Highlights
What are the main findings?
- The low-temperature destruction of PCDD/Fs during FA pyrolysis is enhanced by NHPC.
- More lower-chlorinated PCDD/Fs can be decomposed in the presence of NHPC.
- The heavy metals in fly ash are synergistically solidified with the aid of NHPC.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- NHPC regulates the structure properties and the chemical environment of fly ash.
- The addition of NHPC provides a novel research approach for the synergistic disposal of PCDD/Fs and heavy metals in fly ash.
Abstract
There is an urgent need for energy-efficient disposal and resource utilization of the fly ashes from municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI). The low-energy pyrolysis-based detoxification of is a prerequisite for the harmless treatment and sustainable utilization of the fly ashes. In this study, the nitrogen-doped hierarchical porous carbon (NHPC) was prepared from the biomass-derived corn cobs and used to enhance the low-temperature destruction of PCDD/Fs in the MSWI fly ash. On thermal treatment in pure nitrogen (referring to pyrolysis in) at 350 °C for 30 min, the removal efficiencies of PCDD/Fs in fly ash based on mass (ηmass) and TEQ (ηTEQ) are 87.4% and 76.2%, respectively. After 5 wt.% NHPC is added in fly ash, the ηmass and ηTEQ values can be increased to 94.9% and 90.2%. The NHPC can enhance the decomposition and inhibit the regeneration of PCDD/Fs in fly ash, for the NHPC can regulate the structural properties and optimize the chemical environment of the fly ash. It can eliminate the need for the washing process. In addition, the leaching concentrations of heavy metals such as Cu, Zn, Pb and Cr in fly ash experience significant reductions of 83.3%, 73.7%, 35.6% and 22.9% when the fly ash is pyrolyzed at 350 °C with NHPC. This finding suggests that NHPC cannot only facilitate the decomposition of PCDD/Fs but also immobilizes the typical heavy metals in fly ash during low-energy pyrolysis. It is anticipated that the application of NHPC in the low-temperature pyrolysis of fly ash is of great energy-saving effect and can tackle the issues of PCDD/Fs and heavy metals for fly ash within a single step.
1. Introduction
Incineration has emerged as the preferred solution for addressing the garbage siege issue in large and medium-sized cities in China, for it can achieve the volume reduction, harmless disposal and energy recovery of municipal solid waste [1]. However, the fly ash (FA) produced from the municipal solid waste incinerators (MSWI) is enriched with PCDD/Fs (i.e., polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans) and heavy metals so that they are classified in the National Hazardous Wastes List (HW18) [2]. At this stage, approximately 11 million tons of fly ash generated in China annually is subjected to sanitary landfill, which is expensive and is of high risk of toxic leachability. To advance the construction of “waste-free cities” in China, various local governments (such as Beijing, Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Shanghai) have proposed the policies for “approaching zero landfill” of the hazardous wastes since 2019. Harmless disposal and then recycle utilization of fly ashes are crucial to fulfill these policies. However, the removal or the destruction of PCDD/Fs in fly ashes is a great challenge due to their large molecular weight, high thermal stability, complex chemical structure and trace-level concentrations. Therefore, there is a great demand to develop an advanced detoxification technology with high efficiency and low energy consumption for PCDD/Fs in fly ash.
Low-temperature (<500 °C) pyrolysis in N2 atmosphere turns out to be one of the main streams of PCDD/Fs treatment for fly ash due to its simple operation and relatively low energy consumption [3]. Numerous studies have investigated the optimization of process parameters for low-temperature pyrolysis of fly ash, including key variables such as reaction temperature, residence time, and atmosphere [4,5,6]. However, the destruction efficiencies of PCDD/Fs during the low-temperature pyrolysis process always fluctuate with the characteristics of the fly ashes and are difficult to guarantee at high levels [4,7]. On the one hand, the fly ash is abundant in precursors (e.g., chlorobenzene and chlorophenol), chlorine sources and metal oxides with catalytic activity (e.g., CuO and Fe2O3), which results in the regeneration of PCDD/Fs via precursor synthesis even in an anaerobic or oxygen-deficient atmosphere at 200~450 °C [6,7]. On the other hand, the alkaline compounds in fly ash such as CaO and Ca(OH)2 can consume the chlorine sources and passivate CuCl2, thereby effectively inhibiting the formation of PCDD/Fs [5,6,8]. Weber et al. [7] proposed that the PCDD/F concentration in fly ash follows the “Dualistic principle”, stating that only when the decomposition rate exceeds its formation rate will the PCDD/F concentration gradually decrease. Trinh et al. [9] used a Pd/AC catalyst during fly ash pyrolysis and increased the decomposition efficiency of PCDD/Fs from 80.5% to 98.3% at 350 °C within 15 min. However, the high cost of Pd limits its large-scale application. The same group then switched to a Ni/AC catalyst, which reduced PCDD/Fs by 94.5%, but the leaching concentration of Ni from the fly ash increased due to the relatively weak binding affinity between Ni and AC [10]. Inspired by the above research, this paper proposes a concept to develop an environmentally friendly, inexpensive and efficient additive to regulate the inherent characteristics of fly ash. The aim is to inhibit the regeneration and facilitate the destruction of PCDD/Fs in fly ash, thereby achieving the efficient and stable decomposition of PCDD/Fs in fly ash at low temperatures.
The hierarchical porous carbon (HPC) material obtained from high-temperature pyrolysis of biomass possesses a well-developed three-dimensional interconnected framework with microporous, mesoporous and macroporous structures. It offers numerous mass transfer channels with low resistance and short diffusion paths, making it widely used as a catalyst support, electrode material and high-efficiency adsorbent [11,12,13,14]. Further doping HPC with nitrogen (NHPC) can: (1) form more porous structures and increase the specific surface area of the carbon material, thereby enhancing its adsorption and catalytic properties [13]; (2) alter the chemical environment of carbon atoms, facilitating the electron transport within the carbon matrix [11]; (3) enhance the dispersion of metal elements on the surface of the carbon material, strengthening the synergistic effect between the carbon material and other metal elements [11]; (4) form pyridinic nitrogen (-NH2), pyrrolic nitrogen (-NH), and graphitic nitrogen (-N=) on the surface of the carbon material, further strengthening the π–π bonding interaction between aromatic compounds and the carbon material [14].
Inspired from the above, this paper proposes the use of biomass as a raw material to prepare NHPC and applies it to regulate the low-temperature pyrolysis of fly ash for the first time. By utilizing its substantial specific surface area and excellent electron transport properties, NHPC can facilitate the interaction between the alkaline components and PCDD/Fs as well as their precursors. This, in turn, enhances the decomposition of PCDD/Fs in fly ash and inhibits their formation. The low-temperature pyrolysis of PCDD/Fs in fly ash with traditional activated carbon (AC) and homemade NHPC are compared. It finds that the presence of NHPC can facilitate the low-temperature pyrolysis of PCDD/Fs and also achieve the solidification of heavy metals in fly ash effectively. The physicochemical properties of fly ash before and after the thermal pyrolysis were analyzed to further explore the optimization and regulation mechanisms of NHPC. This lays an important theoretical foundation for achieving efficient and stable detoxification of PCDD/Fs in fly ash at low temperatures, as well as the synergistic immobilization of heavy metals in one single step.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Carbon Materials
The “foaming method” was applied to prepare NHPC [13]. The corn cobs, (NH4)2C2O4·H2O (analytical grade) and KHCO3 (analytical grade) were used as carbon source, nitrogen source and foaming agent, respectively. Initially, corn cobs, (NH4)2C2O4·H2O and KHCO3 were weighed (with a mass ratio of 1:3:1), ground and mixed thoroughly. Thereafter, the mixture was heated to 900 °C at a constant rate of 10 °C/min under a nitrogen atmosphere and then held for 1 h. In this process, the foaming agent KHCO₃ underwent thermal decomposition and generated gaseous products (e.g., CO₂). It promoted the pore formation and resulted in a highly porous structure in the obtained material. Then, the obtained material was collected and soaked with hydrochloric acid at room temperature for 12 h. After that, the filtration and washing were conducted until the filtrate reached a neutral state. Finally, the residue was then subjected to drying at 80 °C for 8 h to obtain NHPC. In this study, 1.2 g of NHPC was obtained from 45 g raw material after the above disposal, with a sample yield of 2.67%.
The activated carbon (AC) used in this study was purchased from Sinopharm Reagent without further treatment. Its specific surface area, pore volume and average pore size are 688 m2/g, 0.41 cm3/g and 1.0 nm, which are detected from N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms. As for NHPC, the above parameters are measured to be 1914.7 m2/g, 0.99 cm3/g and 2.0 nm. Furthermore, the micropores, mesopores and macropores in NHPC account for 70.9%, 27.8% and 1.3%, respectively. Further, the surface elements in NHPC contain C (85.7 wt.%), N (5.4 wt.%) and O (8.9 wt.%), which were determined from EDS analysis. Among these, the N species on NHPC surface exist in three distinct forms such as pyridinic nitrogen (-NH2, 40%), pyrrolic nitrogen (-NH, 34%), and graphitic nitrogen (-N=, 26%) determined from XPS spectra. In order to prevent the influence of material particle size, both AC and NHPC were crushed, grounded and screened with 60–80 mesh before the experiment.
2.2. The Water Washing Experiment
Raw fly ash samples were collected from a baghouse of an MSWI located in Zhejiang Province. The water washing treatment of the fly ash was executed to eliminate the influence of soluble chlorine-containing species on the low-temperature pyrolysis process. An exact 20.0 g raw fly ash was washed with DI water (ratio of 5 mL:1 g) at room temperature with magnetic stirring (200 rpm) for 5 min. After that, the fly ash was filtered and then dried at 110 °C for 24 h to obtain the water washed fly ash. The mass of the fly ash was reduced to 56% of its original value after water washing, and the PCDD/F concentration based on mass and TEQ were increased to 541.2 ng/kg and 27.3 I-TEQ ng/kg, respectively, due to the enrichment and concentration by water washing [15].
2.3. Low-Temperature Pyrolysis Experiment
A laboratory-scale pyrolysis apparatus was designed and constructed as shown in Figure S1. Exact 10.0 g raw fly ash (or water washed fly ash) with or without 0.5 g NHPC (or AC) was placed in a quartz boat and then positioned into the middle of quartz tubular reactor. The experiment was conducted at 300 or 350 °C and each lasted for 30 min. Carrier gas (N2) was controlled at 200 sccm by a mass flow controller and was preheated to 110 °C prior to entering pyrolysis section. Before starting each pyrolysis experiment, the reactor was purged with N2 at a flow rate of 200 sccm for 30 min to completely eliminate any residual O2 from the system. A two-stage toluene was connected after the reactor for adsorbing gas-phase PCDD/Fs formed or released from the fly ash during pyrolysis. It was noteworthy that the concentrations of PCDD/Fs released in gas phase after pyrolysis were around 0.005 ng I-TEQ/kg, which were less than 0.1% of the original concentrations of PCDD/Fs in FA. It could be concluded that PCDD/Fs were effectively destroyed in FA and did not transfer to gas phase during pyrolysis. Thus, further discussion on the characteristics of PCDD/Fs in gas phase is not necessary [3,16]. After experiment, cold water was immediately applied to cool the reactor (containing the treated fly ash) down to room temperature within 1 min to minimize de novo synthesis during cooling period [9]. Each experimental test was conducted at least twice and the average result was calculated. To avoid contamination and carry-over issues, the quartz boat and the reactor were rinsed with acetone and toluene and immersed in 0.25 N HNO3 for 24 h and subsequently cleaned with an ultrasonic bath prior to each experimental test. The abbreviations of each fly ash sample and their treatment conditions are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
The abbreviations of each fly ash sample and their treatment conditions.
2.4. Characterizations and Analysis
The fly ash samples before and after treatment were analyzed using Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Nitrogen adsorption desorption, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF), X-ray powder diffractometer (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectrum (FTIR). Thermogravimetric-Differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA) was also employed to analyze the mass change and thermal effect of the low-temperature pyrolysis process. The detailed information and parameter settings of the aforementioned characterization instruments are described in the Supplementary Materials.
After each experiment run, the pretreatment and quantitative detection of PCDD/Fs residual on FA followed the method HJ 77.3-2008. The FA samples were firstly Soxhlet extracted with toluene for 24 h and then concentrated by rotary evaporator to 10 mL. Prior to extraction, samples were spiked with the 13C labeled compound solution of PCDD/Fs (EPA-1613-C). The concentrated solutions were transferred to acid-silica column and then activated carbon mini-column to remove the impurities, and then further concentrated by a purified nitrogen flow to 30 μL. Finally, the pretreated samples were analyzed for 17 2,3,7,8-substituted PCDD/Fs congeners with high-resolution gas chromatography (HRGC, Thermo Trace GC)/high-resolution mass spectrometer (HRMS, Thermo DFS) using a fused silica capillary DB-5 MS column (60 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm). In our experiments, the recovery rate of each internal standard fulfills the recovery standard of HJ 77.3-2008. The specific operating procedures of the instrument were described in the Supplementary Materials (Shown in Table S1). The decomposition efficiencies of PCDD/Fs based on mass (ηmass, %) and TEQ (ηTEQ, %) are calculated as follows:
where C0,PCDD/Fs and Cd,PCDD/Fs are the mass concentrations or toxic equivalent concentrations of PCDD/Fs in the FA before and after low-temperature pyrolysis.
Typical heavy metals such as Cu, Zn, Pb and Cr were selected and their leaching concentrations from the FA samples before and after pyrolysis were concerned. First of all, the extractant was prepared by mixing the H2SO4 and HNO3 (mass ratio of 2:1) and adjusting the pH value of the solution with DI water to 3.20 ± 0.05 (HJ/T 299-2007). Then, the FA samples were extracted with the prepared extractant (L/S ratio of 10:1 L/kg) under 30 ± 2 r/min for 18 h. Following the extraction process, the solid–liquid separation was conducted using a 90 mm microporous membrane and the concentrations of selected heavy metals in the filtrate were determined by means of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Agilent 7800). The solidification rate of heavy metals (φ, %) is calculated as Equation (2):
where C0,HM and CTP,HM refer to the leaching concentration of heavy metals in fly ash before and after low-temperature pyrolysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PCDD/Fs Destruction by Low-Temperature Pyrolysis
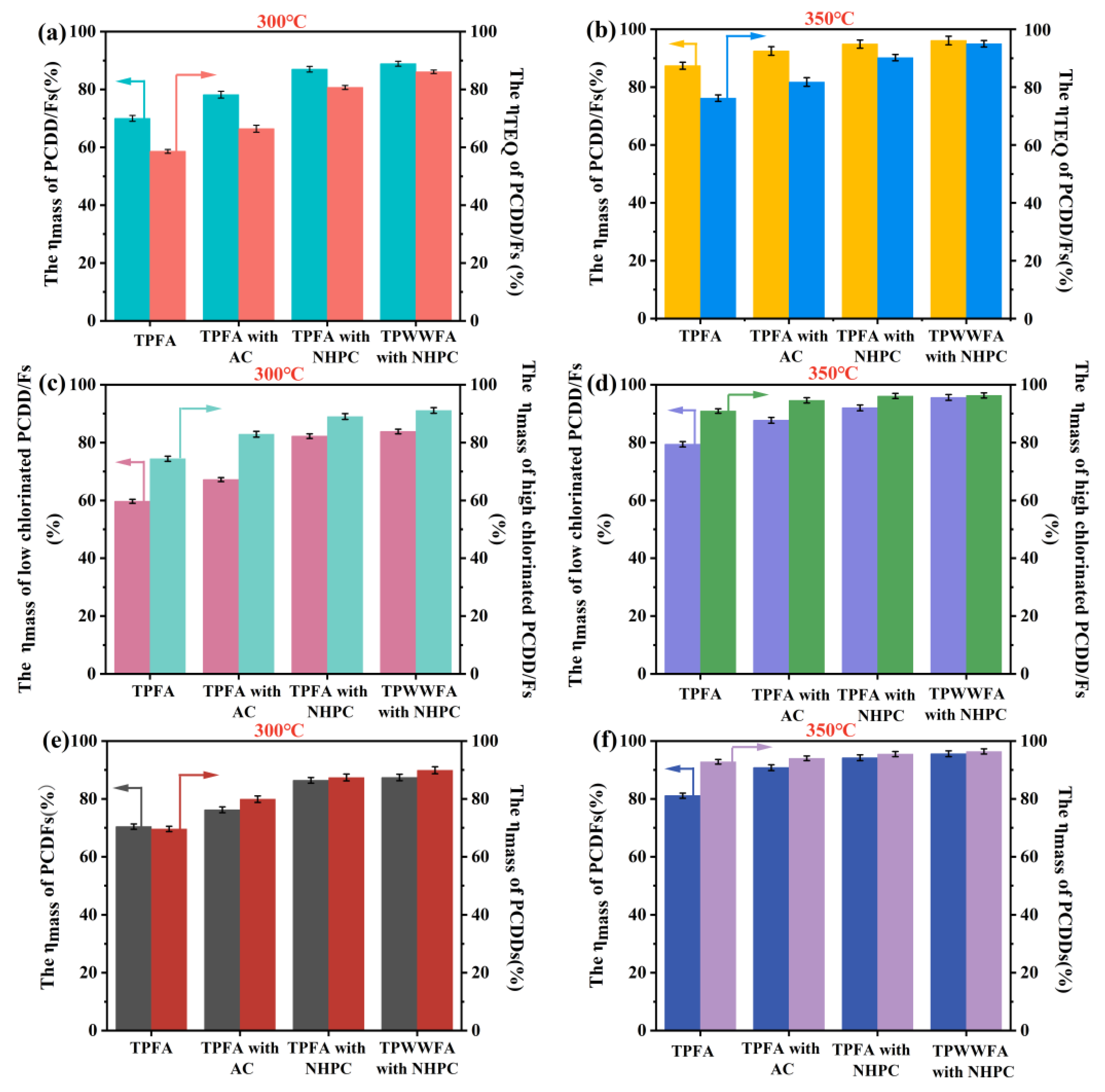
The total destruction efficiencies of 2,3,7,8-substituted PCDD/Fs based on mass (ηmass, %) and TEQ (ηTEQ, %) were illustrated in Figure 1a,b. The findings indicate that the total ηmass and ηTEQ values of PCDD/Fs in TPFA are susceptible to the treatment temperature. The total mass concentration of PCDD/Fs in TPFA decreased from 256.2 ng/kg to 77.0 ng/kg (ηmass = 70.0%) and their TEQ concentration merely dropped from 13.4 ng I-TEQ/kg to 5.5 ng I-TEQ/kg (ηTEQ = 58.6%) after being pyrolyzed at 300 °C. The total ηmass and ηTEQ values of PCDD/Fs in TPFA were increased to 87.4% and 76.2%, respectively when pyrolyzed at 350 °C. The relatively poor destruction efficiencies of PCDD/Fs at 300 °C can be attributed to the presence of PCDD/Fs precursors (e.g., chlorobenzene and chlorophenol) in TPFA. These precursors could be easily condensed and chlorinated to regenerate PCDD/Fs under the catalytic action of some metal oxides in FA [7,9,17]. Increasing temperature could inhibit the regeneration of PCDD/Fs to a certain extent and simultaneously facilitated their decomposition [6,14].
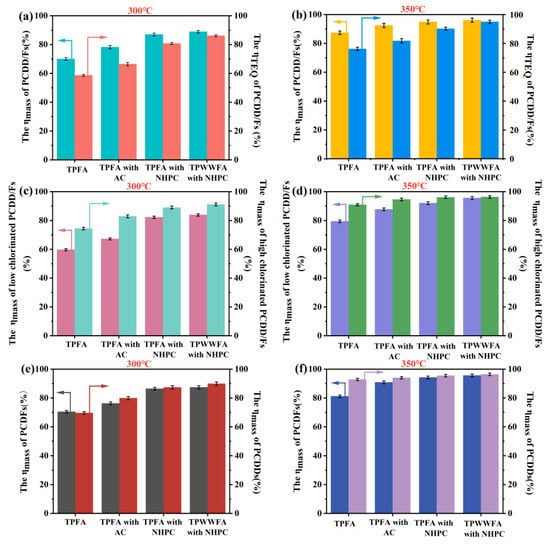
Figure 1.
The total ηmass and ηTEQ of PCDD/Fs of TPFA, TPFA with AC, TPFA with NHPC and TPWWFA with NHPC at 300 °C (a) and 350 °C (b); the ηmass of high- and low-chlorinated PCDD/Fs of TPFA, TPFA with AC, TPFA with NHPC and TPWWFA with NHPC at 300 °C (c) and 350 °C (d); the ηmass of PCDFs and PCDDs in TPFA, TPFA with AC, TPFA with NHPC and TPWWFA with NHPC at 300 °C (e) and 350 °C (f).
Lower ηTEQ values of PCDD/Fs were found compared to their ηmass values possibly due to the dechlorination process of highly chlorinated PCDD/Fs (chlorine-substituted number = 7 or 8) to low-chlorinated PCDD/Fs (chlorine-substituted number = 4, 5 or 6), and similar results have been reported by previous studies [4]. Furthermore, the ηmass values of those highly chlorinated PCDD/Fs were higher than those of low-chlorinated PCDD/Fs by 14.7% (300 °C) and 11.5% (350 °C) as shown in Figure 1c,d. Both of the phenomena could be explained that the bond energy of the C-Cl bond (339 kJ/mol) in PCDD/Fs was weaker than those of the C-C bond (347 kJ/mol), C-O bond (358 kJ/mol) and C=C bond (614 kJ/mol), which led to the preferential dechlorination of PCDD/Fs over ring cleavage [9]. In general, the Toxic Equivalency Factors (TEF) of low-chlorinated PCDD/Fs were larger than those of the highly chlorinated ones. Thus, the transformation of highly chlorinated PCDD/Fs to low-chlorinated ones possibly increased the risk of higher TEQ concentration of PCDD/Fs in TPFA [4]. These findings supported that inhibiting the regeneration as well as inducing the deep dechlorination of PCDD/Fs are pivotal in achieving the complete detoxification of PCDD/Fs with lower energy consumption during low-temperature pyrolysis.
After the FA being pyrolyzed with 5 wt.% AC or NHPC at 300 °C for 30 min, the ηmass values of PCDD/Fs were increased to 78.2% (with AC) and 87.0% (with NHPC), respectively; concurrently, the ηTEQ values were elevated to 66.4% (with AC) and 80.7% (with NHPC), respectively. At 350 °C, the ηmass values of PCDD/Fs in TPFA with AC or with NHPC were raised to 92.5% or 94.9% and their ηTEQ values were recorded as 81.8% or 90.2%, respectively. These results indicated that the addition of AC and NHPC could stimulate the destruction of PCDD/Fs during low-temperature pyrolysis and the promotion effect of NHPC was better compared to AC. This phenomenon could be owed to the following factors: (1) the well-developed three-dimensional interconnected framework structure of NHPC reduced the diffusion resistance of the alkaline metal oxides (e.g., CaO and MgO) and improved their dispersion on the mixture of FA and NHPC; (2) the strong adsorption capacity of NHPC made it be effective in capturing PCDD/Fs and their precursors during pyrolysis [9], which increased the contact probability of PCDD/Fs with alkaline metal oxides and promoted the destruction of PCDD/Fs; (3) the N-doping on the surface of NHPC could further enhance the electron transfer between those metal atoms and the carbon atoms [11], so that enlarged the catalytic activities of the alkaline metal oxides for the decomposition of PCDD/Fs.
The promotional effect of NHPC on the destruction efficiencies of low-chlorinated PCDD/Fs was more obvious than that of AC. The differences between the ηmass values of highly chlorinated and low-chlorinated PCDD/Fs declined from 15.7% (with AC) to 6.8% (with NHPC) at 300 °C and further decreased from 6.9% (with AC) to 4.1% (with NHPC) when pyrolyzed at 350 °C. Figure 1e,f compared the ηmass values of PCDFs and PCDDs under different conditions. The findings implied that the positive effect of carbon material on the destruction of PCDDs is more pronounced than that of PCDFs. It can be explained by the two factors. On the one hand, PCDDs have larger molecular weights and lower saturated vapor pressure in general. This possibly results in the easier capture of PCDDs by carbon materials and subsequently participated in the chemical reactions [16]. On the other hand, PCDFs are more easily synthesized via the condensation, coupling and chlorination of the precursors that results in their lower ηmass values [18].
Water washing has been regarded as an effective method to reduce the chlorine sources needed in PCDD/F regeneration as well as the substances (including CuCl2 and FeCl2) with catalytic activity for PCDD/Fs formation. So that PCDD/F regeneration during FA pyrolysis process can be effectively weakened and their destruction efficiencies can be lifted correspondingly [6,19]. However, this operation not only generates wastewater requiring further treatment but also consumes extra energy. As expected, the contents of Ca, Cl and Na in FA change from 33.87%, 21.73% and 9.48% to 51.76%, 1.38% and 0.36% after being water washed in this work (shown in Table S2), confirming most of the soluble chloride salts in FA can be removed during water washing. However, the ηmass values of PCDD/Fs in TPWWFA with NHPC merely increase by 1.9% (300 °C) and 1.2% (350 °C) when compared to TPFA with NHPC (Figure 1a,b). This result occurs possibly because PCDD/F regeneration during pyrolysis was already controlled under the regulation of NHPC and the water washing can be omitted. In this study, a remarkably lower energy of only 4.5 MJ is required to achieve the 95% of ηmass values at 350 °C with 30 min, highlighting the significant energy-saving effect of NHPC addition in low-temperature pyrolysis of PCDD/Fs.
3.2. The Synergistic Solidification of Heavy Metals
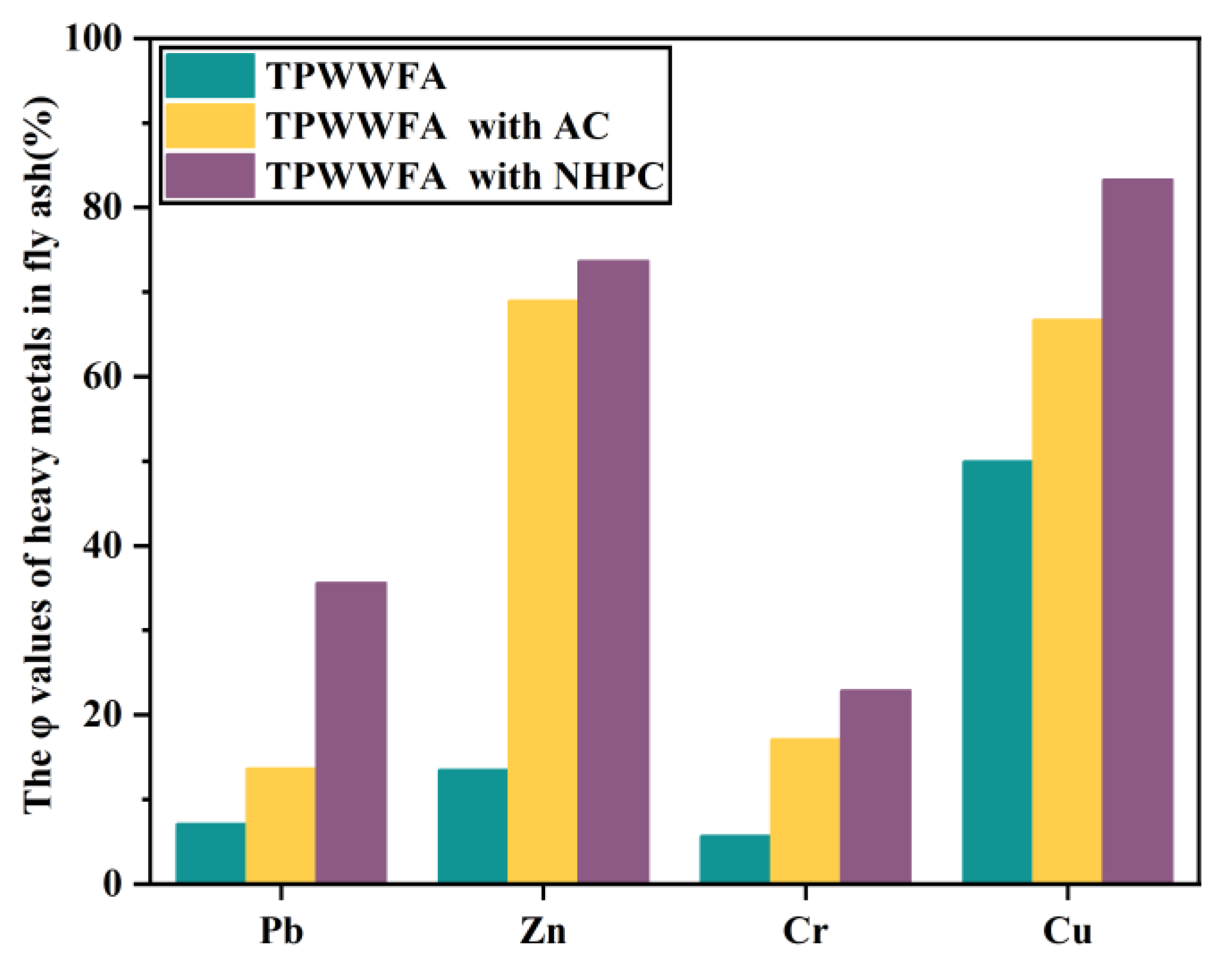
The leaching concentrations of the four typical heavy metals (i.e., Pb, Cr, Cu, and Zn) in TPWWFA, TPWWFA with AC and TPWWFA with NHPC were investigated. The leaching concentrations of Pb, Zn, Cr and Cu in raw FA were 4.730 mg/L, 0.639 mg/L, 0.103 mg/L and 0.007 mg/L, respectively, and decreased to 2.691 mg/L, 0.600 mg/L, 0.035 mg/L and 0.006 mg/L after being water washed. It implies the existence of soluble heavy metals [19,20,21]. Their leaching concentrations were found to be further declined by 7.1%, 13.5%, 5.7% and 50.0% when the WWFA was pyrolyzed at 350 °C, as shown in Figure 2. This result possibly indicates the conversion of the heavy metals in FA from an acid-extractable state to a residual state during the low-temperature pyrolysis process [22]. The solidifications of these heavy metals were further improved with the addition of AC and NHPC, especially for NHPC. It is evidenced by the solidification rates of Pb, Zn, Cr and Cu in the WWFA TP with NHPC are 35.6%, 73.7%, 22.9% and 83.3%, respectively. On the one hand, the larger specific surface area as well as the abundant pore structure of NHPC allow more heavy metals to diffuse and adsorb on the mixture of NHPC and FA. On the other hand, the N elements doped in NHPC possibly enhance the electron transfer between C atoms and the heavy metals, thereby facilitating the solidification of heavy metals [11].
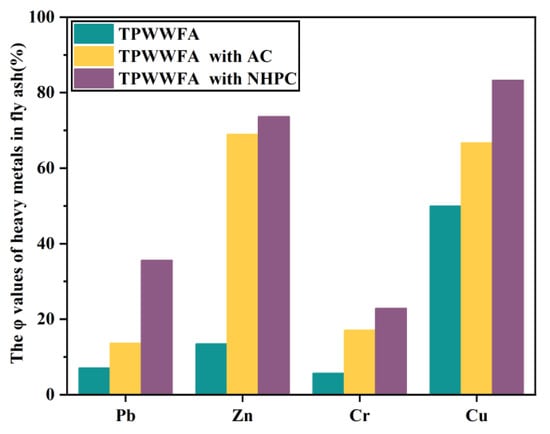
Figure 2.
The φ values of Pb, Zn, Cr and Cu in TPWWFA, TPWWFA with AC and TPWWFA with NHPC.
3.3. The Characterizations of FA Samples
In order to explore the improvement mechanism of NHPC on the low-temperature pyrolysis of FA, the characteristics of the FA, TPFA and TPFA with NHPC were analyzed. Their basic structural parameters are listed in Table 2. The findings indicate that the pyrolysis treatment enlarges the specific surface area and the pore volume of FA. It can be owed to the release of the volatile products from the decomposition of organic pollutants as well as the intrinsic substances in FA (e.g., H2O, NaCl and low-boiling point heavy metals) during the pyrolysis process, which forms additional micropores and mesoporous in FA [23,24]. It also reduces the average pore size of FA. As for TPFA with NHPC, the specific surface area and pore volume of FA sample increase significantly to 90.7 m2/g and 0.087 cm3/g, while the average pore size decreases to 4.7 nm. These provide FA with sufficient sites for the destruction of PCDD/Fs and the solidification of the heavy metals.

Table 2.
The basic structural parameters of FA, TPFA and TPFA with NHPC.
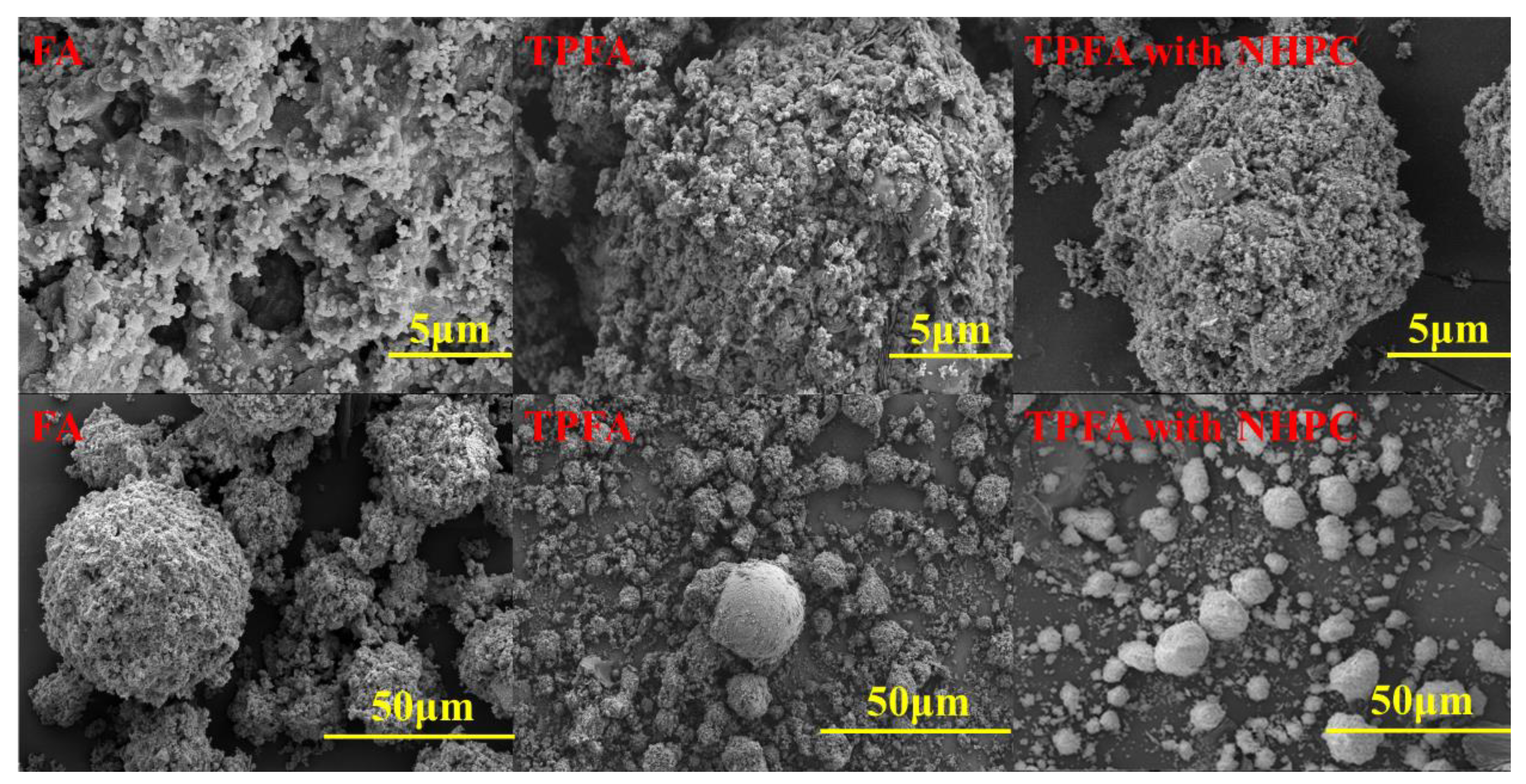
The surface morphologies of FA, TPFA and TPFA with NHPC are shown in the SEM images (Figure 3). The original FA particles are spherical with a substantial number of macropores and mesopores. As for TPFA, the collapse and shrinkage of the partial macropores in FA are observed, while more micropores and mesoporous are found. It coincides with the results determined from N2 adsorption. These possibly result from the decomposition of organics, evolution of the minerals and the overflow of volatile substances. The addition of NHPC further enhances the porosity of FA due to its substantial specific surface area and its well-developed pore structure.

Figure 3.
The SEM images of FA, TPFA and TPFA with NHPC.
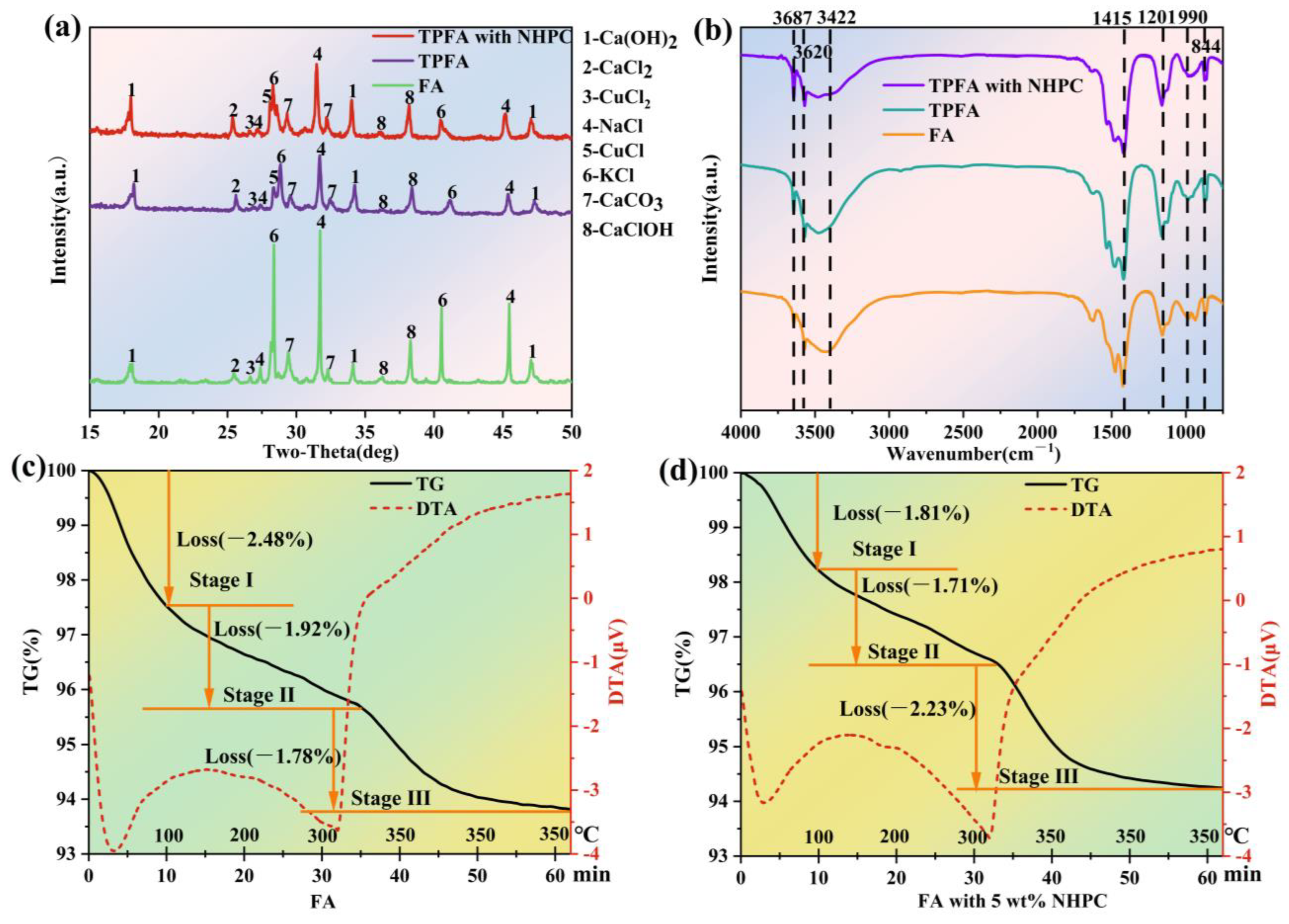
The XRD patterns of FA, TPFA and TPFA with NHPC are illustrated in Figure 4a. The diffraction peaks corresponding to NaCl, KCl, CaClOH, Ca(OH)2 and CaCO3 appear in the XRD pattern of the original FA [9]. Further, small diffraction peaks belonging to CaCl2 and CuCl2 are also observed [25]. As for TPFA, the intensities of the diffraction peaks assigning to NaCl and KCl decrease significantly, confirming their volatilization or conversion during pyrolysis. A slight decrease in the diffraction peaks belonging to Ca(OH)2 and CaClOH is observed, while those of CaCl2 increase slightly. It can probably be explained that the OH groups in Ca(OH)2 and CaClOH are consumed and CaCl2 is formed during PCDD/Fs dichlorination [23]. Furthermore, the diffraction peak for CuCl2 in TPFA becomes smaller, while that of CuCl is observed intensified. It is induced from the reduction of CuCl2 to CuCl when the FA is pyrolyzed. Previous study has reported that CuCl2 shows high catalytic activity towards the synthesis of PCDD/Fs but that of CuCl is poor [9,17]. Thus, the reduction of CuCl2 to CuCl indicates its passivation and possibly leads to the less regeneration of PCDD/Fs in FA. As for TPFA with NHPC, the diffraction peaks belonging to NaCl and KCl decreased slighter comparing with TPFA, possibly due to the excellent adsorption capacity of NHPC reduces their volatilization. However, the diffraction peaks of Ca(OH)2, CaClOH and CaCO3 become stronger in TPFA with NHPC, elucidating that the presence of NHPC improves the dispersion of metal compounds on the surface of FA. Further, the diffraction peak of CuCl becomes stronger in TPFA with NHPC, suggesting that the addition of NHPC can effectively accelerate the passivation of CuCl2.
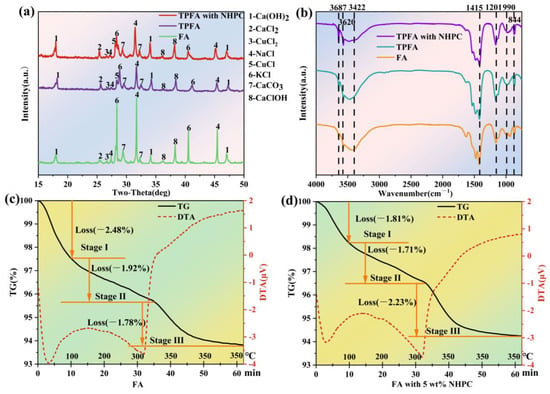
Figure 4.
XRD spectra (a) and FTIR spectra (b) of the FA, TPFA and TPFA with NHPC samples; TG-DTA curves of the FA (c) and FA with 5 wt.% NHPC (d).
Figure 4b displays the FTIR spectra of FA, TPFA and TPFA with NHPC. The peaks positioned at 3687 cm−1, 3620 cm−1 and 3422 cm−1 correspond to the free OH groups [26]. And 1415 cm−1, 1201 cm−1, 990 cm−1 and 844 cm−1 raise due to the stretching and vibration of O-C-O bond, C-O bond in phenolic substances, lipids or -COOH and C-H bond [27,28,29]. It has been reported that the OH groups in FA can serve as the internal hydrogen source, which is necessary for the dechlorination of the chlorinated organic pollutants [30,31]. The decrease in the amount of OH groups in TPFA is attributed to the consumption of these groups by the hydrodechlorination of the chlorinated organic pollutants in FA. The further reduction in the number of OH groups in TPFA with NHPC may imply that the addition of NHPC promotes the hydrodechlorination of the chlorinated organic pollutants in FA and accelerates the consumption of OH groups. Moreover, the intensities of the FTIR peaks attributing to the C-H bond are enhanced in TPFA and TPFA with NHPC, which also proves the occurrence of the hydrodechlorination reaction. The intensities of the peaks belonging to the O-C-O, C-O and COOH groups in TPFA become stronger, which may be generated from the oxidation ring-opening products of organic molecules. That of the COOH group in TPFA with NHPC is further enhanced, indicating the presence of NHPC may facilitate the deep degradation of macromolecular organic pollutants in FA into small ones. The above results demonstrate that the oxidative decomposition as well as the hydrodechlorination of organic pollutants may occur concurrently during the FA pyrolysis process and the presence of NHPC can enhance these two reactions.
TG-DTA analysis simultaneously monitored mass changes and thermal effects during the FA pyrolysis under N₂ atmosphere. The temperature of the FA sample was increased from room temperature to 350 °C at 10 °C/min and then held for 30 min to accurately simulated the low-temperature pyrolysis conditions. The TG-DTA curves are displayed in Figure 4c,d. It is evident that the mass reduction in FA during low-temperature pyrolysis can be divided into three distinct stages. In stage I (below 100 °C), the mass loss can be attributed to the evaporation of the physically adsorbed water in FA and this process requires the absorption of heat [32,33,34]. The mass declined in stage II (100–350 °C) can be explained by the release of the crystalline water and the volatilization of the easily volatile substances in FA. The latter may be induced from the decomposition of the organic compounds [35,36,37], which exhibits a notable exothermic effect. The rapid mass decreased in stage III with the temperature maintaining at 350 °C, can be due to the further destruction of the organic matters in FA, which results in the continuous discharge of their products. Another reason for the mass decrease in stage III can be ascribed to the formation and volatilization of some volatile metal chlorides from the interaction between metal oxides and Cl-containing organic compounds [38,39]. This process exhibits a significant exothermic effect. It is interesting that the presence of NHPC can significantly reduce the mass loss in stages I and II, but accelerates the mass reduction in stage III. The reduced mass loss in stages I and II can be attributed to NHPC enhanced interaction between water molecular/volatile substances and the carbon matrix, which inhibits the desorption of both physically adsorbed water and low-temperature volatile components; The accelerated mass loss in stage III implies that the NHPC can facilitate the decomposition of organic matters (including PCDD/Fs) in FA and the release of the gaseous products.
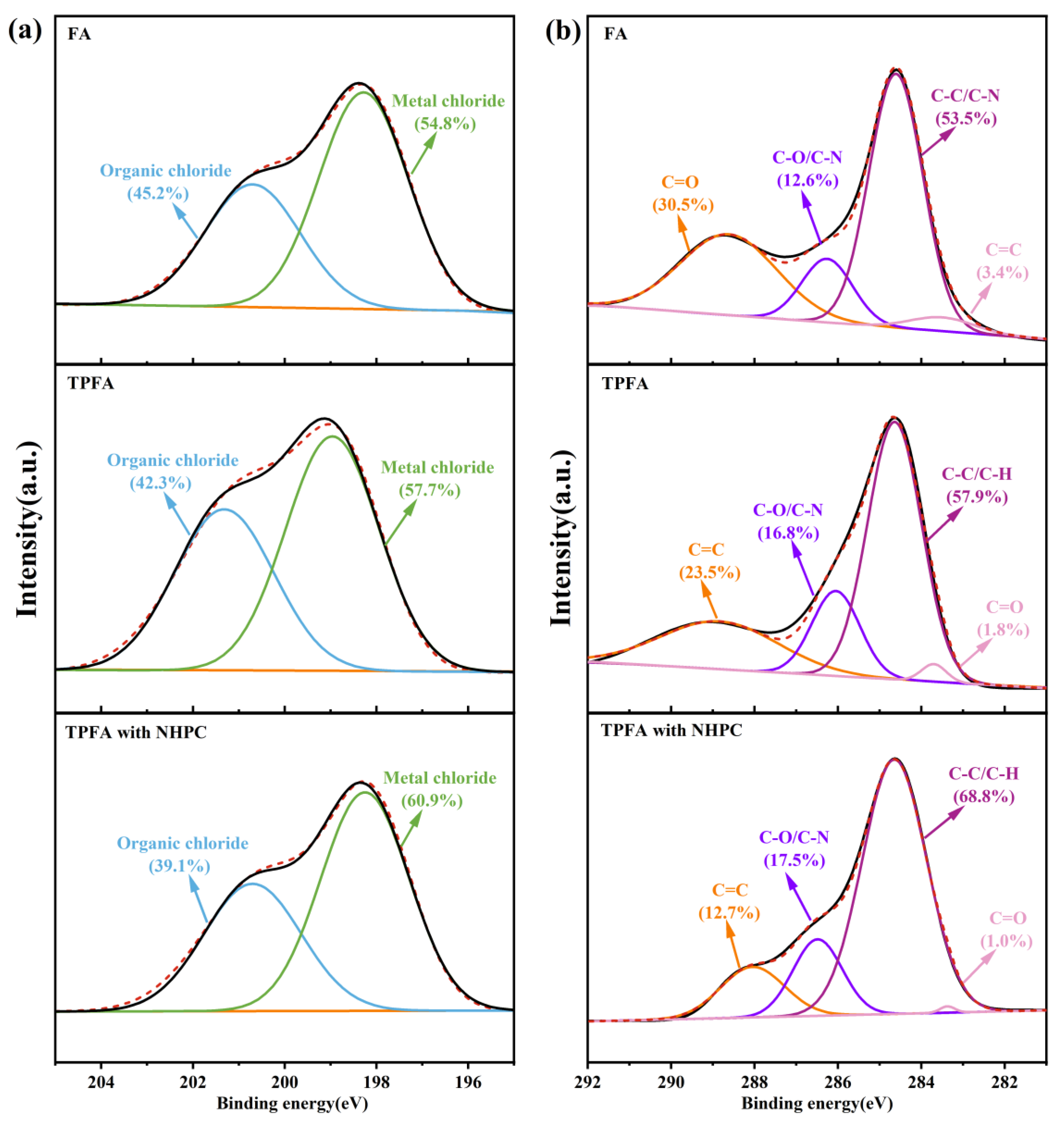
XPS analysis was performed to determine the surface chlorine and carbon elements on FA, TPFA and TPFA with NHPC and the results are shown in Figure 5. The chlorine present in the original FA is predominantly found in the form of the organic chlorine bonded with carbon atoms and the inorganic chlorine connected to metal atoms [40,41]. After pyrolysis, the relative content of the inorganic chlorine increases slightly, indicating the conversion of the organic chlorine to inorganic chlorine in the process. The addition of NHPC can enhance the aforementioned conversion process, thereby leading to an increase in the proportion of inorganic chlorine. This phenomenon may be attributed to the presence of NHPC. On the one hand, it promotes the high dispersion of alkaline metal oxides (e.g., CaO and Ca(OH)2) in FA as well as their electron transfer with the surface carbon atoms, which strengthens their promotion effect on the decomposition of chlorine-containing organic pollutants; on the other hand, the NHPC contains -NH and -NH2 functional groups, which have the capacity to offer the active H protons for the dechlorination of chlorinated organic pollutants. Moreover, the addition of NHPC has been demonstrated to facilitate the reduction of CuCl2 to CuCl. It diminishes the catalytic synthesis of PCDD/Fs and thereby reduces the content of the organic chlorine.
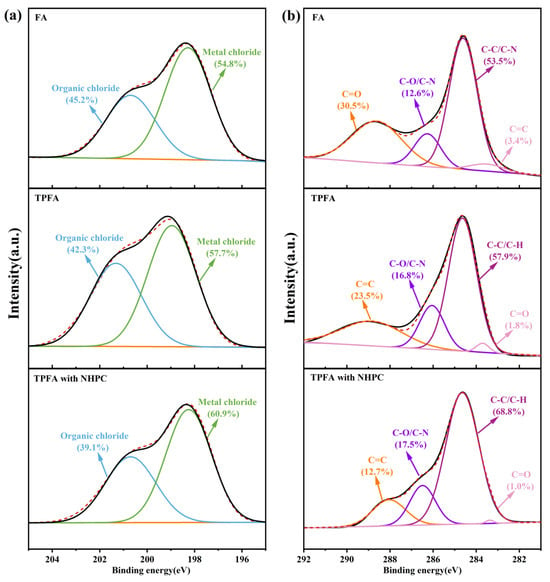
Figure 5.
XPS analysis of Cl 2p (a) and C 1s (b) in FA samples.
Carbon in the original FA exists predominantly in the form of C=O, C-O/C-N, C-C/C-H and C=C [42]. Wang et al. [43] studied the correlation between carbon-containing functional groups and dioxins as well as their precursors. The results show that C=C and C=O have a strong positive correlation with PCDD/Fs and their precursors in FA (R > 0.88); while C-C/C-H and C-O/C-N have a strong negative correlation with PCDD/Fs and their precursors (R = −0.40~−0.96). Comparing with FA, the contents of C=C and C=O decrease in TPFA, while those of C-C/C-H and C-O/C-N increase. This suggests that PCDD/Fs and their precursors in FA are gradually decomposed during the low-temperature pyrolysis. The aforementioned changes are more pronounced after the addition of NHPC, confirming that NHPC can further promote the decomposition of PCDD/Fs and their precursors, and inhibit the reformation of PCDD/Fs.
4. Conclusions
In this study, NHPC was prepared from a typical waste biomass (i.e., corn cobs) using a foaming method and applied as an additive to regulate the low-temperature pyrolysis of FA. The results demonstrate that NHPC exhibits a superior enhancement effect compared to traditional activated carbon (AC). When the FA is co-pyrolyzed with NHPC at 350 °C for 30 min, the removal efficiencies of PCDD/Fs reach 94.88% (mass-based) and 90.23% (TEQ-based), respectively. The addition of NHPC facilitates the low-temperature pyrolysis of PCDD/Fs and inhibits their regeneration through multiple mechanisms:
- (1)
- Enhanced dispersion and activation. NHPC can promote the uniform distribution and catalytic activity of alkali metal oxides on its surface.
- (2)
- Adsorption and contact enhancement. NHPC effectively capture PCDD/Fs and their precursors, increasing their interaction with alkali metal oxides.
- (3)
- Copper species modulation. NHPC facilitates the reduction of CuCl2 to CuCl, thereby passivating its catalytic role in PCDD/F formation.
- (4)
- Electron transfer facilitation. N-doping on the NHPC surface enhances the electron transfer between metal atoms and the carbon matrix, improving the catalytic activity of alkali metal oxides for PCDD/Fs decomposition.
- (5)
- Hydrodechlorination acceleration. The surface -NH and -NH2 groups imported by N doping can provide extra H protons, facilitating PCDD/Fs hydrodechlorination.
Furthermore, NHPC addition significantly reduces the leaching of Pb, Zn, Cr and Cu by 35.6%, 73.7%, 22.9% and 83.3%, respectively. This study confirms that NHPC not only enhances PCDD/Fs decomposition, but also immobilizes serval typical heavy metals in fly ash. These findings provide both experimental and theoretical foundations for developing a novel and integrated approach to simultaneously address PCDD/Fs and heavy metals contamination in fly ash.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr13041202/s1, Figure S1: XPS spectra of N1s of NHPC; Figure S2: SEM-EDS (a), (b) and TEM (c), (d) of NHPC; Figure S3: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup; Table S1: Structure parameters of NHPC; Table S2: Characterization instrument type and operating parameters; Table S3: HRGC-HRMS detection of PCDD/Fs operating parameters; Table S4: The proportion of main elements in fly ash samples before and after water-washed (wt.%).
Author Contributions
Writing—review and editing, M.Y. and Q.W.; writing—original draft, M.Y.; methodology, M.Y. and Q.W.; investigation, M.Y., H.W. and X.W.; data curation, M.Y., H.W. and X.W.; resources, Q.W.; funding acquisition, Q.W.; conceptualization, J.J. and D.L.; supervision, J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (24ZR1454400) and the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (23010503500).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within this article.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (24ZR1454400) and the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (23010503500).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, W.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Li, Q. A comprehensive evaluation of the treatment of lead in MSWI fly ash by the combined cement solidification and phosphate stabilization process. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yan, D.; Li, L.; Wen, Z.; Liu, M.; Lu, S.; Huang, Q. Review of thermal treatments for the degradation of dioxins in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: Proposing a suitable method for large-scale processing. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Qiao, J.; Liu, M.; Kołodyńska, D.; Zhang, M.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Ju, Y.; Ma, J.; Chang, M.-b. Detoxification of municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash by single-mode microwave (MW) irradiation: Addition of urea on the degradation of Dioxin and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Tang, Q.; Gan, M.; Ji, Z.; Fan, X.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X. Co-treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWI FA) and municipal sludge: A innovative method to improve sludge dewatering with fly ash dechlorination. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lin, F.; Li, K.; Zheng, F.; Yan, B.; Che, L.; Tian, W.; Chen, G.; Yoshikawa, K. A critical review on energy recovery and non-hazardous disposal of oily sludge from petroleum industry by pyrolysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B. Degradation technologies and mechanisms of dioxins in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, X. Detoxification, solidification and recycling of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 130349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yuan, W.; Liu, J.; Ye, W.; Lin, J.; Xie, J.; Huang, X.; Gao, S.; Xie, J.; Liu, S.; et al. An integrated process of chemical precipitation and sulfate reduction for treatment of flue gas desulphurization wastewater from coal-fired power plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, M.M.; Chang, M.B. Catalytic pyrolysis: New approach for destruction of POPs in MWIs fly ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, M.M.; Chang, M.B. Transformation of mono- to octa- chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in MWI fly ash during catalytic pyrolysis process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorio, J.L.; Garcia, M.A.S.; Gothe, M.L.; Galvan, D.; Troise, P.C.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Vidinha, P.; Camargo, P.H.C.; Rossi, L.M. Recent advances in the use of nitrogen-doped carbon materials for the design of noble metal catalysts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 481, 215053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zheng, J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Ding, Y.; Han, J.; Jiang, S.; He, S. Pore engineering: Structure-capacitance correlations for biomass-derived porous carbon materials. Mater. Des. 2023, 229, 111904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Huang, X.; Peng, Y.; Lu, S. Hierarchical porous carbon as a highly efficient adsorbent for toluene and benzene. Fuel 2020, 270, 117478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Huang, X.; Tang, M.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Makwarimba, C.P. Synthesis of N-doped hierarchical porous carbon with excellent toluene adsorption properties and its activation mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, X.; Lv, G.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Ni, M.; Yan, J.; Lin, X.; Song, H.; et al. Improving microwave-assisted hydrothermal degradation of PCDD/Fs in fly ash with added Na2HPO4 and water-washing pretreatment. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Yang, T.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Gu, J.; Wang, Y. Enabling efficient and economical degradation of PCDD/Fs in MSWIFA via catalysis and dechlorination effect of EMR in synergistic thermal treatment. Chemosphere 2023, 342, 140164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Ru, Y.; Yan, D. Industrial disposal processes for treatment of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altarawneh, M.; Saeed, A.; Al-Harahsheh, M.; Dlugogorski, B.Z. Thermal decomposition of brominated flame retardants (BFRs): Products and mechanisms. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2019, 70, 212–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Yue, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Qian, G. Dual Positive Effects of Pre-Dechlorine and Low-Temperature Deep Reduction-Keeping on the PCDD/F Removal of Incineration Fly Ash. ACS EST Eng. 2024, 4, 2274–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabias-Blicharz, E.; Franus, W. A critical review on mechanochemical processing of fly ash and fly ash-derived materials. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Peng, Z.; Yu, L.; Sun, Y.; Yong, R.; Helge Karstensen, K. Characterization of heavy metals and PCDD/Fs from water-washing pretreatment and a cement kiln co-processing municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Wang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Zhan, X.; Li, T.; Yang, L. Characterization of typical heavy metals in pyrolysis MSWI fly ash. Environ. Technol. 2018, 40, 3502–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, T. Comprehensive assessment of thermal characteristics, kinetics and environmental impacts of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash during thermal treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 175, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Wu, W.; Jin, B. Investigation of thermal characteristics of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash under various atmospheres: A TG-FTIR study. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 681, 178402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalimoghadam, M.; Vakili, A.H.; Keskin, I.; Totonchi, A.; Bahmyari, H. Solidification and utilization of municipal solid waste incineration ashes: Advancements in alkali-activated materials and stabilization techniques, a review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 122014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Chen, S.; Xie, M.; Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Dong, F.; Dong, X.; Weng, X. H-zeolite supported multi-interface metal catalysts for the catalytic destruction of chlorinated organics. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayiragije, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Song, Z.; Wang, N.; Majima, T.; Zhu, L. Mechanochemically tailoring oxygen vacancies of MnO2 for efficient degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A with peroxymonosulfate. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 307, 121168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Muhammad, F.; Yu, L.; Xia, M.; Huang, X.; Jiao, B.; Lu, N.; Li, D. Solidification/stabilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash using uncalcined coal gangue–based alkali-activated cementitious materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 25609–25620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wen, Y.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Sharma, V.K.; Ma, X. Biochar as a novel carbon-negative electron source and mediator: Electron exchange capacity (EEC) and environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFRs): A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnu, S.N.; Bahurudeen, A.; Athira, G. Comparison of sugarcane bagasse ash with fly ash and slag: An approach towards industrial acceptance of sugar industry waste in cleaner production of cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Doh, J.-H.; Dinh, H.L.; Ong, D.E.L.; Zi, G.; You, I. Effect of Si/Al molar ratio on the strength behavior of geopolymer derived from various industrial waste: A current state of the art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 329, 127134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Mao, T.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Yan, J. Thermal cotreatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with sewage sludge: Phases transformation, kinetics and fusion characteristics, and heavy metals solidification. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Gan, M.; Ji, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.; Huang, X.; Fan, Y. Recent progress on the thermal treatment and resource utilization technologies of municipal waste incineration fly ash: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, K.; Tian, L.; Xie, M.; Zhou, T. Comprehensive understanding the transition behaviors and mechanisms of chlorine and metal ions in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash during thermal treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ji, G.; Zhu, K.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A. Integrated thermal behavior and compounds transition mechanism of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash during thermal treatment process. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wons, W.; Rzepa, K.; Reben, M.; Murzyn, P. Thermal studies of fly ashes expansion. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 143, 2883–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jia, A.; Hou, X.; Wang, X.; Mao, Y.; Wang, W. Thermal co-treatment of aluminum dross and municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: Mineral transformation, crusting prevention, detoxification, and low-carbon cementitious material preparation. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chen, X.; Kong, L.; Li, K.; Wu, C.; Bai, J.; Guo, J.; Guo, Z.; Bai, Z.; et al. Immobilization of heavy metals with chlorine and liquid phase formation during thermal treatment of MSWI fly ash. Fuel 2024, 378, 132949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janković, M.; Janković, B.; Marinović-Cincović, M.; Porobić, S.; Nikolić, J.K.; Sarap, N. Experimental study of low-rank coals using simultaneous thermal analysis (TG–DTA) techniques under air conditions and radiation level characterization. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 142, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, K.; Fu, T.; Gao, J.; Hussain, S.; AlGarni, T.S. Pyrometallurgical recovery of zinc and valuable metals from electric arc furnace dust—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, I.G.; Halder, P.; Patel, S.; Selezneva, E.; Rathnayake, N.; Marzbali, M.H.; Veluswamy, G.; Sharma, A.; Kundu, S.; Surapaneni, A.; et al. Current understanding on the transformation and fate of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances before, during, and after thermal treatment of biosolids. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, M.; Li, K.; Xia, M.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, H.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. Insight into KOH activation mechanism during biomass pyrolysis: Chemical reactions between O-containing groups and KOH. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lv, J.; Ying, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, A.; Lin, X.; Cao, A.; Li, X.; Yan, J. A new insight into the CaO-induced inhibition pathways on PCDD/F formation: Metal passivation, dechlorination and hydroxide substitution. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).