Automatic Active Contour Algorithm for Detecting Early Brain Tumors in Comparison with AI Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
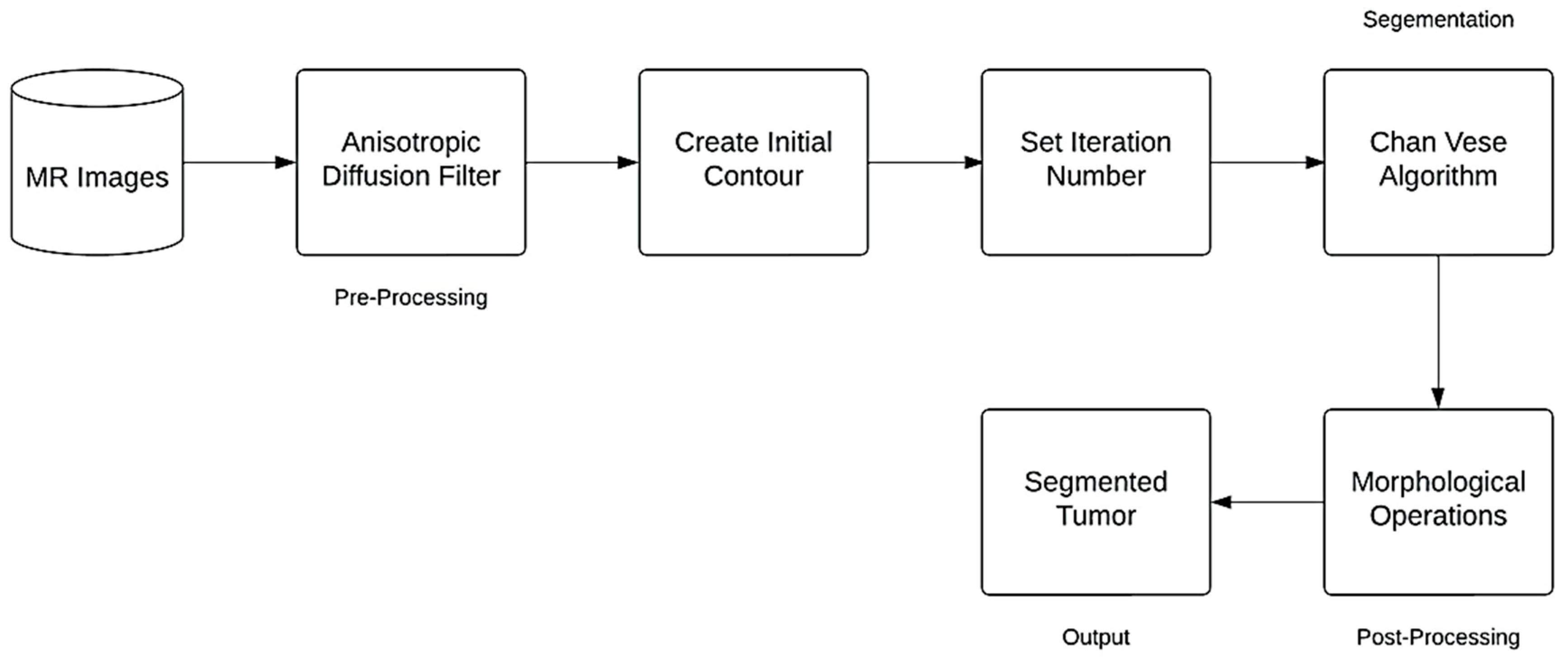
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Anisotropic Diffusion Filter
2.2.2. Contour Initialization
2.2.3. Chan-Vese Algorithm
2.2.4. Post-Processing Method
2.3. Performance Evaluation Measures
2.3.1. Accuracy
2.3.2. Precision
2.3.3. Sensitivity
2.3.4. Specificity
2.3.5. Jaccard Index
2.3.6. Dice Index Coefficient
2.3.7. Hausdorff Distance
3. Results
3.1. Proposed Method Results
3.2. Performance Evaluation Measures Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saini, A.; Kumar, M.; Bhatt, S.; Saini, V.; Malik, A. Cancer causes and treatments. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2020, 11, 3121–3134. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, V.; Kochar, P. Brain cancer: Implication to disease, therapeutic strategies and tumour targeted drug delivery approaches. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A. Benign vs malignant tumours. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, J.; Sharif, M.; Yasmin, M.; Fernandes, S.L. A distinctive approach in brain tumour detection and classification using MRI. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 139, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, E.; Stadlbauer, A.; Windischberger, C.; Quick, H.H.; Ladd, M.E. Magnetic resonance imaging methodology. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Monolisa, G.; Saranya, K. A cluster based segmentation of magnetic resonance images for brain tumour detection. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2013, 14, 669–672. [Google Scholar]
- Lerch, J.P.; van der Kouwe, A.J.W.; Raznahan, A.; Paus, T.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Miller, K.L.; Smith, S.M.; Fischl, B.; Sotiropoulos, S.N. Studying neuroanatomy using MRI. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejer-Oleńska, E.; Wojtkiewicz, J. Utilization of MRI technique in the patient population admitted between 2011 and 2015 to the University Clinical Hospital in Olsztyn. Pol. Ann. Med. 2017, 24, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasung, L.; Turk, E.A.; Ferradal, S.L.; Sutin, J.; Stout, J.N.; Ahtam, B.; Lin, P.-Y.; Grant, P.E. Exploring early human brain development with structural and physiological neuroimaging. Neuroimage 2018, 187, 226–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, T.; Dervenoulas, G.; Politis, M. Advances in MRI methodology. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2018, 141, 31–76. [Google Scholar]
- Jalab, H.A.; Hasan, A.M. Magnetic resonance imaging segmentation techniques of brain tumours: A review. Arch. Neurosci. 2019, 6, e84920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harouni, M.; Karimi, M.; Rafieipour, S. Precise segmentation techniques in various medical images. In Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 117–166. [Google Scholar]
- Havaei, M.; Davy, A.; Warde-Farley, D.; Biard, A.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y.; Pal, C.; Jodoin, P.-M.; Larochelle, H. Brain tumour segmentation with deep neural networks. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Işın, A.; Direkoğlu, C.; Şah, M. Review of MRI-based brain tumour image segmentation using deep learning methods. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 102, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, A.; Khan, Z.; Aslam, F.; Jawed, S.; Shafique, A.; Ali, H. A review: Recent automatic algorithms for the segmentation of brain tumour MRI. In AI and IoT for Sustainable Development in Emerging Countries: Challenges and Opportunities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 505–522. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbarzadeh, R.; Caputo, A.; Tirkolaee, E.B.; Ghoushchi, S.J.; Bendechache, M. Brain tumour segmentation of MRI images: A comprehensive review on the application of artificial intelligence tools. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Verma, V.S. A review on brain tumour segmentation of MRI images. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 61, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A. An automatic brain tumour extraction system using different segmentation methods. In Proceedings of the 2016 Second International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology (CICT), Ghaziabad, India, 12–13 February 2016; pp. 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.S.; Karunakara, K. A comprehensive review on brain tumour segmentation and classification of MRI images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 17611–17643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Singh, V.K.; Trivedi, M.C. Brain tumour segmentation in magnetic resonance imaging using OKM approach. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.; Indira, N.; Prasad, K.V.; Shameem, S. An effective brain tumour detection from t1w MR images using active contour segmentation techniques. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1804, 012174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, C.J.J.; Suganthi, G. Brain tumour segmentation with radius contraction and expansion based initial contour detection for active contour model. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 23793–23819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, C.J.J.; Suganthi, G. Automatic brain tumour segmentation from MRI using greedy snake model and fuzzy C-means optimization. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleid, A.; Alhussaini, K.; Alanazi, R.; Altwaimi, M.; Altwijri, O.; Saad, A.S. Artificial Intelligence Approach for Early Detection of Brain Tumors Using MRI Images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Qureshi, A.N.; Li, J.; Mahmood, T. On the analyses of medical images using traditional machine learning techniques and convolutional neural networks. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 3173–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandel, G.S.; Biswas, M.; Kakde, O.G.; Tiwari, A.; Suri, H.S.; Turk, M.; Laird, J.R.; Asare, C.K.; Ankrah, A.A.; Khanna, N.N.; et al. A review on a deep learning perspective in brain cancer classification. Cancers 2019, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aamir, M.; Namoun, A.; Munir, S.; Aljohani, N.; Alanazi, M.H.; Alsahafi, Y.; Alotibi, F. Brain Tumor Detection and Classification Using an Optimized Convolutional Neural Network. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menze, B.H.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R.; et al. The multimodal brain tumour image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing the cancer genome atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the TCGA-LGG collection. Cancer Imaging Arch. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perona, P.; Malik, J. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Workshop on Computer Vision, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 30 November–2 December 1987; pp. 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Perona, P.; Malik, J. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion (PDF). IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1990, 12, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.F.; Vese, L.A. Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towards Data Science. How to Evaluate Image Segmentation Models. Medium. Towards Data Science. 2020. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-accurate-is-image-segmentation-dd448f896388 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Fernandes, S.L.; Tanik, U.J.; Rajinikanth, V.; Karthik, K.A. A reliable framework for accurate brain image examination and treatment planning based on early diagnosis support for clinicians. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 15897–15908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, C.J.J.; Suganthi, G. Accurate MRI brain tumour segmentation based on rotating triangular section with fuzzy C-means optimization. Sādhanā 2021, 46, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisaeng, K. U-Net++DSM: Improved U-Net++ for brain tumor segmentation with deep supervision mechanism. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 132268–132285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umarani, C.M.; Gollagi, S.G.; Allagi, S.; Sambrekar, K.; Ankali, S.B. Advancements in deep learning techniques for brain tumor segmentation: A survey. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2024, 50, 101576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

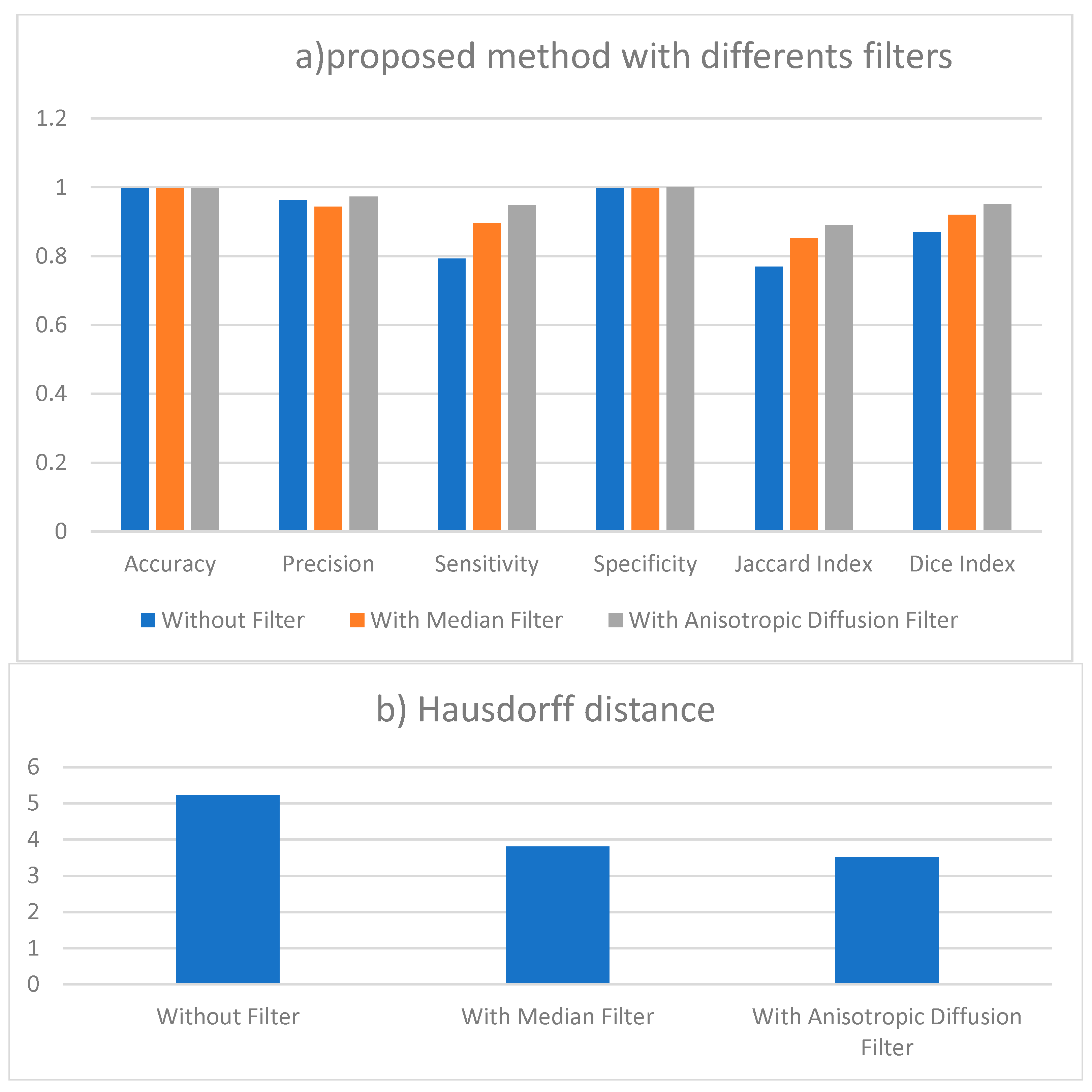

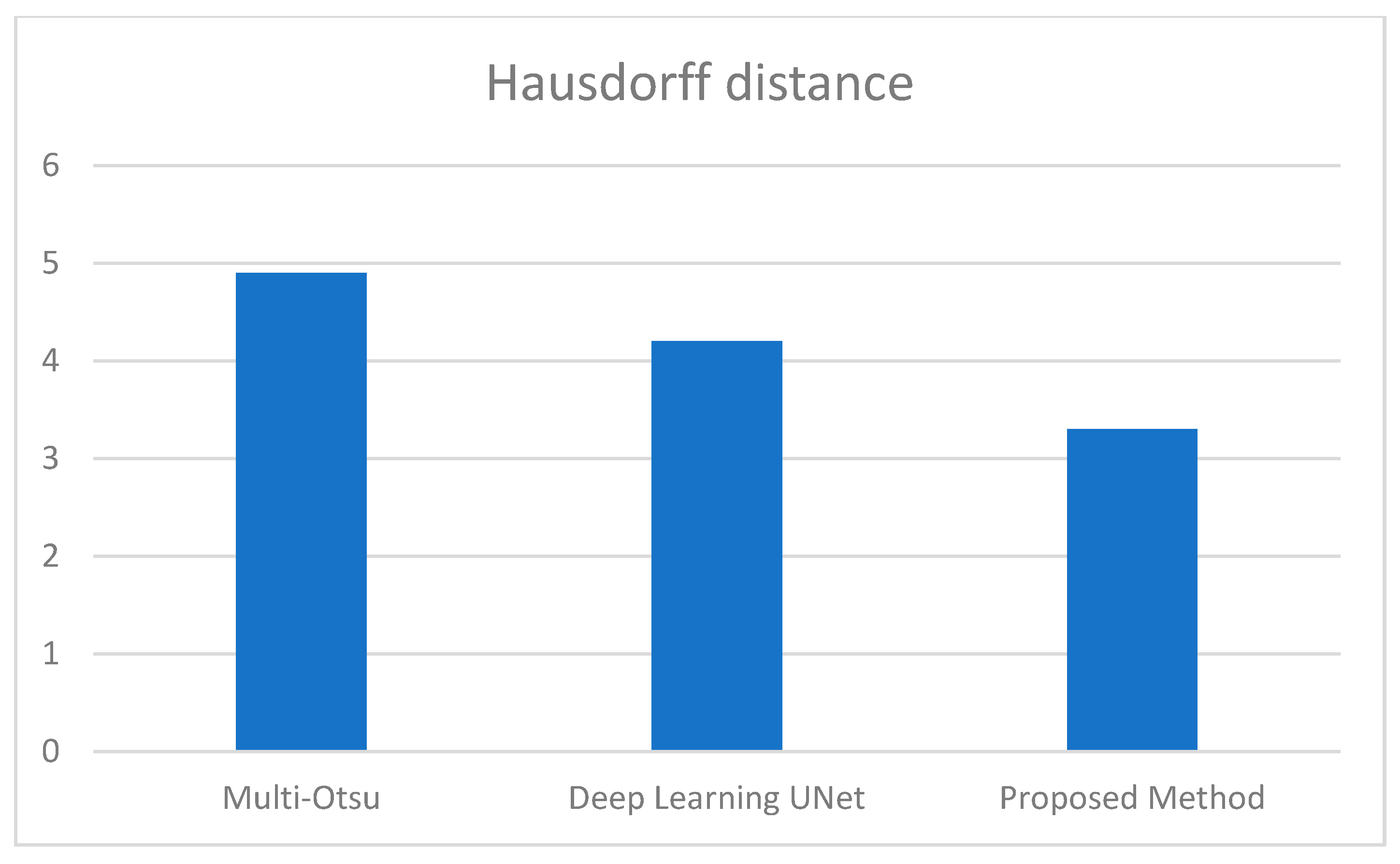
| Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | Jaccard Index | Dice Index | Hausdorff Distance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Filter | 0.997 | 0.963 | 0.793 | 0.997 | 0.769 | 0.869 | 5.217 |
| With Median Filter | 0.998 | 0.944 | 0.897 | 0.998 | 0.852 | 0.92 | 3.8 |
| With Anisotropic Diffusion Filter | 0.998 | 0.973 | 0.948 | 0.999 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 3.3 |
| Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | Jaccard Index | Dice Index | Hausdorff Distance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Otsu | 0.96 | 0.943 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 4.9 |
| Deep Learning UNet | 0.96 | 0.953 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.863 | 0.87 | 4.2 |
| Proposed Method | 0.998 | 0.973 | 0.948 | 0.999 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 3.3 |
| Methods | Average Dice Index | Average Execution Time |
|---|---|---|
| Single path MLDeepMedic | 79% | ~35.6 min |
| U-Net | 85% | ~32.3 min |
| Rescue Net | 95% | 37.5 min |
| Cascaded Anistropic CNN | 87% | ~41.2 min |
| K_Mean and FCM | 67% | ~2.15 min |
| Chan Vese | 89.6% | ~3.2 min |
| Otsu, k-means | 85% | ~3.4 min |
| Multilevel HSO | 87% | ~2.3 min |
| Proposed Method | 95% | 4.2 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almijalli, M.; Almusayib, F.A.; Albugami, G.F.; Aloqalaa, Z.; Altwijri, O.; Saad, A.S. Automatic Active Contour Algorithm for Detecting Early Brain Tumors in Comparison with AI Detection. Processes 2025, 13, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030867
Almijalli M, Almusayib FA, Albugami GF, Aloqalaa Z, Altwijri O, Saad AS. Automatic Active Contour Algorithm for Detecting Early Brain Tumors in Comparison with AI Detection. Processes. 2025; 13(3):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030867
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmijalli, Mohammed, Faten A. Almusayib, Ghala F. Albugami, Ziyad Aloqalaa, Omar Altwijri, and Ali S. Saad. 2025. "Automatic Active Contour Algorithm for Detecting Early Brain Tumors in Comparison with AI Detection" Processes 13, no. 3: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030867
APA StyleAlmijalli, M., Almusayib, F. A., Albugami, G. F., Aloqalaa, Z., Altwijri, O., & Saad, A. S. (2025). Automatic Active Contour Algorithm for Detecting Early Brain Tumors in Comparison with AI Detection. Processes, 13(3), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030867








