Research on Geological–Engineering “Double-Sweet Spots” Grading Evaluation Method for Low-Permeability Reservoirs with Multi-Parameter Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Geological and Engineering Sweet Spot Identification Method
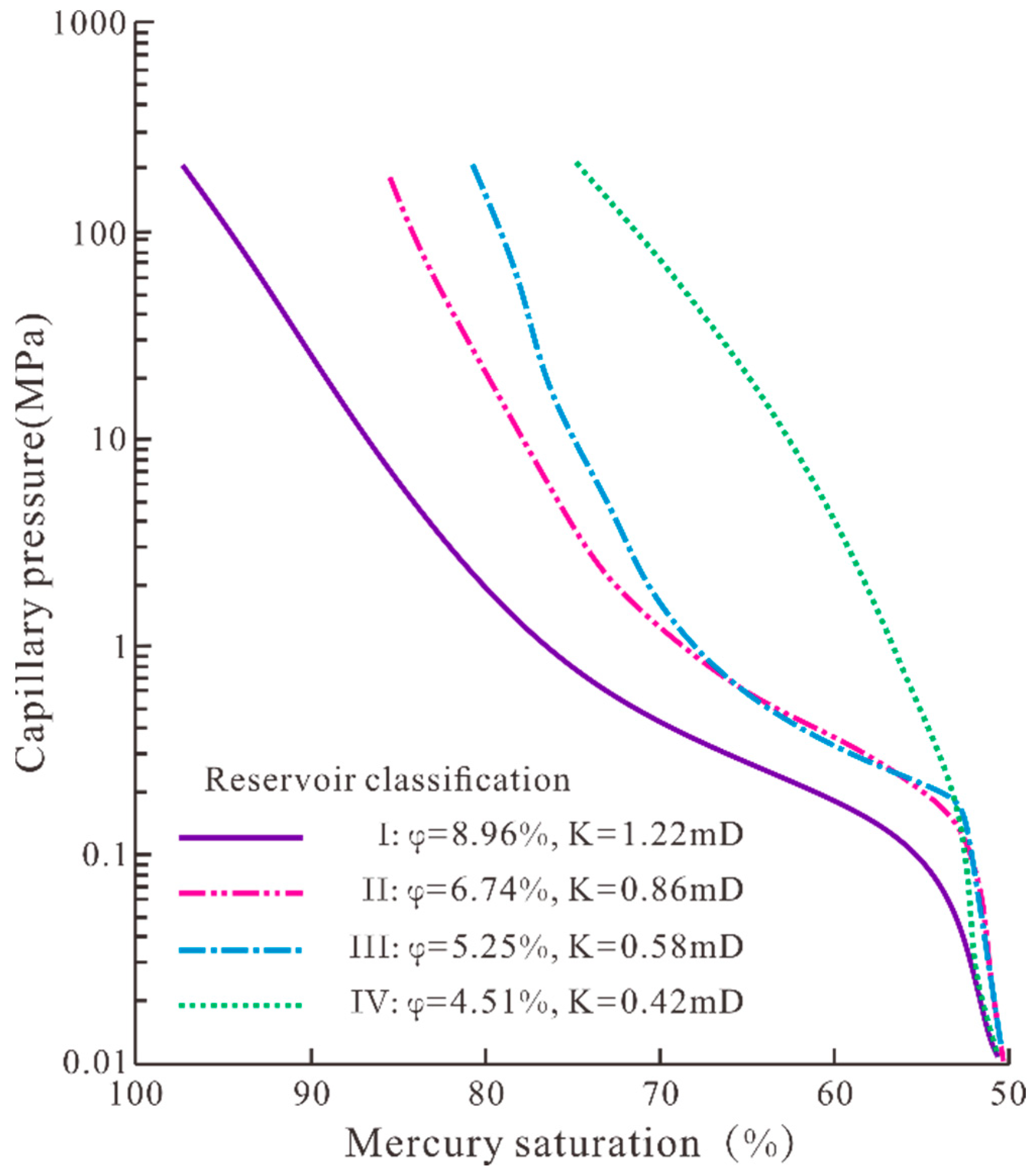
2.1.1. Geological Sweet Spots Parameter Analysis
2.1.2. Engineering Sweet Spot Parameter Analysis
2.2. Geological and Engineering Sweet Spot Analysis Methods
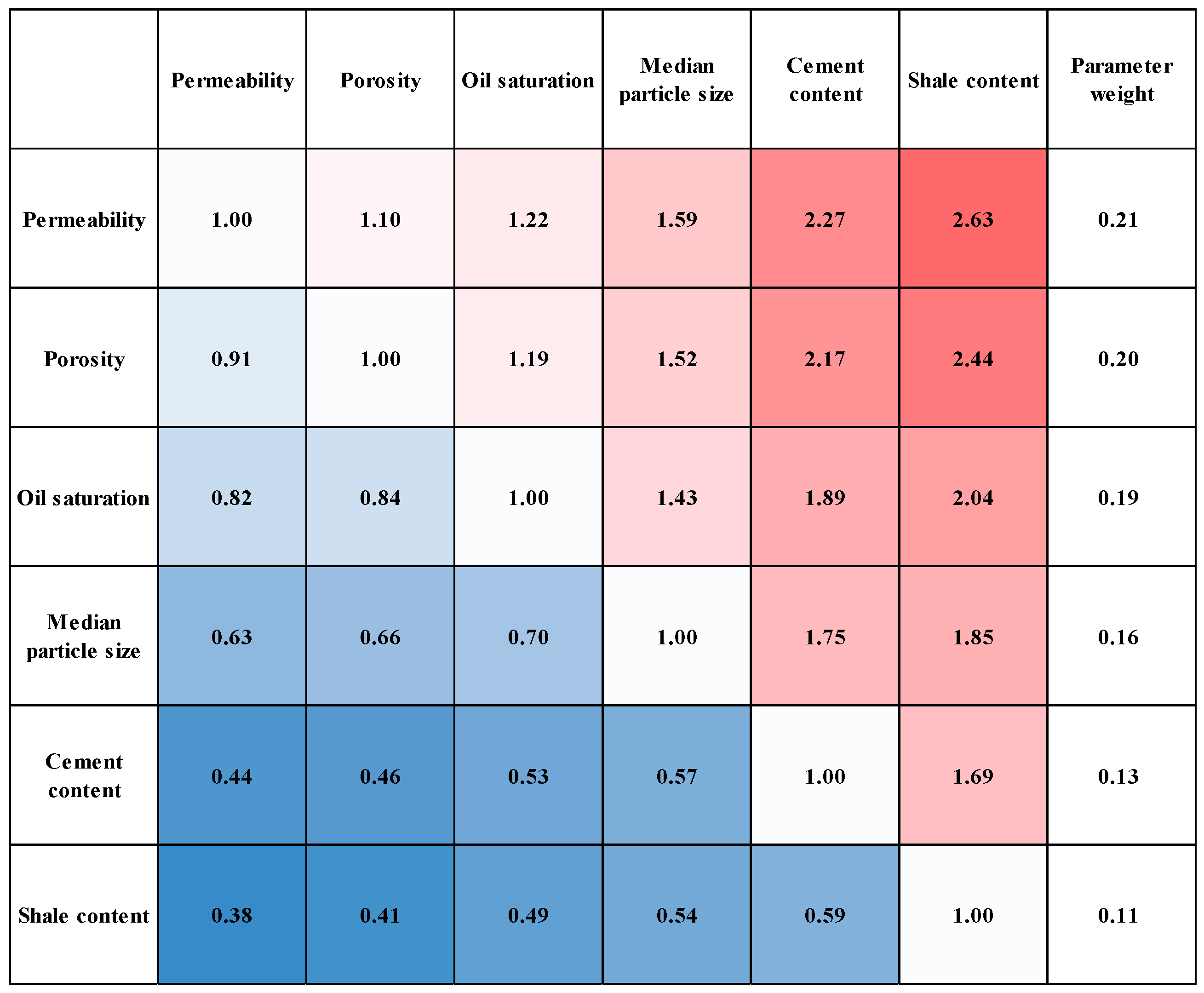
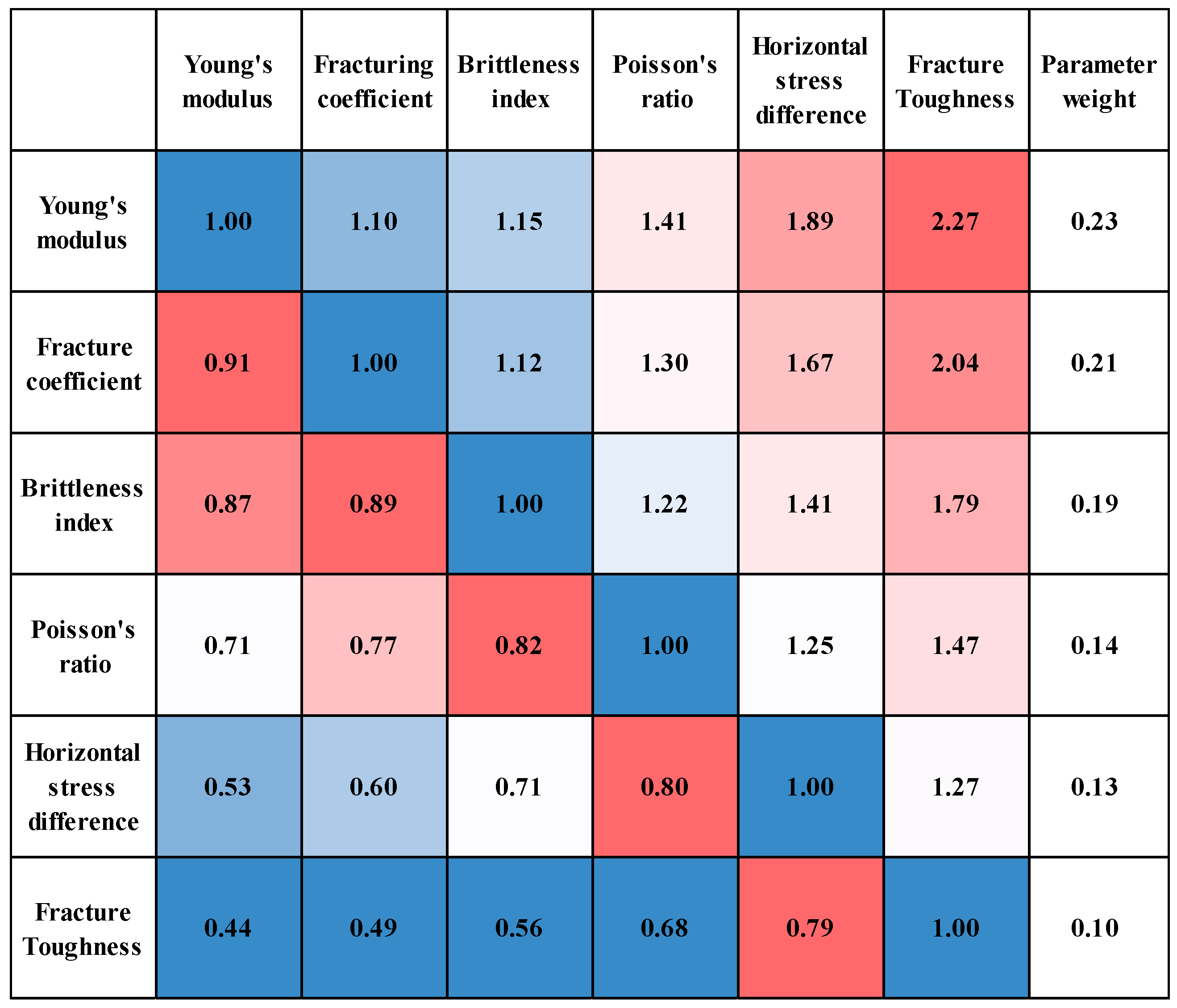
2.2.1. Grey Relational Analysis
- (1)
- Construct comparison and reference sequence
- (2)
- Data normalization
- (3)
- Calculation of correlation degree
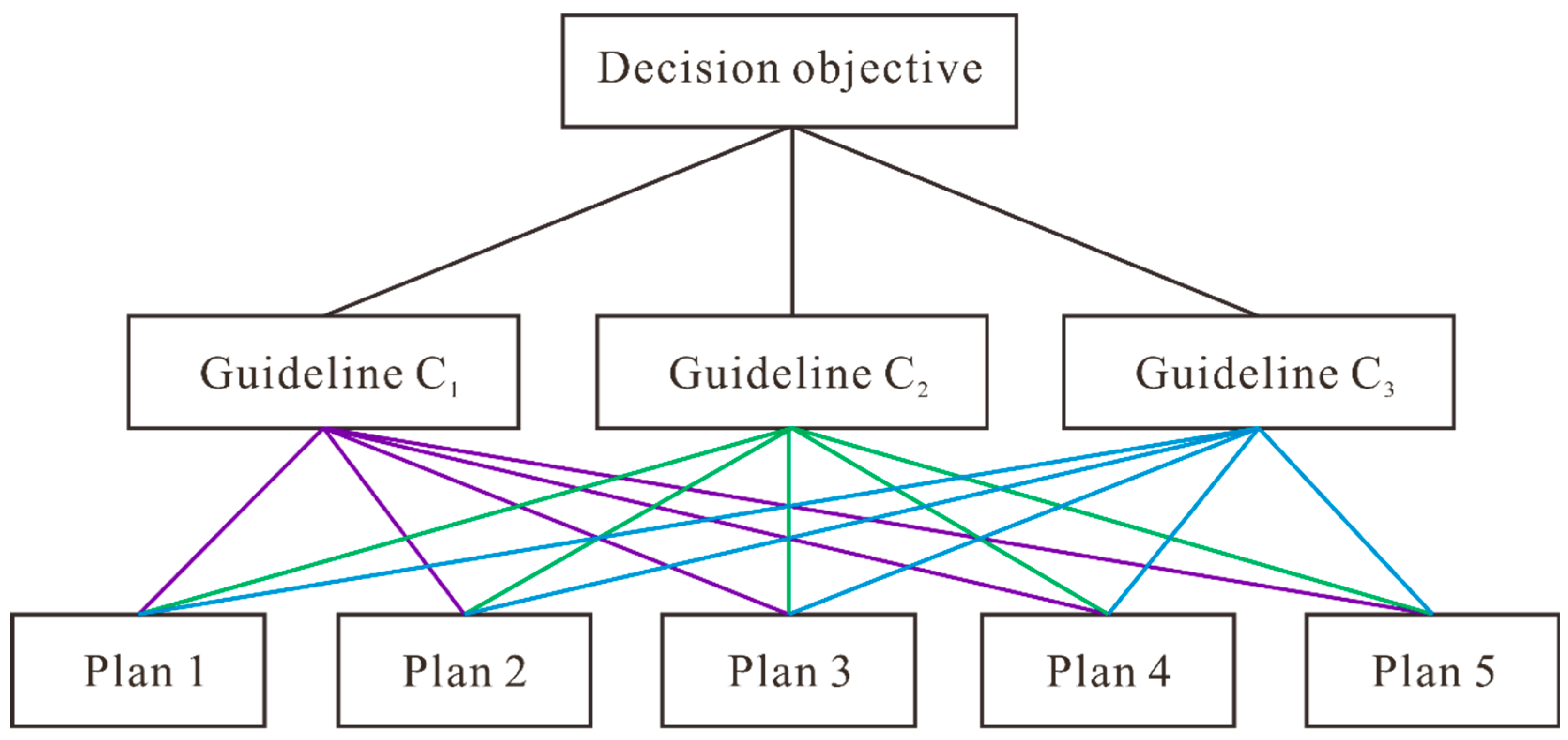
2.2.2. Analytic Hierarchy Process
- (1)
- Establishment of hierarchical structure model
- (2)
- Construct judgement matrix
- (3)
- Single level ranking and consistency test
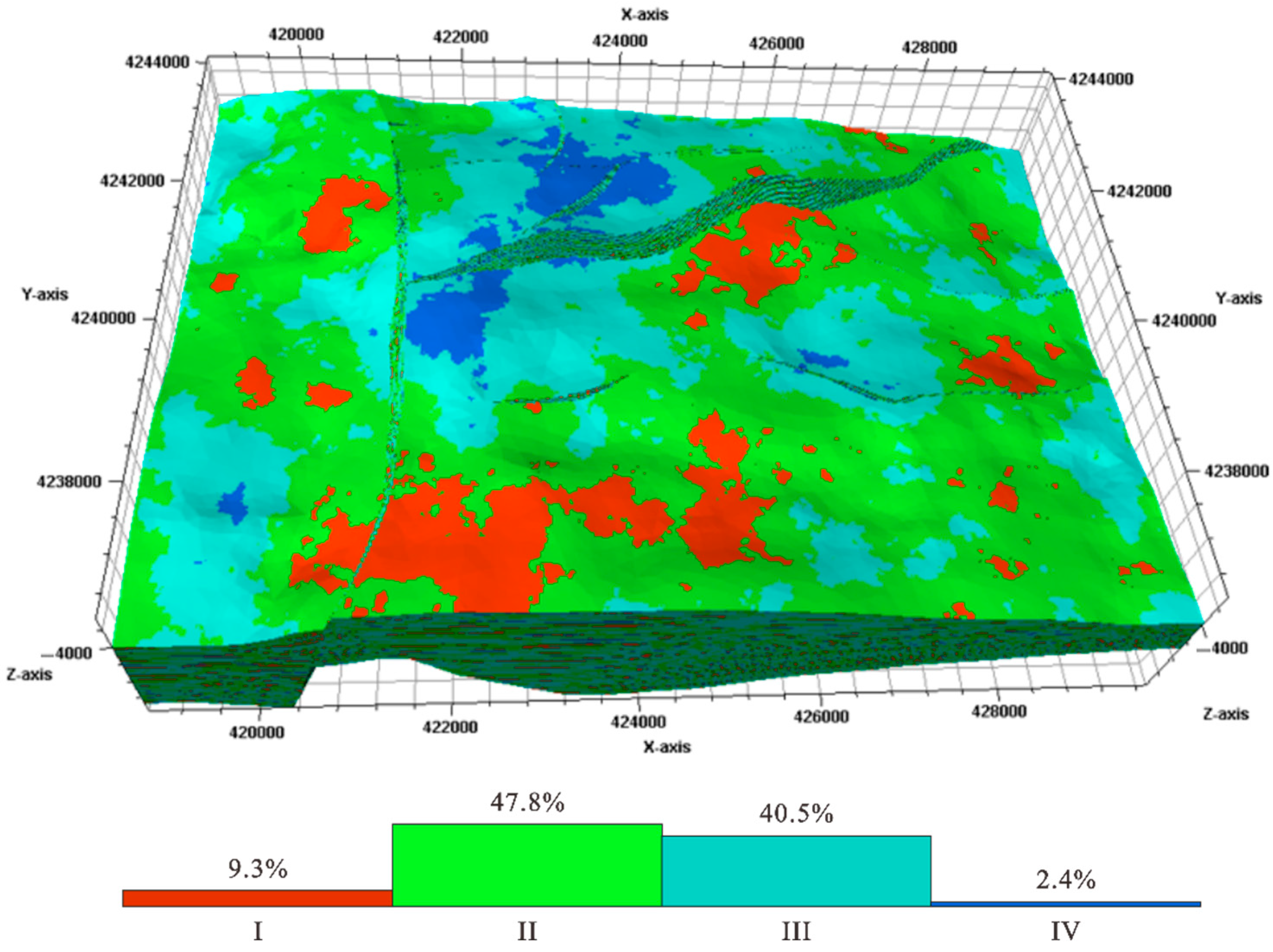
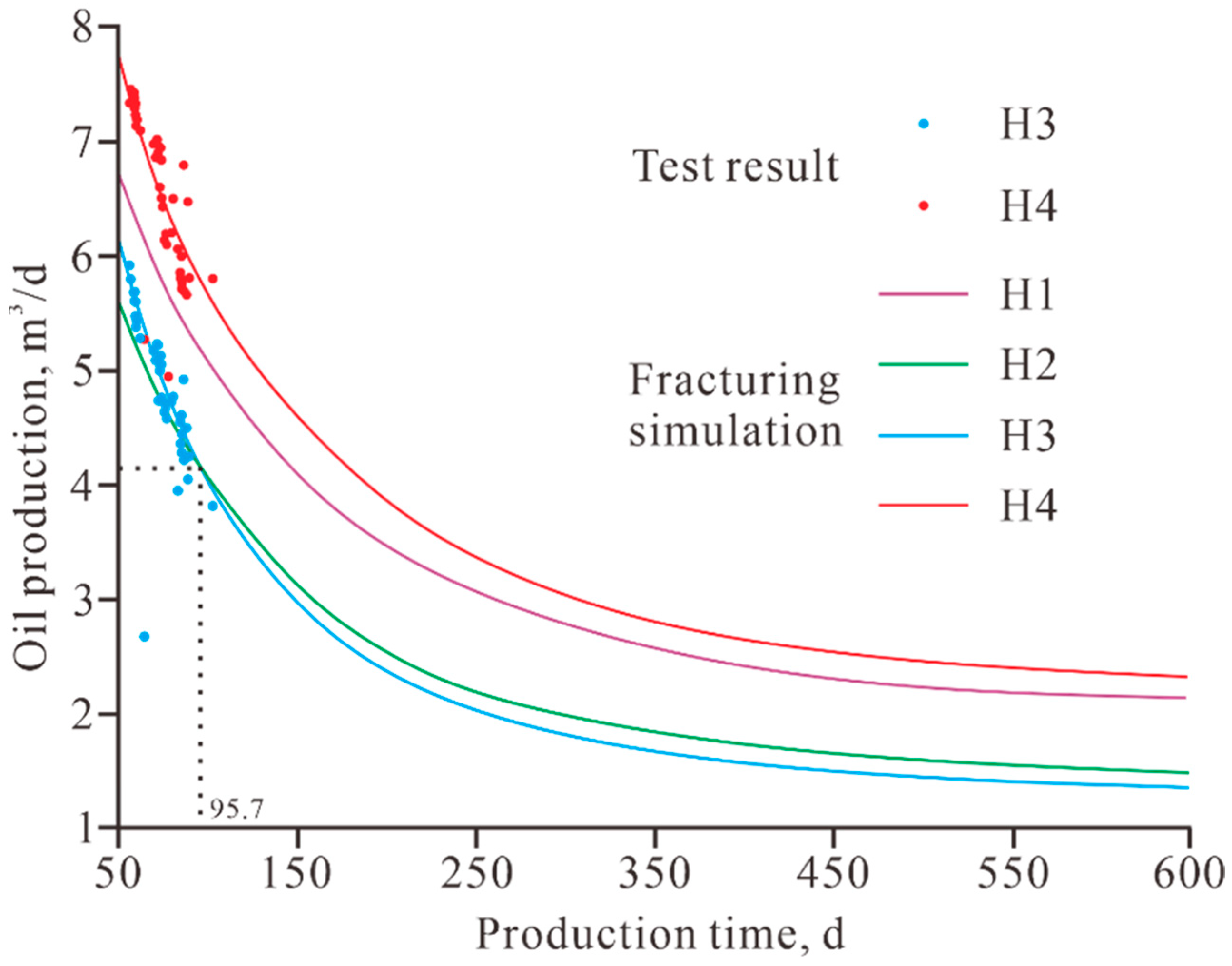
3. Results
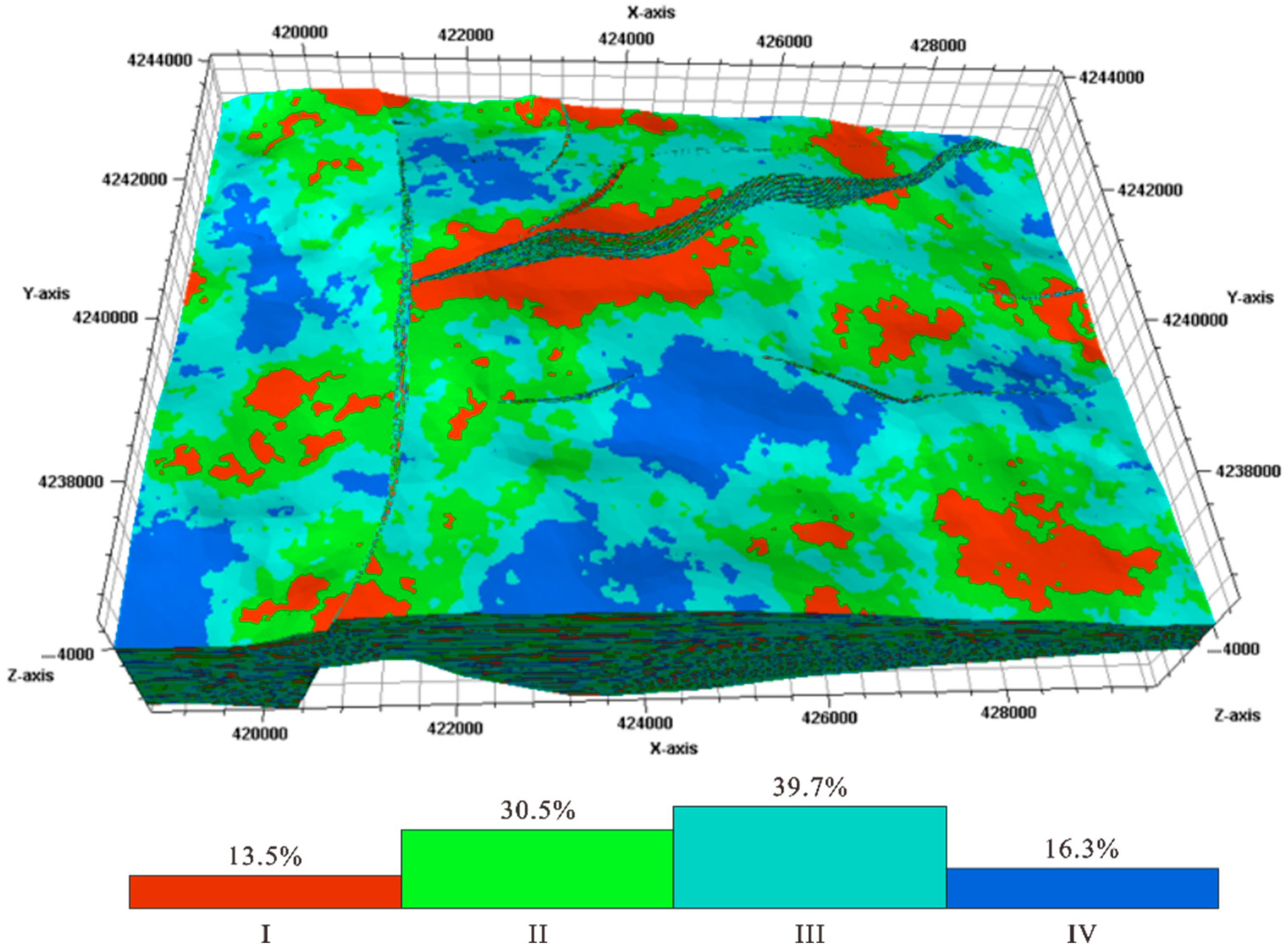
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, M. Reservoir prediction using pre-stack inverted elastic parameters. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 6, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Khalid, P.; Anwar, A.W. Rock physics modelling to assess the impact of spatial distribution pattern of pore fluid and clay contents on acoustic signatures of partially-saturated reservoirs. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2016, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, M.; Ahmed, N.; Khalid, P.; Wei, L.X.; Naeem, M. An application of rock physics modeling to quantify the seismic response of gas hydrate-bearing sediments in Makran accretionary prism, offshore, Pakistan. Geosci. J. 2016, 20, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, Z.L.; Liu, X.W.; Huo, Z.Z.; Guo, P. Using frequency-dependent AVO inversion to predict the “sweet spots” of shale gas reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 102, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.T.; Li, D.Y.; Liu, X.T.; Du, Y.S.; Gong, W. Sweet spot prediction in tight sandstone reservoir based on well-bore rock physical simulation. Pet. Sci. 2019, 16, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagiz, S. Assessment of brittleness using rock strength and density with punch penetration test. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2009, 24, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, D.M.; Hill, R.J.; Ruble, T.E.; Pollastro, R.M. Unconventional shale-gas systems: The Mississippian Barnett Shale of north-central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale-gas assessment. AAPG Bull. 2007, 91, 475–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.K.; Grieser, W.V.; Passman, A.; Tamayo, C.H.; Modeland, N.; Burke, B. A Completions Guide Book to Shale-Play Development: A Review of Successful Approaches Towards Shale-Play Stimulation in the Last Two Decades. In Proceedings of the Canadian Unconventional Resources and International Petroleum Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 19–21 October 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Shah, S.N.; Roegiers, J.C.; Zhang, B. An Integrated Petrophysics and Geomechanics Approach for Fracability Evaluation in Shale Reservoirs. SPE J. 2015, 20, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, Z.; Lai, F.; Wang, L.; Wu, D. Method for evaluation of engineering sweet spots tight sandstone reservoir production wells. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Xiang, J. Three-Dimensional Geological Engineering Double Desert Evaluation of Low-Permeability Sandstone Reservoirs. J. Energy Eng. 2025, 151, 04025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, B.C.; Li, Z.D.; Zhang, H.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Huo, W.X.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.Q.; Li, Y.H. Optimizing hydrate extraction: Balancing stability and production efficiency. Fuel 2025, 384, 134088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, B.C.; Li, Z.D.; Huo, W.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, R.B.; Zhang, H.X.; Xu, Y.Q.; He, Y.F. Phase transitions of CH4 hydrates in mud-bearing sediments with oceanic laminar distribution: Mechanical response and stabilization-type evolution. Fuel 2025, 380, 133185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gan, B.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yu, F. The Control Effect of Equipment Operation on the Formation of Wellbore Hydrates Under the Production Conditions of Deepwater Gas Wells. Processes 2025, 13, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Gong, D.; Zhang, B. A multi-scale geological–engineering sweet spot evaluation method for tight sandstone gas reservoirs. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2023, 10, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tureyen, O.I.; Caers, J. A parallel, multiscale approach to reservoir modeling. Comput. Geosci. 2005, 9, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, P.; Javadpour, F.; Sahimi, M. Data mining and machine learning for identifying sweet spots in shale reservoirs. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 88, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Basu, S.; Vishal, V.; Srivastava, M. Hierarchical clustering of Pristane and Phytane data to identify the sweet spots in the shale reservoirs. Energy Clim. Change 2020, 1, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Chan, S.; Mahmoud, M.; Aljawad, M.S.; Humphrey, J.; Abdulraheem, A. Artificial Intelligence-Based Model of Mineralogical Brittleness Index Based on Rock Elemental Compositions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 11745–11761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.W.; Fan, Z.Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, X. Research progress in brittleness index evaluation methods with logging data in unconventional oil and gas reservoirs. Pet. Sci. Bull. 2016, 1, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, J.; Jing, Y.Q.; Liang, X.; Fan, H.J.; Cai, W.T. Using seismic response characteristics to predict “sweet spot” locations in a low permeability reservoir in the Bohai Sea. Geophys. Prospect. Pet. 2022, 61, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Xiang, Y. An evaluation method of reservoir “sweet spots” in low permeability oilfields of Beibuwan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Equal | Strong | Stronger | Very Strong | Absolutely Strong | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | …… |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.9 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.41 | 1.45 | …… |
| Reservoir Category | Geological Sweet Spots Indicator Factor | Permeability (mD) | Porosity (%) | Oil Saturation (%) | Median Particle Size (mm) | Cement Content (%) | Shale Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.75–1 | >1 | >7 | >57.5 | >0.7 | <6 | 8–15 |
| II | 0.5–0.75 | 0.7–1 | 6–7 | 45–57.5 | 0.5–0.7 | 6–10 | 15–20 |
| III | 0.25–0.5 | 0.5–0.7 | 5–6 | 32.5–45 | 0.3–0.5 | 10–14 | 20–25 |
| IV | 0–0.25 | <0.5 | <5 | <32.5 | <0.3 | >14 | >25 |
| Reservoir Category | Engineering Sweet Spots Indicator Factor | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Fracture Coefficient | Brittleness Index | Poisson’s Ratio | Horizontal Stress Difference | Fracture Toughness (MPa-m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.75–1 | >65 | >0.57 | >0.45 | >0.30 | >0.4 | >3 |
| II | 0.5–0.75 | 45–65 | 0.48–0.57 | 0.35–0.45 | 0.26–0.30 | 0.35–0.4 | 2.5–3 |
| III | 0.25–0.5 | 30–45 | 0.4–0.48 | 0.25–0.35 | 0.23–0.26 | 0.3–0.35 | 2–2.5 |
| IV | 0–0.25 | <30 | <0.4 | <0.25 | <0.23 | <0.3 | <2 |
| Parameter Term | Value |
|---|---|
| Original ground pressure (MPa) | 52.41 |
| Saturation pressure (MP) | 24.43 |
| Crude oil volume factor | 1.4135 |
| Gas–oil ratio | 136 |
| Crude oil viscosity (mPa-s) | 1.41 |
| Temperature (°C) | 123.2 |
| Oil density (g/cm3) | 0.7264 |
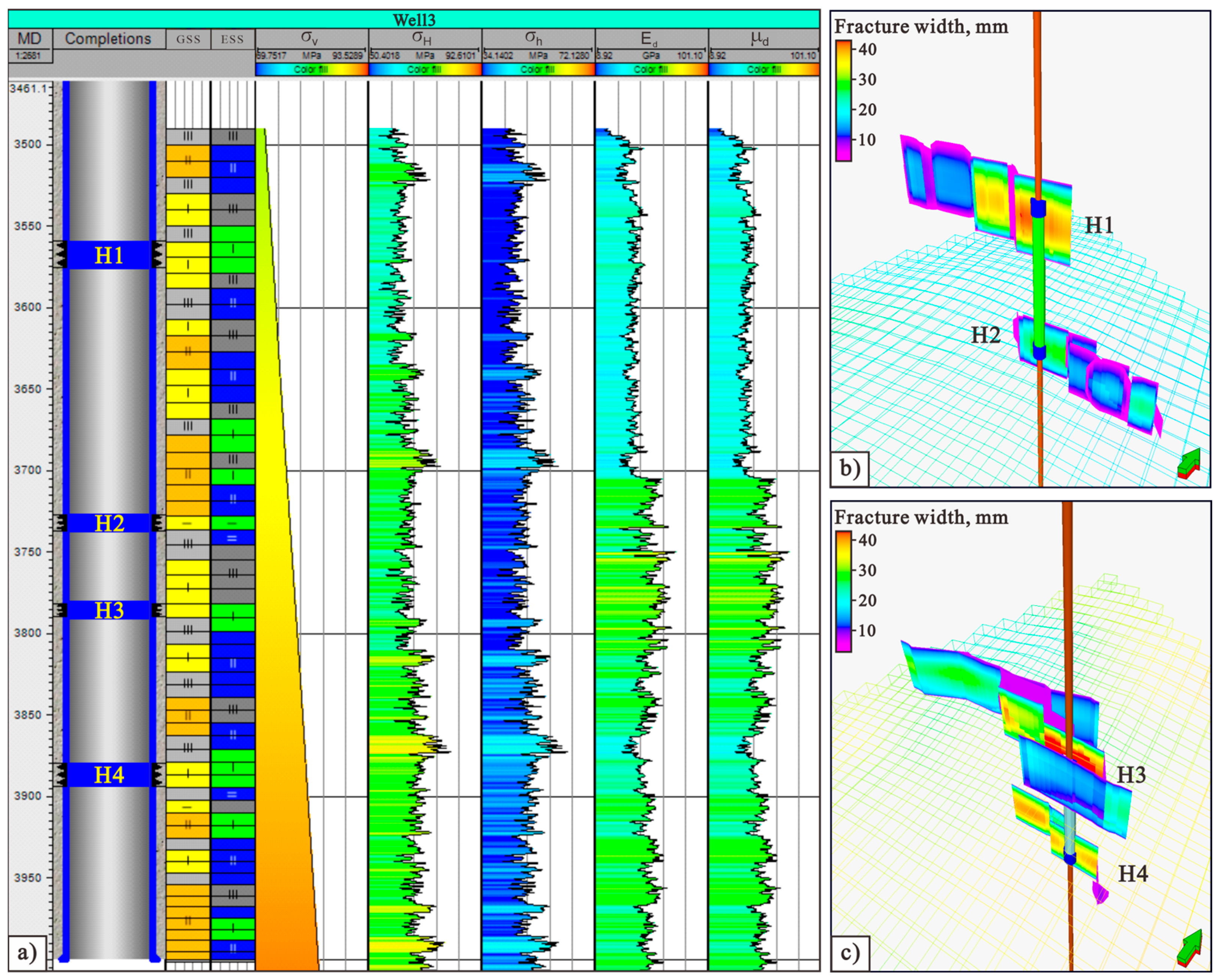
| Horizon | Depth Range | Geological Sweet Spots Indicator Factor | Engineering Sweet Spots Indicator Factor | Fracturing Sand Volume (m3) | Fracturing Fluid Volume (m3) | Simulated Crack Length (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70/140 Mesh Ceramsite | 40/70 Mesh Ceramsite | Total Amount of Proppant | ||||||
| H1 | 3562.47~3575.77 | 0.93 | 0.76 | 10 | 22 | 32 | 631.48 | 81.52 |
| H2 | 3727.91~3736.59 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 30 | 64 | 94 | 596.15 | 100.28 |
| H3 | 3781.71~3789.81 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 36 | 72 | 108 | 847.36 | 147.29 |
| H4 | 3880.05~3894.51 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 11 | 27 | 38 | 548.63 | 123.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ge, Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, S.; Li, Z. Research on Geological–Engineering “Double-Sweet Spots” Grading Evaluation Method for Low-Permeability Reservoirs with Multi-Parameter Integration. Processes 2025, 13, 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092967
Li Y, Zhang H, Ge Y, Liu L, Guo S, Li Z. Research on Geological–Engineering “Double-Sweet Spots” Grading Evaluation Method for Low-Permeability Reservoirs with Multi-Parameter Integration. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092967
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yihe, Haixiang Zhang, Yan Ge, Lingtong Liu, Shuwen Guo, and Zhandong Li. 2025. "Research on Geological–Engineering “Double-Sweet Spots” Grading Evaluation Method for Low-Permeability Reservoirs with Multi-Parameter Integration" Processes 13, no. 9: 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092967
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhang, H., Ge, Y., Liu, L., Guo, S., & Li, Z. (2025). Research on Geological–Engineering “Double-Sweet Spots” Grading Evaluation Method for Low-Permeability Reservoirs with Multi-Parameter Integration. Processes, 13(9), 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092967





