Void Properties in Dense Bed of Cold-Flow Fluid Catalytic Cracking Regenerator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
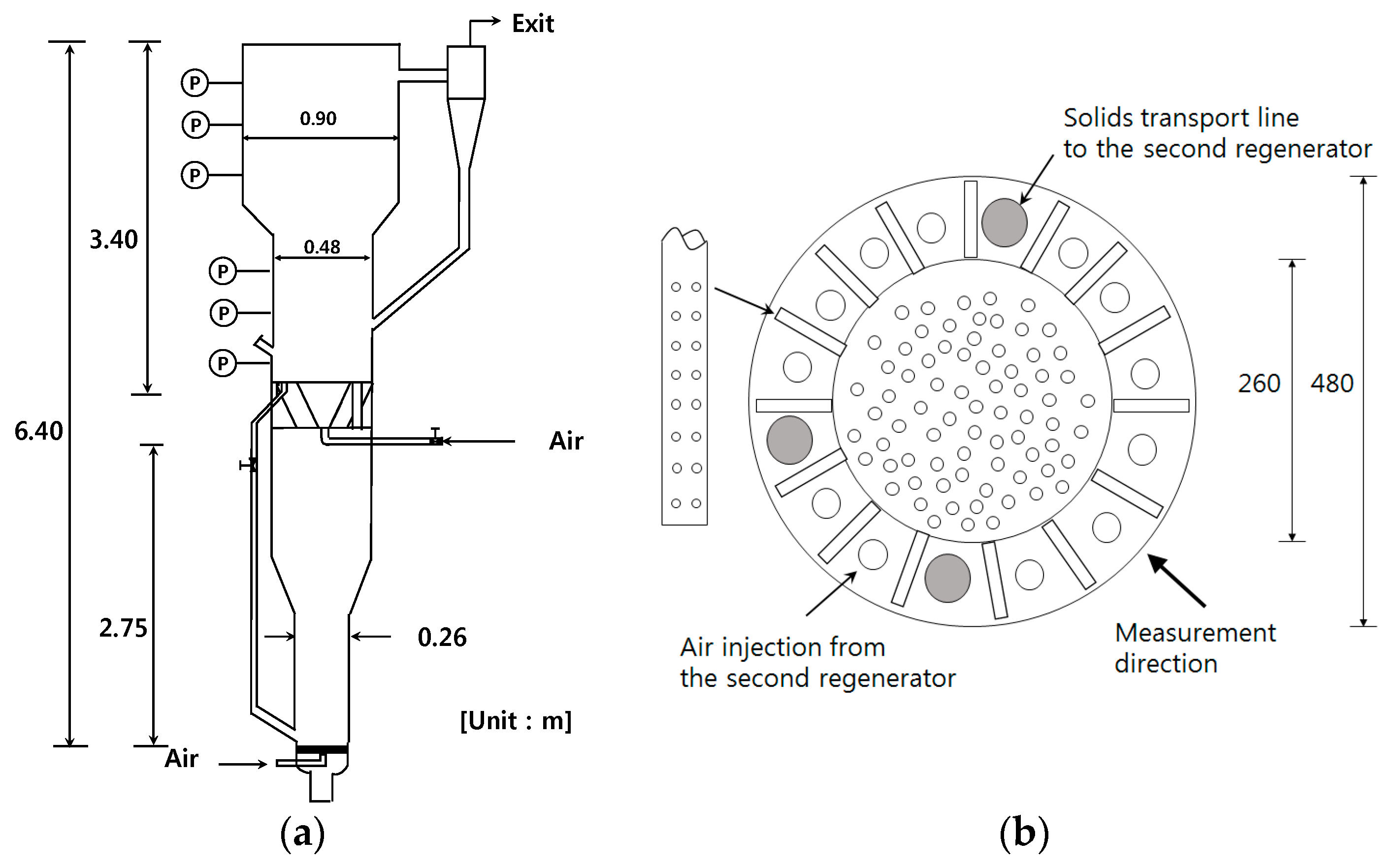
2.1. Materials and Experimental Apparatus
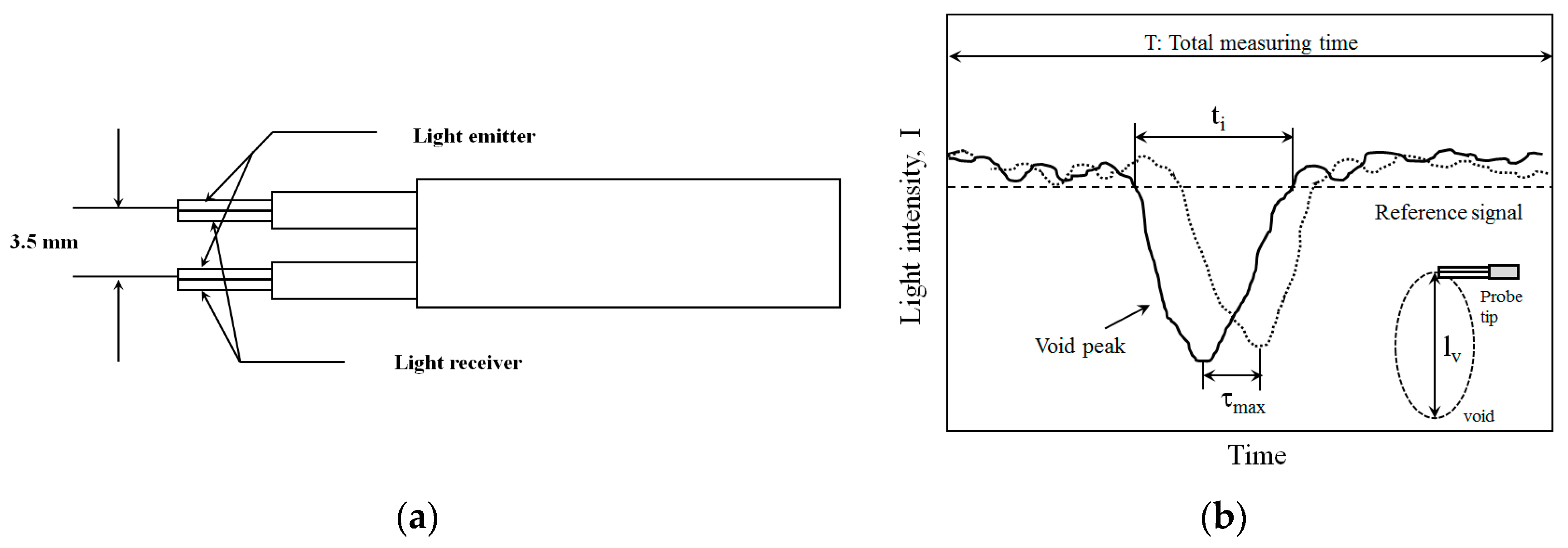
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
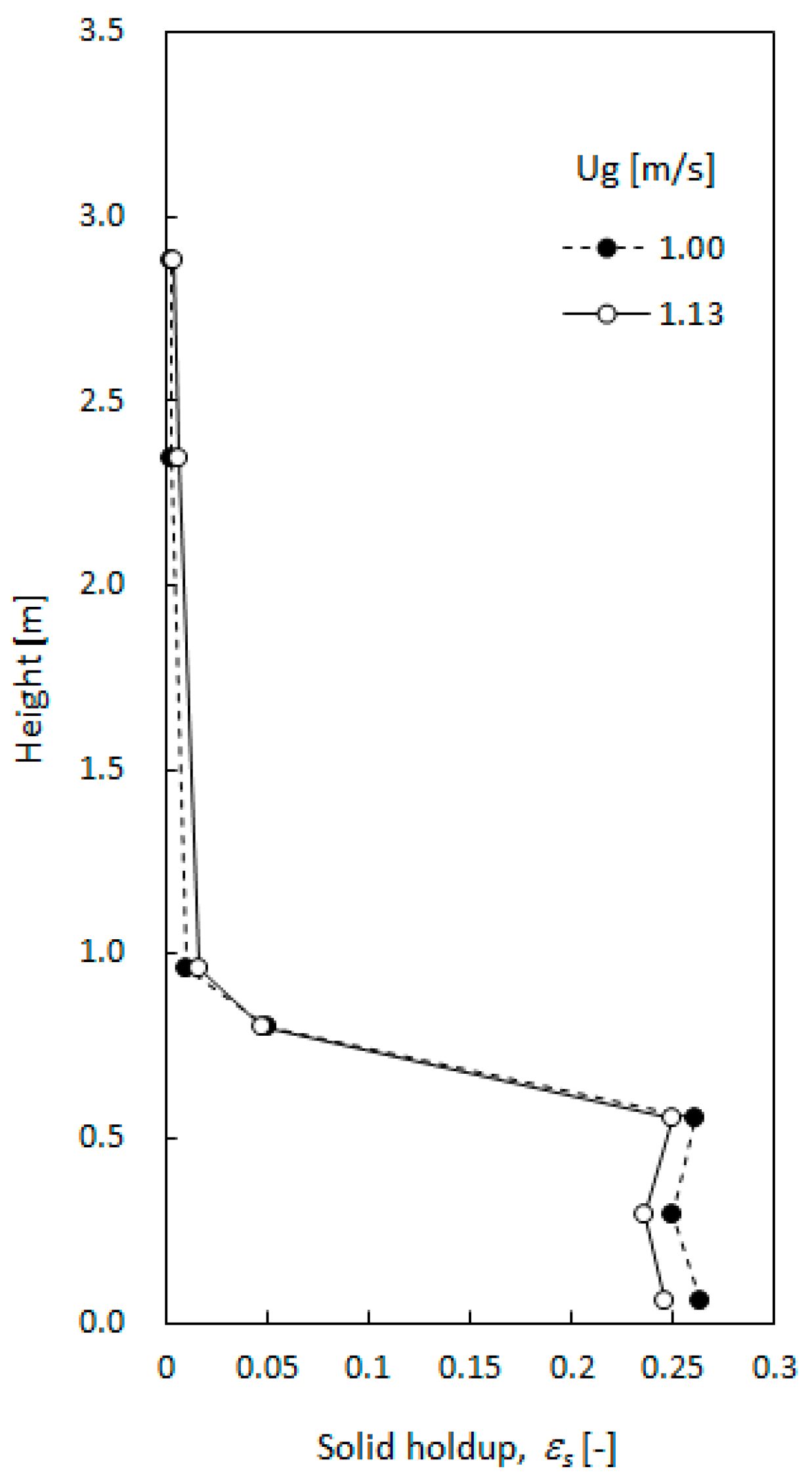
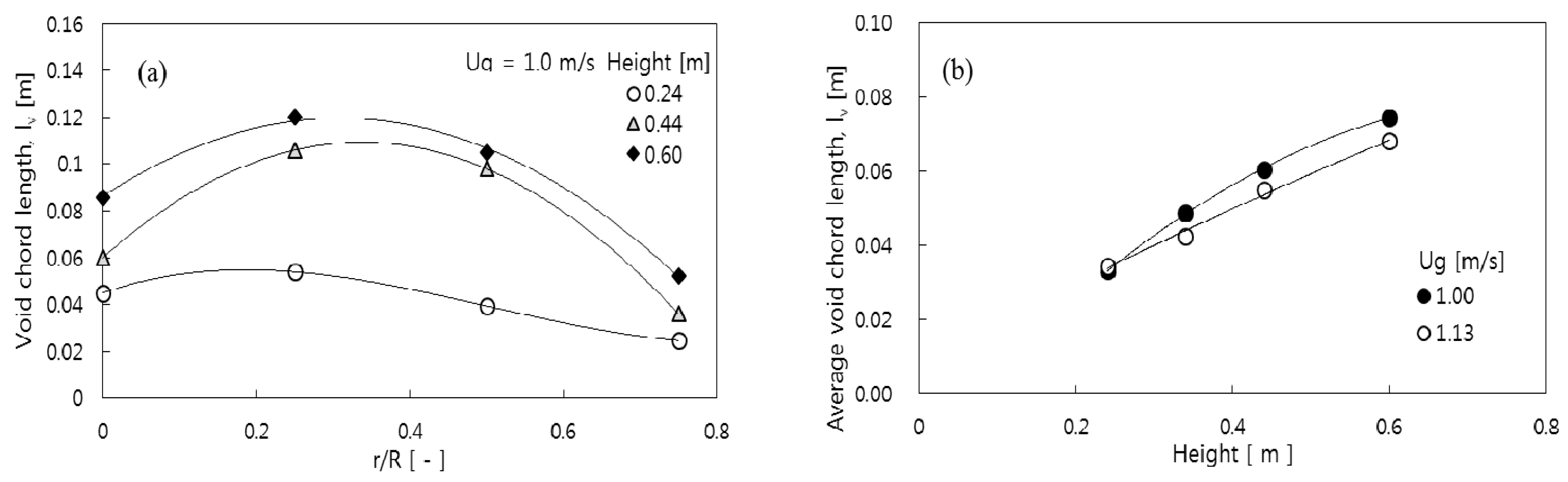
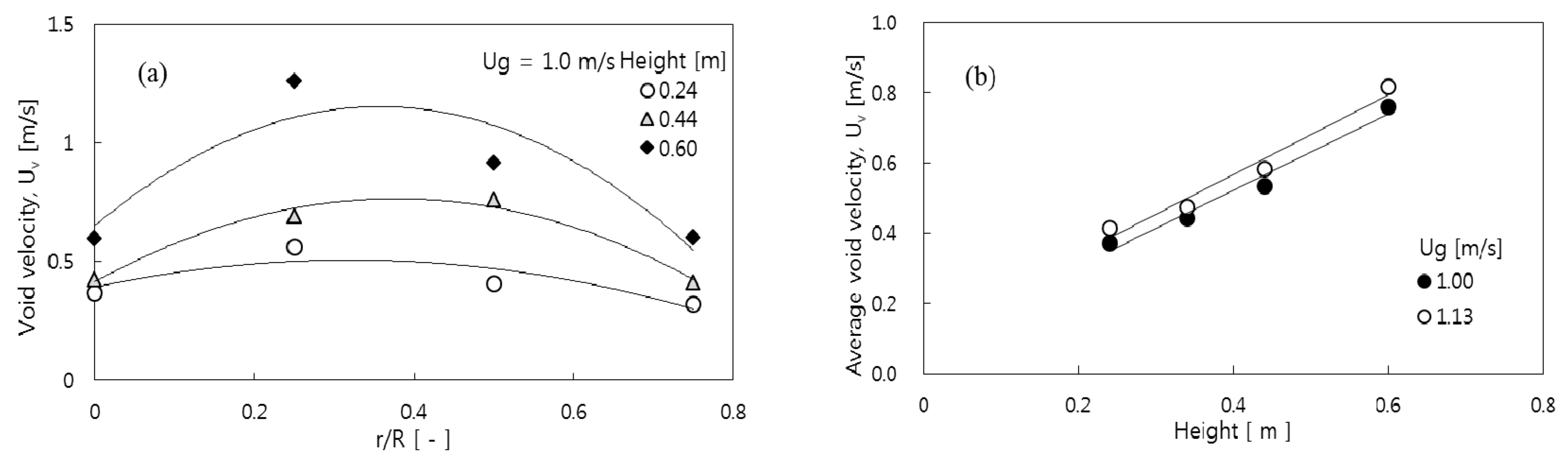
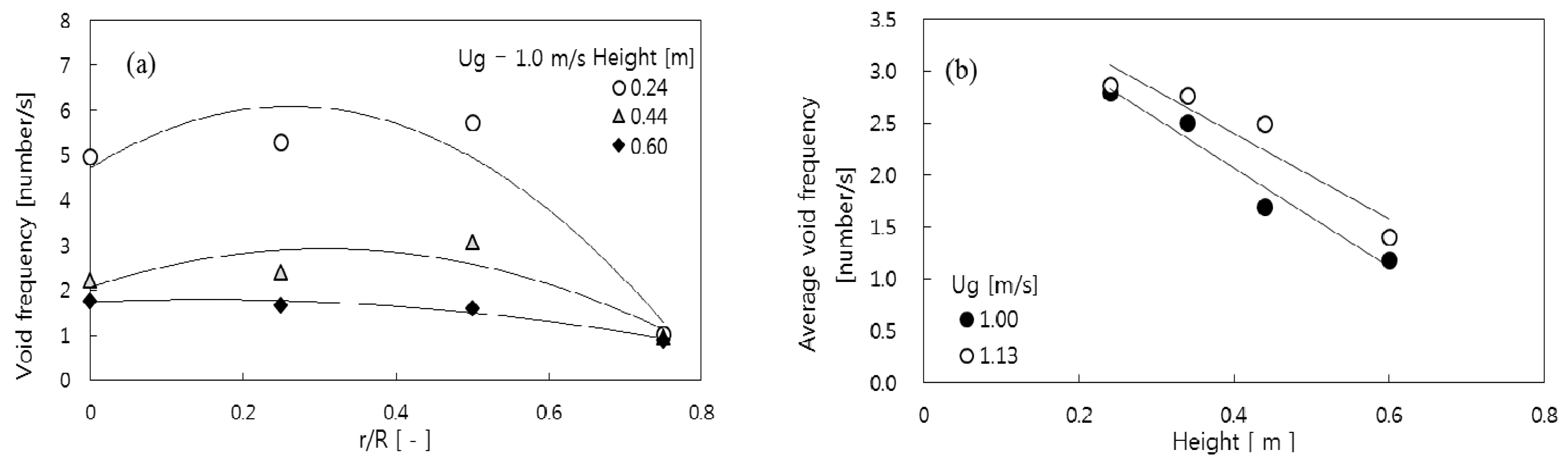
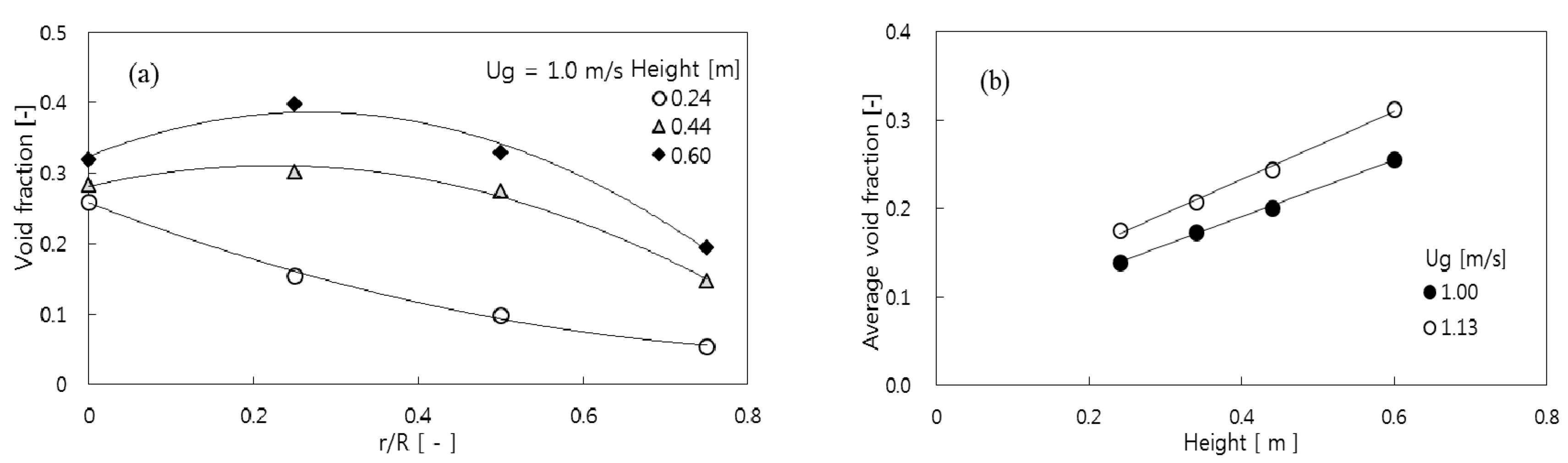
3.1. Void Properties
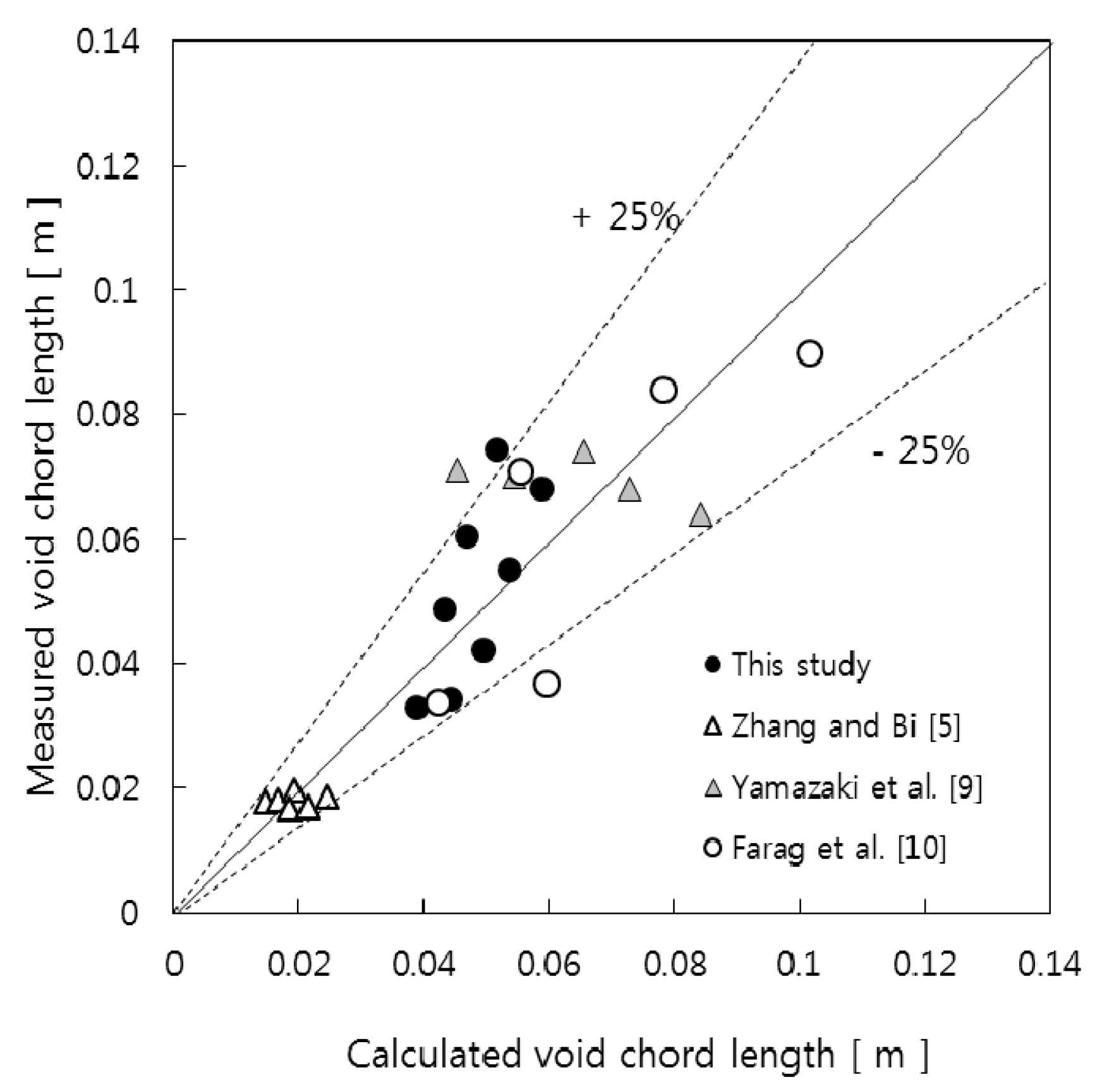
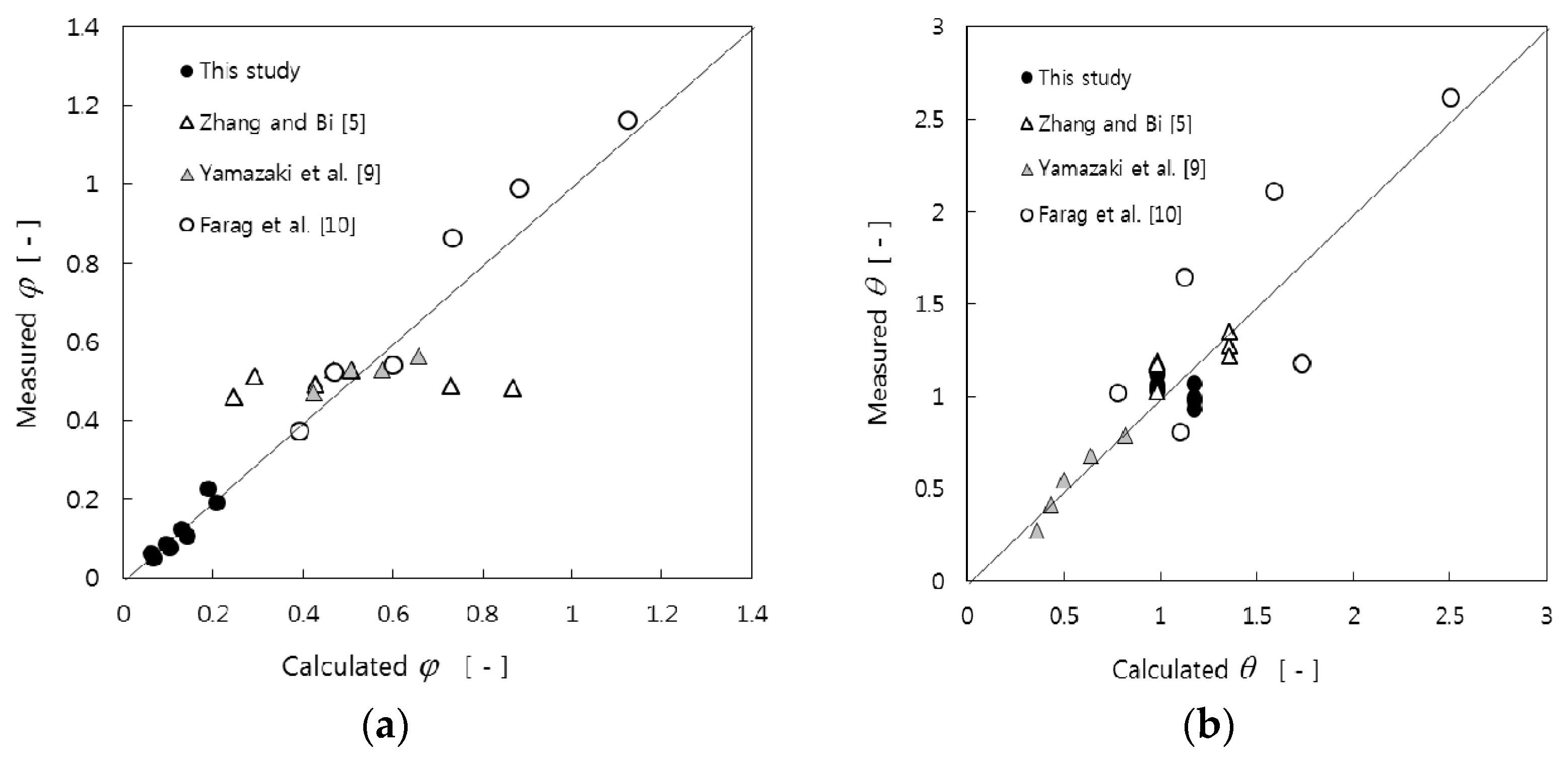
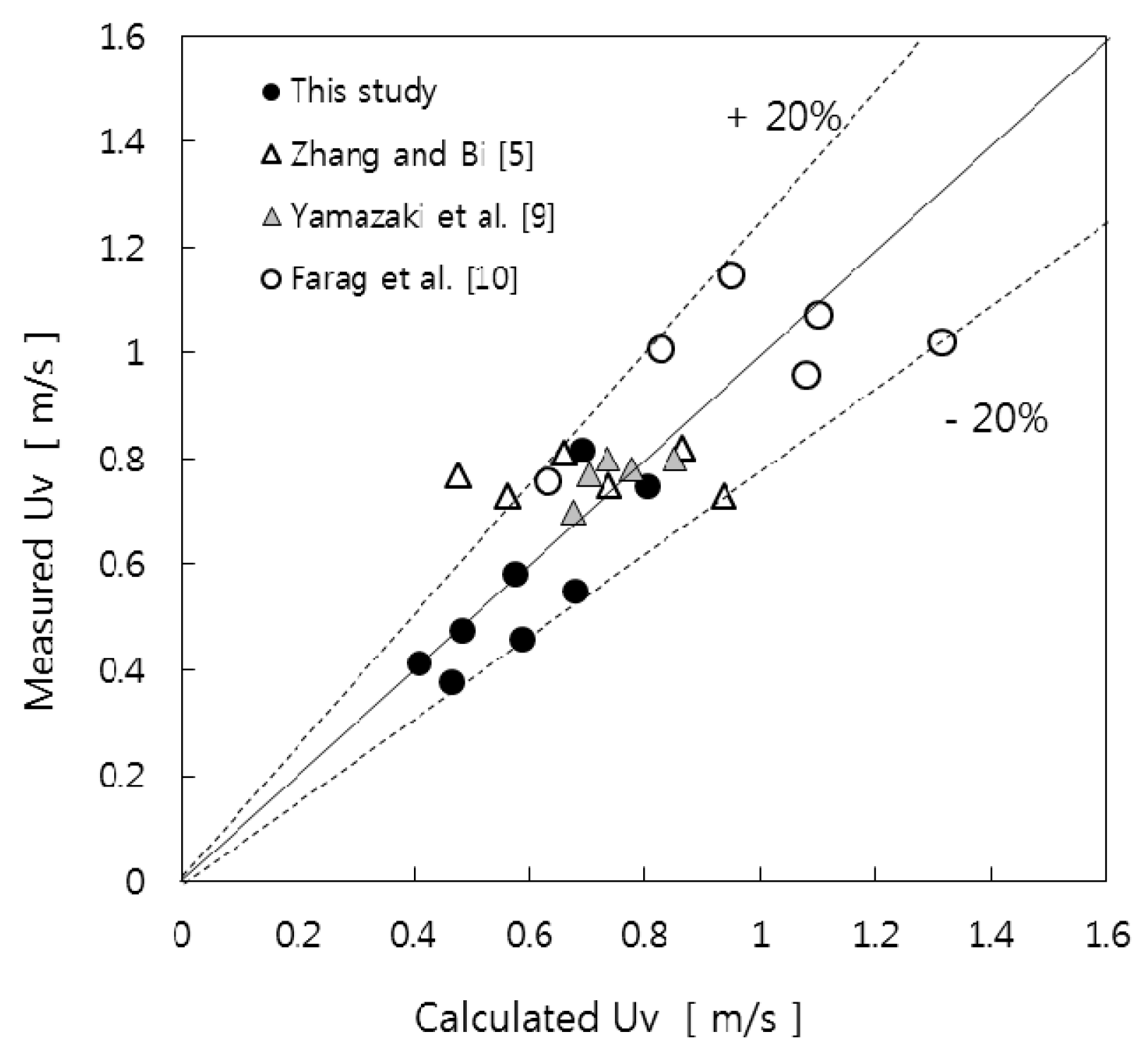
3.2. Prediction of Void Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ar | Archimedes number (dp3ρg(ρp − ρg)g/μ2) [-] |
| d | distance between two probe tips [m] |
| dp | mean particle diameter [m] |
| dv | void diameter [m] |
| Dt | diameter of reactor column [m] |
| FrD | Froude number (Ug/(gDt)0.5) [-] |
| f | void frequency [1/s] |
| g | gravitational constant [m/s2] |
| h | height [m] |
| lv | void chord length [m] |
| Re | Reynolds number ((ρg DtUg/μ) [-] |
| Rep | particle Reynolds number (ρg dpUg/μ) [-] |
| r/R | radial dimensionless coordinate [-] |
| T | total measuring time [s] |
| ti | void contact time with tip of probe [s] |
| Uc | transition velocity from bubbling to turbulent fluidized bed [m/s] |
| Ug | gas velocity [m/s] |
| Umf | minimum fluidization velocity [m/s] |
| Uv | void rising velocity [m/s] |
| Vv | visible void flow rate [m/s] |
| Greek | |
| εs | solid holdup [-] |
| μ | gas viscosity [kg/m s] |
| ρg | gas density [kg/m3] |
| ρp | apparent particle density [kg/m3] |
| ϕ | parameter defined by Equation (8) [-] |
| θ | parameter defined by Equation (6) [-] |
| δ | void fraction [-] |
| τmax | time lag determined by cross-correlation [s] |
References
- Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.W.; Koh, J.S.; Kim, G.R.; Choi, S.; Yoo, I.K. Formation and characterization of deposits in cyclone dipleg of a commercial RFCC reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 14279–14288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, C. Experimental study and modeling on effects of a new multilayer baffle in a turbulent fluid catalytic cracking regenerator. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 2062–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghbeigi, R. Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook, 3rd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 1–42. ISBN 978-0-12-386965-4. [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen, C.G.; Vilela, A.C.F.; Zen, L.D. Fluidized bed modeling applied to the analysis of processes: Review and state of the art. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bi, H.T. Study on void behavior in a turbulent fluidized bed with catalyst powders. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 6862–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Warsito, W.; Fan, L. ECT studies of gas-solid fluidized beds of different diameters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5020–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, J.; Wein, J. Expansion behavior of gas fluidized beds in the turbulent regime. AIChE Symp. Ser. 1994, 301, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Karimipour, S.; Pugsley, T. A critical evaluation of literature correlations for predicting bubble size and velocity in gas-solid fluidized beds. Powder Technol. 2011, 205, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, R.; Asai, M.; Nakajima, M.; Jimbo, G. Characterization of transition regime to a turbulent fluidized bed. In Circulating Fluidized Bed Technol IV; Avidan, A.A., Ed.; AIChE: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 609–614. [Google Scholar]
- Farag, H.I.; Ege, P.E.; Grislingas, A.; De Lasa, H.E. Flow patterns in a pilot plant-scale turbulent fluidized bed reactor: Concurrent application of tracers and fiber optic sensors. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1997, 75, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W. Measurement of carbon nanotube agglomerates size and shape in dilute phase of a fluidized bed. Korean Chem. Eng. Res. 2017, 55, 646–651. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, K.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Han, J.; Park, S.; Lee, D.H. Bubble characteristics by pressure fluctuation analysis in gas-solid bubbling fluidized beds with or without internal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumat, H.; Billet-Duquenne, A.M.; Augier, F.; Mathieu, C.; Delmas, H. On the reliability of an optical fibre probe in bubble column under industrial relevant operating condition. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2005, 29, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Namkung, W.; Kim, S.D. Solids Behavior in Freeboard of FCC Regenerator. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2000, 33, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W. Handbook of Fluidization and Fluid-Particle Systems; Marcel Deckker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 496–497. ISBN 978-0824702595. [Google Scholar]
- Guet, S.; Fortunati, R.V.; Mudde, R.F.; Ooms, G. Bubble velocity and size measurement with a four-point optical fiber probe. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2003, 20, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendat, J.S.; Piersol, A.G. Random Data, Analysis and Measurement Procedures, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 359–416. ISBN 978-0470248775. [Google Scholar]
- Andreux, R.; Chaouki, J. Behaviors of the bubble, cloud, and emulsion phases in a fluidized bed. AIChE J. 2008, 54, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyamoorthy, D.; Horio, M. On the influence of aspect ratio and distributor in gas fluidized beds. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 93, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasic, S.; Leckner, B.; Johnsson, F. Time-frequency investigation of different modes of bubble flow in a gas–solid fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 121, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, F.; Svensson, A.; Leckner, B. Fluidization Regimes in Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers; Potter, O.E., Nicklin, O.J., Eds.; Fluidization VII; Engineering Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.T.; Ellis, N.; Abba, I.A.; Grace, J.R. A state-of-the-art review of gas-solid turbulent fluidization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 4789–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, S.; Rabinovich, E.; Kalman, H. Typical fluidization characteristics for Geldart’s classification groups. Part. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauriol, P.; Cui, H.; Chaouki, J. Gas jet penetration lengths from upward and downward nozzles in dense gas–solid fluidized beds. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Properties | |
|---|---|
| Mean particle diameter [μm] | 70 |
| Apparent particle density [kg/m3] | 2130 |
| Umf [m/s] | 0.011 |
| Uc [m/s] | 0.65 |
| Particles | dp [mm] | ρs [kg/m3] | Ar [-] | Rep [-] | FrD [-] | Dt [m] | h [m] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | Spent FCC | 70 | 2130 | 25 | 1.51, 1.63 | 0.46, 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.24–0.60 |
| Yamazaki et al. [9] | FCC | 64 | 1850 | 16.6 | 1.04–1.62 | 0.48–0.86 | 0.2 | 0.43 |
| Farag et al. [10] | FCC | 65 | 1500 | 14.1 | 0.50–1.06 | 0.18–0.48 | 0.3, 0.5 | 0.63 |
| Zhang and Bi [5] | FCC | 77.6 | 1565 | 25.4 | 1.37, 1.59 | 0.57, 0.72 | 0.19 | 0.35–0.85 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.D. Void Properties in Dense Bed of Cold-Flow Fluid Catalytic Cracking Regenerator. Processes 2018, 6, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6070080
Kim SW, Kim SD. Void Properties in Dense Bed of Cold-Flow Fluid Catalytic Cracking Regenerator. Processes. 2018; 6(7):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6070080
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sung Won, and Sang Done Kim. 2018. "Void Properties in Dense Bed of Cold-Flow Fluid Catalytic Cracking Regenerator" Processes 6, no. 7: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6070080
APA StyleKim, S. W., & Kim, S. D. (2018). Void Properties in Dense Bed of Cold-Flow Fluid Catalytic Cracking Regenerator. Processes, 6(7), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6070080





