Process-Mineralogy-Guided Flotation for Cu-Co Recovery: A Case Study of DRC Copper–Cobalt Sulfide Ore
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Process Mineralogy
2.3. Flotation
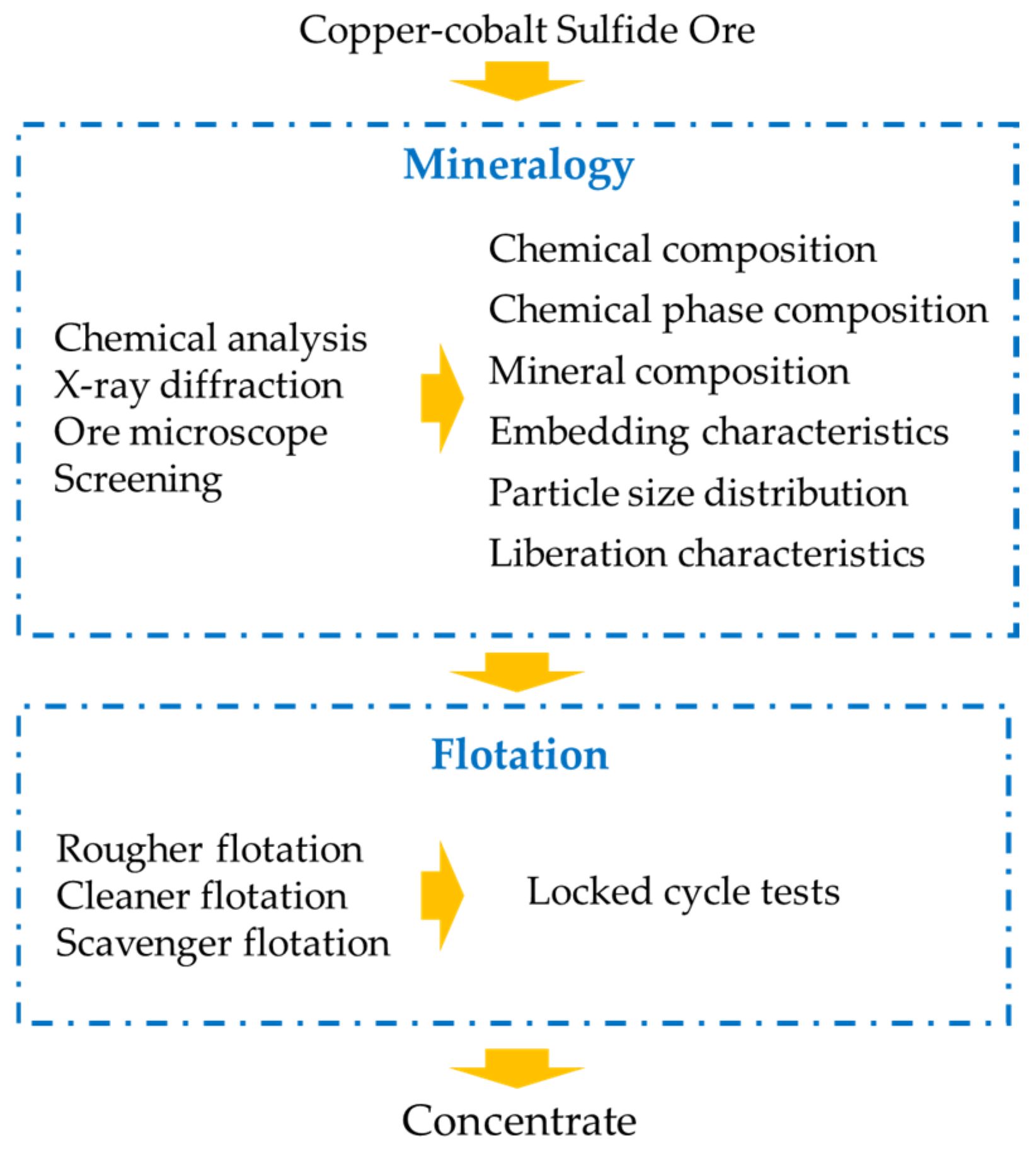
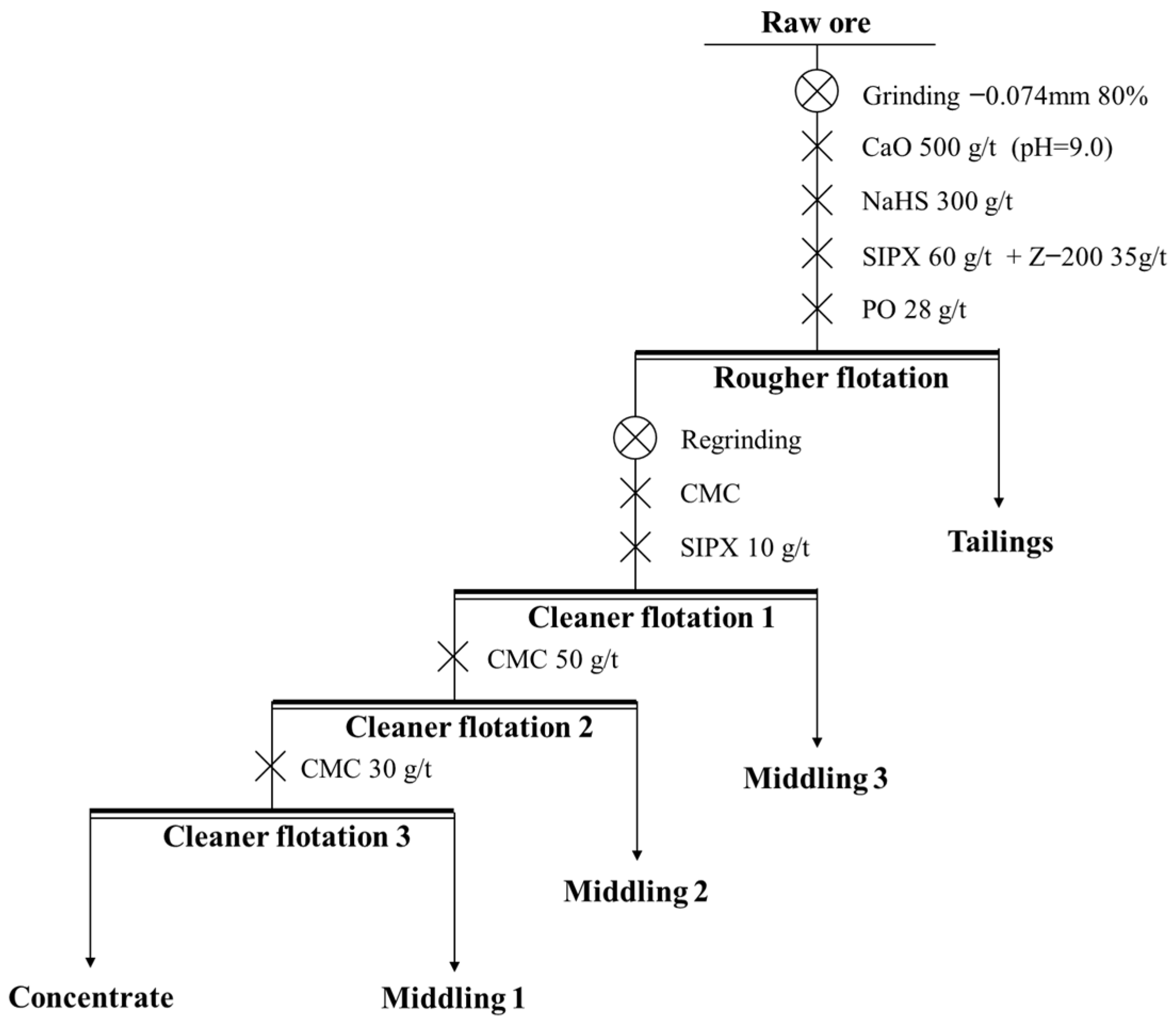
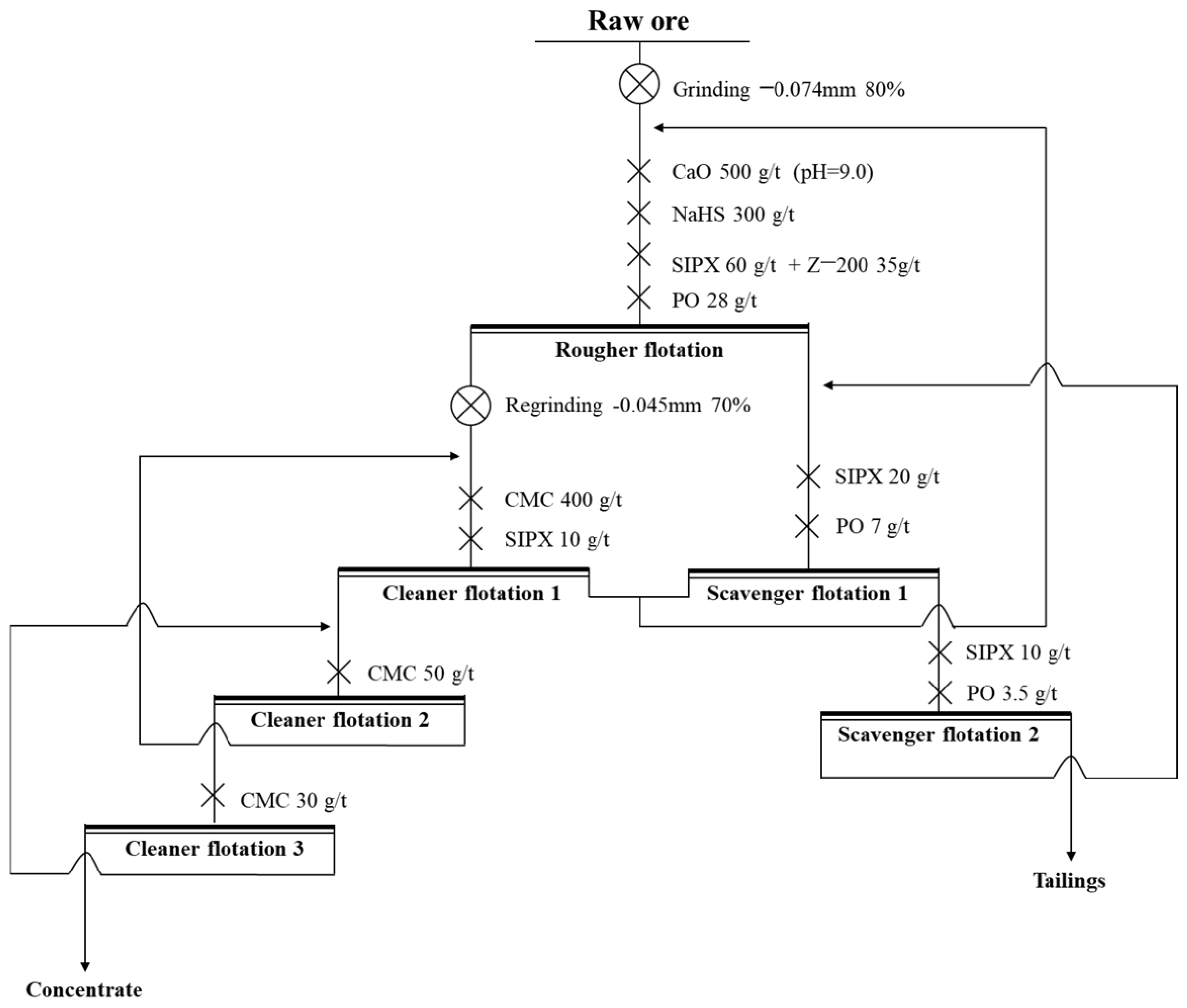
2.4. The Flowchart of the Research
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical and Mineral Composition of Copper–Cobalt Sulfide Ore
3.1.1. Chemical Composition
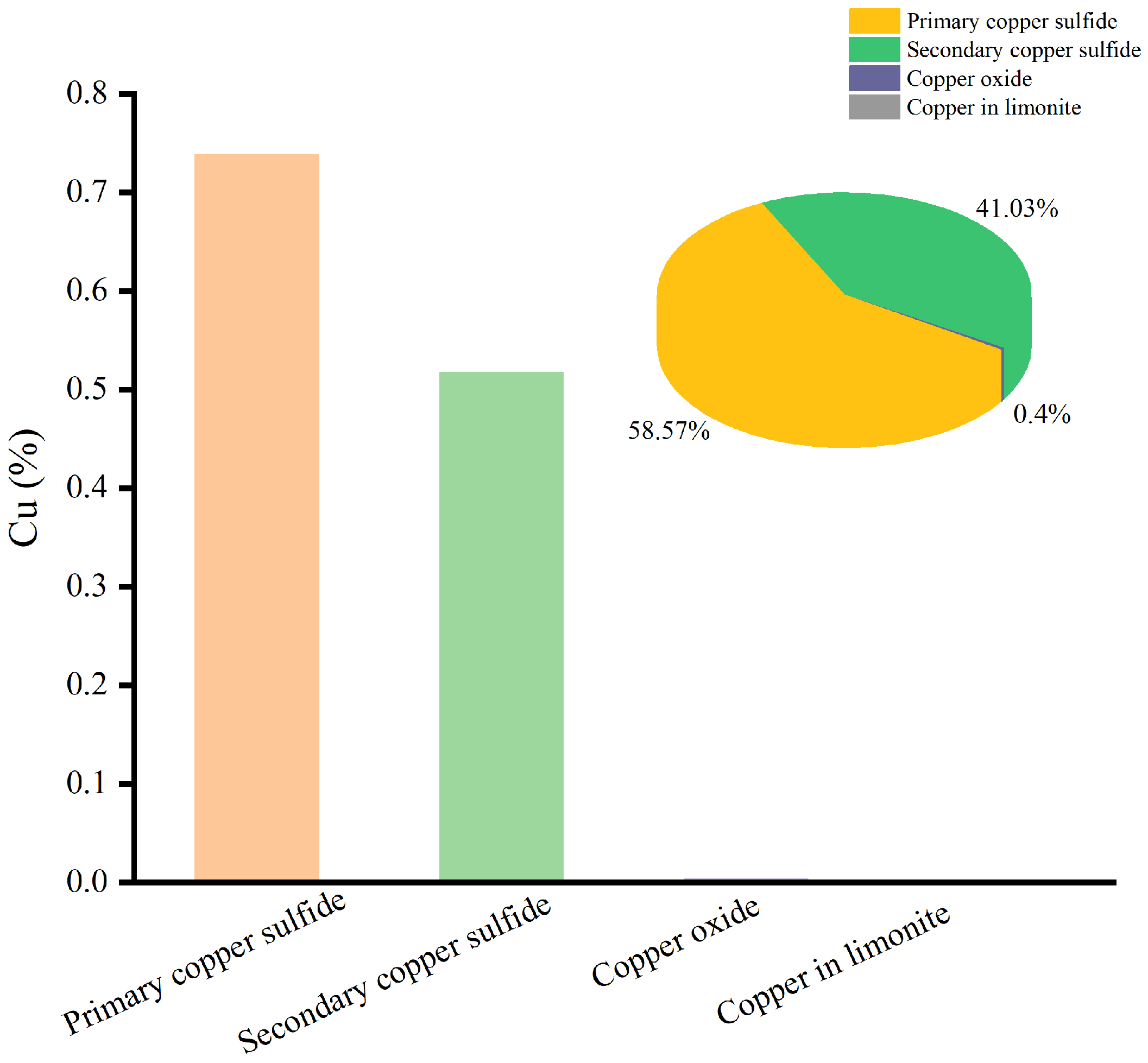
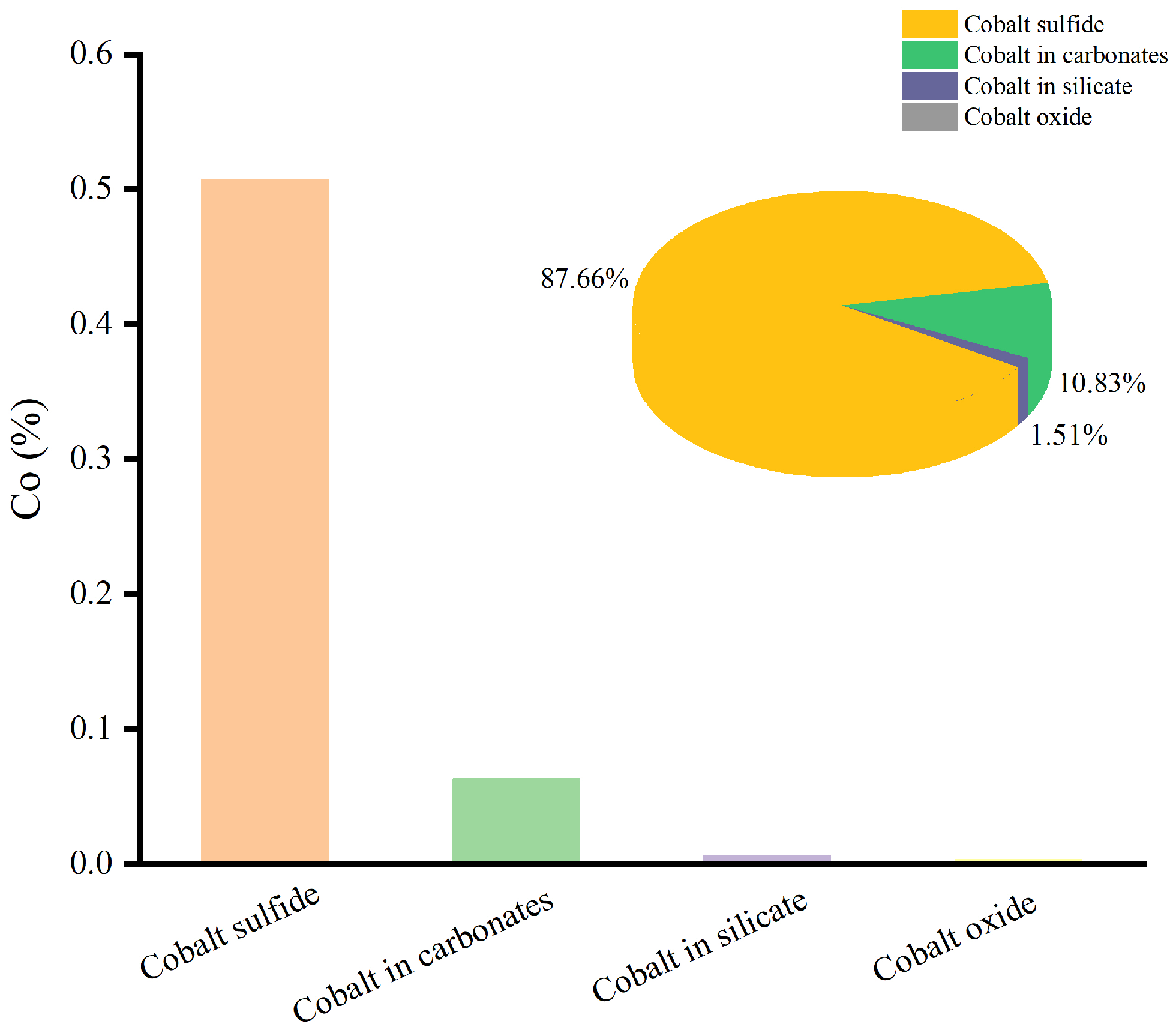
3.1.2. Chemical Phase Composition
3.1.3. Mineral Composition
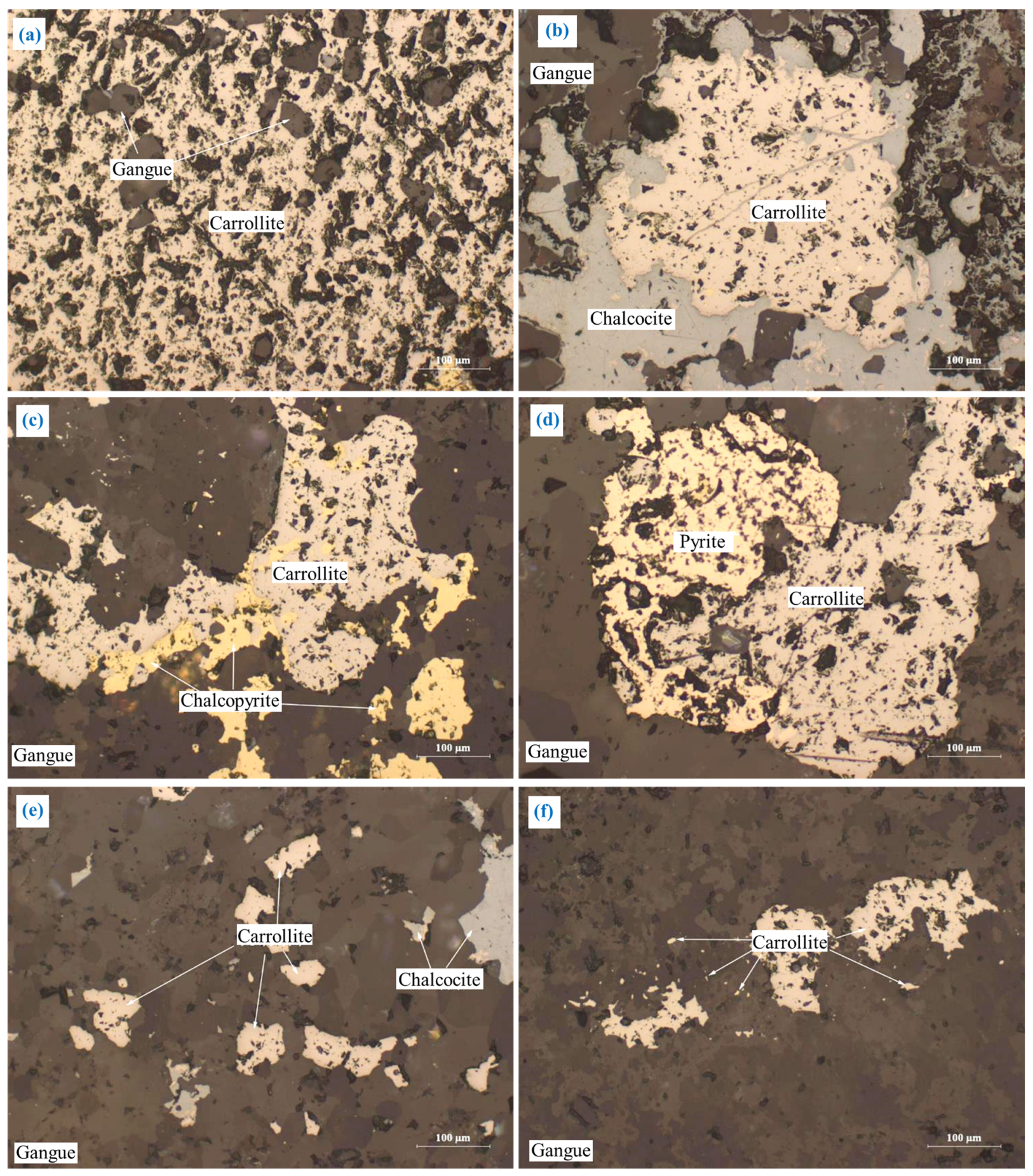
3.2. Embedding Characteristics of Key Cu/Co-Bearing Minerals
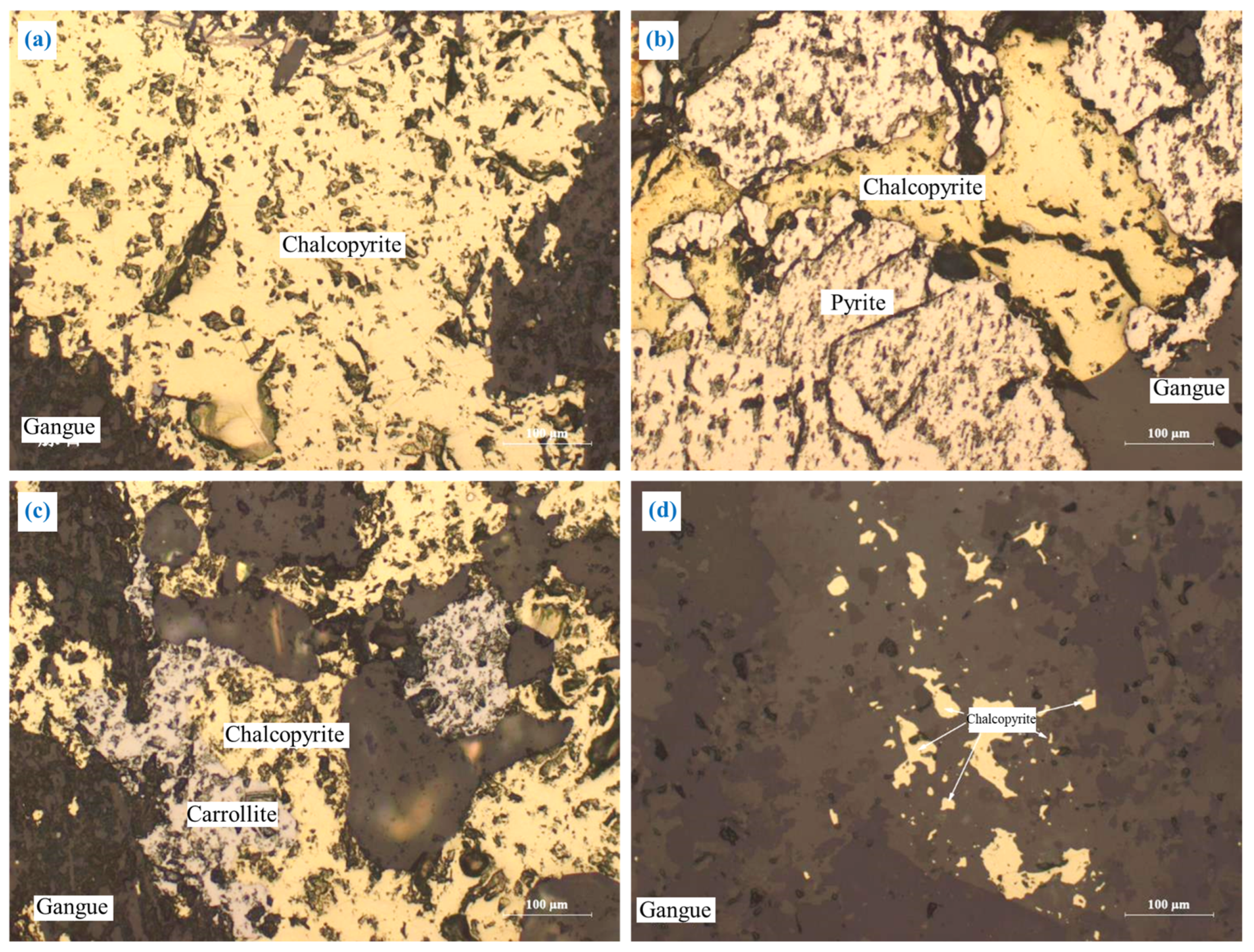
3.2.1. Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2)
3.2.2. Carrollite (CuCo2S4)
3.3. Particle Size Distribution and the Liberation Characteristics of Sulfides
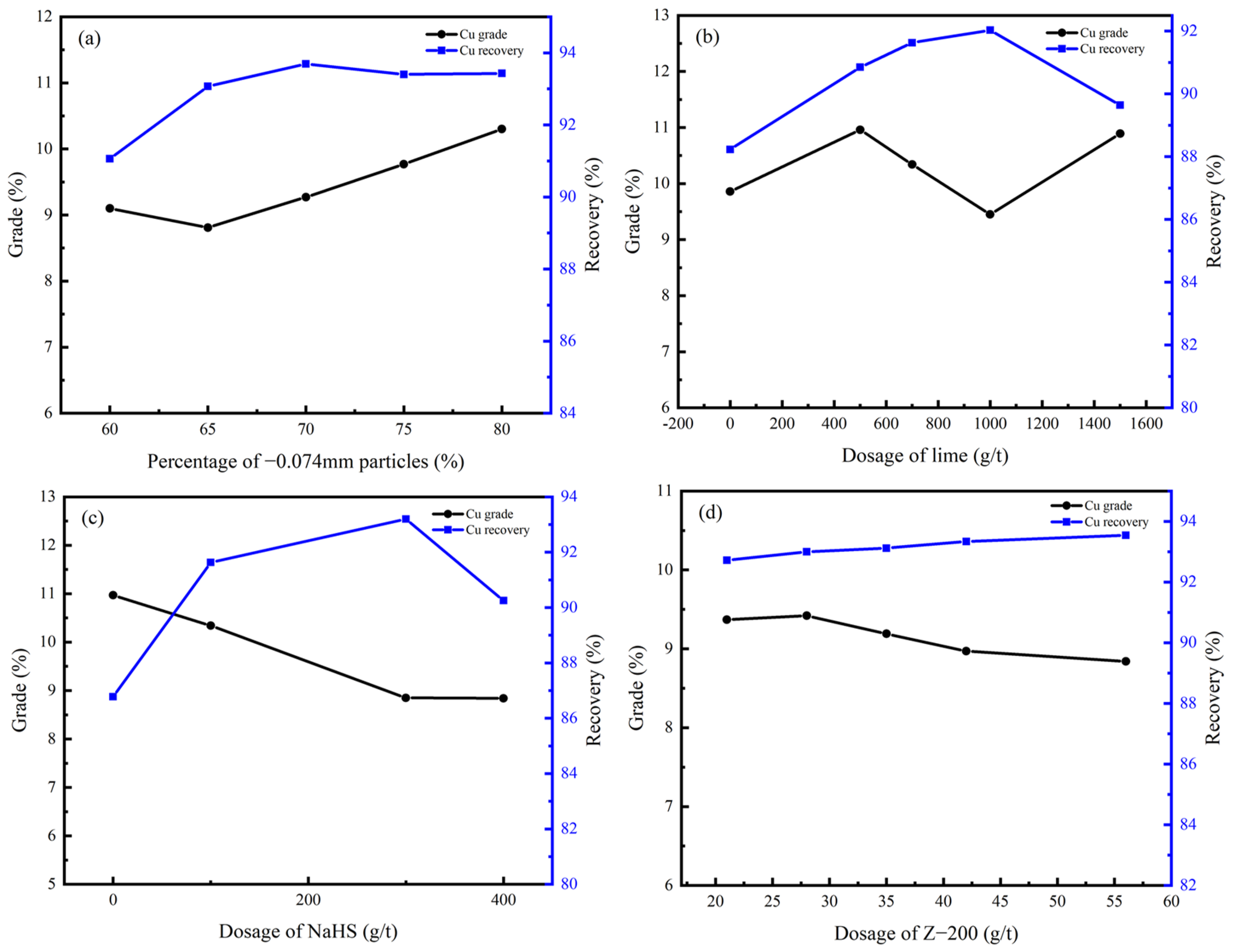
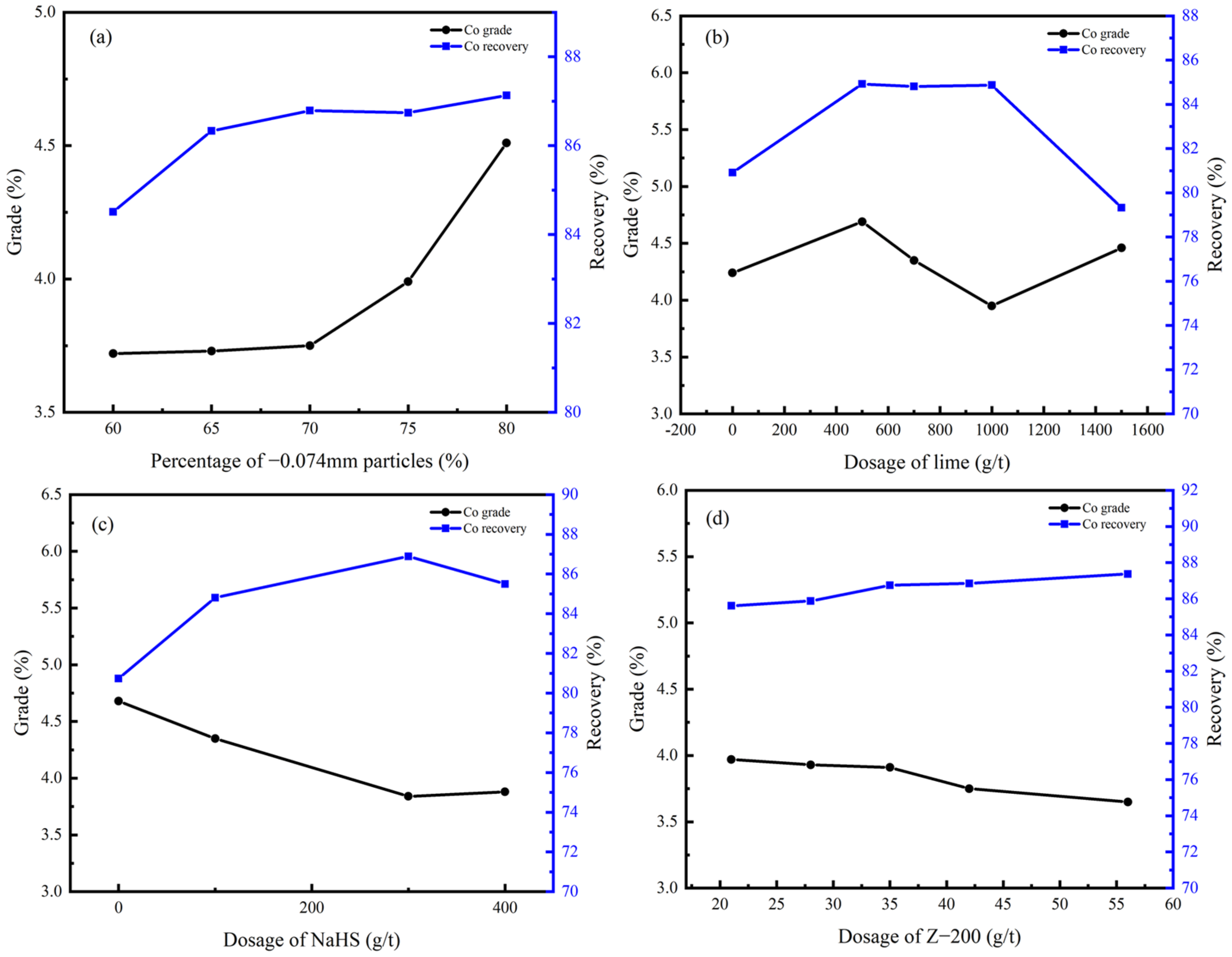
3.4. Flotation Behavior of Copper–Cobalt Sulfide Ore
3.4.1. Rougher Flotation
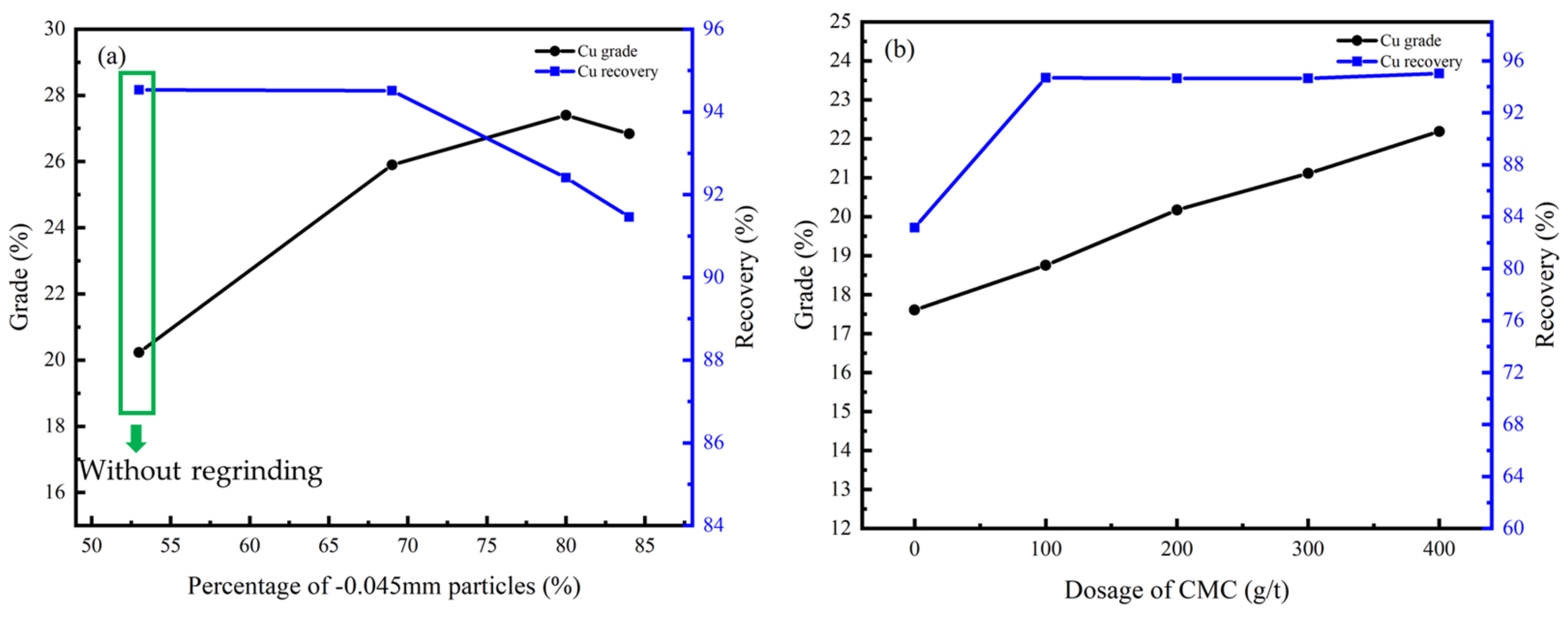
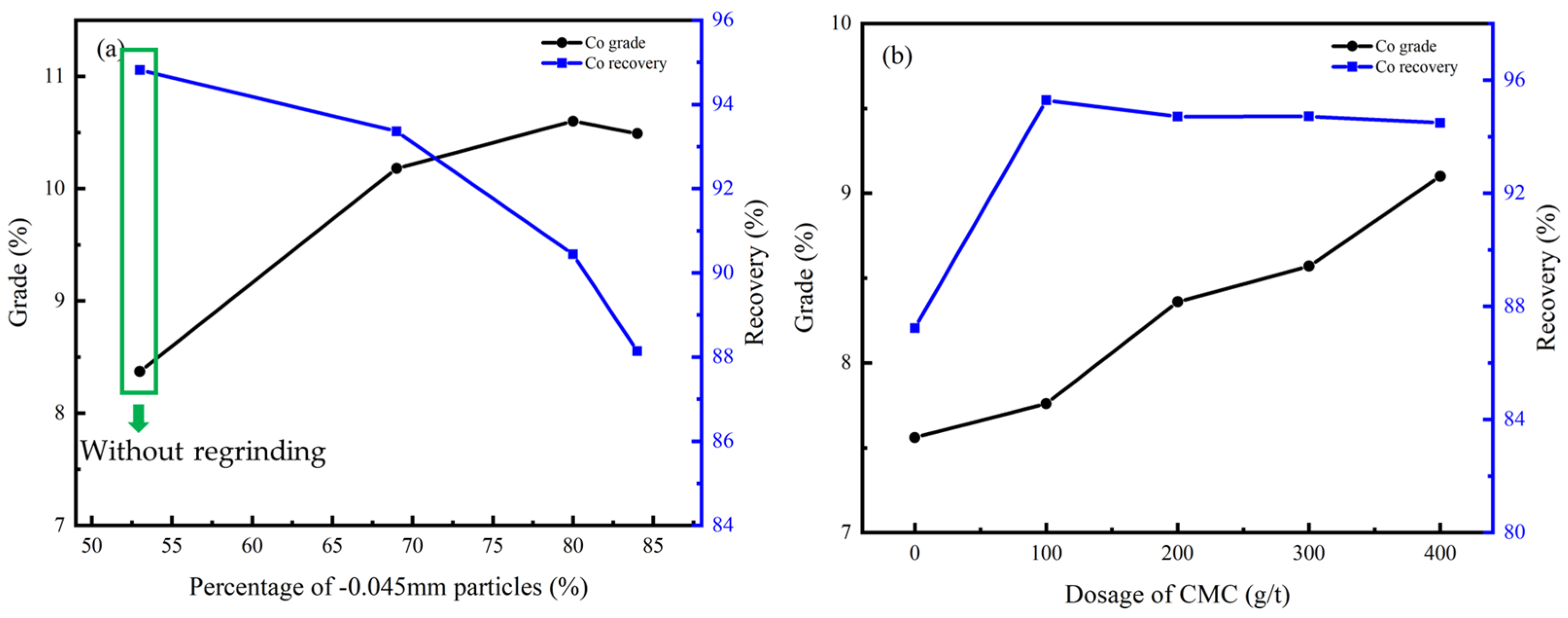
3.4.2. Cleaner Flotation
3.4.3. Scavenger Flotation
3.4.4. Locked-Cycle Tests
3.5. Process-Mineralogy-Guided Flotation for Cu-Co Recovery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, C.; Wang, J.; Qiu, G. Advancements on Chemical-biological Dissolution Mechanism and Leaching Kinetics of Chalcocite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2024, 34, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Cai, T.; Yu, S.; Gao, L.; Huang, L.; Peng, H.; Qiu, G.; Wang, J. How Ferric Salt Enhances the First-Stage Acidic Leaching of Chalcocite: Performance of intermediate Crystallite. JOM 2022, 74, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Leiva, S. Renewable Energy in Copper Production: A Review on Systems Design and Methodological Approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 118978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.; Tripathy, S.; Mandre, N.; Venugopal, R.; Farrokhpay, S. Sustainable Use of Copper Resources: Beneficiation of Low-Grade Copper Ores. Minerals 2022, 12, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Jiang, K.; Cao, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Waters, K.E.; Ma, H. Pressure Leaching Behaviors of Copper-Cobalt Sulfide Concentrate from Congo. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 309, 123010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, F.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; He, L. Kinetics Study on Cobalt Leaching from Cobalt-Bearing Ternary Sulfide in Sulfuric Acid Solution under Atmospheric Pressure. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2024, 34, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crundwell, F.K.; du Preez, N.B.; Knights, B.D.H. Production of Cobalt from Copper-Cobalt Ores on the African Copperbelt—An Overview. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Che, J.; Feng, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Efficient Extraction of Cobalt and Copper: Leveraging Redox Chemistry in Oxide and Sulfide Copper-Cobalt Ores. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Niu, S.; Shen, Z.; Zou, L.; Wang, H. Latest Advances and Progress in the Microbubble Flotation of Fine Minerals: Microbubble Preparation, Equipment, and Applications. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 1244–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turysbekov, D.; Tussupbayev, N.; Kenzhaliev, B.; Narbekova, S.; Semushkina, L. The Effect of Novel Submicronic Solid Activators on Sphalerite Flotability. Minerals 2024, 14, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijsseling, L.T.; Dehaine, Q.; Rollinson, G.K.; Glass, H.J. Mineralogical Prediction of Flotation Performance for a Sediment-Hosted Copper-Cobalt Sulphide Ore. Minerals 2020, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, E.; Lotter, N.O.; Amos, S.R. Process mineralogy as a predictive tool for flowsheet design to advance the Kamoa project. Miner. Eng. 2016, 96–97, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Pan, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M. Studies on the Surface Oxidation and Its Role in the Flotation of Mixed Cu-Ni Sulfide Ore. Powder Technol. 2021, 381, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, R.; Zhai, Q.; Dong, W.; Xie, Z.; Sun, W.; Hu, W. Prospects of Pulp Aeration for the Cleaner Production of Pyrrhotite-Rich Type Copper Sulfide Ore: Mechanism and Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 136921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, R.; Zhai, Q.; Xie, Z.; Sun, W.; Li, P.; Wang, Z. Exploring the Effect of Pulp Aeration and Lime-Aid Grinding on Pyrrhotite-Rich Type Copper Sulfide Ore Flotation Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 311, 123268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moimane, T.; Plackowski, C.; Peng, Y. The Critical Degree of Mineral Surface Oxidation in Copper Sulphide Flotation. Miner. Eng. 2020, 145, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, S.; Ekmekci, Z. Reducing Negative Effects of Oxidation on Flotation of Complex Cu-Zn Sulfide Ores. Minerals 2022, 12, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrinenko, A.A.; Gol’berg, G.Y. Heterocyclic Reagents in Flotation of Sulfide Ore: A Review. J. Min. Sci. 2022, 58, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Yan, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, C.; He, W. Effect of a Novel Phosphate on the Flotation of Serpentine-Containing Copper-Nickel Sulfide Ore. Miner. Eng. 2020, 150, 106276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Godirilwe, L.L.; Haga, K.; Yamada, M.; Shibayama, A. Flotation Behavior and Surface Analytical Study of Synthesized (Octylthio) Aniline and Bis(Octylthio)Benzene as Novel Collectors on Sulfide Minerals. Miner. Eng. 2023, 204, 108422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Duan, W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y. Effect of the Foaming Performance of Ammonium Dibutyl Dithio-Phosphate on the Flotation of Slime-Containing Copper Sulfide Ore. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2022, 58, 153492. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Wu, J.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, T.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y. Flotation Performance, Structure-Activity Relationship and Adsorption Mechanism of a Newly-Synthesized Collector for Copper Sulfide Minerals in Gacun Polymetallic Ore. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 551, 149420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhao, K.; Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z. Upgrading of Talc-Bearing Copper-Nickel Sulfide Ore by Froth Flotation Using Sodium Phytate as Depressant. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 687, 133561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yang, B.; Zeng, M.; Huang, P.; Teng, A. Selective Flotation of Cu-Mo Sulfides Using Xanthan Gum as a Novel Depressant. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalarz, A.; Gloy, G.; Luszczkiewicz, A. Flotation of Sulfide Components of Copper Ore in the Presence of N-Dodecane. Miner. Process Extr. Metall. Rev. 2015, 36, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, G.; Cabrera, P.; Rodriguez, A.; Cuervo, C.; Gutierrez, L. The Effect of an Anionic Polyacrylamide on the Flotation of Chalcopyrite, Enargite, and Bornite. Minerals 2024, 14, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuya, B.; Mulaba-Bafubiandi, A.F. Predicting Optimized Dissolution of Selected African Copperbelt Copper-Cobalt-Bearing Ores by Means of Neural Network Prediction and Response Surface Methodology Modeling. Process Integr. Optim. Sustain. 2023, 7, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengo, M.L.; Kime, M.-B.; Mambwe, M.P.; Nyembo, T.K. A Review of the Beneficiation of Copper-Cobalt-Bearing Minerals in the Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Sustain. Min. 2019, 18, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijsseling, L.T.; Dehaine, Q.; Rollinson, G.K.; Glass, H.J. Flotation of mixed oxide sulphide copper-cobalt minerals using xanthate, dithiophosphate, thiocarbamate and blended collectors. Miner. Eng. 2019, 138, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaine, Q.; Tijsseling, L.T.; Rollinson, G.K.; Glass, H.J. Flotation of a copper-cobalt sulphide ore: Quantitative insights into the role of mineralogy. Miner. Eng. 2024, 218, 108958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.S.; Wang, M.T.; Zhang, G.F.; Gao, Y.Q. Selective depression and adsorption of a novel eco-friendly depressant on the flotation separation of chalcopyrite from carrollite. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 695, 134290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, G.B.; Liu, Y.Y.; Tong, L.L.; Jin, Z.N.; Liu, Z.L. Function of microorganism and reaction pathway for carrollite dissolution during bioleaching. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
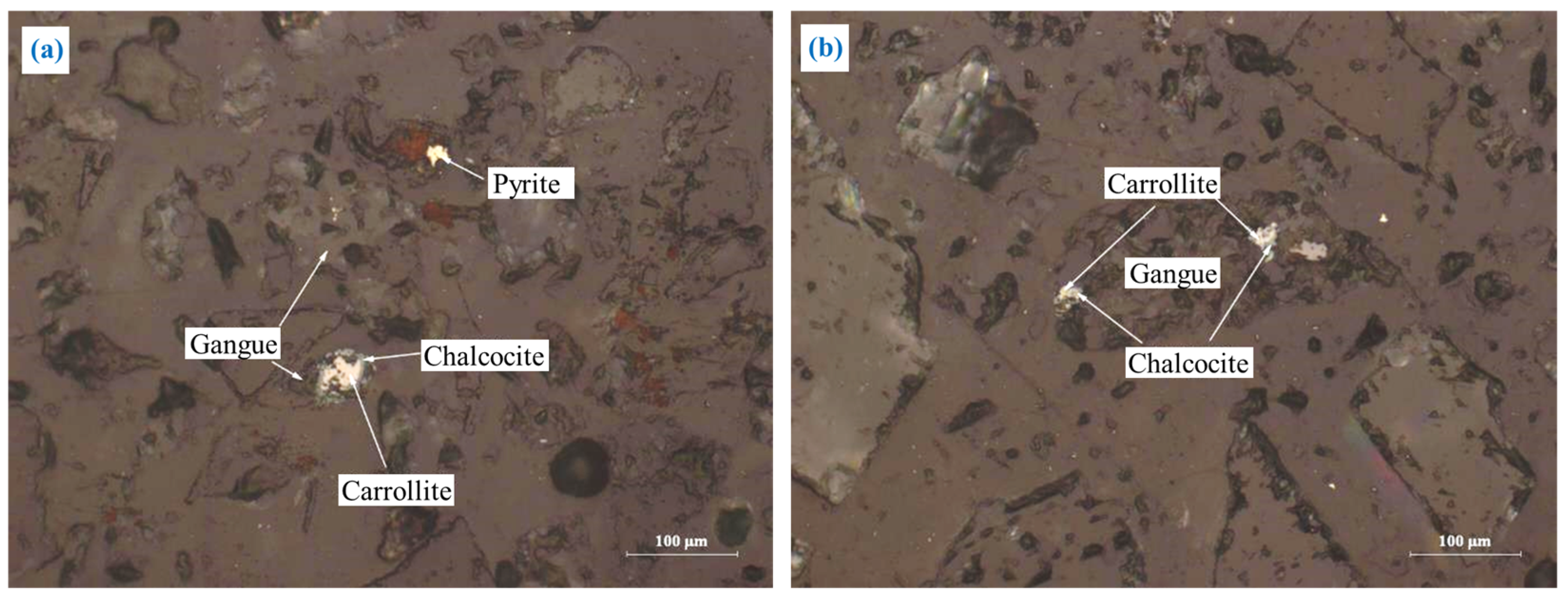






| Component | Cu | Co | Pb | Zn | S | Fe | Mo |
| Content (%) | 1.26 | 0.58 | 0.005 | <0.005 | 1.51 | 1.58 | 0.001 |
| Component | C | SiO2 | Al2O3 | K2O | Na2O | CaO | MgO |
| Content (%) | 6.22 | 38.00 | 2.15 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 14.71 | 13.50 |
| Mineral | Content | Mineral | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) | 2.14 | Dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) | 47.83 |
| Bornite (Cu5FeS4) | 0.26 | Quartz (SiO2) | 33.87 |
| Chalcocite (Cu2S) | 0.18 | Chlorite | 6.38 |
| Malachite (Cu2CO3 (OH)2) | 0.01 | Talc (Mg3Si4O10(OH)2) | 2.92 |
| Carrollite (CuCo2S4) | 1.18 | Kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) | 1.52 |
| Spherocobaltite (CoCO3) | 0.02 | Muscovite mica | 0.85 |
| Heterogenite (CoO(OH)) | 0.01 | Albite (NaAlSi3O8) | 0.76 |
| Pyrite (FeS2) | 0.37 | Potash feldspar (KAlSi3O8) | 0.36 |
| Hematite (Fe2O3) | 0.51 | Magnesite (MgCO3) | 0.20 |
| Limonite (Fe2O3·nH2O) | 0.19 | Calcite (CaCO3) | 0.02 |
| Galena (PbS) | 0.01 | Others | 0.41 |
| Particle Size/mm | Content/% | Cumulant/% |
|---|---|---|
| +1.168 | 2.60 | 2.60 |
| 1.168–0.833 | 9.16 | 11.76 |
| 0.833–0.589 | 9.12 | 20.88 |
| 0.589–0.417 | 9.21 | 30.10 |
| 0.417–0.295 | 9.13 | 39.23 |
| 0.295–0.208 | 7.97 | 47.20 |
| 0.208–0.147 | 8.15 | 55.35 |
| 0.147–0.104 | 8.77 | 64.12 |
| 0.104–0.074 | 9.46 | 73.58 |
| 0.074–0.043 | 10.62 | 84.20 |
| 0.043–0.020 | 9.09 | 93.29 |
| 0.020–0.015 | 2.24 | 95.53 |
| 0.015–0.010 | 1.54 | 97.07 |
| −0.010 | 2.93 | 100 |
| Percentage of −0.074 mm Particles/% | Liberation Degree/% | Locked Particles/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| With Gangue | In Gangue | ||
| 60 | 69.27 | 24.59 | 6.14 |
| 65 | 75.41 | 20.47 | 4.12 |
| 70 | 81.61 | 15.00 | 3.39 |
| 75 | 86.77 | 10.21 | 3.02 |
| 80 | 91.05 | 6.32 | 2.63 |
| Conditions | Variables | Other Flotation Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding fineness | −0.074 mm particles: 60%, 65%, 70%, 75%, 80% | CaO 700 g/t, NaHS 300 g/t, SIPX 60 g/t, Z-200 35 g/t, PO 28 g/t |
| Dosage of CaO | 0, 500, 700, 1000, 1500 (g/t) | −0.074 mm particles 80%, NaHS 300 g/t, SIPX 60 g/t, Z-200 35 g/t, PO 28 g/t |
| Dosage of NaHS | 0, 100, 300, 400 (g/t) | −0.074 mm particles 80%, CaO 500 g/t, SIPX 60 g/t, Z-200 35 g/t, PO 28 g/t |
| Dosage of Z-200 | 21, 28, 35, 42, 56 (g/t) | −0.074 mm particles 80%, CaO 500 g/t, NaHS 300 g/t, SIPX 60 g/t, PO 28 g/t |
| Product | Yield/% | Grade/% | Recovery/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Co | Cu | Co | ||
| Concentrate | 4.06 | 27.23 | 10.88 | 85.52 | 78.13 |
| Middling 1 | 0.90 | 4.85 | 1.91 | 3.38 | 3.04 |
| Middling 2 | 1.37 | 1.60 | 0.76 | 1.70 | 1.85 |
| Middling 3 | 6.70 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 2.70 | 3.34 |
| Middling 4 | 3.32 | 0.99 | 0.34 | 2.53 | 2.00 |
| Middling 5 | 1.86 | 0.53 | 0.20 | 0.76 | 0.65 |
| Tailings | 81.79 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 3.41 | 10.99 |
| Raw ore | 100 | 1.29 | 0.57 | 100 | 100 |
| Product | Yield/% | Grade/% | Recovery/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Co | Cu | Co | ||
| Concentrate | 4.92 | 24.43 | 9.78 | 94.47 | 86.35 |
| Tailings | 95.08 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 5.53 | 13.65 |
| Raw ore | 100 | 1.27 | 0.56 | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Ba, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, T.; Fang, C. Process-Mineralogy-Guided Flotation for Cu-Co Recovery: A Case Study of DRC Copper–Cobalt Sulfide Ore. Processes 2025, 13, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030918
Shi Y, Wang J, Ba H, Liu W, Yang Y, Liu X, Chen T, Fang C. Process-Mineralogy-Guided Flotation for Cu-Co Recovery: A Case Study of DRC Copper–Cobalt Sulfide Ore. Processes. 2025; 13(3):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030918
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yuchen, Jun Wang, Hongfei Ba, Wei Liu, Yiquan Yang, Xinyu Liu, Tianhao Chen, and Chaojun Fang. 2025. "Process-Mineralogy-Guided Flotation for Cu-Co Recovery: A Case Study of DRC Copper–Cobalt Sulfide Ore" Processes 13, no. 3: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030918
APA StyleShi, Y., Wang, J., Ba, H., Liu, W., Yang, Y., Liu, X., Chen, T., & Fang, C. (2025). Process-Mineralogy-Guided Flotation for Cu-Co Recovery: A Case Study of DRC Copper–Cobalt Sulfide Ore. Processes, 13(3), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030918






