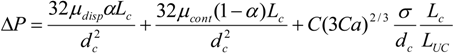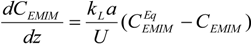Stability Analysis of Reactive Multiphase Slug Flows in Microchannels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Extraction
2.1. Chemicals and Analytics
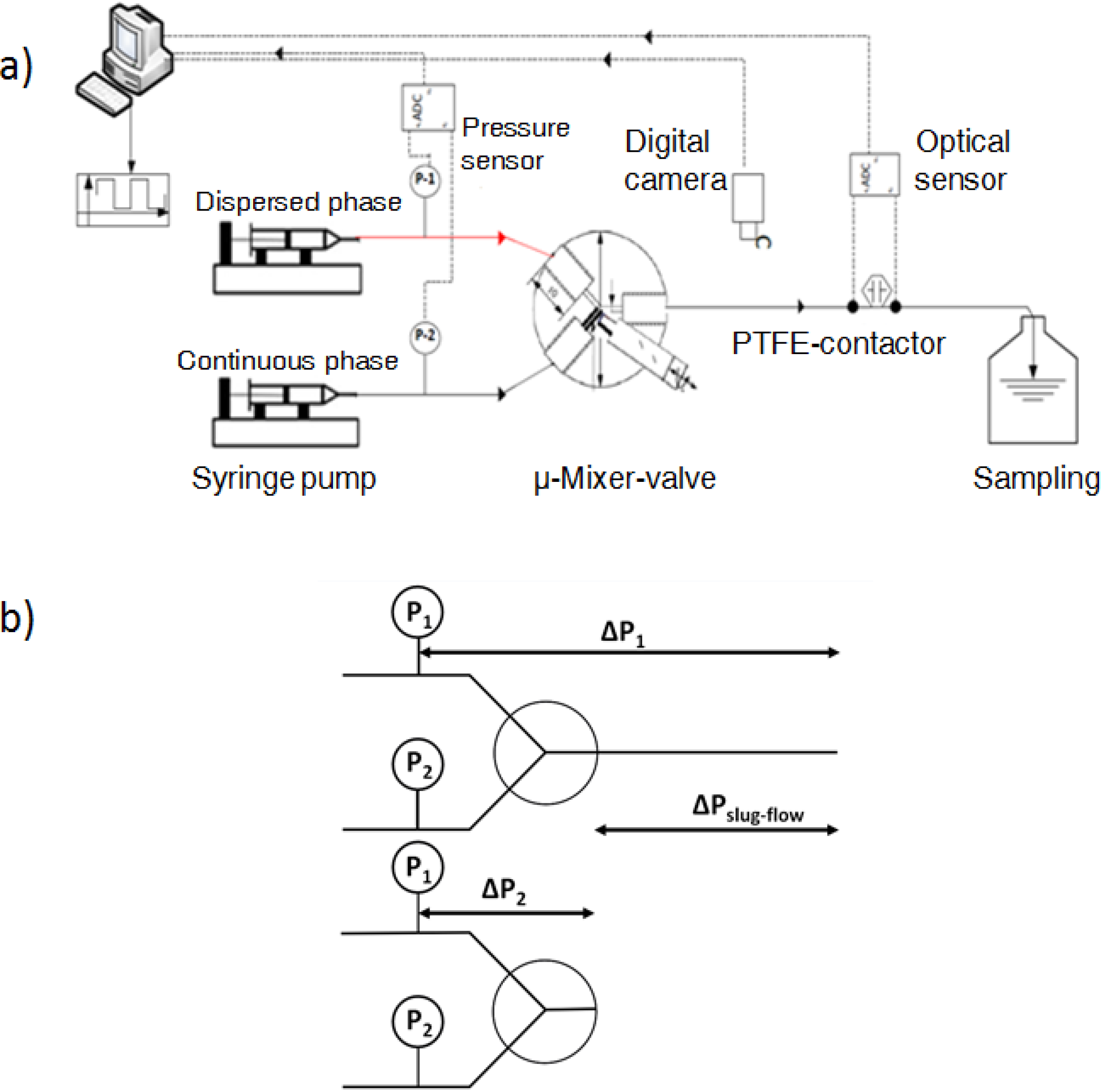
2.2. Experimental Setup



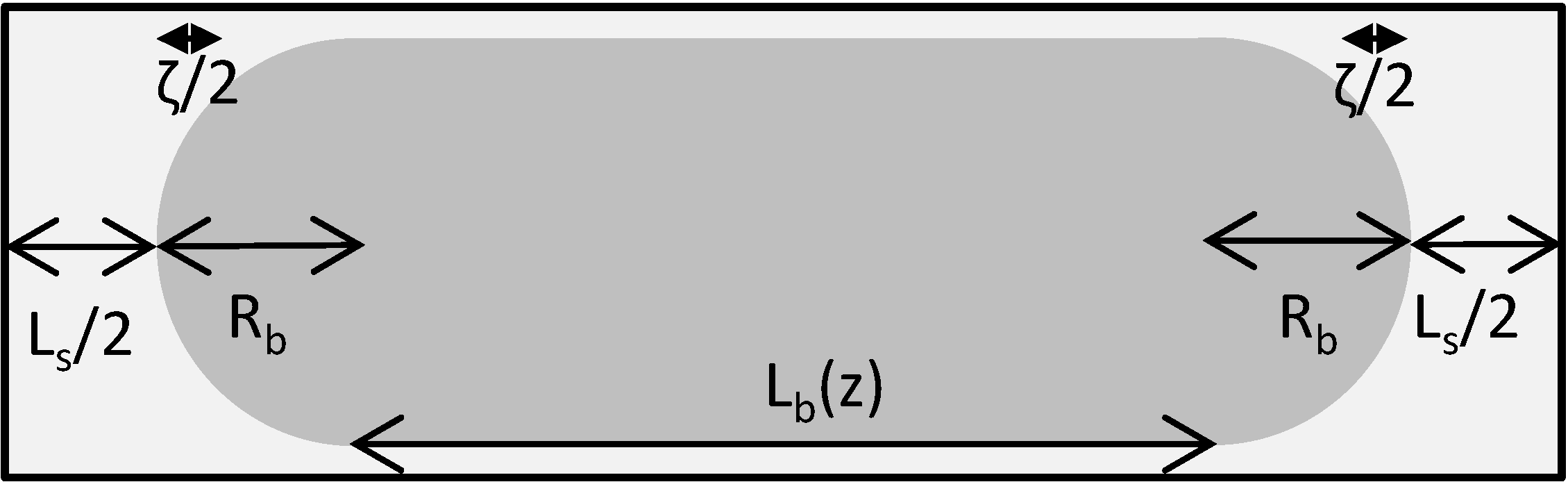
3. Gas-Liquid Model Equations



















4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Simulations
| Parameter | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| σ | 0.072 | N/m |
| µ | 1 | mPa.s |
| ρ | 1000 | kg/m3 |
| H | 3.85 × 10−4 | mol/m3/Pa |
| T | 298 | K |
| P | 101,325 | Pa |
| D | 2 × 10−9 | m2/s |
4.1.1. Gas-Liquid Model Validation
| Parameter | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| dc | 400 | µm |
| LB,0 | 4·dc | µm |
| LS,0 | dc | µm |
| kOH− | 8.5 | m3/mol/s |
| COH− | 0.1 | M |
| yCO2 | 0.4 | ----- |
| LR | 0.1 | m |

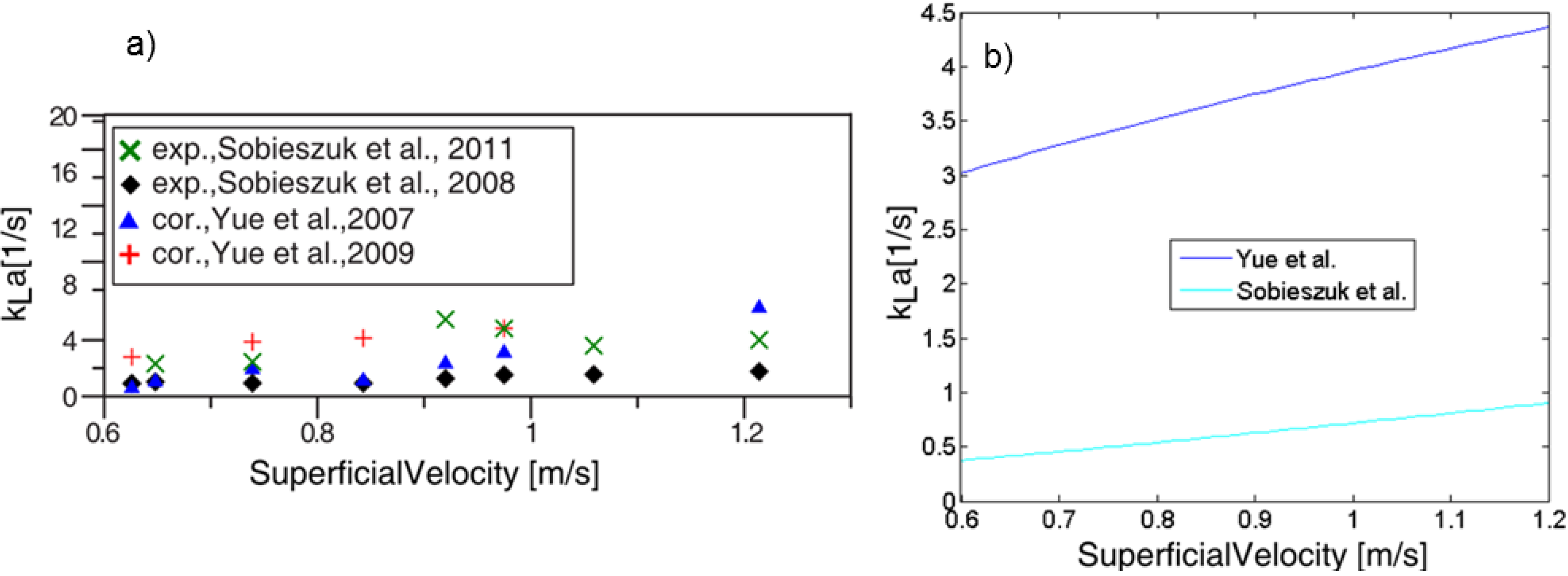
4.1.2. Hydrodynamic Multiplicity
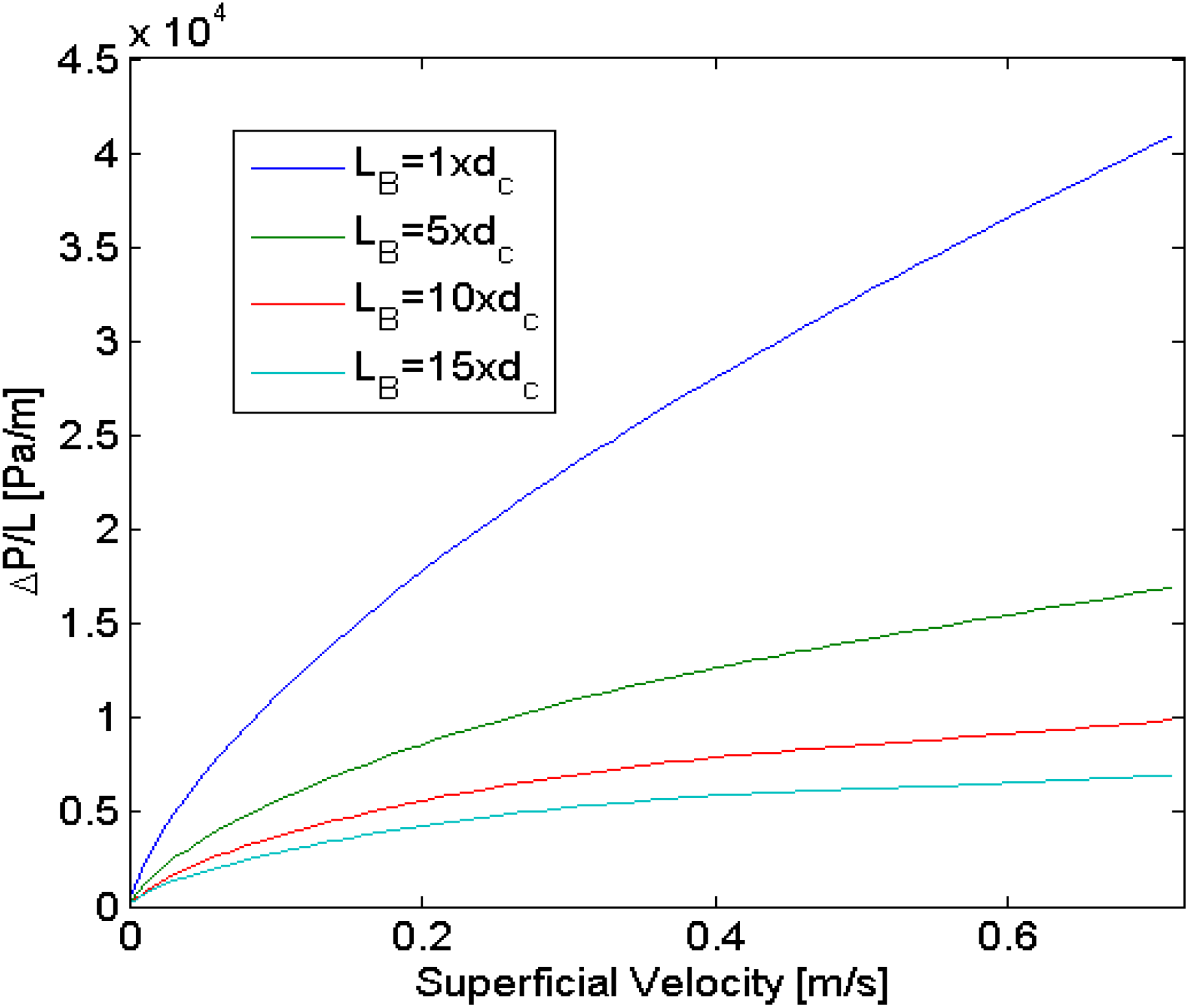

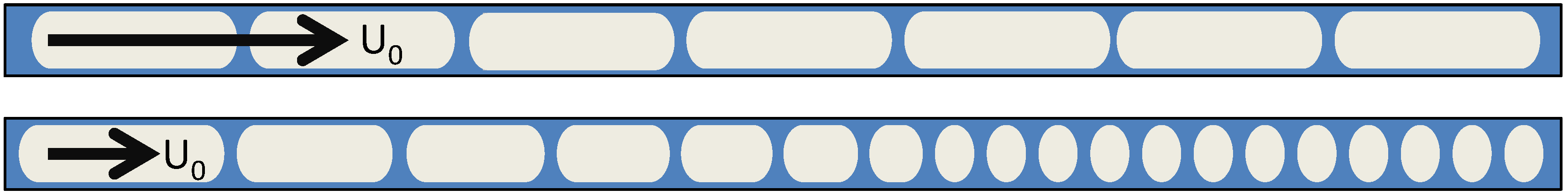
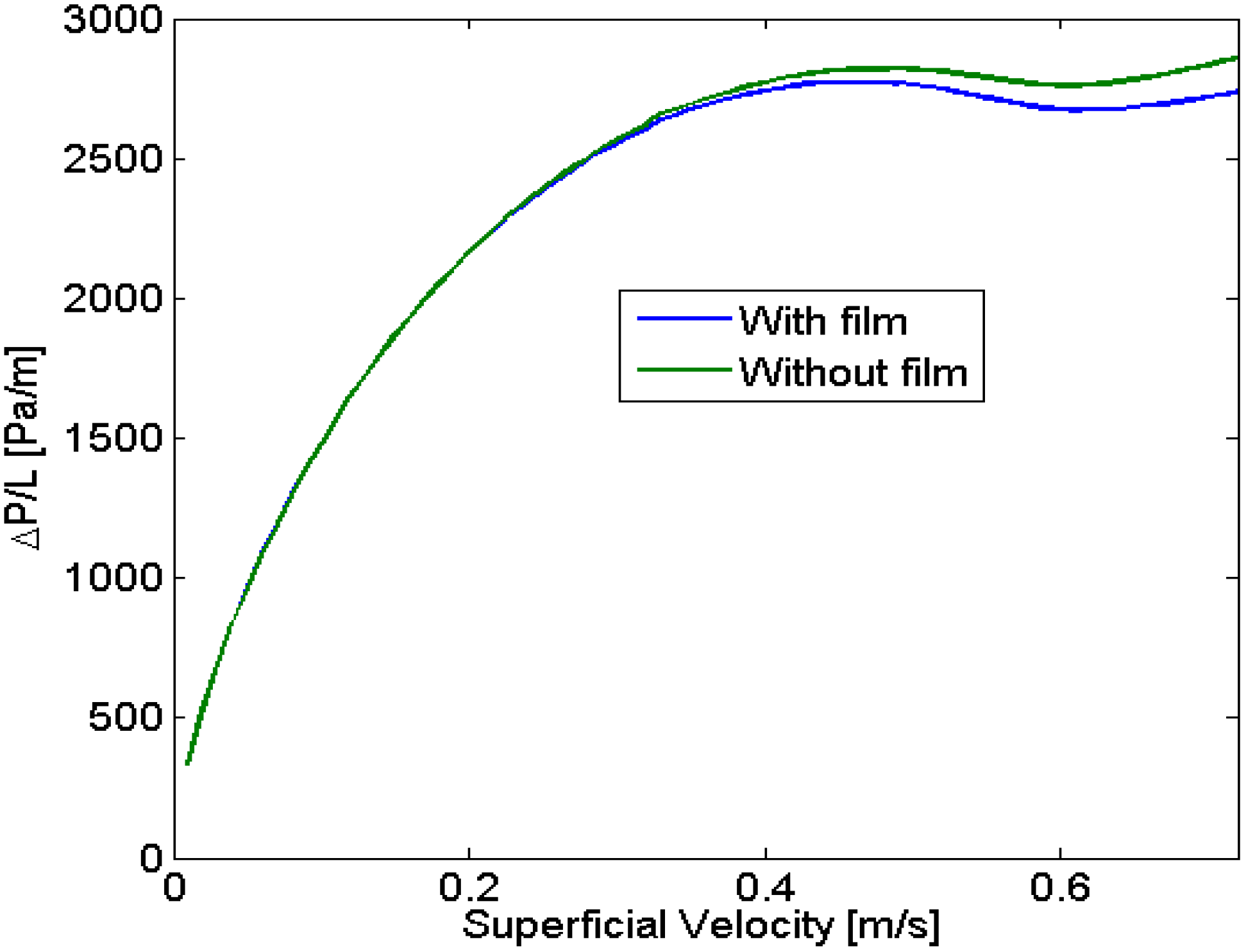
4.1.3. Film Effect
4.1.4. Interfacial Geometry
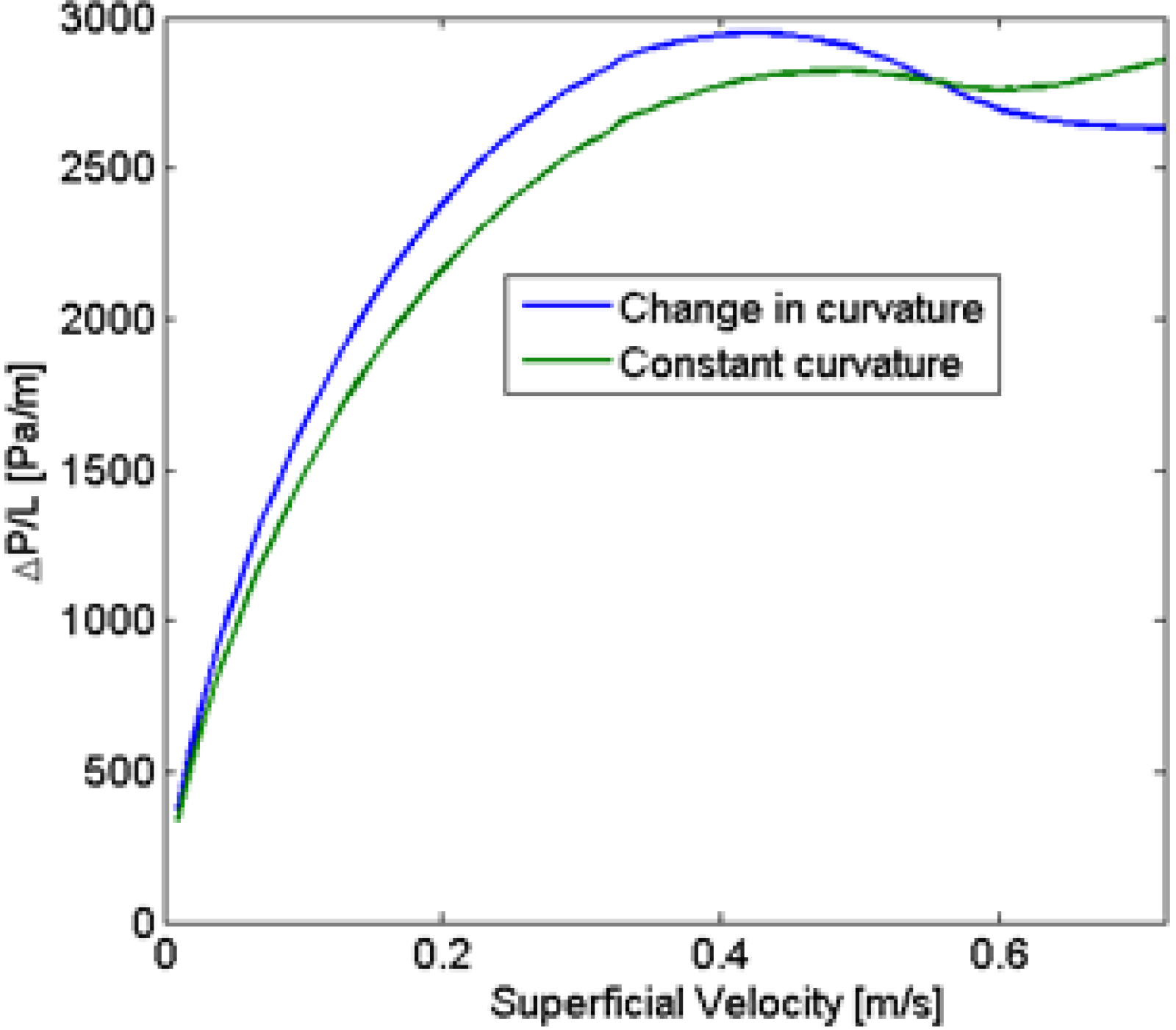
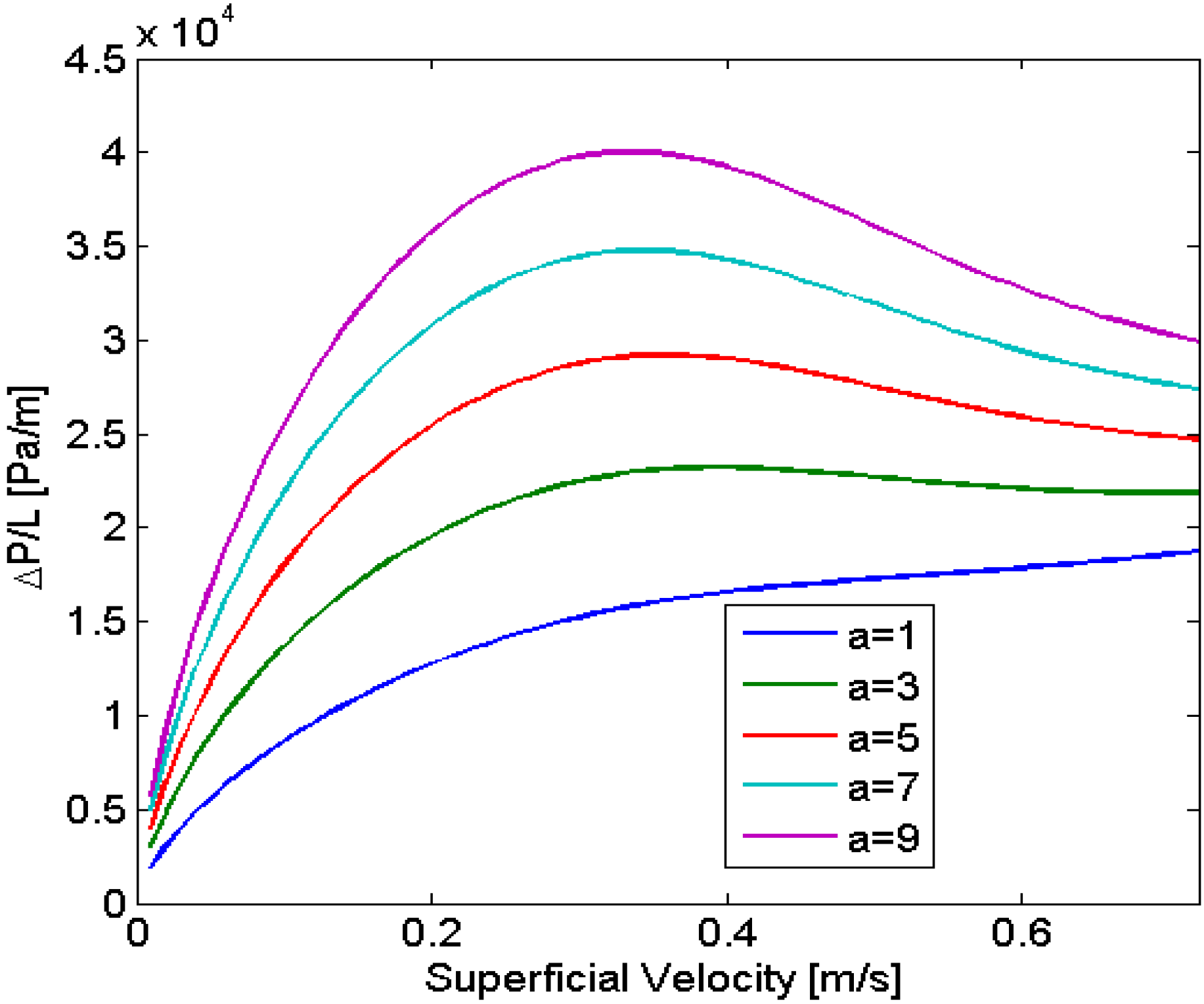
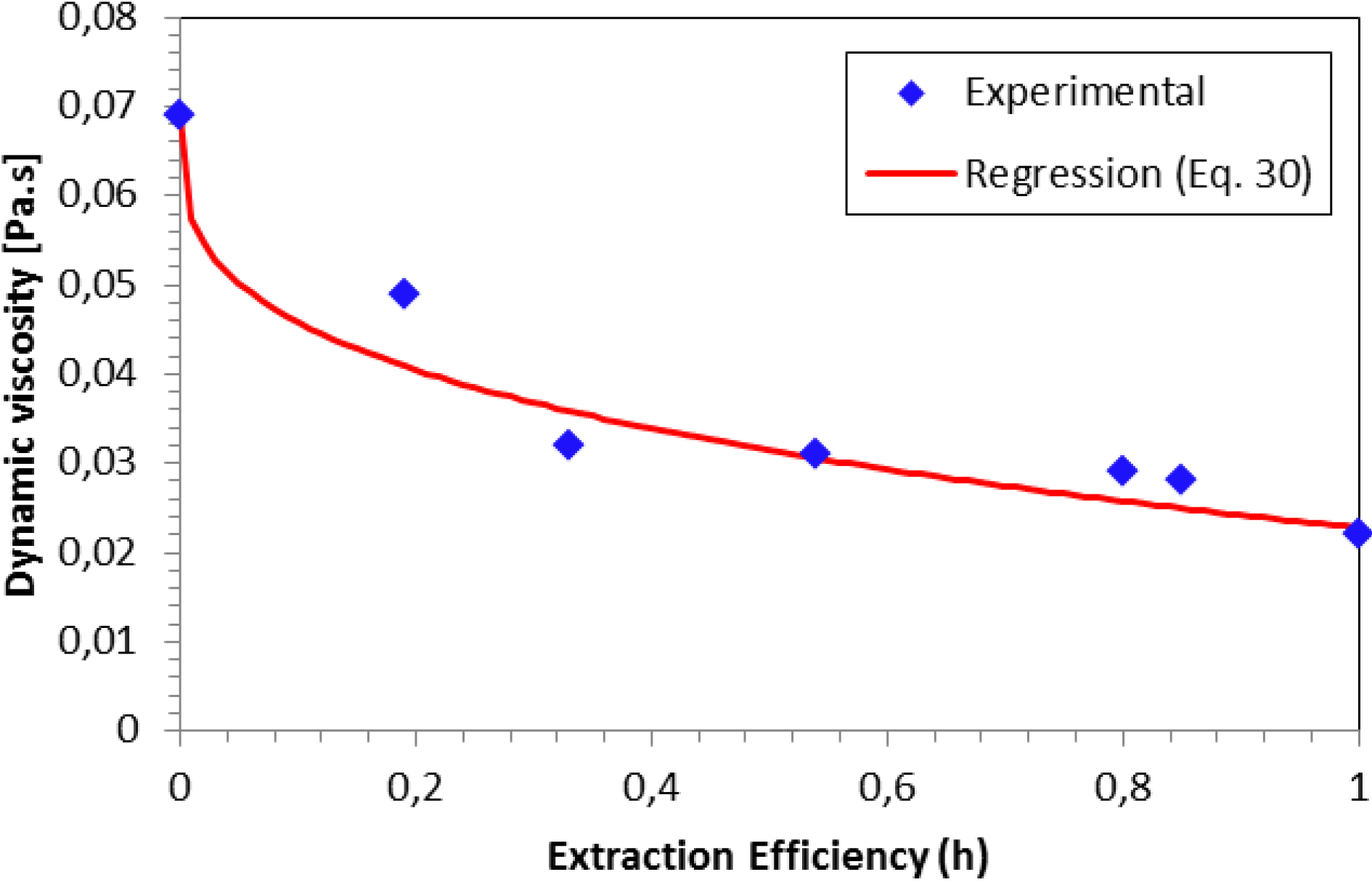
4.1.5. Effect of Viscosity Changes

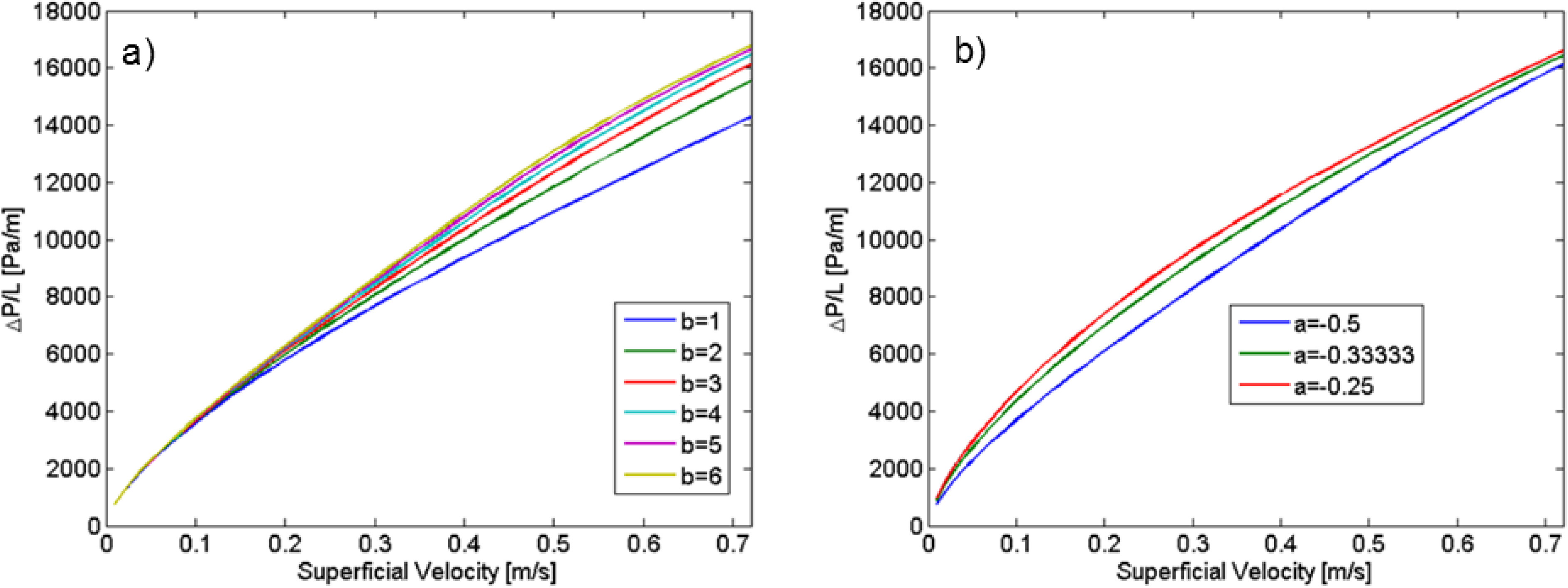
4.1.6. Model Adaptation to the Liquid-Liquid Case
- The pressure drop model was changed to that of a stagnant film model as presented by Jovanovic et al. [23].
- The extraction phenomenon (extraction of acetic acid from n-heptane into an ionic liquid) replaces the chemical absorption (absorption of CO2 in NaOH). The equation representing the concentration change along the channel is the following:
4.2. Experimental Validation: Liquid-Liquid System
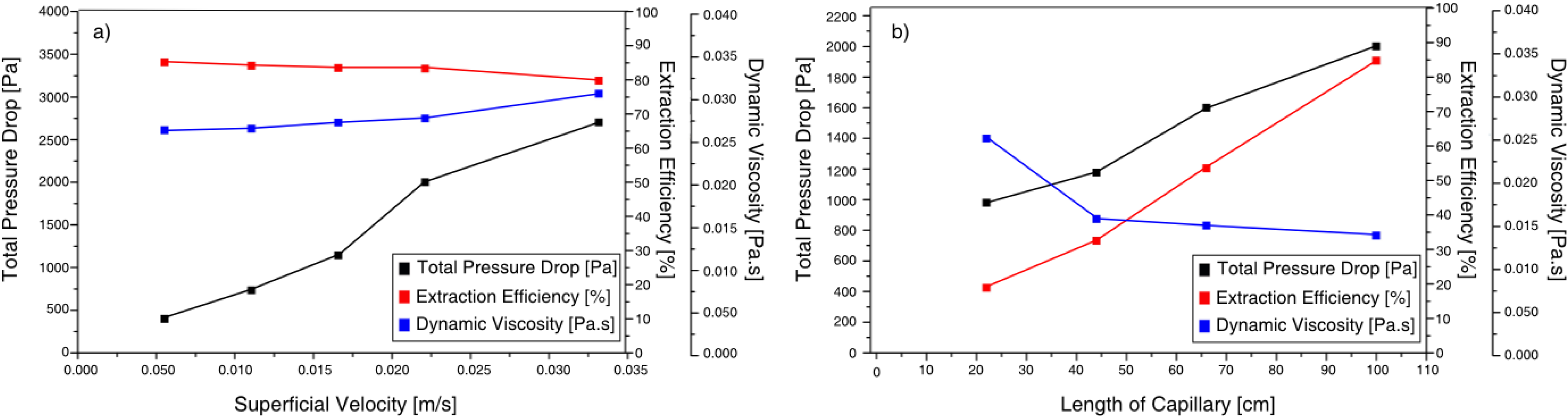
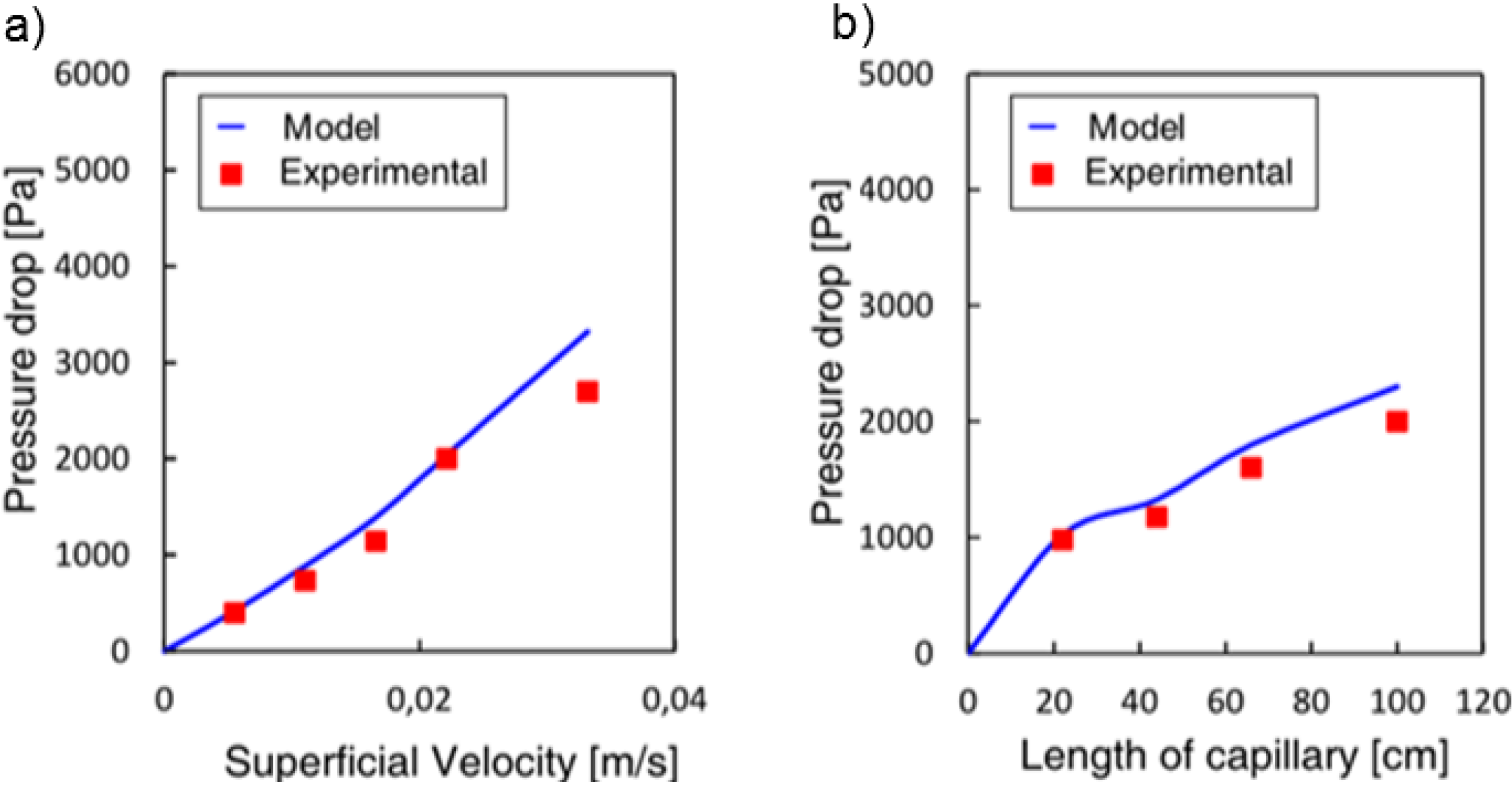
4.2.1. Validation
| Parameter | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| dc | 800 | µm |
| Lcont,0 | 3.75·dc | µm |
| Ldisp,0 | 1.25·dc | µm |
| Lc | 0.2–1 | m |
| σ | 0.0048 | N/m |
| µdisp,0 | 0.069 | Pa.s |
| U | 0.005–0.035 | m/s |
| C | 2.385 | - |
| CEMIM,0 | 1171 | mol/m3 |
| CEMIM, eq | 521 | mol/m3 |
5. Conclusions
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| A | Area | m2 |
| a | Interfacial area | m2/m3 |
| a, b | Viscosity fitting factors | |
| C | Concentration | mol/m3 |
| C | Curvature factor | |
| d | Diameter | μm |
| D | Diffusion coefficient | |
| E | Enhancement factor | - |
| h | Extraction efficiency | - |
| k | Mass transfer coefficient | m/s |
| L | Length | μm |
| N | Number of mol | mol |
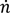 | Molar flow | mol/s |
| P | Pressure | Pa |
| R | Ideal gas constant | |
| T | Temperature | K |
| U | Velocity | - |
| V | Volume | |
| x | Conversion | - |
| y | Molar fraction | mol/mol |
| z | Axial coordinate | m |
Greek symbols
| Symbol | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| α | Liquid phase ratio | |
| μ | Viscosity | Pa.s |
| Δ | Difference | |
| δ | Film Thickness | μm |
| ζ | Correction factor for liquid volume in the bubble cap zone | μm |
| ρ | Density | kg/m3 |
| σ | Surface tension | N/m |
| τ | Mean residence time | s |
Indexes
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Initial |
| A | Related to component A |
| B | Bubble |
| C | Channel |
| Cap | Cap of the bubble |
| Cont | Continuous phase |
| Disp | Dispersed phase |
| EMIM | Related to EMIM-EtSO4 |
| Eq | Equilibrium |
| Film | Liquid film |
| G | Gas |
| I | Inert |
| In | Inlet |
| L | Liquid |
| Out | Outlet |
| S | Slug |
| T | Total |
| TP | Two phase |
| UC | Unit cell |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leclerc, A.; Philippe, R.; Houzelot, V.; Schweich, D.; de Bellefon, C. Gas-liquid Taylor flow in square micro-channels: New inlet geometries and interfacial area tuning. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibel, W.; Wenka, A.; Brandner, J.J.; Dittmeyer, R. Reprint of: Measuring and modeling the residence time distribution of gas flows in multichannel microreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 227, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzer, M.T.; Bakker, J.J.W.; Kapteijn, F.; Moulijn, J.A.; Verheijen, P.J.T. Scaling-up multiphase monolith reactors: Linking residence time distribution and feed maldistribution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 4898–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berčič, G.; Pintar, A. The role of gas bubbles and liquid slug lengths on mass transport in the Taylor flow through capillaries. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 3709–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendorf, M.; Moenter, A.; Moll, T.; Agar, D.; Tiller, J. Polymerisation of butyl acrylate in the two phase slug flow regime of parallel microcapillary reactors. Macromol. Symp. 2011, 302, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador, C.; Gavriilidis, A.; Angeli, P. Flow distribution in different microreactor scale-out geometries and the effect of manufacturing tolerances and channel blockage. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 101, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Boichot, R.; Luo, L.; Gonthier, Y.; Chen, G.; Yuan, Q. Flow distribution and mass transfer in a parallel microchannel contactor integrated with constructal distributors. AIChE J. 2010, 56, 298–317. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rawashdeh, M.; Fluitsma, L.; Nijhuis, T.; Rebrov, E.; Hessel, V.; Schouten, J. Design criteria for a barrier-based gas–liquid flow distributor for parallel microchannels. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181–182, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendorf, M.; Nachtrodt, H.; Mescher, A.; Ghaini, A.; Agar, D.W. Design and control techniques for the numbering-up of capillary microreactors with uniform multiphase flow distribution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 10908–10916. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, R.H.; Green, D.W.; Maloney, J.O. Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook: Physical and Chemical Data, 8th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–517. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.-Z.; Lu, X.-M.; Gui, J.-S.; Xu, W.-G. A new theory for ionic liquids? The interstice model: Part 1. The density and surface tension of ionic liquid EMISE. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, S.; Eskin, D.; Mostowfi, F. Pressure drop of slug flow in microchannels with increasing void fraction: Experiment and modeling. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnier, M.J.F.; Croon, M.H.J.M.; Rebrov, E.V.; Schouten, J.C. Pressure drop of gas–liquid Taylor flow in round micro-capillaries for low to intermediate Reynolds numbers. Microfluid Nanofluid 2010, 8, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Eskin, D.; Mostowfi, F. A model of a bubble train flow accompanied with mass transfer through a long microchannel. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2012, 33, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, S.; Eskin, D.; Mostowfi, F. Two-phase flow in microchannels: The case of binary mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aussillous, P.; Quéré, D. Quick deposition of a fluid on the wall of a tube. Phys. Fluids 2000, 12, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanfir, M.; Gavriilidis, A.; Wille, C.; Hessel, V. Carbon dioxide absorption in a falling film microstructured reactor: Experiments and modeling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandu, C.; Liu, H.; Krishna, R. Mass transfer from Taylor bubbles rising in single capillaries. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 6430–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Chen, G.; Yuan, Q.; Luo, L.; Gonthier, Y. Hydrodynamics and mass transfer characteristics in gas–liquid flow through a rectangular microchannel. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 2096–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszuk, P.; Pohorecki, R.; Cygański, P.; Grzelka, J. Determination of the interfacial area and mass transfer coefficients in the Taylor gas–liquid flow in a microchannel. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 6048–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Gavriilidis, A.; Angeli, P. Mass transfer during Taylor flow in microchannels with and without chemical reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzer, M.T.; Kapteijn, F.; Moulijn, J.A.; Kleijn, C.R.; Heiszwolf, J.J. Inertial and interfacial effects on pressure drop of Taylor flow in capillaries. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 2428–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, J.; Zhou, W.; Rebrov, E.V.; Nijhuis, T.; Hessel, V.; Schouten, J.C. Liquid-liquid slug flow: Hydrodynamics and pressure drop. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Munera Parra, A.A.; Antweiler, N.; Nagpal, R.; Agar, D.W. Stability Analysis of Reactive Multiphase Slug Flows in Microchannels. Processes 2014, 2, 371-391. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr2020371
Munera Parra AA, Antweiler N, Nagpal R, Agar DW. Stability Analysis of Reactive Multiphase Slug Flows in Microchannels. Processes. 2014; 2(2):371-391. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr2020371
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunera Parra, Alejandro A., Nicolai Antweiler, Rachit Nagpal, and David W. Agar. 2014. "Stability Analysis of Reactive Multiphase Slug Flows in Microchannels" Processes 2, no. 2: 371-391. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr2020371
APA StyleMunera Parra, A. A., Antweiler, N., Nagpal, R., & Agar, D. W. (2014). Stability Analysis of Reactive Multiphase Slug Flows in Microchannels. Processes, 2(2), 371-391. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr2020371