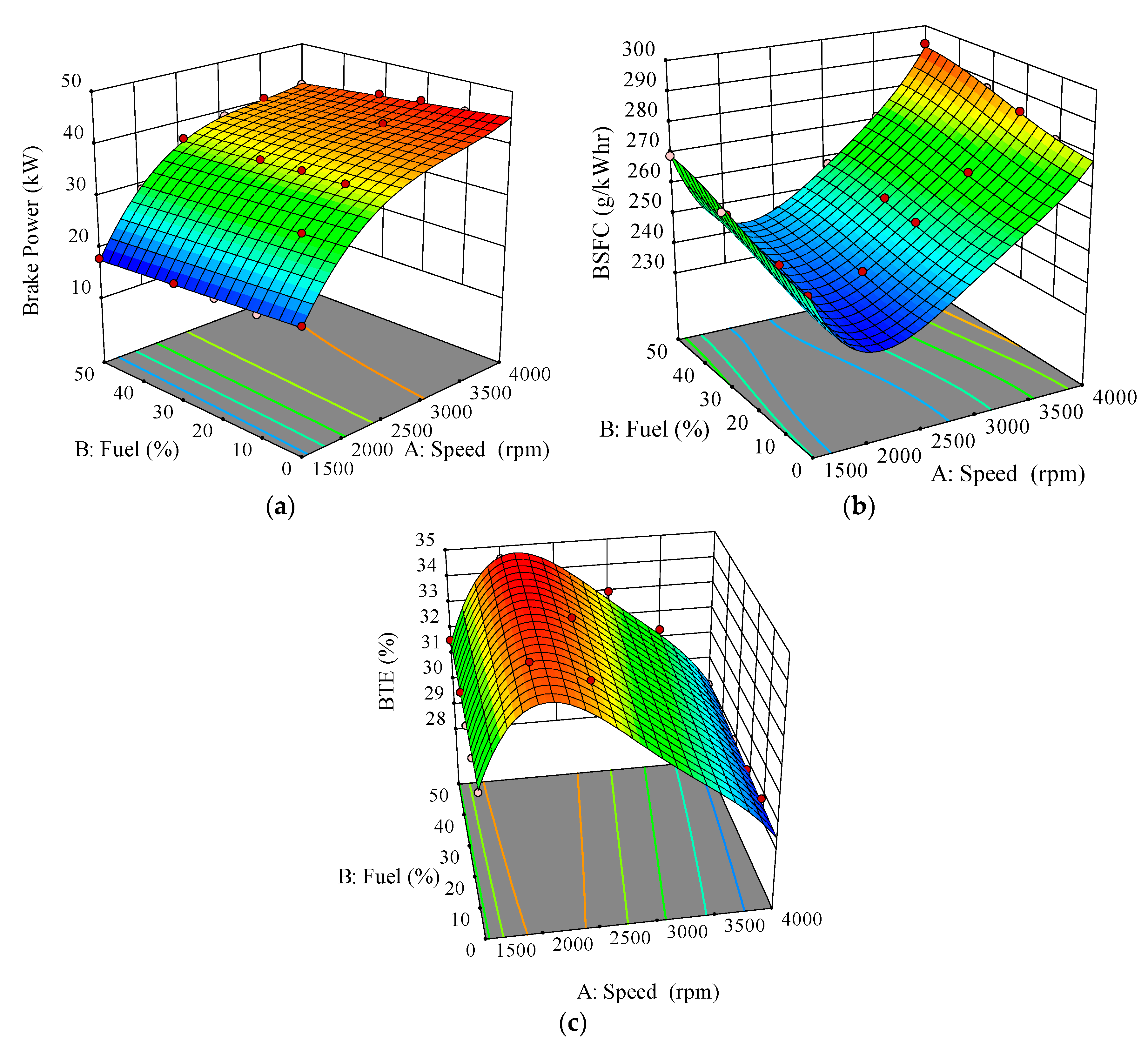
3.1.1. Brake Power
3.1.2. Brake Specific Fuel Consumption
3.1.3. Brake Thermal Efficiency
3.2. Exhaust Emissions
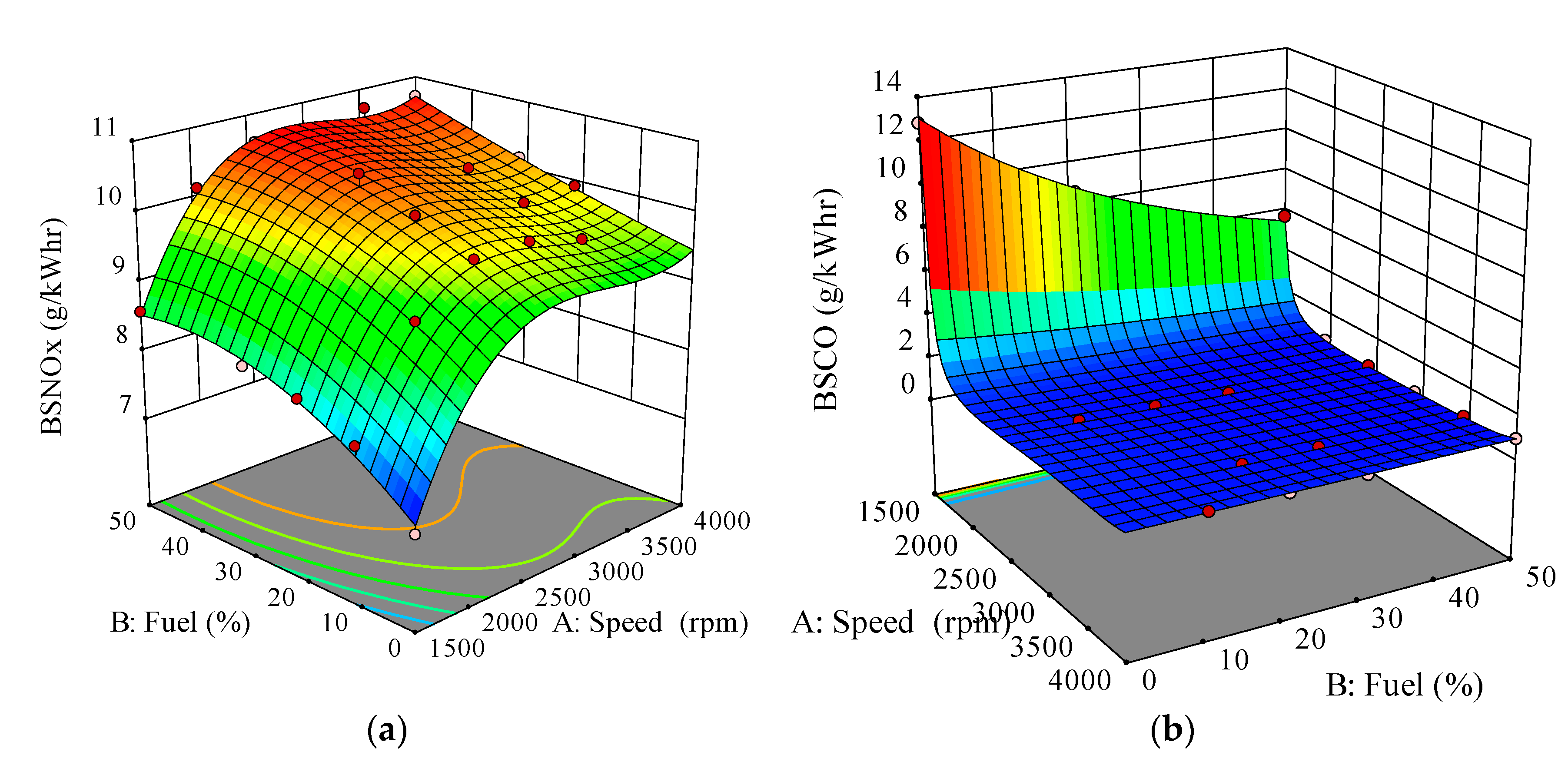
3.2.1. Brake Specific Nitrogen Oxide
3.2.2. Brake Specific Carbon Monoxide
3.2.3. Brake Specific Carbon Dioxide
3.2.4. Smoke Opacity
3.3. Combustion Characteristics
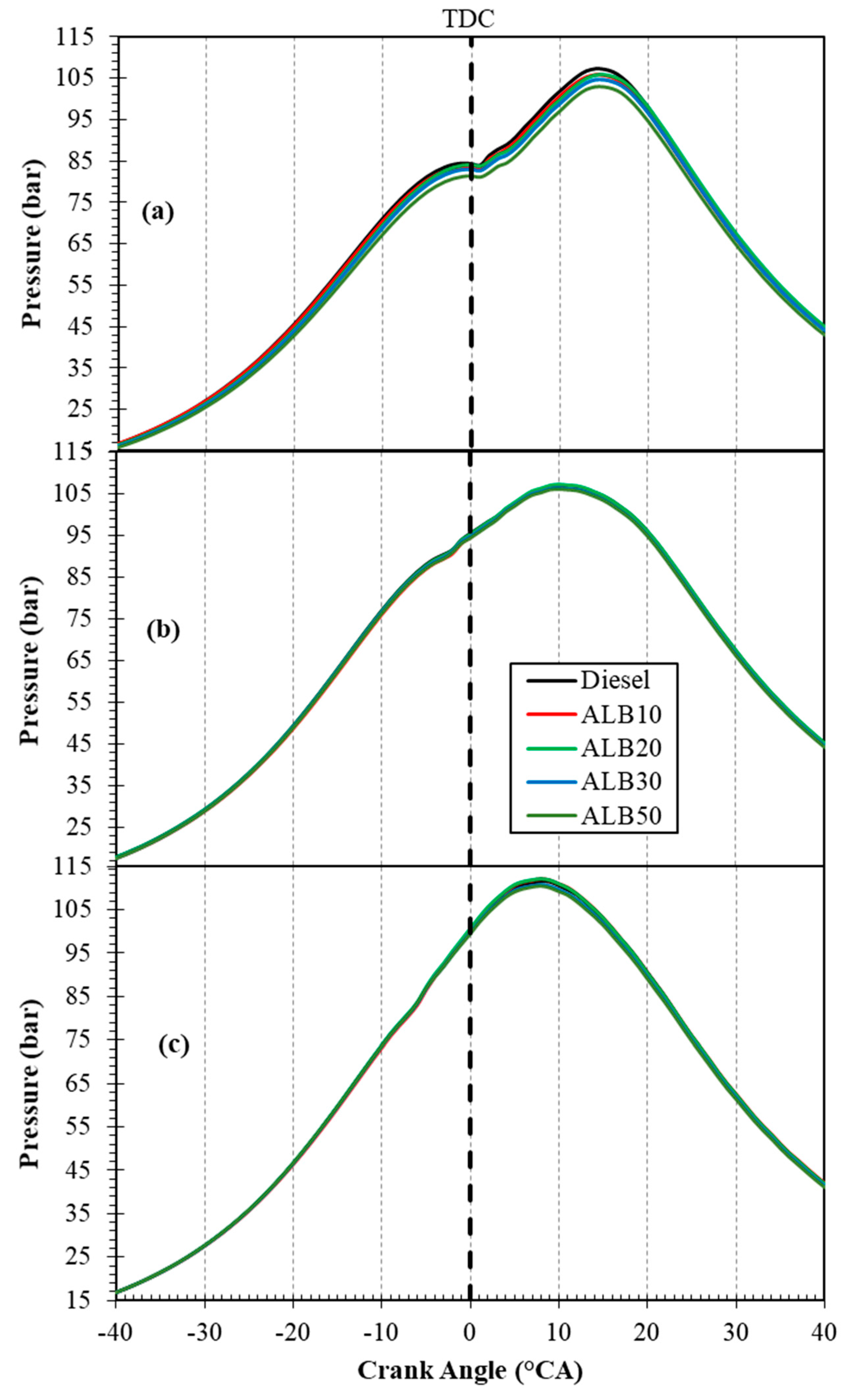
3.3.1. Cylinder Combustion Pressure
3.3.2. Heat Release Rate
3.3.3. Fuel Combustion Duration
4. Conclusions
- A prominent decline in engine brake power was found across all engine speeds due to the smaller calorific value of ALB. The highest reduction of 3.17 kW was obtained for ALB50 at the engine speed of 4000 rpm compared to baseline diesel. Besides, the use of ALB elevated the BSFC with respect to the conventional diesel fuel. Furthermore, the BTE of ALB50 is consistently higher than other fuels for all engine speeds.
- In terms of engine-out emissions, the BSNOx emission increased for all the ALB-blended fuels as compared to that for the baseline diesel under all tested engine speeds. The largest increment in BSNOx recorded was approximately 1.56 g/kWhr for the ALB50 at 1500 rpm. On the other hand, the exhaust emissions also showed enhancement with reduced BSCO, BSCO2 and smoke emissions by using ALB-blended fuels across all engine speeds.
- On the combustion aspects, the ALB-blended fuels indicated the deteriorations in the peak combustion pressure and peak HRR during the premixed combustion stage, probably as a result of lower calorific value of the ALB blends as compared to the conventional diesel fuel. On the other hand, shorter combustion durations were also observed for all the ALB–diesel blends. With an increasing portion of ALB in blends, more rapid combustion occurred for the fuel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Owusu, P.A.; Sarkodie, S.A. A review of renewable energy sources, sustainability issues and climate change mitigation. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1167990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sharma, M.P. Selection of potential oils for biodiesel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banković-Ilić, I.; Stamenković, O.S.; Veljković, V. Biodiesel production from non-edible plant oils. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3621–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudul, H.M.; Hagos, F.Y.; Mamat, R.; Adam, A.A.; Ishak, W.F.W.; Alenezi, R. Production, characterization and performance of biodiesel as an alternative fuel in diesel engines—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.C.; Gupta, T.; Agarwal, A.K. Performance evaluation of a biodiesel fuelled transportation engine retrofitted with a non-noble metal catalysed diesel oxidation catalyst for controlling unregulated emissions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, E.; Schauer, J.J.; Quraishi, T.A.; Mahmood, A. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of fine and coarse particulate matter in Lahore, Pakistan. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakob, Z.; Narayanan, B.; Padikkaparambil, S. A review on the oxidation stability of biodiesel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Raja, I.A.; Rizwan, M.; Rashid, N.; Mahmood, Q.; Shah, F.A.; Pervez, A. Potential of microalgal biodiesel production and its sustainability perspectives in Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sharma, M. Assessment of potential of oils for biodiesel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, P.; Guido, C.; Beatrice, C.; Pellegrini, L. Impact of hydrocracked diesel fuel and Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil blends on the fuel consumption of automotive diesel engines. Fuel 2018, 222, 718–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlan, A. Techno-economic assessment of pathways for electricity generation in northern remote communities in Canada using methanol and dimethyl ether to replace diesel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayed, M.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M.; Mahlia, T.; Husnawan, M.; Liaquat, A. Prospects of dedicated biodiesel engine vehicles in Malaysia and Indonesia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Nugroho, Y.; Shakeel, S.; Li, Z.; Martinkauppi, B.; Hiltunen, E. Using microalgae to produce liquid transportation biodiesel: What is next? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaqiang, E.; Pham, M.; Zhao, D.; Deng, Y.; Le, D.; Zuo, W.; Zhu, H.; Liu, T.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, Z. Effect of different technologies on combustion and emissions of the diesel engine fueled with biodiesel: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 620–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Rahman, M. Performance and emission characteristics of biodiesel–diesel blend and environmental and economic impacts of biodiesel production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graboski, M.S.; McCormick, R.L. Combustion of fat and vegetable oil derived fuels in diesel engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1998, 24, 125–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhas, A.; Jayaraj, S.; Muraleedharan, C. Use of vegetable oils as I.C. engine fuels—A review. Renew. Energy 2004, 29, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macor, A.; Avella, F.; Faedo, D. Effects of 30% v/v biodiesel/diesel fuel blend on regulated and unregulated pollutant emissions from diesel engines. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 4989–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, G.; Karvembu, R.; Anand, R. Effect of metal based additive on performance emission and combustion characteristics of diesel engine fuelled with biodiesel. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3694–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ge, Y.; Tan, J.; You, K.; Han, X.; Wang, J. Characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons emissions of diesel engine fueled with biodiesel and diesel. Fuel 2010, 89, 2040–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özener, O.; Yüksek, L.; Ergenç, A.T.; Ozkan, M. Effects of soybean biodiesel on a DI diesel engine performance, emission and combustion characteristics. Fuel 2014, 115, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, B.S.; Kumar, N.; Muk Cho, H. A study on the performance and emission of a Diesel engine fuelled with Jatropha biodiesel oil and its blends. Energy 2012, 37, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keera, S.; El Sabagh, S.; Taman, A. Castor oil biodiesel production and optimization. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caresana, F. Impact of biodiesel bulk modulus on injection pressure and injection timing. The effect of residual pressure. Fuel 2011, 90, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szybist, J.P.; Song, J.; Alam, M.; Boehman, A.L. Biodiesel combustion, emissions and emission control. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.J.; Boehman, A.L.; Martin, G.C. An Experimental Investigation of the Origin of Increased NOx Emissions When Fueling a Heavy-Duty Compression-Ignition Engine with Soy Biodiesel. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2009, 2, 789–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamodaran, G.; Krishnan, R.; Pochareddy, Y.K.; Pyarelal, H.M.; Sivasubramanian, H.; Ganeshram, A.K. A comparative study of combustion, emission, and performance characteristics of rice-bran-, neem-, and cottonseed-oil biodiesels with varying degree of unsaturation. Fuel 2017, 187, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitoe, B.V.; Máquina, A.D.V.; Santana, F.B.; Gontijo, L.C.; Santos, D.Q.; Neto, W.B. Monitoring of biodiesel content and adulterant presence in methyl and ethyl biodiesels of jatropha in blends with mineral diesel using MIR spectrometry and multivariate control charts. Fuel 2017, 191, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varatharajan, K.; Rani, D. Screening of antioxidant additives for biodiesel fuels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Gardy, J.; Demirbas, A.; Rashid, U.; Budzianowski, W.; Pant, D.; Nizami, A. Waste to biodiesel: A preliminary assessment for Saudi Arabia. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Yang, W.; Chou, S.; Chua, K. Combustion and emissions characteristics of diesel engine fueled by biodiesel at partial load conditions. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.-H.; Ng, H.K.; Gan, S. Engine-out characterisation using speed–load mapping and reduced test cycle for a light-duty diesel engine fuelled with biodiesel blends. Fuel 2011, 90, 2700–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A. Progress and recent trends in biodiesel fuels. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahirul, M.I.; Brown, R.; Senadeera, W.; Ashwath, N.; Rasul, M.; Rahman, M.; Hossain, F.M.; Moghaddam, L.; Islam, M.; O’Hara, I. Physio-chemical assessment of beauty leaf (Calophyllum inophyllum) as second-generation biodiesel feedstock. Energy Rep. 2015, 1, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabani, A.; Cesar, A.D.S. Calophyllum inophyllum L.—A prospective non-edible biodiesel feedstock. Study of biodiesel production, properties, fatty acid composition, blending and engine performance. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiya, M.; Rasul, M.; Khan, M.; Ashwath, N.; Azad, A.K. Prospects of 2nd generation biodiesel as a sustainable fuel—Part 1: Selection of feedstocks, oil extraction techniques and conversion technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 1109–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.M.Y.; Atabani, A.; Badruddin, I.A.; Badarudin, A.; Khayoon, M.; Triwahyono, S. Recent scenario and technologies to utilize non-edible oils for biodiesel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabani, A.; Mahlia, T.; Badruddin, I.A.; Masjuki, H.; Tong, C.W.; Lee, K.T. Investigation of physical and chemical properties of potential edible and non-edible feedstocks for biodiesel production, a comparative analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.; Oliveros, R.; Sánchez, M.; Moraschini, A.; Martínez, M.; Aracil, J. Influence of blending vegetable oil methyl esters on biodiesel fuel properties: Oxidative stability and cold flow properties. Energy 2014, 65, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzi, S.; Garcia, I.L.; Lopez-Gimenez, F.; De Castro, M.D.L.; Dorado, G.; Dorado, M.P. The Ideal Vegetable Oil-based Biodiesel Composition: A Review of Social, Economical and Technical Implications. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2325–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumis, E.G. A statistical investigation of biodiesel physical and chemical properties, and their correlation with the degree of unsaturation. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 858–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Importance of biodiesel as transportation fuel. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 4661–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, H.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.; Teoh, Y.; Chuah, H. Effect of Calophyllum Inophyllum biodiesel-diesel blends on combustion, performance, exhaust particulate matter and gaseous emissions in a multi-cylinder diesel engine. Fuel 2018, 227, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.; Das, L.; Babu, M.; Arora, P.; Singh, V.; Kumar, N.; Varyani, T. Comparative evaluation of performance and emission characteristics of jatropha, karanja and polanga based biodiesel as fuel in a tractor engine. Fuel 2009, 88, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, B.K.; Sahoo, N.; Saha, U.K. Adjusting the operating characteristics to improve the performance of an emulsified palm oil methyl ester run diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 69, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabektas, M. The effects of turbocharger on the performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine fuelled with biodiesel. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palash, S.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M.; Atabani, A.; Fattah, I.R.; Sanjid, A. Biodiesel production, characterization, diesel engine performance, and emission characteristics of methyl esters from Aphanamixis polystachya oil of Bangladesh. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 91, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivevele, T.T.; Kristóf, L.; Bereczky, Á.; Mbarawa, M.M. Engine performance, exhaust emissions and combustion characteristics of a CI engine fuelled with croton megalocarpus methyl ester with antioxidant. Fuel 2011, 90, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, W.N.M.W.; Mamat, R.; Masjuki, H.; Najafi, G. Effects of biodiesel from different feedstocks on engine performance and emissions: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibullah, M.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M.; Zulkifli, N.; Masum, B.; Arslan, A.; Gulzar, M. Friction and wear characteristics of Calophyllum inophyllum biodiesel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, Y.; How, H.G.; Balakrishnan, N.K.; Le, T.; Nguyen, H. Performance, Emissions, Combustion and Vibration Analysis of a CI Engine Fueled with Coconut and Used Palm Cooking Oil Methyl Ester. Processes 2020, 8, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhul, A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Shahir, S.A.; Reham, S.S.; Shancita, I. Biodiesel production, properties and emissions test characteristics of non-edible fuels in Diesel engine. J. Sci. Res. Dev. 2016, 3, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.K. Biofuels (alcohols and biodiesel) applications as fuels for internal combustion engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 233–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devan, P.; Mahalakshmi, N. A study of the performance, emission and combustion characteristics of a compression ignition engine using methyl ester of paradise oil–eucalyptus oil blends. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.; Das, L.; Babu, M.; Naik, S. Biodiesel development from high acid value polanga seed oil and performance evaluation in a CI engine. Fuel 2007, 86, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, N.; Tomar, V.; Kalsi, G. Comparative Study of Performance and Emission Characteristics of Fish Oil and Calophyllum Inophyllum Oil Bio-Diesel in a Light Duty Diesel Engine; SAE Internation: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Baskar, P.; Kumar, A.S. Effects of oxygen enriched combustion on pollution and performance characteristics of a diesel engine. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silitonga, A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Mahlia, T.; Ong, H.C.; Tong, C.W. Experimental study on performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine fuelled with Ceiba pentandra biodiesel blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 76, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kasaby, M.; Nemitallah, M.A. Experimental investigations of ignition delay period and performance of a diesel engine operated with Jatropha oil biodiesel. Alex. Eng. J. 2013, 52, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, B.; Nanthagopal, K.; Vignesh, D.S. Calophyllum inophyllum methyl ester biodiesel blend as an alternate fuel for diesel engine applications. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirkude, J.B.; Padalkar, A.S. Performance and emission analysis of a compression ignition: Engine operated on waste fried oil methyl esters. Appl. Energy 2012, 90, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, H.; Teoh, Y.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M. Impact of coconut oil blends on particulate-phase PAHs and regulated emissions from a light duty diesel engine. Energy 2012, 48, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.C.; Masjuki, H.H.; Mahlia, T.; Silitonga, A.; Tong, C.W.; Yusaf, T. Engine performance and emissions using Jatropha curcas, Ceiba pentandra and Calophyllum inophyllum biodiesel in a CI diesel engine. Energy 2014, 69, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Grift, T.E.; Hansen, A.C. Effect of biodiesel on engine performances and emissions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, C.R.; De Carvalho, J.A.; Silveira, J.L. Biodiesel CO2 emissions: A comparison with the main fuels in the Brazilian market. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah, I.R.; Kalam, M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Wakil, M. Biodiesel production, characterization, engine performance, and emission characteristics of Malaysian Alexandrian laurel oil. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 17787–17796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, C.; Kumar, N.; Mishra, P.C.; Kar, B. In-Cylinder Combustion and Emission Characteristics of an Agricultural Diesel Engine Fuelled with Blends of Diesel and Oxidatively Stabilized Calophyllum Methyl Ester; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Das, L.M. Biodiesel Development and Characterization for Use as a Fuel in Compression Ignition Engines. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2000, 123, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Reitz, R.D. Effect of biodiesel saturation on soot formation in diesel engines. Fuel 2016, 175, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, S.; Saravanan, N.; Ilangkumaran, M. Influence of injection timing on performance, emission and combustion characteristics of a DI diesel engine running on fish oil biodiesel. Energy 2016, 116, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, K.; Vasudevan, D.; Sheeba, K. Performance, emission and combustion characteristics of biodiesel fuelled variable compression ratio engine. Energy 2011, 36, 5385–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukkaya, E. Effects of biodiesel on a DI diesel engine performance, emission and combustion characteristics. Fuel 2010, 89, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine fueled with biodiesel/PODE blends. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, P.S.; Sakhare, N.M.; Lahane, S. Investigation of Combustion Characteristics of a Cottonseed Biodiesel Fuelled Diesel Engine. Procedia Technol. 2016, 25, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, A.; Sairam, K.; Velraj, R. Combustion Analysis of Polanga (Calophyllum inophyllum) Biodiesel. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 812, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.; Agarwal, A.K. Performance, emissions and combustion characteristics of Karanja biodiesel in a transportation engine. Fuel 2014, 119, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraj, K.; Sathiyagnanam, A. Combustion characteristics of a DI diesel engine fuelled with blends of methyl ester of cotton seed oil. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2016, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittle, J.A.; Knight, B.M.; Jacobs, T.J. The Impact of Biodiesel on Injection Timing and Pulsewidth in a Common-Rail Medium-Duty Diesel Engine. SAE Int. J. Engines 2009, 2, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.L.N.; Prasad, B.D.; Sampath, S.; Rajagopal, K. Combustion Analysis of Diesel Engine Fueled with Jatropha Oil Methyl Ester—Diesel Blends. Int. J. Green Energy 2007, 4, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Fatty Acid Name (Systematic) | Structure | Formula | Molecular Mass | Mass Fraction (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lauric (Dodecanoic) | 12:0 | C12H24O2 | 200 | 0.1 |
| 2 | Myristic (Tetradecanoic) | 14:0 | C14H28O2 | 228 | 0.1 |
| 3 | Palmitic (Hexadecanoic) | 16:0 | C16H32O2 | 256 | 14.5 |
| 4 | Stearic (Octadecanoic) | 18:0 | C18H36O2 | 284 | 13.2 |
| 5 | Arachidic (Eicosanoic) | 20:0 | C20H40O2 | 312 | 0.8 |
| 6 | Palmitoleic (Hexadec-9-enoic) | 16:1 | C16H30O2 | 254 | 0.3 |
| 7 | Oleic (Cis-9-Octadecanoic) | 18:1 | C18H34O2 | 282 | 46.1 |
| 8 | Linoleic (Cis-9-cis-12 Octadecanoic) | 18:2 | C18H32O2 | 280 | 24.7 |
| 9 | Linolenic (Cis-9-cis-12) | 18:3 | C18H30O2 | 278 | 0.2 |
| Saturated fatty acid | 28.7 | ||||
| Unsaturated fatty acid | 71.3 | ||||
| Total | 100 | ||||
| Properties | Unit | Crude Alexandrian Laurel Oil | Limit (ASTM D6751) | Limit (EN 14214) | Alexandrian Laurel Biodiesel | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil content | % | 75 | - | - | - | - |
| Free fatty acid | % | 29.66 | - | - | - | - |
| Kinematic viscosity @ 40 °C | mm2/s | 53.17 | 1.9–6.0 | 3.5–5.0 | 4.27 | D445 |
| Density @ 15 °C | kg/m3 | 951.1 | 880 | 860–900 | 878.5 | D127 |
| Acid number | mg KOH/g | 59.33 | 0.5 max | 0.5 max | 0.45 | D664 |
| Calorific value | MJ/kg | 38.51 | - | 35 | 40.1 | D240 |
| Flash point | °C | 195.5 | 130 min | 120 min | 168.5 | D93 |
| Pour point | °C | - | - | - | 2 | D2500 |
| Cloud point | °C | - | report | - | 2 | D2500 |
| Cold filter plugging point | °C | - | - | - | 1 | D6371 |
| Oxidation stability @ 100 °C | hours | - | 3 min | 6 min | 13.08 | EN14112 |
| Cetane number | - | - | 47 min | 51 min | 59.6 | D6890 |
| Carbon | wt.% | - | 77 | - | 75.8 | D5291 |
| Hydrogen | wt.% | - | 12 | - | 12.5 | D5291 |
| Oxygen | wt.% | - | 11 | - | 11.72 | D5291 |
| Properties | Unit | Diesel Fuel | Biodiesel Blends | ALB10 | ALB20 | ALB30 | ALB50 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limit (ASTM D7467) | Test Method | |||||||
| Kinematic viscosity @ 40 °C | mm2/s | 3.34 | 1.9–4.1 | D445 | 3.55 | 3.61 | 3.98 | 4.25 |
| Density @ 15 °C | kg/m3 | 839.0 | 858 max | D127 | 851.0 | 855.1 | 857.9 | 867.9 |
| Acid number | mg KOH/g | 0.12 | 0.3 max | D664 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.28 |
| Calorific value | MJ/kg | 45.31 | 35 | D240 | 44.80 | 44.17 | 43.58 | 42.34 |
| Flash point | °C | 71.5 | 52 | D93 | 77.5 | 79.5 | 82.5 | 83.5 |
| Pour point | °C | 1 | Not specified | D2500 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Cloud point | °C | 8 | Not specified | D2500 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Oxidation stability @ 100 °C | hours | >30 | 6 | EN14112 | 25.08 | 24.08 | 20.08 | 19.26 |
| Cetane number | - | 52 | 47 min | D6890 | 52.4 | 53.9 | 55.8 | 56.7 |
| Engine Type | Diesel, four strokes, turbocharged, DI |
| Fuel system | High-pressure common-rail (up to 140 MPa) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 |
| Bore | 76.0 mm |
| Stroke | 80.5 mm |
| Displacement | 1461 cm3 |
| Compression Ratio | 18.25:1 |
| Maximum power | 48 kW @ 4000 rpm |
| Maximum torque | 160 Nm @ 2000 rpm |
| Measurement | Measurement Range | Accuracy | Measurement Techniques | % Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load | ±600 Nm | ±0.1 Nm | Strain gauge type load cell | ±0.25 |
| Speed | 0–10,000 rpm | ±1 rpm | Magnetic pick up type | ±0.1 |
| Time | - | ±0.1 s | - | ±0.2 |
| Fuel flow measurement | 0.5–36 L/hr | ±0.04 L/hr | Positive displacement gear wheel flow meter | ±0.5 |
| NOx | 0–5000 ppm | ±1 ppm | Electrochemical | ±1.3 |
| Smoke | 0–100% | ±0.1% | Photodiode detector | ±1 |
| Pressure sensor | 0–25,000 kPa | ±10 kPa | Piezoelectric crystal type | ±0.5 |
| Crank angle encoder | 0–12,000 rpm | ±0.125° | Incremental optical encoder | ±0.03 |
| Computed | ||||
| Brake specific fuel consumption (BSFC) | - | ±5 g/kWhr | - | ±1.5 |
| Brake thermal efficiency (BTE) | - | ±0.5% | - | ±1.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teoh, Y.H.; How, H.G.; Le, T.D.; Nguyen, H.T. Alexandrian Laurel for Biodiesel Production and its Biodiesel Blends on Performance, Emission and Combustion Characteristics in Common-Rail Diesel Engine. Processes 2020, 8, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8091141
Teoh YH, How HG, Le TD, Nguyen HT. Alexandrian Laurel for Biodiesel Production and its Biodiesel Blends on Performance, Emission and Combustion Characteristics in Common-Rail Diesel Engine. Processes. 2020; 8(9):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8091141
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeoh, Yew Heng, Heoy Geok How, Thanh Danh Le, and Huu Tho Nguyen. 2020. "Alexandrian Laurel for Biodiesel Production and its Biodiesel Blends on Performance, Emission and Combustion Characteristics in Common-Rail Diesel Engine" Processes 8, no. 9: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8091141
APA StyleTeoh, Y. H., How, H. G., Le, T. D., & Nguyen, H. T. (2020). Alexandrian Laurel for Biodiesel Production and its Biodiesel Blends on Performance, Emission and Combustion Characteristics in Common-Rail Diesel Engine. Processes, 8(9), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8091141





