Rheological Investigation of Water-Based Drilling Fluids Using Synthesized ZnO with TiO2 and Activated Carbon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of TiO2-Coated ZnO Nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation of Activated Carbon from Banana Peel
2.4. Preparation of Water-Based Drilling Mud
2.5. Analytical Characterization
2.6. Rheological Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
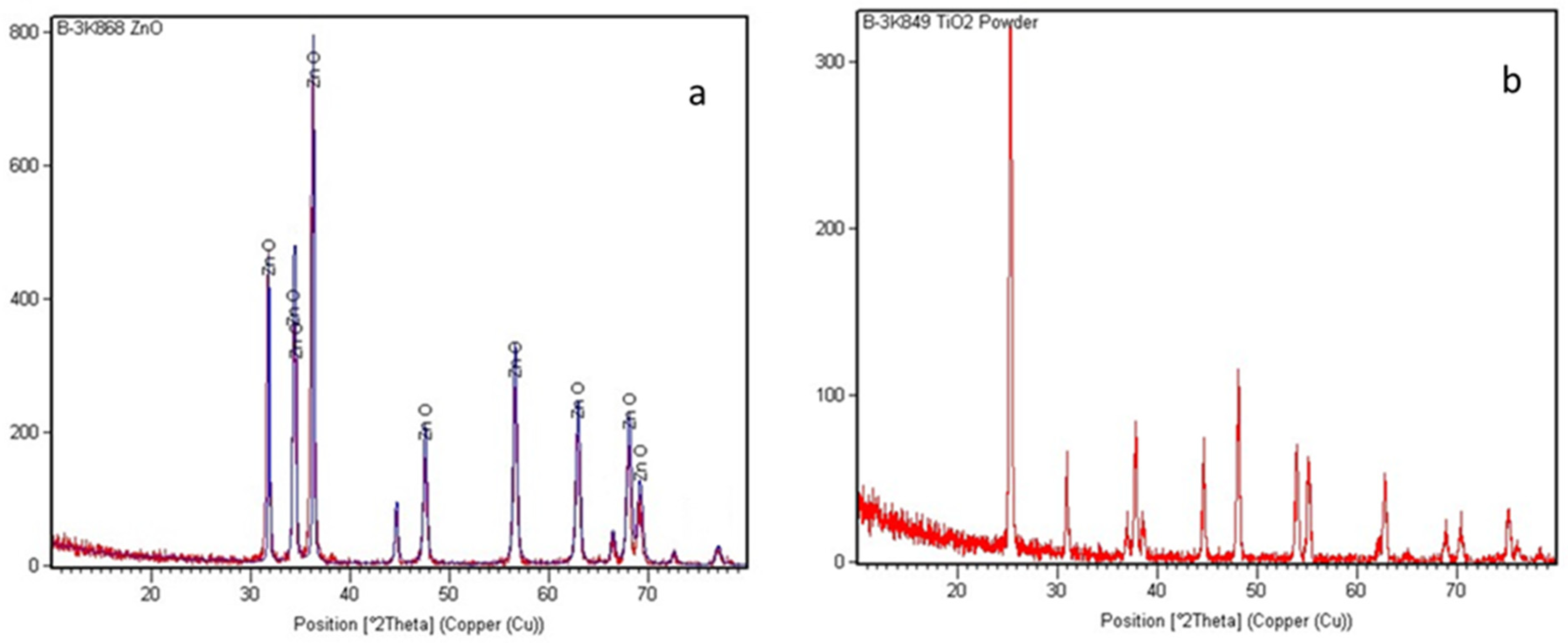
3.1. Analytical Structural and Morphological Analysis of TiO2 and ZnO
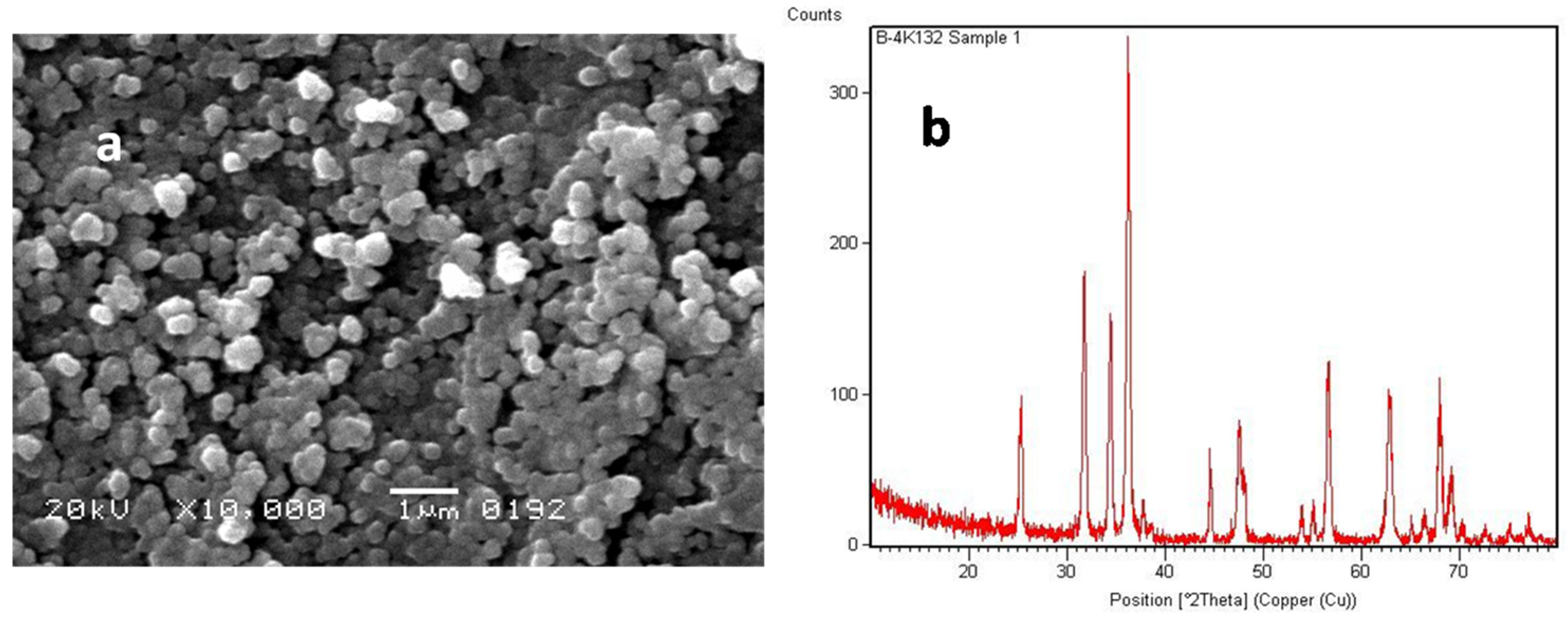
3.2. XRD and SEM Analysis of Synthesized ZnO
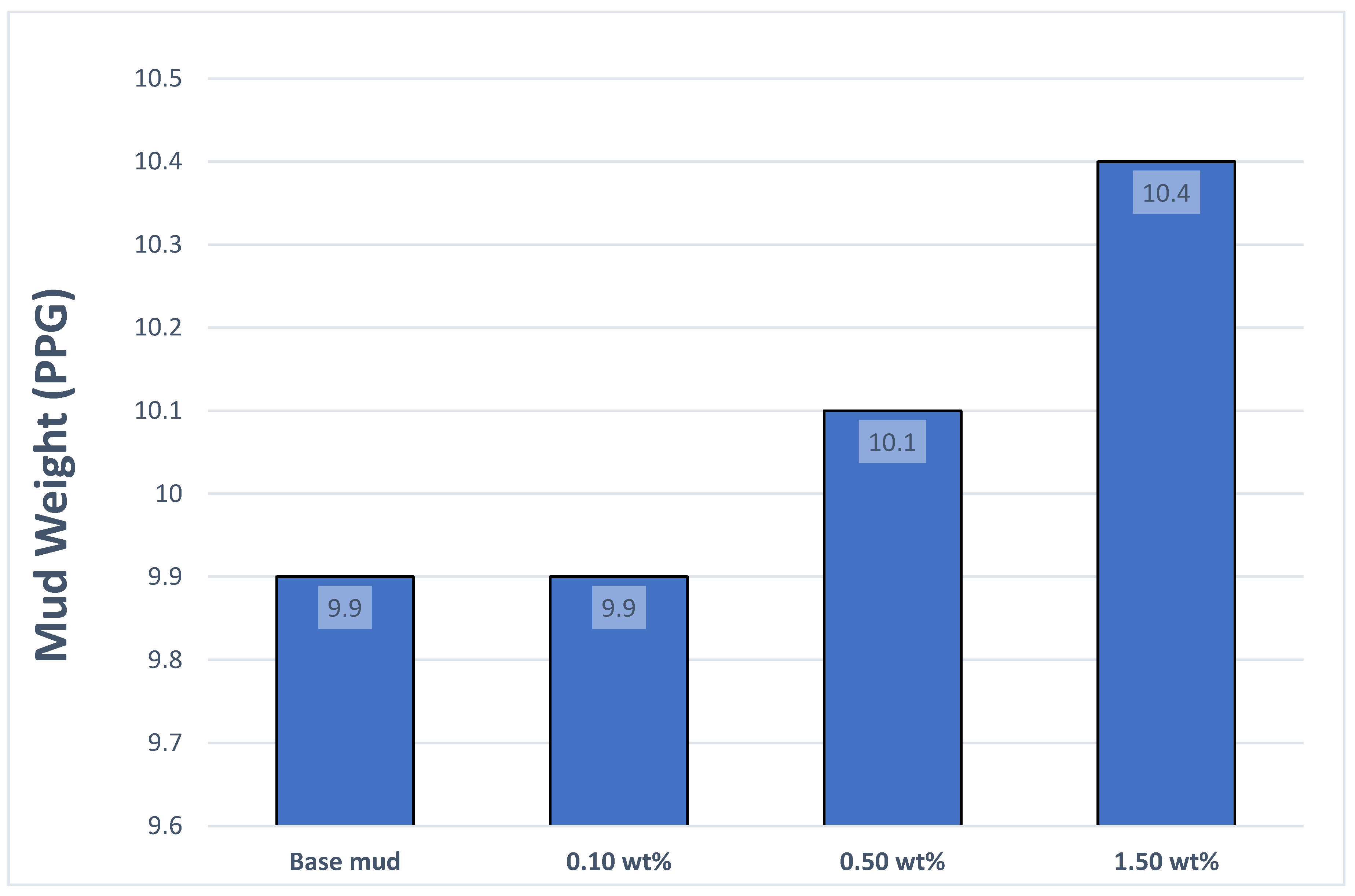
3.3. Mud Weight and Specific Gravity of Drilling Mud
3.4. Rheological Characterization
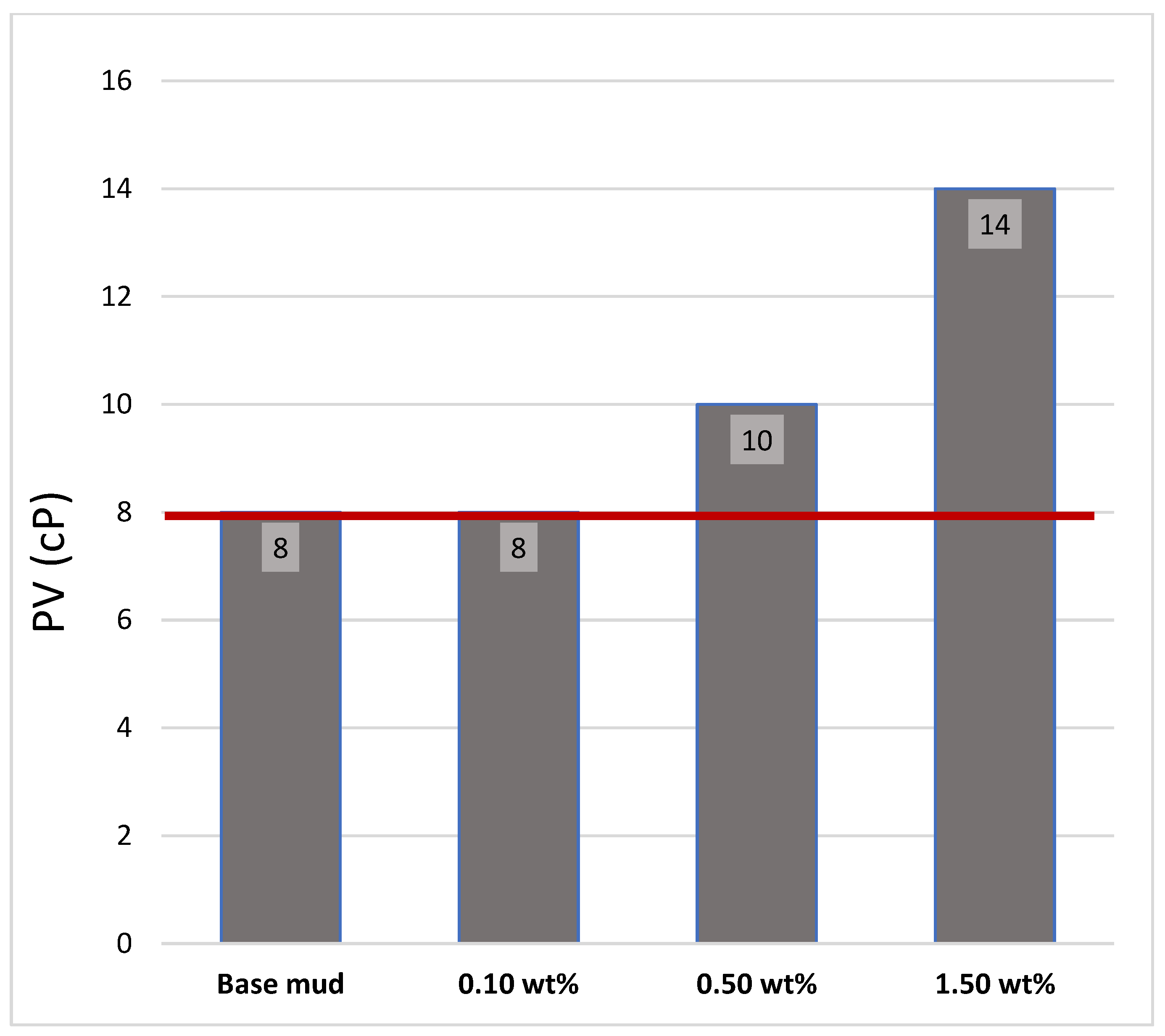
3.4.1. Plastic Viscosity (PV)
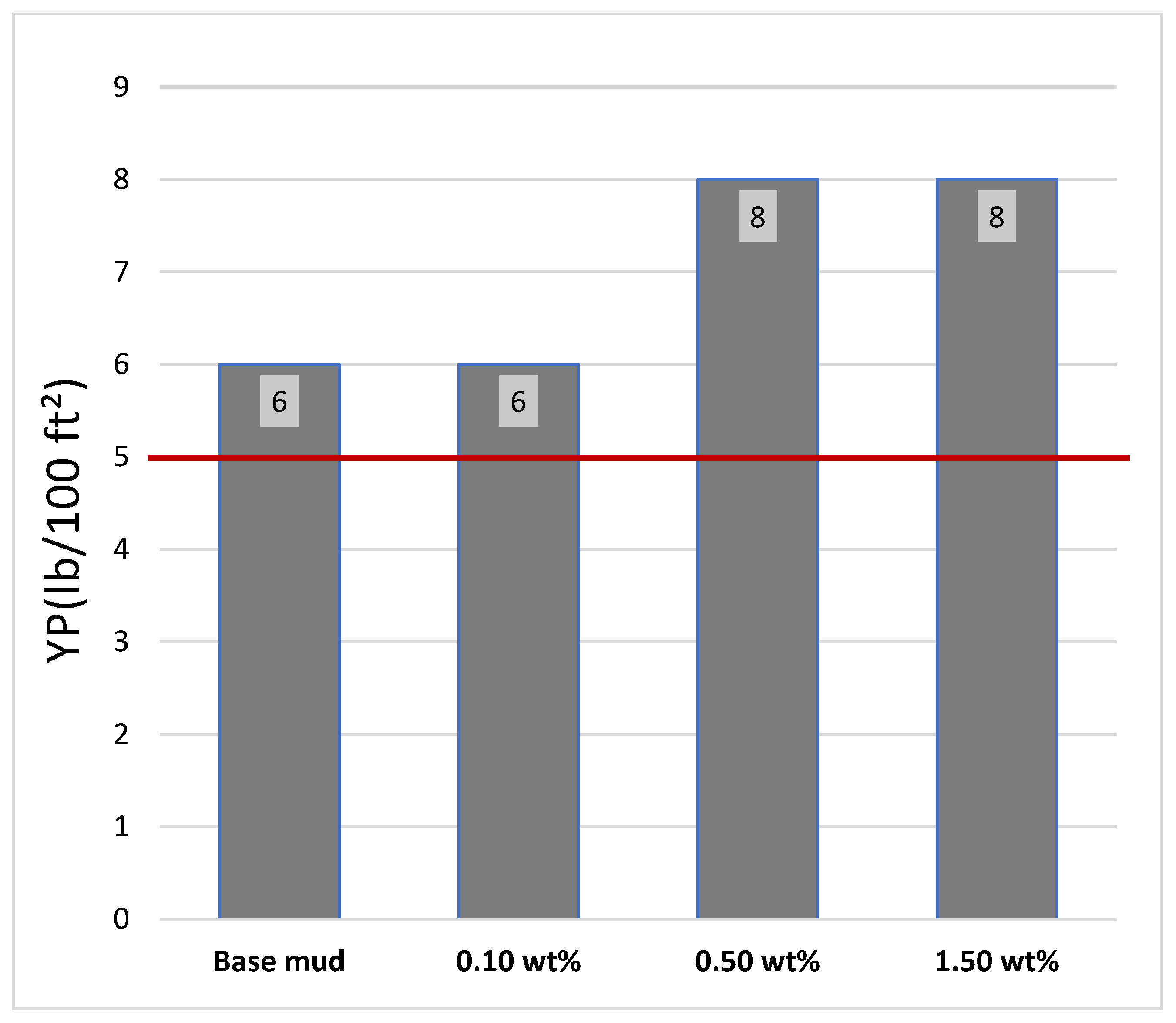
Yield Point
Gel Strength
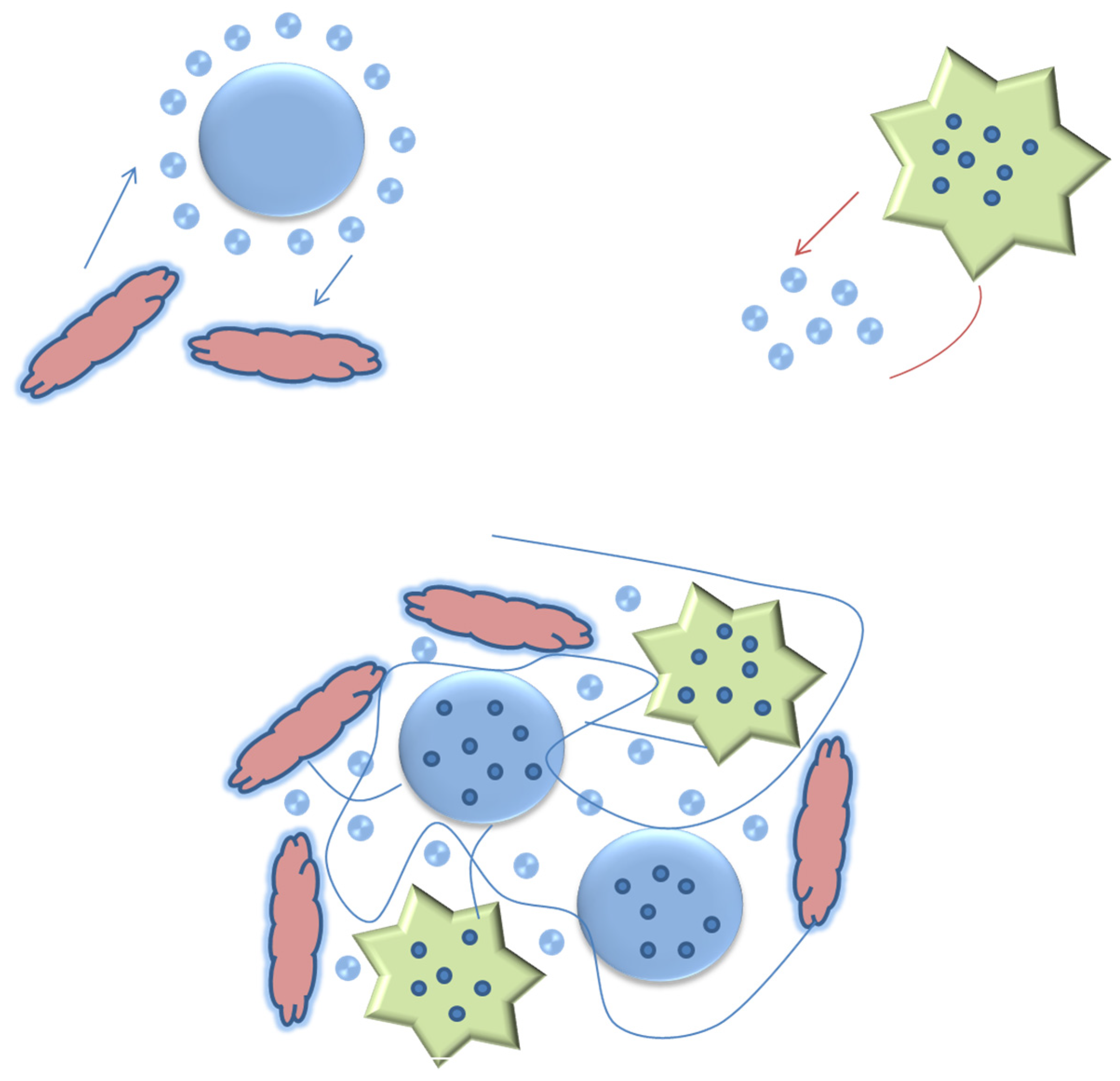
4. Mechanism of Enhancement
5. Environmental and Economic Implications
6. Conclusions
- 1.
- Successful synthesis and characterization.
- PVA helped in the formation of the uniform TiO2 coating on ZnO that was investigated by XRD and SEM analysis in Figure 4a,b.
- 2.
- Significant rheological improvements.
- Plastic viscosity was increased by ~25% at 0.50 wt% and ~75% at 1.50 wt%.
- Yield point was increased by ~33% at 0.50 wt% and 1.50 wt% additive levels.
- Gel strength improved by 25–75% (10 s) and 12.5–50% (10 min), depending on dosage, indicating stronger structural integrity during static time.
- 3.
- Synergistic effect on TiO2-coated ZnO nanoparticles.
- The mixture of additives performed well, and the effects of each separate component showed better dispersion and stronger particle networks.
- 4.
- Environmental and economic considerations.
- Agricultural waste conversion into activated carbon is an eco-friendly and economical option compared with the regular ones.
- The composite configuration is completely in line with green nanoparticles, and it also lessens the negative impact on the environment while performing at a good level.
- 5.
- Oilfield application.
- The improved viscosity, yield point, and gel strength make this additive system suitable for operational drilling conditions requiring stable and efficient WBM performance.
- The formulation remains compatible with standard mud systems and does not adversely affect mud density.
Limitations
- The current research was applied to the rheological characterization at ambient temperature; due to temporary limitations in the HPHT (high-pressure, high-temperature) aging-cell availability, the HPHT rheological evaluations were not carried out. To overcome this, targeted HPHT tests (150 °C, 30 MPa; 16 h aging) on the base, single-additive, and hybrid formulations have been planned to find out the variations in PV, YP, and gel strength and to set the temperature–pressure resistance limits of the materials. These experiments will be done as part of specific follow-up research.
- This research did not investigate long-term stability for 7-day and 14-day or 100-cycle simulated circulation experiments. The long-term stability tests used to measure the time-dependent variations of PV, YP, and gel strength, as well as the possible additive degradation mechanisms, will be carried out in the next phase of the study to analyze the long-term stability evaluation of the formulated drilling fluids.
- The limitation of this study is the comparison of banana-peel-derived activated carbon with other activated carbons, including coal-based products, due to laboratory limitations. However, in literature, the use of fruit-peel-derived activated carbons typically possesses higher porosity, greater surface functionalization, and enhanced adsorption behavior relative to coal-based activated carbon.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lysakova, E.I.; Skorobogatova, A.D.; Neverov, A.L.; Minakov, A.V. Investigation of the effect of spherical nanoparticle additives on the properties of drilling fluids modified by carbon nanotubes. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2025, 41, 101442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Song, G.; Olortegui-Revoredo, J.; Kwon, P.; Chung, H. Dispersant-Induced Enhancement of Rheological Properties in Metal–Photopolymer Mixtures for 3D Printing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Yang, J.; He, H.; Wei, J.; Zhu, Y. Influences of Additives on the Rheological Properties of Cement Composites: A Review of Material Impacts. Materials 2025, 18, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, M.S.; Jaafar, M.T.; Rashid, F.L.; Togun, H.; Rasheed, M.K.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Al-Amir, Q.R.; Mohammed, H.I.; Sarris, I.E. Sustainable Drilling Fluids: A Review of Nano-Additives for Improved Performance and Reduced Environmental Impact. Processes 2024, 12, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Al-Afnan, S.; Elkatatny, S.; Hussein, I. Prevention of Barite Sag in Water-Based Drilling Fluids by A Urea-Based Additive for Drilling Deep Formations. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeel, S.; Aslam, A.; Zhang, J. Advances in Polymer Nanocomposites for Drilling Fluids: A Review. Materials 2025, 18, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlBajalan, A.R.; Rasol, A.A.A.; Norddin, M.N.A.M. Graphene and bio-graphene nanosheets in water-based mud (WBM): A pathway to sustainable and high-performance drilling muds. Emergent Mater. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channei, D.; Jannoey, P.; Thammaacheep, P.; Khanitchaidecha, W.; Nakaruk, A. From Waste to Value: Banana-Peel-Derived Adsorbents for Efficient Removal of Polar Compounds from Used Palm Oil. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, M.G.; Kasaw, E.; Lübben, J.F. Valorization of Banana Peel Using Carbonization: Potential Use in the Sustainable Manufacturing of Flexible Supercapacitors. Micromachines 2023, 14, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkalbani, A.K.; Chala, G.T.; Alkalbani, A.M. Experimental investigation of the rheological properties of water base mud with silica nanoparticles for deep well application. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 102147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasieczna-Patkowska, S.; Cichy, M.; Flieger, J. Application of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy in Characterization of Green Synthesized Nanoparticles. Molecules 2025, 30, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdu, V.-A.; Győrgy, R. X-ray Diffraction Data Analysis by Machine Learning Methods A Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraveo-Castro, C.d.R.; Rodríguez-Guerra, Y.; Fuentes-Montero, L.; González-Jacquez, A.I.; Fuentes-Cobas, L.E.; Montero-Cabrera, M.E. Procedures for X-Ray Diffraction Phase Analysis: The Case of Fine Sediments from Peña Blanca, Chihuahua, Mexico. Crystals 2025, 15, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukarman; Kristiawan, B.; Khoirudin; Abdulah, A.; Enoki, K.; Wijayanta, A.T. Characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles for nanomaterial applications: Crystallite size, microstrain and phase analysis using multiple techniques. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 38, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, Z.A.; Lalji, S.M.; Parveen, K.; Qureshi, M.F.; Nasreen, S.; Al-Khayri, J.M.; Al-Dossary, O.; Alsubaie, B.; Shehata, W.F.; Almaghasla, M.I. Optimization of nanofluid stability using response surface methodology: A study on PAM/sodium alginate-ZnO systems. Chem. Pap. 2025, 79, 8131–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, Z.A.; Zhao, W.; Ali-zada, A.; El-Bahy, S.M.; Lalji, S.M. Stability and settling dynamics of Al2O3/TiO2 nanofluids: An ImageJ-based quantification with response surface methodology. Chem. Pap. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, Z.A.; Qureshi, M.F.; Bhutto, D.K.; Parveen, K.; Lalji, S.M.; Khan, M.A.; Li, M.; Gurbanova, L.; Al-Onozi, W.A. Full factorial analysis with ANOVA and physiochemical investigation of ZnO/Al2O3 with pure bore at low salinity to improve oil recovery. Chem. Pap. 2025, 79, 6279–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, Z.A.; Lalji, S.M.; Yasin, Q.; Bentalib, A.; Bin Jumah, A. Performance of nanoparticle MgO/TiO2 nanofluids with Pure bore: Insight into statistical and analytical approach. Chem. Pap. 2025, 79, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orudzhev, F.; Gadzhiev, M.; Abdulkerimov, M.; Muslimov, A.; Krasnova, V.; Il’ichev, M.; Kulikov, Y.; Chistolinov, A.; Volchkov, I.; Tyuftyaev, A.; et al. Plasma-Assisted Synthesis of TiO2/ZnO Heterocomposite Microparticles: Phase Composition, Surface Chemistry, and Photocatalytic Performance. Molecules 2025, 30, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marny, M.; Sowa, M.; Kazek-Kęsik, A.; Rokosz, K.; Raaen, S.; Chapon, P.; Viter, R.; Pshenychnyi, R.; Simka, W.; Michalska, J. Shaping the Structure and Properties of TiO2-ZnO Oxide Coatings Produced by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation on Titanium Substrate. Materials 2023, 16, 7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, C. TiO2 Coated ZnO Nanorods by Mist Chemical Vapor Deposition for Application as Photoanodes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Nefzaoui, E.; Marty, F.; Erfan, M.; Bastide, S.; Leprince-Wang, Y.; Bourouina, T. TiO2-Coated ZnO Nanowire Arrays: A Photocatalyst with Enhanced Chemical Corrosion Resistance. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Pervaiz, E.; Ahmed, I.; Noor, T. Remarkable improvement in drilling fluid properties with graphitic-carbon nitride for enhanced wellbore stability. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medved, I.; Gaurina-Međimurec, N.; Novak Mavar, K.; Mijić, P. Waste Mandarin Peel as an Eco-Friendly Water-Based Drilling Fluid Additive. Energies 2022, 15, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leusheva, E.; Brovkina, N.; Morenov, V. Investigation of Non-Linear Rheological Characteristics of Barite-Free Drilling Fluids. Fluids 2021, 6, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.A.; Gailani, R.; Abdullah, A.D.; Jaf, P.T.; Simo, S.M.; Abdalqadir, M.; Faris, V.M. Performance evaluation of the nano-biodegradable drilling fluid using the greenly synthesized zinc nanorods and gundelia seed waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 51381–51400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dike, H.N.; Chibueze, L.N.; Ipinsokan, S.; Adewumi, C.N.; Olabode, O.; Olaniyan, D.D.; Pius, I.E.; Oke, M.A. An Evaluation of the Rheological and Filtration Properties of Cow Bone Powder and Calcium Carbonate as Fluid-Loss Additives in Drilling Operations. Processes 2025, 13, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, S.; Al-Shargabi, M.; Wood, D.A.; Rukavishnikov, V.S.; Minaev, K.M. Synthetic polymers: A review of applications in drilling fluids. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 475–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, W.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Li, X.; Wei, Q. A decoupling model for fatigue life assessment of double wellhead system with subsea suction anchor. Ocean Eng. 2024, 311, 118896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Guo, T.; Cao, G. Characteristics of sodium p-styrenesulfonate modified polyacrylamide at high temperature under dual scale boundary. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 073115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, Z. Electromagnetic Tomography for Multiphase Flow in the Downhole Annulus. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.E.; Al-Majed, A. Fundamentals of Sustainable Drilling Engineering; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Pan, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ba, X.; Guo, L.; Han, Y. Mitigation Effects and Prediction Formulae of Stratum Disturbance by Different Slurry Pressures and Filter Cake Parameters in Slurry Shield Tunneling. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, J.; He, H.; Peng, Z.; Pu, J.; Zheng, L.; Gu, X. A Thermo-Stable Polymeric Surfactant for Enhanced Heavy Oil Recovery via Hot Water Chemical Flooding. Langmuir 2025, 41, 29180–29195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, M.; Bhaumik, A.K.; Mandal, A. Performance of water-based drilling fluids for deepwater and hydrate reservoirs: Designing and modelling studies. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1709–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Alsaihati, A.; Elkatatny, S. An Overview of the Common Water-Based Formulations Used for Drilling Onshore Gas Wells in the Middle East. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 6867–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, D.; Gao, H.; Hu, Y.; Duan, L. Real-Time Measurement of Drilling Fluid Rheological Properties: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashari, Z.A.; Aamir, M.; Kumar, B.; Aziz, H.; Soomro, N.A.; Lalji, S.M.; Tahir, F. Stability analysis of nanofluid with aluminum oxide and polyacrylamide for enhanced oil recovery: Insight into experimental investigation. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2024, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, Z.A.; Aamir, M.; Lalji, S.M.; Murtaza, M.; Yamin, Y.; Haider, M.; Bilal, M.; Al-Onozi, W.A.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Iqbal, R.; et al. Stability and Efficiency of Magnesium Oxide-Sodium Alginate Combination in Low Salinity EOR Processes: An Integrated Approach of CCD. Chem. Pap. 2025, 79, 4363–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalji, S.M.; Ali, S.I.; Lashari, Z.A.; Panjwani, S.K.; Burney, M. Performance evaluation of Si/Fe3O4 nanoparticles in water-based mud in presence of different Mg2+, K+, Na+ salts: Experimental and stability visualization study. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 8379–8396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, Z.A.; Lalji, S.M.; Kumar, D.; Bilal, A. Physiochemical analysis of titanium dioxide and polyacrylamide nanofluid at low salinity. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 3629–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, Z.A.; Haq, B.; Al-Shehri, D.; Zaman, E.; Al-Ahmed, A.; Lashari, N. Recent Development of Physical Hydrogen Storage: Insights into Global Outlook and Future Applications. Chem. Asian J. 2024, 19, e202300926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, A.U.; Muneer, R.; Lashari, Z.A.; Hashmet, M.R.; Osei-Bonsu, K.; Abdala, A.; Rabbani, H.S. Recent advancements in novel nanoparticles as foam stabilizer: Prospects in EOR and CO2 sequestration. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 407, 125209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, N.A. Laboratory evaluation of an innovative polyfraction nanoemulsion for enhanced oil recovery in carbonate reservoirs. Unconv. Resour. 2025, 8, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, N.A.; Ansari, U.; Shams, B.; Memon, M.K.; Bhutto, D.K.; Rui, Z.; Pan, Y. Optimizing Gas Well Deliquification: Experimental Analysis of Surfactant-Based Strategies for Liquid Unloading in Gas Wells for Enhanced Recovery. Unconv. Resour. 2025, 7, 100200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, N.A.; Ansari, U.; Shams, B.; Memon, M.K.; Bhutto, D.K.; Rui, Z.; Pan, Y. Experimental Assessment of the Stability and Impact of Water-Based Fracturing Fluid with and without Triethanolamine (TEA). Fuel Commun. 2025, 23, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


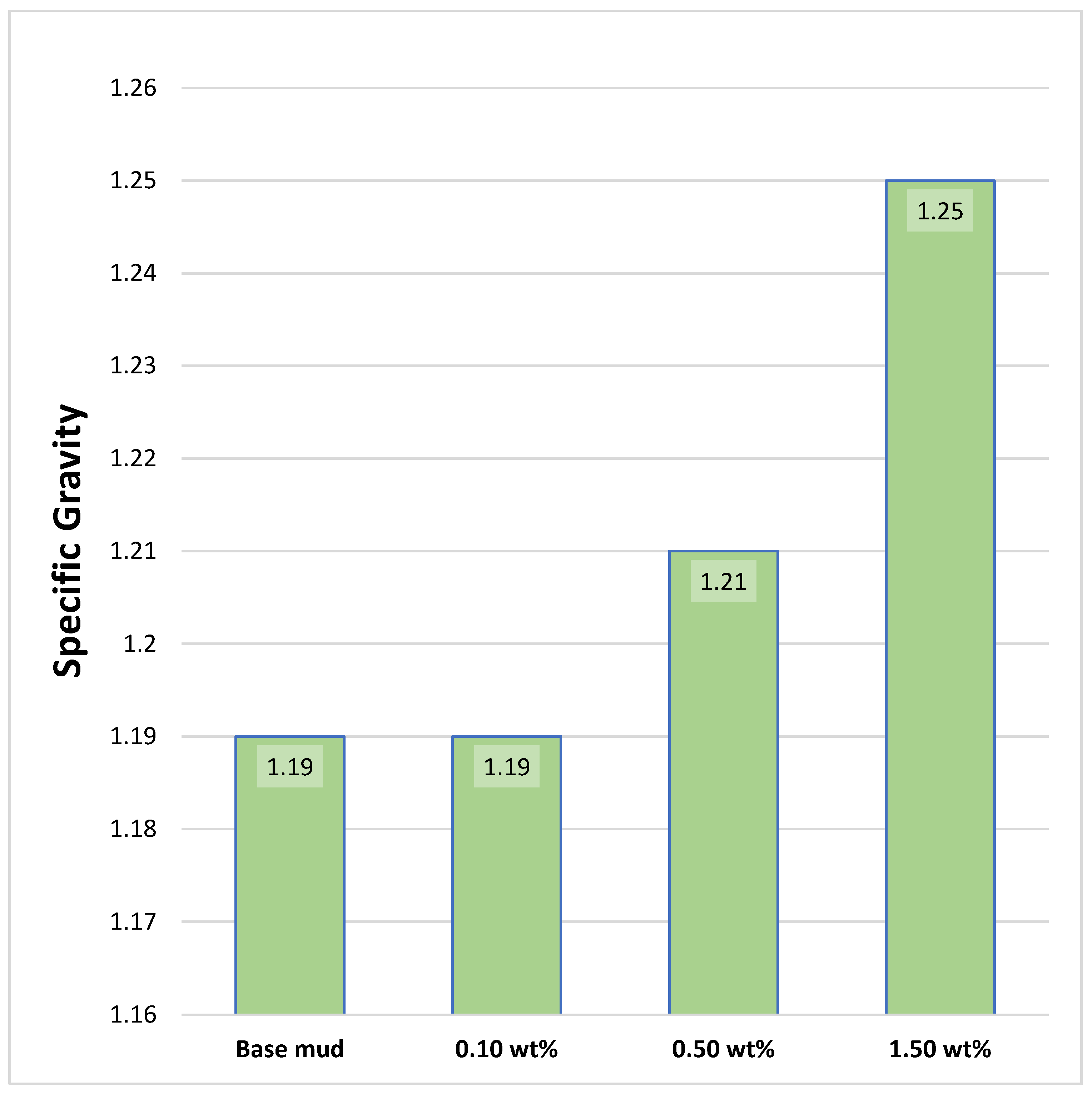

| References | Year | Materials | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | 2025 | NPs + carbon nanotubes | Improved rheological and filtration properties under HPHT conditions |
| [2] | 2024 | Fruit-peel-derived AC | Great filtration control and increased YP were observed. |
| [4] | 2025 | ZnO NPs | Reduced shale swelling. |
| [3] | 2025 | TiO2 + ZnO + surfactants | The dispersion and rheological properties were improved, and the settling time was reduced. |
| [6] | 2023 | Bentonite + AC | Improved stability and reduced filtration losses. |
| [5] | 2022 | NPs + Polymers | The stability and GS improved without increasing the mud density. |
| Material/Equipment | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Zinc Oxide (ZnO), Powder Form | Nanoparticle used as a base |
| Titanium Dioxide (TiO2), Powder Form | Coating nanoparticles on ZnO |
| PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) | As a binder for coating |
| Dried Banana Peels | Raw material for AC |
| NaOH | Acts as an activating agent for AC preparation |
| Deionized Water | For washing and mixing |
| Magnetic Stirrer | For mixing homogeneity |
| Filter paper and Funnel | For the filtration purpose |
| Oven | For heating purposes |
| Barite | To increase the density of mud |
| Bentonite | Viscosity and gel strength improvement |
| PAC | To control the fluid loss |
| PAM | Used as a viscosifier |
| CaCl2 | For shale stability and swelling reduction |
| Soda Ash | To remove the calcium |
| Mud Balance and Viscometer | For the mud density and rheology tests |
| Ingredient Amount | (Per 350 mL Mud Sample) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Bentonite | 25 g | to increase viscosity and gel strength |
| Water | 325 mL | base fluid |
| Soda Ash | 0.25 g | to remove calcium and soften water |
| Barite | 85 g | to increase mud density |
| PAC | 4 g | to control fluid loss and improve filter cake quality |
| CaCl2 | 10 g | to stabilize shale and reduce swelling |
| PAM | 1 g | as a viscosifier and flocculant |
| Sample Code | Description | Bentonite (g) | Barite (g) | PAC (g) | PAM (g) | CaCl2 (g) | TiO2–ZnO (g) | AC (g) | Total Additive wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM | Base mud | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TZ-0.10 | TiO2–ZnO only | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.1 |
| TZ-0.50 | TiO2–ZnO only | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 1.75 | 0 | 0.5 |
| TZ-1.50 | TiO2–ZnO only | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 5.25 | 0 | 1.5 |
| AC-0.10 | AC only | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 0.35 | 0.1 |
| AC-0.50 | AC only | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 1.75 | 0.5 |
| AC-1.50 | AC only | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 5.25 | 1.5 |
| TZ/AC-0.10 | Combined (1:1) | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 0.175 | 0.175 | 0.1 |
| TZ/AC-0.50 | Combined (1:1) | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 0.875 | 0.875 | 0.5 |
| TZ/AC-1.50 | Combined (1:1) | 25 | 85 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 2.625 | 2.625 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Wang, T.; Lashari, Z.A.; Zhao, W. Rheological Investigation of Water-Based Drilling Fluids Using Synthesized ZnO with TiO2 and Activated Carbon. Processes 2026, 14, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010081
Liu C, Wang T, Lashari ZA, Zhao W. Rheological Investigation of Water-Based Drilling Fluids Using Synthesized ZnO with TiO2 and Activated Carbon. Processes. 2026; 14(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chunping, Tingting Wang, Zeeshan Ali Lashari, and Wanchun Zhao. 2026. "Rheological Investigation of Water-Based Drilling Fluids Using Synthesized ZnO with TiO2 and Activated Carbon" Processes 14, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010081
APA StyleLiu, C., Wang, T., Lashari, Z. A., & Zhao, W. (2026). Rheological Investigation of Water-Based Drilling Fluids Using Synthesized ZnO with TiO2 and Activated Carbon. Processes, 14(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010081







