Multi-Objective Black-Start Planning for Distribution Networks with Grid-Forming Storage: A Control-Constrained NSGA-III Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
3. Optimization and Algorithmic Framework
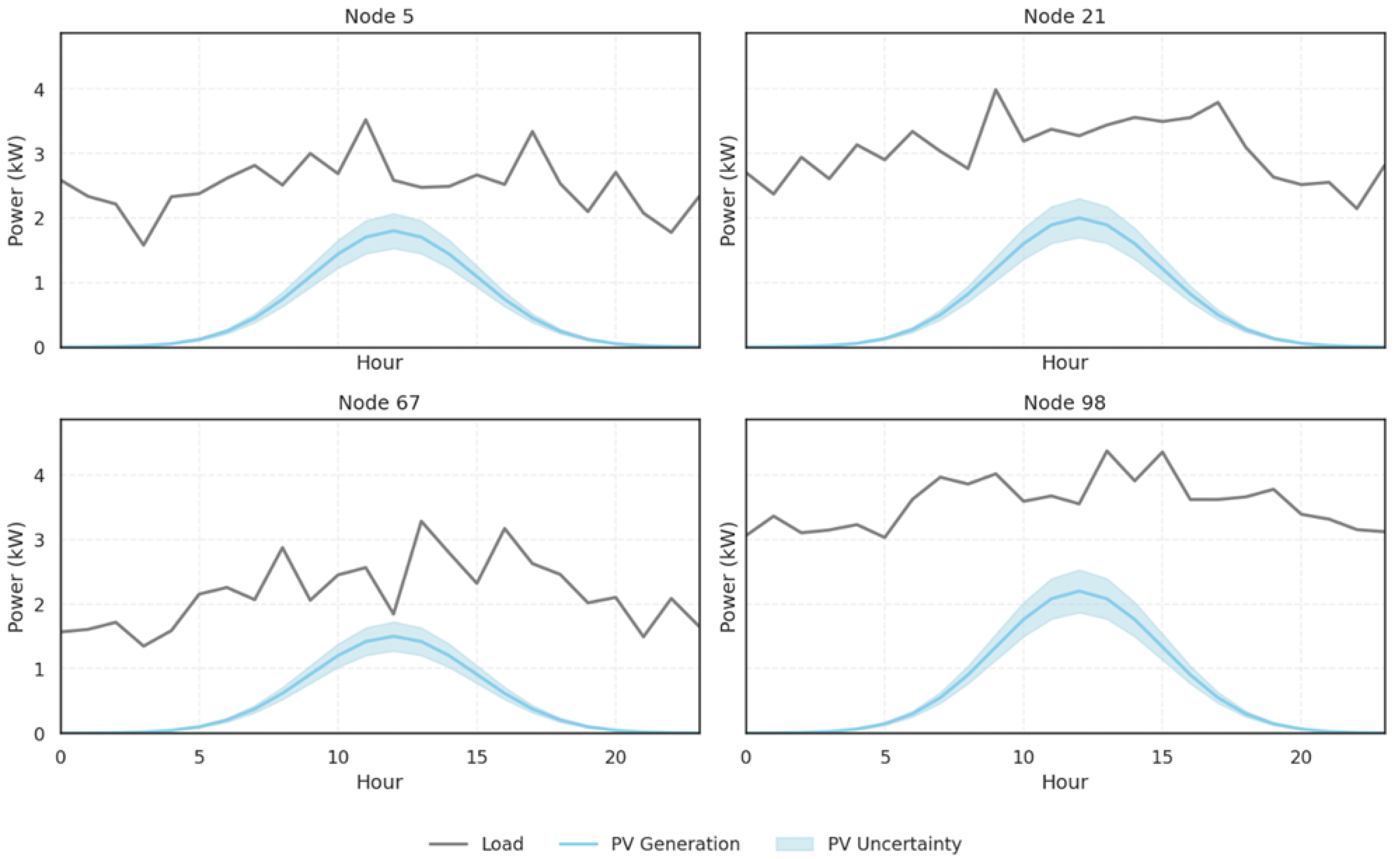
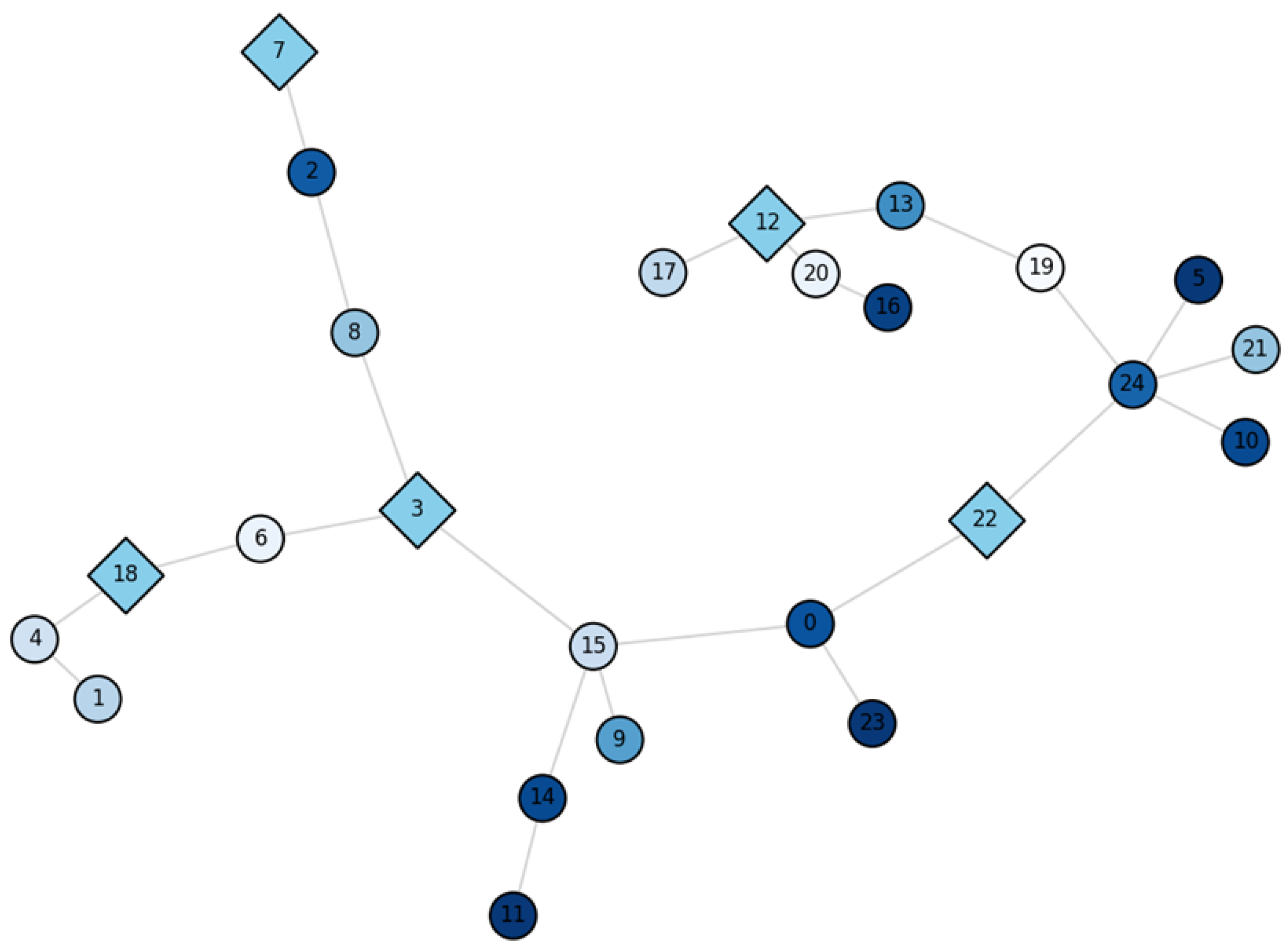
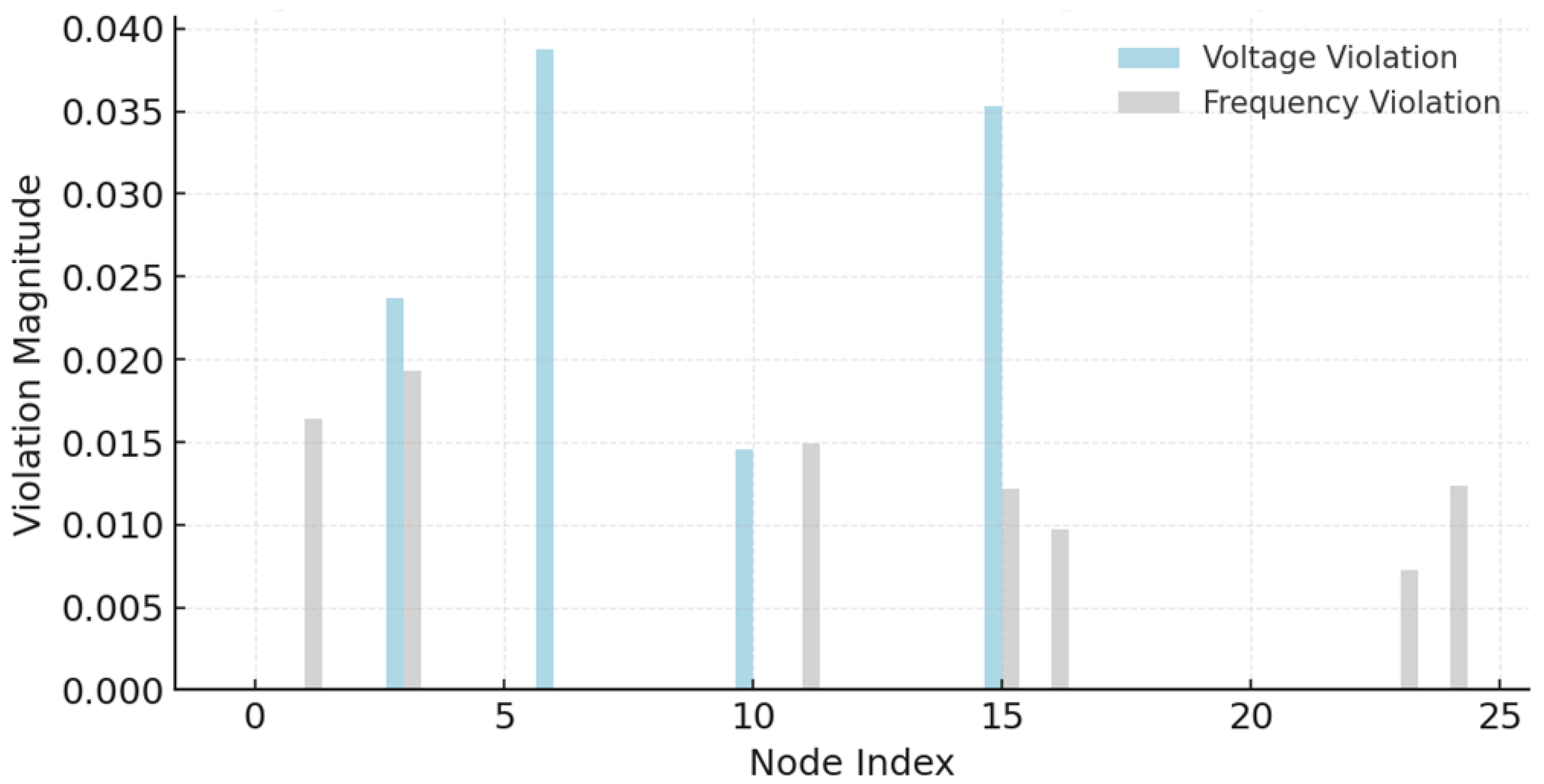
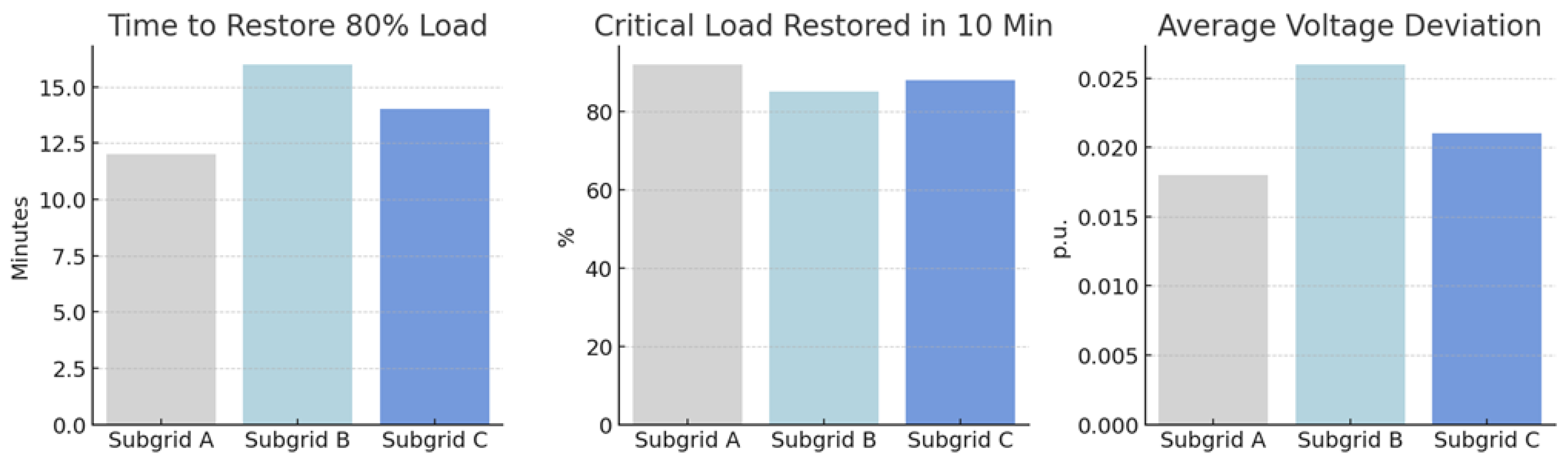
4. Case Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Description |
| Restoration completion time at node (s) | |
| Synchronization delay at node (s) | |
| Voltage deviation penalty (p.u.) | |
| Priority weight of critical node | |
| GFES presence indicator (binary) | |
| Energization status of node (binary) | |
| Voltage magnitude at node (p.u.) | |
| Nominal voltage (p.u.) | |
| f | System frequency (Hz) |
| Frequency control authority of GFES | |
| State of charge of GFES (%) | |
| Discharge and charge power (kW) | |
| Maximum apparent power of GFES (kVA) | |
| Droop coefficient (Hz/kW) | |
| Voltage phase angle (rad) | |
| Line current (A) | |
| Thermal capacity of line (A) | |
| Connection matrix between nodes (binary) | |
| Slack variable for unmet critical loads | |
| Restoration path decision vector | |
| Subgrid partition configuration | |
| Objective value for metric m | |
| Pareto rank in NSGA-III | |
| Crowding distance for diversity preservation | |
| Restoration path energy loss (kWh) | |
| Penalty from voltage/frequency violations | |
| Convergence gap threshold in NSGA-III | |
| Load surge risk weight | |
| Load block surge multiplier | |
| GFES strength for frequency regulation |
References
- Earthdata, N. Power Outage in Spain (Black Marble Imagery of the Iberian Blackout). In NASA Earth Science Data and Information System (ESDIS); Wiley: Berlin, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, K. Fuzzy model predictive control for frequency regulation of temporary microgrids during load restoration. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2024, 18, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutani, G.; Santantonio, S.; Brunetta, G.; Caldarice, O.; Demichela, M. An energy community for territorial resilience: Measurement of the risk of an energy supply blackout. Energy Build. 2021, 240, 110906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busby, J.W.; Baker, K.; Bazilian, M.D.; Gilbert, A.Q.; Grubert, E.; Rai, V.; Rhodes, J.D.; Shidore, S.; Smith, C.A.; Webber, M.E. Cascading risks: Understanding the 2021 winter blackout in Texas. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2021, 77, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanny, J.; Goldoni, L.R.F.; Medeiros, B. The 2019 Venezuelan blackout and the consequences of cyber uncertainty. Rev. Bras. Estud. Def. 2020, 7, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basumallik, S.; Eftekharnejad, S.; Johnson, B.K. The impact of false data injection attacks against remedial action schemes. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 123, 106225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.P.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Fei, X.; Hu, Z.; Alhazmi, M.; Yan, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, S.; et al. Electric Vehicle Charging Planning: A Complex Systems Perspective. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 754–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solat, A.; Gharehpetian, G.B.; Naderi, M.S.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A. On the control of microgrids against cyber-attacks: A review of methods and applications. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Lyu, H.; Liang, G.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.Y. On Vulnerability of Renewable Energy Forecasting: Adversarial Learning Attacks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 3650–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Optimal Operation with Dynamic Partitioning Strategy for Centralized Shared Energy Storage Station with Integration of Large-scale Renewable Energy. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzolini, G.; Fusco, A.; Gioffrè, D.; Matrone, S.; Ramaschi, R.; Saleptsis, M.; Simonetti, R.; Sobic, F.; Wood, M.J.; Ogliari, E.; et al. Impact of PV and EV Forecasting in the Operation of a Microgrid. Forecasting 2024, 6, 591–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardian, T. ‘Blackouts Can Happen Anywhere’: How Power Systems Worldwide Can Collapse. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/business/2025/may/02/blackouts-energy-outage-risks-europe-worldwide-spain-portugal-france (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Zhao, A.P.; Alhazmi, M.; Huo, D.; Li, W. Psychological modeling for community energy systems. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye-Boateng, K.; Ghorbani, A.A.; Lashkari, A.H. Implementation of a Trust-Based Framework for Substation Defense in the Smart Grid. Smart Cities 2023, 7, 99–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govea, J.; Gaibor-Naranjo, W.; Villegas-Ch, W. Transforming Cybersecurity into Critical Energy Infrastructure: A Study on the Effectiveness of Artificial Intelligence. Systems 2024, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Xie, F.; Wang, Z.; Dong, C. Resilience Measurement of Bus–Subway Network Based on Generalized Cost. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lücker, F.; Timonina-Farkas, A.; Seifert, R.W. Balancing Resilience and Efficiency: A Literature Review on Overcoming Supply Chain Disruptions. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2024, 34, 1495–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazdag, B.A.; Van Quaquebeke, N.; Besiou, M. Diversity and Inclusion Under Pressure: Building Relational Resilience into Humanitarian Operations. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2024, 34, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; You, F. Broaden sustainable design and optimization of decarbonized campus Energy systems with scope 3 emissions accounting and social ramification analysis. Appl. Energy 2024, 373, 123963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Cui, Y.; Yan, G.; Huang, Y.; Fan, Z. Distributed energy management of multi-area integrated energy system based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 157, 109867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Liu, T.; Shan, Y. A comprehensive survey on NSGA-II for multi-objective optimization and applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 15217–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, R.; Jahangir, M.H. Multi-objective optimization of a hybrid renewable energy system supplying a residential building using NSGA-II and MOPSO algorithms. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 294, 117515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Li, X. An improved NSGA-III algorithm based on distance dominance relation for many-objective optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 117738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.K.; Dash, D.P.; Basu, M. Application of NSGA-II for environmental constraint economic dispatch of thermal-wind-solar power system. Renew. Energy Focus 2022, 43, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhou, G.; Xu, Z.; Jia, Y. Resilient Topology Design for EV Charging Network Based On Percolation-Fractal Analytics. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2024, 15, 3341–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Qiu, J.; Lin, J.; Yao, Z.; Liang, Q.; Lu, X. Planning of a multi-agent mobile robot-based adaptive charging network for enhancing power system resilience under extreme conditions. Appl. Energy 2025, 395, 126252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Zhao, A.P.; Wang, Y.; Alhazmi, M. Hybrid energy storage for dairy farms: Enhancing energy efficiency and operational resilience. J. Energy Storage 2025, 114, 115811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Explainable spatiotemporal multi-task learning for electric vehicle charging demand prediction. Appl. Energy 2025, 384, 125460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Gu, C.; Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Alhazmi, M. Integrated energy-water systems for community-level flexibility: A hybrid deep Q-network and multi-objective optimization framework. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 4813–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Onoye, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Catthoor, F. Transient Response and Non-Linear Capacity Variation Aware Unified Equivalent Circuit Battery Model. In Proceedings of the 8th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion (WCPEC), Milan, Italy, 26–30 September 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | Resilience Score | Restoration Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| MILP-based | 0.71 | 15.3 |
| NSGA-II based | 0.78 | 14.2 |
| Proposed NSGA-III | 0.85 | 12.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Shao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Piao, Z.; Cao, Y. Multi-Objective Black-Start Planning for Distribution Networks with Grid-Forming Storage: A Control-Constrained NSGA-III Framework. Processes 2025, 13, 2875. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092875
Wu L, Shao Y, Gong Y, Zhao Y, Piao Z, Cao Y. Multi-Objective Black-Start Planning for Distribution Networks with Grid-Forming Storage: A Control-Constrained NSGA-III Framework. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2875. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092875
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Linlin, Yinchi Shao, Yu Gong, Yiming Zhao, Zhengguo Piao, and Yuntao Cao. 2025. "Multi-Objective Black-Start Planning for Distribution Networks with Grid-Forming Storage: A Control-Constrained NSGA-III Framework" Processes 13, no. 9: 2875. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092875
APA StyleWu, L., Shao, Y., Gong, Y., Zhao, Y., Piao, Z., & Cao, Y. (2025). Multi-Objective Black-Start Planning for Distribution Networks with Grid-Forming Storage: A Control-Constrained NSGA-III Framework. Processes, 13(9), 2875. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092875





