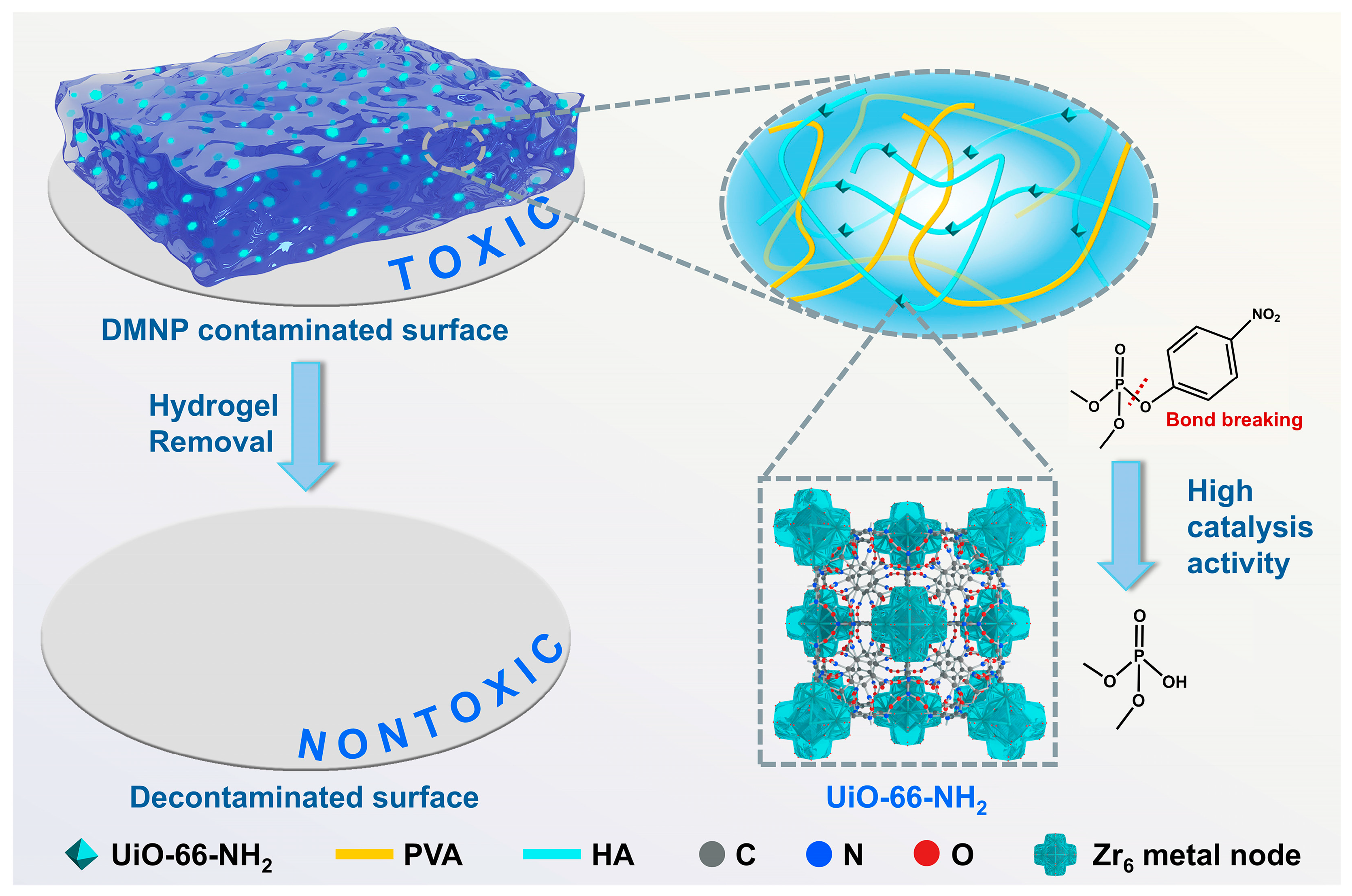
Zr-MOF Crosslinked Hydrogel for High-Efficiency Decontamination of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Synthesis of U6N
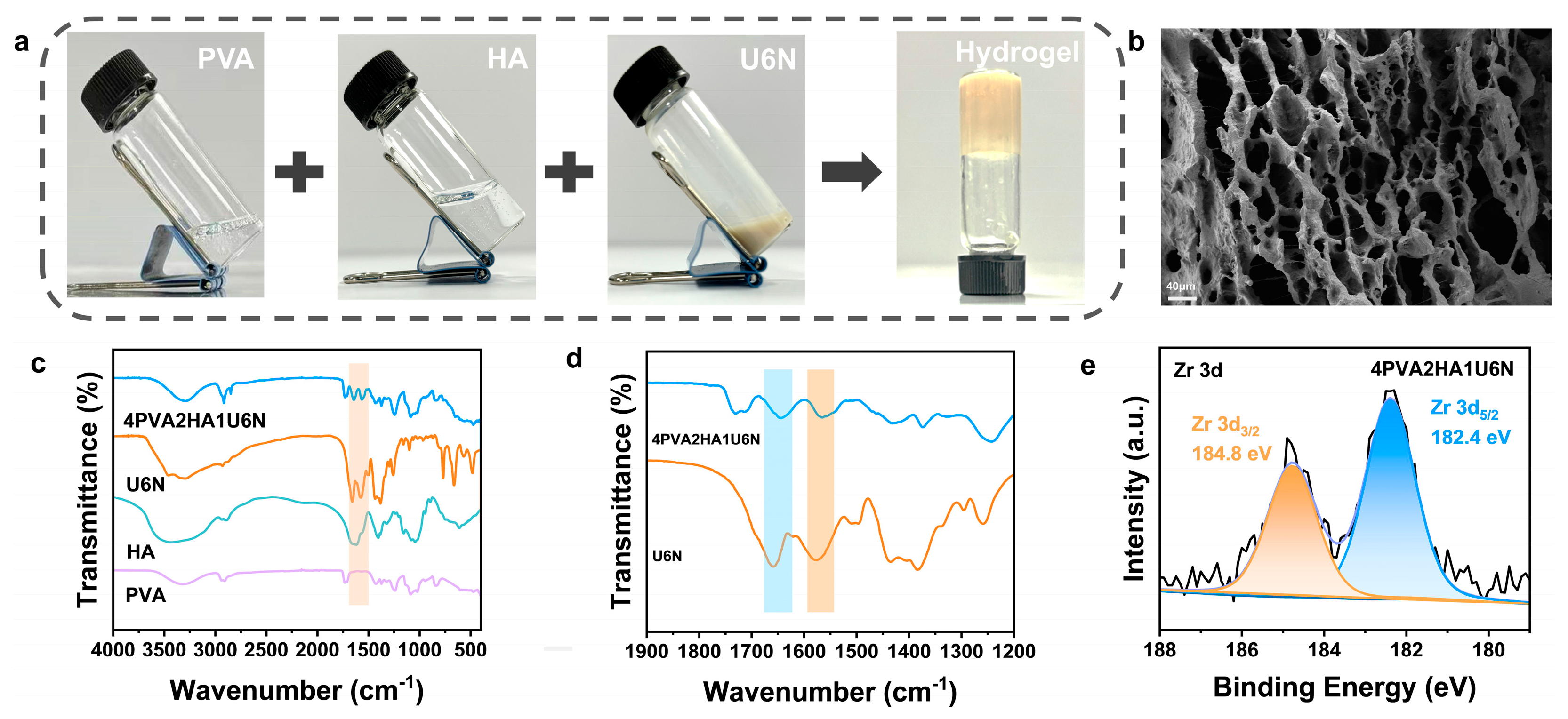
2.3. Formation of PVA/HA/U6N
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Catalytic Degradation of DMNP by U6N and PVA/HA/U6N
2.6. Adhesive Properties and Peelability of the Hydrogel
3. Results and Discussion
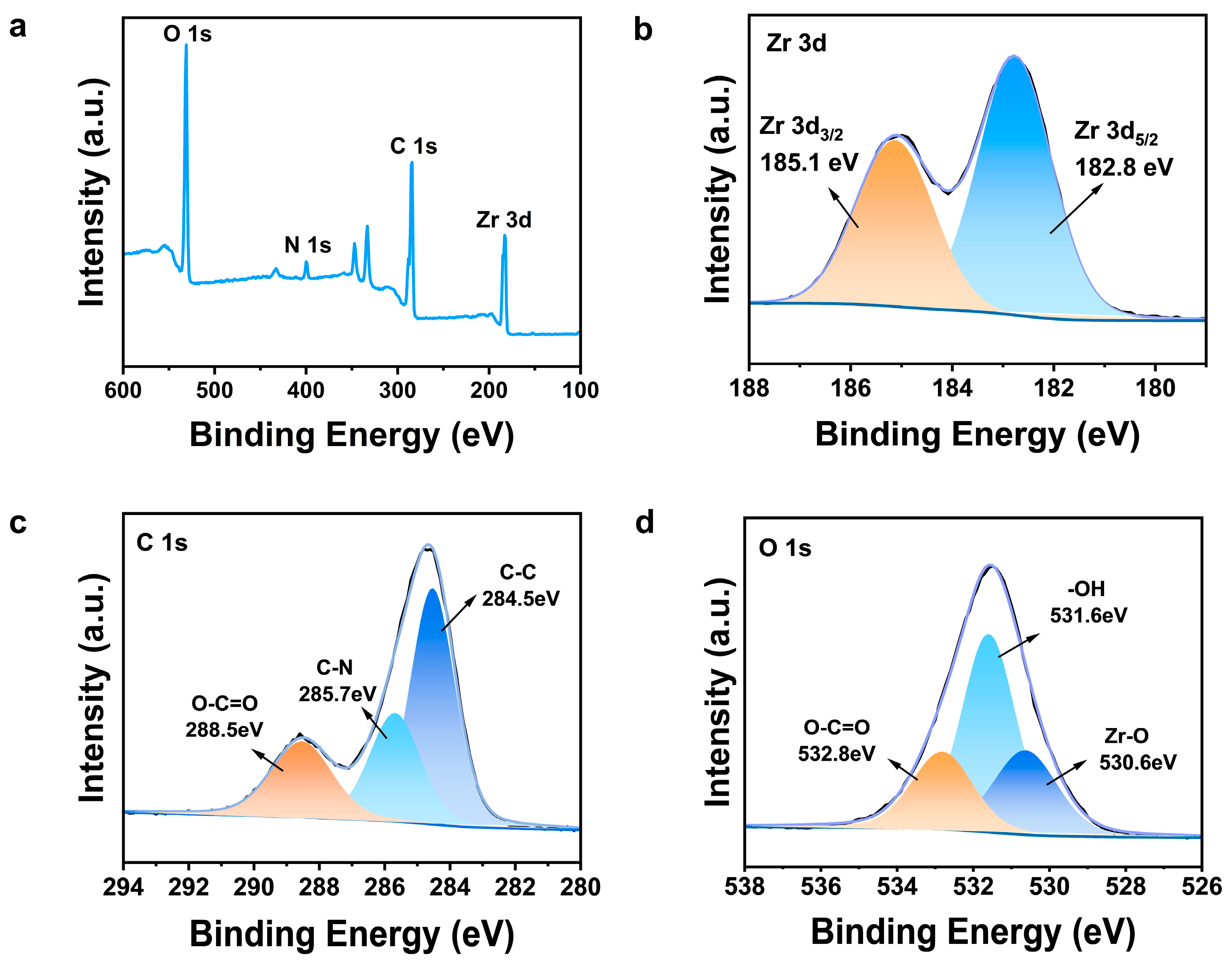
3.1. Characterization of U6N
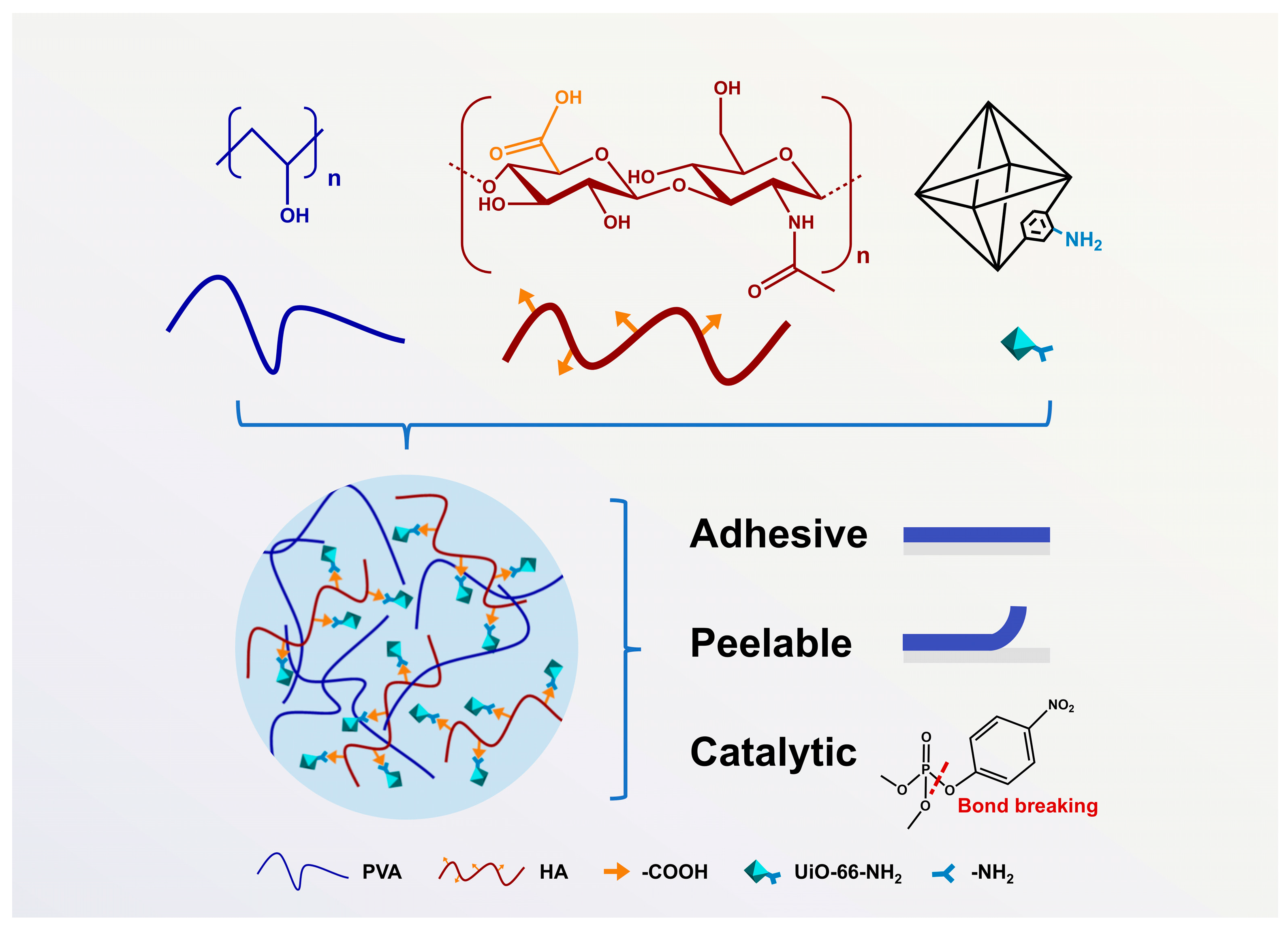
3.2. Characterization of PVA/HA/U6N Hydrogels
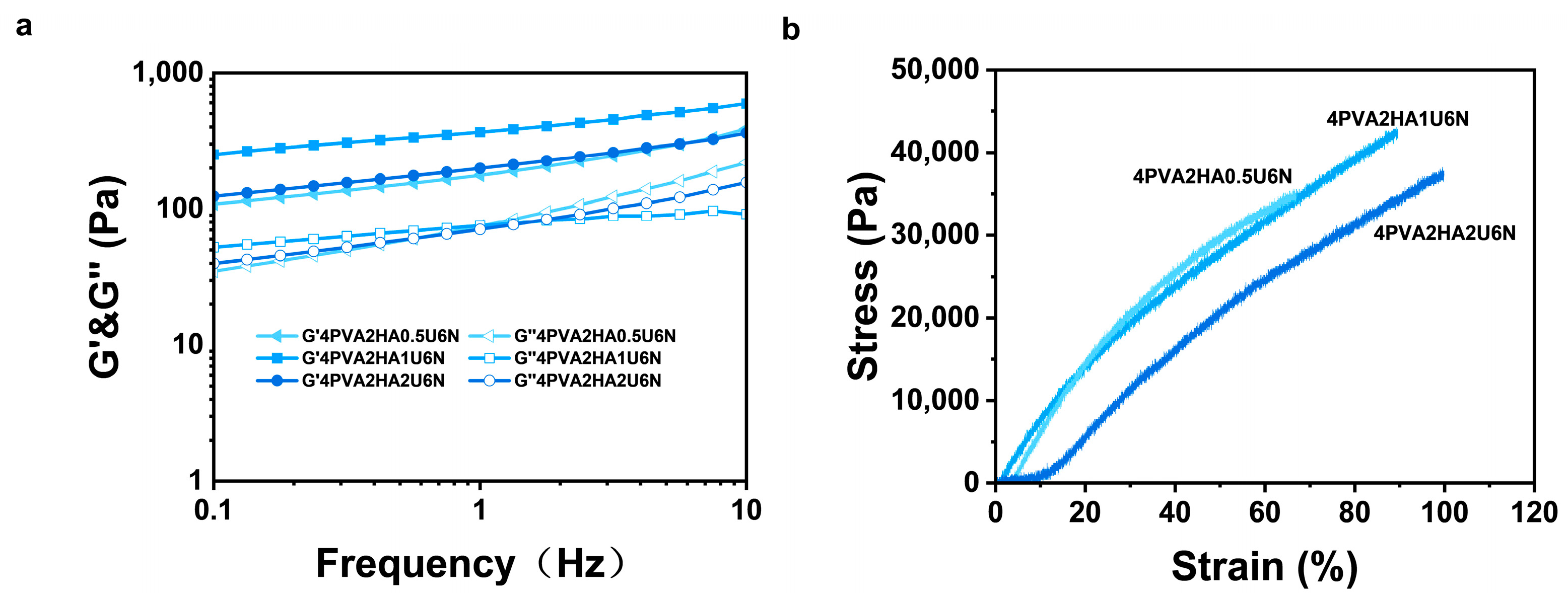
3.3. Mechanical Properties Testing of PVA/HA/U6N Hydrogels
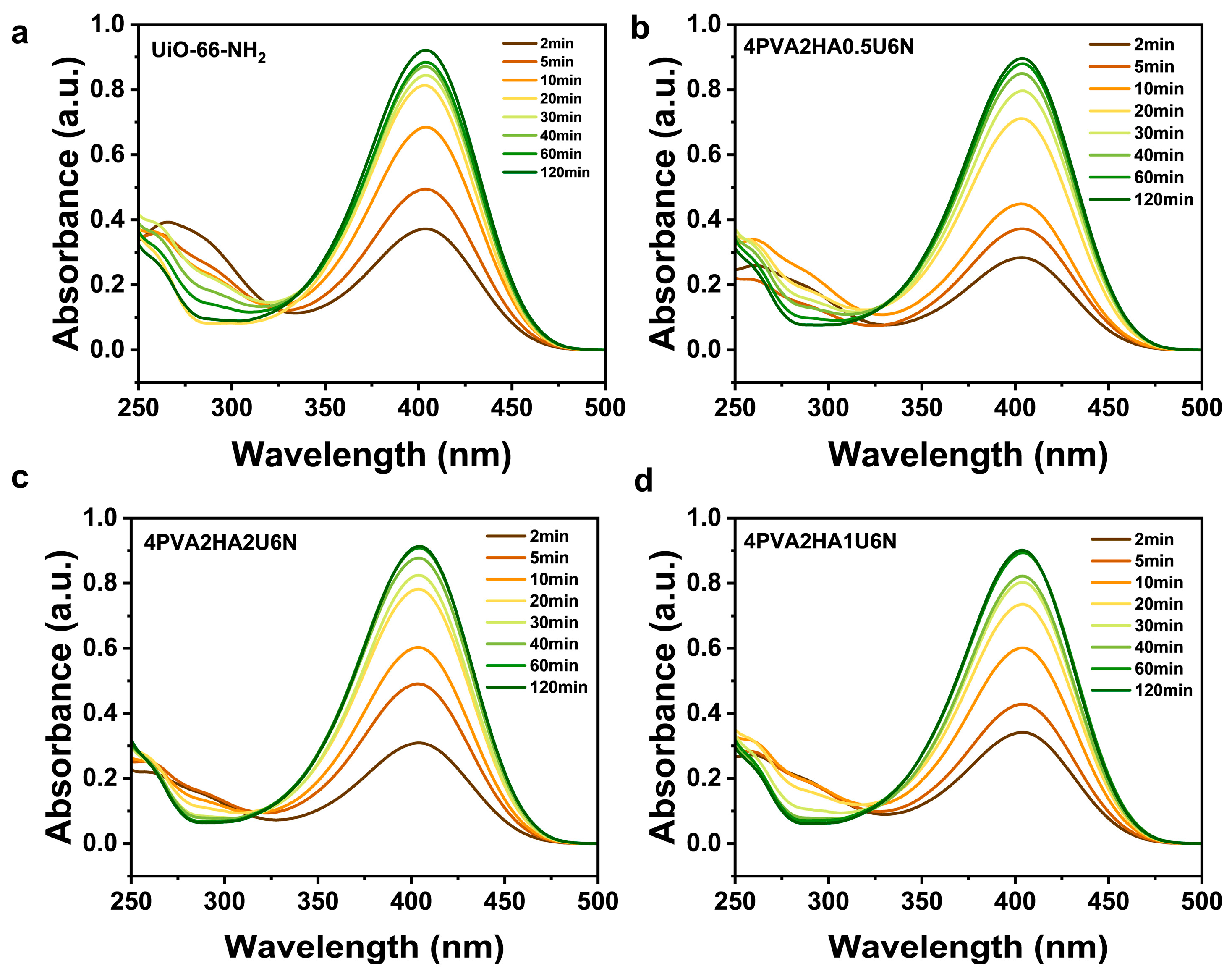
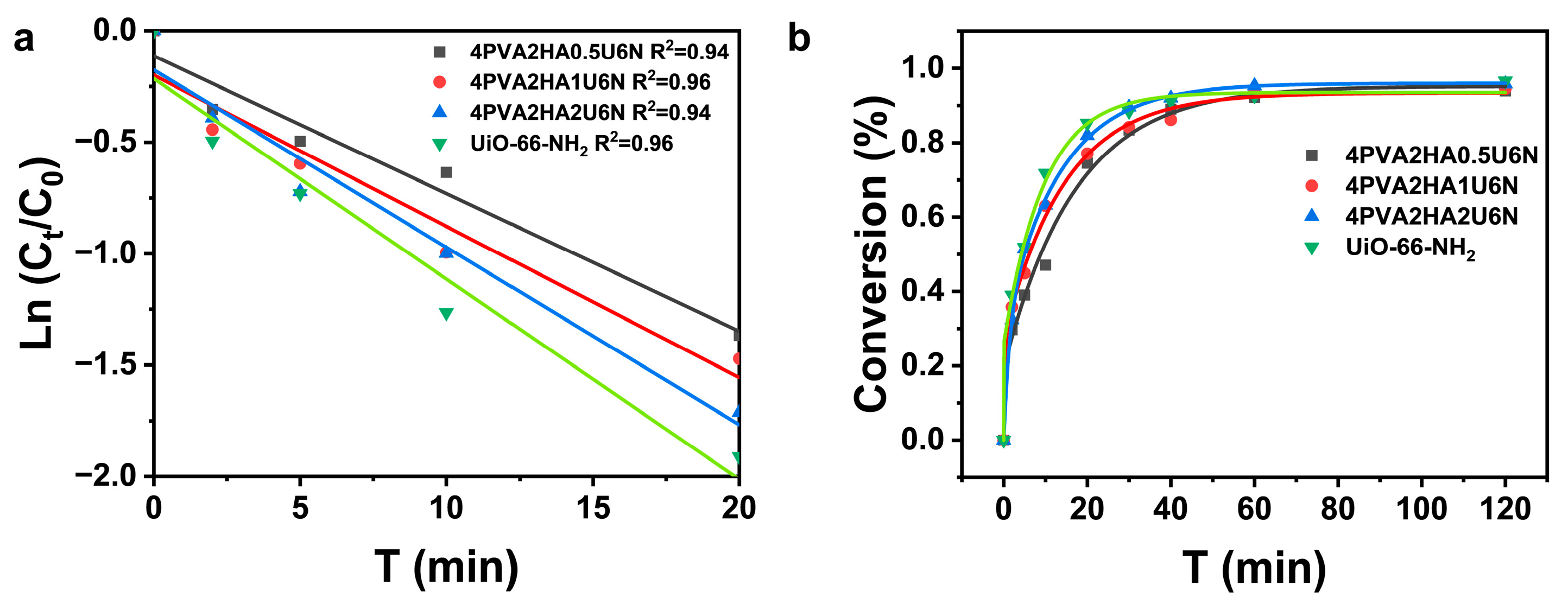
3.4. Catalytic Degradation of DMNP by U6N and PVA/HA/U6N Hydrogels
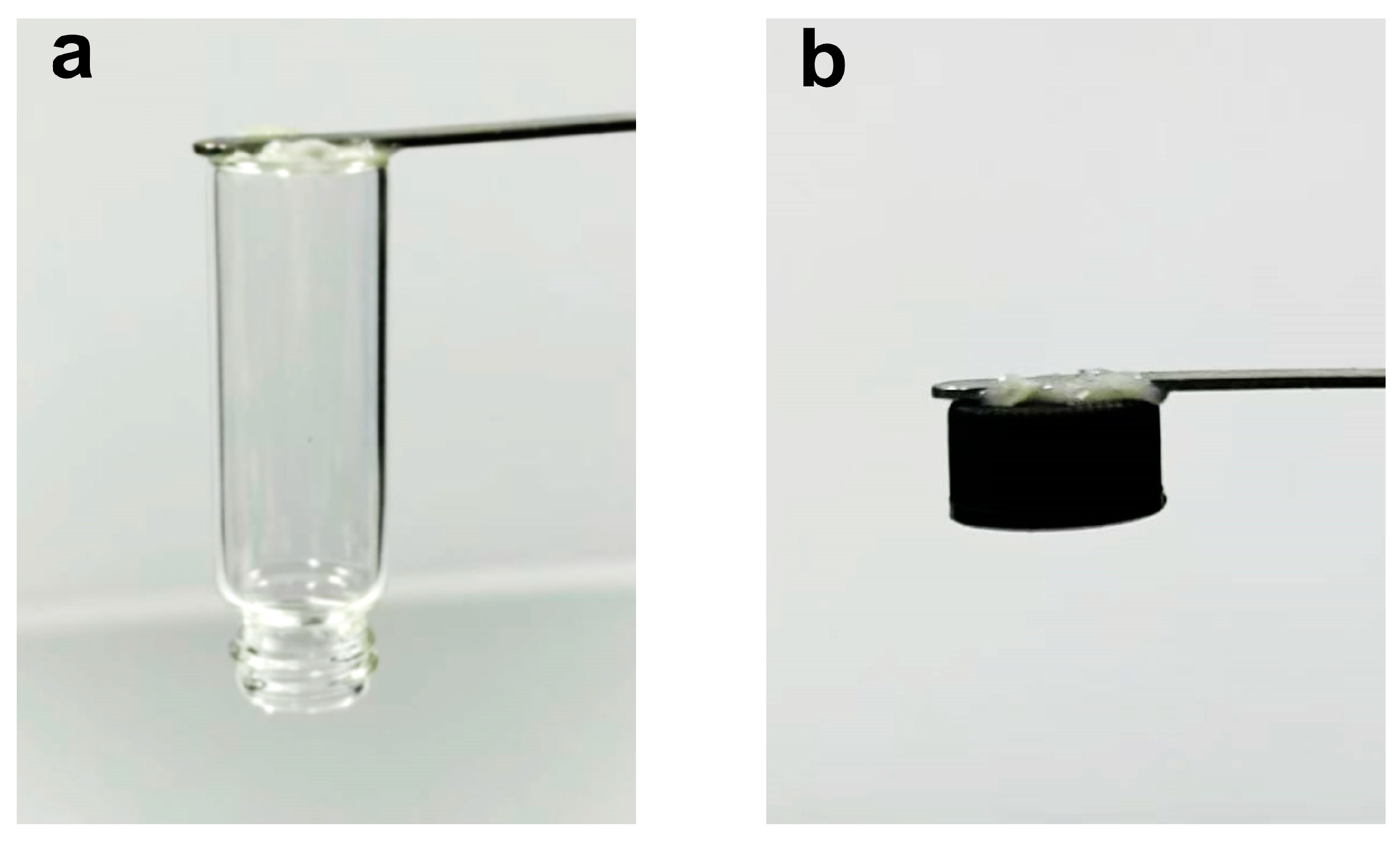
3.5. Adhesive Properties and Peelability of PVA/HA/U6N Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chauhan, S.; Chauhan, S.; D’Cruz, R.; Faruqi, S.; Singh, K.K.; Varma, S.; Singh, M.; Karthik, V. Chemical Warfare Agents. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 26, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangerich, A.; Esser, C. Chemical Warfare in the First World War: Reflections 100 Years Later. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1909–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Sheng, R.; Chen, T.; Rodrigues, J.; Song, Q.-H.; Hu, X.; Zeng, L. Molecular Engineered Optical Probes for Chemical Warfare Agents and Their Mimics: Advances, Challenges and Perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 463, 214527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.; Giuliano, E.A.; Sinha, N.R.; Mohan, R.R. Ocular Toxicity of Mustard Gas: A Concise Review. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 343, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szinicz, L.; Worek, F.; Thiermann, H.; Kehe, K.; Eckert, S.; Eyer, P. Development of Antidotes: Problems and Strategies. Toxicology 2007, 233, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigley, A.N.; Raushel, F.M. The Evolution of Phosphotriesterase for Decontamination and Detoxification of Organophosphorus Chemical Warfare Agents. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 308, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisio, C.; Carniato, F.; Palumbo, C.; Safronyuk, S.L.; Starodub, M.F.; Katsev, A.M.; Marchese, L.; Guidotti, M. Nanosized Inorganic Metal Oxides as Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Degradation of Chemical Warfare Agents. Catal. Today 2016, 277, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.W.; Procell, L.R.; O’Connor, R.J.; Munavalli, S.; Carnes, C.L.; Kapoor, P.N.; Klabunde, K.J. Reactions of VX, GB, GD, and HD with Nanosize Al2O3. Formation of Aluminophosphonates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, L.; Pomerantz, N.; Schreuder-Gibson, H.; Hatton, T.A. Degradation of Chemical Threats by Brominated Polymer Networks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18761–18774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, L.; Schreuder-Gibson, H.; Creasy, W.R.; McGarvey, D.J.; Fry, R.A.; Hatton, T.A. Degradation of Chemical Warfare Agents by Reactive Polymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins-Wildman, D.L.; Kim, M.; Sullivan, K.P.; Plonka, A.M.; Frenkel, A.I.; Musaev, D.G.; Hill, C.L. Buffer-Induced Acceleration and Inhibition in Polyoxometalate-Catalyzed Organophosphorus Ester Hydrolysis. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7068–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.W.; Peterson, G.W.; Mahle, J.J. Effect of Adsorbed Water and Surface Hydroxyls on the Hydrolysis of VX, GD, and HD on Titania Materials: The Development of Self-Decontaminating Paints. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3598–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCoste, J.B.; Peterson, G.W. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Air Purification of Toxic Chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5695–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, M.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; An, T. Solar-Light-Triggered Regenerative Adsorption Removal of Styrene by Silver Nanoparticles Incorporated in Metal–Organic Frameworks. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Wen, M.; Li, G.; An, T.; Zhao, H. In Situ Growth of Well-Aligned Ni-MOF Nanosheets on Nickel Foam for Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Typical Volatile Organic Compounds. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 9462–9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; An, T.; Yamashita, H. Metal–Organic Framework-Based Nanomaterials for Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Gaseous Pollutants: Recent Progress and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1006–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, N.; Feng, M.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; An, T. Near-Infrared Light Induced Adsorption–Desorption Cycle for VOC Recovery by Integration of Metal–Organic Frameworks with Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 1858–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploskonka, A.M.; DeCoste, J.B. Insight into Organophosphate Chemical Warfare Agent Simulant Hydrolysis in Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Liu, Y.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Instantaneous Hydrolysis of Nerve-Agent Simulants with a Six-Connected Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 6899–6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Hao, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, M.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, L.; Duan, R.; Yang, Y. Solid-State Degradation and Visual Detection of the Nerve Agent GB by SA@UiO-66-NH2@PAMAM Hydrogel. Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 6205–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Wasson, M.C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Idrees, K.B.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Cao, R.; Chen, Y.; et al. Near-Instantaneous Catalytic Hydrolysis of Organophosphorus Nerve Agents with Zirconium-Based MOF/Hydrogel Composites. Chem Catal. 2021, 1, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Q.; Li, B.-X.; Qu, J.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Yang, D. Spontaneously Super-Hygroscopic MOF-Gel Microreactors for Efficient Detoxification of Nerve Agent Simulant in Atmospheric Environments. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 328, 122516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redy Keisar, O.; Nahum, V.; Yehezkel, L.; Marcovitch, I.; Columbus, I.; Fridkin, G.; Chen, R. Active and Strippable PVA/Borax/NaBO 3 Hydrogel for Effective Containment and Decontamination of Chemical Warfare Agents. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5359–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toader, G.; Ginghina, R.-E.; Bratu, A.E.; Podaru, A.I.; Pulpea, D.; Rotariu, T.; Gavrilă, A.M.; Diacon, A. Ionic Crosslinked Hydrogel Films for Immediate Decontamination of Chemical Warfare Agents. Gels 2024, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, T.; Qu, J.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Yang, D. Solar-Thermally Enhanced Catalytic Hydrolysis of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulant with UiO-66-NCS Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shan, W.; Lou, Z.; Xiong, Y. Synthesis of Porous UiO-66-NH2-Based Mixed Matrix Membranes with High Stability, Flux and Separation Selectivity for Ga(III). Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Han, R. Adsorption of Phosphate on UiO-66-NH2 Prepared by a Green Synthesis Method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heu, R.; Ateia, M.; Awfa, D.; Punyapalakul, P.; Yoshimura, C. Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Micropollutants in Water by Zr-MOF/GO Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.A.; Liu, Y.-T.; Chen, S.-Y. Adsorption of Fluoride to UiO-66-NH2 in Water: Stability, Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, W.; Han, Y.; Luo, X.; Tang, W.; Yue, T.; Li, Z. A Straightforward Strategy to Synthesize Supramolecular Amorphous Zirconium Metal-Organic Gel for Efficient Pb(II) Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 126744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wu, B.; Lo, I.M.C. Fabrication of Silica-Free Superparamagnetic ZrO2@Fe3O4 with Enhanced Phosphate Recovery from Sewage: Performance and Adsorption Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 319, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, P.; Başlak, C.; Kılıçoğlu, P.; Kula, İ.H.; Koçer, M.B.; Albayatı, S.H.M. A Simple UiO-66-NH2@MWCNTs-COOH Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Sensitive Detection of Tert-Butylhydroquinone in Edible Oils. Microchem. J. 2024, 205, 111331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Peng, Y. Designing ZIF-8/Hydroxylated MWCNT Nanocomposites for Phosphate Adsorption from Water: Capability and Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.; Tang, M.; Xu, G.; Wang, C. Zr-MOF Crosslinked Hydrogel for High-Efficiency Decontamination of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulant. Processes 2025, 13, 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13040973
Li S, Wang L, Zhang J, Liang Y, Tang M, Xu G, Wang C. Zr-MOF Crosslinked Hydrogel for High-Efficiency Decontamination of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulant. Processes. 2025; 13(4):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13040973
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Saijie, Lei Wang, Jiayi Zhang, Yun Liang, Min Tang, Guilong Xu, and Chunyu Wang. 2025. "Zr-MOF Crosslinked Hydrogel for High-Efficiency Decontamination of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulant" Processes 13, no. 4: 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13040973
APA StyleLi, S., Wang, L., Zhang, J., Liang, Y., Tang, M., Xu, G., & Wang, C. (2025). Zr-MOF Crosslinked Hydrogel for High-Efficiency Decontamination of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulant. Processes, 13(4), 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13040973





