Controlling Mannitol Polymorphism for Enhanced Dispersibility in Spray Freeze-Dried Inhalable Microparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulations
2.2. Spray Freeze-Drying
2.3. Particle Size and Morphology
2.4. Powder X-Ray Diffraction
2.5. In Vitro Drug Deposition
2.6. In Vitro Drug Dissolution
2.7. Analytical Quantification of SS
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. F1 Formulation
3.1.1. Morphology and Size
3.1.2. Crystallinity
3.2. F2–F13 Formulations
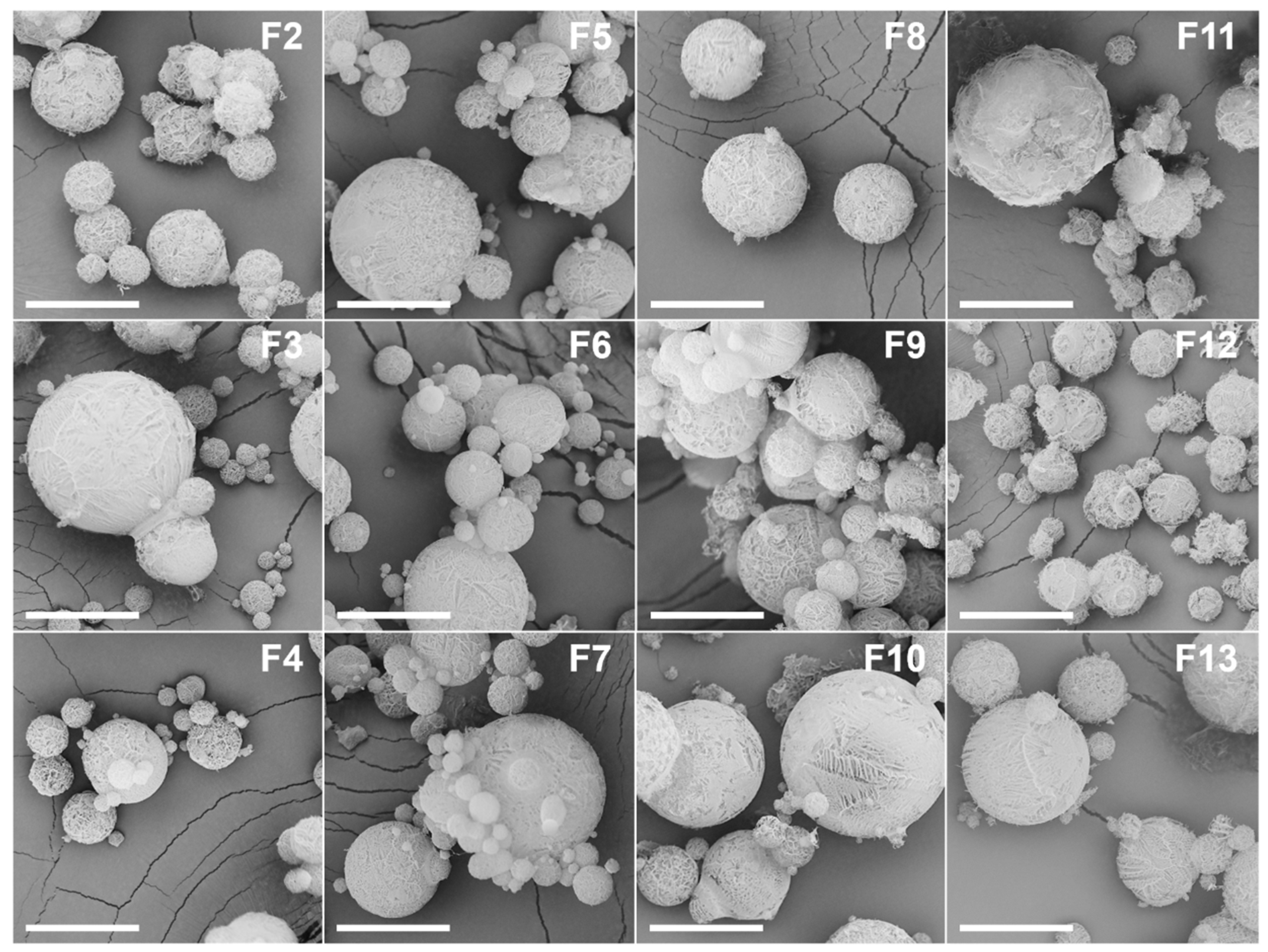
3.2.1. Morphology and Size
3.2.2. Crystallinity
3.2.3. In Vitro Deposition
3.2.4. In Vitro Dissolution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEV | Device |
| DEX | Dextran |
| DPI | Dry Powder Inhaler |
| ED | Emitted Dose |
| FPF | Fine-Particle Fraction |
| GSD | Geometric Standard Deviation |
| HPβCD | 2-hydroxypropyl beta cyclodextrin |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| IP | Induction Port |
| LL | L-leucine |
| MAN | Mannitol |
| MMAD | Mass Median Aerodynamic Diameter |
| MOC | Micro-Orifice Collector |
| MP | Microparticle |
| NGI | Next Generation Impactor |
| PRE | Pre-Separator |
| PS80 | Polysorbate 80 |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| PXRD | Powder X-Ray Diffraction |
| RD | Recovered Dose |
| RF | Recovered Fraction |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| SF | Spray Freezing |
| SFD | Spray Freeze-Drying |
| SS | Salbutamol Sulphate |
References
- Adali, M.B.; Barresi, A.A.; Boccardo, G.; Pisano, R. Spray Freeze-Drying as a Solution to Continuous Manufacturing of Pharmaceutical Products in Bulk. Processes 2020, 8, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishali, D.A.; Monisha, J.; Sivakamasundari, S.K.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Spray Freeze Drying: Emerging Applications in Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 300, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, T.; López-Iglesias, C.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Stachewicz, U.; Barros, J.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Alnaief, M.; García-González, C.A. A Pathway from Porous Particle Technology Toward Tailoring Aerogels for Pulmonary Drug Administration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 671381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labiris, N.R.; Dolovich, M.B. Pulmonary Drug Delivery. Part II: The Role of Inhalant Delivery Devices and Drug Formulations in Therapeutic Effectiveness of Aerosolized Medications. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 56, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasero, L.; Susa, F.; Limongi, T.; Pisano, R. A Review on Micro and Nanoengineering in Powder-Based Pulmonary Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 659, 124248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.; Mohanto, S.; Manne, R.; Rajendran, R.R.; Deepak, A.; Edapully, S.J.; Patil, T.; Katari, O. Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery System: The Magic Bullet for the Treatment of Chronic Pulmonary Diseases. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3671–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Yip, L.; Chow, M.Y.T.; Chow, S.F.; Chan, H.K.; Kwok, P.C.L.; Lam, J.K.W. Porous and Highly Dispersible Voriconazole Dry Powders Produced by Spray Freeze Drying for Pulmonary Delivery with Efficient Lung Deposition. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 560, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.C.; Peters, J.I.; Williams, R.O., III. Influence of Particle Size on Regional Lung Deposition—What Evidence Is There? Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 406, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasero, L.; Susa, F.; Chiavarino, R.; Limongi, T.; Sulpizi, A.; Guidi, T.; Pisano, R. Tailoring Dry Microparticles for Pulmonary Drug Delivery: Ultrasonic Spray Freeze-Drying with Mannitol and Salbutamol Sulphate. Processes 2023, 11, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasero, L.; Sulpizi, A.; Guidi, T.; Pisano, R. Spray Freeze-Drying for Inhalable L-Leucine, Mannitol-Based Microparticles: The Impact of Process Variables, L-Leucine, and Crystallinity on Aerosolization Properties. Powder Technol. 2025, 455, 120788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, B.; Zhao, Y.Y. Dry Powder for Pulmonary Delivery: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, H.; Okuda, T.; Hira, D.; Kojima, H.; Shimada, Y.; Okamoto, H. Inhalable Spray-Freeze-Dried Powder with L-Leucine That Delivers Particles Independent of Inspiratory Flow Pattern and Inhalation Device. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, A.; Nie, T.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, W. A Critical Review on Engineering of D-Mannitol Crystals: Properties, Applications, and Polymorphic Control. Crystals 2022, 12, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoorne, V.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Van Snick, B.; Peeters, E.; Monteyne, T.; Gomes, P.; De Beer, T.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Continuous Manufacturing of Delta Mannitol by Cospray Drying with PVP. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 501, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, S.G.; Schaldach, G.; Littringer, E.M.; Mescher, A.; Griesser, U.J.; Braun, D.E.; Walzel, P.E.; Urbanetz, N.A. The Impact of Spray Drying Outlet Temperature on the Particle Morphology of Mannitol. Powder Technol. 2011, 213, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penha, F.M.; Gopalan, A.; Meijlink, J.C.; Ibis, F.; Eral, H.B. Selective Crystallization of D-Mannitol Polymorphs Using Surfactant Self-Assembly. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 3928–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, N.; Zeng, L.; Mangal, S.; Nie, H.; Rowles, M.R.; Guo, R.; Han, Y.; Park, J.H.; Zhou, Q. Effects of Moisture-Induced Crystallization on the Aerosol Performance of Spray Dried Amorphous Ciprofloxacin Powder Formulations. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.S.; Lau, R.W.M. Effect of Particle Shape on Dry Particle Inhalation: Study of Flowability, Aerosolization, and Deposition Properties. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.; Bairagi, A.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, S.B.; Mehra, N.K. Recent Advances in the Development of Microparticles for Pulmonary Administration. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonvico, F.; Chierici, V.; Varacca, G.; Quarta, E.; D’angelo, D.; Forbes, B.; Buttini, F. Respicelltm: An Innovative Dissolution Apparatus for Inhaled Products. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinari, T.; Forbes, R.T.; York, P.; Kawashima, Y. Moisture Induced Polymorphic Transition of Mannitol and Its Morphological Transformation. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 247, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, J.; Sapra, B.; Bhandari, S.; Jindal, M.; Tiwary, A.K. Understanding Pharmaceutical Polymorphic Transformations I: Influence of Process Variables and Storage Conditions. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 1123–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cares-Pacheco, M.G.; Calvet, R.; Vaca-Medina, G.; Rouilly, A.; Espitalier, F. Inverse Gas Chromatography a Tool to Follow Physicochemical Modifications of Pharmaceutical Solids: Crystal Habit and Particles Size Surface Effects. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, F.; Mahlin, D.; Welch, K.; Gaisford, S.; Alderborn, G. Effect of Surface Energy on Powder Compactibility. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2750–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinari, T.; Forbes, R.T.; York, P.; Kawashima, Y. The Improved Compaction Properties of Mannitol after a Moisture-Induced Polymorphic Transition. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 258, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhoorne, V.; Bekaert, B.; Peeters, E.; De Beer, T.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Improved Tabletability after a Polymorphic Transition of Delta-Mannitol during Twin Screw Granulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Wu, J.X.; Yang, M.; Young, P.M.; Van Den Berg, F.; Rantanen, J. Particle Size Dependence of Polymorphism in Spray-Dried Mannitol. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.D.; Wu, W.D. Spray Freeze Dried Uniform Mannitol Microspheres. Powder Technol. 2024, 434, 119312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traini, D.; Scalia, S.; Adi, H.; Marangoni, E.; Young, P.M. Polymer Coating of Carrier Excipients Modify Aerosol Performance of Adhered Drugs Used in Dry Powder Inhalation Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 438, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsian, A.R.; Vatanara, A.; Rahmati, M.R.; Gilani, K.; Khosravi, K.M.; Najafabadi, A.R. Inhalable Budesonide Porous Microparticles Tailored by Spray Freeze Drying Technique. Powder Technol. 2014, 260, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barresi, A.; Ghio, S.; Fissore, D.; Pisano, R. Freeze Drying of Pharmaceutical Excipients Close to Collapse Temperature: Influence of the Process Conditions on Process Time and Product Quality. Dry. Technol. 2009, 27, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoorne, V.; Almey, R.; De Beer, T.; Vervaet, C. Delta-Mannitol to Enable Continuous Twin-Screw Granulation of a Highly Dosed, Poorly Compactable Formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.C.K.; Pan, H.W.; Lam, J.K.W. Inhalable Protein Powder Prepared by Spray-Freeze-Drying Using Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin as Excipient. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eedara, B.B.; Bastola, R.; Das, S.C. Dissolution and Absorption of Inhaled Drug Particles in the Lungs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanning, S.; Süverkrüp, R.; Lamprecht, A. Pharmaceutical Spray Freeze Drying. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 488, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, L.; Su, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Beck-Broichsitter, M.; Muenster, U.; Chen, L.; Mao, S. Engineering Large Porous Microparticles with Tailored Porosity and Sustained Drug Release Behavior for Inhalation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 155, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| % (w/w) db | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAN | SS | DEX | PVP | HPβCD | PS80 | IF, h | Temperature, °C | |
| F1 | 99 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1, 5 | −20, 5, |
| F2 | 94 | 1 | 5 | - | - | - | 1 | |
| F3 | 89 | 1 | 10 | - | - | - | 1 | |
| F4 | 79 | 1 | 20 | - | - | - | 1 | |
| F5 | 94 | 1 | - | 5 | - | - | 1 | |
| F6 | 89 | 1 | - | 10 | - | - | 1 | |
| F7 | 79 | 1 | - | 20 | - | - | 1 | |
| F8 | 94 | 1 | - | - | 5 | - | 1 | |
| F9 | 89 | 1 | - | - | 10 | - | 1 | |
| F10 | 79 | 1 | - | - | 20 | - | 1 | |
| F11 | 98.99 | 1 | - | - | - | 0.01 | 1 | |
| F12 | 98.9 | 1 | - | - | - | 0.1 | 1 | |
| F13 | 98.6 | 1 | - | - | - | 0.4 | 1 | |
| , µm | , µm | , - | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 5 h | 1 h | 5 h | 1 h | 5 h | |
| −20 °C | 14.711.5 | 17.212.7 | 3.32.6 | 3.82.8 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
| 5 °C | 17.214.2 | 15.913.5 | 3.8 3.2 | 3.63.0 | 2.3 | 2.7 |
| 17.211.6 | 16.1 | 3.82.6 | 3.62.8 | 1.9 | 2.3 | |
| , µm | , µm | Span, - | , µm | , µm | Span, - | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2 | 16.112.7 | 3.62.8 | 2.4 | F8 | 18.013.4 | 4.03.0 | 2.3 |
| F3 | 15.412.9 | 3.42.9 | 2.9 | F9 | 16.7 12.9 | 3.72.9 | 2.2 |
| F4 | 13.611.8 | 3.02.6 | 2.5 | F10 | 15.811.0 | 3.52.5 | 2.2 |
| F5 | 11.210.8 | 2.52.4 | 2.4 | F11 | 16.812.8 | 3.82.9 | 2.3 |
| F6 | 9.47.8 | 2.11.7 | 2.5 | F12 | 17.710.9 | 4.0 2.4 | 1.7 |
| F7 | 12.113.6 | 2.73.0 | 3.2 | F13 | 16.3 11.6 | 3.6 2.6 | 2.0 |
| F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | |
| FPF, % | 23.7 ± 4.6 | 15.5 ± 2.5 | 16.1 ± 0.8 | 21.3 ± 0.7 | 16.7 ± 2.7 | 9.6 ± 1.6 |
| MMAD, µm | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 4.8 ± 0.4 | 6.7 ± 0.8 |
| GSD, - | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 |
| F8 | F9 | F10 | F11 | F12 | F13 | |
| FPF, % | 53.2 ± 7.6 | 47.7 ± 11.7 | 54.6 ± 1.6 | 40.2 ± 3.5 | 39.1 ± 7 | 39.5 ± 2 |
| MMAD, µm | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 2.6 ± 0.1 |
| GSD, - | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Pasero, L.; Silenzi, A.; Sulpizi, A.; Guidi, T.; Pisano, R. Controlling Mannitol Polymorphism for Enhanced Dispersibility in Spray Freeze-Dried Inhalable Microparticles. Processes 2026, 14, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010006
Pasero L, Silenzi A, Sulpizi A, Guidi T, Pisano R. Controlling Mannitol Polymorphism for Enhanced Dispersibility in Spray Freeze-Dried Inhalable Microparticles. Processes. 2026; 14(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010006
Chicago/Turabian StylePasero, Lorena, Andrea Silenzi, Adamo Sulpizi, Tomaso Guidi, and Roberto Pisano. 2026. "Controlling Mannitol Polymorphism for Enhanced Dispersibility in Spray Freeze-Dried Inhalable Microparticles" Processes 14, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010006
APA StylePasero, L., Silenzi, A., Sulpizi, A., Guidi, T., & Pisano, R. (2026). Controlling Mannitol Polymorphism for Enhanced Dispersibility in Spray Freeze-Dried Inhalable Microparticles. Processes, 14(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010006








