New TLC-Densitometric Method for the Quantification of Donepezil in Tablets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Drug Solutions
2.3. Donepezil Solutions Exposed to Stress Conditions
2.4. Method Validation
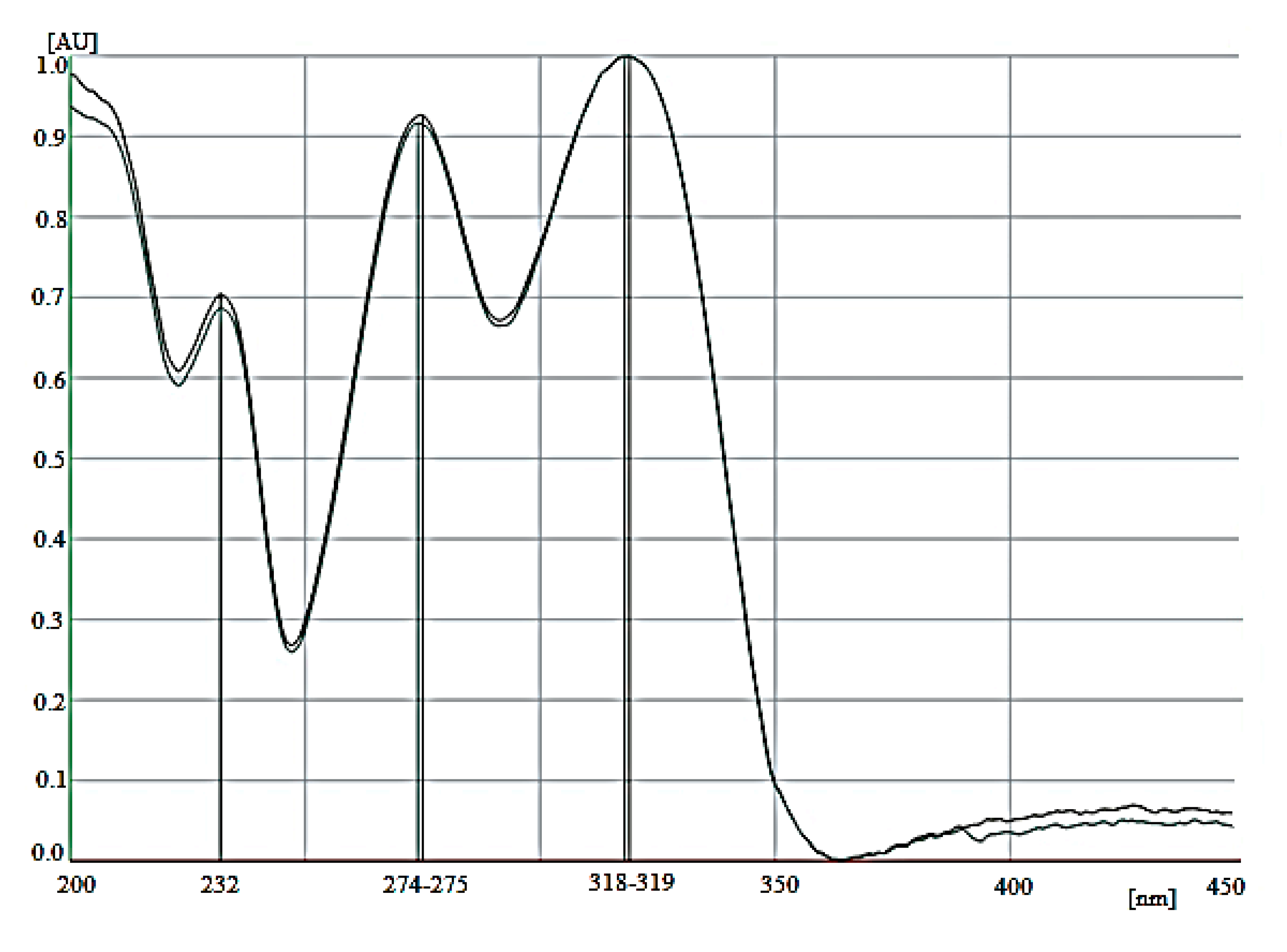
2.4.1. Selectivity
2.4.2. Range and Linearity
2.4.3. Precision
2.4.4. Accuracy
2.4.5. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
2.4.6. Robustness
2.5. Quantitative Determination of Donepezil in Donecept and Cogiton Preparation
2.6. Comparison of Determination of Donepezil in Tablets Using Two Ranges (Calibration Curves)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation
3.1.1. Selectivity
3.1.2. Range and Linearity
3.1.3. Accuracy
3.1.4. Precision
3.1.5. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
3.1.6. Robustness
3.2. Quantitative Determination of Donepezil in the Tested Pharmaceutical Preparations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mangialasche, F.; Solomon, A.; Winblad, B.; Mecocci, P.; Kivipelto, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical trials and drug development. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winblad, B. Donepezil in Severe Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Demen. 2009, 24, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janiec, W. Compendium of Pharmacology; Medical Publishing House PZWL: Warsaw, Poland, 2021. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.S.; Solairaj, P.; Thangathirupathi, A. Analytical method development and validation of donepezil hydrochloride tablets by RP-HPLC. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, K.B.; Peh, K.K.; Tan, Y.T.F. RP-HPLC analytical method development and optimization for quantification of donepezil hydrochloride in orally disintegrating tablet. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 26, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saleh, H.M.; Ragab, G.H.; Amin, A.S.; Kamel, E.S. Stability-indicating HPLC method for determination of donepezil hydrochloride in pure and in tablet dosage forms. Asian J. Pharm. Anal. Med. Chem. 2016, 4, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul-Sattar, M.D.; Achanta, S. Development and validation of a simple method for simulations estimation of memantine and donepezil in pharmaceutical dosage forms by using RP-HPLC. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 10, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Bulduk, I.; Aydin, B.S. Simple high-performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of Donepezil HCl in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Chem. Metrol. 2020, 14, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korany, M.A.; Mahgoub, H.; Haggag, R.S.; Ragab, M.A.A.; Elmallah, O.A. Development of a green stability-indicating HPLC–DAD method for the determination of donepezil hydrochloride in the presence of its related substance and degradation products. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, G.H.; Bahgat, E.A. Development of bioanalytical HPLC method for simultaneous determination of the antialzhiemer, donepezil hydrochloride and the antidepressant, citalopram hydrobromide in raw materials, spiked human plasma and tablets dosage form. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2019, 77, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barot, T.G.; Patel, P.K. RP-HPLC Method for the Estimation of Donepezil Hydrochloride Dosage form. J. Chem. 2009, 6, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Kumar, S.S.; Dutta, P.K. Stability-indicative HPLC determination of donepezil hydrochloride in tablet dosage form. Pharm. Chem. J. 2012, 45, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonassif, M.A.; Hefnawy, M.M.; Kassem, M.G.; Mostafa, G.A. Determination of donepezil hydrochloride in human plasma and pharmaceutical formulations by HPLC with fluorescence detection. Acta. Pharm. 2011, 61, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzoman, N.Z.; Hefnawy, M.; Al-majed, A.; Alanazi, A.; Mostafa, G.; Arabia, S. Chiral stability-indicating HPLC method for analysis of donepezil in pharmaceutical formulations. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2013, 8, 825–834. [Google Scholar]
- Shirwaikar, A.; Devi, S.; Rajagopal, P.L.; Kiron, S.S.; Sreejith, K.R. Development and validation of analytical method for determination of donepezil hydrochloride in pure and dosage forms. Asian. J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2014, 7, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, G.; Sofu, Ü.; Kul, D. Development of low-cost, fast, and sensitive voltammetric methods for the determination of donepezil using unmodified carbon paste electrode. Monatsh. Chem. 2024, 155, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Ali, M.; Ahmad, S.; Bhavna, M. Stability-Indicating HPTLC method for determination od donepezil hydrochloride in bulk drug and pharmaceutical dosage form. Chem. Anal. 2009, 54, 1501–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, L.L.; Dongre, N. Development and validation of stability indicating HPTLC method for determination of donepezil hydrochloride and its related substances in bulk drug and pharmaceutical dosage form. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2023, 16, 2890–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH. Harmonised Tripartite Guideline: Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology, Q2(R1); ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q2%28R1%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Ferenczi-Fodor, K.; Renger, B.; Végh, Z. The frustrated reviewer—Recurrent failures in manuscripts describing validation of quantitative TLC/HPTLC procedures for analysis of pharmaceuticals. J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2010, 23, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy-Turák, A.; Végh, Z.; Ferenczi-Fodor, K. Validation of the quantitative planar chromatographic analysis of drug substances. III. Robustness testing in OPLC. J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 1995, 8, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi-Fodor, K.; Nagy-Turák, A.; Végh, Z. Validation and monitoring of quantitative thin layer chromatographic purity tests for bulk drug substances. J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 1995, 8, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Hendix, C.D. What every technologist should know about experiment design. Chem. Technol. 1979, 9, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- USP. The United States Pharmacopeia, 34th ed.; United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kafkala, S.; Matthaiou, S.; Alexaki, P.; Abatzis, M.; Bartzeliotis, A.; Katsiabani, M. New gradient high-performance liquid chromatography method for determination of donepezil hydrochloride assay and impurities content in oral pharmaceutical formulation. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1189, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salakolusu, S.; Katari, N.K.; Sharma, G.V.R.; Rendedula, D.P.; Ranga, M.; Kaliyaperumal, M.; Raghupathi, J.K. Utilizing cutting-edge analytical techniques for the Identification, Isolation, and structural characterization of donepezil HCl forced degradation products. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111665. [Google Scholar]
- Ruela, A.L.M.; Santos, M.G.; Figueiredo, E.C.; Pereira, G.R. LC-PDA and LC-MS studies of donepezil hydrochloride degradation behavior in forced stress conditions. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2014, 25, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar]
- BOC Sciences. Available online: https://www.bocsci.com/im-donepezil-and-impurities-list-794.html?srsltid=AfmBOooqc3BCTzTvuv4weZP6VuJO4UvPjfyof4CKQAUVtp39VF6_9ROZ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J. Validation of Analytical Procedures. In Evaluation and Quality Control of Analytical Measurement Results, 1st ed.; Konieczka, P., Namieśnik, J., Eds.; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 2017; pp. 225–299. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe. European Pharmacopoeia, 8th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
| Method Characteristic | Donepezil | |
|---|---|---|
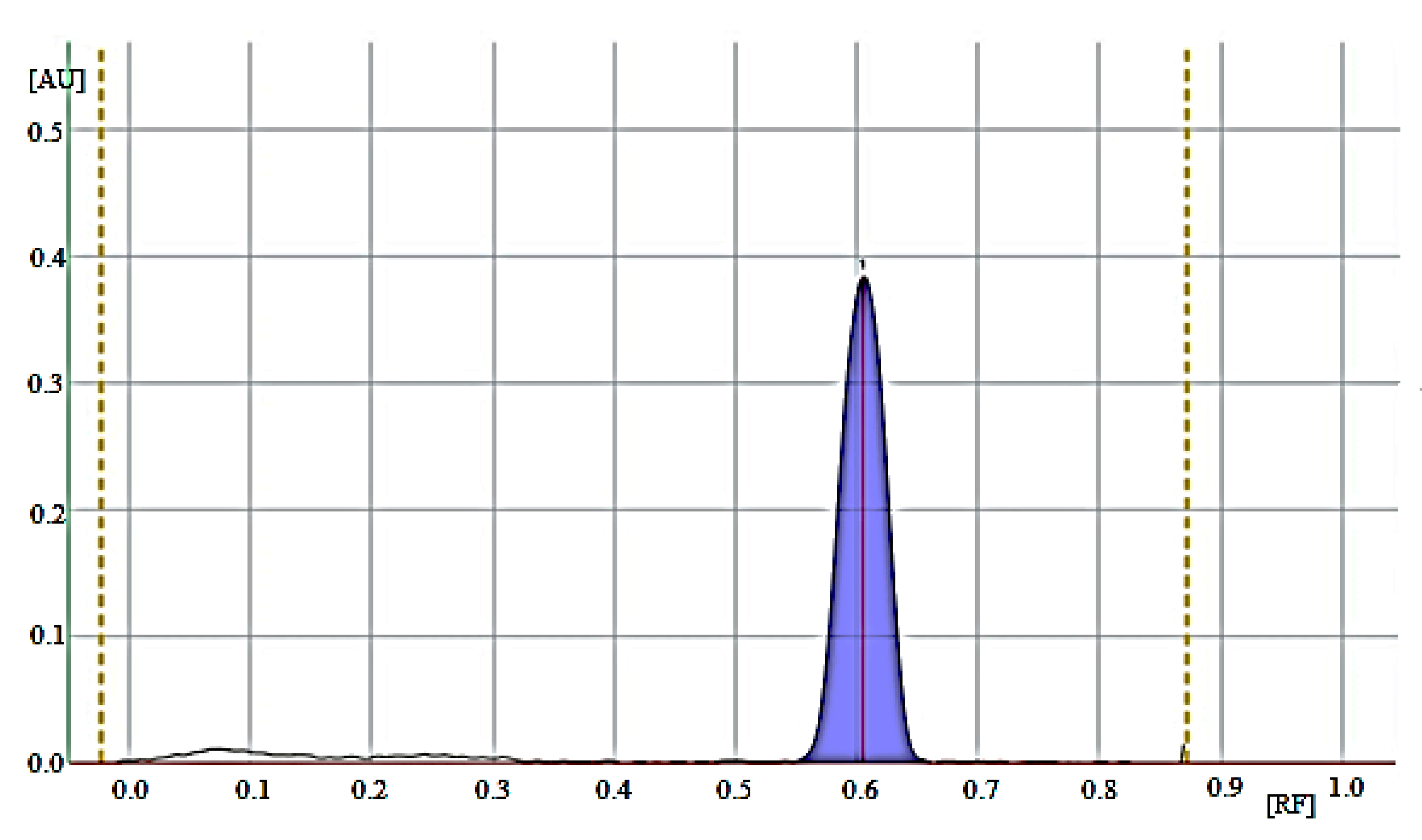
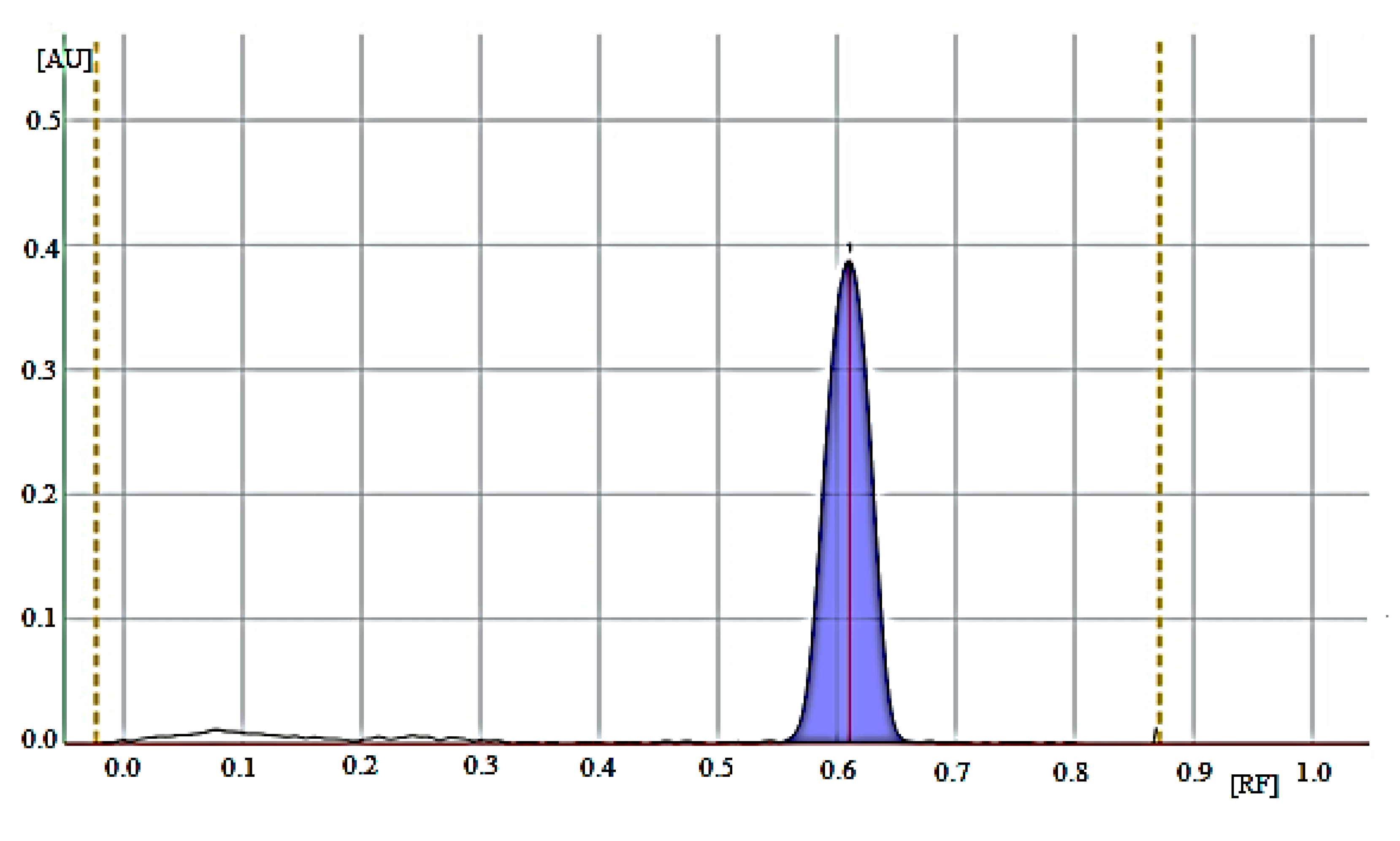
| Retardation factor (RF) | 0.62 ± 0.03 | |
| LOD [µg/spot] | 0.049 | |
| LOQ [µg/spot] | 0.147 | |
| Range [μg/spot] | 1.0–5.0 | |
| Linearity [μg/spot] | A = x ·0.00397(±0.00008) + 0.00920(±0.0027) n = 5, r = 0.9994, s = 0.00025, F = 2425, p < 0.0001 | |
| For tablets | ||
| Cogiton (CG) | Donecept (DT) | |
| Accuracy (n = 6) | ||
| for 50% standard added | R = 98.0%; CV = 1.17% | R = 99.8%; CV = 1.40% |
| for 100% standard added | R = 96.1%; CV = 0.88% | R = 97.3%; CV = 1.49% |
| for 150% standard added | R = 96.3 %; CV = 1.09% | R = 96.9%; CV = 1.82% |
| Average recovery | 96.8% | 98.0% |
| Precission (CV, [%]) | ||
| Intraday (n = 3) | ||
| for 1.0 µg/spot | 2.66 | 0.93 |
| for 3.0 µg/spot | 1.09 | 0.32 |
| for 5.0 µg/spot | 0.52 | 0.69 |
| Interday (n = 3) | ||
| for 1.0 µg/spot | 0.88 | 0.85 |
| for 3.0 µg/spot | 0.47 | 1.09 |
| for 5.0 µg/spot | 0.28 | 0.50 |
| Range [μg/spot] | 0.2–1.0 | |
| Linearity [μg/spot] | A = 0.01058 (±0.00020) x + 0.00261 (±0.00013) n = 9, r = 0.9988; s = 0.00015, F = 2896, p ˂ 0.0001 | |
| For tablets | ||
| Cogiton (CG) | Donecept (DT) | |
| Accuracy (n = 6) | ||
| for 50% standard added | R = 99.2%; CV = 2.01% | R = 98.4%; CV = 1.89% |
| for 100% standard added | R = 98.9%; CV = 1.11% | R = 98.2%; CV = 2.13% |
| for 150% standard added | R = 97.8%; CV = 1.25% | R = 97.1%; CV = 1.78% |
| Average recovery | 98.6% | 97.9% |
| Precission (CV, [%]) | ||
| Intraday (n = 3) | ||
| for 0.2 µg/spot | 1.73 | 2.04 |
| for 0.6 µg/spot | 2.15 | 0.99 |
| for 1.0 µg/spot | 2.66 | 0.93 |
| Interday (n = 3) | ||
| for 0.2 µg/spot | 1.89 | 1.23 |
| for 0.6 µg/spot | 1.11 | 2.18 |
| for 1.0 µg/spot | 0.88 | 0.85 |
| Robustness (CV, [%]) | robust | robust |
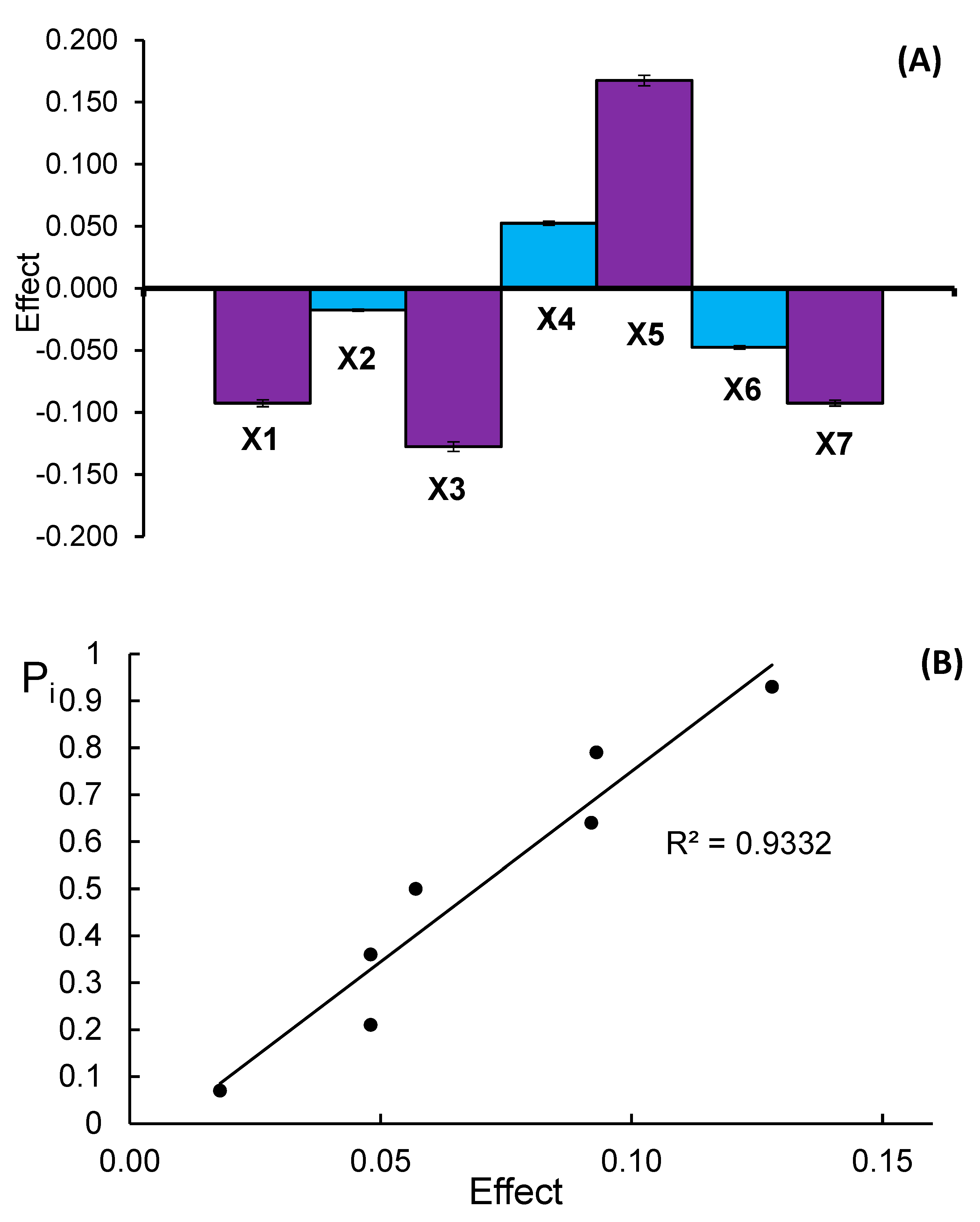
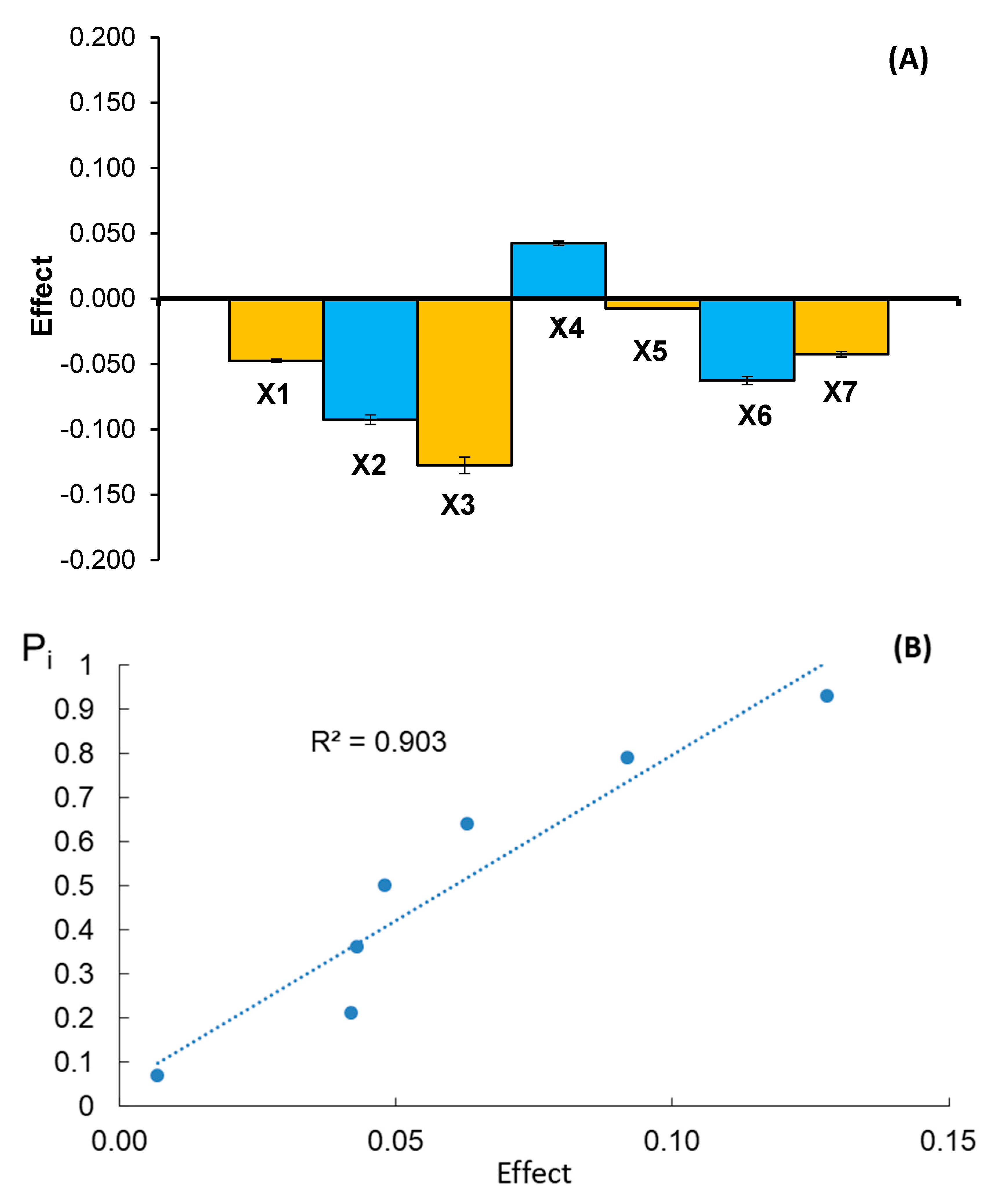
| Experiment No | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | Donepezil Content (yi) [mg/Tablet] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | DT | |||||||||
| 1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 4.89 | 4.78 | |
| 2 | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | 4.99 | 5.02 | |
| 3 | + | - | + | - | - | + | - | 4.78 | 4.88 | |
| 4 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | 5.03 | 5.02 | |
| 5 | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | 5.07 | 4.89 | |
| 6 | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | 4.89 | 4.92 | |
| 7 | - | - | + | + | - | - | + | 4.88 | 4.99 | |
| 8 | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | 5.22 | 5.09 | |
| Size of effect | CG | −0.092 | −0.018 | −0.128 | 0.052 | 0.168 | −0.048 | −0.093 | ||
| DT | −0.048 | −0.092 | −0.128 | 0.043 | −0.007 | −0.063 | −0.042 | |||
| The label claim [mg] | 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| Average amount [mg] | 4.97 | 4.95 | ||||||||
| Variance | 0.019 | 0.010 | ||||||||
| Standard deviation (SD) | 0.14 | 0.10 | ||||||||
| Coefficient of variation [CV, %] | 2.8 | 2.0 | ||||||||
| Standardized skewness | 0.730 | −0.390 | ||||||||
| Standardized kurtosis | 0.172 | −0.206 | ||||||||
| Technique | LOD | Intraday Precision (CV, %) | Interday Precision (CV, %) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP-HPLC-UV | 0.03 µg/mL | 0.24–1.83 | 1.41–1.81 | [5] |
| RP-HPLC-UV | 0.14 µg/mL | 0.512–1.150 | 0.228–1.351 | [6] |
| RP-HPLC-UV | 2.96 µg/mL | <2 | <2 | [7] |
| RP-HPLC-UV | 1.40 µg/mL | 1.44 | 3.54 | [8] |
| RP-HPLC-DAD | 0.031 µg/mL | <2 | <2 | [9] |
| RP-HPLC-DAD | 0.017 µg/mL | 0.358–0.655 | 1.522–2.679 | [10] |
| RP-HPLC-PDA | 0.04 µg/mL | <2 | <2 | [11] |
| RP-HPLC-FLD | 5.0 ng/mL | <2 | <2 | [13] |
| Chiral HPLC | 10 ng/mL | 1.01–1.29 | 0.57–1.28 | [14] |
| Spectrophotometric | 0.0770 µg/mL | 0.1723 | 0.3140 | [15] |
| HPTLC | 15.4 ng/spot | 0.086–0.303 | 0.218–0.357 | [17] |
| HPTLC | 80.85 ng/spot | - | - | [18] |
| TLC | 0.049 µg/spot = 49 ng/spot = 9.8 µg/mL | <3 | <3 | In this work |
| Donepezil in | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cogiton | Donecept | |||
| Calculated Using Range [µg/Spot] | ||||
| 1.0–5.0 | 0.2–1.0 | 1.0–5.0 | 0.2–1.0 | |
| Number of analyses | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| Content in tablet [mg] | ||||
| 1 | 4.77 | 5.02 | 4.76 | 4.89 |
| 2 | 5.06 | 4.87 | 5.04 | 4.97 |
| 3 | 4.94 | 4.92 | 4.86 | 5.09 |
| 4 | 4.98 | 4.85 | 4.99 | 5.01 |
| 5 | 5.02 | 4.96 | 5.07 | 4.87 |
| 6 | 4.94 | 4.91 | 4.88 | 4.93 |
| 7 | 4.98 | 5.03 | 5.01 | 4.94 |
| 8 | 5.02 | 4.98 | 4.95 | 4.90 |
| 9 | 5.10 | 4.89 | 5.02 | 4.97 |
| Average [mg] | 4.98 | 4.94 | 4.95 | 4.95 |
| Average using two ranges [mg] | 4.96 | 4.95 | ||
| Label claimed [mg/tablet] | 5 | 5 | ||
| Amount of donepezil (%) in relation to the label claim | 99.6 | 98.8 | 99.0 | 99.0 |
| Amount of donepezil (%) using two ranges in relation to the label claim | 99.2 | 99.0 | ||
| Standardized skewness (n = 9) | −1.587 | 0.304 | −1.083 | 1.171 |
| Standardized kurtosis (n = 9) | 1.688 | −0.805 | −0.001 | 0.583 |
| Standard deviation (SD) | 0.094 | 0.064 | 0.101 | 0.068 |
| Coefficient of variation [CV, %] | 1.88 | 1.30 | 2.04 | 1.37 |
| Confidence interval of arithmetic mean with confidence level equal to 95% | µ = 4.98 ± 0.06 | µ = 4.94 ± 0.02 | µ = 4.95 ± 0.08 | µ = 4.95 ± 0.05 |
| t calculated | 0.852 | 0.000 | ||
| t(95%.16) tabulated | 2.120 | 2.120 | ||
| F calculated | 1.72 3.44 | 2.21 3.44 | ||
| F(95%.f1=f2=8) tabulated | ||||
| Standardized skewness (n = 18) | −0.842 | −0.733 | ||
| Standardized kurtosis (n = 18) | 0.281 | 0.153 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parys, W.; Pyka-Pająk, A. New TLC-Densitometric Method for the Quantification of Donepezil in Tablets. Processes 2025, 13, 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041106
Parys W, Pyka-Pająk A. New TLC-Densitometric Method for the Quantification of Donepezil in Tablets. Processes. 2025; 13(4):1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041106
Chicago/Turabian StyleParys, Wioletta, and Alina Pyka-Pająk. 2025. "New TLC-Densitometric Method for the Quantification of Donepezil in Tablets" Processes 13, no. 4: 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041106
APA StyleParys, W., & Pyka-Pająk, A. (2025). New TLC-Densitometric Method for the Quantification of Donepezil in Tablets. Processes, 13(4), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041106







