Power Load Forecasting System of Iron and Steel Enterprises Based on Deep Kernel–Multiple Kernel Joint Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
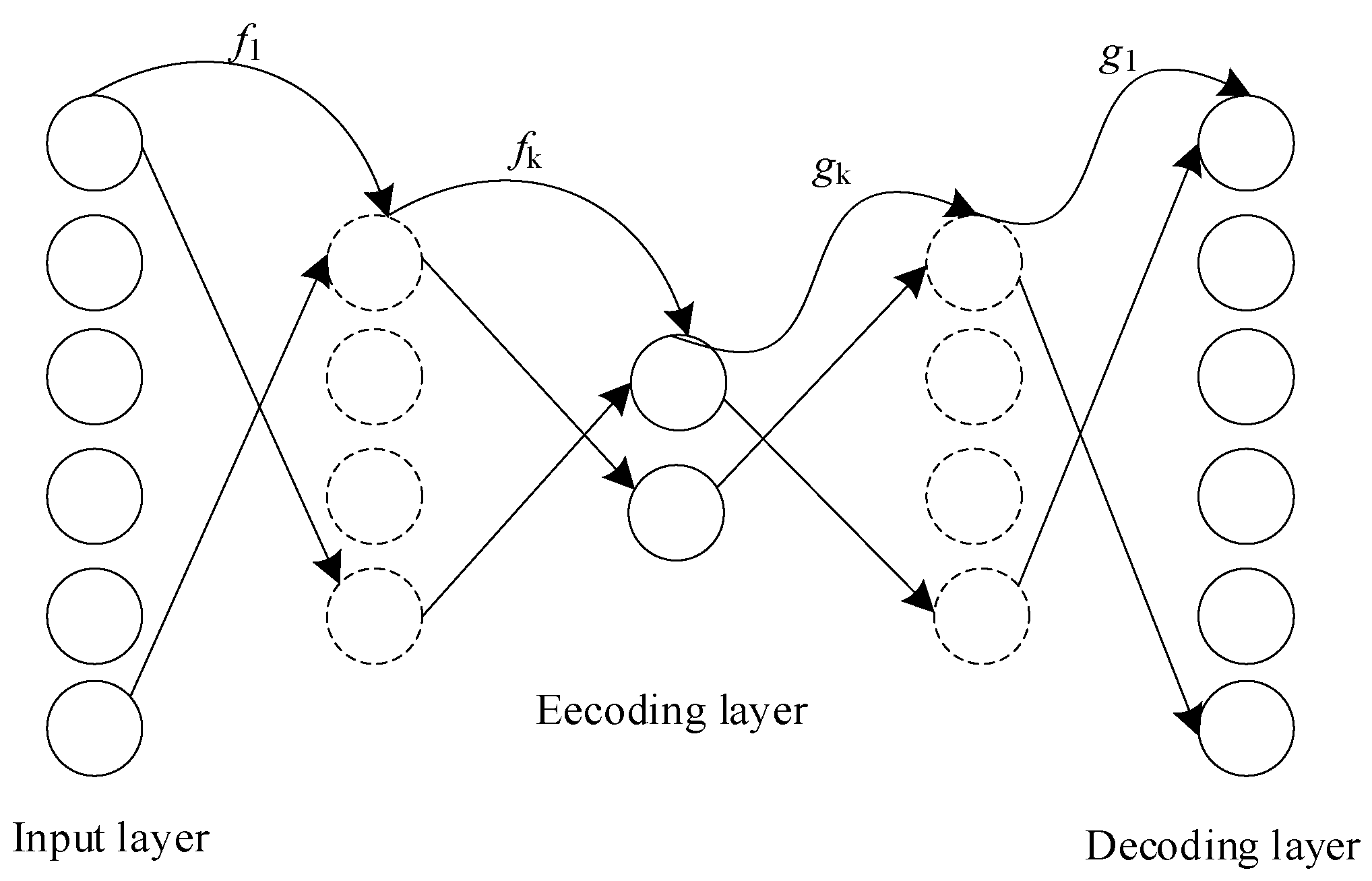
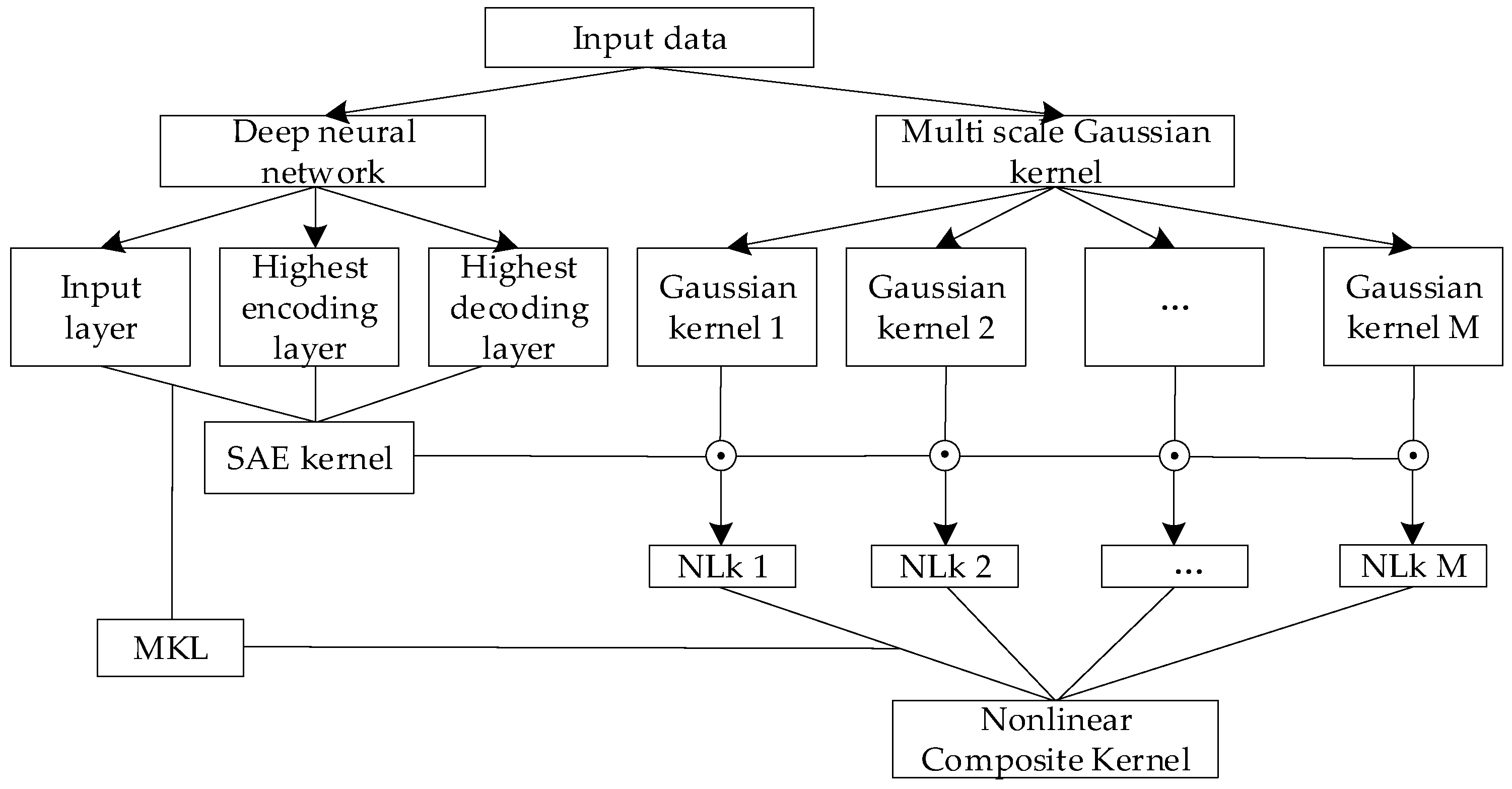
2. Deep Multi-Kernel Joint Learning Model
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Benchmark Dataset
3.2. Power Load Forecasting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, X.; Chen, F.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Peng, Y.; Pang, J. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis Method for Transformer Driven by Multiple Vibration Data. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2774, 4255–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Shen, C.; Wang, C.; Jing, T.; Liu, Z.; Xu, W. Physical Metallurgy Guided Industrial Big Data Analysis System with Data Classification and Property Prediction. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 3029–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen, M.; Alpaydin, E. Multiple kernel learning algorithms. J. Mach. Res. 2011, 12, 2211–2268. [Google Scholar]
- Anan, M.; Kanaan, K.; Benhaddou, D.; Nasser, N.; Qolomany, B.; Talei, H.; Sawalmeh, A. Occupant-Aware Energy Consumption Prediction in Smart Buildings Using a LSTM Model and Time Series Data. Energies 2024, 17, 6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Li, C.; Shen, Y.; He, A. A Hybrid Model Equipped with the Minimum Cycle Decomposition Concept for Short-Term Forecasting of Electrical Load Time Series. Neural Process. Lett. 2017, 46, 1059–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitidis, A.I.; Bargiotas, D.; Daskalopulu, A.; Laitsos, V.M.; Tsoukalas, L.H. Enhanced Short-term Load Forecasting using Artificial Neural Networks. Energies 2021, 14, 7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hu, H. Deep Kernel Mapping Support Vector Machine based on Multilayer Perceptron. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2016, 42, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Lv, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, W. Long Term Prediction Model based on Deep Denoising Kernel Mapping. Control Decis. 2019, 34, 989–996. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Dong, J.; Peng, K. A Novel Hierarchical Detection and Isolation Framework for Quality-related Multiple Faults in Large-scale Processes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.F.; Yu, H.; Wang, G. A Quality-related Fault Detection Approach Based on Dynamic Least Squares for Process Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 63, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhang, H. Multiple Kernel Learning for Label Relation and Class Imbalance in Multi-label Learning. Inf. Sci. 2022, 613, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Li, S.; Yu, F. Ulta-short-term and Short-term Power Load Single-step and Multi-step Prediction Considering Spatial Association. Comput. Eng. 2024, 7, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Aiolli, F.; Donini, M. Easymkl. A Scalable Multiple Kernel Learning Algorithm. Neurocomputing 2015, 169, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Research on Theory and Algorithm of Support Vector Machine. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanzadeh, S.; Danyali, H.; Karami, A.; Helfroush, M.S. A Novel Graph-Based Multiple Kernel Learning Framework for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 3075–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W. Bridging Deep and Multiple Kernel Learning: A Review. Inf. Fusion 2021, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uğurel, E.; Huang, S.; Chen, C. Learning to Generate Synthetic Human Mobility Data: A Physics-Regularized Gaussian Process Approach based on Multiple Kernel Learning. Transp. Res. Part B 2024, 189, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Kurata, E. An Efficient Kernel Machine Technique for short-term Load Forecasting under Smart Grid Environment. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, L.; Baladron, C.; Aguiar, J.M.; Carro, B.; Sanchez-Esguevillas, A.; Lloret, J. Artifical Neural Networks for Short-term Load Forecasting in Microgrids Environment. Energy 2014, 75, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

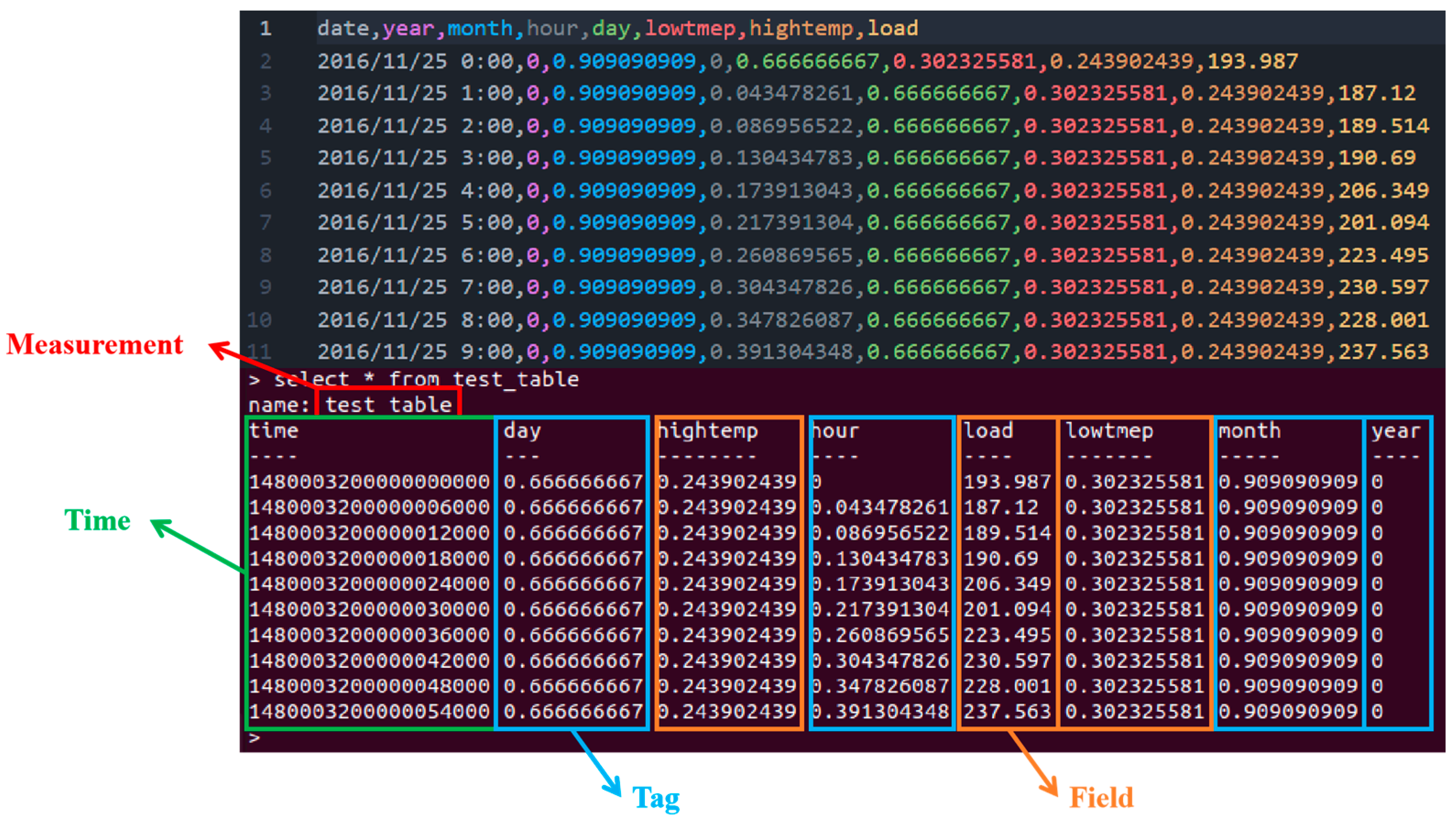

| Serial | Dataset | Sample Size | Dimension | LSVM-MKL/ Before Optimization | ElmanNeural Network/ Before Optimization | Seq2Seqmodel/ BeforeOptimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MON1 | 124 + 432 | 6 | 87.73 ± 0.01/66.46 ± 0.00 | 86.04 ± 0.17/67.25 ± 0.62 | 87.18 ± 0.28/66.65 ± 0.01 |
| 2 | MON2 | 169 + 432 | 6 | 86.66 ± 0.28/65.60 ± 0.01 | 86.60 ± 0.24/73.38 ± 0.01 | 84.19 ± 0.36/65.19 ± 1.10 |
| 3 | MON3 | 122 + 432 | 6 | 95.37 ± 0.01/82.28 ± 0.10 | 95.14 ± 0.01/82.12 ± 0.90 | 95.08 ± 0.11/81.94 ± 0.00 |
| 4 | HOR | 300 + 68 | 25 | 83.82 ± 0.01/80.81 ± 1.09 | 83.75 ± 0.73/80.88 ± 0.00 | 87.13 ± 0.64/81.32 ± 1.05 |
| 5 | OOC1 | 1022 | 40 | 79.24 ± 2.62/76.67 ± 1.26 | 80.19 ± 1.47/78.58 ± 1.20 | 77.14 ± 1.35/75.05 ± 1.79 |
| 6 | OOC2 | 912 | 25 | 81.24 ± 1.28/79.84 ± 1.51 | 78.86 ± 2.02/77.16 ± 1.76 | 82.49 ± 1.41/80.23 ± 1.84 |
| 7 | ION | 351 | 34 | 95.06 ± 1.35/87.64 ± 1.31 | 94.23 ± 1.17/87.70 ± 2.29 | 94.97 ± 1.60/88.01 ± 2.06 |
| 8 | SON | 208 | 60 | 83.08 ± 4.01/76.88 ± 3.02 | 84.38 ± 3.84/75.29 ± 1.93 | 83.41 ± 3.44/77.21 ± 3.75 |
| 9 | SPL | 1535 | 60 | 92.17 ± 1.91/90.05 ± 1.96 | 92.02 ± 0.95/89.86 ± 1.45 | 91.35 ± 1.65/90.23 ± 1.43 |
| 10 | BRE1 | 699 | 9 | 96.79 ± 0.81/86.43 ± 0.81 | 96.63 ± 2.66/85.06 ± 1.06 | 96.91 ± 0.78/86.73 ± 0.66 |
| 11 | BRE2 | 569 | 30 | 95.63 ± 2.01/84.86 ± 3.02 | 93.72 ± 2.61/83.72 ± 2.66 | 95.37 ± 2.35/85.21 ± 3.41 |
| 12 | PRO | 106 | 55 | 76.23 ± 7.49/74.53 ± 4.83 | 77.08 ± 4.75/58.87 ± 2.66 | 76.89 ± 6.48/75.57 ± 5.04 |
| 13 | CLI | 540 | 18 | 91.96 ± 1.27/81.96 ± 1.28 | 92.28 ± 1.22/82.28 ± 1.22 | 92.15 ± 1.46/82.15 ± 1.05 |
| 14 | BLO | 748 | 5 | 78.03 ± 2.42/75.91 ± 1.34 | 74.10 ± 2.94/72.35 ± 3.02 | 78.58 ± 1.88/77.47 ± 1.28 |
| 15 | BAN | 512 | 35 | 71.13 ± 2.27/69.94 ± 2.73 | 68.28 ± 4.42/66.15 ± 3.47 | 72.79 ± 1.79/70.88 ± 2.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Sun, R.; Qin, D. Power Load Forecasting System of Iron and Steel Enterprises Based on Deep Kernel–Multiple Kernel Joint Learning. Processes 2025, 13, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020584
Zhang Y, Wang J, Sun J, Sun R, Qin D. Power Load Forecasting System of Iron and Steel Enterprises Based on Deep Kernel–Multiple Kernel Joint Learning. Processes. 2025; 13(2):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020584
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Junsheng Wang, Jie Sun, Ruiqi Sun, and Dawei Qin. 2025. "Power Load Forecasting System of Iron and Steel Enterprises Based on Deep Kernel–Multiple Kernel Joint Learning" Processes 13, no. 2: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020584
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, J., Sun, J., Sun, R., & Qin, D. (2025). Power Load Forecasting System of Iron and Steel Enterprises Based on Deep Kernel–Multiple Kernel Joint Learning. Processes, 13(2), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020584







