Rapid TLC with Densitometry for Evaluation of Naproxen Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Stock and Working Standard Solutions
2.3. Chromatographic Conditions
2.4. Validation of Method
2.4.1. Specificity of Method
Stability Study of Naproxen on Silica Gel
Stability of Naproxen in Form of Solutions
2.4.2. Linearity and Range
2.4.3. Accuracy
2.4.4. Precision
2.4.5. Detection Limit (LOD) and Quantification Limit (LOQ)
2.5. Densitometric and Spectrodensitometric Analysis
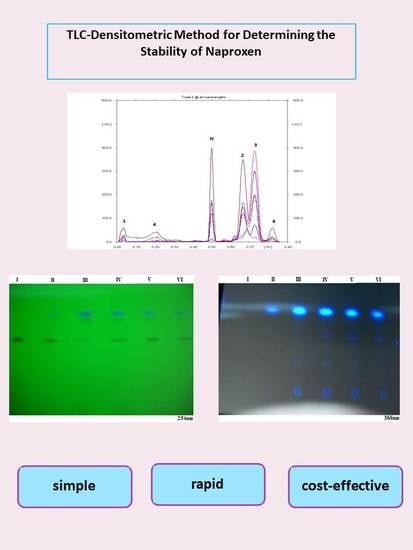
2.6. Photographs of TLC Chromatograms
2.7. Statistical Evaluation of Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Stability (Effect of UV Radiation) Study of Naproxen on Silica Gel
3.2. Stability Study of Naproxen Examined in Form of Proper Solutions Exposed to UV Radiation
3.2.1. Estimation of Stability of Naproxen in Form of Solutions after 5 h of Exposure to UV Radiation
3.2.2. Estimation of Stability of Naproxen in Form of Various Solutions after 10 h of Exposure to UV light
3.3. Validation of Methods
3.3.1. Specificity
3.3.2. Accuracy
3.3.3. Linearity and Range
3.3.4. Precision
3.3.5. Detection (LOD) and Quantification (LOQ) Limits
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waterman, K.C.; Adami, R.C. Accelerated aging: Prediction of chemical stability of Pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 293, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, S.; Singla, D.; Sakhuja, N. Stability testing of pharmaceutical products. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Blessy, M.; Patel, R.D.; Prajapati, P.N.; Agrawal, Y.K. Development of forced degradation and stability indicating studies of drugs—A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2014, 4, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ICH. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline: Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products, International Conference on Harmonization Guidance Documents, Q1A (R2); ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; Available online: http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q1A_R2/Step4/Q1A_R2__Guideline.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2020).
- Kothapalli, L.P.; Shahane, R.R.; Nanda, R.K.; Thomas, A.B. Development and validation of stability indicating HPTLC method for simultaneous estimation of Domperidone maleate and Naproxen sodium in pharmaceutical formulations. Asian J. Res. Chem. 2016, 9, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalluri, B.N.; Mrudula, B.; Chitralatha, K.; Sultana, S.A.; Chandra, T.U. Development of stability indicating RP-HPLC-PDA method for the simultaneous analysis of naproxen sodium and diphenhydramine hydrochloride in bulk and tablet dosage forms. Indian Drugs 2015, 52, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hamid, M.H.M.; Elsaman, T. A stability-indicating RP-HPLC-UV method for determination and chemical hydrolysis study of a novel naproxen prodrug. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 5285671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Songnaka, N.; Sawatdee, S.; Atipairin, A. Stability-indicating HPLC method for determination of naproxen in an extemporaneous suspension. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2018, 11, 4332–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatarao, P.; Kumar, M.N.; Kumar, M.R. Novel validated stability-indicating UPLC method for the estimation of naproxen and its impurities in bulk and drugs and pharmaceutical dosage form. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, P.S.; Sait, S.; Hotha, K.K. Estimation of naproxen related substances in sumatriptan succinate and naproxen sodium tablets by UPLC. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 9717–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.S.; Krishna, R.M.; Vekaria, N.A.; Sumathi, R.V.; Mantena, B.P.V. Determination of potential impurities of naproxen sodium in soft gelatin capsules dosage by using Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chem. Lett. 2016, 6, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittal, S.P.; Rao, S.V.; Ramakrishna, K. Stability indicating RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of potential impurities of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium in fixed dose combination. Rasayan J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.S.; Saita, S.; Vasudevmurthy, G.; Vishwanatha, B.; Prasada, V.; Reddy, S.J. Stability indicating simultaneous estimation of assay method for naproxen and esomeprazole in pharmaceutical formulations by RP-HPLC. Der Pharma Chem. 2011, 3, 553–564. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.T.; Rao, L.V. A validated stability-indicating UHPLC method for determination of naproxen and its related compounds in bulk drug samples. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 4, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyka, A.; Bober, K.; Klimczok, W.; Stefaniak, M. Densitometric investigations of chemical durability of pyrocatechol. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2006, 29, 3017–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyka, A.; Klimczok, W. Use of thin layer chromatography to evaluate the stability of methyl nicotinate. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2009, 32, 1299–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyka, A.; Gurak, D. Use of RP-TLC and densitometry to analytical characteristic of vitamin K1. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2009, 32, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyka, A.; Wiatr, E.; Kwiska, K.; Gurak, D. Validation thin layer chromatography for the determination of naproxen in tablets and comparison with a pharmacopeil method. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2011, 34, 829–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyka, A.; Nieduziak, A. Application of spectrophotometry to naproxen determination in pharmaceutical preparations. Farm. Pol. 2010, 66, 673–676. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Krzek, J.; Starek, M. Densitometric determination of naproxen, and of naproxen methyl ester, its impurity, in pharmaceutical preparations. J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2004, 17, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhole, R.P.; Shinde, S.S.; Chitlange, S.S.; Wankhede, S.B. A high-performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) method for simultaneous determination of diphenhydramine hydrochloride and naproxen sodium in tablets. Anal. Chem. Insights 2015, 10, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Moety, E.M.; Al-Obaid, A.M.; Jado, A.I.; Lotfi, E.A. Coupling of TLC and UV-measurement for quantification of naproxen and its main metabolite in urine. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1988, 13, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Strock, J.; Sherma, J. Development of HPTLC-densitometry methods for quantifying naproxen sodium, loperamide hydrochloride and loratadine in pharmaceutical tablets using a model procedure reported earlier to transfer TLC screening methods for fake and substandard drugs. Trends Chromatogr. 2016, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- DrugBank. Available online: https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00788 (accessed on 28 May 2020).
- USP. The United States Pharmacopeia, 34th ed.; United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sádecká, J.; Cakrt, M.; Hercegová, A.; Polonský, J.; Skacáni, I. Determination of ibuprofen and naproxen in tablets. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 25, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, N.; Keyhanian, F. Simple, sensitive and selective spectrophotometric assay of naproxen in pure, pharmaceutical preparation and human serum sample. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2015, 72, 867–875. [Google Scholar]
- Mabrouk, M.M.; Hammad, S.F.; Mansour, F.R.; El-Khateeb, B.Z. Simultaneous determination of naproxen and diphenhydramine by reversed phase liquid chromatography and derivative spectrophotometry. Der Pharma Chem. 2015, 7, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Shevchenko, G.; Kulichenko, S. Alkalimetric determination of hydrophobic pharmaceuticals using stabilized o/w emulsions. Chem. Pap. 2008, 62, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aresta, A.; Palmisano, F.; Zambonin, C.G. Determination of naproxen in human urine by solid-phase microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 39, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayanan, V.; Zhang, Y.; Yoshihara, S.; Shirakashi, T. Voltammetric assay of naproxen in pharmaceutical formulations using boron-doped diamond electrode. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanik, S.; Yilmaz, S.; Saglikoglu, G.; Sadikoglu, M.; Tonguc Yayintas, Ö. Voltammetric and chromatographic determination of naproxen in drug formulation. J. Sci. Perspect. 2019, 3, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afzali, M.; Jahromi, Z.; Nekooie, R. Sensitive voltammetric method for the determination of naproxen at the surface of carbon nanofiber/gold/polyaniline nanocomposite modified carbon ionic liquid electrode. Mikrochem. J. 2019, 145, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeragoni, A.K.; Sindgi, V.M.; Satla, S.R. Bioanalytical validated LC-MS method for determination of naproxen in human plasma. Int. J. Mod. Trends Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Satterwhite, J.H.; Boudinot, F.D. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of ketoprofen and naproxen in rat plasma. J. Chromatogr. 1988, 431, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinç, E.; Özdemir, A.; Aksoy, H.; Üstündağ, Ö.; Balean, D. Chemometric determination of naproxen sodium and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride in tablets by HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, B.; Sahin, H.; Erdem, A.F. Determination of naproxen in human plasma by GC-MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muneer, S.; Muhammad, I.N.; Abrar, M.A.; Munir, I.; Kaukab, I.; Sagheer, A.; Zafar, H.; Sultana, K. High performance liquid chromatographic determination of naproxen in prepared pharmaceutical dosage form and human plasma and its application to pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. Sep. Tech. 2017, 8, 1000369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krokos, A.; Tsakelidou, E.; Michopoulou, E.; Raikos, N.; Theodoridis, G.; Gika, H. NSAIDs determination in human serum by GC-MS. Separations 2018, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monser, L.; Darghouth, F. Simultaneous determination of naproxen and related compounds by HPLC using porous graphitic carbon column. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 32, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabaidur, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.A.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Mohsin, K.; Bousiakou, L.G.; Karikas, G.A. UPLC-MS method for the simultaneous determination of naproxen, fluvastatin and ibuprofen in waste water samples. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 24, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Herrera, M.; Honda, L.; Richter, P. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-time-of-flight high resolution mass spectrometry to quantify acidic drugs in wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1423, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Salama, A.; Nasser, W.S.; Uheida, A. Photodegradation of ibuprofen, cetirizine, and naproxen by PAN-MWCNT/TiO2-NH2 nanofiber membrane under UV light irradiation. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, T.; Mukhtar, N.H.; Lim, H.N.; See, H.H. Mixed matrix membrane tip extraction coupled with UPLC-MS/MS for the monitoring of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in water samples. Separations 2020, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillip, T.M.; Wellner, E.F. Measurement of naproxen in human plasma by chip-based immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, Y.; Xue, H.; Wang, X.; Lian, K. Determination of naproxen in human urine by capillary electrophoresis with chemiluminescence detection. Glob. Drugs Ther. 2018, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ICH. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline: Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology, Q2 (R1); ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; Available online: http://www.ich.org/products/guidelines/efficacy/article/efficacy-guidelines.html (accessed on 28 May 2020).
- Ferenczi-Fodor, K.; Renger, B.; Végh, Z. THE frustrated reviewer—Recurrent failures in manuscripts describing validation of quantitative TLC/HPTLC procedures for analysis of pharmaceuticals. J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod TLC 2010, 23, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dołowy, M.; Pyka-Pająk, A. Comparison of the limits of detection and quantification of estradiol hemihydrate determined by thin-layer chromatography using different chromatographic conditions. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2016, 39, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampilek, J.; Dolowy, M.; Pyka-Pajak, A. Estimating limits of detection and quantification of ibuprofen by TLC-densitometry at different chromatographic conditions. Processes 2020, 8, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starek, M.; Krzek, J.; Stoch, M. Densitometric analysis of 2-arylpropionate derivatives in pharmaceutical preparations. J. Planar Chromatogr.-Mod. TLC 2008, 21, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Solution No. | Sample Appearance | |
|---|---|---|
| After 5 h of Exposure to UV Light | After 10 h of Exposure to UV Light | |
| II | light yellow color, transparent, after dilution with an ethanol—colorless solution | light yellow color, transparent; a few crystals of crystallized substances dissolve upon dilution with an ethanol, and the solution becomes colorless |
| III | colorless | yellow, straw color, even after dilution; some misshapen precipitate which disappear after dilution with an ethanol and shaking |
| IV | colorless | yellow color goes into orange, stable after dilution; presence of misshapen precipitate which disappear after dilution with an and shaking |
| V | colorless | yellow color goes into light orange, stable after dilution; presence of misshapen precipitate which disappear after dilution with an ethanol and shaking |
| VI | yellow color, also after dilution with an ethanol | dark yellow color with orange hue (the strongest color of all solution), stable after dilution; no other precipitates, a few crystals of crystallized substances dissolve upon dilution with an ethanol |
| Sample Exposure Conditions/ Mobile Phase Used in TLC Analysis | Compound (a) | RF Values | Absorption Wavelength (nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure of naproxen to UV light on silica gel | A: TOL-ACE-CHL (2:5:12, v/v/v) | N 1 2 3 | 0.29 0.02 0.70 ÷ 0.71 0.89 ÷ 0.90 | 229; 272; 316; 329 210; 232; 260 227; 271; 316; 326 249; 259; 313 | |
| B: AcOH-Hex-ACE (0.10:10:10, v/v/v) | N 1 2 3 | 0.44 ÷ 0.47 0.03 ÷ 0.04 0.71 ÷ 0.75 0.78 ÷ 0.81 | 229; 273; 316; 329 204; 231; 266 227; 277; 313 249; 260; 311 | ||
| Exposure of solution of naproxen during | 5 h | A: TOL-ACE-CHL (2:5:12, v/v/v) | N 1 2 3 4 | 0.25 ÷ 0.31 0.03 ÷ 0.04 0.65 ÷ 0.66 0.85 ÷ 0.86 0.81 | 229; 272; 317; 329 228 ÷ 230; 275 227; 263 ÷ 282 258 ÷ 260; 310 ÷ 312 227; 280; 330 |
| 10 h | N 1 2 3 4 | 0.24 ÷ 0.29 0.02 ÷ 0.03 0.66 ÷ 0.67 0.85 ÷ 0.87 0.81 | 229; 272; 317; 330 229 ÷ 234; 273 ÷ 282 227; 272; 316; 328 248; 260; 312 227; 264; 280 | ||
| Exposure of solution of naproxen during | 5 h | B: AcOH-Hex-ACE (0.10:10:10, v/v/v) | N 1 2 3 4 | 0.47 ÷ 0.50 0.03 ÷ 0.04 0.67 ÷ 0.69 0.73 ÷ 0.75 0.18 ÷ 0.19 | 229; 272; 318; 329 227 ÷ 231; 282 (for solution No. 6) 227; 273; 329 210; 249; 260; 313 211; 231 |
| 10 h | N 1 2 3 4 5 6 | 0.50 ÷ 0.51 0.03 ÷ 0.04 0.66 ÷ 0.68 0.73 ÷ 0.74 0.19 ÷ 0.21 0.45 0.82 | 229; 272; 317; 329 229 ÷ 233; 283 (for solution No. 6) 227; 272; 317; 327 249; 260; 311 200 ÷ 202 202; 233; 238; 273 203; 227; 273; 327 | ||
| Method Characteristics | Results |
|---|---|
| Specificity | Specific |
| Range (μg spot −1) | 0.04 ÷ 1.00 |
| Linearity (μg spot −1) | A = 18201.2(±113.2) x + 975.3(±28.9) n = 16; r = 0.999; F = 12302 |
| Detection Limit (LOD) (μg spot −1) | 0.013 |
| Quantification Limit (LOQ) (μg spot −1) | 0.040 |
| Accuracy | |
| naproxen added in % (n = 5) | |
| 80% | R = 99.2%; CV = 1.89% |
| 100% | R = 101.8%; CV = 1.25% |
| 120% | R = 99.1%; CV = 0.86% |
| Precision (CV, (%)) | |
| Repeatability | |
| for 0.25 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.22 |
| for 0.50 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.08 |
| for 0.75 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.49 |
| Intermediate | |
| for 0.25 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.08 |
| for 0.50 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.53 |
| for 0.75 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.22 |
| Method Characteristics | Results |
|---|---|
| Specificity | Specific |
| Range (μg spot −1) | 0.08 ÷ 1.00 |
| Linearity (μg spot −1) | A = 9413.1(±82.4) x + 1575.3(±49.4) N = 12; r = 0.999; F = 13,401 |
| Detection Limit (LOD) (μg spot −1) | 0.026 |
| Quantification Limit (LOQ) (μg spot −1) | 0.080 |
| Accuracy | |
| naproxen added in % (n = 5) | |
| 80% | R = 102.3%; CV = 1.51% |
| 100% | R = 98.4%; CV = 1.18% |
| 120% | R = 100.3%; CV = 0.93% |
| Precision (CV, (%)) | |
| Repeatability | |
| for 0.25 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.13 |
| for 0.50 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.28 |
| for 0.75 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.27 |
| Intermediate | |
| for 0.25 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.28 |
| for 0.50 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.36 |
| for 0.75 μg spot −1 (n = 3) | 1.31 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parys, W.; Dołowy, M.; Pyka-Pająk, A. Rapid TLC with Densitometry for Evaluation of Naproxen Stability. Processes 2020, 8, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080962
Parys W, Dołowy M, Pyka-Pająk A. Rapid TLC with Densitometry for Evaluation of Naproxen Stability. Processes. 2020; 8(8):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080962
Chicago/Turabian StyleParys, Wioletta, Małgorzata Dołowy, and Alina Pyka-Pająk. 2020. "Rapid TLC with Densitometry for Evaluation of Naproxen Stability" Processes 8, no. 8: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080962
APA StyleParys, W., Dołowy, M., & Pyka-Pająk, A. (2020). Rapid TLC with Densitometry for Evaluation of Naproxen Stability. Processes, 8(8), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080962