Study on Rapid Screening Method for Different Chemical Flooding Methods in Heavy-Oil Reservoirs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemical Flooding Mathematical Model
2.1. Chemical Flooding Types and Component Settings
2.2. Physicochemical Mechanism Characterization Models
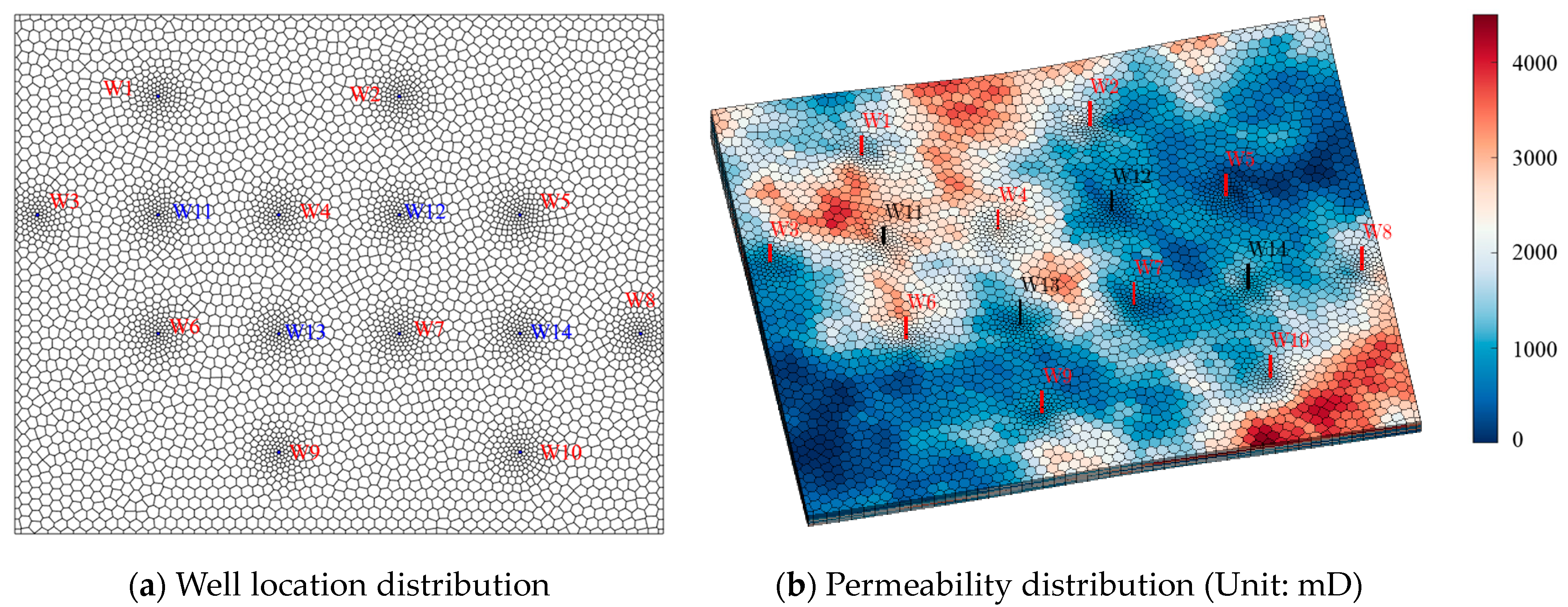
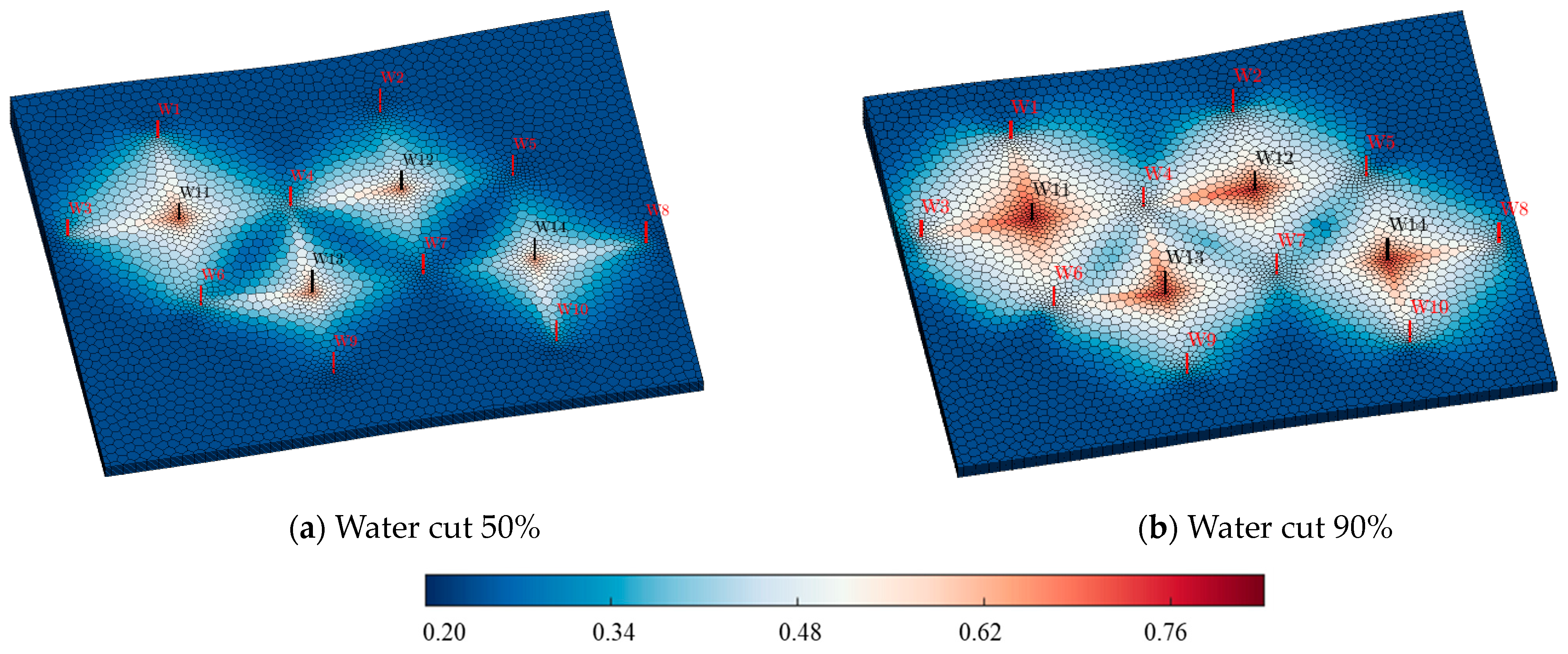
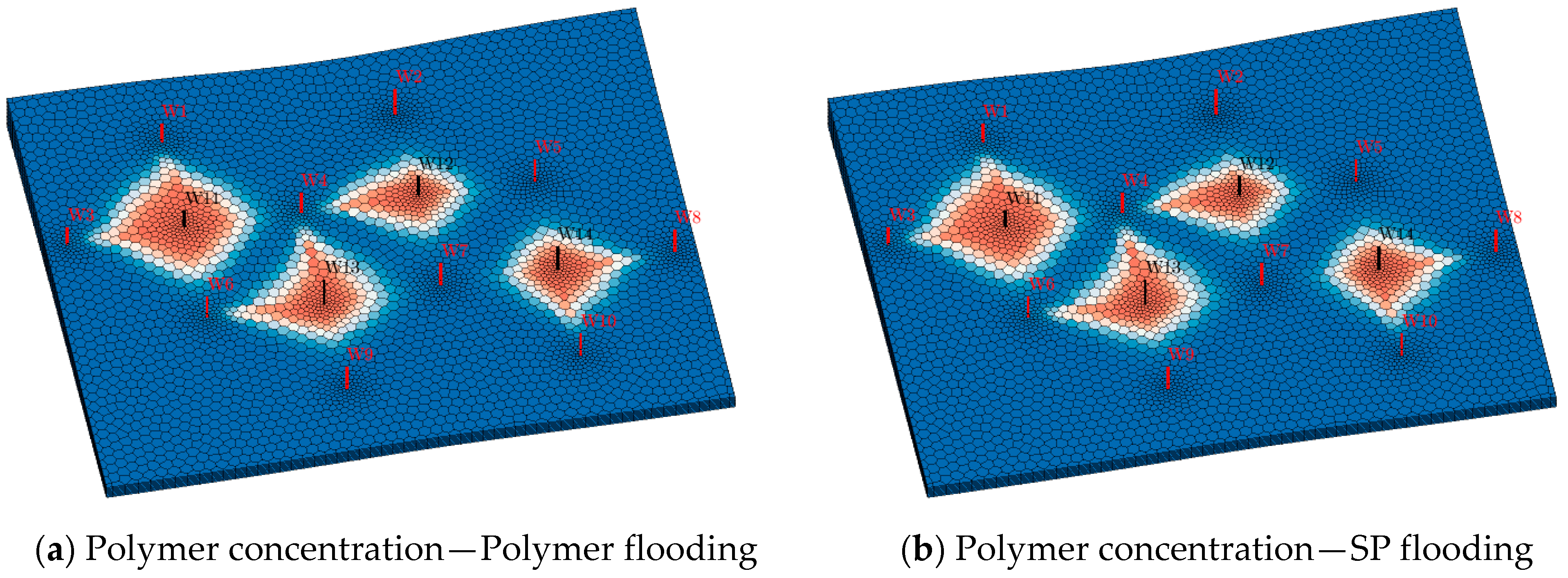
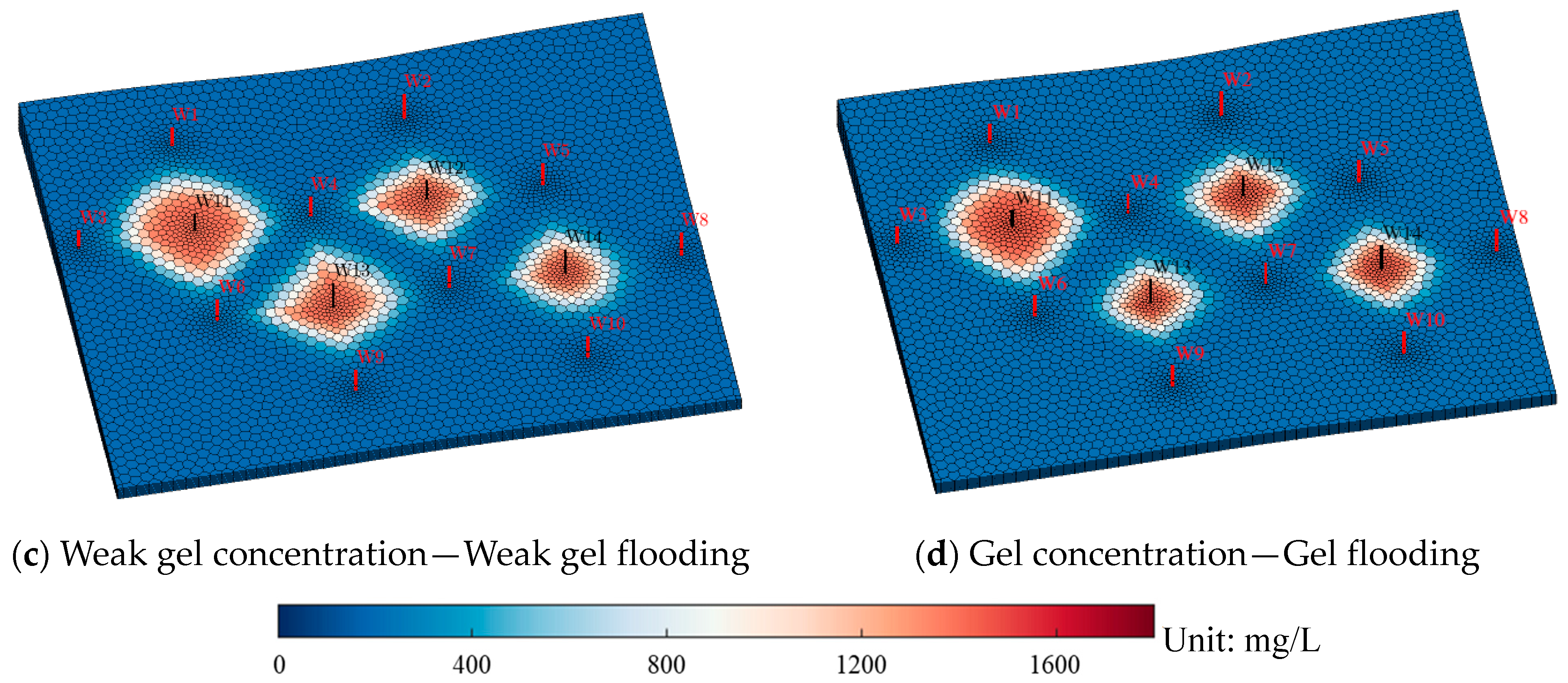
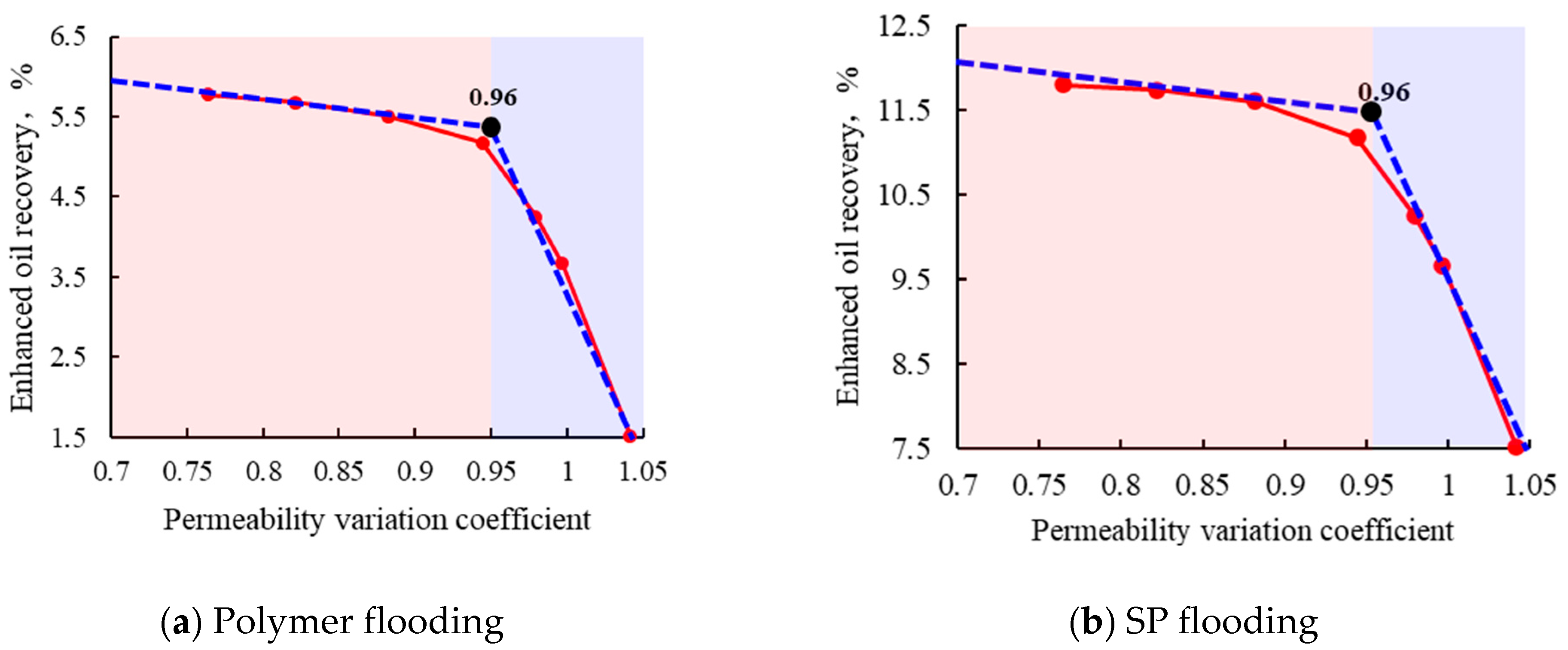
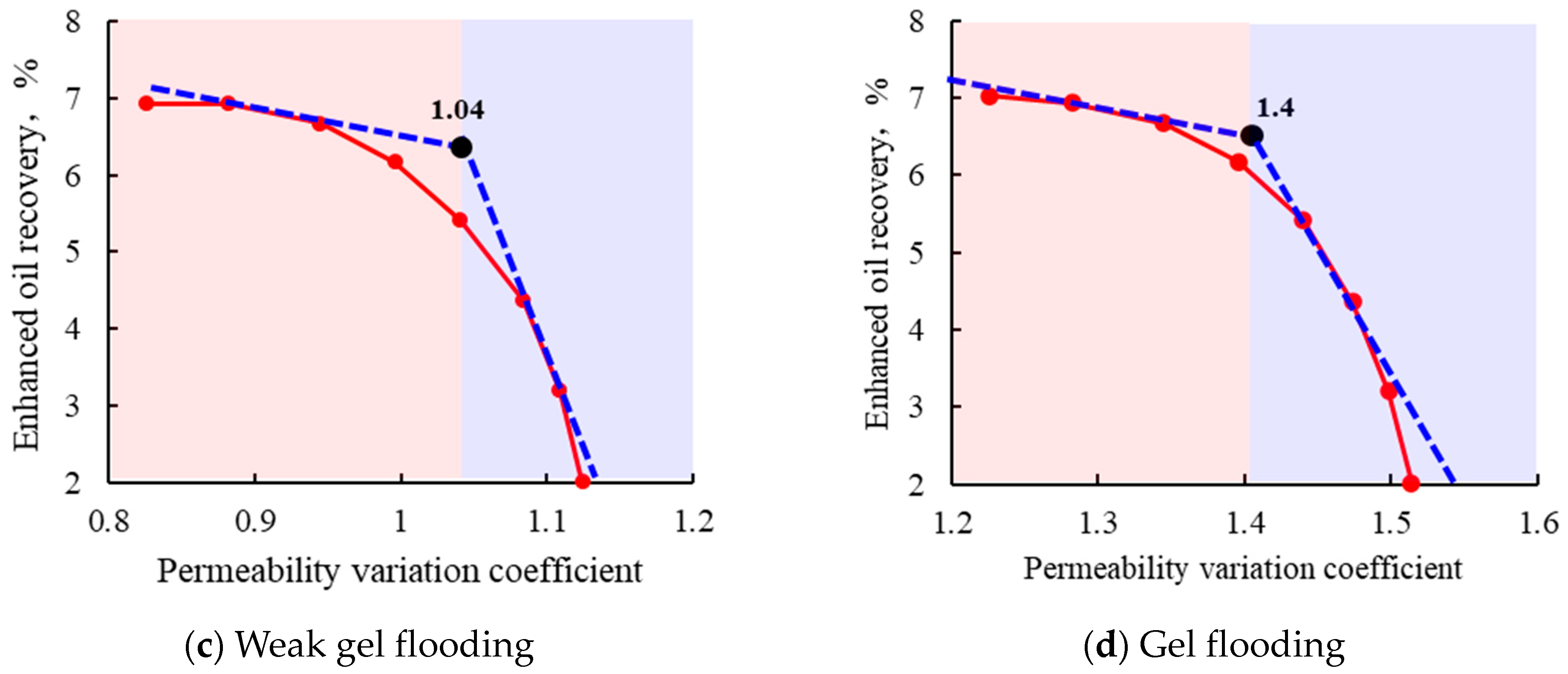
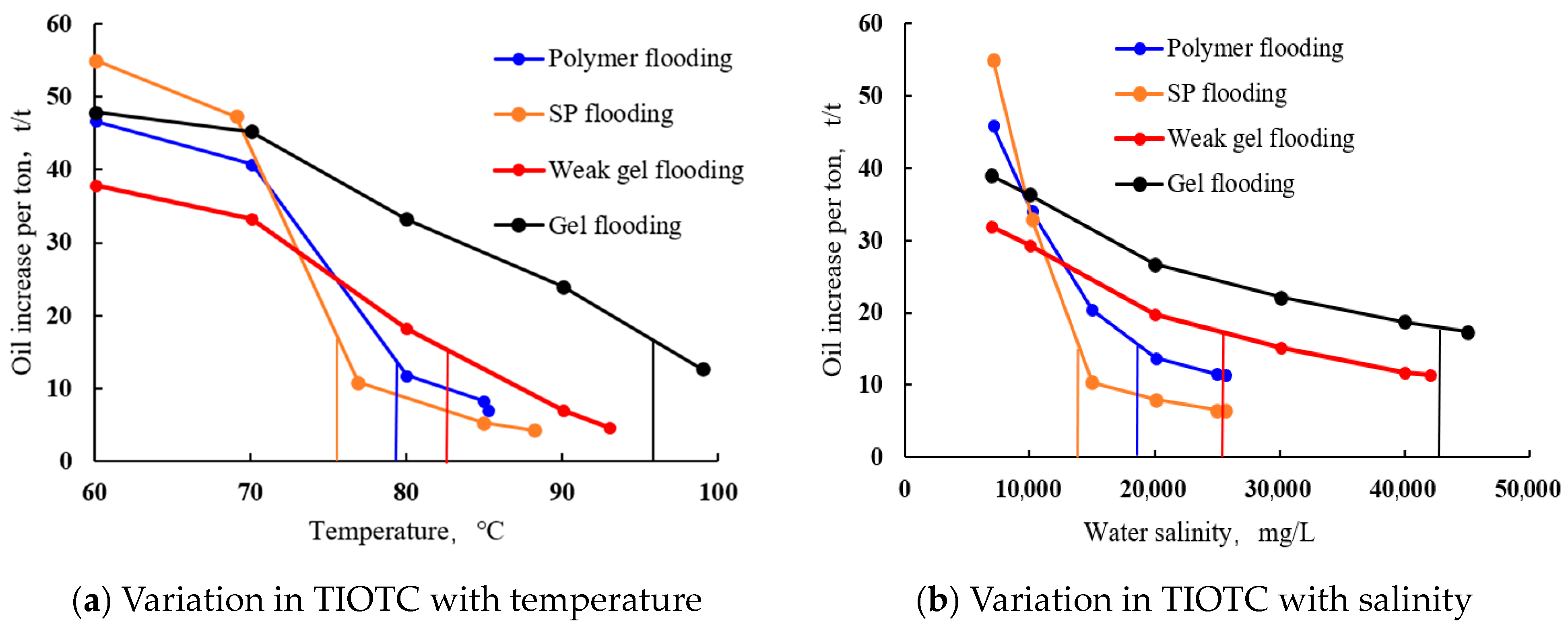
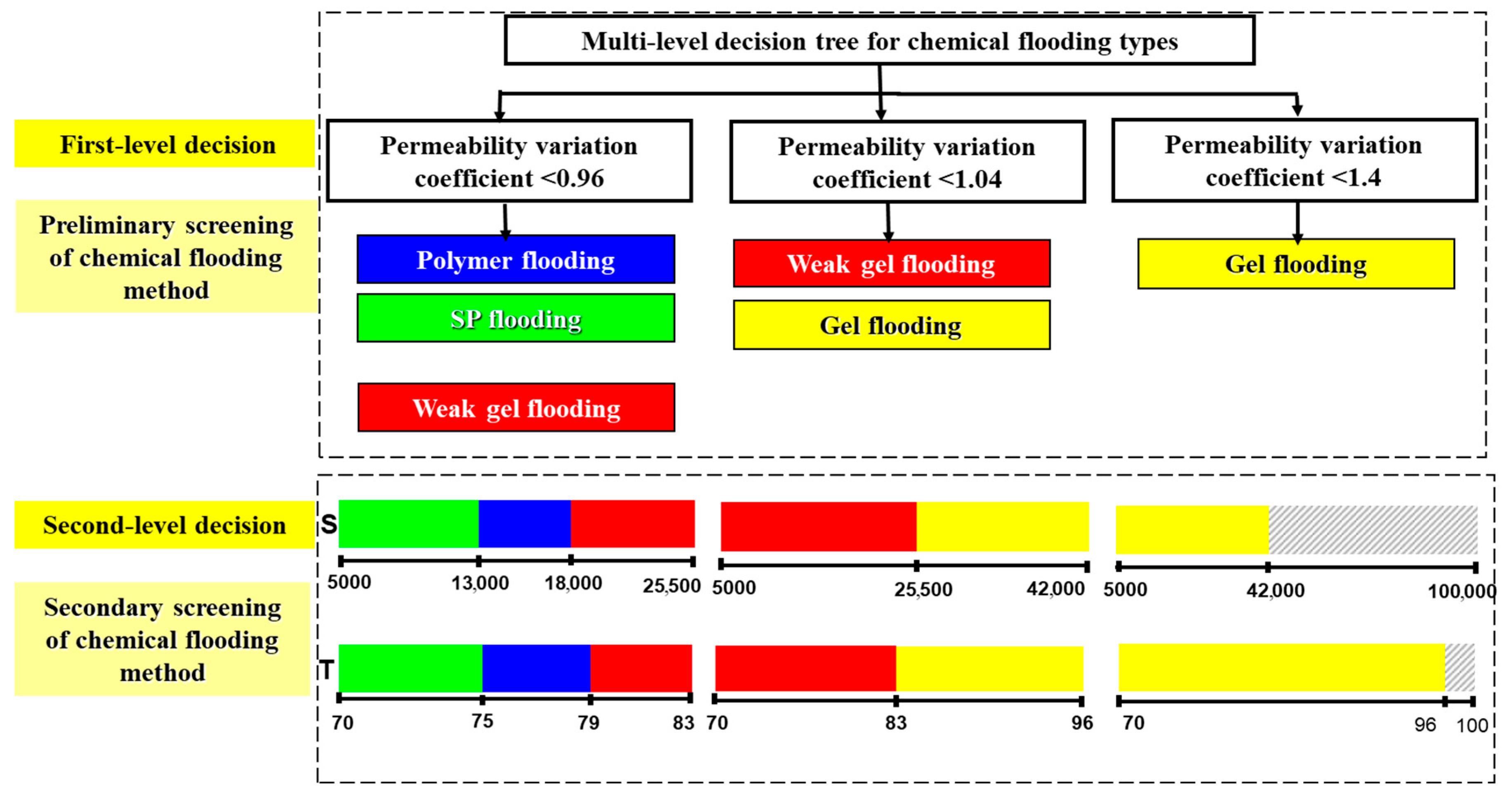
3. Adaptability Study of Different Chemical Flooding Methods
4. Framework Validation Against Field Practices
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Temizel, C.; Canbaz, C.H.; Tran, M.; Abdelfatah, E.; Jia, B.; Putra, D.; Irani, M.; Alkouh, A. A comprehensive review heavy oil reservoirs, latest techniques, discoveries, technologies and applications in the oil and gas industry. In Proceedings of the SPE International Heavy Oil Conference and Exhibition, Kuwait City, Kuwait, 10–12 December 2018; SPE: Dallas, TX, USA, 2018; p. D012S024R001. [Google Scholar]
- Amirian, E.; Dejam, M.; Chen, Z. Performance forecasting for polymer flooding in heavy oil reservoirs. Fuel 2018, 216, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Blackbourn, G.; Ma, F.; He, Z.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Luan, T.; Wu, Z. Heavy oils and oil sands: Global distribution and resource assessment. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2019, 93, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y. Development and research status of heavy oil enhanced oil recovery. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 5015045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Shu, Q.; Wu, G.; Yang, Y. Development technology and direction of thermal recovery of heavy oil in China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2022, 43, 1664. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.H. Experiences of polymer flooding projects at Shengli Oilfield. In Proceedings of the SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 31 March–2 April 2014; SPE: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; p. SPE-169652-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H. How to select polymer molecular weight and concentration to avoid blocking? Field Practices Experience. In Proceedings of the IOR 2019–20th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Pau, France, 8–10 April 2019; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Lv, C.; Fu, X.; Nie, J. Review of practical experience by polymer flooding at Daqing. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2009, 12, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Han, P.; Shao, Z.; Hou, W.; Seright, R.S. Sweep improvement options for the Daqing oil field. In Proceedings of the SPE/DOE Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Tulsa, OK, USA, 22–26 April 2006; SPE: Beijing, China, 2006; p. SPE-99441-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Tao, J.; Lyu, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, H.; Meng, E.; et al. Recent advances in polymer flooding in China. Molecules 2022, 27, 6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, M.; Jigang, J.; Wang, X. Study on oil displacement efficiency of surfactant-polymer flooding in heterogeneous reservoir. Energy Power Eng. 2015, 7, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhong, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhao, P.; Yuan, Y.; Han, X. Characteristics of weak-gel flooding and its application in LD10-1 oilfield. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24935–24945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Wu, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xing, P.; Xu, Q.; Li, D.; Cong, X.; Liu, J. Research on the formulation system of weak gel and the influencing factors of gel formation after polymer flooding in Y1 block. Processes 2022, 10, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Hosseini, L. An overview of the polymer gel technique to improve the efficiency of water flooding into oil reservoirs (with introduction of a new polymer). Int. J. Chem. Pet. Sci. (IJCPS) 2013, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, J. Laboratory experimental optimization of gel flooding parameters to enhance oil recovery during field applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 14968–14976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouenne, S. Polymer flooding in high temperature, high salinity conditions: Selection of polymer type and polymer chemistry, thermal stability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 195, 107545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Han, M.; AlSofi, A.M. Synergistic effects between different types of surfactants and an associating polymer on surfactant–polymer flooding under high-temperature and high-salinity conditions. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 14484–14498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, K.; Hou, J.; An, Z.; Zhai, M.; Liu, W. Experimental study on combining heterogeneous phase composite flooding and streamline adjustment to improve oil recovery in heterogeneous reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 194, 107478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, B.; Schuman, T.; Al Brahim, A.; Bai, B. Ultra-high temperature resistant preformed particle gels for enhanced oil recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Liu, L. Dynamic sweep experiments on a heterogeneous phase composite system based on branched-preformed particle gel in high water-cut reservoirs after polymer flooding. Gels 2023, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Yin, X.; Cao, R.; Zeng, P.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Luo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y. In situ crosslinked weak gels with ultralong and tunable gelation times for improving oil recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 432, 134350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, Z.; Said, I.M.; Jan, B.M. In situ organically cross-linked polymer gel for high-temperature reservoir conformance control: A review. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likozar, B.; Krajnc, M. Cross-linking of polymers: Kinetics and transport phenomena. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, P.S.; Gupta, A.K. Determination of thermodynamic parameters from Langmuir isotherm constant-revisited. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 225, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Pu, W.; Jin, X.; Shen, C.; Ren, H. Review of the micro and Macro mechanisms of gel-based plugging agents for enhancing oil recovery of unconventional water flooding oil reservoirs. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z. Micro and Macro Flooding Mechanism and Law of a Gel Particle System in Strong Heterogeneous Reservoirs. Gels 2024, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, G. Review on polymer flooding technology. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 675, p. 012199. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Ge, J.; Shi, X. Surfactant–polymer binary oil-displacement agents suitable for multiple oilfield blocks. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2023, 44, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józefczyk, J. Decision-making algorithms in two-level complex operation system. Decis. Support Syst. 2004, 38, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verly, G. Sequential Gaussian simulation: A Monte Carlo method for generating models of porosity and permeability. In Generation, Accumulation and Production of Europe’s Hydrocarbons III: Special Publication of the European Association of Petroleum Geoscientists No. 3; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 345–356. [Google Scholar]
- An, Z.; Zhou, K.; Hou, J.; Wu, D.; Pan, Y.; Liu, S. Research on the main controlling factors for injection and production allocation of polymer flooding. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2023, 145, 043201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liang, S.; Tan, S.; Sun, Z.; Yu, Y. Experimental study on surface-active polymer flooding for enhanced oil recovery: A case study of Daqing placanticline oilfield, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 1206–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, A. Development and application of dilute surfactant–polymer flooding system for Shengli oilfield. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2009, 65, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, A.; Bai, B.; Schuman, T. Comprehensive review of polymer and polymer gel treatments for natural gas-related conformance control. Gels 2022, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Method | Primary Mechanism | Primary Application Condition | Typical Implementation Field |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer flooding | Improves mobility ratio by increasing aqueous phase viscosity. | Reservoirs with moderate heterogeneity, improving volumetric sweep efficiency. | Daqing Oilfield, China; partial blocks in Permian Basin, the United States; Pelican Lake Oilfield, Canada; Mangala Oilfield, India |
| Surfactant–polymer flooding | Reduces interfacial tension and improves mobility ratio simultaneously. | Reservoirs with high remaining oil saturation, targeting both sweep and displacement efficiency. | Shengli Oilfield, China; Daqing Oilfield, China; (Liaohe Oilfield, China |
| Weak gel/gel flooding | Selectively plugs high-permeability thief zones, diverting flow to unswept areas. | Heterogeneous reservoirs with severe channeling or fractures, achieving profile modification. | Shengli Oilfield, China; Liaohe Oilfield, China; Bohai Oilfield, China; Prudhoe Bay, the United States |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir thickness, m | 24 | Oil viscosity, mPa·s | 75 |
| Average porosity | 0.31 | Net gross ratio | 0.7 |
| Average permeability, mD | 2000 | Total injection rate, m3/d | 672 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 1.0 | Surfactant concentration, % | 0.4 |
| Polymer concentration, mg/L | 1500 | Strong gel, mg/L | 1500 |
| Weak gel, mg/L | 1500 | , kg/m3 | 2.2 |
| rrk, 1/s | 0.15 | ns | 2.0 |
| γ1/2, 1/s | 6.0 | A2 | 1.4 |
| A1 | 1.4 | A3 | −0.001 |
| Srwl | 0.24 | Srwh | 0.0 |
| Srol | 0.25 | Sroh | 0.0 |
| nwl | 2.0 | nwh | 1.00 |
| nol | 2.0 | nohhhh | 1.0 |
| b | 4.0 | Rkmax | 2.0 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, P.; Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M. Study on Rapid Screening Method for Different Chemical Flooding Methods in Heavy-Oil Reservoirs. Processes 2025, 13, 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092992
Zhang L, Gao Z, Liu Y, Li Y, Zhou K, Wang P, Zhang K, Wang C, Zhang M. Study on Rapid Screening Method for Different Chemical Flooding Methods in Heavy-Oil Reservoirs. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092992
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Li, Zhixin Gao, Yongge Liu, Yipu Li, Kang Zhou, Pengbo Wang, Kun Zhang, Chunlin Wang, and Mengfan Zhang. 2025. "Study on Rapid Screening Method for Different Chemical Flooding Methods in Heavy-Oil Reservoirs" Processes 13, no. 9: 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092992
APA StyleZhang, L., Gao, Z., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Zhou, K., Wang, P., Zhang, K., Wang, C., & Zhang, M. (2025). Study on Rapid Screening Method for Different Chemical Flooding Methods in Heavy-Oil Reservoirs. Processes, 13(9), 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092992






