Evaluation of the Complex Impact of Major Factors and Derivation of Important Priorities in the Wastewater Treatment Process for Nutrient Removal Using Multiple Regression Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phase-Separated BNR Process for Biological Nutrient Removal
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overall Performances and Complex Influence of Various Environmental and Operating Factors
3.2. Multiple Regression Analysis for Deriving Major Influencing Factors on Nitrogen Removal
3.3. Multiple Regression Analysis for Deriving Major Influencing Factors on Phosphorus Removal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, J.; Nakhla, G. Interaction of denitrification and P removal in anoxic P removal system. Desalination 2006, 201, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.; Tayà, C.; Guisasola, A.; Baeza, J.A. Understanding the detrimental effect of nitrate presence on EBPR systems: Effect of the plant configuration. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 1508–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Stensel, H.D.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Burton, F. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Resource Recovery, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Xue, T.; Li, B.; Dai, X.; Peng, Y. Treating low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) wastewater in simultaneous nitrification-endogenous denitrification and phosphorus removal (SNDPR) systems by strengthening anaerobic intracellular carbon storage. Water Res. 2015, 77, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisawi, H.A.O. Performance of wastewater treatment during variable temperature. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, M.V.; Ribes, J.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J. An advanced control strategy for biological nutrient removal in continuous systems based on pH and ORP sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostace, G.S.; Baeza, J.A.; Guerrer, J.; Guisasola, A.; Cristea, V.M.; Agachi, P.S.; Lafuente, J. Development and economic assessment of different WWTP control strategies for optimal simultaneous removal of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2013, 53, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheumann, R.; Kraume, M. Influence of hydraulic retention time on the operation of a submerged membrane sequencing batch reactor (SM-SBR) for the treatment of greywater. Desalination 2009, 246, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, P.; Tang, T.; Hu, Z. Roles of SRT and HRT of an algal membrane bioreactor system with a tanks-in-series configuration for secondary wastewater effluent polishing. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 85, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wu, D.; Hu, Z. Impact of hydraulic retention time on organic and nutrient removal in a membrane coupled sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 2014, 55, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigger, G.T.; Littleton, H.X. Characterization of simultaneous nutrient removal in staged, closed-loop bioreactors. Water Environ. Res. 2000, 72, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, G.; Lemaire, R.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. Effectiveness of an alternating aerobic, anoxic/anaerobic strategy for maintaining biomass activity of BNR sludge during long-term starvation. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2590–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayà, C.; Guisasola, A.; Baeza, J.A. Assessment of a bioaugmentation strategy with polyphosphate accumulating organisms in a nitrification/denitrification sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7678–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Truax, D.D.; Magbanua, B.S. Optimization of operating parameters of intermittent aeration-type activated sludge process for nitrogen removal: A simulation-based approach. Water Environ. Res. 2011, 83, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, P.; Izadi, P.; Eldyasti, A. Enhancement of simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal using intermittent aeration mechanism. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 109, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.P.; Min, S.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Park, J.U.; Kim, M.S. A study on the influence of a sewage treatment plant’s operational parameters using the multiple regression analysis model. Environ. Eng. Res. 2014, 19, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat, S.; Altowayti, W.A.H.; Othman, N.; Asharuddin, S.M.; Saeed, F.; Basurra, S.; Eisa, T.A.E.; Shahir, S. Prediction of wastewater treatment plant performance using multivariate statistical analysis: A case study of a regional sewage treatment plant in Melaka, Malaysia. Water 2022, 14, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Multiple linear regression. Nat. Methods. 2015, 12, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.R.; Speckman, P.L. Multivariate regression trees for analysis of abundance data. Biometrics 2004, 60, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanen, J.; Sahlstedt, K.; Miettinen, K. Wastewater treatment plant design and operation under multiple conflicting objective functions. Environ. Model Softw. 2013, 46, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg, C. Regression Analysis Microsoft Excel, 1st ed.; Que Publishing: Seattle, WA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Lu, G.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics of pellets with immobilized activated sludge and its performance in increasing nitrification in sequencing batch reactors at low temperatures. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 42, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, F.; Guo, F.; Ye, L.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic analysis on seasonal microbial variations of activated sludge from a full-scale wastewater treatment plant over 4 years. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Hang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Yu, H. Tuning of activated sludge in winter based on respirogram profiles under standard and site temperatures. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, Y.; Dong, S.; Lan, S.; Zhou, H.; Tan, Z.; Li, X. Mixed nitrifying bacteria culture under different temperature dropping strategies: Nitrification performance, activity, and community. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; Wu, M.; Xing, M.; Yang, J.; Gao, N.; Pan, M. Impacts of temperature and nitrifying community on nitrification kinetics in a moving-bed biofilm reactor treating polluted raw water. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, M.A.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A. Bioaugmentation for nitrification at cold temperatures. Water Res. 2004, 38, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, L.; Peng, D.; Wei, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L. Nitrogen removal from an AAO pilot plant with nitrifier bioaugmentation after seasonal deterioration. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 5136–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.H.; Chang, D.; Kang, S.W.; Hur, J.M.; Han, S.B.; Sunwoo, Y. Effect of cycle length and phase fraction on biological nutrients removal in temporal and spatial phase separated process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D.A. Statistical Models: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kvam, P.; Vidakovic, B.; Kim, S. Nonparametric Statistics with Applications to Science and Engineering with R, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.; Cohen, P.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. Applied Multiple Regression: Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Timothy, Z.K. Multiple Regression and Beyond: An Introduction to Multiple Regression and Structural Equation Modeling, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Meeker, W.; Escobar, L.; Pascual, F. Statistical Methods for Reliability Data, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Sood, S.; Mishra, S. Development of multiple linear regression model for biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) removal efficiency of different sewage treatment technologies in Delhi, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahs-Vaughn, D.L.; Lomax, R.G. Statistical Concepts: A Second Course; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Salkind, N.; Frey, B. Statistics for People Who (Think They) Hate Statistics: Using Microsoft Excel, 5th ed.; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wassersteina, R.L.; Lazara, N.A. The ASA Statement on p-Values: Context, Process, and Purpose. Am. Stat. 2016, 78, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiese, M.S.; Ronna, B.; Ott, U. p value interpretations and considerations. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E928–E931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Y. Effects of rapid temperature rising on nitrogen removal and microbial community variation of an-oxic/aerobic process for ABS resin wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 5509–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Luo, W.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L. Effects of temperature on the characteristics of nitrogen removal and microbial community in post solid-phase denitrification biofilter process. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019, 16, 4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



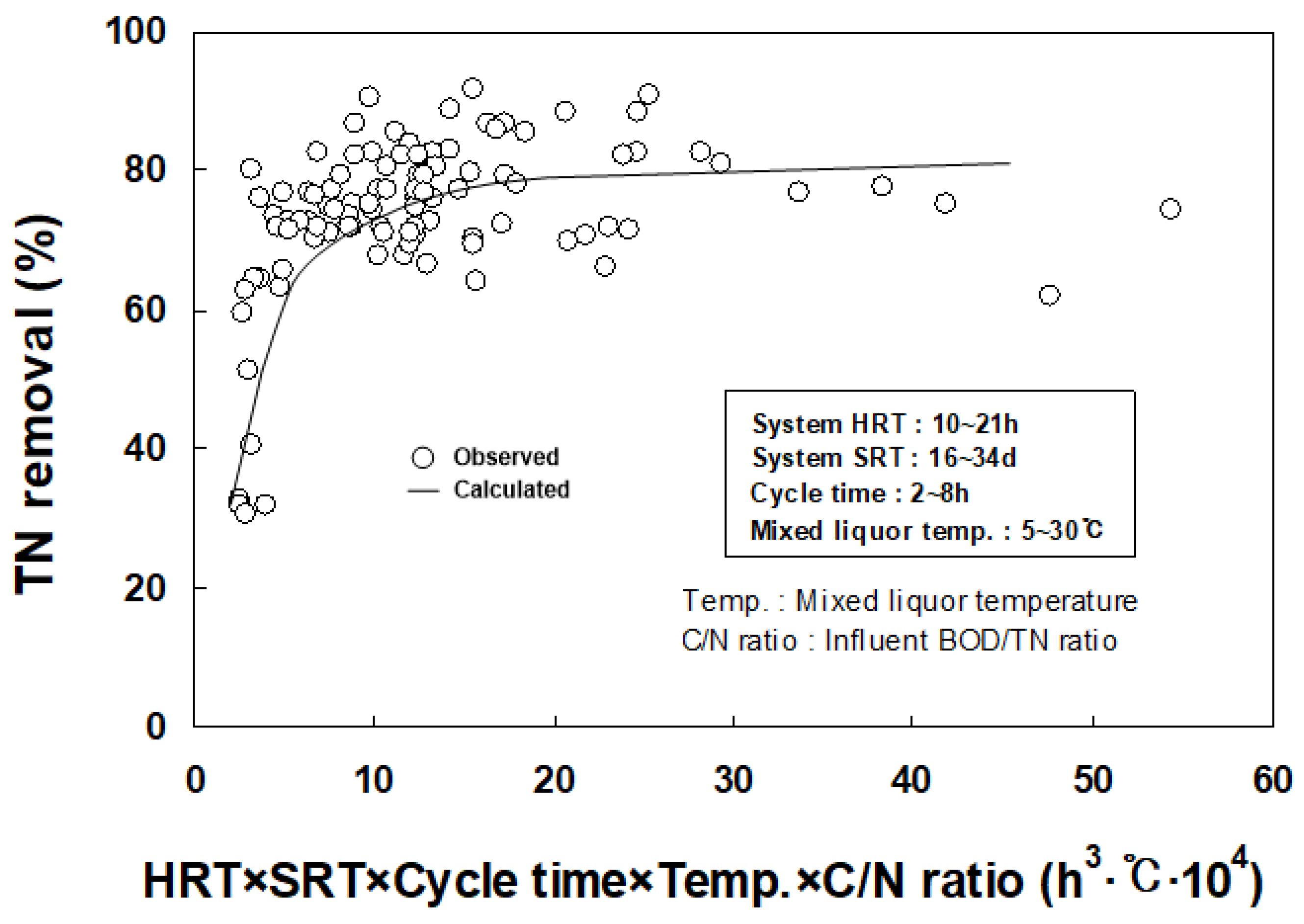

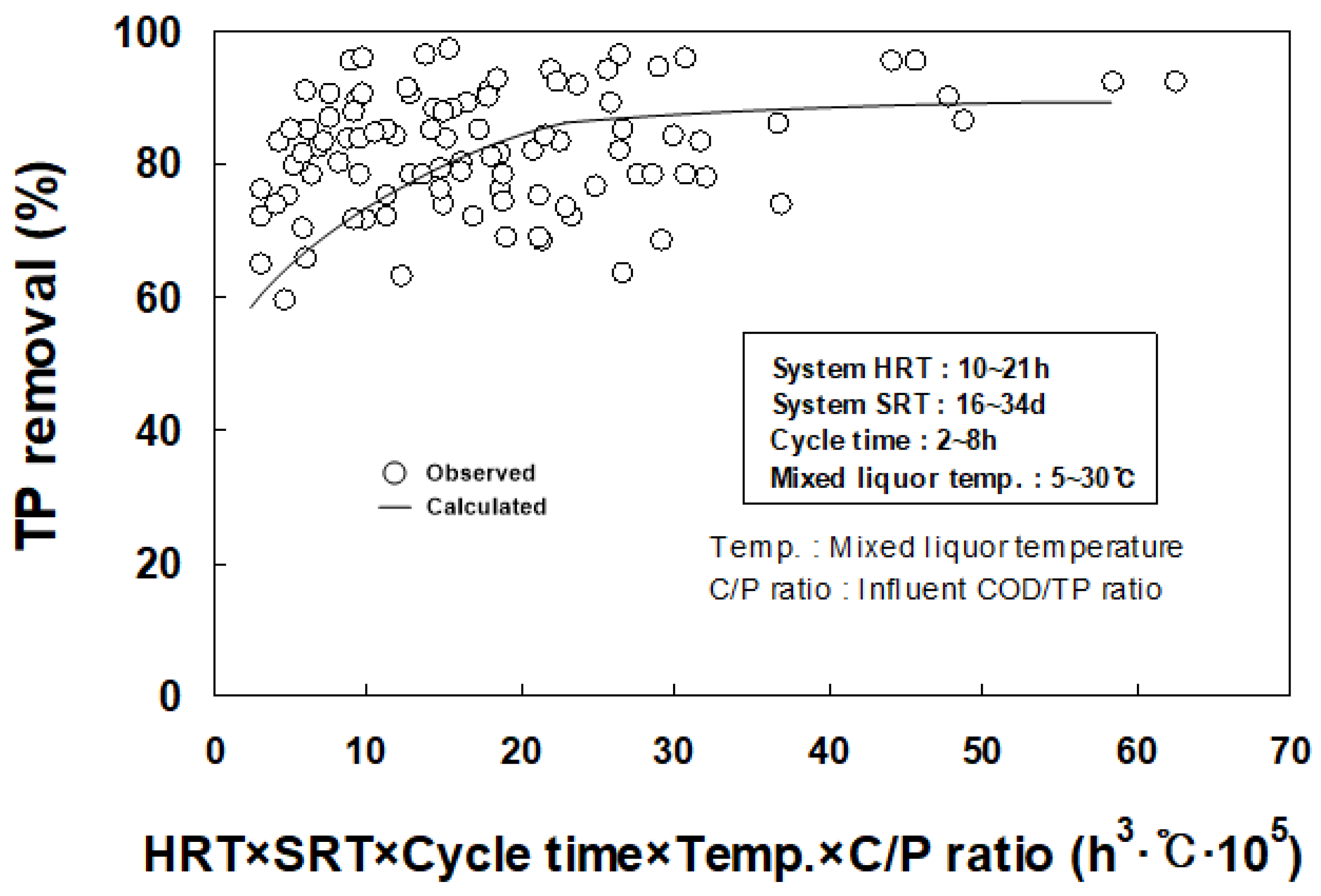
| Parameters | HRT (Based on the Volume Excluding the Intrachannel Clarifier) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 h | 14 h | 21 h | |||||||
| Flowrate: 76.8 m3/d | Flowrate: 54.9 m3/d | Flowrate: 36.6 m3/d | |||||||
| Influent | Effluent | Removals (%) | Influent | Effluent | Removals (%) | Influent | Effluent | Removals (%) | |
| Water temperature (°C) | 18–29 (24) | 22–30 (25) | - | 15–28 (21) | 10–30 (19) | - | 18–23 (20) | 20–24 (22) | - |
| pH | 6.9–7.4 (7.2) | 6.7–7.2 (7.0) | - | 6.9–8.2 (7.2) | 6.9–7.7 (7.2) | - | 6.8–7.8 (7.4) | 6.8–7.4 (7.2) | - |
| CODCr (mg/L) | 165–315 (250) | 10–35 (20) | 81.8–96.8 (93.8) | 135–430 (285) | 15–65 (28) | 80.0–95.5 (89.9) | 240–270 (250) | 20–35 (30) | 86.0–92.0 (88.1) |
| BOD (mg/L) | 130–150 (140) | 5–10 (8) | 92.3–96.6 (94.6) | 96–250 (150) | 2–15 (8) | 89.6–98.7 (94.7) | 100–150 (120) | 4–10 (6) | 90.0–97.3 (94.7) |
| TN (mg/L) | 24.2–37.9 (31.5) | 4.3–12.2 (9.6) | 67.8–83.2 (76.7) | 31.7–54.0 (38.6) | 2.7–10.2 (8.4) | 64.5–93.2 (77.5) | 32.3–36.0 (33.9) | 9.9–12.9 (10.9) | 64.1–71.3 (67.9) |
| TP (mg/L) | 4.38–6.15 (4.89) | 0.36–1.20 (0.59) | 89.7–97.2 (91.3) | 2.80–6.84 (4.84) | 0.14–1.56 (0.9) | 65.4–97.6 (82.3) | 3.54–4.72 (4.15) | 0.98–1.50 (1.15) | 63.4–78.5 (72.2) |
| TSS (mg/L) | 80–250 (135) | 5–20 (10) | 83.3–96.4 (88.2) | 85–280 (155) | 3–27 (16) | 81.7–94.3 (89.1) | 100–170 (130) | 12–23 (16) | 83.8–92.9 (87.6) |
| VSS (mg/L) | 35–230 (120) | 5–15 (7) | 82.4–97.8 (91.9) | 70–245 (120) | 3–25 (11) | 81.0–97.8 (90.7) | 88–135 (115) | 8–18 (12) | 86.7–93.6 (89.3) |
| SRT (d) | 29–32 (31) | 16–34 (25) | 23–36 (27) | ||||||
| MLSS (mg/L) | 1830–4580 (3390) | 2280–4070 (3140) | 2640–3880 (3390) | ||||||
| Regression statistic | |||||
| Multiple correlation coefficient | 0.778690051 | ||||
| Coefficient of determination(R2) | 0.637146384 | ||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.618048826 | ||||
| Standard error | 0.156201799 | ||||
| Number | 101 | ||||
| Variance analysis | |||||
| Degree of freedom | Degree of squares | Mean square | F-ratio | Significant F-ratio | |
| Regress | 5 | 1.874714923 | 0.374942985 | 15.36714433 | 4.72567 × 10−11 |
| Residuals | 95 | 2.317905186 | 0.024399002 | ||
| Total | 100 | 4.192620109 | |||
| Coefficient | Standard error | t-statistic | p-value | Lower 95% | |
| ln[A] | 2.53285708 | 0.360409921 | 7.027711865 | 3.16736 × 10−10 | 1.817353434 |
| ln[HRT] | 0.301356561 | 0.103834028 | 2.902290967 | 0.004604693 | 0.095220101 |
| ln[SRT] | 0.148289919 | 0.064780729 | 2.289105426 | 0.024288129 | 0.019684003 |
| ln[Cycle time] | −0.126020924 | 0.071734981 | −1.756756915 | 0.072181346 | −0.268432765 |
| ln[Temp.] | 0.239140707 | 0.03925371 | 6.092180975 | 2.36338 × 10−8 | 0.161212295 |
| ln[C/N ratio] | 0.026278969 | 0.073800953 | 0.356078994 | 0.082257095 | 0.172792281 |
| Regression statistic | |||||
| Multiple correlation coefficient | 0.748108769 | ||||
| Coefficient of determination (R2) | 0.620044976 | ||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.609521027 | ||||
| Standard error | 0.085134199 | ||||
| Number | 101 | ||||
| Variance analysis | |||||
| Degree of freedom | Degree of squares | Mean square | F-ratio | Significant F-ratio | |
| Regress | 5 | 0.498692904 | 0.099738581 | 13.76116115 | 4.19653 × 10−10 |
| Residuals | 95 | 0.688544017 | 0.007247832 | ||
| Total | 100 | 1.187236922 | |||
| Coefficient | Standard error | t-statistic | p-value | Lower 95% | |
| ln[A] | 4.730344102 | 0.224303784 | 21.08900714 | 1.30583 × 10−37 | 4.285045109 |
| ln[HRT] | −0.184131911 | 0.055983305 | −3.289050407 | 0.0281 | −0.295272744 |
| ln[SRT] | −0.057220387 | 0.037278173 | −1.534956836 | 0.0027 | −0.131226866 |
| ln[Cycle time] | 0.119584995 | 0.038845472 | 3.078479682 | 0.0014 | 0.042467039 |
| ln[Temp.] | 0.150864404 | 0.021090788 | 7.153094595 | 1.75175 × 10−10 | 0.108993925 |
| ln[C/P ratio] | 0.065272286 | 0.028211388 | 2.313685739 | 0.0328 | 0.121278932 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, M.-S.; Choi, Y.-J.; Hong, K.-H. Evaluation of the Complex Impact of Major Factors and Derivation of Important Priorities in the Wastewater Treatment Process for Nutrient Removal Using Multiple Regression Analysis. Processes 2025, 13, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030833
Kang M-S, Choi Y-J, Hong K-H. Evaluation of the Complex Impact of Major Factors and Derivation of Important Priorities in the Wastewater Treatment Process for Nutrient Removal Using Multiple Regression Analysis. Processes. 2025; 13(3):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030833
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Moon-Seok, Ye-Jin Choi, and Ki-Ho Hong. 2025. "Evaluation of the Complex Impact of Major Factors and Derivation of Important Priorities in the Wastewater Treatment Process for Nutrient Removal Using Multiple Regression Analysis" Processes 13, no. 3: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030833
APA StyleKang, M.-S., Choi, Y.-J., & Hong, K.-H. (2025). Evaluation of the Complex Impact of Major Factors and Derivation of Important Priorities in the Wastewater Treatment Process for Nutrient Removal Using Multiple Regression Analysis. Processes, 13(3), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030833






